
Long-Term Forecast of Regional Economy Based on Least Squares
Support Vector Machine
Litao Fan
School of Economics and Management, Guangxi Vocational and Technical College of Communications,
Nanning 530023, Guangxi, China
Keywords: Least Squares Support Vector Machine, Regional Economy, Medium- and Long-Term Forecasting, Support
Vector Machine.
Abstract: Regional economic growth is a demand-led change. By reasonably forecasting and studying the patterns and
operating mechanisms of economic growth changes in a specific range of regions, we will promote the
sustainable growth of regional economy and society. In order to address the shortcomings of the existing
research on regional economic forecasting in the medium and Long-Term, this paper briefly discusses the
index system and sample data of the forecasting model proposed in this paper based on the least squares
support vector machine (LLSSVM) and regional economic forecasting methods. The design of the
forecasting model is also discussed, and the results of the least squares support vector machine for medium-
and Long-Term regional economic forecasting are finally analyzed experimentally. The experimental data
show that the error between the prediction results of least squares support vector for a city's economic GDP
and the actual results is small, and its accuracy rate for a city's economic GDP prediction is about 96.5% on
average, which is significantly better than the other two prediction models. Therefore, it is verified that the
game model simulation based on ant colony algorithm performs better.
1 INTRODUCTION
There is a close relationship between regional
economic development and national economic
development and people's social living standards,
and the correct prediction and analysis of the law of
economic development changes in the region is
beneficial to the continuous development of the
national economy and regional economy.
Nowadays, an increasing number of scholars
have conducted a large number of studies in medium
and Long-Term forecasting of regional economies
through various technical and systematic tools and
have achieved some results through practical
research. Archit derives a general differential
equation describing the cyclical and trend
components of Long-Term economic growth. The
equation is based on an induced investment
nonlinear gas pedal model. A method is proposed to
solve the approximate solution of the nonlinear
differential equation by decomposing the solution
into a rapidly oscillating business cycle and a slowly
varying trend using the KBM averaging method.
The model gives rough estimates of the threshold at
which the system destabilizes and falls into a crisis
recession and is one of the main results of the
model. The model is used to forecast the
macroeconomic dynamics of the United States in the
sixth Kondratieff cycle (2018-2050). For this
forecast, Archit uses a fixed productive capital
function dependent on the long-run Kondratieff
cycle and the medium-run Juglar and Kuznets
cycles. More accurate forecasting of the timing of
crises and recessions is based on the accelerated
log-cycle oscillation model (Archit 2018). Salimova
G proposes a model for forecasting socio-economic
trends in a region. The model envisages the
construction of three = models: matrix predictor,
autoregressive model and binary choice logit model.
This approach ensures adequate reproduction of the
system dynamics of regional socio-economic
development indicators. It is also tested by specific
examples that illustrate the opportunities of
multidimensional economic and mathematical
modeling of difficult socio-economic phenomena
and processes. The development of the model
provides for the implementation of multivariate
forecasting calculations (Salimova G 2022). The aim
of Greyling L research is to develop an appropriate
542
Fan, L.
Long-Term Forecast of Regional Economy Based on Least Squares Support Vector Machine.
DOI: 10.5220/0012036500003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 542-547
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

mathematical model for Long-Term forecasting of
technological progress and economic growth in the
digital age. To achieve its goal, the
Schumpeter-Kondratieff theory of innovation and
cycles is the most suitable economic-technical
cluster of economic development for Long-Term
forecasting of technological progress and economic
growth. Greyling L developed an information model
for forecasting technological progress based on the
growth rate of endogenous technological
information in the economy. It also gives the main
regimes of producing technological information
corresponding to the era of information and digital
economy, as well as the Lagrange's theorem that
generates them. The model is validated with the
information LW of the U.S. economy from
1982-2018, with highly accurate approximations to
both technological progress and economic growth
(Greyling L 2022). Although there is a wealth of
existing research on regional economic forecasting
in the medium and Long-Term, there are certain
shortcomings in regional economic forecasting in
the medium and Long-Term based on least squares
support vector machines.
In this paper, based on the established least
squares support vector machine (LLSSVM)
regression forecasting model, an evaluation index
system for regional economic forecasting is
constructed with the economic development of a city
as the background of the empirical study, and the
selected sample data are screened for indicators and
the data set is pre-processed for normalization. The
least squares support vector machine (LLSSVM)
and the characteristics and properties of regional
economic development are used to describe in detail
the basis for the establishment of the forecasting
model. The prediction accuracy of LLSSVM for
regional economy is compared with PCA and SVM,
and the results show that the prediction accuracy
based on LLSSVM) is better than that of PCA and
SVM models.
