
A Study of the Factors Influencing Labour Productivity in the
Construction Industry from a Lean Perspective: A Structural
Equation Modelling Approach
Liangqing Sun
1,*
, Lixuan Jiang
1
, Erlong Wang
2
and Wei Zeng
2
1
School of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Technology, Pukou, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
2
China Construction Third Bureau Group Limited, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Keywords: Labour Productivity, Resource Efficiency, Process Efficiency, Structural Equation Modelling.
Abstract: Labour productivity in the construction industry is an important factor in measuring the development level of
the construction industry. In order to better promote the development of the construction industry and to
facilitate the improvement of labour productivity in the construction industry, the study takes the influencing
factors of labour productivity in the construction industry as the object, defines the two dimensions of resource
efficiency and process efficiency of labour productivity influencing factors from a lean perspective, and
constructs the structure of "influencing factors - resource and process efficiency - labour productivity". A
structural equation model of "influencing factors - resources, process efficiency - labour productivity" was
constructed. The final results confirm the importance of resource efficiency and process efficiency in
improving labour productivity, and suggest countermeasures based on the findings of the study.
1 INTRODUCTION
As an important industrial sector of the national
economy, the construction industry plays an
immeasurable role in the stable development of the
economy. In recent years, the number of enterprises
in the construction industry has gradually expanded
in scale, but the industry as a whole has performed
with low efficiency, poor profitability, low average
technological content and, in particular, a seriously
low level of labour productivity, which is not in line
with the scale of the industry. Therefore, how to
improve labour productivity in the construction
industry has become the focus of research to promote
sustainable growth in the construction industry. A
comprehensive overview of the current state of
research at home and abroad shows that there is
currently more research on the factors influencing
labour productivity in the construction industry, but
there is a lack of research on the loss of labour
productivity due to the waste that exists in the
process. Therefore, from a lean perspective, the
influencing factors of labour productivity are
distinguished into two dimensions, namely resource
efficiency and process efficiency, and the paths and
degrees of influence of each influencing factor on
labour productivity through resource efficiency and
process efficiency are studied by constructing
structural equation models, and suggestions and
countermeasures are put forward in response to the
analysis results, which are of great significance in
promoting the improvement of labour productivity in
the construction industry.
2 CURRENT STATE OF
DEVELOPMENT OF THE
CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY
UNDER DATA ANALYSIS
2.1 Analysis of the Current Situation of
Labour Employment in the
Construction Industry
The construction industry is labour-intensive and
requires a large number of manual workers to
complete operational tasks. At the same time, the
educational level requirement is low and the relevant
positions absorb a large number of migrant workers.
Through big data analysis, in terms of age
distribution, 38.78% of labour workers in the
236
Sun, L., Jiang, L., Wang, E. and Zeng, W.
A Study of the Factors Influencing Labour Productivity in the Construction Industry from a Lean Perspective: A Structural Equation Modelling Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0012028800003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 236-246
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

construction industry are aged over 50, 26.94% are
aged 40-49, 22.98% are aged 30-39, 7.41% are aged
25-29, and 3.89% are aged under 24. According to the
China Human Capital Report 2020 published by the
Human Capital and Labour Economics Research
Centre of the Central University of Finance and
Economics, the average age of China's population is
38.8 years old (approximately 39 years old). It can be
seen that nearly 66% of labour workers in the
construction industry are older than the average age
of China's population, and there is a lack of young,
high-quality labour resources in the construction
labour market.
50 or more
40-49 YO
30-39 YO
25-29 YO
24 or less
38.78%
26.94%
22.98%
7.41%
3.89%
Figure 1: Construction labour age release.
2.2 Analysis of the Current State of
Materials Utilization in the
Construction Industry
Rough construction is widespread, leading to a
serious waste of materials, energy and human
resources. In addition, the various segments of the
construction industry are disconnected from each
other and building materials are basically supplied in
the form of raw materials, resulting in a large amount
of manual reprocessing of raw materials once they
arrive at the construction site and a large amount of
actual loss of materials. For example, raw materials
of various sizes are delivered to the construction site,
"dismembered" to form a large amount of
construction waste and then shipped out of the city.
