
Analysis of the Effect of Business Model Innovation on the
Sustainability Performance of Manufacturing Enterprises Based on
Fixed Effects Model
Wenyan Pan
*
and Shuheng Song
School of Safety Science and Emergency Management, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
Keywords: Business Model Innovation, Business Performance, Sustainable Economy.
Abstract: Manufacturing is the backbone of China's economy and the driver of economic growth, and the role of
sustainable development of manufacturing enterprises for the national economy cannot be ignored. The
innovation of business models gives vitality to enterprises and continuously promotes the improvement of
their economic and environmental performance. Therefore, exploring the connection between the business
model innovation of manufacturing firms and their sustainability performance is of great concern. The
research takes panel data of China’s listed manufacturing enterprises from 2010 to 2016 as an example to
construct regression models and uses content analysis to empirically verify that both novelty-centered and
efficiency-centered business model innovation significantly and positively affect the sustainability
performance of the listed manufacturing enterprises.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the context of accelerating the transformation of
economic development mode, the sustainable
development of enterprises has increasingly become
a heated topic in the related field of research. At
present, the manufacturing industry, which is the
pillar industry of China's national economy, is under
great pressure to transform and upgrade. Innovation,
as the root of the development of the manufacturing
industry, has become an essential issue to facilitate its
sustainable development. Business model innovation
taps new business values for enterprises, reduces
transaction costs, improves production efficiency,
increases profit income, and promotes the sustainable
and healthy development of enterprises. This is why
it is of great significance to study business model
innovation in manufacturing companies nowadays.
Based on the background above, the study sets the
research object as A-share listed manufacturing
enterprises from 2010 to 2016 and uses this as a
sample to study the effect of business model
innovation on the sustainable development
performance of the listed manufacturing enterprises
in China, with a view to exploring effective ways to
promote the sustainable development of
manufacturing firms.
2 THEORETICAL ANALYSIS
AND HYPOTHESIS
Corporate business model innovation energizes the
inherent business model through continuous
innovation, creating new growth drivers and
competitive advantages, thus continuously promoting
the expansion of new markets and creating new
engines for the increase of corporate operating
income and profits. Li Wei (2017) found that
efficiency-centered business model innovation
significantly and positively affects the market and
financial performance of enterprises, while novelty-
centered business model innovation positively
influences the financial performance in
manufacturing SMEs. Given that the concept of
sustainable development has received increasing
attention in recent years, research on the
sustainability performance of enterprises has also
emerged. The concept of sustainable development
demands that companies focus on both economic and
environmental benefits and achieve the integration
and coordination of profit growth and environmental
protection. Mao Shiying (2011) highlighted the
significant role of business model innovation in the
development of the green economy. Business model
innovation, as a new form of innovation, can greatly
Pan, W. and Song, S.
Analysis of the Effect of Business Model Innovation on the Sustainability Performance of Manufacturing Enterprises Based on Fixed Effects Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0012029100003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 263-269
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
263

promote the implementation of green development
strategies. Zhou Wenyong et al. (2012) pointed out
that the business model innovation of manufacturing
enterprises in the low-carbon context can promote the
growth of their own profits and the sustainability of
their development. The results of the above-
mentioned studies show that the continuous
innovation of enterprise business models can
significantly contribute to the improvement of the
financial and environmental performance of
enterprises. Based on this, it is inferred that both
novelty-centered and efficiency-centered business
model innovation can effectively contribute to the
sustainable development of enterprises.
Wu Jun et al. (2016) point out that novelty-
centered business model innovation promotes
business development by creating a new business
model that increases people's willingness to pay and
improves the user experience, thereby sustaining
value creation, improving market reputation,
expanding the user base, and creating a sustainable
competitive advantage. At the same time, driven by
the concept of sustainability, companies create new
products and low-carbon services that are beneficial
to the environment through the introduction of
creative trading and business models, thus promoting
their own environmental performance. Based on this,
this paper proposes H1: Novelty-centered business
model innovation can positively and significantly
improve enterprise sustainability performance.