2 MEDIUM- AND LONG-TERM
FORECASTING OF REGIONAL
ECONOMY BASED ON LEAST
SQUARES SUPPORT VECTOR
MACHINE
2.1 Least Squares Support Vector
Machine (LLSSVM)
LLSSVM adopts the empirical risk minimization
criterion and uses kernel functions to solve nonlinear
regional economic forecasting problems, which can
be solved as linear forecasts in the new economic
characteristics (Sun F 2022).
At this point the decision function can be
expressed as:
ckhuk +⋅= )()(
ϑ
(1)
where
h
is a vector of regional economic weights
and
c is an offset. The structural risk minimization
principle is used to find the value of this vector.
The LLSSVM optimization problem can be
expressed as:
),...2,1(
2
1
2
1
),,(min
1
2
2
,,
XivhvchW
X
i
i
vch
=+=
=
λ
(2)
where,
λ
is the penalty parameter and
i
v
denotes
the prediction error. From the above equation, it can
be seen that the loss function is directly defined in
the least squares support vector machine as the sum
of squares of the errors (Iliovits M 2022).
The expression of the prediction model for
nonlinear regression can be written as:
=
+=
X
j
jii
cuuGuk
1
),()(
β
(3)
In the above equation,
i
β
is the multiplier of
regional economy and
)(
, ji
uuG is the kernel
function, which satisfies the conditions of regional
economic development. The kernel function chosen
in this paper is
)
2
exp()(
2
2
ϖ
ji
ji
uu
uuG
−
−=
.
2.2 Regional Economic Forecasting
Methods
Regional economic forecasting can be divided into
different categories according to different methods
(Virtanen H 2022).
(1) According to the scope involved in economic
forecasting, it can be divided into macro and micro
economic forecasting. Macroeconomic forecasting
generally refers to forecasting based on the national
economy and the scope of operation of regional
units. Microeconomic forecasting refers to
forecasting on the basis of the scope of operation of
Long-Term Forecast of Regional Economy Based on Least Squares Support Vector Machine
543

production units (Klopp R N 2022).
(2) Long-Term, medium- and Long-Term
economic forecasts, short-term and near-term
forecasts are classified according to the length of the
forecast period. Long-term economic forecasting
refers to making forecasts for more than five years.
Medium-term economic forecasting refers to
forecasting for one to five years (Raj A 2022).
(3) Static and dynamic economic forecasts can
be classified according to the temporal state of the
forecast. Static economic forecasting is based on the
expectation of the cause-effect relationship arising
from macro things in a region (Falahat M 2022).
Dynamic economic forecasting, on the other hand,
refers to the prediction of future economic
development based on the course and dynamics of
macro things generated in a region.
3 INVESTIGATION AND STUDY
OF REGIONAL ECONOMIC
FORECASTING IN THE
MEDIUM AND Long-Term
BASED ON LEAST SQUARES
SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
3.1 Regional Economic Forecasting
Index System
The index system studied in this paper is based on
the composition of gross domestic product (GDP),
and the factors affecting the regional economic
growth include three aspects: investment,
consumption, and import and export. Economic
growth is the result of the configuration of these
main factors among different organizations (Slama F
B 2022).
Investment: fixed asset investment and
real utilization of foreign capital.
Consumption: In this paper, the total retail
sales of consumer goods is chosen to reflect the
level of consumption of the population, and
government fiscal expenditure is chosen to reflect
government consumption.
Import and export: the import and export
of foreign trade are selected to reflect the import and
export situation.
Resources: total energy consumption,
investment in environmental protection, deposit
balance of financial institutions, and investment in
education.
3.2 Data Selection
The data set of this paper is the bottom data of
business and industry business system of a
provincial industrial and commercial bureau, and the
time span of the data set is from 2011 to 2021,
among which there are 87641 records in the original
data set of industrial and commercial data of a city,
in order to improve the prediction accuracy of the
model, the data set after pan-Chinese processing is
shown in Table 2, this paper takes the data from
2011-2021 as the training set, and takes the data
from 2017 and In this paper, the data from
2011-2021 are used as the training set, and the data
from 2017 and 2021 are used as the test set for
testing the prediction model (Caputo F 2022)
Table 1: Selected data after processing.
Corporate logo
Enterprise
type
Enterprise scale Area Industrial division
50221198BABA H 1 02 005
50221198BABA L 3 04 006
50221198BABA F 2 02 006
50221198BABA Y 2 02 005
50221198BABA G 3 04 005
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
544
4 RESEARCH ON THE
APPLICATION OF REGIONAL
ECONOMIC MEDIUM- AND
LONG-TERM FORECASTING
BASED ON LEAST SQUARES
SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
4.1 Construction of Regional Economic
Medium and Long-Term
Forecasting Model Based on Least
Squares Support Vector Machine
According to the characteristics of the regional
economy in the medium and Long-Term, it is
necessary to consider the characteristics of the
medium and Long-Term development stages when
building the forecasting model. According to the
actual regional economic development in recent
years, the overall target of economic development of
a city in 2021 is predicted, and it is necessary to
grasp the two points of bottom limit and high limit.
