
Security of Digital Item Transaction on Blockchain and a Design of
Decentralized E-Gallery
Jingyue Dou
Beijing-Dublin International College, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, China
Keywords: Blockchain, Non-Fungible Token, Digital Art, Transaction Security.
Abstract: The development of blockchain technology and the market scale of cryptocurrency offer more opportunities
to design different application cases of blockchain techniques. Therefore, many developers try to build trans-
action platforms for digital items and value the ownership of them. Some game applications (e.g., the Cryp-
tokitties), achieve the transaction of digital characters or game assets. To protect the benefits of owners and
artists, security schemes for transactions and system management are important. This research analyzes the
security schemes and application cases of the cryptocurrency protocol, smart contract, and on-chain file man-
agement. The important reasons and advantages of applying these techniques are explained in this study.
Furthermore, a design for a decentralized E-gallery application is introduced. The functions of user interaction
and a deposit scheme used in smart contracts are described. In addition, the purpose of the E-gallery design
is to offer a possible solution to achieve open and secure transaction of digital art. These results shed light on
guiding further exploration of decentralized transaction and NFT security.
1 INTRODUCTION
The potential of the blockchain system was first mo-
tivated by the research of Satoshi in 2008 (Nakamoto,
2008). In this research, he discussed concepts such as
hash chain, public-key cryptography, and proof of
work, and he built a possible solution for decentral-
ized transactions. The credit and value of Bitcoin are
supported by the incentives for miners and the Prove
of Work mechanism. Due to the limitations of
Bitcoin, Vitalik published Ethereum to improve the
level of scalability of the blockchain system. Vitalik
explains that people are allowed to develop complex
applications such as the decentralized exchange by
deploying smart contracts (Buterin, 2014). The mar-
ket capitalization of Ethereum has reached $194 bil-
lion (Ether Total Supply and Market Capitalization
Chart, 2022). Many designs are possible as Ethereum
expands the application of blockchain. One of the
most popular blockchain applications is decentralized
exchanges like IDEX (Wu, 2021). They offer token
transaction services by deploying smart contracts on
the Ethereum blockchain. The total volume of IDEX
has reached $2.4 billion (IDEX, 2019). In addition,
according to the research of Wu et al., games and
gambling applications are also attractive to users. By
the end of 2018, there were over 150 games and gam-
bling Dapps like the Cryptokitties on the Ethereum
platform (Wu, 2021).
The blockchain system faces many security issues
which are harmful to the wealth of individuals and
corporations. There are several types of attack meth-
ods. Many researchers mention the Majority (51%)
Consensus Attack and Double-Spending Attack,
which are general types of blockchain attacks (Zhang,
2019; Lin, 2017; Li, 2020). When a single miner con-
trols more than half of the hashing power of the entire
blockchain, the 51% Attack can be launched for ille-
gal transactions or disturbing the mining business
(Zhang, 2019; Lin, 2017; Li, 2020). Double-Spending
Attacks may use the flaws of validation to copy the
tokens or enjoy free services (Zhang, 2019; Li, 2020).
Attackers can use the gap between transaction initia-
tion and validation to get the output before the trans-
action is mined to be invalid (Li, 2020). Harry and
Piekarska mention the anonymity issues of block-
chain and the related risk of the Double-Spending At-
tack (Halpin, 2017). In addition, flaws in crypto-
graphic operations, including the vulnerability of
RSA, secp256k1 curve and SHA-256 need to be fixed
(Dasgupta, 2019). According to the research of
Dipankar et al., the consequences of attacks on ex-
498
Dou, J.
Security of Digital Item Transaction on Blockchain and a Design of Decentralized E-Gallery.
DOI: 10.5220/0012035600003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 498-503
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
changes are serious. From 2014 to 2017, the ex-
changes, including Mt. Gox, Bitstamp and Coincheck
lost 130 thousand Bitcoins and 500 million NEM to-
kens (Dasgupta, 2019). Therefore, it’s important to
improve the security level of blockchain transactions
and explore more sufficient protection methods.
