
The Role of SETD2 and VHL in Promoting Renal Fibrosis
Yangtian Yan
Dulwich Zhuhai International High School, China
Keywords: Renal Fibrosis, SETD2, VHL, Inflammation-Related Genes, Tumour Suppressor Genes, Knockout.
Abstract: An excess accumulation of extracellular matrix is involved in renal fibrosis, which usually leads to a loss of
function when scar tissues replace normal tissues. This process is stimulated by multiple different
pathogenic factors that trigger the cascades of reparation converging in molecular signals responsible for
initiating and driving fibrosis. SETD2 and VHL are both tumour suppressor genes, the former acts as an
epigenetic modifier that is responsible for trimethylation of H3K36, and the latter works by controlling
extracellular matrix formation, apoptosis response, and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Whether
SETD2 and VHL play roles in promoting the occurrence of renal fibrosis is still unknown. Therefore, by
creating the mouse model with the specific knockout of VHL and SETD2 genes, our experiment analyses
their effects on the kidney tissue. The result indicates that there is an up-regulation for the expression level
of inflammation-related genes in the mouse kidney model with both VHL and SETD2 knocked out other
than with VHL-KO only, in combination with the HE, Masson, and Sirius Red staining images we
performed, we can get a conclusion that these two genes, SETD2 and VHL, can trigger the occurrence of
renal fibrosis. These results can provide a solid theoretical basis for the molecular mechanism of action and
prospects of relevant drug screening and clinical targeted therapy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Renal fibrosis is the final manifestation of chronic
kidney disease (CKD), which can be characterized
by tubulointerstitial fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis
(Cho, 2010). Even though a range of diseases related
to kidney such as glomerulonephritis, diabetes
mellitus, atherosclerosis and even polycystic kidney
disease, can be the main factors causing CKD, renal
fibrosis is always the common final result of CKD
(Cho, 2010). It appears to be a harmful process
leading to renal function deterioration inevitably,
independently of the previous renal diseases which
cause the original symptoms. Chronic Kidney
Disease and Renal Fibrosis affect 10% of the world's
population, and a significant proportion of people
progress to end-stage renal failure, requiring lifelong
dialysis and kidney transplants, placing a huge
financial burden on patients, families, and societies.
An excessive accumulation and deposition of
extracellular matrix (ECM) components are the main
characteristics of renal fibrosis that occur in almost
every type of CKD (Liu, 2006). It is worth knowing
that among many different fibrogenic factors that
regulate the process of renal fibrosis, transforming
growth factor-β (TGF-β) is the one that plays a
central role. The epithelial to mesenchymal
transition (EMT) of tubular epithelial cells means
they are transformed into mesenchymal fibroblasts
migrating to adjacent interstitial parenchyma, along
with local and circulating cells constitute the
principal mechanism of renal fibrosis (Humphreys,
2018). For the occurrence of renal fibrosis, although
many in vitro studies emphasize the significance of
one specific cellular event such as the activation of
fibroblast, it should be kept in mind that no single
type of isolated cell has the ability of initiating and
sustaining an entire scale of renal fibrosis (Liu,
2006). Many experimental studies have been carried
out to explain the specific pathway of renal fibrosis
and some significant progress has already been made
in the understanding of the cellular and molecular
mechanisms of renal fibrosis.
VHL is an important tumour suppressor gene, and
its mutation can promote the occurrence of renal
cancer. A person with VHL has nearly a 100%
chance of developing one or more VHL tumours in
their lifetime (Von Hippel-Lindau, 2022). Early
inactivation of VHL is commonly seen in clear-cell
renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), and insights gained
386
Yan, Y.
The Role of SETD2 and VHL in Promoting Renal Fibrosis.
DOI: 10.5220/0012021400003633
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine (ICBB 2022), pages 386-391
ISBN: 978-989-758-637-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

from the functional analysis of pVHL have provided
the foundation for the routine treatment of advanced-
stage ccRCC with novel targeted therapies (Gossage,
2015). It is shown that VHL can influence the
content of the extracellular matrix, a proper
extracellular matrix cannot be organized in cells
lacking VHL. This in conjunction with enhanced
production of VEGF-A favours angiogenesis and
tumourigenesis (Patard, 2009). pVHL can also bind
with transcription factors, which will lead to a
decrease in the stability of certain mRNAs and
inhibit the transcription of genes such as VEGF-A
(Pal, 1997). The role of VHL in renal fibrosis is
undiscovered, but the variation of VHL and the
mechanism of renal fibrosis have some similarities,
such as the effect on extracellular matrix.