Statistical analysis of the data shows that, compared
to the construction of buildings in developed
countries, the use of steel is 10% to 25% higher per
square metre and the use of cement is 80 kg higher
per square metre. It can be seen that although China's
construction industry is developing rapidly, the
transition process from rough construction to fine
construction has been relatively slow.
2.3 Analysis of the Current State of
Management in the Construction
Industry
On the one hand, there are deficiencies in the
management system of construction enterprises,
leading to the emergence of poor execution,
especially by those located at the end of management.
On the other hand, basic aspects of the system of
ownership, distribution, personnel and operating
procedures of the enterprise are not adapted to the
increasingly competitive environment. In addition,
the regulations and technical specifications
governing the conduct of the construction market are
still imperfect, the appraisal system lacks objective
criteria, and employees are not motivated to work
efficiently.
3 FACTORS AFFECTING
LABOUR PRODUCTIVITY IN
THE CONSTRUCTION
INDUSTRY
Analysing the current state of development of the
construction industry provides a basis for studying
labour productivity in the construction industry.
From the level of the construction industry, domestic
and foreign researchers based on a large number of
analyses and studies have obtained the factors
influencing labour productivity in the construction
industry such as technology level, management
capacity, wage level, labour force, material and
equipment, external environment and capital
investment.
Huo Chunting (2013) analysed the factors
influencing labour productivity in construction
enterprises by building a structural equation model,
and the results showed that human resources and
material inputs have an indirect positive impact on
labour productivity in enterprises. Li Qingxiu (2017)
used DEA-Malmquist index and multiple regression
models to evaluate the total factor productivity,
technical efficiency and technology level of China's
construction industry. The factors affecting the
technological progress of the construction industry in
different regions were identified, and the evaluation
results showed that technological investment and
asset investment promote the development of total
factor productivity and put forward rationalization
suggestions. Liu Guiwen et al. (2011) established a
labour productivity growth function model to analyse
the degree of influence of technological progress and
A Study of the Factors Influencing Labour Productivity in the Construction Industry from a Lean Perspective: A Structural Equation
Modelling Approach
237

capital deepening on labour productivity growth, and
concluded that the positive influence of technological
progress on labour productivity is greater than that of
capital investment, and the actual growth rate of
average labour productivity in China's construction
industry is lower. Liu and Qin (2010) used a linear
regression model to analyse the impact of wages on
labour productivity in the construction industry, and
concluded that wages have a facilitating effect on
labour productivity, and each increase of 1 yuan in
wages can lead to an increase of 1.45 yuan in labour
productivity.
From the perspective of construction
professionals, foreign scholars DBH (2009)
identified constraints that negatively affect labour
productivity such as skills shortages in the sector,
procurement methods for construction projects, the
impact of regulations and lack of innovation in
certain sectors of the industry, particularly in relation
to construction materials.Jarkas (2012) et al.
identified factors that affect labour productivity,
which were further divided into Bekr (2016) found
that poor planning and scheduling, shortage of
materials on project sites, shortage of equipment and
tools, lack of skilled labour, poor site management,
rework due to construction errors, obsolete and
inefficient equipment, lack of supervisory
experience, delayed payments to suppliers, and slow
response from consultants inspecting the work can
lead to labour productivity losses in the construction
industry. Loss of labour productivity. Shamil (2016),
through literature research, came up with 46 factors
that affect labour productivity. 36 engineers were
interviewed face-to-face through questionnaires and
interviews, and analysis of the questionnaire data
revealed that project management factors such as
efficiency of project planning, working environment,
procurement methods, experience of managers,
technical knowledge, and inefficient site layout all
affect labour productivity. On the other hand, found
through questionnaires that the management level of
managers had a significant impact on labour
productivity (Almeida and Carneiro 2009; Alinaitwe
and Mwakali 2007; Abdulaziz and Bitar 2012).
Based on an in-depth study of the relevant
literature, the various factors affecting labour
productivity performance can usually be categorised
into five areas, referred to as the 5Ms, namely
management and control, labour, materials and
equipment, external factors and incentives, which
further provides the basis for constructing the
research model for the thesis.