To reduce the risk of blockchain attacks and solve
the vulnerability of transactions, the security mecha-
nisms of applications and smart contracts need to be
designed properly. Owing to the increase in transac-
tions of digital products and non-fungible tokens
(NFT), it is essential to focus on protecting the own-
ership of digital items and the transaction process of
NFT. This research will introduce some security tech-
niques and application examples used in digital prod-
ucts and NFT transactions. Then, a design for a de-
centralized E-gallery demo based on NFT will be de-
scribed. The possible deposit scheme in this design
may solve the credit issues of transactions between
artists and customers. Meanwhile, the limitations and
potential improvement of digital item transactions
will be investigated.
2 NFT TECHNIQUES AND
SECURITY SCHEMES
2.1 Token Standards
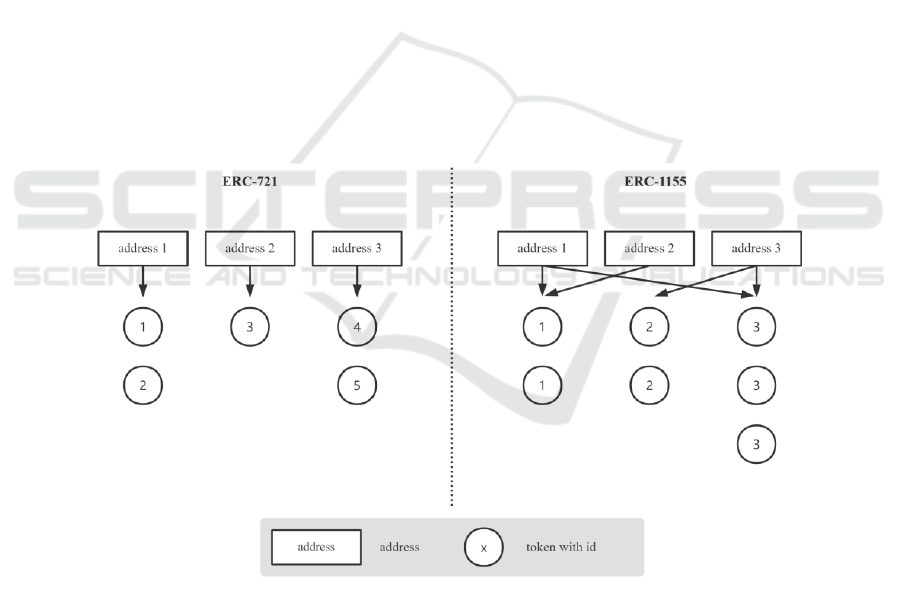
Non-fungible tokens always confirm to the ERC-721
interface and the pair of token ID and contract address
can ensure the token is unique globally (Das, 2021;
Wang, 2021). The ERC-721 interface has four essen-
tial methods, and the approve method can be used to
add a URL towards a metadata JSON that usually pre-
sents the attributes of the digital product (Das, 2021).
Therefore, digital products such as images or charac-
ters can use the token ID to generate a unique identi-
fication (Wang, 2021). Furthermore, Wang et al. de-
scribe another token standard that extends the func-
tionality of tokens. ERC-1155 token IDs can repre-
sent different configurable token types and tokens of
the same type are fungible (Wang, 2021). Attributed
to this feature, ERC-1155 tokens may be more diffi-
cult to be attacked than ERC-721 tokens. The differ-
ences between ERC-721 and ERC-1155 are shown in
Fig. 1.
Figure 1: Differences between ERC-721 and ERC-1155 [Owner-draw].
2.2 Privacy-Preserving Smart Contract
Unfortunately, the hash data and transaction ad-
dresses related to tokens may be exploited by hackers
to transfer ownership or get personal information. Ac-
cording to the research of Wang et al., the transpar-
ency of smart contracts is dangerous for NFT buyers.