Zott et al. (2007) argue that efficiency-centered
business models can promote the improvement of
transaction efficiency by reconfiguring the value
chain, thus saving more costs for business partners.
Wang Xuejun et al. (2016) point out that through
efficiency-centered business model innovation,
enterprises bring into play their resource allocation
and value chain integration capabilities to save scarce
decision-making opportunities and operating costs
for themselves and their partners, thus promoting
their value creation and sustainable development.
Based on this, this paper proposes H2: Efficiency-
centered business model innovation can positively
and significantly improve corporate sustainability
performance.
3 DATA AND RESEARCH
DESIGN
3.1 Sample and Data Sources
In the study, the 2016 A-share listed companies with
the top 500 innovation capabilities are used as the
research sample, and the data from 2010 to 2016 of
the listed manufacturing companies on the list are
studied. The secondary data involved in the study
were obtained from Wind and CSMAR. The data of
novelty-centered and efficiency-centered business
model innovation were coded and quantitatively
scored for the content of CSR reports using the
content analysis method. In this paper, the sample is
screened as follows: (1) Delete ST and *ST
enterprises. (2) Delete delisted companies in that
year. (3) Remove the samples with a large number of
missing important data of observations of relevant
variables. Finally, a total of 620 valid samples were
obtained. This study utilized Stata for the data
processing of the variables.
3.2 Variable Definition
(1) Novelty-centered and efficiency-centered
business model innovation. According to the study of
Zott et al. (2007), the forms of business model
innovation were divided into two categories:
efficiency-based innovation and novelty-based
innovation. And with reference to the study of Mallin
et al. (2012), the content analysis method was used to
code and quantitatively assign values to the content
of the social responsibility reports of the studied
manufacturing companies from 2010 to 2016. The
method of assigning scores is as follows: 0 points for
the part lacking relevant textual descriptions; 1 point
for the part involving relevant textual descriptions; 2
points for the part involving in-depth descriptions or
quantification; the final score is the average of the
scores.
(2) Sustainability performance of enterprises.
Referring to the study of Ilias (2018), corporate
sustainability performance was divided into two
dimensions: financial and environmental
performance. And with reference to the study of Xie
Xuemei et al. (2021), the financial performance and
environmental performance of enterprises are
measured by the total asset return and the
environmental score of social responsibility of listed
companies, respectively. Finally, referring to the
research method of Xi Longsheng et al. (2022), the
entropy weighting method is used to calculate the
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
264
combined score of the two dimensions, and the final
score is used to measure corporate sustainability
performance. The data of the two indicators are first
normalized in Python, and then the combined score is
calculated based on the weights.
(3) Control variables. Firm size (Size), the gearing
ratio (Lev), years on the market (ListAge), and
growth rate of operating income (Growth) were used
as control variables. In addition, dummy variables are
also set to control for yearly and individual effects.
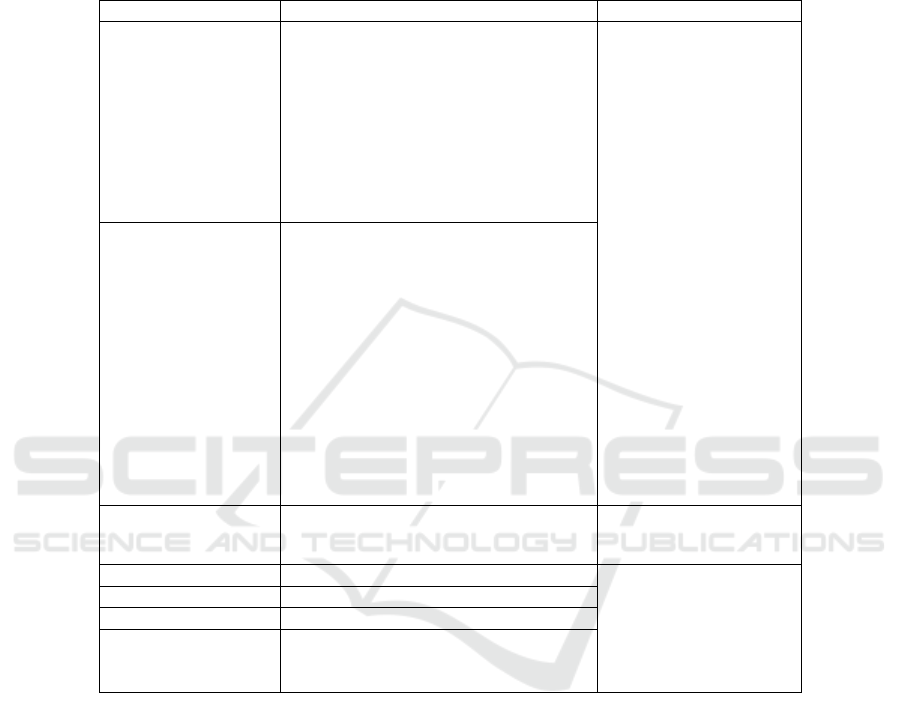
Table 1: Variable Definition.