4 A THEORETICAL MODEL OF
THE FACTORS INFLUENCING
LABOUR PRODUCTIVITY IN A
LEAN PERSPECTIVE
4.1 Application of Lean Construction
Theory
Lean construction is derived from lean production,
which is a successful application of the principles of
economic production in the field of building
construction. This new construction management
model can effectively help construction companies to
reduce costs, improve the quality of their work,
increase their real profitability and play a huge role in
the process of schedule control, safety management
and environmental management.
Furthermore, researchers of lean construction
argue that the labour production process in the
construction industry focuses only on the resource
level of utilisation and lacks attention to the waste
that exists in a large number of processes, resulting in
low labour productivity. Resource efficiency and
process efficiency is an important aspect of lean
construction, where resource rationalisation and
reliable processes not only improve labour
productivity and project performance, but also lead to
faster delivery of construction projects at lower cost
and higher quality.
4.2 Resource Efficiency and Process
Efficiency
Efficiency is the amount of work done per unit of
time. In management terms, efficiency refers to the
ratio between the various inputs and outputs of an
organisation in a given time.
Resource efficiency refers to the efficiency of the
input and output of resources, usually using human
resources, capital resources and natural resources as
input factors. In the concept defined in this paper,
resource efficiency refers to the maximisation of the
value created given the input conditions of various
resources (labour, materials and equipment, etc.) and
examines the value created in the process of
development and utilisation of resources in an
integrated manner. The input indicators for
measuring resource efficiency are natural resources,
human and capital resources, etc., and the output
indicator is the useful value created.
Process efficiency is the amount of compliant
product or service that a process can deliver in a given
amount of time given a certain amount of resources
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
238

invested. In Lean thinking, the variability of work
processes increases the amount of waste and hinders
the performance of the system, so labour productivity
losses can be reduced by improving process
efficiency and eliminating waste.
This study addresses the topic of workforce
management, focusing on site productivity
improvements. exploratory research by Kisi (2017)
and others identifies system and operational
inefficiencies to estimate optimal labour productivity.
modig and Ahlström (2015) propose 'process
efficiency' to reflect the relationship between time
spent creating value and total time. while 'resource
efficiency' focuses on maximising the utilisation of
machines and individual workers. Therefore, this
paper uses 'process efficiency' and 'resource
efficiency' to distinguish between two different
sources of labour productivity. Time-motion studies
and PPC metrics are used to measure both 'resource
efficiency' and 'process efficiency'.
4.3 Theoretical Model of Factors
Influencing Labour Productivity
At the individual project level, there are two branches
of productivity performance measurement. The Lean
approach focuses more on performance measures
based on project schedule, processes and procedures
than the traditional approach which focuses only on
the optimisation of resource utilisation, providing a
useful framework for the industry to improve labour
productivity. Based on this logic, 'resource efficiency'
and 'process efficiency' were selected as key
antecedent variables affecting labour productivity in
the construction industry, based on the relationship
between the influencing factors and the resource
efficiency input indicators and process efficiency
influencing factors, including management and
control, labour, external factors and incentives. Based
on the relationship between the influencing factors
and resource efficiency input indicators and process
efficiency influencing factors, the five key factors of
management and control, labour, materials and
equipment, external factors and incentives are further
divided into two dimensions: resource and process,
and the differences between the influencing factors of
different dimensions are analysed to draw a labour
productivity model mediated by resource efficiency
and process efficiency. The research model of this
paper is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 2: Research model.
5 RESEARCH DESIGN AND
DATA COLLECTION
5.1 Questionnaire Design
By consolidating several literature descriptions of the
same variable differentiation and distinguishing
between factors that fall under resource efficiency
and process efficiency, specific measures of each
variable and literature sources were derived as shown
in Table 1. The study was conducted on the basis of a
questionnaire with questionnaire measure items using
a 5-point Likert scale to assess the likelihood of
influencing factors (1=very unlikely, 5=very likely)
that determine productivity. The completed
questionnaire was reviewed, progressively revised
and refined and finally validated. The final
questionnaire consisted of 11 factors and 41
measures.