Everyone on the blockchain can access the addresses
and hash information of the contracts and launch at-
tacks based on the link ability feature of NFT (Wang,
2021). To address this information disclosure issue,
researchers suggest developers use privacy-preserv-
ing smart contracts (Wang, 2021). Li et al. mention
the Hawk framework where people can develop pri-
Security of Digital Item Transaction on Blockchain and a Design of Decentralized E-Gallery
499
vacy-preserving smart contracts on it with automati-
cally generated cryptographic protocols (Li, 2020;
Kosba, 2016).
Figure 2: Application of using IPFS with smart contract
[Owner-draw].
2.3 InterPlanetary File System (IPFS)
IPFS is often used to save metadata or images of dig-
ital items. Because of the tampering risk for data
stored outside the blockchain (Wang, 2021), develop-
ers save NFT-related data on IPFS. The files will be
linked to the content identifier (CID), which is a
unique address in the system. When the content of the
data is changed, the CID will also change at the same
time to prevent tampering. Furthermore, IPFS data is
divided into blocks and stored in the Mercle DAG,
after which IPFS maintains a distributed hash table to
manage the stored data (Das, 2021). The application
process of IPFS is illustrated in Fig. 2.
3 APPLICATION OF NFT
SECURITY SCHEMES
On account of the scalability and security features of
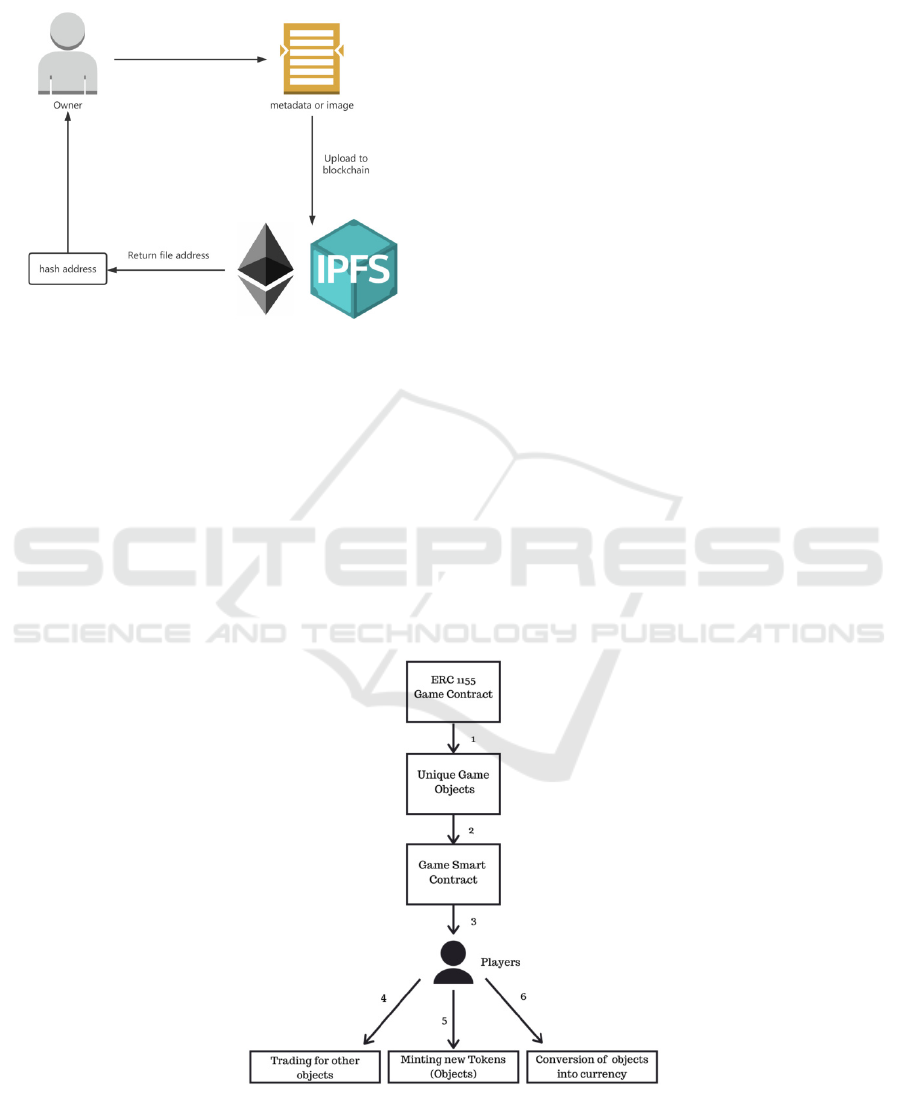
the ERC-1155, this protocol is valuable for digital
product transactions. Muthe et al. introduce their so-
lution for game networks based on NFT. To increase
the attributes of game assets and the security level,
they decided to use ERC-1155 for their decentralized
network. The non-fungible configurations of game
assets can reduce the risk of tampering. Furthermore,
the fungible feature of the same type of token can en-
sure the game balance for all players (Muthe, 2020).