Variable Definitions Sources
Novelty
①A novel transaction method is adopted
②The new business model brings new
partners to the company
③Provides a new way of combining
information, services, and products
④The company adopts a novel way to
motivate its partners
⑤ The company continuously improves
the business model
Corporate Social
Responsibility Report
Efficiency
① Reduces marketing, transaction, or
communication costs for its partners
②The flow of products, services, and
information in the transaction process is
transparent
③Enterprises can know a lot of
information about products, services,
and partners
④Enterprises exchange and share
information with partners in the
transaction process
⑤New business models make
transactions more efficient
Score
Entropy weighted sum of Roa and CSR
rating environmental score
Hexun, Wind
Size ln(total assets)
Wind
Lev ln
(
current
y
ea
r
- listed
y
ear+1
)
ListA
g
e Total liabilities/total assets at
p
eriod en
d
Growth
Operating income for the year /
Operating income for the previous year -
1
3.3 Model Construction
To test hypotheses H1 and H2, the study constructs
the following empirical models.
𝑆𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒
𝛼
𝛼
𝑁𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑡𝑦
𝛼
𝑆𝑖𝑧𝑒
𝛼
𝐿𝑖𝑠𝑡𝐴𝑔𝑒
𝛼
𝐿𝑒𝑣
𝛼
𝐺𝑟𝑜𝑤𝑡
ℎ
𝑌𝑒𝑎𝑟
𝜀
1
𝑆𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒
𝛼
𝛼
𝐸𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
𝛼
𝑆𝑖𝑧𝑒
𝛼
𝐿𝑖𝑠𝑡𝐴𝑔𝑒
𝛼
𝐿𝑒𝑣
𝛼
𝐺𝑟𝑜𝑤𝑡
ℎ
𝑌𝑒𝑎𝑟
𝜀
2
4 DATA RESULTS AND
ANALYSIS
4.1 Descriptive Statistics
Table 2 shows the results of descriptive statistics of
the indicators in the study. According to Table 2, the
mean value of novelty-centered business model
innovation is 0.371, while the mean value of
efficiency-centered business model innovation is
0.407. In comparison, the degree of novelty-centered
business model innovation is lower than that of
efficiency-centered business model innovation. This
Analysis of the Effect of Business Model Innovation on the Sustainability Performance of Manufacturing Enterprises Based on Fixed Effects
Model
265
reflects that the sample companies are more