And in the process of LSSVM forecasting model
establishment, two penalty parameters and
activation functions need to be determined. If the
penalty parameter is small, the phenomenon of
under-learning of prediction is likely to occur: if the
penalty value is too large, the phenomenon of
over-learning of prediction is likely to occur. If the
kernel function is too small, the SVM is prone to the
risk of overtraining and vice versa. For this reason, a
medium- and Long-Term economic forecasting
model based on least squares support vector
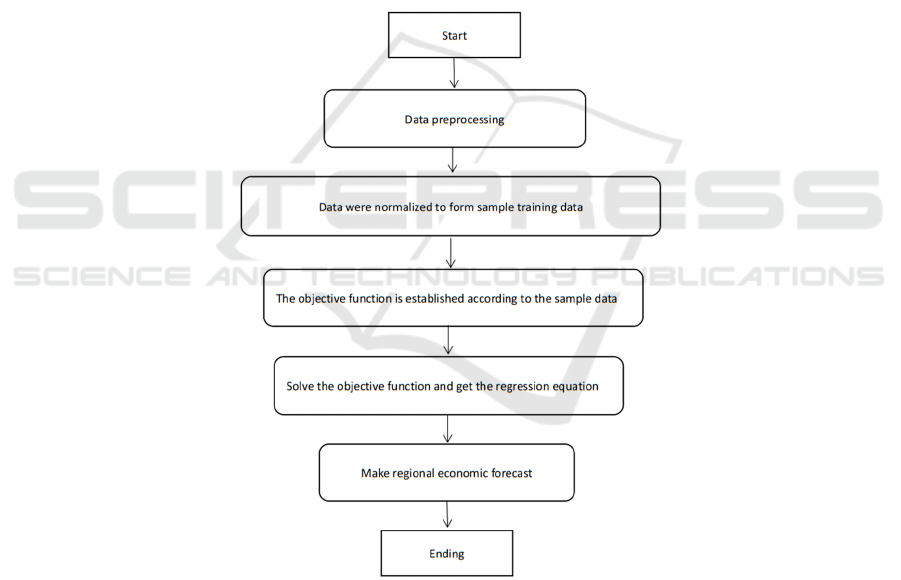
machine is designed as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: LSSVM prediction model diagram.
After fully studying the principle of LSSVM we
can follow the following process to model:
Historical regional economic data anomaly
data identification and pre-processing.
Normalization of historical data to form a
training sample matrix.
empirically determine the penalty
parameters and kernel functions to establish the
objective function.
Solving the objective function to obtain
the regression equation.
Forecast the medium- and Long-Term
development trend of the regional economy using
the obtained regression equation;
Long-Term Forecast of Regional Economy Based on Least Squares Support Vector Machine
545
4.2 Application of Least Squares
Support Vector Machine Based
Regional Economic Medium- and
Long-Term Forecasting
In order to verify the validity of this paper, two other
similar models are introduced for comparison, one is
using principal component analysis (PCA) to extract
components from the original independent variable
data, and then using SVM regression modeling and
forecasting; the other is using direct SVM modeling,
that is, not extracting components from the original
independent variable data, but directly performing
SVM regression modeling and forecasting. In order
to ensure the validity of the method comparison, the
parameters of the latter SVM were chosen to be the
same as those of the LSSVM. Then the five sample
components obtained after pre-processing were used
to build the regression models and to make
predictions, so as to obtain the predicted and actual
results of the economic GDP from 2017 to 2021 for
statistical analysis, and the accuracy of the
predictions of the three models was obtained as
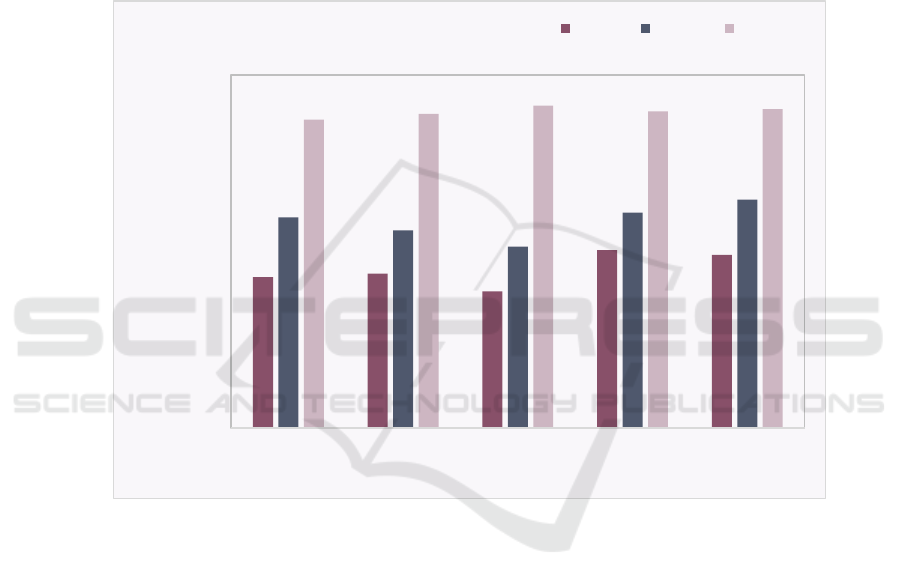
shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: comparison of forecasting accuracy.
