
Dual Environmental Regulation, Technological Innovation and Green
Total Factor Productivity of Manufacturing Industry:
Based on the Development Background of Information Technology
Kun Xie and Xiaoling Xu
*
School of Economics and Management, Shanghai Institute of Technology, Shanghai, China
Keywords: Dual Environmental Regulation, Technological Innovation, Manufacturing Green Total Factor Productivity,
Threshold Regression Model, Information Technology.
Abstract: In the context of the development of information technology, the impact of technological innovation on the
green transformation of manufacturing industry will be affected by the intensity of environmental regulation.
Therefore, based on the perspective of dual environmental regulation, the path of technological innovation
affecting green transformation of manufacturing industry is discussed. The empirical results show that
technological innovation has a significant promoting effect on the improvement of manufacturing total factor
productivity, and with the improvement of the formal environmental regulation level, the promoting effect of
technological innovation on improving manufacturing green total factor productivity is gradually weakened;
while in the informal environment When the level of regulation is between the second threshold and the third
threshold, technological innovation has the greatest effect on promoting green total factor productivity of
manufacturing; when the level of dual environmental regulation exceeds the threshold, the impact of
technological innovation on the improvement of green total factor productivity in manufacturing will also
reduce.
1 INTRODUCTION
In today's society, the development of manufacturing
industry is inseparable from the support of
information technology. The continuous innovation
and development of information technology also
promote the high-quality development of
manufacturing industry. Theoretical and practical
experience shows that technological innovation is not
only the source of power to transform the mode of
economic development, but also the main driving
force for the green transformation of the
manufacturing industry (Jaffe and Karen, 1997).
However, in fact, technological innovation is affected
by many factors in the process of promoting the
development of the manufacturing industry, among
which the most significant is the environmental
regulation factor. A major feature of the
transformation of the manufacturing industry is the
improvement of total factor productivity, and
technological innovation is mainly achieved through
technological progress and the improvement of
market competitiveness (Abramovitz, 1993). Under
the background of specialized division of labor, the
technological progress brought about by
technological innovation is the driving force for the
transformation of the manufacturing industry. The
realization of technological progress by increasing
R&D investment and independent research and
development can ensure that the output remains
unchanged, while reducing the production costs of
enterprises (Gallego et al. 2015). Since the 1990s,
with the introduction of the environmental Kuznets
curve, the research on environmental regulation has
gradually increased ( Moutinho et al. 2020).
Environmental regulation consists not only of formal
environmental regulation from the government, but
also informal environmental regulation formed by the
public (Tian and Feng, 2020) Due to the different
operating mechanisms of the two types of
environmental regulations, the impact mechanisms
on technological innovation and the green
transformation of manufacturing are also different.
According to the theory of "Porter Hypothesis"
(Porter and Linde, 1995) the impact of formal
environmental regulation mainly changes through the
288
Xie, K. and Xu, X.
Dual Environmental Regulation, Technological Innovation and Green Total Factor Productivity of Manufacturing Industry: Based on the Development Background of Information Technology.
DOI: 10.5220/0012029700003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 288-294
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

game between the "compliance cost" effect and the
"innovation compensation" effect (Peuckert, 2014).
Under the appropriate formal environmental
regulation, in order to legally avoid the cost of
pollutant discharge, and to obtain government
environmental protection subsidy funds, enterprises
will increase technological innovation to improve the
production process (Porter and Linde, 1995).
However, when the intensity of formal environmental
regulation is unreasonable, enterprises often adopt
negative measures such as “tail-end governance” to
deal with formal environmental regulation, which
will lead to a reduction in enterprise output,
productivity and innovation motivation (Gray and
Ronald, 2003). Under the reasonable intensity of
informal environmental regulation, the government,
the public and enterprises form an organic whole, and
the green product consumption market is further
expanded. In order to maintain competitiveness in the
green market, enterprises must increase technological
innovation. Therefore, in the context of the rapid
development of information technology, the
relationship between technological innovation and
environmental regulation is more complex, which
leads to the path of technological innovation in
promoting green change in manufacturing industry
will change with the level of environmental
regulation.