Set domain containing 2 (SETD2) Set domain
containing 2 (SETD2) is a histone modifier that is
generally known as the single human gene
responsible for trimethylation of lysine 36 of histone
H3 (H3K36). H3K36me3 readers recruit protein
complexes to carry out specific processes, such as
transcription elongation, RNA processing, and DNA
repair, to determine the impact of this histone
modification. Histone H3K36 trimethylation is a
highly conserved chromatin mark related to
transcriptional elongation, and it accumulates mainly
across the body of genes that are actively
transcribed. Cells tend to become significantly
vulnerable and sensitive to DNA-damaging agents
after loss of the H3K36me3 mark through SETD2
mutation or loss (Li, 2016). SETD2 mutation can
promote the occurrence of ccRCC, its mutation rate
in clinical patients is as high as 12%, ranking third,
which can lead to structural abnormalities in renal
tubules. A series of researches have revealed that
SETD2 is mutated or its function is lost in a range of
solid cancers (Hu, 2020), lung cancer,
gastrointestinal cancer, renal cancer, pancreatic
cancer, osteosarcoma, and so on. Mutation, or
functional loss, of the SETD2 gene produces
dysfunction in corresponding tissue proteins so that
a series of adverse functions will be leaded
(Molenaar, 2022).
Now, little is known about the roles of SETD2 or
VHL in renal fibrosis, so by analyzing the mouse
renal tubular tissue with the specific knockout of
VHL and SETD2 genes, the specific possible
molecular mechanism of action can be elucidated,
which provides a solid theoretical basis and
development prospect for corresponding drug
screening and clinical targeted therapy.
2 METHODS
2.1 Mice Preparation
Setd2fl/fl mice were generated as described [ref].
The Ksp-Cre mice (B6.CgTg (Cdh16-cre) 91Igr/J)
and VHLfl/fl mice were purchased from The Jackson
Laboratory.
Setd2fl/fl mice were mated with Ksp-Cre mice to
generate Ksp-Cre; Setd2flox/flox (Setd2–KO) mice
in C57BL/6 background. SETD2–KO mice were
mated with VHLfl/fl mice to generate Ksp-Cre;
VHLfl/fl&Setd2fl/fl mice (Setd2-VHL-KO) housing
under the same condition.
2.2 DNA Extraction from Mouse Tail
for Genotyping
Cutting the tip of the mouse tail and place it into an
Eppendorf tube and then add 100ul to 150ul reagent
A depending on the size of your tail sample. Boil the
sample at 95 to 98°C for 1 hour or so till the tail is
“melted”. Cool down to room temperature. Adding
equal volume of reagent B and then mixing well.
Centrifuging the Eppendorf tube at full speed for 5
minutes. Finally, take 1ul to 2ul supernatant for PCR.
2.3 Buffer Recipe
Reagent A: 25Mm NaOH/0.2Mm EDTA
Note: 5x stock solution which can be kept at
room temp
Reagen B: 40Mm Tris HCl (pH 5.5)
2.4 RNA Isolation and Quantitative
Qrt-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from fresh kidney samples.
cDNA (complementary DNA) was made using the
Prime Script RT reagent kit and subjected to
quantitative RT-PCR. Calculating the relative
abundance of mRNA by normalization to actin-beta
or GAPDH mRNA.
The primer sequences are as follows: Il1rap-
Forward: 5’-TGCCTGGGGGAATTGTCAC-3’,
Il1rap-Reverse: 5’-
CTTAGCCCGCTTCAGCTCTTT-3’; Il18r1-
Forward: 5’-TCACCGATCACAAATTCATGTGG-
3’, Il18r1-Reverse: 5’-
TGGTGGCTGTTTCATTCCTGT-3’; Il7r-Forward:
5’-GCGGACGATCACTCCTTCTG-3’, Il7r-
Reverse: 5’-AGCCCCACATATTTGAAATTCCA-
3’; Il1r1-Forward: 5’-
GTGCTACTGGGGCTCATTTGT-3’, Il1r1-
The Role of SETD2 and VHL in Promoting Renal Fibrosis
387
Reverse: 5’-GTGCTACTGGGGCTCATTTGT-3’
(Fig.2).
