
Quality Evaluation and Spatial Differentiation of Rural Human
Settlements: A Case Study of Sichuan Province, China
Lie Zhang
*a
School of Public Administration, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Keywords: Rural Human Settlements, Spatial Analyst Technology, Governance Strategies.
Abstract: Taking Sichuan Province as a typical case, this paper constructs an evaluation index system of rural human
settlements quality in terms of infrastructure, public services and ecological environment, and uses GIS
spatial analysis technology, entropy power method and hierarchical analysis method to measure and
spatially analyze the rural human settlements quality. The main conclusions are as follows: the quality of
rural human settlements in Sichuan Province can be divided into four types, with an overall 'multilevel core-
edge' dispersion pattern and obvious differences among cities and states. Rural human settlements are a
complex system, and their quality is closely related to the natural, social and economic conditions of
regional development. The rural human settlements should be improved by establishing a governance model
based on 'core-edge' circle radiation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human settlements are usually divided into urban
and rural human settlements (Zhu et al., 2021), and
rural human settlements refer to the material and
non-material elements that meet the basic needs of
farmers ' production and life in the rural regional
system (Zhu et al., 2018). Compared with the study
of rural human settlements environment, the current
experts and scholars in the field of urban human
settlements environment have more research, and
research methods are relatively mature. Due to the
early implementation of the urban-first development
strategy in China, there is a clear ‘dual’
characteristic between urban and rural human
settlements as a result of lagging rural development
(Liu, Hu, & Li, 2014). With the rapid development
of the economy and the continuous advancement of
urbanization, the rural human settlements highlight
many problems: ecological environment destruction,
excessive utilization of resources, imperfect
infrastructure, and so on. The Chinese government
has released a number of measures to address these
issues, including the three-year action plan for the
improvement of rural human settlements, and the
rural revitalization strategy. To increase the levels of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9273-8173
rural settlements in provinces, these policies and
actions serve as guidance. Evaluating the quality
level of rural human settlements and proposing
corresponding governance strategies are of great
significance to the sustainable development of rural
human settlements.
At present, scholars ' research on rural human
settlements mainly focuses on the suitability of
human settlements, the evaluation and spatial
differentiation of urban and rural human settlements,
the demand of different groups for human
settlements, the influencing factors and dynamic
mechanism of human settlements evolution, and the
transformation of human settlements (Wang et al.,
2018; Hu, Wang, 2020; Li, 2018). In addition,
researchers have studied rural housing and building
forms (Savchenko & Borodina, 2017; Zhu, Fang &
Wang, 2018). The rich research results have laid a
theoretical foundation for this paper, however, in
terms of research regions, there are fewer studies on
regions with a huge span of terrain conditions.
Therefore, Sichuan province is chosen as a
typical study unit (including various topographical
features such as plateau, mountainous hills, and
plains) in this paper. By constructing the evaluation
index system of rural human settlements
environment quality, this paper comprehensively
uses GIS spatial analysis technology, entropy weight
method, and analytic hierarchy process to evaluate
114
Zhang, L.
Quality Evaluation and Spatial Differentiation of Rural Human Settlements: A Case Study of Sichuan Province, China.
DOI: 10.5220/0012070800003624
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2022), pages 114-119
ISBN: 978-989-758-658-3
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

and analyze the quality level of rural human
settlements environment in Sichuan Province. On
this basis, the corresponding governance strategies
are put forward in order to provide a reference for
the practice of rural human settlements environment
improvement.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Index System Construction
The rural human settlements are a multi-level and
multi-type complex system composed of a rural
ecological environment and social environment.
Following the principles of scientificity and
operability, five first-level indicators of
infrastructure, public service, ecological
environment, living quality, and rural economic
status were selected. Nineteen second-level
indicators such as rural radio coverage, TV
coverage, and rural per capita housing area were
used to establish a rural human settlements quality
measurement index system (Table 1).
Table 1: Rural human settlements quality evaluation index system.
