
International Big Four, Customer Concentration and Audit Fees
Hongli Ma
a
Beijing Jiaotong University, China
Keywords: International Big Four, Customer Concentration, Audit Fees.
Abstract: With the development of economy, enterprises in the supply chain are competing more and more as a whole,
so the downstream of the supply chain and the customers of enterprises are becoming more and more
important for the development of enterprises. They are the main source of economic interests of enterprises
and have an important impact on the economic activities of enterprises, so they may have an impact on audit
expenses. This paper takes A-share listed companies as the research object, establishes an empirical regression
model, and studies how the customer concentration of enterprises in the supply chain affects the audit cost
from the perspective of the supply chain. In addition, when the audit unit of the enterprise is the Big Four, the
effect of customer concentration on reducing audit fees is not significant. In the non-big four enterprises, the
concentration of clients significantly reduces the audit fees.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, with the development of economic
globalization and industrial diversification,
enterprises in the supply chain are no longer in the
traditional relationship of buying and selling, but as a
new type of partnership, the mutual influence is more
and more serious, the relationship is more and more
close, and the external competition is more and more
as a whole (Kotabe et al., 2003). Supply chain
relationship refers to the business relationship and
personal friendship created by supply chain member
enterprises in daily purchasing and sales activities (Li
and Liu, 2016), including upstream supplier
relationship and downstream customer relationship.
So in pursuit of the stability of supply chain,
enterprises will keep close contact with their
upstream and downstream enterprises From the
perspective of supply chain stability, business
activities of enterprises are completed through the
connection of supply chain, and the interruption and
transfer of key nodes in the supply chain will bring
huge losses to enterprises (Dhaliwal et al., 2016).As
a community of interests, neither customer nor
supplier can stand alone in the face of difficulties.
Different from market-oriented transactions in
western developed economies, in the Chinese market
with widespread overcapacity, enterprises tend to rely
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7046-7111
more on downstream customers than upstream
suppliers (Shi and Qin, 2018), and advantageous
information brought by supply chain relationships
spills over to businesses through customer
relationships. The closer the relationship between the
customers and the enterprise the customer
concentration is higher, the more it helps enterprises
to establish long-term and stable customer
relationship with customers, the more it helps
enterprises to strengthen cooperation with customers
and maintain stable profits, also helps to promote the
company's management ability, management level
and the brand effect, resolve the company's financial
and non-financial business risk. Previous studies have
shown that customer concentration will have an
impact on the operating activities, cost structure and
profitability of enterprises, such as earnings quality,
bank credit, financing cost, investment behavior, etc.
As an important stakeholder, auditors' decisions are
also influenced by the concentration of clients, such
as audit quality and auditor selection. However, there
are relatively few researches on audit fees. Wang et
al. (2014) pointed out that the higher the client
concentration, the lower the audit fee. However, the
size and reputation of accounting firms will also
affect the impact of client concentration on audit fees.
This is because accounting firms with large scale and
high reputation do not lack clients, but the clients
24
Ma, H.
International Big Four, Customer Concentration and Audit Fees.
DOI: 10.5220/0012022900003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 24-29
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

need them to improve the credibility of audit reports,
so these accounting firms tend to have a higher say in
audit bargaining. Therefore, this paper studies the
relationship between client concentration and audit
fees from the perspective of different scale and
reputation of accounting firms.
This paper uses Chinese A-share listed companies
from 2016 to 2021 as empirical samples to study the
relationship between client concentration and audit
fees based on different sizes and reputations of
accounting firms. The empirical results show that
customer service concentration has a significant
negative impact on audit costs. In addition, if the
accounting firm has a large scale and high reputation,
the negative correlation between client concentration
and audit fees is not significant, while if the
accounting firm has a small scale and low reputation,
the negative correlation between client concentration
and audit fees is more significant.
