
Analysis on the Financial Performance of OFDI Based on Principal
Component Analysis: The Case of Sinomine Resource Group
Company
Qian Yang and Gang Fang
*
Business school, Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology, Beijing, China
Keywords: SINOMINE, Outward Foreign Direct Investment, Principal Component Analysis, Financial Performance.
Abstract: Sinomine Resource Group Co., Ltd (SINOMINE) is taken as the case object in order to better measure the
influence of OFDI of resource-based enterprises on corporate performance. With the help of SPSS software
and principal component analysis method, this paper tests the financial performance of its OFDI. The study
shows that the overall financial performance of the company is good, but its profitability needs to be improved.
In addition, this article summarises the characteristics of SINOMINE's overseas expansion in two phases by
looking at its OFDI activities since its listing. The first phase of the company's location selection mainly
focused on Asian and African countries, while the second phase of overseas expansion focused on the
European and American markets.
1 INTRODUCTION
At the beginning of the 21st century, Chinese
resource-based enterprises began to gradually move
towards the international market and actively
participate in the competition and resource
redistribution in the world resource market. SONG
(2013) points out that Chinese resource-based
enterprises' outward direct investment is mainly
resource-oriented, and Sinomine Resource Group
Co., Ltd (SINOMINE) is one of the important
enterprises in China's "going out" solid mineral
exploration technology service industry. The
company has established a dominant position in the
international market for integrated geological
services, and has strengthened its control over global
mineral resources through direct investments in
foreign mining companies, mainly through greenfield
investments and cross-border mergers and
acquisitions.
In this paper, to explore the financial performance
of SINOMINE's outward foreign direct investment
(OFDI), the principal component analysis in SPSS
(Statistical Product and Service Solutions) was used
to further reduce the number of financial indicators to
a smaller number of comprehensive evaluation
*
Corresponding author
indicators. HUANG (2010) points out that the idea of
dimensionality reduction can be used to transform
multidimensional parameter indicators into several
low-dimensional principal component indicators.
Principal component analysis provides a visual and
comprehensive picture of the performance of
SINOMINE as a result of its continued overseas
expansion.
2 INTRODUCTION OF
SINOMINE
Founded in 1999, SINOMINE's main businesses
include solid mineral exploration technology services
and mineral rights development, rare metals
development and utilization, and lithium new energy,
etc. In 2014, SINOMINE was listed on the Shenzhen
Stock Exchange, becoming the first A-share listed
company in China's geological exploration services.
Since its establishment, SINOMINE has been
actively responding to China's "the belt and road"
policy and vigorously exploring overseas markets.
The company has more than 20 subsidiaries at home
and abroad and owns a total of 95 mining rights
worldwide, mainly in Canada, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
276
Yang, Q. and Fang, G.
Analysis on the Financial Performance of OFDI Based on Principal Component Analysis: The Case of Sinomine Resource Group Company.
DOI: 10.5220/0012029300003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 276-281
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
With a global presence in more than 40 countries and
regions in Asia, Africa, Europe, America and Oceania,
SINOMINE has developed a good market reputation
and a bright future with its rich experience in the field
of overseas solid mineral exploration.
3 ANALYSIS OF THE CURRENT
SITUATION OF SINOMINE
OFDI
The overseas expansion of resource-based enterprises
is characterised by geographical selection. The
current reserves of major metals and non-metallic
minerals are mainly located in four countries and
regions, namely the United States, Canada, Australia
and South Africa, which has a great influence on the
layout of SINOMINE's overseas expansion. From
SINOMINE's overseas expansion steps since its
listing in 2014, this paper divides its overseas
expansion into two main phases, with 2014 to 2017
being the first phase and 2018 to date being the
second phase. The division is mainly based on the
first statistics of rare light metals business such as
lithium salts and caesium rubidium salts under the
main business of SINOMINE's annual report in 2018,
which accounted for 23.61% of the total operating
revenue, gradually equal to the share of businesses
such as solid mineral exploration (23.94%). further
overseas expansion in 2019 made the rare light metals
business account for 42.55% of the total operating
revenue The business will become a major revenue
generator.