2 MODEL CONSTRUCTION AND
INDICATOR SELECTION
Based on the above analysis, to empirically test
whether there is a threshold effect of environmental
regulation when technological innovation promotes
the green transformation of the manufacturing
industry, the following panel threshold regression
model is established for research:
01 1 2
123 2
()
()()
it it it
it
mitit
Green lnT I ER lnT
IER lnTIER
Controls V
αα
γ
α
γγα γ
αμε
=+ × ≤ +
×<≤+ × >
++++
01 1
21 2
32
()
()
()
it it
it
it
mitit
Green lnT I INER
lnT I IN E R
lnT I IN E R
Controls V
ββ γ
βγ γ
βγ
βμ
ε
=+ × ≤ +
×< ≤
+× >
++++
01 1
21 2
32
()
()
()
it it
it
it
mitit
Green lnT I CossER
lnT I CossER
lnT I CossER
Controls V
χχ γ
χγ γ
χγ
χμ
ε
=+ × ≤
+×< ≤
+× >
++++
Among them, Green
it
is the green total factor
productivity of manufacturing, t represents the year, i
represents the province, β0 represents the intercept
term, Controls represents all control variables, Vi
represents the individual effect, and ɛit represents the
random disturbance term. γi represents the i threshold
values (i=1, 2, 3), I(·) is the indicator function, and µi
represents the time fixed effect. The threshold
variables of the above models are formal
environmental regulation (ER) and informal
environmental regulation (INER) and dual
environmental regulation (CossER) expressed as
(ER×INER).
Explained variable: manufacturing green total
factor productivity (Green). Its calculation method
relies on the EBM-GML model. The measurement of
total factor productivity will inevitably involve the
input and output in the production process, and one of
the characteristics of green total factor productivity is
that the output indicators take into account the
unexpected output.
Capital input is represented by the total social
fixed asset investment in the manufacturing industry
in each province; labor input is measured by the
average number of workers employed in the
manufacturing industry in each province; since there
is no statistical data on direct manufacturing energy
input in each province, this paper draws on Zhang and
Qiao (2021)
The method of estimating the final
energy consumption of the manufacturing industry in
each province is used to characterize the energy input
index.
The expected output is measured by the operating
income of the manufacturing industry, and the
undesired output mainly refers to the output of
pollutants in the production process, which is
generally represented by the "three wastes"
emissions. Characterization of carbon dioxide
emissions.
Since the direct result measured by the EBM-
GML model is the growth rate of green total factor,
the green total factor productivity of each year is
calculated based on the multiplication method of Lei
et al. (2020).
Core explanatory variable: technological
innovation (T). In the existing research on measuring
technological innovation indicators, it is mainly
measured from the perspective of input and output.
This paper uses the internal expenditure of
manufacturing R&D funds in each province to
measure, in order to avoid the biased results caused
by data heteroscedasticity, logarithmic processing.
Core explanatory variable: dual environmental
regulation (CossER). Based on the research purpose
of this paper, the characterization variables of
environmental regulation are selected from both
Dual Environmental Regulation, Technological Innovation and Green Total Factor Productivity of Manufacturing Industry: Based on the
Development Background of Information Technology
289
formal and informal aspects. Formal Environmental
Regulation (ER). Calculated as follows:
*
it
it
it
ER
ER
R
=
Among them, ER
it
*
is the ratio of industrial
pollution control investment to gross industrial output
value, and R
it
is the ratio of gross industrial output
value to regional GDP. The larger the ER
it
value, the
greater the intensity of formal environmental
regulation in the region.
Informal Environmental Regulation (INER).
Referring to the research of Wheeler and Pargal
(1996), the indicators of income level, education
level, and population density were selected, and the
entropy weight method was used to combine the three
indicators into one indicator to represent informal
environmental regulation variables.
Controls: Referring to existing research, the
regional economic development level (PGDP),
government intervention (GOV), human capital
(HUM) and transportation infrastructure level
(ROAD) were used as control variables in this study.