The research significance of this paper may be as
follows: First, the study of audit fees, the study of
factors affecting audit fees is conducive to
strengthening the government's supervision of the
audit market, so as to standardize the competition of
the audit market. Secondly, this paper studies the
influence of customer concentration on audit costs,
and points out the direction for enterprises to reduce
audit costs. Enterprises could maintain close contact
with customers, so as to increase their right to speak
in bargaining, so as to reduce audit costs. Finally, the
paper supplements the literature on the impact of
client concentration on audit fees. The influence of
client concentration on audit fees is more significant
when the enterprise has a larger voice.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
THEORETICAL ANALYSIS
Audit fee is the price agreed upon by the supply and
demand parties for audit services. It is a certain
amount of fees charged by the accounting firm to the
auditee after providing audit services, that is, the price
of audit services provided by certified public
accountants. Audit fee consists of three parts: audit
product cost, risk cost and normal profit of the firm
(Wu, 2003). Audit product cost refers to the cost of
executing necessary audit procedures and issuing
audit reports, which generally depends on enterprise
characteristics such as scale and business complexity,
corporate governance and internal control. And the
risk cost mainly refers to the litigation loss and the
potential cost of restoring reputation.
Customers are the most important economic
entities in market transactions. Through implicit or
explicit contractual arrangements, customers bring
core economic benefits to the company and are the
main source for the company to obtain sustainable
competitive advantages. High customer
concentration means a close relationship between the
company and customers. Long-term and stable
transactions between the company and customers in
the supply chain can promote information sharing
between the company and customers, so as to
improve the efficiency of inventory management and
the recovery rate of accounts receivable, which is
conducive to the improvement of the company's
performance (Feng et al., 2019). Large customers
help to stabilize the supply chain, enhance the
stability of the company's earnings, and the capital
market will also produce a positive response.
Customer relationship can affect business activities,
cost structure and profitability. The high degree of
integration between the buyer and the seller can
enhance the ability of the supplier to serve customers,
promote both parties to increase sales, reduce costs,
and improve the profitability of both parties. The
purchasing power of customers affects the price
strategy, operation and product design, marketing and
customer service activities, and then affects the cost
structure and profit of the enterprise. Previous studies
have also shown that client concentration can affect
audit quality (Hung, 2021; Zhao et al., 2021) and
audit pricing (Wang, 2020).
The customer characteristics of enterprises can
also affect the cost of audit products and risk costs,
and ultimately affect the audit fees If an enterprise has
a close relationship with its customers and a strong
performance correlation, the stronger the degree of
mutual influence between the two, the situation of
mutual prosperity and mutual loss will occur between
the two. Then the retailer with large customers will
have higher returns and earnings stability. (Gosman
et al., 2004). In short, companies with large customers
perform better, have lower own risk and audit risk; If
enterprises can realize supply chain integration with
customers (Kalwani and Narayandas, 1995), the
improvement of enterprise operation efficiency will
reduce the holding level of factors affecting audit
expenses such as cash, inventory and accounts
receivable (Patatoukas, 2012). At the same time,
since enterprises mainly trade with a few important
customers, The business complexity is reduced,
which may reduce the audit effort and thus the audit
cost. In summary, the hypothesis of this paper is as
follows:
International Big Four, Customer Concentration and Audit Fees
25

Hypothesis 1: The higher the customer
concentration, the lower the audit risk, the smaller the
audit workload, and the lower the audit fee.
There are big and small accounting firms, and
there are high and low reputation accounting firms. In
related studies, scholars often divide accounting firms
into the Big Four and non-Big Four accounting firms.
According to the study, DeAngelo (1981) proposed
that large firms have higher independence and higher
audit quality. The audit quality of Big Four firms is
higher than that of non-Big Four firms (Beatty,1989;
Palmrose,1988). Compared with non-Big Four
accounting firms, Big Four accounting firms have
higher audit fees (Li and Tang, 2020). Audit product
cost, risk cost and audit fee constitute the firm's
normal profit, and audit fee is the accounting firm and
the audited unit can compete with each other. In the
current market, the Big Four accounting firms have
larger scale and higher reputation. Compared with
non-Big Four accounting firms, they also have more
say in bargaining with audited companies. This is
because accounting firms with large scale and high
reputation, such as the Big Four international
accounting firms, do not lack clients, but the clients
need them to improve the credibility of audit reports,
so these accounting firms tend to have a higher say in
audit bargaining. However, due to the long
establishment time, large scale and high reputation of
the Big Four accounting firms, it is difficult for the
audited companies to play games with them, thus
reducing their normal profits and ultimately reducing
audit fees. Therefore, this paper puts forward the
following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 2a: The audit firm is a non-Big Four
accounting firm with a small scale and low reputation,
and the audited firm has a high degree of client
concentration, which can significantly reduce the
audit fee.
