
Network Learning Platform Evaluation System Design and Case
Capital Budget
Zhenghua Yue
The College of Alameda, U.S.A.
Keywords: E-Learning Platform, On-Line Study System, On-Line Education Material, E-Learning Platform Evaluation
System, Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP).
Abstract: In order to comprehensively evaluate the explosive growth of e-learning platform in recent years, this paper
constructs the evaluation system design and case capital budget of e-learning platform on the basis of
extensive research, uses analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to construct the judgment matrix of evaluation
index, determines the weight of each index, tests the consistency of the judgment matrix, and calculates the
weight of secondary index. Based on this index system, an online learning platform in China is analyzed and
evaluated. The results show that the evaluation system and method are effective.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the National Medium and Long-term Educational
Reform and Development Project Summary (2010-
2020) promulgated 2010, the construction of
lifelong education system and learning-oriented
society is overall planned and the goal of “basic
realization of education modernization, basic
formation of learning-oriented society and becoming
a human resource power” is established [see State
council 2010]. E-learning platform is undoubtedly
an important carrier in the construction of a learning
society, as well as an important means of practicing
lifelong education and lifelong learning. In recent
years, as internet-study is surging countrywide,
various E-learning platforms are emerging.
Scientific and reasonable evaluation on the E-
learning platform can improve the customer
satisfaction, the quality and efficiency as well as the
sustainable and healthy development of the platform.
The existing website platform evaluations fall into
two categories: the evaluation aims to general
website platform and the evaluation aims to specific
types of website platform. The researches on the
latter mostly focus on the e-commerce website
platform evaluation, government website platform
evaluation, and university website platform
evaluation. However, the researches on the
evaluation of E-learning platform websites are rare.
2 RELATIVE STUDY
Currently, the main body of the website platform
evaluation mainly includes the evaluation agencies
and scholars, whose evaluation criteria are not
uniform. Lots of world famous evaluation agencies
like comScore, Nile Company, Argus Associate can
provide website evaluation services. ComScore [see
comScore] is the world's leading internet and
digital media data statistic analysis agency. Based on
its MediaMetrix index, the agency releases the
website traffic rankings, and provides the most
comprehensive digital measurement solutions to the
industry website. Nile Company [see Nielsen ratings]
is a well known American internet market survey and
statistics company. The Nielsen ratings system
evaluates a website through its navigation, response
time, credibility, and content, etc., and provides
reference data for a company to formulate its media
delivery plan. Argus Associate [see Argus Associate]
proposed the evaluation of a website should base on
the site resource description, subjective evaluation,
design level, organization, and resource guidelines.
Scholars from all over the world put forward
website platform evaluation methods from different
perspectives. Some view website as a information
system and evaluate the site from the perspective of
internet information resource. Richmond [see
Richmond] proposes “10C” indices for internet
information resource evaluation. The “10C” means
204
Yue, Z.
Network Learning Platform Evaluation System Design and Case Capital Budget.
DOI: 10.5220/0012028200003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 204-213
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
Content, Credibility, Critical thinking, Copyright,
Citation, Continuity, Censorship, Connectivity,
Comparability and Context. Some evaluate a
website from the perspective of usability. Aziz and
his team [see Aziz et al.]
suggest evaluate a website
from the aspects of utility, benefit, learnability,
satisfaction, equal accessibility, etc. Ke Qing and her
team [see Ke Qing et al.2011] construct an index
system to evaluate the usability of the website
platform, which includes website size, website
quality, website promotion, website assistant
function, user emotion and so on. Some evaluate a
website from the perspective of user-perception. Pei
Ling and her team [see Pei Ling et al. 2009] design a
user-oriented measurement site information service
quality evaluation system based on the principle of
service quality management. The system includes
general impression, customer service indices, future
forecasts, technical indices, information indices,
interface indices and functional indices. While some
of the scholars evaluate a website form the
perspective of integrity. Gan Liren and his team [see
Gan Liren and Cai Lei 2003] evaluate a website
from its organization, symbol, website navigation,
retrieval system design, etc., based on information
architecture (IA) theory. Feng Yingjian [see Feng
Yingjian 2016] indicates that a complete corporate
website, no matter how complex it is, can be divided
into four components: structure, content, function
and service, and the website can be evaluated from
the four aspects.
The existing evaluation systems are mostly set
up from the manager’s point of view. Most of them
are based on the following foundations: one is the
actual data. For example, the resources the site has,
the number of students registered (rate), students’
participation in learning, course selection status quo,
etc., these data are generally provided by the
respondents. The other is expert grading. The
experts grade every evaluation index according to
the grading requirement after the establishment of
stratified evaluation index, such as resource type,
function provision [see Sun Meng 2015].
3 EVALUATION INDEX SYSTEM
AND THE WEIGHT SETTING
OF E-LEARNING PLATFORM
This research is based on the four website
components scholar Feng Yingjian putting forward-
structure, content, function and service. Based on
wide investigation and experts interviews and
combined with the characteristics of E-learning
platform, we set the evaluation index system and the
weight of each index by AHP.