The specific meaning of each control variable
indicator: the per capita GNP of each province is used
to reflect the regional economic development level,
and the logarithm is used to process it; the ratio of
government fiscal expenditure to regional GDP is
used to measure government intervention; the
average education years of each province is used to
express Human capital; the ratio of the mileage of
railways and highways in each province to the
provincial area is used to represent the level of
transportation infrastructure.
Most of the sample data mentioned above can be
obtained from the 2012-2021 China Industrial
Statistical Yearbook, the China Science and
Technology Statistical Yearbook, the China Statistical
Yearbook, the 2012-2020 China Environmental
Statistical Yearbook, and China 30 Statistical
yearbook query for each province (because of the
limited availability of relevant data in Tibet and Hong
Kong and Macao), and use interpolation method to
supplement individual missing values in the data. The
data of the price variables involved are uniformly
based on 2011 Flatten. Table 1 shows the descriptive
statistics of the main variables.
Table 1: Descriptive statistics.
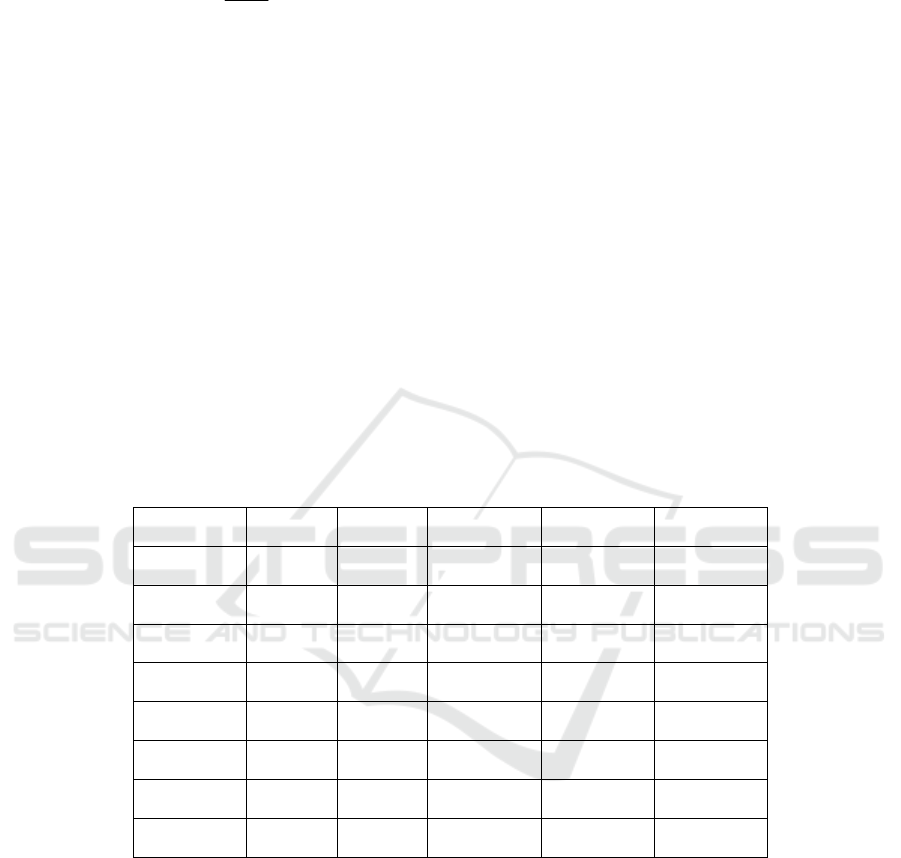
Variable N Average SD Min Max
Green 300 1.316 0.263 0.831 2.358
ER 300 1.226 1.437 0.041 8.163
INER 300 0.17 5 0.171 0.038 0.943
lnT 300 14.087 1.460 10.619 16.96
GOV 300 0.250 0.103 0.110 0.643
lnPGDP 300 10.841 0.436 9.705 12.013
HUM 300 0.360 0.254 0.135 1.716
ROAD 300 11.711 0.840 9.441 12.898
Table 2 reports the test results of repeated sampling
using the Bootstrap method for 1000 times. It can be
seen that when ER is used as the threshold variable,
the F values of the single threshold and the double
threshold have passed the 1% significance test,
indicating that with the increase of ER intensity ,
there is a double threshold effect with threshold
values of 0.8900 and 2.2261 between technological
innovation and manufacturing green transformation;
When INER is used as the threshold variable, the F
values of single threshold and double threshold have
passed the 5% significance test, indicating that with
the increase of INER, there is a double threshold
value of 0.0693 and 0.5255 between technological
innovation and manufacturing green transformation.