Hypothesis 2b: The audit firm is a Big Four
accounting firm with a large scale and high
reputation. Even if the auditee has a high
concentration of customers, it can not significantly
reduce its audit fee.
3 RESEARCH DESIGN
3.1 Sample Source
This paper selected A-share listed companies from
2016 to 2021 as the initial sample and conducted the
following screening: ① Financial and insurance
companies were excluded; (2) Eliminate ST or *ST
companies; ③ Remove companies with incomplete
data from the sample. You end up with 11,868
observations. In order to eliminate the influence of
extreme values, the continuous variables in the model
are shrunk at 1% and 99% quantile levels. All sample
data were collected from CSMAR Database. Data
screening and processing are mainly done by Excel
and stata15 software. In this paper, the first two codes
of 2012 China Securities Regulatory Commission
industry classification standard are adopted to divide
the industry.
3.2 Variable Definitions
3.2.1 Explained Variable: Audit Fee
According to the research of Wang Xiongyuan et al.
(Wang,2014), the natural logarithm of audit fees in
the financial statements of listed companies is used to
measure audit fees (infe).
3.2.2 Explanatory Variable: Customer
Concentration
According to the research of Zhang Min et al.
(Zhang,2012), the proportion of the annual sales of
the top five customers in the total annual sales in the
financial statements of listed companies is used to
measure the customer concentration degree (ab).
The variables are defined as follows:
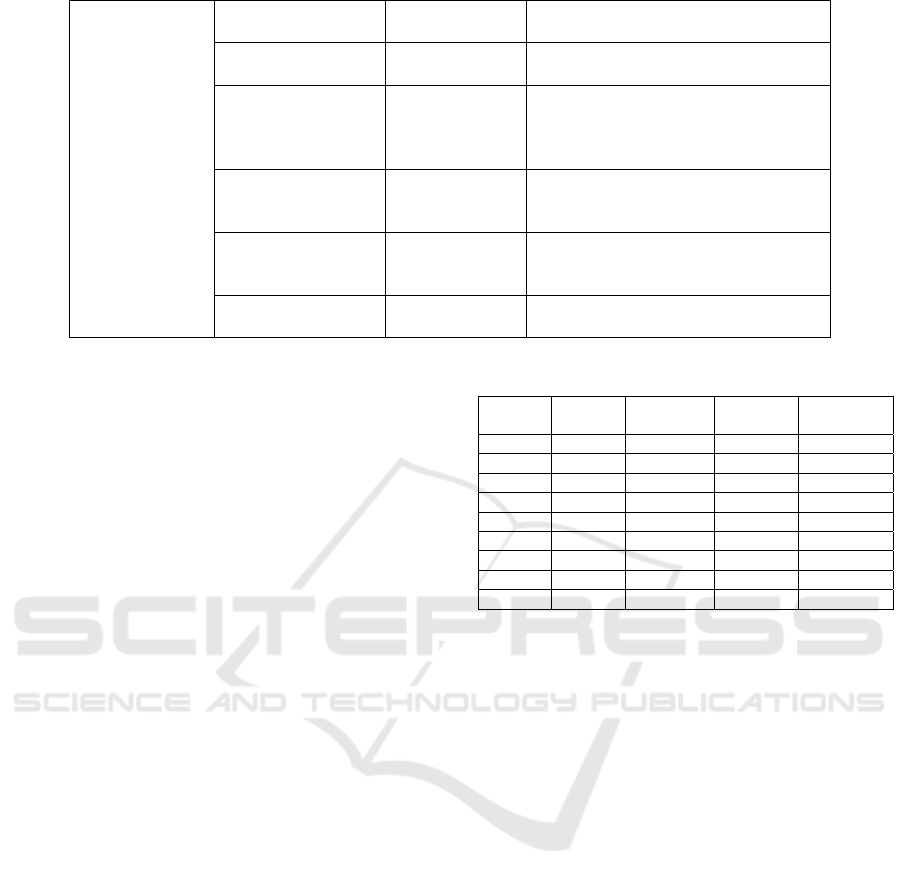
Table 1: Variable definition table.