3.1 Index System Setting
The evaluation index system built in this thesis
includes six primary indices and the corresponding
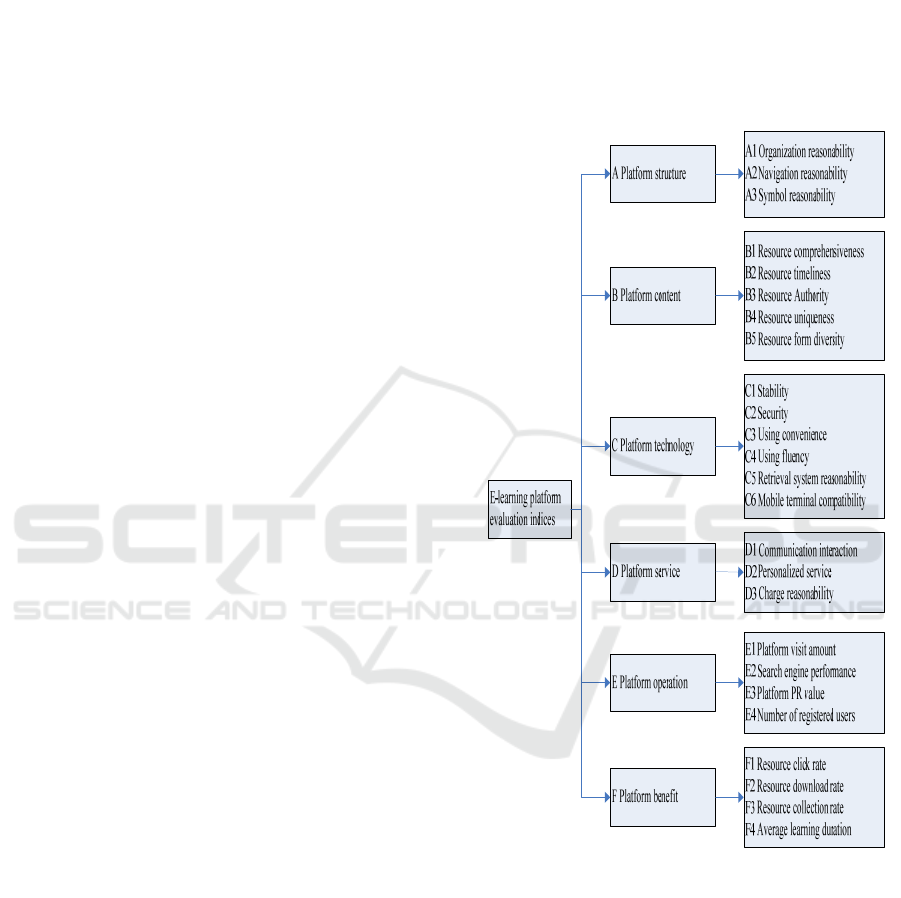
twenty five secondary indices. Show in diagram 1.
Diagram 1: The Evaluation Index model of E-learning
Platform.
3.1.1 Platform Structure
Platform structure reflects the E-learning platform
overall structure. It embodies in organization system,
navigation system and symbol system. Table 1 is the
meaning and key points of evaluation of each index.
Network Learning Platform Evaluation System Design and Case Capital Budget
205
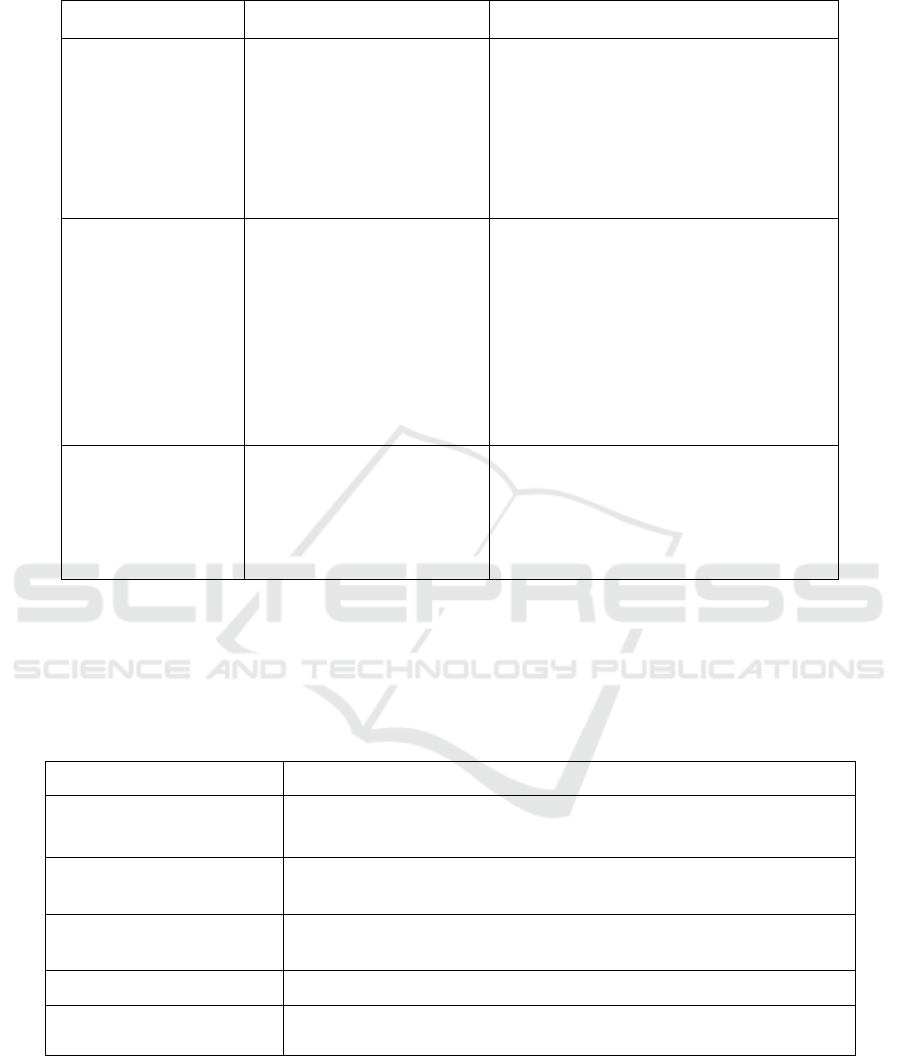
Table 1: Platform structure index.
Name of index Index interpretation Key points of evaluation
A1 Organization
reasonability
The organization system is
responsible for the
classification of information,
and hierarchical division of
the website content. It is the
basis for building a navigation
system.
Whether the organization structure is clear,
the classification logic is scientific and
reasonable, and whether the hierarchical tree
structure is employed in information
organization, whether the information
guidance is of high efficiency.
A2 Navigation
reasonability
Navigation system allows the
users to know their location
and path. The navigation
system is divided into global
navigation, local navigation,
contextual navigation and
supplementary navigation [see
Chen Lanjie 2007].
Whether the content of global navigation is
comprehensive and the location is consistent.
Whether the content of local navigation is
comprehensive and the location is consistent.
Whether the content of contextual navigation
is abundant and relevant. Whether the
supplementary navigation is comprehensive
and how is the consistency with other
navigations.
A3 Symbol
reasonability
Symbol is the description of
the information represented by
navigation elements with an
appropriate vocabulary [see
Wang Yongfang and Hu Yaolei
2014].