From the experimental data in Figure 2, it can be
seen that the accuracy of LSSVM's regional
economic forecasts from 2017 to 2021 is higher than
that of PCA and SVM in general. The accuracy of
the PCA and SVM GDP forecasts is only 85.1% on
average, while the accuracy of the LSSVM forecasts
is 97.4% and 96.9% for 2019 and 2020 respectively.
As well as LSSVM has an accuracy of 97.1% in
forecasting economic GDP for 2021, the other two
models have an accuracy of only 84.70% and
89.40% in forecasting economic GDP, respectively.
Therefore, it can be found that the least squares
support vector machine proposed in this paper is
better than the other two models in predicting the
regional economy in the medium and Long-Term,
and its superiority of prediction is verified.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, through an in-depth study of regional
economic forecasting methods and least squares
support vector machines, an LSSVM model was
established based on the relevant data and index
system of a city from 2011-2021, and the predicted
economic GDP from 2017-2021 was successfully
predicted, and the fitting effect was very satisfactory
according to the prediction error. Then, the LSSVM
model was trained and tested with PCA and SVM
models, and the errors of the prediction results and
the actual results were statistically analyzed for
accuracy comparison. Finally, it is verified that the
LSSVM model fits better than the other two models.
70,00%
75,00%
80,00%
85,00%
90,00%
95,00%
100,00%
2017 2018 2019 2020 2021
Value
Year
PCA SVM LSSVM
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
546

REFERENCES
Archit, Kumar, Nayak, et al. Growth, Instability and
Export Performance of Banana in India - An
Economic Analysis [J]. Agricultural Situation in India,
2018, 74(10):25-33.
Caputo F, Fiano F, Riso T, et al. Digital platforms and
international performance of Italian SMEs: an?
exploitation-based overview [J]. International
Marketing Review, 2022, 39(3):568-585.
Falahat M, Soto-Acosta P, Ramayah T. Analysing the
importance of international knowledge, orientation,
networking and commitment as entrepreneurial culture
and market orientation in gaining competitive
advantage and international performance[J].
International Marketing Review, 2022, 39(3):463-481.
Greyling L, Makhoba B P, Kaseeram I. Asymmetric and
threshold effects of public debt on economic growth in
SADC: a panel smooth transition regression analysis
[J]. African Journal of Economic and Management
Studies, 2022, 13(2):165-176.
Iliovits M, Harding L, Pill J. Language use in an
English-medium instruction university in Lebanon:
Implications for the validity of international and local
English tests for admissions[J]. Journal of
English-Medium Instruction, 2022, 1(2):153-179.
Klopp R N , Franco J F H , Hogenesch H , et al. Effect of
medium-chain fatty acids on growth, health, and
immune response of dairy calves[J]. Journal of Dairy
Science, 2022, 105 (9):7738-7749.
Raj A, Misra J P, Khanduja D. Modeling of Wire
Electro-Spark Machining of Inconel 690 Superalloy
Using Support Vector Machine and Random Forest
Regression Approaches[J]. Journal of Advanced
Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 21(03):557-571.
Salimova G, Ableeva A, Valishina N, et al. Regional
Product, Employment, and Labor Productivity in the
Context of Sustainable Development [J]. Journal of
Industrial Integration and Management, 2022,
07(03):349-365.
Slama F B, Oussii A A, Klibi M F. The rough road towards
accounting harmonization of a developing country
with a French accounting culture[J]. Accounting
Research Journal, 2022, 35(4):490-507.
Sun F, Shi G. Study on the application of big data
techniques for the third-party logistics using novel
support vector machine algorithm[J]. Journal of
Enterprise Information Management, 2022,
35(4/5):1168-1184.
Virtanen H, Kock S. Striking the right balance in tension
management. The case of coopetition in small- and
medium-sized firms[J]. Journal of Business &
Industrial Marketing, 2022, 37(13):33-47.
Long-Term Forecast of Regional Economy Based on Least Squares Support Vector Machine
547