variable type
variable name variable symbol variable definition
explained
variable
audit fee infe
Natural logarithm of audit fee area
explaining
variable
Concentration of
customers
ab
The proportion of the annual sales of
the top five customers to the total
annual sales
control variable The enter
p
rise scale size Natural lo
g
of endin
g
total assets
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
26
Corporate financial
levera
g
e
lev
Total liabilities at year-end/total assets
at
y
ea
r
-en
d
Cash flow from
operating activities
cf
Cash flow from operating
activities/total assets
Type of Audit
Opinion
Q
If the audit opinion of the enterprise in
the last period is the standard
unqualified opinion, the value is 1;
otherwise, the value is 0
If the big four big4
If there are four accounting firms in
the current period, the value is 1;
otherwise, the value is 0
Discretionary
accruals
ada
Discretionary accrual earnings
management level calculated using the
modified Jones model
Return on assets roa
Average annual balance of net
p
rofit/total assets
3.3 Econometric Model
This paper mainly studies the relationship between
client concentration and audit fees. By referring to
factors affecting audit fees, this paper constructs a
panel model as shown in Equation (1) for empirical
analysis.
infe =β
0
+β
1
ab
i,t
+β
2
control
i,t
+μ
t
+μ
i
+ε (1)
Among them, infe
i,t
is the audit expense of the
enterprise in a certain year; ab
i,t
is the customer
concentration degree of an enterprise in a certain year.
control
i,t
is the control variable; μ
t
and μ
i
are year
fixed effects and individual fixed effects,
respectively. ε is the model disturbance term.
4 EMPIRICAL RESULT
4.1 Descriptive Statistics
Table 2 is the descriptive statistical results of each
variable, from which it can be seen that the minimum
value of enterprise audit fee (infe) is 11.513, and the
maximum value is 18.146. It indicates that there are
great differences in audit fees of sample companies,
and audit fees of different companies are different,
indicating that audit fee standards are different, and
enterprises may reduce their audit fees by some
means. The mean, minimum, maximum and standard
deviation of enterprise customer concentration (ab)
are 23.306, 0.01, 157.89 and 33.243, respectively,
indicating that the customer concentration of different
enterprises varies greatly. Some sample companies
maintain a close relationship with their customers, but
some sample companies do not. They don't even have
regular customers.
Table 2: Descriptive statistical results of main variables.
variable mean standard
deviation
minimum maximum
infe 13.776 0.651 11.513 18.146
ab 33.243 23.306 0.01 157.89
ada 0.072 0.143 0 6.223
lev 0.409 0.206 0.008 3.919
size 22.247 1.348 17.786 28.624
roa 0.044 0.089 -1.872 0.969
Q 0.970 0.171 0 1
b
ig4 0.061 0.239 0 1
cf 0.051 0.075 -1.794 0.879
4.2 Multivariate Regression Analysis
This paper first put all the sample data into the
regression model to test the hypothesis 1 of this paper,
and the specific regression results are shown in
column (1) in Table 3. Then, this paper divided the
samples into two groups according to whether the
enterprise's auditing unit is a Big Four accounting
firm, and put them into the regression model to test
the hypotheses 2a and 2b of this paper. Specific
regression results are shown in columns (2) and (3) in
Table 3. From the analysis of regression results, it can
be seen that: first, the P-value of F-test statistic in the
three regression models is all 0. This indicates that the
model is effective to a certain extent. Secondly, the
regression coefficient of customer concentration and
audit fees is negative, which verifies the negative
correlation between them. In addition, in the group
whose accounting firms are not the Big Four, the
negative correlation between client concentration and
audit expenses is still significant, while in the group
whose accounting firms are the big Four, the
relationship between client concentration and audit
expenses is not significant.