3.1 First Phase of Expansion 2014-2017
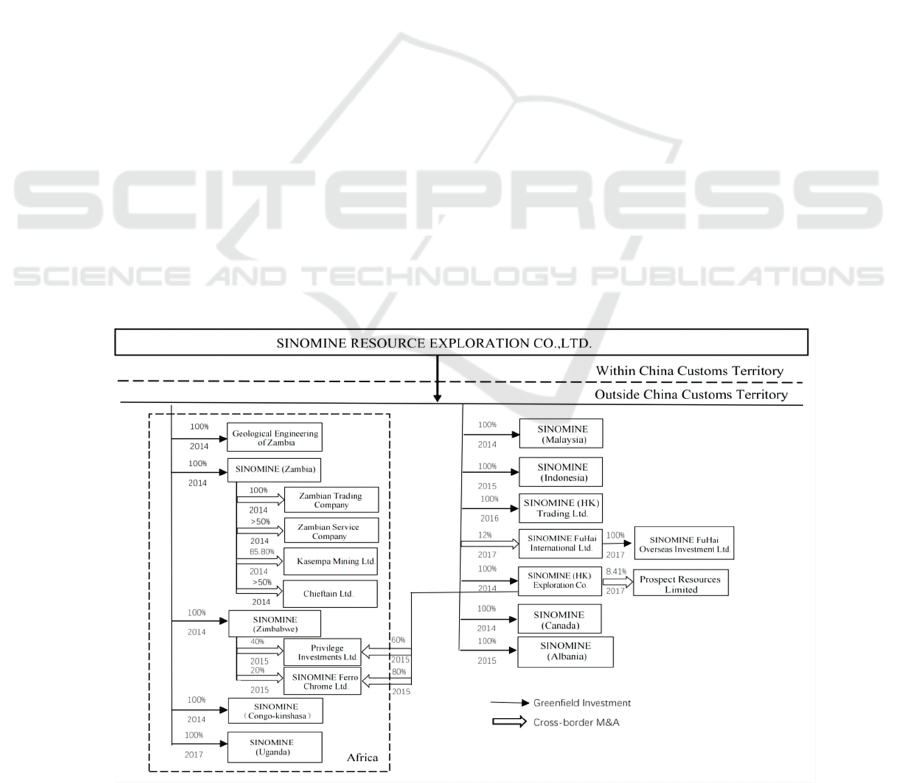
From 2014 to 2017, SINOMINE's choice of location
for overseas expansion was mainly focused on Asia
and Africa. The first phase of expansion was
concentrated in Africa, particularly in Zambia (as
shown in Figure 1).SINOMINE has been working
with Zambia for a long time, mainly with the
Zambian ministry of education, the army and
hospitals, and has undertaken some of the country's
major international projects while helping to repair
local schools and some infrastructure, contributing to
the development of the local economy.
The Zambian business has been the main source
of revenue generation for SINOMINE's overseas
operations for the last four years, accounting for an
average of 48.6% of total revenue over the four years.
However, as SINOMINE expanded into other African
countries such as Zimbabwe, Congo and Uganda, the
share of the Zambian business in the overall overseas
business trended downwards. Albania, which has rich
mineral resources in Europe and is an important
country along the "belt and road" route, has also
become an important step in SINOMINE's overseas
expansion.
The highest proportion of SINOMINE's major
operating revenue was from solid mining exploration
and technical services. In 2015, the company's
revenue
declined significantly, mainly due to the
Figure 1: 2014-2017 SINOMINE Overseas Subsidiaries and Holding Companies.
Analysis on the Financial Performance of OFDI Based on Principal Component Analysis: The Case of Sinomine Resource Group Company
277
continued downturn in the global mining market and
the devaluation of the Zambian currency, which is the
main source of overseas revenue generation, resulting
in a reduction in consolidated revenue due to
translation differences in foreign currency financial
statements. In 2016, SINOMINE established a
dedicated international trading company and the
proportion of international trade revenue has
increased year on year since then.