The consistency of symbol; the intelligibility
of symbol; the accuracy of symbol.
3.1.2 Platform Content
Platform content is the core and soul of E-earning
platform. The assessment of the platform content is
reflected in five aspects: comprehensiveness,
timeliness, authority, uniqueness, form diversity.
Table 2 shows the key points of evaluation of each
index.
Table 2: Platform content index.
Name of index Key points of evaluation
B1 Resource
comprehensiveness
Whether the platform is comprehensive or professional, and whether
resources type coverage is comprehensive.
B2 Resource timeliness
How is the update frequency of platform resource, whether the content is
out of date
B3 Resource authority
Whether the platform resource publishing agency is authoritative. How is
the authority level of the content interpreter.
B4 Resource uniqueness Whether the platform has a certain resource exclusively owned by itself.
B5 Resource form diversity
Resources provide the versions information, such as the video, audio, text,
PPT, etc,.
3.1.3 Platform Technology
Platform technology is the guarantee of the normal
operation of the network learning platform. It’s
necessary to consider the following aspects on the
technical side: stability, security, using convenience,
using fluency, retrieval system reasonability, and
mobile terminal compatibility. Table 3 shows the
key points of examination of each index.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
206
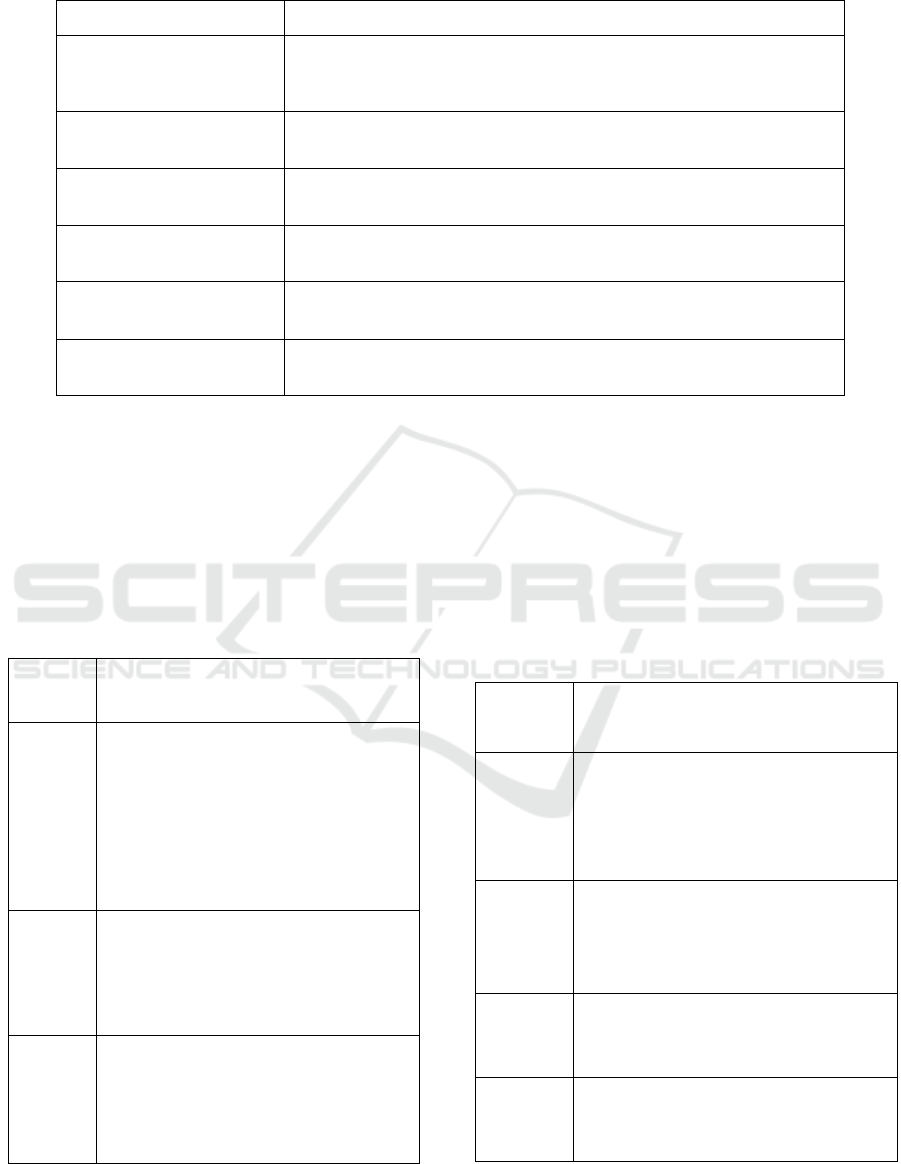
Table 3: Platform technology index.
Name of index Key points of evaluation
C1 Stability
With professional maintenance and disaster recovery function; without
missing chain and broken chain; can identify human error, with less
coding error.
C2 Security
Provide a security platform for the users and resources; maintain and
upgrade regularly.
C3 Using convenience
It’s easy to use the platform and with high operational efficiency, do not
deliberately remember its function and process.
C4 Using fluency
Platform information and resources can be downloaded fast, after
corresponding processing, the users feel good.
C5 Retrieval system
reasonability
The searching interface is good, with diversify searching forms, fast
searching speed, and error correction capability.
C6 Mobile terminal
compatibility
With mobile platform, can log in with different kinds of social platform
membership accounts.
3.1.4 Platform Service
The network learning platform need interact with
learners in order to play its function better. The
service of platform embodies in the following three
aspects: communication interaction, personalized
service, charge reasonability. Table 4 shows the key
points of evaluation of each index.
Table 4: Platform service index.
Name of
index
Key points of evaluation
D1
Commu
nication
interacti
on
Platform provide the communication
interface for the first users to log in,
provide the communication platform for
learners, such as learning group, forum,
etc., provide the communication interface
between learners and teachers.
D2
Personal
ized
service
Set up personal learning file for the
learners, recommend personalized
learning materials. The learners can
customize their own learning content.
D3
Charge
reasonab
ility
The ratio of the free resource, the price
reasonability of the charged resource.