Tar
g
et indicators Wei
g
ht Attribute
Infrastructure Y
1
Water su
pp
l
y
covera
g
e
4.95 +
Y
2
Gas su
pp
l
y
covera
g
e
4.04 +
Y
3
Main road hardenin
g
rate
7.24 +
Y
4
Proportion of villages with street
lam
p
s on main roads
1.08 +
Y
5
Radio and television covera
g
e
5.78 +
Public services
Y
6
Proportion of rural minimum living
securit
y
p
o
p
ulation in the rural
p
o
p
ulation
10.29 -
Y
7
Proportion of villages with farmers'
amateur cultural or
g
anizations
7.22 +
Y
8
Pro
p
ortion of villa
g
es with clinics
3.25 +
Y
9
The
p
roportion of villages with
kindergartens and nurseries
8.94 +
Ecological environment
Y
10
Rural fertilizer consumption
4.89 -
Y
11
Rural electricity consumption
5.97 +
Y
12
Proportion of villages with
centralized or partially centralized domestic
waste dis
p
osal
5.30 +
Y
13
The proportion of villages with the
centralized or partially centralized treatment
of domestic sewa
g
e
5.11 +
Living qualit
y
Y
14
Rural per capita housing area
6.3 +
Y
15
Proportion of reinforced concrete
structure housing households
4.74 +
Y
16
The proportion of brick (stone) wood
structures housin
g
households
3.57 -
Rural
economic situation
Y
17
Proportion of rural employees
3.55 +
Y
18
Rural per capita gross output value of
agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and
fisher
y
3.10 +
Y
19
Per capita disposable income of rural
households
4.68 +
Quality Evaluation and Spatial Differentiation of Rural Human Settlements: A Case Study of Sichuan Province, China
115

2.2 Data Sources and Methods
2.2.1 Overview of the Study Area
Sichuan Province is located in southwestern China
and has 21 administrative regions. The longitude and
latitude of Sichuan Province are (26° 03'N-34°
19'N, 92° 21'E-108° 12'E). The terrain conditions
in the province are complex and diverse, and the
natural, social, and economic development
conditions of various cities and states are
significantly different, which makes the
development of cities and states in Sichuan Province
significantly different.
2.2.2 Data Sources
the data used in this paper are derived from the
Statistical Yearbook of Sichuan Province (2020), the
Statistical Data of Sichuan Province in 2020, the
Statistical Bulletin of Sichuan Province in 2020, the
statistical yearbooks of cities and states in Sichuan
Province, and the satellite remote sensing images of
Sichuan Province. The spatial analysis objects
include 18 cities and 3 autonomous prefectures in
Sichuan Province, and the relevant spatial data are
derived from the vector map of cities and states in
Sichuan Province.
2.2.3 Standardization of Indicators
Because different evaluation indicators have
different dimensions, the study uses the extreme
value standardization method to dimensionless
process the index values, and there are positive
indicators and negative indicators.
WhenY
is a positive index:
𝐾
=
(1)
WhenY
is a negative index:
K
=
(2)
In the formula K
is the normalized indicator
value, Y
is the specific evaluation index value of the
area under a certain index.
2.2.4 Determine the Index Weight
The combination of the analytic hierarchy process
and entropy method to determine the weight is a
more scientific method (Qi, Wang, 2021). The
weight results (𝑊
)are shown in Table 1.
2.2.5 Comprehensive Calculation of Rural
Human Settlements Quality
Calculating the quality of rural human settlements
(S
) based on index weight(𝑊
) and dimensionless
value(K
), The calculation formula is as follows:
S
=
∑
𝑊
∙𝐾
(𝑖 = 1,2,3 … 𝑛
) (3)
whereS
is the score of the quality of rural human
settlements, S
∈[0,1].
2.2.6 GIS Spatial Analysis Method
Establishing a spatial analysis database of rural
human settlements quality based on ArcGIS10.2
platform. Firstly, add fields to the study units in
vector format, enter each study unit corresponding to
the rural human settlements quality index separately,
and realize the spatial link between the rural habitat
quality values and the study units in vector format.