2.5 Histology and IHC Staining
Fixing mouse kidneys in 10% formaldehyde, then
embedding them in paraffin, and staining for
Masson’s trichrome (Sigma-Aldrich) and Picrosirius
red (Abcam) separately after cutting them in 5μm
thickness. Measurement of the tissue fibrotic area
could be identified with contrastive images.
Fixing tissues in 10% buffered formalin and then
sectioning them for hematoxylin and eosin staining.
RNA sequencing and analyses
For IHC staining, treating paraffin-embedded
tissues with 0.01 mol/L sodium citrate (pH 6.0) to
deparaffinized, rehydrate, and subject them to a
heat-induced epitope retrieval step. 0.3% (v/v)
hydrogen peroxide in distilled water was used to
block the activity of endogenous peroxidase. Then
incubating the sections with 0.3% Triton X-100 in
PBS (137 mmol/L NaCl, 2.7 mmol/L KCl, 10
mmol/L Na2HPO4, 2 mmol/L KH2PO4, pH 7.4) for
15 minutes, followed by 1 hour’s 10% goat serum in
PBS.
3 RESULTS
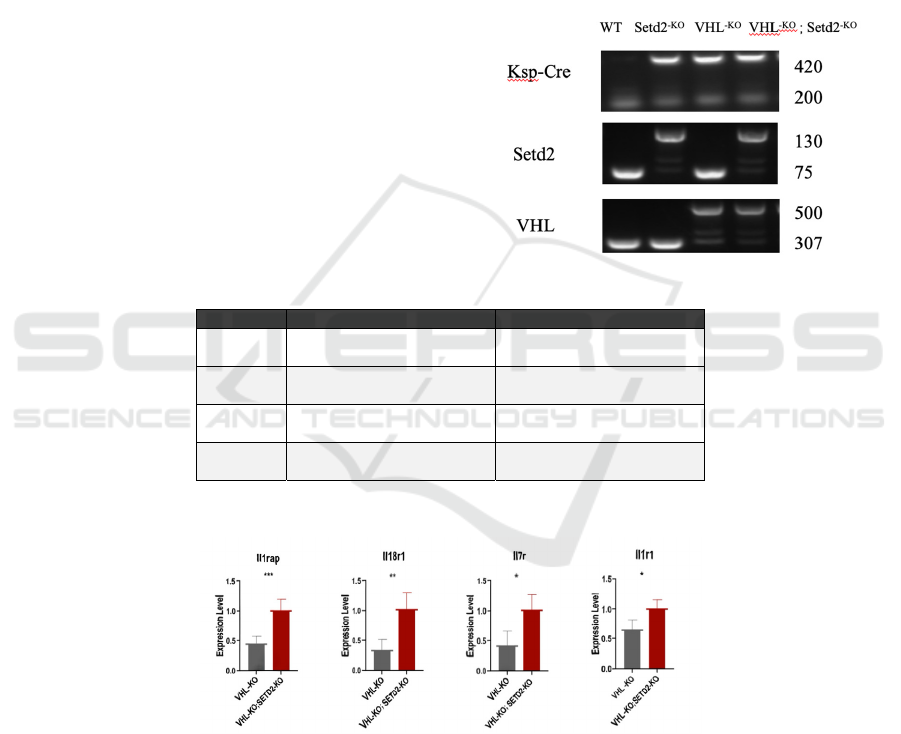
To ensure that the mouse gene model is needed for
the experiment, we carried out PCR tests to identify
the genotype. It can be seen that the fourth column is
the model of SETD2 and VHL double knockout. At
this time, the band size of SETD2 is 130bp and that
of VHL is 500bp. The third column is the model of
only knocking out the VHL gene; the band sizes of
SETD2 and VHL are 75bp and 500bp respectively.
The second column represents a model with only
SETD2 knockout. (Fig.1).
Figure 1: Results of mouse DNA PCR test.
QueryID forward reverse
Il1rap TGCCTGGGGGAATTGTC
AC
CTTAGCCCGCTTCAGCT
CTTT
Il18r1 TCACCGATCACAAATTC
ATGTGG
TGGTGGCTGTTTCATTC
CTGT
Il7r GCGGACGATCACTCCTT
CTG
AGCCCCACATATTTGAA
ATTCCA
Il1r1 GTGCTACTGGGGCTCAT
TTGT
GTGCTACTGGGGCTCAT
TTGT
Figure 2: Inflammation related genes are up-regulated in SETD2 knockout mice.