Table 1: Construction of variables and sources of factors influencing labour productivity.
Potential variables Measurement problem items Source
Management factors
(MC)
MC1 Construction Management Capability Doloi et al. (2012), Dai et al.
(2009), Huang et al. (2008),
Ibbs and McEniry (2008),
Bernold and AbouRizk
(2010), and Ghoddousi and
Hosseini (2012)
MC2 Site Management
MC3 Communication
MC4 construction method
MC5 rework
MC6 Lack of supervision
A Study of the Factors Influencing Labour Productivity in the Construction Industry from a Lean Perspective: A Structural Equation
Modelling Approach
239

MC7 overtime
MC8 on-site storage
Workforce (skills)
(W)
W1 Workforce Training Kazaz and Ulubeyli (2004),
Hanafi et al. (2010), Durdyev
et al. (2013)
Bernold and AbouRizk
(2010), and Mojahed and
Aghazadeh (2008)
W2 Worker experience and skills
W3 Education level of the workforce
Labour force (mobility)
(W)
W4 Production technology and process changes
W5 Change in labour capacity
W6 Workers' personal wishes
Materials and equipment
(availability)
(ME)
Availability of ME1 equipment tools Alonso et al. (2007), Pratibha
and Gaikwad (2015), Kazaz
et al. (2008), and Page (2010)
Availability of ME2 materials
Suitability or adequacy of the plant and equipment
used for ME3
Materials and equipment
(utilisation)
(ME)
ME4 Delayed supply of construction materials
Shortage of materials on site for ME5 project
Lack of tools and equipment on the ME6 market
External factors
(administrative)
(E)
E1 Economic situation Ghoddousi and Hosseini
(2012), Moselhi and Khan
(2010), Durdyev et al. (2017),
and Ratcliffe and Stubbs
(2003)
E2 Excessive influence of the owner on the
construction
p
rocess
E3 regulations and laws
External factors (natural)
(E)
E4 Health and safety conditions
E5 Meteorological conditions
E6 accident
Incentives
(M)
Amount of M1 compensation Van Tam et al. (2018).
Hiyassat et al. (2016),
Mahamid (2013a) Hiyassat
et al. (2016) Mahamid et al.
(2013), Jarkas (2015)
M2 creates competition
M3 job satisfaction
Motivation of M4 workers
M5 facilitation opportunities
M6 Awards and Punishments
Resource efficiency
(RE)
RE1 Programme Completion Rate (PPC) Buchan et al. (2006), Kazaz
et al. (2008), Smith (2013),
Gouett et al. (2011),Hwang et
al. (2018),Neve et al. (2020a)
RE2 Direct working time (DW)
RE3 Non-value added working time (NVAW)
Process efficiency
(PE)
PE1 Programme Completion Rate (PPC)
PE2 direct working time (DW)
PE3 Non-value added working time (NVAW)
Labour productivity
(P)
P1 project duration Soekiman et al. (2011) and
Kazaz et al. (2016)
P2 Quality objectives achieved
P3 Projected cost of quality
5.2 Results of Data Collection
The data collection process took the form of a
professional questionnaire published on a website
and the information required from those working in
the construction industry (skilled workers, architects,
builders, engineers, quantity surveyors and project
managers). A total of 300 questionnaires were
distributed (50 face-to-face and 250 via an online
questionnaire). At the end of the survey, a total of 201
valid questionnaires were identified and the sample
size met the basic requirements. Based on the 201
collected data, a questionnaire reliability analysis was
carried out through SPSS software, and the results
showed that the Cronbach's alpha value for the whole
questionnaire reached 0.937, indicating that the
questionnaire had good reliability.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
240

6 RESEARCH FINDINGS AND
ANALYSIS
6.1 Reliability and Validity Tests of the
Measurement Model
Firstly, the suitability test of the model. Suitability
tests were carried out by SPSS 22.0 to reduce the data
set dimensional data according to principal
components, where the KMO test value was 0.901
and the statistical value of Bartlett's sphere test had a
probability of significance of 0.000, indicating that
the questionnaire data met the prerequisite
requirements for factor analysis.