Then, according to the natural breakpoint method,
the quality value of rural human settlements is
divided into four grades, and the spatial
differentiation map of rural human settlements
quality in Sichuan Province is drawn.
3 QUALITY AND ITS SPATIAL
DIFFERENTIATION RESULTS
According to Table 1 and the above formula, the
rural human settlements index of Sichuan province
is derived, and the spatial differentiation map of
rural human settlements’ environment quality is also
drawn based on GIS spatial analysis technology
(Figure 1). The quality of rural human settlements in
Sichuan Province generally shows a 'multilevel core-
periphery' divergence pattern, with obvious
differences among cities and states. With Chengdu
and Deyang as the two cores, their rural human
settlements quality is the highest; while the quality
of prefecture-level cities at the edges of Sichuan
Province, such as Ganzi, Aba and Bazhong, is the
lowest.
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
116
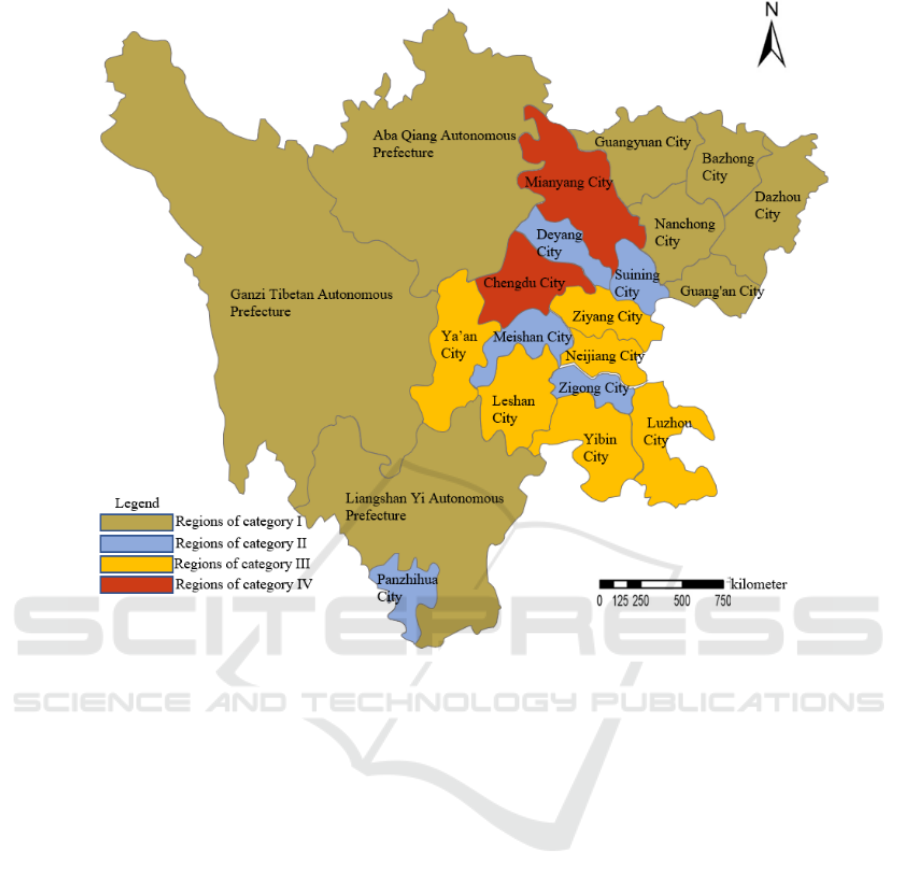
Figure 1: Spatial pattern of rural human settlements quality in Sichuan Province.
(1) Regions of category I. They are mainly
located in Ganzi, Aba, and Liangshan regions in the
western Sichuan plateau, and in five cities including
Bazhong and Dazhou in northeastern Sichuan. In
terms of infrastructure, Liangshan Autonomous
Prefecture has the lowest rural radio coverage and
TV coverage in the province, and the proportion of
main roads in the village is also the lowest in the
province. In terms of public service facilities, first of
all, the total number of rural subsistence allowances
in this area is large, and the proportion of the total
number is high. Secondly, the proportion of farmers '
amateur cultural organization villages is the lowest
in the province. Finally, the proportion of villages
with clinics and kindergartens is also at the lowest
level in the province. In terms of ecological
environment, firstly, the natural conditions of such
areas are harsh, with many mountainous plateaus
and a more fragile ecological environment.