Figure 3: Results of qPCR test of inflammation related genes.
Many studies have shown that inflammation
shares some of the same biological mechanisms as a
range of other conditions, such as fibrosis
(Inflammation, 2022). Increased expression levels of
inflammation-related genes suggest the presence of
diseases with the same mechanism. The gray column
of each graph in Fig. 3 represents the expression
level of inflammation-related genes in the VHL-KO
model, and the red column represents the expression
level in the VHL-KO and SETD2-KO models. It can
be seen that Il1r1 and Il7r have significant rises from
the gray column to the red column, and the before
and after comparisons of Il18r1 and Il1rap are more
obvious. The results of the qPCR test for four
inflammation-related genes indicate that the
Knockout of SETD2 in VHL knockout mouse
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
388
kidneys results in renal fibrosis in mice because we
can see that the expression level of these
inflammation-related genes all experience an up-
regulation in the mouse kidney model with both VHL
and SETD2 knocked out other than VHL-KO only
(Fig.3).
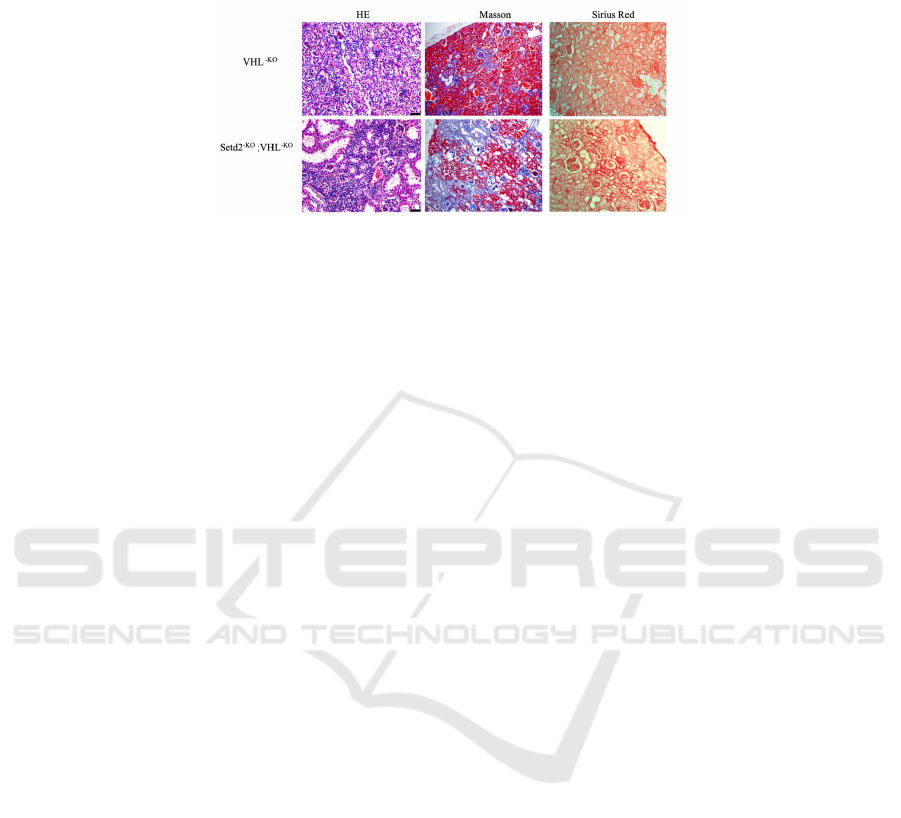
Figure 4: Knockout of SETD2 in VHL knockout mouse kidneys results in renal fibrosis in mouse(scale bars, 80um).
Knockout of SETD2 in VHL knockout mouse
kidneys results in renal fibrosis in mice (scale bars,
80um)
By staining the renal tubular tissue of the mouse
kidney model with VHL knockout only and the
mouse kidney model with both SETD2 and VHL
knockout at the same time, we can see that there is
more cellular fibrosis in the double knockout mouse
model (Fig.4). In HE staining, the blue stained part
represents the nucleus. In the double knockout model
experiment, we can find a significant increase in the
number of nuclei in the tissue. In Masson's staining,
blue represents fibers, and Sirius Red staining is on a
yellow background, in which the red part is the
fibrotic part. Both of these two staining images show
a vivid upward trend in the occurrence of fibrosis
from VHL-KO only to SETD2-KO and VHL-KO.