threshold effect; When CossER is used as the
threshold variable, only the F value of a single
threshold passes the 1% significance test, indicating
that as the intensity of CossER increases, there is a
single threshold effect with a threshold value of
0.0986 between technological innovation and
manufacturing green transformation.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
290
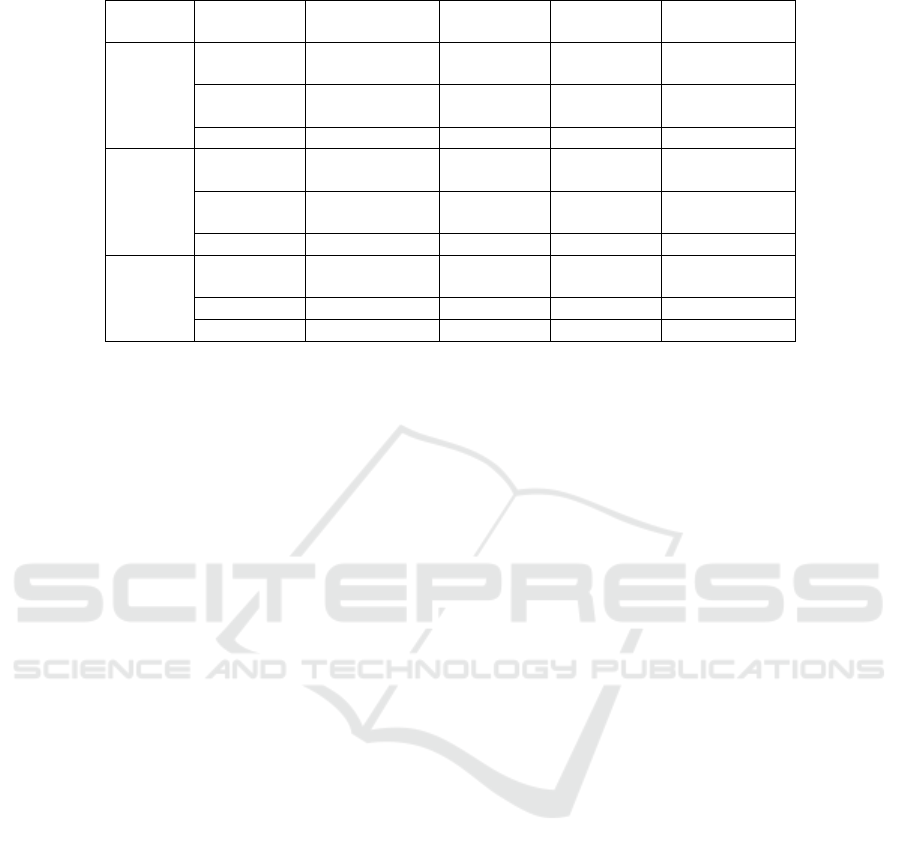
Table 2: Threshold effect test.
Variable Thresh-old
numbe
r
Threshold F value P value Confidence
interval
ER single 0.8900 30.71
***
0.004 [0.8345,
0.9268]
double 2.2261 22.64
**
0.013 [2.1774,
2.2486]
tri
p
le 0.2712 11.58 0.683
lnER
single 0.0693 33.54
**
0.025 [0.0686,
0.0699]
double 0.5255 32.79
**
0.012 [0.5225,
0.5308]
triple 0.5410 15.93 0.355
Coss
-ER
single 0.0986 54.12
***
0.000 [0.0975
,0.0988]
double 0.2668 9.60 0.189
triple 0.0337 7.06 0.651
Note: 1) The P value and confidence interval are the results obtained by the Bootstrap method repeated sampling 1000 times;
2) ***, *** and * indicate that the regression coefficients are significant at the 1%, 5% and 10% levels, respectively.