Secondly, the reliability of the model was tested
using the widely used criterion of Cronbach's alpha
coefficient greater than 0.7, and then the reliability of
the model was tested according to the criterion that
the overall correlation coefficient (CITC) of the items
should not be less than 0.5 as proposed by the scholar
Churchill. The analysis showed that the Cronbach's
alpha coefficient for each construct was greater than
0.8 and the CITC values were all above 0.5,
indicating that the questionnaire had high reliability.
Finally, the model convergent validity was tested.
The convergent validity of the measurement model
was subjected to a validation-type factor analysis.
Further assessment of the structural model could only
be performed if the fit of the measurement model met
acceptable criteria. As can be seen from Table 2
below, the standardised factor loadings for each
question were greater than 0.5 or more, and the
residuals were positive and significant. The
composite reliability (C.R.) values were greater than
0.7 and the average variance extracted (AVE) values
were greater than 0.5, all of which met the criteria for
convergent validity and the fit was within acceptable
limits. The model was retained for subsequent
analysis.
Table 2: Results of the validation factor analysis.
Structure
Title
item
Non-
standardised
factor loadin
g
s
Standard
Error S.E.
C.R. (t-
value)
P
Standardise
d factor
loadin
g
s
CR AVE
Workforce
(Skills)
W1 1 0.788
0.801 0.573
W2 1.091 0.098 11.127 *** 0.753
W3
0.988 0.091 10.901 *** 0.729
Incentives
M1
1 0.759
0.88 0.551
M2
1.056 0.083 12.716 *** 0.768
M3
1.034 0.084 12.26 *** 0.742
M4
1 0.083 12.051 *** 0.73
M5
0.957 0.083 11.562 *** 0.703
M6
1.044 0.084 12.404 *** 0.75
External factors
(Nature)
E4
1 0.742
0.84 0.637
E5
1.089 0.089 12.296 *** 0.784
E6
1.232 0.094 13.068 *** 0.864
Materials and
equipment
(Utilisation)
ME4
1 0.855
0.866 0.684
ME5
0.999 0.065 15.303 *** 0.826
ME6
0.931 0.063 14.78 *** 0.799
External factors
(Administrative)
E1
1 0.782
0.792 0.56
E2
1.026 0.097 10.549 *** 0.715
E3
1.055 0.097 10.845 *** 0.747
Materials and
equipment
(Availability)
ME1
1 0.816
0.867 0.685
ME2
1.211 0.079 15.378 *** 0.873
ME3
1.145 0.081 14.123 *** 0.791
Workforce
(Mobility)
W4
1 0.846
0.896 0.741
W5
1.168 0.066 17.651 *** 0.876
W6
1.119 0.065 17.296 *** 0.861
A Study of the Factors Influencing Labour Productivity in the Construction Industry from a Lean Perspective: A Structural Equation
Modelling Approach
241

Management and
control
MC1
1 0.818
0.899 0.529
MC2
1.033 0.07 14.661 *** 0.786
MC3
0.884 0.069 12.747 *** 0.707
MC4
0.774 0.065 11.856 *** 0.667
MC5
0.908 0.072 12.596 *** 0.7
MC6
0.833 0.07 11.877 *** 0.668
MC7
0.916 0.073 12.503 *** 0.696
MC8
0.915 0.065 14.017 *** 0.76
Resource
efficiency
RE1
1 0.802
0.789 0.557 RE2
0.956 0.088 10.872 *** 0.757
RE3 0.919 0.091 10.086 *** 0.674
Process efficiency
PE1
1 0.867
0.792 0.563
PE2
0.723 0.072 10.015 *** 0.648
PE3
0.804 0.074 10.867 *** 0.719
Labour
productivity
P1 1 0.698
0.822 0.608 P2 1.312 0.121 10.844 *** 0.861
P3 1.218 0.112 10.884 *** 0.772
6.2 Studies Based on Structural
Equation Modelling
6.2.1 Evaluation of the Overall Fit of the
Model
Table 4 details the key fit indicators from the
structural model tests. When compared to the
recommended values given for the fitness indicators,
the fitted values for the fitness indicators fall within
the recommended values. It can be seen that the
setting of the theoretical model is acceptable.