3.1.5 Platform Operation
Platform operation is the guarantee of the
sustainable and healthy development of E-learning
platform. Platform operation embodies in the visits
amount growth, the search engine performance, the
platform PR value and the number of registered
users. The key points of examination of each index
are shown in table 5.
Table 5: Platform operation index.
Name of
index
Key points of examination
E1 The
visits
amount
situation
The platform visits amount, the growth
rate of PV values in fixed cycle, the
amount of independent identity visitors,
the quantity of per capita page visit,
average page visit depth, the bounce
rates.
E2 The
performan
ce of
search
engine
Whether be included by the main search
engine and ranks in the front places.
The
platform
PR value
Whether the PR values or weight are
greater than 4.
E4 The
number of
registered
users
The overall number of registered users;
the growth rate of registered users.
Network Learning Platform Evaluation System Design and Case Capital Budget
207
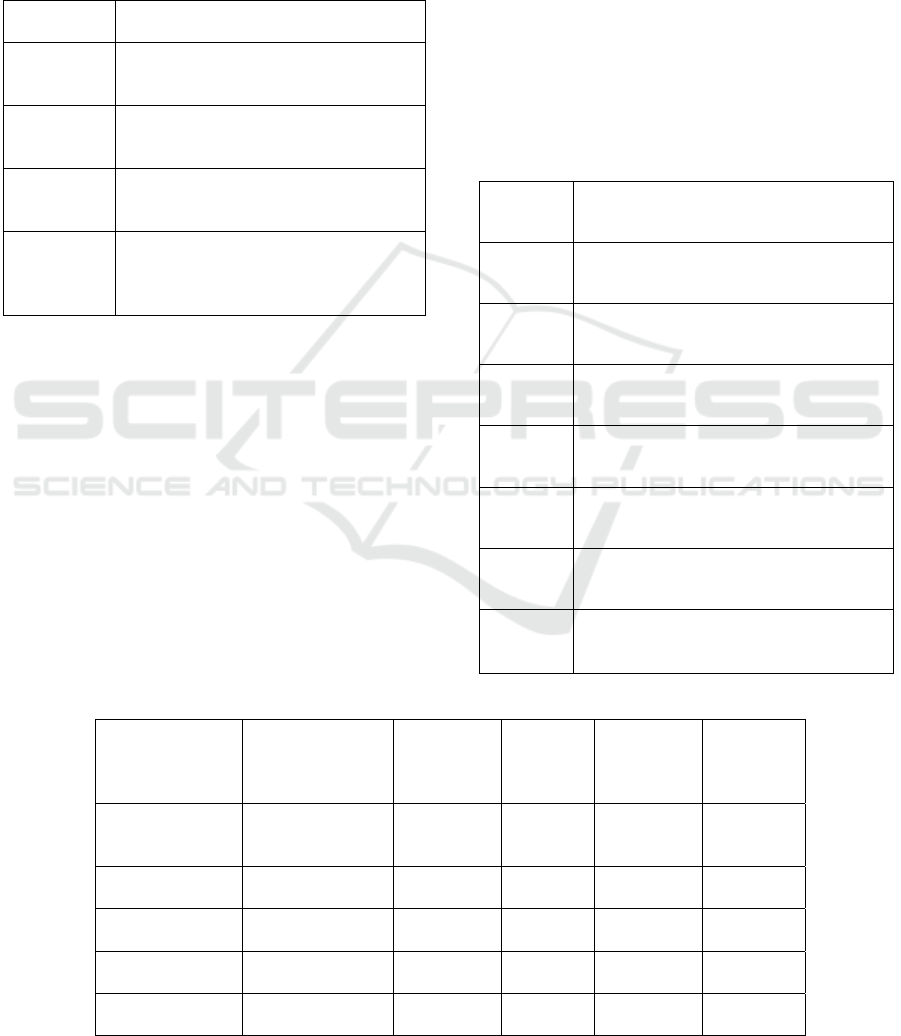
3.1.6 Platform Benefit
Platform benefit directly reflects the use situation of
E-learning platform. It is reflected in the resource
click rate, download rate, collection rate and the user
average learning duration. The key points of
evaluation of each index are shown in Table 6.
Table 6: Platform benefit index.
Name of
index
Key points of evaluation
F1 Resource
click rate
The click frequency of resource in
fixed cycle; the average click duration;
the click rate.
F2 Resource
download
rate
The download frequency of resource in
fixed cycle; the download rate.
F3 Resource
collection
rate
The collection frequency of resource in
fixed cycle; the collection rate.
F4 Users
average
learning
duration
The average learning duration of
registered users.
3.2 Index Weight Setting
The index weight of this evaluation system was set
by AHP based on the investigation. The procedures
are as follows:
3.2.1 The Construction of Judgement
Matrix
Take the secondary indices under “B Platform
Content” as an example. We set the evaluation
factors as {B1, B2, …, Bm}, and B represent the
target, then the judgement matrix is:
In the weight calculation of platform content B
(B1, B2, B3, B4, B5), the respondent has to make a
judgement on Bi and Bj, to decide which is more
important and how much it is important. And the
importance of each index is evaluated according to
the 1-9 proportion scale [see Qiu Junping 2009]
shown in Table 7. The final judgment matrix is
given in Table 8.
Table 7: 1-9 Proportion scale.
Scale b
ij
Meaning
1
The two factors have the same
importance
3 Factor i is slightly important than factor j
5
Factor i is obviously important than
factor j
7
Factor i is strongly important than factor
j
9
Factor i is extremely important than
factor j
2,4,6,8
The median of the two adjacent
judgments
Reciproc
al
b
ji
refers to the comparative judgment of
factor i and j, there are b
ji=
1/b
ij
Table 8: “B platform content” judgement matrix.
B platform
content
B1 Resource
comprehensivene
ss
B2
Resource
timeliness
B3
Resource
Authority
B4
Resource
uniqueness
B5
Resource
form
diversit
y
B1 Resource
comprehensiven
ess
1 1/4 1/5 1/2 1/3
B2 Resource
timeliness
4 1 1/2 3 2
B3 Resource
Authorit
y
5 2 1 4 3
B4 Resource
uniqueness
2 1/3 1/4 1 1/2
B5 Resource
form diversit
y
3 1/2 1/3 2 1
11 12 1
21 22 2
12
m
m
mm
bb b
bb b
B
b b bmm
=
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
208
3.2.2 Calculate the Relative Weights of the
Lower-Level Indices to the
Upper-Level Indices
(1) Normalize every column of judgement matrix B
(2) Add the normalized judge matrix according
to rows
(3) Normalize the vector
The resulting vector is the
required weight vector.