The system architecture is exhibited in Fig. 3. In gen-
eral, game objects are created by ERC-1155 contracts
to ensure their unique attributes and are rendered by
following the rules created by the game contract.
When the players get the game objects, these game
assets will be added to their wallet. Subsequently,
players can trade their game assets with other users or
transfer them to tokens. Therefore, the ERC-1155 is a
flexible and secure protocol that can be expanded
properly to fit the application cases.
Figure 3: Application of game assets transaction based on ERC-1155 token (Muthe, 2020).
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
500

Liao et al. build a management system for casino
facilities. They apply the Hawk model to develop pri-
vacy-preserving smart contracts to protect the per-
sonal information of transactions. Due to the Hawk
model dividing the contract into public and private
parts, researchers use this feature to develop the pub-
lic and private pool to offer customized anonymous
services (Liao, 2018). When users initialize transac-
tions between a public pool and a private account, the
information is transparent to other users. However,
when users spend their money in the private pool,
other users cannot see the transaction information,
such as the amount of transaction or addresses (Liao,
2018). The application of the Hawk model protects
the user privacy and reduces the risk of attacks, as
well as maintaining the transparency options for user
interactions.
Many digital trading applications use the IPFS to
save metadata and images on the blockchain. To use
IPFS in NFT transactions, tampering attacks are hard
to launch due to the hash block structure (Das, 2021;
Muthe, 2020). Meanwhile, the gas fee for accessing
the on-chain data has been reduced (Wang, 2021).
Karapapas et al. adopt the IPFS to save digital art for
their systems and the system structure is depicted in
Fig. 4. Image files are collected by the company from
artists and uploaded to IPFS after encryption. Cus-
tomers need to interact with the smart contracts on
Ethereum and IPFS to pay for their characters and
collect the digital art for their wallets (Karapapas,
2021). Furthermore, Muthe et al. extend the role of
IPFS in blockchain services. Instead of using central-
ized game servers, researchers decided to use the
IPFS to transfer node state information and achieve
consensus. The IPFS will be involved in proxy com-
putation to support decentralized network communi-
cation by using the Bitswap protocol (Muthe, 2020).
Figure 4: Application of digital art transaction based on IPFS (Karapapas, 2021).
4 DESIGN OF E-GALLERY
APPLICATION
The purpose of this design is to try to find and build
an efficient design for the E-gallery DApp. Previous
essays and prototypes were analyzed to find a possi-
ble solution for building the NFT token for transac-
tions. The solution of digital painting combined with
the NFT token can ensure the unique copyright of
painting (Das, 2021; Wang, 2021). The ERC-721 pro-
tocol is decided to use as digital arts are non-fungible
and unnecessary to separate the attributes to different
types of tokens. Meanwhile, the usage of the market-
place paid by artists and transactions of the NFT to-
ken can provide fees to access the blockchain or pro-
duce benefits. Therefore, the NFT token can solve the
problems of copyright security and gas fee payment.