concerned with the improvement of their overall
efficiency than with the degree of novelty of their
business models. The very large value of 0.960 and
the very small value of 0.0435 for the sustainability
performance of manufacturing firms show a large
extreme difference, indicating that there are
significant differences in sustainability performance
among firms
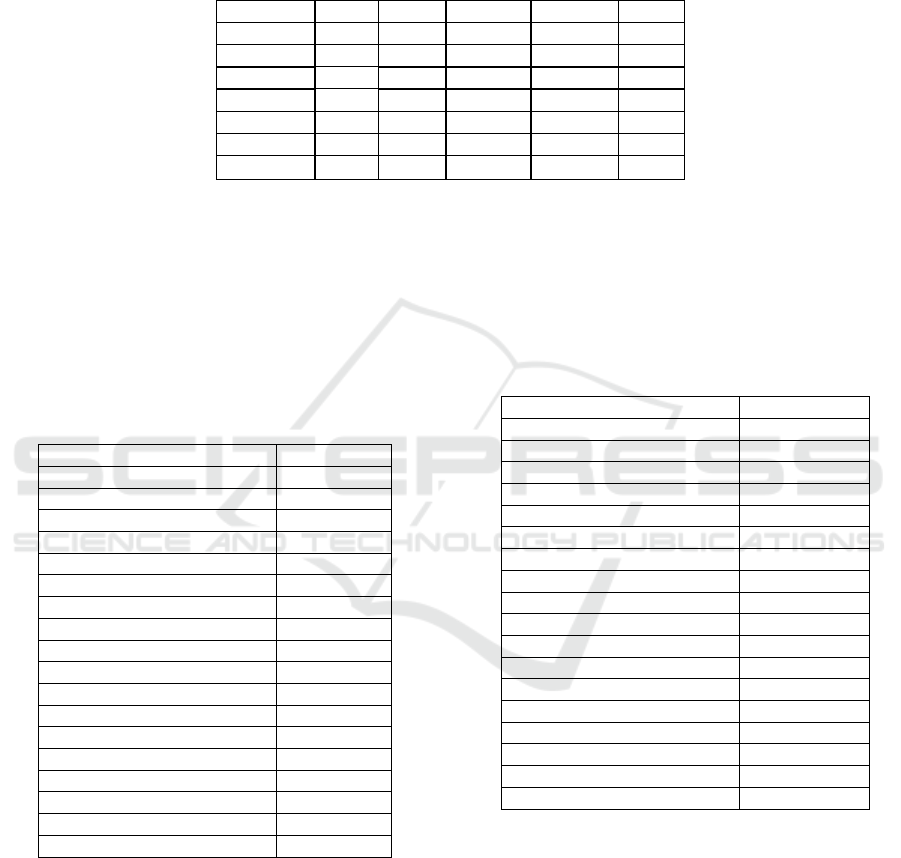
Table 2: Descriptive Statistics.
Variable N Max Min Mean S
d
Novelt
y
620 1.400 0 0.371 0.260
Efficienc
y
620 1.400 0 0.407 0.298
Score 620 0.960 0.0435 0.404 0.153
Size 620 26.06 20.39 23.27 1.116
ListAge 620 3.219 0 2.531 0.495
Lev 620 0.821 0.0341 0.488 0.174
Growth 620 6.817 -0.487 0.170 0.382
4.2 Regression Results
In this paper, fixed effects regressions were
conducted on the sample according to the empirical
model. The regression results are shown respectively
in Table 3 and Table 4.
Table 3: Regression Results of Novelty-centered Business
Model Innovation and Sustainability Performance of the
Listed Manufacturing enterprises.
Variable Score
Novelt
y
0.062**
(
2.24
)
Size 0.029
(1.34)
ListAge 0.046
(
1.26
)
Lev -0.070
(
-0.87
)
Growth 0.018
(1.57)
Constant -0.343
(
-0.72
)
R-s
q
uare
d
0.283
F 18.97
Number of Company 91
Company FE YES
Year FE YES
Observations 620
*** p<0.01, ** p<0.05, * p<0.1
According to Table 3, The R-square of model (1)
is above 28%, and F-value is 18.97, which is
significant at the significance level of p<0.001,
indicating that the model is meaningful. The
regression results show that the regression coefficient
between novelty-centered business model innovation
and sustainability performance of manufacturing
enterprises is 0.062 with a p-value significant at a 5%
level of significance, indicating that there is a
significant positive effect of novelty-centered
business model innovation on the sustainability
performance of the listed manufacturing enterprises
and H1 is verified.
Table 4: Regression Results of Efficiency-centered
Business Model Innovation and Sustainability Performance
of the listed Manufacturing enterprises.