In 2017, supported by the accelerated global
economic recovery and the phased stabilisation of the
Chinese economy, prices of most global metal
products continued to shake out higher, especially for
bulk commodities such as copper, aluminium, zinc
and lead, which all rose by more than 20% in
aggregate during the year, and prices of minor metal
varieties related to new energy and materials also
surged, as the global mining market started a new
development cycle.
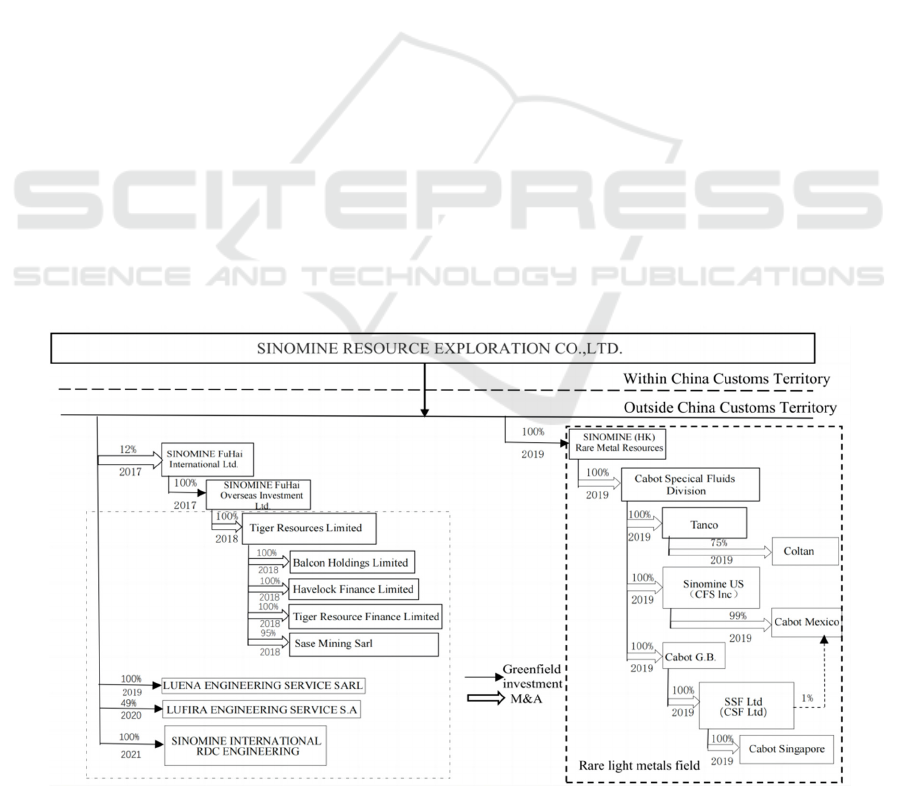
3.2 Second Phase of Expansion
2018-Present
With the accumulation of international experience,
SINOMINE has become more and more proficient in
expanding its business abroad and has gradually
started to enter some of the American countries.In
2017, SINOMINE acquired Dongpeng New
Materials Company in China, which marked the
gradual focus on rare and light metals, and in 2019,
SINOMINE established a wholly-owned subsidiary,
SINOMINE(Hong Kong, China). In the same year,
SINOMINE acquired Gabot Special Fluids Division,
and through its 100% holding in Gabot Special Fluids
Division, it ventured into the United States, the
United Kingdom, Mexico, Canada and other
countries. It is worth noting that the 2017 annual
report did not yet have the revenue amount of the
operating details of rare light metals, the following
year the enterprise began to specialise in the statistics
of the project accounted for as much as 23.61%,
second only to the share of solid mineral exploration
business. In 2020, the operating revenue of rare light
metals business has reached 54.85%, the share of
solid mineral exploration business began to decrease.
The acquisition of Gabot's Specialty Fluids
Division in 2019 enabled SINOMINE to acquire the
mineral rights to Tanco in Canada, making it the
world's largest mining company to mine cesium
garnets. The world's available cesium garnet resources
are currently concentrated in three main mining areas,
including the Bikita mine in Zimbabwe, the Tanco
mine in Canada and the Sinclair mine in Australia. The
Bikita mine supplies raw materials to SINOMINE's
subsidiary, Dongpeng company, and to Arbor in the
USA. This acquisition not only gives SINOMINE 126
international patents for the deep processing and
application of cesium resources, but also gives it
control over 75% of the world's cesium resources.