3 OUTCOME OF PRACTICE
From the threshold regression results, it can be seen
that there are significant differences in technological
innovation on the green transformation of
manufacturing under different environmental
regulation intensities.
When ER is in the low-intensity range, the
regression coefficient of technological innovation to
the green transformation of the manufacturing
industry is 0.174; when ER is in the medium-intensity
range, the regression coefficient of technological
innovation to the green transformation of the
manufacturing industry is 0.164; when ER is in the
high-intensity range, the regression coefficient of
technological innovation on the green transformation
of manufacturing is 0.154. That is to say, as the
intensity of formal environmental regulation
continues to exceed the threshold, technological
innovation maintains a positive role in promoting the
green transformation of manufacturing, but this role
is also weakening. The reason may be that the
transformation and upgrading of my country's
manufacturing industry is still in the "pain period",
and the "following cost" effect produced by formal
environmental regulation still constrains the
development of manufacturing enterprises, and the
regulatory costs generated may lead to "negative
behavior" of enterprises. , that is, reducing pollutant
emissions by reducing production, thereby reducing
the profit margin of enterprises and weakening the
innovation power of enterprises, so the role of
technological innovation in promoting the
transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing
industry is further weakened.
When INER is in the low-intensity range, the
regression coefficient of technological innovation to
the green transformation of manufacturing is 0.217;
when INER is between 0.0693 and 0.5255, the
regression coefficient of technological innovation to
the green transformation of the manufacturing
industry is 0.236; When INER is greater than 0.5255,
the regression coefficient of technological innovation
on the green transformation of manufacturing is
0.200. This shows that with the increasing intensity of
informal environmental regulation, the positive effect
of technological innovation on the green
transformation of manufacturing industry shows a
trend of first increasing and then decreasing. The
reason may be that under informal environmental
regulation, the green consumer market has a good
development prospect. In order to meet the needs of
the green consumer market, enterprises will increase
green technology innovation and green product
development, but when informal environmental
regulation crosses the second threshold At the same
time, in order to deal with excessive public opinion
pressure, enterprises will occupy too much of their
own resources, which will reduce the investment in
technological innovation, and the role of
technological innovation in promoting the green
transformation of manufacturing industry will
decrease.
When CossER is in the low-intensity range, the
regression coefficient of technological innovation to
the green transformation of the manufacturing
industry is 0.218; when CossER intensity is greater
than 0.0986, the regression coefficient of
Dual Environmental Regulation, Technological Innovation and Green Total Factor Productivity of Manufacturing Industry: Based on the
Development Background of Information Technology
291
technological innovation to the green transformation
of the manufacturing industry is 0.206. This shows
that the intensity of dual environmental regulation
needs to be maintained within an appropriate
intensity, so that the role of technological innovation
in promoting the green transformation of
manufacturing can be at a high level. Manufacturing
enterprises are facing more and more stringent
government system constraints and public opinion
pressure. The focus of enterprises' resource allocation
will gradually shift, and the core competitiveness of
enterprises will be reduced, thus weakening the role
of technological innovation in promoting the green
transformation of manufacturing.