As can be seen from column (1) in Table 3, the
coefficient of customer concentration (ab) is -0.001,
indicating
that the customer concentration of
International Big Four, Customer Concentration and Audit Fees
27
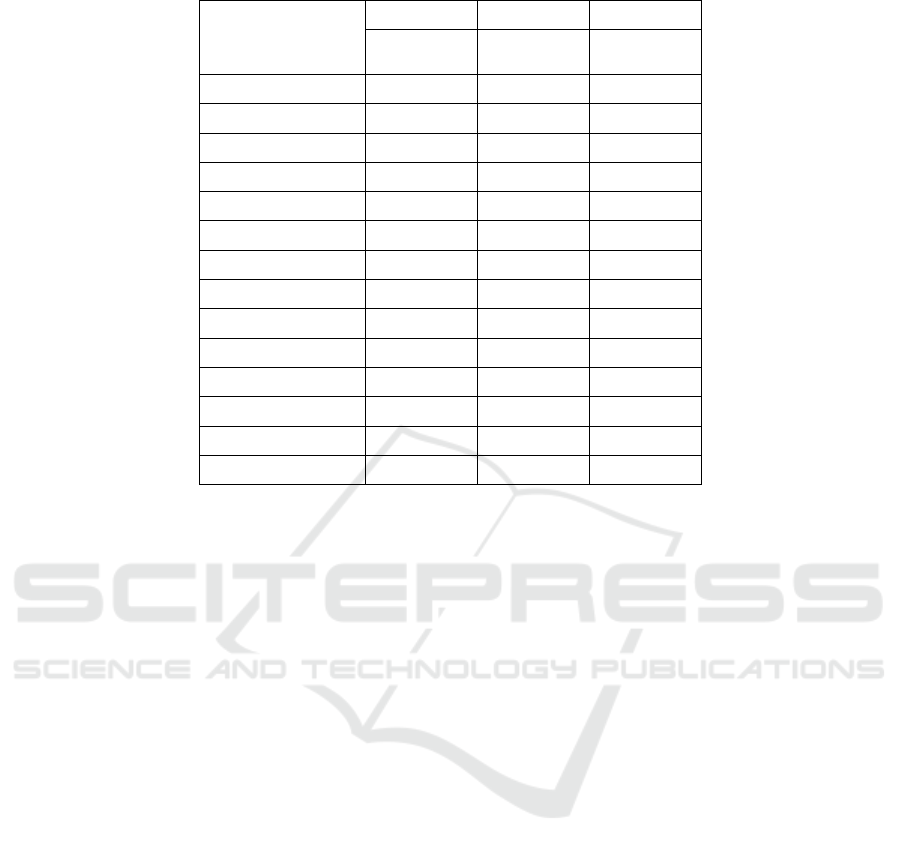
Table 3: Regression results.
variable
infe infe infe
(1)All
the sam
p
les
(2)
b
i
g
4=1
(3)
b
i
g
4=0
ab -0.001*** 0.000 -0.001***
ada 0.029 0.125 0.026
lev 0.002 -0.358** 0.025
size 0.337*** 0.437*** 0.322***
roa -0.409*** -0.383* -0.393***
Q -0.114*** -0.007 -0.113***
big4 0.372*** 4.618*** 0.000***
cf 0.244*** -0.120 0.258***
_cons 6.414*** 0.000*** 6.731***
Vintage effect control control control
Individual effect control control control
N 11868 672 11196
P 0 0 0
R2 0.560 0.615 0.464
Note: *** indicates a significant correlation at the 0.01 level (bilateral).
enterprises negatively affects the audit expenses of
enterprises to some extent, which verifies hypothesis
1 in this paper. For enterprise, customer concentration
is high, means that companies with large customer,
and maintain good relationship with customers, to
some extent this ensures the stability of revenue
sources, and to ensure the stability, higher earnings
and earnings to reduce audit risk and audit work, by
reducing product cost and risk cost audit, And
ultimately lower audit fees.
From (2) column in the table 3 (3) as you can see,
in the enterprise audit units for the big four, enterprise
customer concentration and the relationship between
audit fees is not significant, but in the enterprise audit
units for the big four accounting firms, corporate
customers remain negative correlation relationship
between concentration and audit fees, and
significantly. This is because the big four accounting
firm after years of accumulation of experience, has a
high brand advantage and higher audit quality,
compared with the big four have higher competitive
advantage, so even if the customer of the enterprise
concentration is higher, the big four are often in a
favorable position when negotiating with the
enterprise, audit fees will not be lowered.