Table 3: Model fit.
Fitted
indicators
Acceptable range
Measured
values
CMIN - 941.357
DF - 741
CMIN/DF <3 1.270
GFI >0.8 0.868
AGFI >0.8 0.847
RMSEA <0.08 0.031
IFI >0.9 0.966
TLI(NNFI) >0.9 0.962
CFI >0.9 0.966
6.2.2 Results of Testing the Research
Hypothesis
The structural relationships between the latent
variables and the estimates of their standardised path
coefficients, t-values and hypothesis testing results
are shown in 5. As can be seen, all hypotheses passed
the t-test and the path coefficients were significant at
the confidence level of α = 0.001. The final model of
the factors influencing labour productivity in the
construction industry (path relationship) and the
standardised path coefficients between each of its
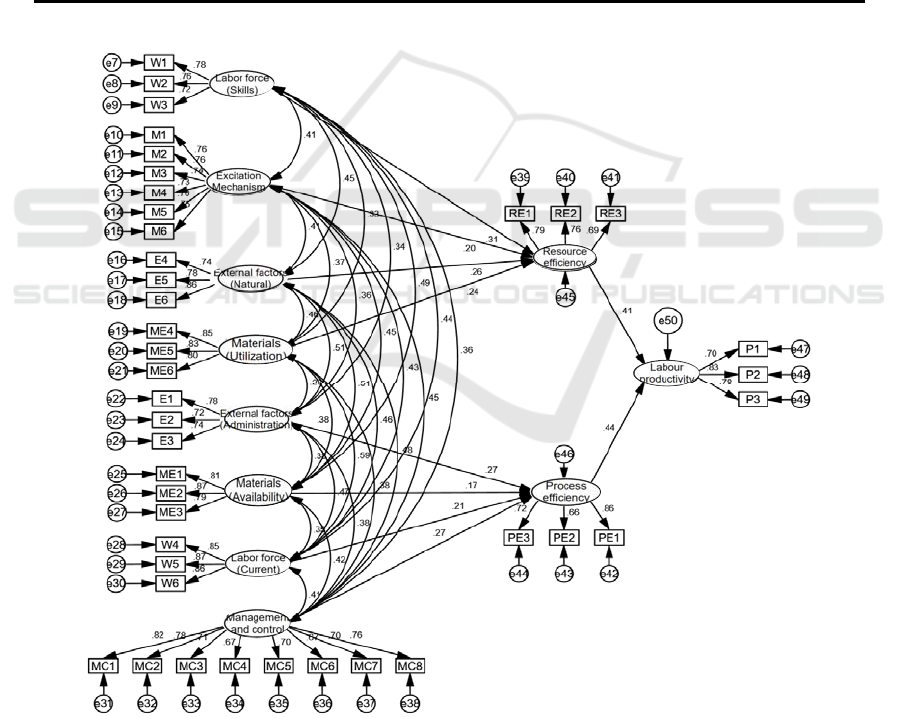
internal variables are obtained, as shown in Figure 2.
Table 4: Structural equation model path coefficients.