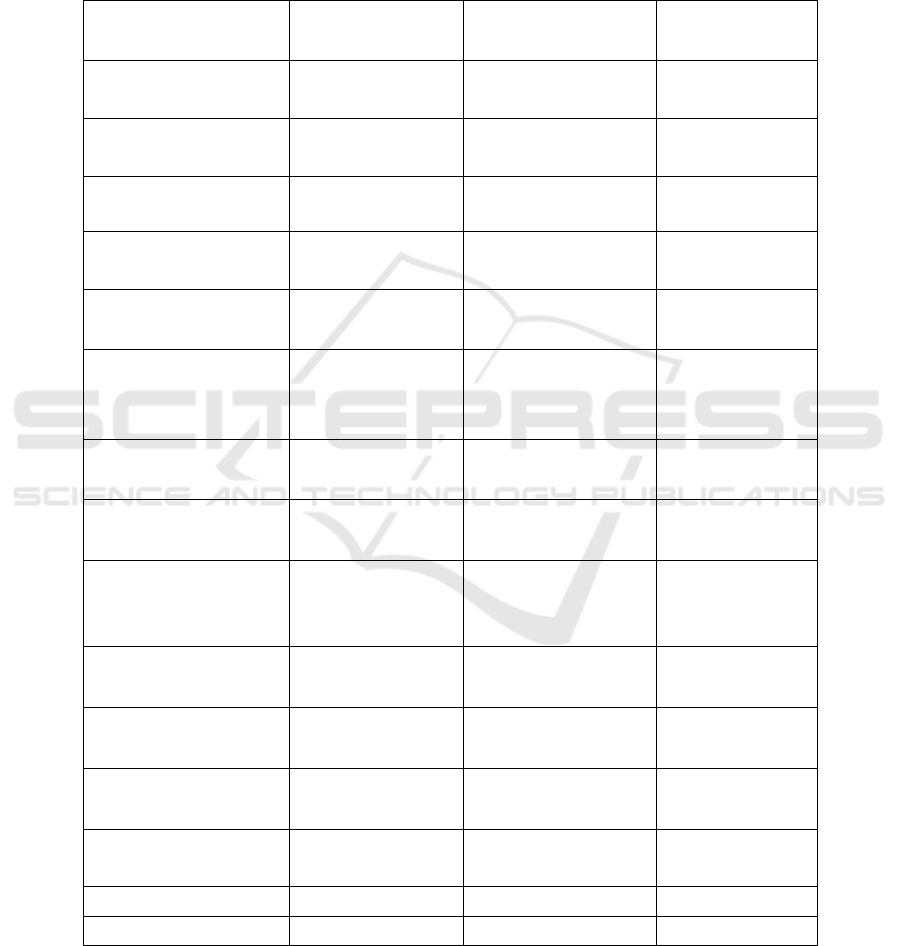
Table 3: Threshold model regression results.
Var iab le ER INER CossER
GOV 1.686
***
(4.32)
1.940
***
(5.13)
1.502
***
(3.82)
lnPGDP 0.575
***
(5.97)
0.352
***
(3.54)
0.521
***
(5.39)
HUM 2.476
***
(3.36)
3.356
***
(4.76)
2.389
***
(3.23)
ROAD -0.012
(-0.07)
0.288
(1.78)
0.098
(0.60)
lnT(ER≤0.8900)
0.174
***
(3.55)
lnT(0.8900<ER≤
2.2261)
0.164
***
(3.35)
lnT(ER>2.2261)
0.154
***
(3.11)
lnT(INER≤0.0693)
0.217
***
(4.46)
lnT(0.0693<INER≤
0.5255)
0.236
***
(4.86)
lnT(INER>0.5255)
0.200
***
(4.18)
lnT(CossER≤0.0986)
0.218
***
(4.47)
lnT(CossER>0.0986)
0.206
***
(4.22)
Constant -8.482
***
(-5.48)
-10.842
***
(-7.31)
-9.697
***
(-11.25)
N 300 300 300
F 74.76
***
79.43
***
86.93
***
In order to verify the robustness of the above
empirical results, this paper adopts the proxy variable
of replacing technological innovation, which is
different from the original index. Therefore, based on
the perspective of innovation output, the number of
manufacturing patents is selected as the proxy
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
292
variable of technological innovation. Repeat the
above steps to obtain the estimation results in Table 4
and Table 5. It can be seen from the estimation results
in the observation table that they are basically
consistent with the previous ones, so the research
conclusions drawn are considered to be robust.