This breaks the monopoly of foreign companies in the
energy industry and establishes SINOMINE's global
pricing power in the cesium resource chain. This has
greatly enhanced SINOMINE's industry position in
the world energy community.
Figure 2 2018-2021 SINOMINE Overseas Subsidiaries and Holding Companies
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
278
4 ANALYSIS OF SINOMINE'S
FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE
Resource-based companies cannot show very
significant financial performance as quickly as
consumer-based companies after an acquisition. In
order to study the long-term corporate development
of SINOMINE, this paper uses principal component
analysis to analyse the financial performance of
SINOMINE from 2014 to 2021.
4.1 Data Sources and Description of
Indicators
This article obtains data from sina finance and selects
SINOMINE quarterly financial indicators from 2014
to 2021 Due to some missing data in 2014, some
quarterly indicators with incomplete data were
excluded, and 28 sets of data samples were finally
retained. Based on WANG et al. (2014), this paper
focuses on three aspects of profitability, solvency and
operating capacity, and selects nine indicators to
analyse the financial performance of SINOMINE
after several outward direct investments in recent
years. In this paper, the indexes are appropriately
revised according to the positive treatment of the
moderate indexes of corporate financial indicators by
Xu et al. (2000). The index of gearing ratio is mainly
adjusted based on Equation X
=1/|X
|(i=1, 2, …,
n).
Table 1: Main financial indicators.
Profitability
Return on Equity (X
)
Rate of Return on Total Assets (X
)
Return on Assets (X
)
Solvency
Current Ratio (X
)
Aci
d
-test Ratio (X
)
Cash Ratio (X
)
Asset-liability Ratio (X
)
Operating
capacity
Total Assets Turnove
r
(X
)
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
(X
)
4.2 Empirical Analysis
The 336 financial data were measured by SPSS.26
software. The test results from the KMO and Bartlett's
test showed that the value of KMO was 0.680. YANG
et al. (2020) concluded that a KMO value greater than
0.6 met the requirements for factor analysis. The
Bartlett sphericity test significance was 0.000, which
was less than the significance level of 0.05, so the data
could be continued for factor analysis.
In this paper, the three common factors with
eigenvalues greater than one were extracted using
principal component analysis, with variance
contribution rates of 40.423%, 35.451% and 15.005%
respectively, and the cumulative total variance
contribution rate was 90.879%. The three common
factors selected in this paper can cover the
information contained in the nine indicators and
basically meet the calculation criteria.
Table 2: Total Variance Explained.
Comp
onen
t
Initial Eigenvalues Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings
Total % of Variance Cumulative % Total % of Variance Cumulative % Total % of Variance Cumulative %
1 3.827 42.524 42.524 3.827 42.524 42.524 3.638 40.423 40.423
2 3.191 35.453 77.977 3.191 35.453 77.977 3.191 35.451 75.874
3 1.161 12.902 90.879 1.161 12.902 90.879 1.350 15.005 90.879
4 0.456 5.065 95.944
-- -- -- -- -- --
5 0.199 2.209 98.152
-- -- -- -- -- --
6 0.080 0.890 99.043
-- -- -- -- -- --
7 0.066 0.739 99.781
-- -- -- -- -- --
8 0.014 0.150 99.932
-- -- -- -- -- --
9 0.006 0.068 100.000
-- -- -- -- -- --
As can be seen from Table 3, the two indicators
with the largest loadings in common factor F1 are
total assets margin and return on net assets, which
mainly reflect the profitability of the enterprise and
are therefore named profitability factor. The two
indicators that contribute the most to the loadings of
common factor F2 are the quick ratio, the current ratio
and the cash ratio, which mainly measure the
solvency of the enterprise and are therefore named the
debt service factor. The largest contributor to
common factor F3 is the accounts receivable turnover
ratio, and is therefore named the operating capacity
factor.
Analysis on the Financial Performance of OFDI Based on Principal Component Analysis: The Case of Sinomine Resource Group Company
279

Table 3: Component Score Coefficient Matrix.