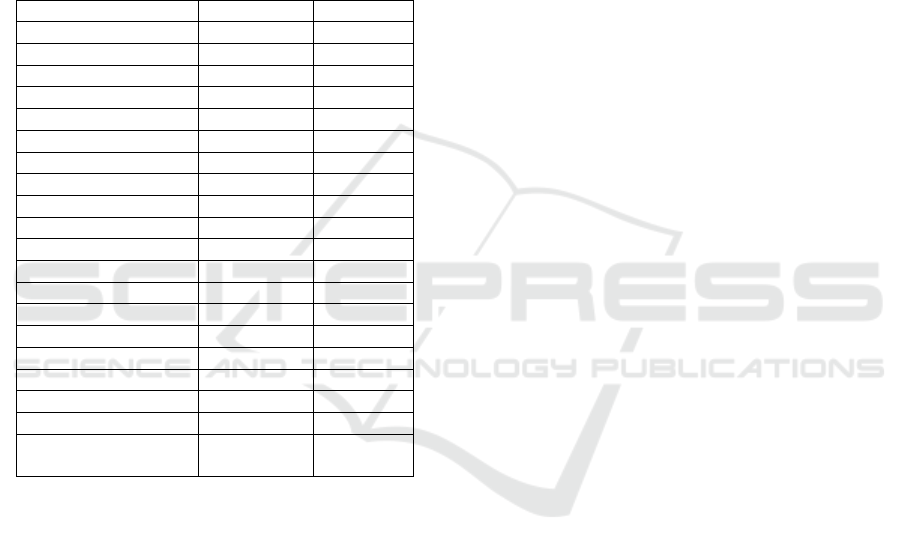
Variable Score
Efficienc
y
0.067***
(
2.64
)
Size 0.033
(1.53)
ListAge 0.045
(
1.16
)
Lev -0.102
(
-1.24
)
Growth 0.022*
(1.79)
Constant -0.417
(
-0.90
)
R-s
q
uare
d
0.284
F 17.95
Number of Company 91
Company FE YES
Year FE YES
Observations 620
*** p<0.01, ** p<0.05, * p<0.1
According to Table 4, the R-square of model (2)
is above 28%, and the F-value is 17.95, which is
significant at the 1% level of significance, indicating
that the model has a good fit and the ability to explain
the variables. From the regression results, the
regression coefficient between efficiency-centered
business model innovation and the sustainability
performance of manufacturing enterprises is 0.067,
with a p-value significant at a 1% level of
significance, indicating that there is a significant
positive effect of efficiency-centered business model
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
266
innovation on the sustainability performance of the
listed manufacturing enterprises. Thus, H2 can be
verified.
4.3 Robustness Test
For the purpose of verifying the robustness of the
findings above, the study draws on the research
approach of Chen Qiangyuan (2020), and the
variables are winsorized on the 1% quantile. The
conclusions are drawn in line with the previous paper,
which shows that the conclusions are reliable.
Table 5: Robustness Test.
Variable Score Score
Novelt
y
0.057**
(
2.05
)
Efficienc
y
0.066***
(2.66)
Size 0.025 0.027
(1.19) (1.34)
ListA
g
e 0.052 0.049
(
1.18
)
(
1.06
)
Lev -0.056 -0.085
(-0.71) (-1.06)
Growth 0.020 0.028
(
0.78
)
(
1.05
)
Constant -0.266 -0.307
(
-0.58
)
(
-0.70
)
R-square
d
0.286 0.288
F 18.47 17.61
Number of Company 91 91
Com
p
an
y
FE YES YES
Year FE YES YES
Observations
620 620
*** p<0.01, ** p<0.05, * p<0.1
5 CONCLUSIONS
5.1 Research Conclusion
The study classifies the types of business model
innovation into two forms and discusses the impact of
novelty-centered as well as efficiency-centered
business model innovation on the sustainability
performance of manufacturing enterprises,
respectively. Based on the 2010-2016 Shanghai and
Shenzhen A-share data, the findings of this paper
conclude that both novelty-centered and efficiency-
centered business model innovations significantly
and positively affect the sustainability performance of
manufacturing firms and the continuous innovation of
business models can significantly contribute to the
continuous improvement of the sustainability
performance of manufacturing firms. Manufacturing
enterprises should actively carry out both types of
business model innovation to expand markets, reduce
supply chain costs, create long-term competitive
advantages, empower the transformation and
development of enterprises, and promote their own
sustainable development.