Path relationships
Standard
i-sation
factor
Non-
standardized
coefficients
Standard
error
T-
value
P
Assuming
establishment
of support
Resource
efficienc
y
<--
Workforce
(skills)
0.313 0.358 0.084 4.275 *** Support
Resource
efficienc
y
<-- Incentives 0.203 0.214 0.071 3.032 0.002 Support
Resource
efficiency
<--
External
factors
(
natural
)
0.26 0.308 0.088 3.502 *** Support
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
242

Resource
efficiency
<--
Materials and
equipment
(utilisation)
0.235 0.213 0.061 3.499 *** Support
Process
efficiency
<--
External
factors
(administrative
)
0.266 0.321 0.091 3.529 *** Support
Process
efficiency
<--
Materials and
equipment
(
availabilit
y)
0.171 0.221 0.087 2.526 0.012 Support
Process
efficienc
y
<--
Labour force
(
mobilit
y)
0.213 0.226 0.074 3.054 0.002 Support
Process
efficienc
y
<--
Management
and control
0.271 0.3 0.076 3.954 *** Support
Labour
p
roductivit
y
<--
Process
efficienc
y
0.411 0.338 0.061 5.57 *** Support
Labour
p
roductivit
y
<--
Resource
efficienc
y
0.441 0.326 0.055 5.97 *** Support
Note: ***=P<0.001
6.2.3 Analysis of Resource and Process
Mediation Effects
This paper applies the Bootstrap technique to re-
estimate the standard errors and confidence intervals
for the indirect effect and the results of the validation
data are shown in Table 6. Following the
determination criteria that the upper and lower
intervals of Bias-corrected and Percentile do not
contain 0 and Z > 1.96 or Z= 1.96, which proves that
the indirect effect holds, the data show that both
resource efficiency and process efficiency have
significant indirect effects.
Table 5: Resource, process efficiency intermediary validation.
Paths
Indirect effects
Bias-Corrected Percentile
95% CI 95% CI
Valuation Lower Upper Lower Upper
1 Labour force (skills)
→ resource efficiency
→
labour productivity
0.129 0.05 0.25 0.034 0.225
2 Incentives →
Resource efficiency →
Labour productivity
0.083 0.017 0.203 0.009 0.187
3 External factors
(nature) → resource
efficiency → labour
p
roductivit
y
0.107 0.016 0.263 0.011 0.249
4 Materials and
equipment (utilisation)
→ resource efficiency
→ labour productivity
0.097 0.035 0.194 0.02 0.171
5 External factors
(administrative) →
process efficiency →
0.117 0.026 0.262 0.024 0.258
A Study of the Factors Influencing Labour Productivity in the Construction Industry from a Lean Perspective: A Structural Equation
Modelling Approach
243
6 Materials and
equipment (availability)
→ process efficiency →
labour productivity
0.075 0.007 0.18 0.003 0.174
7 Labour (mobility) →
process efficiency →
labour productivity
0.094 0.03 0.191 0.019 0.171
8 Management and
control → Process
efficiency → Labour
productivity
0.119 0.043 0.244 0.032 0.227
Figure 3: Final model of factors influencing labour productivity in the construction industry.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
244

7 STRATEGIES FOR
SUSTAINABLE LABOUR
PRODUCTIVITY GROWTH IN
THE CONSTRUCTION
INDUSTRY
The final model shows that the impact of resource
efficiency and process efficiency on labour
productivity in the construction industry is verified to
exist, with the process aspect having a more
significant impact on labour productivity than the
traditional resource utilisation dimension. Factors
such as labour (skills), incentives, external factors
(nature) and material and equipment (utilisation)
affect labour productivity by influencing resource
efficiency and hence labour productivity. Of these,
labour force skills are the most important factor with
a path coefficient of 0.313 and material and
equipment utilisation with a path coefficient of 0.235.
It is therefore necessary to provide regular training
for workers and to enhance the maintenance and
renewal of materials and equipment for construction
projects. In addition, management and control,
external factors (administrative), labour (mobility)
and material and equipment availability factors have
an impact on process efficiency, with management
and control being the most important factor with a
path coefficient of 0.271. Clearly, the construction
project management team plays an important role in
conveying tasks and instructions to workers. The
results are therefore reasonable, as inadequate
management and control can lead to a reduction in
construction labour productivity.
The findings suggest that improving labour
productivity in the construction industry can be
considered from both resource and process
perspectives, with more focus on performance
measurement based on project objectives (schedule,
cost and quality), and improving resource utilisation
and optimising process efficiency based on lean
theory, thereby achieving the goal of improving
labour productivity.
8 CONCLUSION
Firstly, we systematically review and analyse the
influencing factors of labour productivity in the
construction industry, identify the potential
influencing factors of labour productivity in the
construction industry from five levels: management
and control, labour, external factors, materials and
equipment and incentives, and introduce resource
efficiency and process efficiency, transforming the
influencing factors of labour productivity from the
traditional resource utilisation perspective to the
resource-process optimisation objective The model
of labour productivity is constructed. The model
provides a reliable model basis and practical guidance
for decision-making on labour productivity in the
construction industry.