Name F1 F2 F3
𝑋
0.250 0.018 0.057
𝑋
0.248 0.007 0.061
𝑋
0.282 -0.022 -0.291
𝑋
-0.008 0.307 -0.033
𝑋
0.014 0.306 -0.091
𝑋
-0.074 0.284 0.319
𝑋
0.130 0.186 -0.559
𝑋
0.276 -0.036 -0.089
𝑋
0.039 0.092 0.543
The formula for calculating the principal
component factor is 𝐹
=𝑏
𝑋
+𝑏
𝑋
+…+𝑏
𝑋
.The
formula for scoring the overall financial performance
evaluation indicators is 𝐹 = 𝑊
× 𝐹
+ 𝑊
× 𝐹
+
𝑊
× 𝐹
.Where is 𝑊
, 𝑊
, 𝑊
determines the
weighting of each composite indicator based on the
cumulative variance contribution.
In terms of profitability indicator F1, there was
little overall volatility (as shown in Table
5).SINOMINE's larger profitability indicator in 2015
was
mainly due to the continued downturn in the
Table 4: Principal component factor scores and composite scores.
Date of report F1 F2 F3 F
2014-12-31 -0.0263 0.4479 0.4170 0.2319
2015-03-31 -0.1099 0.4801 0.4689 0.2158
2015-06-30 -0.0161 0.3206 0.2549 0.1600
2015-09-30 -0.0914 0.5382 0.5170 0.2547
2015-12-31 0.0394 0.2112 0.1596 0.1263
2016-03-31 -0.0467 0.2150 0.1919 0.0948
2016-06-30 0.0240 0.1441 0.0806 0.0802
2016-09-30 0.0017 0.1539 0.1250 0.0814
2016-12-31 0.0487 0.1681 0.1126 0.1059
2017-03-31 -0.0251 0.1370 0.1092 0.0603
2017-06-30 0.0350 0.0966 0.0381 0.0595
2017-09-30 0.0122 0.0979 0.0713 0.0554
2017-12-31 0.0642 0.1232 0.0583 0.0863
2018-03-31 -0.0206 0.1161 0.0913 0.0512
2018-06-30 0.0119 0.1573 0.1211 0.0866
2018-09-30 0.0081 0.0787 0.0568 0.0437
2018-12-31 0.0090 0.1957 0.1741 0.1091
2019-03-31 -0.0296 0.1755 0.1623 0.0821
2019-06-30 0.0194 0.1041 0.0703 0.0608
2019-09-30 0.0041 0.1299 0.1142 0.0714
2019-12-31 0.0124 0.1740 0.1501 0.0982
2020-03-31 -0.0337 0.1824 0.1682 0.0839
2020-06-30 -0.1067 0.5549 0.5702 0.2631
2020-09-30 -0.1205 0.5878 0.6165 0.2775
2020-12-31 -0.0871 0.5606 0.5776 0.2753
2021-03-31 -0.1210 0.5656 0.5853 0.2634
2021-06-30 -0.1310 0.7309 0.7525 0.3511
2021-09-30 -0.0482 0.4243 0.4395 0.2166
global mining market and the contraction of the
geological exploration business. During this period,
the main overseas revenue came from the Zambian
region, where the devaluation of the Zambian
currency led to a reduction in consolidated earnings
due to translation differences in foreign currency
financial statements. 2019 saw the acquisition of
Canadian cesium metal mineral rights, helping the
company to gain control of the global cesium
resource chain. In 2020, however, SINOMINE's
business is impacted by the global outbreak of the
New Crown epidemic and profitability does not
improve effectively and tends to decline. 2021, when
the epidemic is effectively controlled, SINOMINE's
profitability increases. Foreign direct investment by
resource-based companies does not tend to improve
performance significantly in a short period of time, as
mineral exploration takes a long time, so the overall
profitability effect is not good in the short term.