(4) Calculate the maximum eigenvalue of the
matrix
For any ( ),
is the i
th
component of vector AW.
The results obtained after the above-mentioned
processing on judgment matrix are shown in Table 9.
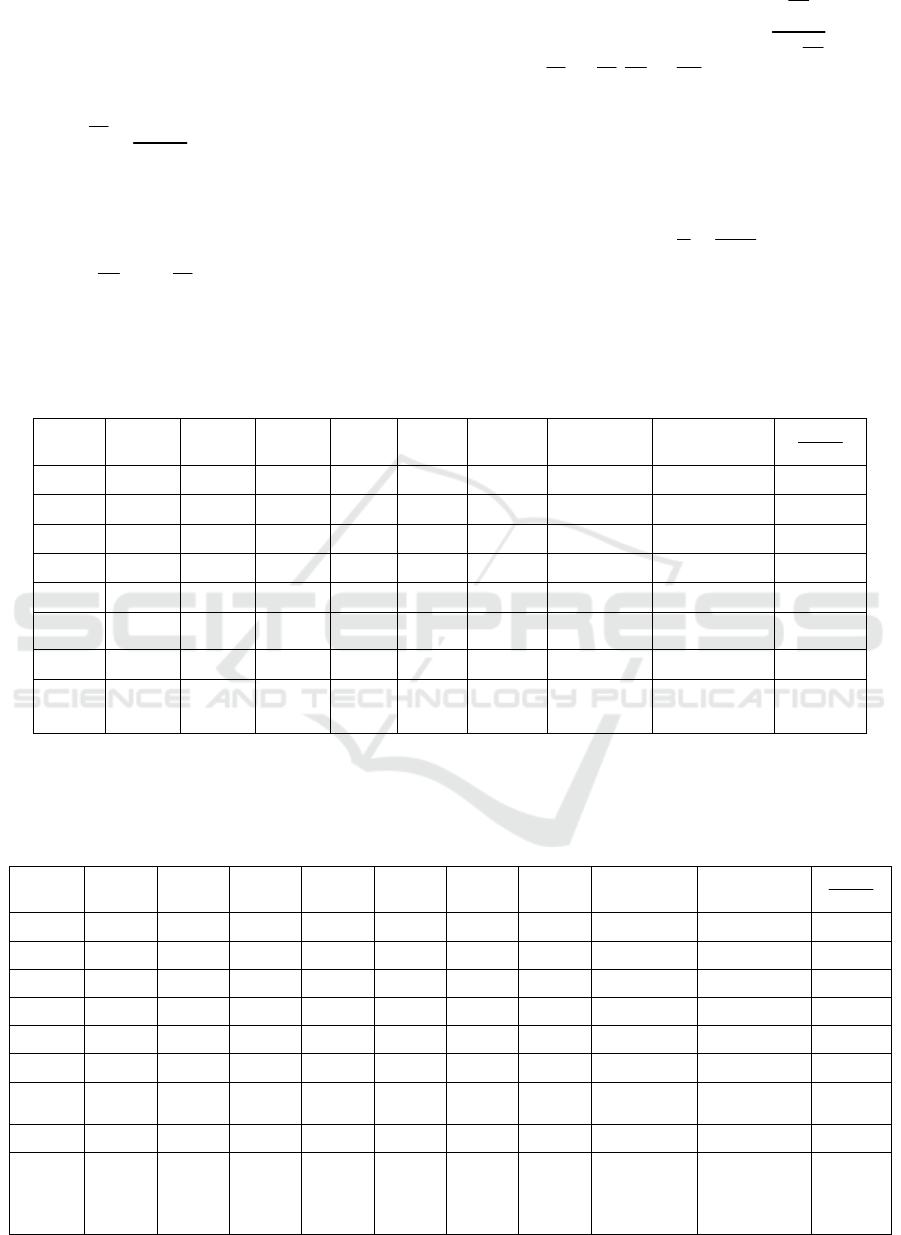
Table 9: The weight and the maximum eigenvalue of judgement matrix B.
B B1 B2 B3 B4 B5
Row
sum
Normalized
weight W
AW
B1 0.0667 0.0612 0.0876 0.0476 0.0488 0.3119 0.0624 0.3140 5.0345
B2 0.2667 0.2449 0.2190 0.2857 0.2927 1.3089 0.2618 1.3372 5.1080
B3 0.3333 0.4898 0.4380 0.3810 0.4390 2.0811 0.4162 2.1291 5.1154
B4 0.1333 0.0816 0.1095 0.0952 0.0732 0.4929 0.0986 0.4952 5.0234
B5 0.2000 0.1224 0.1460 0.1905 0.1463 0.8053 0.1611 0.8150 5.0603
column
sum
1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 5.0000
Sum: 25.3416
the maximum
eigenvalue:
5.0683
The weights and the maximum eigenvalues of
the overall matrix T and the judgement matrix A, C,
D, E, F can be calculated according to the above
method, as shown in Table 10, Table 11, Table 12,
Table 13, Table 14 and Table 15 respectively.
Table 10: The weights and the maximum eigenvalues of the overall matrix T.