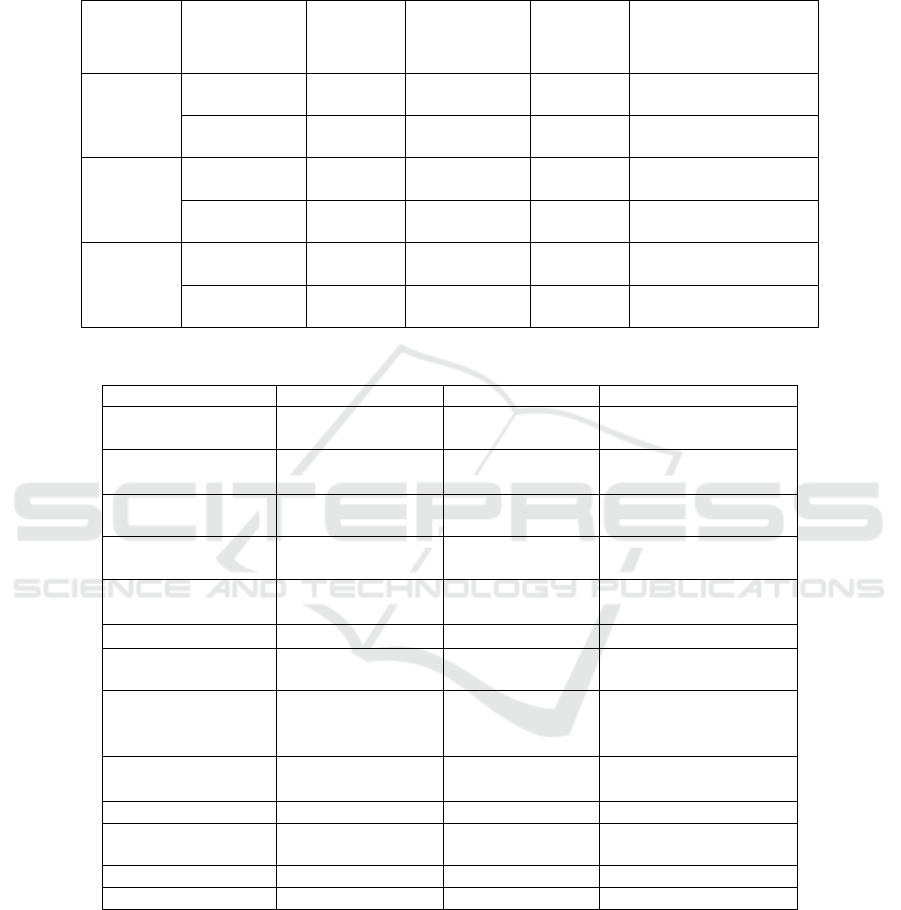
Table 4: Threshold effect test (robustness check).
Variab-le Threshold
Thres-
hold
F P
Confide
-nce
interval
ER
single 0.5315 36.44
***
0.000
[0.7888
,0.9268]
double 2.2261 23.86
**
0.004
[2.1774
,2.2486]
lnER
single 0.0693 34.35
**
0.011
[0.0686
,0.0699]
double 0.5396 32.79
*
0.094
[0.5307
,0.5410]
Coss
-ER
single 0.0986 51.80
***
0.000
[0.0975
,0.0988]
double 0.2668 11.55
*
0.080
[0.2386
,0.2681]
Table 5: Threshold model regression results (robustness check).