5.2 Suggestions
For the government, it should pay great attention to
the importance of enterprise business model
innovation, strengthen relevant institutional
construction, write the goal of promoting the
development of business model innovation into the
policy platform, create a broad development space for
the optimization of enterprise transaction model and
business model with an inclusive and prudent
attitude, provide excellent business environment for
enterprises, and escort manufacturing enterprises to
achieve innovation and improve the sustainability of
development from a macro perspective.
For manufacturing enterprises in China, they need
to make reasonable use of the government's macro
policies while continuously exploring business
models that are suitable for their sustainable
development. Enterprises should eliminate the
either/or thinking and take into account the efficiency
and innovation of business models. They should
actively improve their trading methods, introduce
environmentally friendly products and green services,
integrate the concept of environmental sustainability
into innovation, make energy-saving and low-carbon
development an important goal of their business
operations, reduce material consumption and save
costs through creative improvements in their trading
models, and achieve coordinated development of
their economic, social and environmental
performance.
5.3 Limitation
Although this study uses a scientific approach to the
analysis, there may still be some methodological and
empirical limitations. The study has the following
shortcomings: First, the article uses content analysis
as one of the main data collection methods, and the
content analysis method itself has a certain subjective
nature. Secondly, the research sample size of this
article is relatively small and only the enterprises in
the list of top 500 listed companies in the
manufacturing industry are selected. The subsequent
research can expand the sample to improve the
Analysis of the Effect of Business Model Innovation on the Sustainability Performance of Manufacturing Enterprises Based on Fixed Effects
Model
267

general applicability of the conclusions. Finally, the
data collection may be biased to a certain extent due
to the differences in the disclosure level of social
responsibility reports of different enterprises.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledge the sponsorship from the
Ministry of Education of Humanities and Social
Science Project of China under Grant number
21YJC630104, and the Independent Innovation
Foundation of Wuhan University of Technology
Project under project number 226821005.
REFERENCES
Bu Yiran, Yao Chao. Analysis of the relationship between
business model and sustainable competitive advantage
[J]. Research on Finance and Economics, 2011(11):
126-130.
Chen Qiangyuan, Lin Sitong, Zhang Xing. China's
technology innovation incentive policy: incentivized
quantity or quality[J]. China Industrial Economics,
2020(04):79-96.
Chi Kaoxun, Shao Yueting. Business model innovation,
resource integration and performance of start-ups[J].
Foreign Economics and Management,2020,42(03):3-
16.
Christine Mallin, Giovanna Michelon & Davide Raggi, D.
Monitoring Intensity and Stakeholders’ Orientation:
How Does Governance Affect Social and
Environmental Disclosure? J Bus Ethics 114, 29–43
(2013).
Christoph Zott, Raphael Amit, (2007) Business Model
Design and the Performance of Entrepreneurial Firms.
Organization Science 18(2):181-199.
Elisabeth Albertini, 2014, “A Descriptive Analysis of
Environmental Disclosure: A Longitudinal Study of
French Companies”, Journal of Business Ethics, Vol.
121 (2), pp.233~254
Hu Baoliang. The relationship between business model
innovation, technological innovation and corporate
performance: An empirical study based on GEM-listed
companies [J]. Science and Technology Progress and
Countermeasures,2012,29(03):95-100.
Ilias Alexopoulos, Kostas Kounetas & Dimitris Tzelepis,
T., 2018, “Environmental and Financial Performance.
Is There a Win-win or a Win-loss Situation? Evidence
From the Greek Manufacturing, Journal of Cleaner
Production, Vol.197, pp.1275~1283.
Jia Xingping, Liu Yi. The external environment, internal
resources, and corporate social responsibility[J].
Nankai Management Review,2014,17(06):13-18+52.
Li Wei. Strategic orientation, business model innovation,
and business performance-an empirical analysis based
on data from manufacturing SMEs in China[J].