T A B C D E F
Row
sum
Normalized
weight W
AW
A 0.0923 0.1020 0.0778 0.0706 0.1290 0.1429 0.6146 0.1024 0.6218 6.0694
B 0.3692 0.4082 0.4669 0.4235 0.3226 0.2857 2.2761 0.3794 2.3562 6.2111
C 0.2769 0.2041 0.2335 0.2824 0.2581 0.2381 1.4930 0.2488 1.5459 6.2126
D 0.1846 0.1361 0.1167 0.1412 0.1935 0.1905 0.9626 0.1604 0.9864 6.1486
E 0.0462 0.0816 0.0584 0.0471 0.0645 0.0952 0.3930 0.0655 0.3952 6.0335
F 0.0308 0.0680 0.0467 0.0353 0.0323 0.0476 0.2607 0.0434 0.2634 6.0639
column
sum
1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 6.0000
Sum: 36.7392
the
maximum
eigenvalue:
6.1232
1
, 1, 2, ,
ij
ij
m
kj
k
ij m
b
b
b
=
==
1
1,2, ,i
m
i
j
j imbW
=
==
{
}
12 m,,
T
W
ωω ω
=
1
i
i
m
j
j
w
w
w
=
=
1, 2 ,()
T
m
Wwww=
max
λ
1
1
()
max
m
i
AW i
m
i
w
λ
=
=
1, 2, ,im=
()iAW
i()
i
AW
w
i()
i
AW
w
Network Learning Platform Evaluation System Design and Case Capital Budget
209
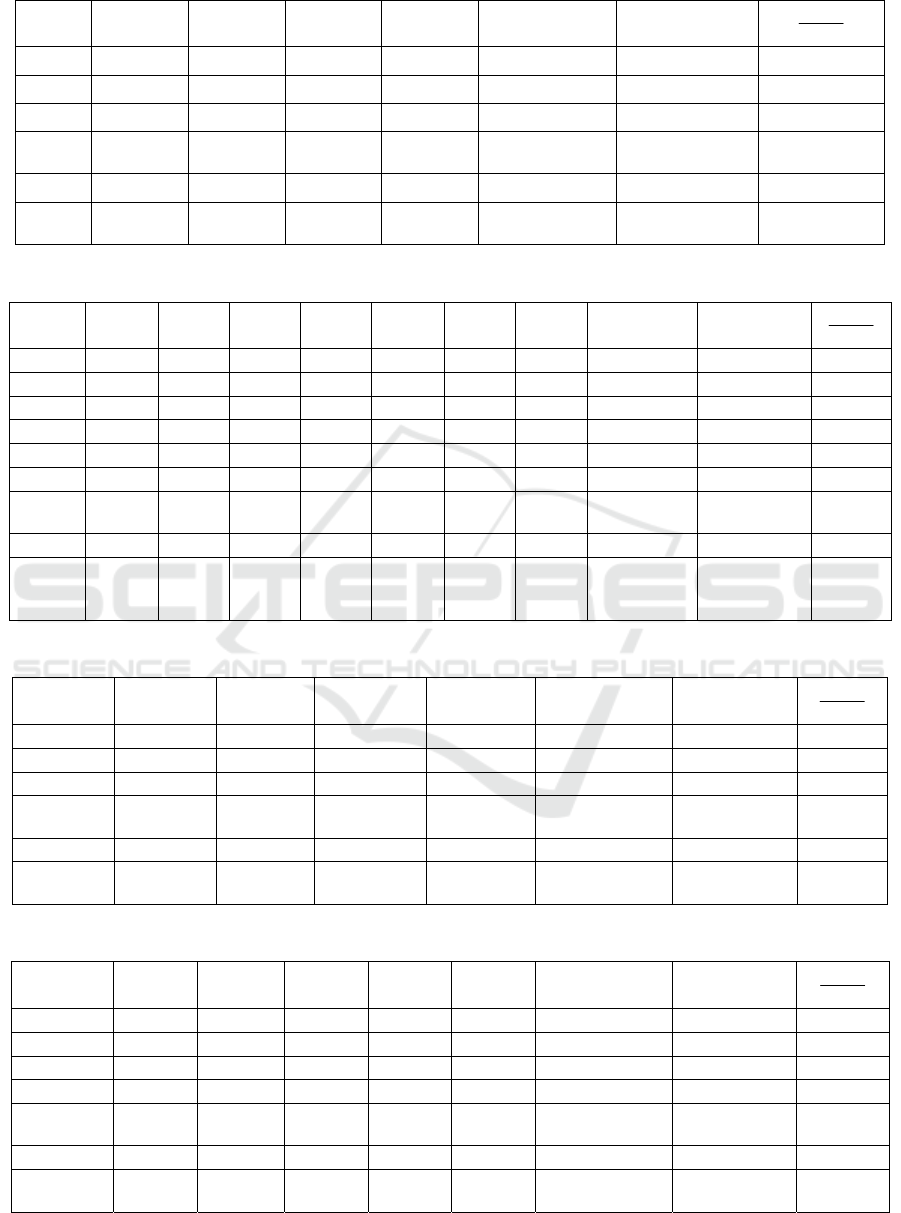
Table 11: The weights and the maximum eigenvalues of the judgement matrix A.
A A1 A2 A3 Row sum
Normalized
weight W
AW
A1 0.1667 0.1818 0.1429 0.4913 0.1638 0.4921 3.0044
A2 0.5000 0.5455 0.5714 1.6169 0.5390 1.6248 3.0147
A3 0.3333 0.2727 0.2857 0.8918 0.2973 0.8943 3.0085
column
sum
1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 3.0000
Sum: 9.0276
the maximum
ei
g
envalue:
3.0092
Table 12: The weights and the maximum eigenvalues of the judgement matrix C.
C C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6
Row
sum
Normalized
weight W
AW
C1 0.0923 0.0706 0.1020 0.0778 0.1429 0.1290 0.6146 0.1024 0.6218 6.0694
C2 0.1846 0.1412 0.1361 0.1167 0.1905 0.1935 0.9626 0.1604 0.9864 6.1486
C3 0.3692 0.4235 0.4082 0.4669 0.2857 0.3226 2.2761 0.3794 2.3562 6.2111
C4 0.2769 0.2824 0.2041 0.2335 0.2381 0.2581 1.4930 0.2488 1.5459 6.2126
C5 0.0308 0.0353 0.0680 0.0467 0.0476 0.0323 0.2607 0.0434 0.2634 6.0639
C6 0.0462 0.0471 0.0816 0.0584 0.0952 0.0645 0.3930 0.0655 0.3952 6.0335
column
sum
1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 6.0000
Sum: 36.7392
the
maximum
ei
g
envalue:
6.1232
Table 13: The weights and the maximum eigenvalues of the judgement matrix D.