Therefore, we can conclude that simultaneous
mutations of SETD2 and VHL can induce the
occurrence of renal fibrosis.
4 CONCLUSION
By creating the mouse model with the specific
knockout of VHL and SETD2 genes, we analyze its
effects on the kidney tissue. From the up-regulation
for the expression level of inflammation-related
genes (including Il1rap, Il18r1, Il7r, and Il1r1) in the
mouse kidney model with both VHL and SETD2
knocked out other than with VHL-KO only,
combined with the HE, Masson and Sirius Red
staining images we performed, we can get a
conclusion that these two genes of SETD2 and VHL
can also trigger the occurrence of renal fibrosis.
These inflammation-related genes also play a role
in the study of fibrosis. Pro-inflammatory proteins
can be synthesized by the induction of Interleukin 1
(IL-1) during tissue damage or infection, IL-1 does
this by forming a complex with an interleukin 1
receptor and an accessory protein at the cell
membrane (Rouillard, 2016). This gene is
responsible for encoding the interleukin-1 receptor
accessory protein (Il1rap). Il1rap can recognize IL-1
and it is the co-receptor for signaling pathways.
Interleukin 18 receptor 1 (Il18r1) is a protein-coding
gene that encodes a cytokine receptor that belongs to
the interleukin-1 receptor group. Interleukin 18 (Il18)
is specifically bound to this receptor, which is also a
pro-inflammatory cytokine (IL18R1, 2022).
Instructions for making the interleukin-7 (Il-7)
receptor alpha chain are provided by the Interleukin-
7 receptor subunit alpha (Il7r) gene. These Il-7
receptors can be embedded in the cell membrane of
cells in the immune system (New11., 2008). They
are usually found in B cells, T cells, and also the
early blood-forming cells that give rise to them.
Interleukin-7 (Il-7) is a protein that can interact with
the Il-7 receptor at the cell surface to regulate the
activity of immune system cells (Plumb, 2017).
Signaling across the Il-7 receptor helps mature B
cells and T cells to develop properly and it also
stimulates the later proliferation of these cells (Corfe,
2012). Similarly, the interleukin-1 receptor type 1
(Il1r1) gene encodes a cytokine receptor which also
belongs to the IL-1 receptor family. It is a significant
mediator involved in many cytokine-induced
immune and inflammatory responses (IL1R1, 2022).
Some studies suggested that pro-inflammatory
stimuli can induce this receptor and it may be
involved in the function of helper T cells (IL1R1
protein overview, 2022). These series of responses
caused by the cytokine interleukin released by
inflammatory-related molecules are proof of the
persistence of inflammation, and also directly or
indirectly reflect the development of fibrosis.
The results indicate that there is an up-regulation
for the expression level of inflammation-related
The Role of SETD2 and VHL in Promoting Renal Fibrosis
389

genes in the mouse kidney model with both VHL and
SETD2 knocked out other than with VHL-KO only.
It is known that renal fibrosis is a kind of
pathophysiological change, which is a gradual
process of renal function from health to injury, then
to loss of function. Due to the stimulation of trauma,
infection, inflammation, blood circulation disorders,
immune response, and other pathogenic factors, cells
of the kidney are damaged, and a large amount of
collagen deposition and accumulation appear in the
later stage of development [2], causing the renal
parenchyma to gradually harden and form scars until
the kidney completely loses organ function [3]. The
process of hardening in the kidney is also the process
of renal fibrosis. In the three staining methods we
used, HE, Masson, and Sirius Red staining, the image
results indicate an increasing tendency of tissue
fibrosis from the mouse model with VHL-KO only to
that with both SETD2-KO and VHL-KO. Therefore,
we can get the conclusion that the knockout of
SETD2 in VHL knockout mouse kidneys results in
renal fibrosis in mice.
However, SETD2 and VHL are well known as
tumour suppressor genes and their effects of mutation
are mainly found and studied in clinical patients with
renal clear cell carcinoma (ccRCC). In this
experiment, we did not study carcinogenic effects, so
some potential limitations about the specific
knockout of these two genes may also be present
throughout the process. More experiments need to be
done and these results have to be repeatedly
deliberated to give out a more reliable conclusion.
Taken together, these results obtained can provide
a solid theoretical basis for the mechanism of
molecular action and prospects for corresponding
drug screening and clinical target therapy.