Many NFT-based applications, such as Cryptokitties,
introduced IPFS as a solution for storing metadata
and images in a decentralized system. Therefore, it is
decided to achieve the E-gallery prototypes by using
a gateway API to upload or get information from the
IPFS. The IPFS gateway provided by the Pinata or In-
fura can provide a convenient and efficient solution
for IPFS interaction and may decrease the cost of us-
ing IPFS. The NFT token and purchase contracts are
deployed on the Georli test network on the Ethereum
platform. Users can interact with the front-end com-
ponents implemented by the web3 dependency to ac-
cess the IPFS or deployed smart contacts. In addition,
the payment and identification services will be pro-
vided by Metamask.
This application offers a decentralized transaction
platform for digital arts. The agency is unnecessary
Security of Digital Item Transaction on Blockchain and a Design of Decentralized E-Gallery
501

because artists can communicate and trade with cus-
tomers directly. Furthermore, because NFT schemes
prevent copying and tampering, they can provide
more secure ownership protection than traditional
online transactions. Artists can publish their works
for sale and communicate with customers directly. A
customer can pay for the NFT linked to the metadata
and image files as collections. A deposit scheme is
used in payment contracts to solve the security prob-
lem of dishonest artists or customers in a decentral-
ized system. When an artist publishes their digital art,
they need to pay a deposit equal to the art price, which
will be saved in a safety wallet and set to be frozen.
Customers also need to pay the deposit to prevent dis-
honest actions. The total deposit should be double the
price of the digital art. After customers confirm the
deal, the deposit will be returned to their own wallets.
However, if there are dishonest artists, the total de-
posit will be given to customers to compensate for
their loss. The dishonest behavior will be judged by
website employees to avoid fake reports.
In the next step, encouraging and security
schemes will be added to this design. To attract more
artists to join the platform, a deposit discount scheme
or popular rank list can be implemented. Otherwise,
it is essential to divide public and private businesses
separately by deploying the Hawk model to write pri-
vacy-preserving contracts to protect personal infor-
mation and reduce the risk of attacks. This system can
be used for the transaction of poster designs or pho-
tography arts in the future. The decentralized NFT
system can protect the ownership of digital arts for
customers and help artists earn more benefits since
there is no agency. Compared with a centralized web-
site, this system may offer a more open social envi-
ronment and secure transaction services.
5 LIMITATION AND OUTLOOKS
FOR BLOCKCHAIN
TRANSACTION
The limitation of the blockchain transaction system is
mainly one of scalability. When new blocks are added
to the network, every block in the decentralized sys-
tem needs to achieve consensus. Owing to the con-
sensus scheme, after the transaction is initialized, it
needs a long period of time to update the blockchain
and finish the transaction. Meanwhile, the transaction
fee is expensive if users prefer rapid transaction
speed. Therefore, Bitcoin can only achieve seven
transactions per second while Ethereum can achieve
fifteen times per second. The issues of transaction de-
lay and expensive gas fees may lead to a limited in-
crease in blockchain transaction users. The scalability
issues limit the application cases of blockchain tech-
nology and the competition with traditional transac-
tion methods such as Visa.
Many researchers are trying to find possible solu-
tions to solve the issue of blockchain transactions.
Poon et al. contributed to improving the transaction
speed and building the Lightning Network in 2016.
They provide direct transaction services between two
users to save time spent on the consensus and reduce
the cost of blockchain resources (Poon, 2016). This
off-chain transaction solution may offer a better ex-
perience for individuals. In addition, Kwon et al. try
to build an open network for every blockchain to
achieve inter-blockchain operations and improve the
performance of scalability. The Cosmos network is
supported by the Tendermint engine and the Inter-
Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol (Kwon,
2022). Tendermint organizes blockchain protocols
and consensus schemes into an engine so that devel-
opers can simplify the processes of blockchain build-
ing and concentrate on application design by using
any language. Meanwhile, the IBC protocol supports
the transmission of tokens and data between hetero-
geneous chains based on instant finality. Therefore,
the Cosmos network will simplify the blockchain
building process and expand application cases. As-
cribed to the consensus algorithm and protocols the
Cosmos used, instant transactions may be possible to
achieve (Kwon, 2022). Eventually, the contribution
of this research may help to achieve better perfor-
mance in terms of scalability and usability.