D D1 D2 D3 Row sum
Normalized
weight W
AW
D1 0.5455 0.5000 0.5714 1.6169 0.5390 1.6248 3.0147
D2 0.1818 0.1667 0.1429 0.4913 0.1638 0.4921 3.0044
D3 0.2727 0.3333 0.2857 0.8918 0.2973 0.8943 3.0085
column
sum
1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 3.0000
Sum: 9.0276
the maximum
eigenvalue:
3.0092
Table 14: The weights and the maximum eigenvalues of the judgement matrix E.
E E1 E2 E3 E4
Row
sum
Normalized
weight W
AW
E1 0.2609 0.3077 0.3000 0.2400 1.1086 0.2771 1.1201 4.0416
E2 0.1304 0.1538 0.2000 0.1600 0.6443 0.1611 0.6469 4.0160
E3 0.0870 0.0769 0.1000 0.1200 0.3839 0.0960 0.3853 4.0152
E4 0.5217 0.4615 0.4000 0.4800 1.8633 0.4658 1.8872 4.0513
column
sum
1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 4.0000
Sum: 16.1242
the maximum
eigenvalue:
4.0310
i()
i
AW
w
i()
i
AW
w
i()
i
AW
w
i()
i
AW
w
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
210

Table 15: The weights and the maximum eigenvalues of the judgement matrix F.
F F1 F2 F3 F4
Row
sum
Normalized
weight W
AW
F1 0.2609 0.3000 0.3077 0.2400 1.1086 0.2771 1.1201 4.0416
F2 0.0870 0.1000 0.0769 0.1200 0.3839 0.0960 0.3853 4.0152
F3 0.1304 0.2000 0.1538 0.1600 0.6443 0.1611 0.6469 4.0160
column
sum
1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 4.0000
Sum: 16.1242
the
maximum
eigenvalue:
4.0310
3.2.3 Consistency Test
Consistency test is the weight reasonable test of
each judgement matrix after the weights are
calculated.
The Calculation formula for CR (Consistency
ratio):
The Calculation formula for CI (Consistency
index) (m is the order of the judgement matrix):
RI refers to the average random consistency
index, the value table shown in table 16 [see Qiu
Junping 2009].
Table 16: The average random consistency index.
order 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
RI 0 0 0.58 0.9 1.12 1.24 1.32 1.41 1.45 1.49 1.51
When CR ≤ 0.1, that the weight order of the
level has a satisfactory consistency, otherwise the
elements value of the judgement matrix need to be
re-adjusted.
Based on the formula, the CR of matrix T, A, B,
C, D, E, F are 0.0199, 0.0079, 0.0152, 0.0199,
0.0079, 0.0115, 0.0115 respectively. The weight
order of the level obviously has a satisfactory
consistency.
3.2.4 The Synthetic Weight Calculation
The calculation of synthetic weight of each level
index to the system target is the secondary index
weight multiplied by the primary index it belonged.
The results are shown in table 17.
Table 17: Evaluation index weight table.
Primary index
(weight)
Secondary index
Secondary index
relative weight
Synthetic
weight
The certain
platform grade
A Platform
structure
(0.1024)
A1 Organization
reasonabilit
y
0.1638 0.0168 90 1.512
A2 Navigation
reasonabilit
y
0.539 0.0552 80 4.416
A3 Symbol
reasonabilit
y
0.2973 0.0304 80 2.432
B Platform
content
(0.3794)
B1 Resource
comprehensiveness
0.0624 0.0237 88 2.0856
B2 Resource
timeliness
0.2618 0.0993 85 8.4405
B3 Resource Authorit
y
0.4162 0.1579 90 14.211
i()
i
AW
w
CI
CR
R
I
=
max
1
m
CI
m
λ
−
=
−
iW
iY
iiWY
Network Learning Platform Evaluation System Design and Case Capital Budget
211
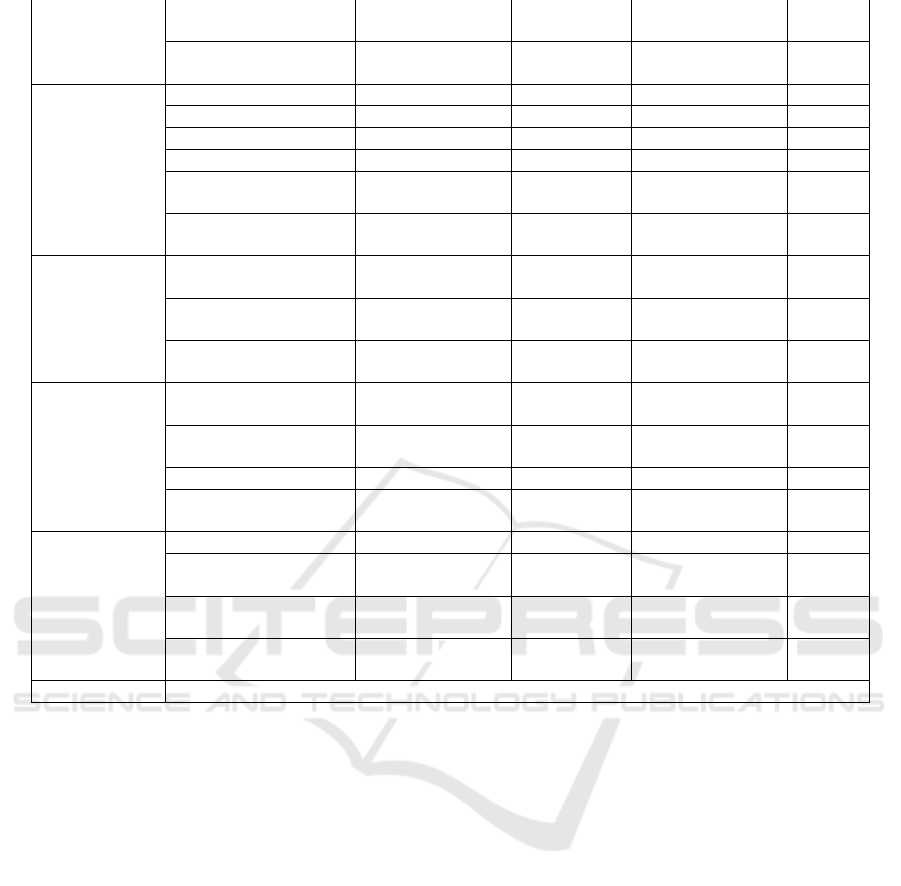
B4 Resource
uni
q
ueness
0.0986 0.0374 70 2.618
B5 Resource form
diversit
y
0.1611 0.0611 70 4.277
C Platform
technology
(0.2488)
C1 Stabilit
y
0.1024 0.0255 90 2.295
C2 Securit
y
0.1604 0.0399 85 3.3915
C3 Using convenience 0.3794 0.0944 88 8.3072
C4 Using fluency 0.2488 0.0619 85 5.2615
C5 Retrieval system
reasonabilit
y
0.0434 0.0108 87 0.9396
C6 Mobile terminal
com
p
atibilit
y
0.0655 0.0163 90 1.467
D Platform
service
(0.1604)
D1 Communication
interaction
0.539 0.0865 86 7.439
D2 Personalized
service
0.1638 0.0263 80 2.104
D3 Charge
reasonabilit
y
0.2973 0.0477 80 3.816
E Platform
operation
(0.0655)
E1 Platform visits
amount
0.0106 0.0182 90 1.638
E2 Search engine
p
erformance
0.1611 0.0106 90 0.954
E3 Platform PR value 0.096 0.0063 86 0.5418
E4 Number of
registered users
0.4658 0.0305 90 2.745
F Platform
benefit
(0.0434)
F1 Resource click rate 0.2771 0.0120 85 1.02
F2 Resource download
rate
0.096 0.0042 80 0.336
F3 Resource collection
rate
0.1611 0.0070 85 0.595
F4 Average learning
duration
0.4658 0.0202 88 1.7776
Total 84.6203
4 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
According to the established evaluation system
design of e-learning platform and the case capital
budget, evaluate a popular e-learning platform in
China. For the four indicators A, B, C and D, ten