REFERENCES
Cho MH. Renal fibrosis. Korean J Pediatr. 2010 Jul;
53(7):735-40. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2010.53.7.735. Epub
2010 Jul 31. PMID: 21189948; PMCID:
PMC3004484.
Corfe SA, Paige CJ. The many roles of IL-7 in B cell
development; mediator of survival, proliferation and
differentiation. Semin Immunol. 2012 Jun;24(3):198-
208. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2012.02.001. Epub 2012
Mar 14. PMID: 22421572.
Gossage L, Eisen T, Maher ER. VHL, the story of a
tumour suppressor gene. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015
Jan;15(1):55-64. doi: 10.1038/nrc3844. PMID:
25533676.
Humphreys BD. Mechanisms of Renal Fibrosis. Annu Rev
Physiol. 2018 Feb 10;80:309-326. doi:
10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034227. Epub 2017
Oct 25. PMID: 29068765.
Hu M, Zhang Q, Lai J, Liu X. SETD2, an epigenetic
tumor suppressor: a focused review on GI tumor.
Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020 Jan 1;25(4):781-
797. doi: 10.2741/4834. PMID: 31585917.
IL1R1 protein overview: Sequence, structure, function and
protein ... (n.d.). Retrieved August 11, 2022, from
https://www.sinobiological.com/resource/il1r1/protein
s
Inflammation: What is it, causes, symptoms & treatment.
Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Retrieved August 2022, from
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21660
-inflammation.
Liu Y. (2006). Renal fibrosis: new insights into the
pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney international,
69(2), 213–217. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5000054
Li J, Duns G, Westers H, Sijmons R, van den Berg A, Kok
K. SETD2: an epigenetic modifier with tumor
suppressor functionality. Oncotarget. 2016 Aug
2;7(31):50719-50734. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9368.
PMID: 27191891; PMCID: PMC5226616.
Molenaar, T. M., & van Leeuwen, F. (2022). SETD2:
from chromatin modifier to multipronged regulator of
the genome and beyond. Cellular and molecular life
sciences: CMLS, 79(6), 346.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04352-9
New11. Palmer, M. J., Mahajan, V. S., Trajman, L. C.,
Irvine, D. J., Lauffenburger, D. A., & Chen, J. (2008).
Interleukin-7 receptor signaling network: an integrated
systems perspective. Cellular & molecular
immunology, 5(2), 79–89.
https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2008.10
Patard JJ, Rioux-Leclercq N, Masson D, Zerrouki S, Jouan
F, Collet N, Dubourg C, Lobel B, Denis M, Fergelot
P. Absence of VHL gene alteration and high VEGF
expression are associated with tumour aggressiveness
and poor survival of renal-cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
2009 Oct 20;101(8):1417-24. doi:
10.1038/sj.bjc.6605298. Epub 2009 Sep 15. PMID:
19755989; PMCID: PMC2768461.
Pal, S., Claffey, K. P., Dvorak, H. F., & Mukhopadhyay,
D. (1997). The von Hippel-Lindau gene product
inhibits vascular permeability factor/vascular
endothelial growth factor expression in renal cell
carcinoma by blocking protein kinase C pathways.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 272(44), 27509–
27512. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.44.27509
Plumb AW, Sheikh A, Carlow DA, Patton DT, Ziltener
HJ, Abraham N. Interleukin-7 in the transition of bone
marrow progenitors to the thymus. Immunol Cell Biol.
(2017) 95:916–24. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.68
Rouillard AD, Gundersen GW, Fernandez NF, Wang Z,
Monteiro CD, McDermott MG, Ma'ayan A. The
harmonizome: a collection of processed datasets
gathered to serve and mine knowledge about genes
and proteins. Database (Oxford). 2016 Jul 3;2016. pii:
baw100.
U.S. National Library of Medicine. (n.d.). IL18R1
interleukin 18 receptor 1 [homo sapiens (human)] -
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
390

gene - NCBI. National Center for Biotechnology
Information. Retrieved August 11, 2022, from
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/8809.
U.S. National Library of Medicine. (n.d.). IL1R1
interleukin 1 receptor type 1 [homo sapiens (human)] -
gene - NCBI. National Center for Biotechnology
Information. Retrieved August 5, 2022, from
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/3554/
Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL). Johns Hopkins Medicine.
(n.d.). Retrieved September 19, 2022, from
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-
and-diseases/von-hippellindau-vhl
The Role of SETD2 and VHL in Promoting Renal Fibrosis
391