Secondly, the ratio of centralized treatment of
domestic waste and centralized treatment of
domestic sewage in this region is the lowest in
Sichuan Province. In terms of living conditions, the
western plateau of Sichuan, encompassing Ganzi,
Aba, and Liangshan Autonomous Prefecture, has a
low per capita dwelling area; home building
materials are primarily brick (stone) and wood
constructions, and housing safety and comfort are
quite poor. In terms of rural economic level, this
region is far below the provincial average, including
the total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal
husbandry, and fishery per capita in rural areas and
the level of disposable income per capita of rural
households is very low.
(2) Regions of category II. They include Deyang
City, Meishan City, Zigong City, Suining City, and
Panzhihua City. Common features of this type of
area: First, the level of infrastructure is average. The
proportion of the main road in the village is tarmac
road surface and the proportion of the main road in
the village with street lights is located in the average
level of the cities and states in the province, and the
transportation facilities are more perfect; the
proportion of villages with gas is higher. Second, the
level of public services is higher. The proportion of
villages with amateur cultural organizations for
Quality Evaluation and Spatial Differentiation of Rural Human Settlements: A Case Study of Sichuan Province, China
117

farmers, health offices, kindergartens, and nurseries
is higher than the provincial average. Third, the
ecological environment is better. The amount of
fertilizer application is less compared to the first
category of areas, but overall the amount of fertilizer
application is higher; the villages have higher
electricity consumption and the residents have
convenient living. Fourth, the living conditions are
better. The residential area is larger. The proportion
of households with brick and stone structures is
larger, which restricts the improvement of living
quality; the proportion of households with reinforced
concrete structures needs to be increased in order to
improve the overall living quality of villagers in the
area. Fifth, the economic development level of the
countryside is average, and the proportion of
employed people in the countryside is high.
(3) Regions of category III. The region has the
following common characteristics. First, the level of
infrastructure is comparatively good. The region's
rural radio coverage and television coverage rate of
more than 90 percent, are at a high level in the
province; the proportion of gas villages in general, in
the general level of four types of regions. Second,
the level of public services is high. Farmers' amateur
cultural organizations, kindergartens, and nurseries
account for a higher proportion, ranking second
among the four types of regions; the proportion of
villages with health rooms is at the leading level in
the province. Third, the ecological environment is
average. Fertilizer application is high, second only to
Dazhou City, Meishan City, and Guangyuan City in
the high-value area of fertilizer application. Fourth,
the quality of residence is good. The region's per
capita living area is higher, and the proportion of
households with reinforced concrete structures is
also higher, second only to the first category of
regions. Fourth and fifth, the level of economic
development in the countryside is better. The total
output value of agriculture, forestry, animal
husbandry, and fishery per capita in the countryside
as well as the average level of disposable income per
capita in the countryside is higher than the average
level in the province.
(4) Regions of category Ⅳ. This region includes
Chengdu and Mianyang. The basic characteristics of
this type of area: First, the infrastructure conditions
are good. The villages in this category are located in
the Chengdu Plain Economic Zone, and get better
development by virtue of the local infrastructure
conditions and the radiation conditions of the urban
area; the quality of rural habitat is at an excellent
level; the average coverage rate of radio and TV
coverage is close to 100%; the proportion of main
roads with street lights is high, and the proportion of
roads with tarmac is high; the proportion of villages
with gas access is high. Second, the level of public
services is high. Good public services enable local
residents to enjoy better public service protection.