people who often study on the platform are invited
to score the second-level evaluation indicators with
full marks, and the average value is calculated as the
score of each indicator. For the two indexes E and F,
we interviewed the management and maintenance
personnel of the platform, searched relevant data
through professional tools, and comprehensively
gave the scores of each secondary index. As shown
in Table 17, the comprehensive score of this
platform can be calculated as 84.6203, which is also
consistent with our subjective judgment.
5 CONCLUSION AND
PROSPECTS
This paper draws on the theoretical and methodical
achievements of the academic circles at home and
abroad in the evaluation of the website platform,
especially the online education website platform.
According to the characteristics of network learning
platform and the intensive research, an online study
platform index system is built from six aspects and
each index weigh is set by Analytic Hierarchy
Process. Then a case study based on one certain
online study platform is conducted according to the
system.
For the survey sample data is limited in the
process of index setting and case study, the accuracy
of the weight and grade needs to be improved in the
future. In the next step, we will expand the survey
and interview samples to have a further research.
Meanwhile, we will develop automatic evaluation
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
212

tools to improve the efficiency of the evaluation and
make the process of the evaluation more exercisable.
REFERENCES
[Argus Associate 2017] Argus Associate EB/OL. 2017-6-
10 http://www.gotoargus.com/
[Aziz et al. 2015] Aziz, N. S. Kamaludin and A., Sulaiman,
N.: “Assessing web site usability measurement”;
EB/OL.2017 -06 -11. http://openedu.shtvu.org.cn/u-
pload/qikanfile/201406041 439324233.pdf.
[Chen Lanjie 2007] Chen Lanjie: “Discussion on the
Micro-information Architecture of the Local
Government Website-on the Inspection Object of
Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen Government
Website”; J. Information Science, 25, 6 (2007), 852-
857.
[comScore 2017] comScore EB/OL
http://www.comscore.com.
[Feng Yingjian 2016] Feng Yingjian: “Web Marketing
Theory and Practice”; M. 5
th
version. Beijing:
Tsinghua University Press, (2016), 84.
[Gan Liren and Cai Lei 2003] Gan Liren and Cai Lei: “On
the Application of Information Architecture——
Examination & Evaluation of the Government
Websites in China”; J. Information studies: Theory
& Application, 26, 6 (2003), 487-491.
[Ke Qing et al.2011] Ke Qing, Wang Xiufeng, Zheng
Yanning and Pan Yunta: “Website Usability Indicators
and Calculation Methods Based on Site Traffic
Statistics”; J. Library and Information Service, 55, 20
(2011), 138-143.
[Mingxuan Wu et al. 2014] Mingxuan Wu, Ergun Gide
and Rod Jewell: “The EBS management model: an
effective measure of e-commerce satisfaction in SMEs
in the service industry from a management
perspective”; Electronic Commerce Research, 14,
1(2014), 71-86.
[Mingxuan Wu et al. 2012] Mingxuan Wu, Rod Jewell and
Ergun Gide: “An eyeball diagram: illustrating the
common CSFs in e-commerce business satisfaction
for successful adoption of e-commerce systems by
SMEs”, Int. J. Electronic Customer Relationship
Management, 6, 2(2012), 169-192.
[Nielsen ratings 2017] Nielsen ratings EB/OL
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Niel sen_ratings
[Pei Ling et al.2009] PeiLing and Wang Jintao: “Research
on User -Oriented Appraisal Framework of Website
Information Service Quality”; J. Journal of
Information, 5 (2009), 60-64.
[Qiu Junping 2009] Qiu Junping: “Information Analysis”;
M. Beijing: Science Press, (2009), 227-231.
[Richmond 2013] Richmond, B.: “Ten C's For
Evaluating Internet Sources”; EB/OL. 2017-06-11
http://www.juniata.edu/services/library/redesign/links
we-beval/10cswebeval.pdf.
[State council 2010] The State council: “National Medium
and Long-term Educational Reform and Development
Project Summary (2010-2020)”, (2010).
[Sun Meng 2015] Sun Meng: “Design and Empirical
Study of Evaluation Criteria for Communitye-
learning Systems”; D. East China Normal University,
(2015)
[Wang Yongfang and Hu Yaolei 2014] Wang Yongfang
and Hu Yaolei: “Analysis on the Key indicators affect
the Government portal information disclosure and
efficiency”; J. E-government, 3 (2014), 73-81.
Network Learning Platform Evaluation System Design and Case Capital Budget
213