Var iab le ER INER CossER
lnT(ER≤
0.5315)
0.103
***
(2.78)
lnT(0.5315<
ER≤2.2261
)
0.092
***
(2.48)
lnT(ER>2.2261)
0.069
*
(
1.87
)
lnT(INER≤
0.0693)
0.046 (1.22)
lnT(0.0693<
INER≤0.5396
)
0.080
***
(2.13)
lnT(INER>0.5396)
0.031 (0.81)
lnT(CossER≤0.0986
)
0.125
***
(
3.34
)
lnT(0.0986<
CossER≤
0.2668
)
0.106
***
(2.85)
lnT(CossER
>0.2668)
0.095
**
(2.55)
Controls Control Control Control
Constant term -7.107
***
(-3.60)
-9.381
***
(
-4.78
)
-6.433
***
(
-3.25
)
N
300 300 300
F
73.61
***
72.41
***
74.28
***
4 CONCLUSION AND
SUGGESTION
This study analyzes the impact of technological
innovation on green total factor productivity in
manufacturing from the perspective of environmental
regulation. According to the analysis of the above
results: The role of technological innovation in
promoting green transformation of manufacturing
industry will weaken as the intensity of formal
environmental regulation increases; As the intensity
of informal environmental regulation increases, the
impact of technological innovation on the green
transformation of the manufacturing industry has a
Dual Environmental Regulation, Technological Innovation and Green Total Factor Productivity of Manufacturing Industry: Based on the
Development Background of Information Technology
293

significant double threshold feature. When the
informal environmental regulation is in the optimal
range (0.0693 < INER ≤ 0.5255), technological
innovation has a significant impact on the
manufacturing industry. The promotion effect of
green transition is higher than the other two intervals.
Based on the above analysis conclusions and in
combination with the development background of
information technology in China, suggestions are
made for the green transformation of manufacturing
industry:
Give full play to the advantages of information
technology, formulate formal environmental
regulatory policies reasonably, and strengthen the
government's regulatory capacity while ensuring the
mandatory force of formal environmental regulation.
Through Internet information technology,
improve the public's awareness of environmental
protection, increase the public's participation in the
environmental supervision and governance system,
ensure that the government, the public and enterprises
cooperate with each other, and transform reasonable
public demand for environmental protection into a
driving force for enterprise technology innovation
and green transformation of the manufacturing
industry.
REFERENCES
Abramovitz, Moses. (1993). The Search for the Sources of
Growth: Areas of Ignorance, Old and New. J. The
Journal of Economic History. 53,217–243.
Gallego, Juan Miguel, et al. (2015). Innovation and
Productivity in the Colombian Service and
Manufacturing Industries. J. Emerging Markets
Finance and Trade. 51,612–634.
Gray, Wayne B, and Ronald J Shadbegian. (2003). Plant
Vintage, Technology, and Environmental Regulation. J.
Journal of Environmental Economics and Management.
46, 384–402.
Jaffe, Adam B., and Karen Palmer. (1997). Environmental
Regulation and Innovation: A Panel Data Study. J.
Review of Economics and Statistics. 79, 610–619.
Lei Yutao, Zhang Shuwen, Sun Jingjing. (2020). The impact
mechanism and empirical research of environmental
regulation on the green transformation of
manufacturing industry. J. Science and Technology
Progress and Countermeasures. 37, 63-70.
Moutinho, Victor, et al. (2020). Determinants of the
Environmental Kuznets Curve Considering Economic
Activity Sector Diversification in the OPEC Countries.
J. Journal of Cleaner Production. 271, 1226.
Porter, M E, and Linde C V D. (1995). Green and
Competitive: Ending the Stalemate. J. Long Range
Planning. 28, 128–129.
Peuckert, Jan. (2014). What Shapes the Impact of
Environmental Regulation on Competitiveness?
Evidence from Executive Opinion Surveys. J.
Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions. 10,
77–94.
Porter, Michael E, and Claas van der Linde. (1995). Toward
a New Conception of the Environment-
Competitiveness Relationship. J. Journal of Economic
Perspectives. 9, 97–118.
Pargal, Sheoli, Wheeler, David. (1996). Informal
Regulation of Industrial Pollution in Developing
Countries: Evidence from Indonesia. J. Journal of
Political Economy, University of Chicago Press.
104(6), 1314-1327.
Tian, Ying, and Feng Chao. (2020). The Effects of Different
Types of Internal Controls on Self-Control. J. Journal of
Strategic Innovation and Sustainability. 14,30.
Zhang Youzhi, Qiao Yuhe. (2021). Research on the Impact
of Environmental Regulation on Green Total Factor
Productivity of Manufacturing: PSM-DID Test Based
on Carbon Emissions Trading Policy. J. Ecological
Economy. 37, 30-36.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
294