Secondly, the relationship between labour
productivity factors was analysed using structural
equation modelling and the final structural model was
derived based on acceptable GOF measures. The
analysis of the model's parameter estimation showed
that the effects of resource efficiency and process
efficiency on labour productivity were significantly
present. In addition, among the influencing factors,
labour force skills, management and control are the
most important factors affecting resources and
processes respectively.
Finally, through quantitative research, the
relationship between labour productivity influencing
factors and resource efficiency and process efficiency
is verified, and it is proposed that the practice of
focusing on both resources and processes in the
labour production process in the construction
industry achieves improved labour productivity and
project performance to deliver construction projects
faster with lower costs and higher quality. It also
provides a theoretical basis for subsequent in-depth
research on labour productivity in the construction
industry.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study contains funds: Ministry of Housing and
Urban-Rural Development: 2019 Science and
Technology Plan Project (2019-R-017); Jiangsu
Provincial Department of Housing and Urban-Rural
Development Science and Technology Service
Project: Research on Lean Construction
Implementation Strategy and Key Benchmark
Creation in Jiangsu Province Construction Industry
(202140755). Enterprise Cooperation Project:
Research on Process Interpolation and Efficiency
Improvement of Modern General Hospital from the
Perspective of Lean Construction (202141076).
A Study of the Factors Influencing Labour Productivity in the Construction Industry from a Lean Perspective: A Structural Equation
Modelling Approach
245

REFERENCES
Abdulaziz M, Jarkas, Camille G, Bitar. Factors Affecting
Construction Labor Productivity in Kuwait[J].
Management, 2012(138):811-820.
Almeida R,Carneiro P. The Return to the Firm Investment
in Human Capital [J]. Labour Economics,2009(16):97-
106.
Alinaitwe H M, Mwakali J A, Hansson B. Factors affecting
the productivity of building craftsmen-studies of
Uganda[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and
Management,2007, 13(3):169-176.
Bekr, G. A Mahamid.(2016). "Study of Significant Factors
Affecting Labor Productivity at Construction Sites in
Jordan: Site Survey. "Journal of Engineering
Technology (JET).4(1) 92-97.
DBH (Department of Building and Housing). (2009).
"Report of the building and construction sector
productivity taskforce." Wellington, New Zealand.
Huo Chunting. Research on the analysis of labor
productivity level of enterprises in China's construction
industry [D]. Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013.
Jarkas, A. M., and Bitar, C. G. (2012). "Factors affecting
construction labor productivity in Kuwait." J. Constr.
Eng. Manage., 10.1061/(ASCE)CO .1943-
7862.0000501, 811-820.
Kisi,K.P., N. Mani, E. M. Rojas, and T. Foster. 2017.
"Optimal productivity in labor-intensive construction
operations:Pilot study. "J. Constr. Eng. Manage.
143(3):04016107.https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CO .
1943-7862.0001257.
Li Qingxiu. Research on total factor productivity and
influencing factors of China's construction industry
[D]. Northeast University of Finance and Economics,
2017.
Liu Guiwen, Diao Yanbo, Chen Lisan. Analysis of the
impact of technological progress on labor productivity
in the construction industry[J]. Science and Technology
Progress and Countermeasures, 2011, 28(13):52-55.
Liu QJ, Qin DW. Research on the relationship between
wages and labor productivity in construction
enterprises[J]. Cooperative Economics and
Technology, 2010, (392):30-31.
Modig, Niklas; Åhlström, Pär (2015), This is Lean:
Resolving the Efficiency Paradox. Stockholm:
Rheologica Publishing.-ISBN: 978-91- 87791-09-3.
Naoum S G. Factors influencing labor productivity on
construction sites:a state-of-the-art literature review
and a survey[J].International Journal International
Journal of Productivity and Performance
Management,2016,65(3):401-421.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
246