Third, a good ecological environment. The villages
in this type of area have high electricity
consumption and a high proportion of villages with
the centralized treatment of domestic garbage and
domestic sewage, which directly improves the level
of the local ecological environment. Fourth, high
quality of a residence. The per capita housing area is
higher than the provincial average; the average
proportion of households with reinforced concrete
structures exceeds the provincial average. Fifth, the
high level of rural economic development, the per
capita disposable income of rural residents exceeds
the provincial average.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
GOVERNANCE STRATEGIES
This paper constructs an index system for evaluating
the quality of rural human settlements in Sichuan
Province in terms of infrastructure, public services
and ecological environment, and evaluates the
quality level of rural human settlements in Sichuan
Province by using GIS spatial analysis techniques,
entropy weight method and hierarchical analysis
method, and draws its spatial divergence map. The
results show that the quality of rural human
settlements in Sichuan Province generally shows a
'multilevel core-periphery' divergence pattern, with
obvious differences among cities and states. Overall,
the quality level of human settlements in plain areas
is higher than that in hilly areas, and the quality level
of human settlements in plateau and mountainous
areas in western Sichuan is the lowest. Rural human
settlements are a complex system, and their quality
is closely related to the natural, social, and economic
conditions of regional development.
Based on the evaluation results of rural human
settlements quality in Sichuan Province and its
spatial differentiation regulations, this paper
proposes a corresponding governance strategy: to
establish a 'core-edge' circle radiation-based
governance model. Specifically, first of all, the cities
of each city and state with high-quality rural human
settlements should be the ‘core’, and the key towns
with poor quality rural human settlements should be
the ‘edge’, and the economic, social, political and
ecological links between the edge and the core
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
118

should be established and strengthened. Then,
according to local conditions, and classification
guidance, improve the ecological conditions of rural
human settlements in marginal areas, the level of
economic development, living environment. At the
same time, the government should promote the
equalization of infrastructure and public service
facilities from the core to the edge.
The quality evaluation methods and spatial
analysis techniques in this paper provide effective
tools for the comprehensive analysis of rural human
settlements quality, while the proposed governance
strategies provide certain policy references for the
sustainable development of rural human settlements
environment.
REFERENCES
Hu, Q., Wang, C. (2020). Quality evaluation and
division of regional types of rural human
settlements in China. Habitat International,105:
102278.
Li, B., Zeng, C., Dou, Y., et al. (2018). The
evolution and driving mechanism of the living
environment of traditional villages based on the
'Sansheng' space: Taking Lanxi Village,
Jiangyong County, Hunan Province as an
example. Advances in Geographical Sciences,
37(5):677-687.
Liu, Y., Hu, Z., & Li, Y. (2014). Process and cause
of urban-rural development transformation in the
Bohai Rim Region, China. Journal of
Geographical Sciences, 24 (6), 1147–1160.
Qi, Y., Wang, L. (2021). Application of AHP-
entropy weight method in hazards susceptibility
assessment in a mountain town. Bulletin of
Surveying and Mapping, (6): 112-116.
Savchenko, A., & Borodina, T. (2017). Rural
architectural and planning forms as a source of
diversity for urban environment (case study of
Moscow). European Countryside, 9, 560–576.
Wang, M., Li, X. (2018). Suitability Evaluation of
Urban Human Settlement Environment: a case
study of Four Districts in Dalian. Western
Journal of Human Settlement Environment,
33(04):48-53.
Zhu, Y., Zhou, X., Luo, J., et al. (2021). Evaluation
of the quality of rural human settlements in urban
agglomerations in the middle reaches of the
Yangtze River and its spatial and temporal
differentiation. Economic Geography, 41(04):
127-136.
Zhu, Y., Sun, X., Jie, Y., et al. (2018). Measurement
and optimization of human settlements cultural
environment quality based on rural revitalization
strategy: a case study of the middle reaches of
the Yangtze River. Economic Geography,
9(38):176-182.
Zhu, Y. Y., Fan, X. N., Wang, C., & Sang, G. C. J.
(2018). Analysis of heat transfer and thermal
environment in a rural residential building for
addressing energy poverty. Applied Sciences-
Basel, 8, 2077.
Quality Evaluation and Spatial Differentiation of Rural Human Settlements: A Case Study of Sichuan Province, China
119