In terms of solvency indicator F2, SINOMINE's
solvency was low for a long time due to the high
OFDI activity after the IPO. The company's revenue
from the rare metals business increased significantly
in 2019, which led to higher solvency, and the
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
280

company's debt maturity in 2021, which led to lower
solvency, so there were large fluctuations. It is worth
mentioning that frequent overseas expansions have
led to a rise in the company's operating income and a
strengthening of debt servicing capacity. In terms of
operating capacity indicator F3, the successive
overseas expansions since SINOMINE's IPO have
increased the pressure on the company's operations.
However, with the accumulation of international
experience, SINOMINE's overall operating position
is good.
In terms of the composite indicator F, there was
an overall downward trend in the indicator from 2014
to 2016. From 2017 to 2019, the overall score is
stable, with SINOMINE consolidating its solid
exploration while starting to strategically target
lithium and rare metals in the context of an
accelerating global economic recovery. In 2020,
SINOMINE's overall financial performance will be
significantly higher as it takes control of most of the
world's metallic cesium claims. In 2021, the
company's significant decline is mainly due to the
maturity of its debt, which will need to be repaid.
Overall, SINOMINE's OFDI in recent years has
improved the company's long-term financial
performance.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper examines the status of SINOMINE's OFDI
since its IPO. The analysis shows that SINOMINE's
early OFDI was mainly in mineral-rich regions in
Africa, while its later OFDI was mainly in rare
metals, with a shift from Africa to Canada, Australia
and the United States. In terms of long-term financial
performance, SINOMINE's profitability has not been
satisfactory since its IPO, but the numerous OFDIs
have increased the company's international
experience and improved its operating and debt
servicing capacity. The global impact of the new
crown epidemic in 2020 has caused a significant
decline in the overall performance of resource-based
companies. According to the study, overall
profitability will show an upward trend in 2021 and
financial performance is expected to improve in the
future.
SINOMINE's overseas subsidiaries and holding
companies are located in many countries and regions
such as Africa, Southeast Asia, Central Asia and
Southern Europe, and are exposed to risks such as
exchange rate changes, political unrest and
institutional issues that may affect the revenue of
overseas operations. Therefore, it is important to
improve the risk warning mechanism to prepare for
possible risks in advance and to reduce the series of
negative impacts caused by risks. Secondly, from the
perspective of financial consolidation, SINOMINE's
foreign investment activities are relatively frequent.
In particular, there are several acquisitions taking
place at the same time in the same year, making it
more difficult for the company to integrate its
finances. The company can introduce a digital
management system to improve its ability to manage
and analyse its assets through the digital
transformation of its finances. From the perspective
of resource integration, enterprises should optimise
the allocation of resources, including natural
resources, human resources and resources with
unique advantages, etc. SINOMINE can strengthen
the integration efforts of the upstream and
downstream industrial chains and can integrate the
logistics system to improve operational efficiency.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Support by: “Beijing Higher Education
Undergraduate Teaching Reform Innovation Project”
project (Project No.: 202110012004); “The first batch
of new liberal arts research and reform practice
projects of the Ministry of Education” project (Project
No.: 2021140009); Beijing Education Science "14th
Five-Year Plan" Project for 2021” project (Project
No.: 3067-0001).
REFERENCES
HUANG Y. L.(2010).Statistical Analysis of Data - SPSS
Principles and Applications[M].Higher Education
Press, 26-27.
SONG Y. C.(2013).Examining the effectiveness of China's
OFDI purpose: A resource-seeking OFDI as a
perspective [J].Inquiry into Economic Issues, 8, 123-
129.
WANG D., CHEN R.(2014).Evaluation of financial
performance of mineral resource-based listed
companies: Based on a sustainable development
perspective [J].Friends of Accounting, 26, 25-30.
XU G. X., SHAN X. Q., HU H. H.(2000). Comprehensive
evaluation of business performance of listed companies
and its empirical study [J].Statistics, 09, 44-51.
YANG L. H., YUAN H. C.(2021).A study on the impact of
institutional distance on firms' overseas M&A
performance: Based on the moderating effect of
overseas M&A experience, bilateral investment
cooperation relationship[J].Communication of Finance
and Accounting, 8,67-70.
Analysis on the Financial Performance of OFDI Based on Principal Component Analysis: The Case of Sinomine Resource Group Company
281