5 CONCLUSIONS
With the development of economy, enterprises in the
supply chain compete more and more as a whole, and
the relationship between suppliers and customers is
becoming closer and closer. Good customer
relationship can bring many advantages to
enterprises, such as reducing the degree of financing
constraints and improving the profitability of
enterprises. As a stakeholder of enterprises, the
decision of auditors will also be affected by the
concentration of enterprises' customers. This paper
makes an empirical analysis by combining customer
concentration with audit fees. The results show that
client concentration can significantly reduce audit
fees. In addition, the effect of client concentration on
the reduction of audit fees is different in whether the
audit unit of the enterprise is the Big Four accounting
firms. When the audit unit of the enterprise is the big
four accounting firms, the effect of client
concentration on the reduction of audit fees is not
significant. However, in non-big four auditing firms,
client concentration significantly reduces audit
fees(that is, the expenditure paid by the audited entity
to the auditing entity).
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
28

REFERENCES
Beatty R P(1989). Auditor Reputation and the Pricing of
Initial Public Offerings. J. The Accounting Review. 64
(04), 693-709.
DeAngelo L E(1981). Auditor Size and Audit Quality. J.
Journal of Accounting and Economics.3 (03), 183-199.
Dhaliwal, D., J. S. Judd, M. Serfling, and S. Shaikh(2016).
Customer Concentration Risk and the Cost of Equity
Capital. J. Journal of Accounting and Economics. 61
(1), 23-48.
Gosman M, Kelly T, Olsson P, et al.(2004).The
Profitability and Pricing of Major Customers. J. Review
of Accounting Studies. 19, 117-139.
Hong Jinming (2021). Auditor Characteristics, Client
concentration and Audit Quality. J. Journal of Hunan
University of Science and Technology (Social Science
Edition). 24 (04), 01-110.
Kalwani M U. and Narayandas N,(1995). Long-Term
Manufacturer-Supplier Relationships: Do They Pay Off
for Supplier Firms? J. Journal of Marketing. (59), 1-16.
Kotabe, M., X. Martin, and H. Domoto(2003). Gaining
from Vertical Partnerships: Knowledge Transfer,
Relationship Duratio, and Supplier Performance
Improvement in the U.S. and Japanese Automotive
Industries. J. Strategic Management Journal. 24.(4),
293-316.
Li Q, Y, Tang H,C(2020). Does Big4 have audit fee
differences? -- Preliminary evidence based on the
Chinese market. J. Contemporary Accounting
Review.3 (03), 37-70.
Li R,S, Liu H,X(2016). Supply chain relationship and
commercial credit financing: Competition or
cooperation. J. Contemporary Finance and Economics.
(4), 115-127.
Palmrose Z(1988). An Analysis of Auditor Litigation and
Audit Service Quality[J].The Accounting Review. 63
(01), 55-73.
Patatoukas P N(2012). Customer-Base Concentration:
Implications for Firm Performance and Capital
Markets. J. The Accounting Review.(187),363-392.
Shi J,Y, Qin J,C(2018). Financing constraints, customer
relationships and corporate cash holdings. J. Journal of
Systems Management. (5), 844-853.
Wang H,B, Xia X, Chen S,Z(2020). Customer
concentration, earnings management and audit pricing.
J. Finance and Accounting Monthly. (06), 95-102.
Wang X,Y, Wang P, Zhang J,P(2014). Customer
concentration and audit fees: Customer risk or supply
chain integration. J. Audit Research. (06), 72-82.
Wu L,N(2003). Analysis of the Impact of Earnings
Management on Audit Expenses: Evidence from the
First audit Expense Disclosure of Chinese Listed
Companies. J. Accounting Research. (12), 39-44.
Yin F, Wang B, Liu C, L(2019). The Influence of Customer
Concentration on Corporate Performance: An
Empirical analysis based on Social Network Theory. J.
Journal of Hohai University (Philosophy and Social
Sciences Edition). 21 (5), 51-57, 106-107.
Zhang M, Ma L,J, Zhang S(2012). Vendor-client
relationship and auditor selection. J. Accounting
Research. (12), 81-86+95.
Zhao Y, Gao J, Wang X, R, Qiao G,T(2021). Customer
concentration and audit quality. J. Friends of
Accounting. (21),107-115.
International Big Four, Customer Concentration and Audit Fees
29