6 CONCLUSION
In summary, this research discusses the security
schemes of digital art transactions based on the NFT
and introduces a design for a decentralized E-gallery
application. The techniques and applications of NFT
security are described, including the token standard,
privacy-preserving contract and IPFS. In addition, the
functions and structure of the E-gallery design are in-
troduced based on the ERC-721 token and IPFS. A
possible deposit scheme is also proposed to solve the
credit issue of digital art transactions. However, the
design still needs more functions to offer a more com-
plete experience for users and more security schemes
to prevent attacks such as tampering. Although this
system needs improvement, the design offers an open
social environment and secure ownership of digital
items without centralized agency. It can also be used
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
502

in the digital art transaction of photographic or
graphic design. Overall, these results offer a guideline
for digital item transaction based on NFT.
REFERENCES
Buterin, V.: A next-generation smart contract and decen-
tralized application platform. White paper 3.37: 2-1
(2014).
Dasgupta, D., John, M. S., Kishor, D. G.: A survey of block-
chain from security perspective. Journal of Banking and
Financial Technology 3.1: 1-17 (2019).
Das, D., Bose, P., Ruaro, N., Kruegel, C., Vigna, G.: Un-
derstanding security Issues in the NFT Ecosystem.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.08893 (2021).
Ether Total Supply and Market Capitalization Chart,
<https://etherscan.io/stat/supply>, last accessed
2022/9/18.
Halpin, H., Marta, P.: Introduction to Security and Privacy
on the Blockchain. 2017 IEEE European Symposium
on Security and Privacy Workshops (EuroS & PW).
IEEE (2017).
IDEX - decentralized Ethereum asset exchange. 2019,
<https://idex.market/>, last accessed 2022/9/18
Karapapas, C., Iakovos, P., George C. P.: Fully Decentral-
ized Trading Games with Evolvable Characters using
NFTs and IPFS. 2021 IFIP Networking Conference
(IFIP Networking). IEEE (2021).
Kosba, A., Miller, A., Shi, E., Wen, Z., Papamanthou, C.:
Hawk: The blockchain model of cryptography and pri-
vacy-preserving smart contracts. 2016 IEEE sympo-
sium on security and privacy (SP). IEEE (2016).
Kwon, J., Ethan, B.: Cosmos: A network of distributed
ledgers. <https://cosmos. network/whitepaper>, last ac-
cessed 2022/9/18.
Liao, D., Wang, X.: Applications of blockchain technology
to logistics management in integrated casinos and en-
tertainment. Informatics. 5.4: 44. MDPI (2018).
Lin, I., Tzu-Chun, L.: A survey of blockchain security is-
sues and challenges. Int. J. Netw. Secur. 19.5: 653-659
(2017).
Li, X., Jiang, P., Chen, T., Luo, X., Wen, Q.: A survey on
the security of blockchain systems. Future Generation
Computer Systems 107: 841-853 (2020).
Muthe, K., B., Khushboo, S., Karthik, E. N.: A blockchain
based decentralized computing and NFT infrastructure
for game networks. 2020 Second International Confer-
ence on Blockchain Computing and Applications
(BCCA). IEEE (2020).
Nakamoto, S.: Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash sys-
tem. Decentralized Business Review 21260 (2008).
Poon, J., Thaddeus, D.: The bitcoin lightning network:
Scalable off-chain instant payments. (2016).
Wang, Q., Li, R., Wang, Q., Chen, S.: Non-fungible token
(NFT): Overview, evaluation, opportunities and chal-
lenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.07447 (2021).
Wu, K., Ma, Y., Huang, G., Liu, X: A first look at block-
chain‐based decentralized applications. Software: Prac-
tice and Experience 51.10: 2033-2050 (2021).
Zhang, R., Rui, X., Ling, L.: Security and privacy on block-
chain. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 52.3: 1-34
(2019).
Security of Digital Item Transaction on Blockchain and a Design of Decentralized E-Gallery
503