Business Research, 2017, (01):34-41.
Mao Lei, Wang Zongjun, Wang Lingling. Institutional
investors' shareholding preferences, screening
strategies and corporate social performance[J].
Management, 2012,25(03):21-33.
Mao Shiying. The value orientation of business model
innovation from the perspective of the green economy
[J]. Ecological Economy,2011(11):118-121.
Martin Geissdoerfer, Doroteya Vladimirova, Steven Evans.
Sustainable business model innovation: A review[J].
Journal of cleaner production,2018,198:401-416.
Pang Changwei, Li Yuan, Duan Guang. Integration
capability and firm performance: the mediating role of
business model innovation[J]. Management Science,
2015, 28(05):31-41.
Su Yi, Yu Yueqi, Li Dan. Research on the impact of
corporate innovation capacity on sustainable
development capacity--based on the moderating role of
government subsidies[J]. East China Economic
Management,2018,32(11):112-117.
Wang Lingling, Wang Zongjun, Mao Lei. A study on
corporate social responsibility and institutional
investors' shareholding preferences[J]. Enterprise
Economics, 2013,32(07):163-167.
Wang Xuedong, Kuang Haibo, Dong Dahai. Research on
the mechanism of corporate social responsibility
embedded in business model innovation[J]. Scientific
Research Management, 2019,40(05):47-56.
Wang Xuejun, Sun Bing. The relationship between efficient
business models, dual marketing capabilities, and value
creation - the moderating role based on relationship
embedding [J]. Modern Finance and Economics
(Journal of Tianjin University of Finance and
Economics),2017,37(06):89-100.
Wen Zhonglin, Ye Baojuan. Mediated effects analysis:
Methods and model development[J]. Advances in
Psychological Science,2014,22(05):731-745.
Wei Zelong, Zhang Linqian, Wei Zesheng, Yang Tong.
Business model design and firm performance: the
moderating role of strategic flexibility[J]. Management
Review, 2019,31(11):171-182.
Wu Chunyou, Zhu Qinghua, Geng, Yong. Green supply
chain management and sustainable development of
enterprises[J]. China Soft Science,2001(03):67-70.
Wu Jun, Zhang Jianqi, Liu Heng, Guo Zisheng. Novel
business model innovation and firm performance: the
moderating role of effectual and causal reasoning[J].
Science and Science and Technology Management,
2016, 37(04):59-69.
Wu Xiaobo, Zhao Ziyi. Antecedent issues of business
model innovation: a review of research and outlook[J].
Foreign Economics and Management, 2017,39(01):
114-127.
Xiao Hongjun, Yang Zhen. Sustainable business model
innovation: a review of research and outlook[J].
Foreign Economics and Management,2020,42(09):3-
18.
Xi Longsheng, Zhao Hui. Executive dual environmental
cognition, green innovation and corporate sustainability
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
268

performance [J]. Economic Management, 2022, 44(03):
139-158.
Xie Xuemei, Zhu Qiwei. How to break the problem of
"harmonious coexistence" in the green innovation
practice of enterprises? [J]. Management World, 2021,
37(01): 128-149+9.
Yang Yifan, Wang Wei, Ao Jingning, Wei Yunjie, Ji
Mengchen, Jiang Mao, Xu Dawei, Hu Yi, Qiao Han,
Wang Shouyang. Analysis of business models of
manufacturing enterprises[J]. Science and Technology
for Development,2015(02):167-176.
Yi Jiabin, Xie Dongmei, Gao, Jinwei. An empirical study
on the factors influencing business model innovation of
high-tech enterprises-Based on knowledge perspective
[J]. Scientific Research Management, 2015,36(02):50-
59.
Zhou Fangzhao, Pan Wanying, Fu Hui. ESG responsibility
performance of listed companies and institutional
investors' shareholding preference: empirical evidence
from Chinese A-share listed companies[J]. Scientific
Decision Making,2020(11):15-41.
Analysis of the Effect of Business Model Innovation on the Sustainability Performance of Manufacturing Enterprises Based on Fixed Effects
Model
269
