
Research on Tourists' Perception of Scenic Byways Based on Text Big
Data: Taking Grass Skyline as an Example
Xinrong Dai
a
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Tourists' Perception, Travelogues, Content Analysis, Grass Skyline.
Abstract:
This paper analyzed high-frequency words, social semantic network and emotions of tourists based on online
travelogues using ROST CM6 to study the tourists' perceptual characteristics of the Grass Skyline from the
perspectives of cognition and emotion, and analyzed the relationship between tourists' perceptions and the
spatial patterns of the scenic byway. It is found that the high-frequency words show a “core—sub-core—
periphery” structure, and tourists' cognitive evaluation can be divided into three dimensions: tourist attraction,
tourist supporting facilities, public environment and services. The paper also shows that tourists to the Grass
Skyline are mainly positive and neutral emotions and there are differences in tourists' emotions at different
locations and sections, with a great proportion of positive emotions than negative emotions. The purpose of
this research is to provide references for the construction and management of the scenic byway.
1 INTRODUCTION
Scenic byways are landscape roads that possess
aesthetic, natural, tourism, cultural, historical, and
archaeological values along the roadside or in the
visual field, combining transportation and tourism
functions(Eby and Molnar 2002, Yu et al. 2006).
From the perspective of experience, scenic byways
are not only tourism transit places or tourism
channels in the tourism system, but also linear
experience spaces. The scenic byways carrying
tourism flow only by transportation function are
transformed into direct tourism destinations(Zhang
et al. 2020). The Grass Skyline is not only a tourist
transit place but also a linear tourist destination.
The studies related to tourism perception mainly
focus on the conceptual definition of tourists'
perception, the influencing factors of tourists'
perception, and the evaluation of the effects brought
by tourism projects on tourists' perception. With in-
depth research on tourism experience and tourists'
perception, some scholars began to study the
relationship between spatio-temporal behavior and
tourists' emotions. But there are relatively few
studies that combine tourists' perceptions with
spatio-temporal characteristics of scenic byways.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0893-7223
The study tries to answer three questions: what
kind of image does the Grass Skyline have in tourists'
minds? What are the characteristics of tourists'
perceptions of the Grass Skyline? What are the
relationships between tourists' perceptions and the
spatial changes of the scenic byway? To answer the
above questions, this study adopts content analysis to
analyze travelogues and uses ROST CM6 to study
tourists' perceptual characteristics of the Grass
Skyline. The study also attempts to analyze the
spatial changes of tourists' emotions and analyze the
reasons for the pattern, to provide suggestions for the
management of the Grass Skyline.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Study Area
The Grass Skyline is located in Zhangjiakou City,
Hebei Province. The Grass Skyline was completed in
August 2019, from Gu Yuan County in the east to
Shangyi County in the west. The Grass Skyline
includes Zhangbei Grass Skyline and Guyuan Grass
Skyline. Zhangbei Grass Skyline was opened to
traffic in 2012, and there are many tourism resources
Dai, X.
Research on Tourists’ Perception of Scenic Byways Based on Text Big Data: Taking Grass Skyline as an Example.
DOI: 10.5220/0012072700003624
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2022), pages 239-243
ISBN: 978-989-758-658-3
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
239
distributed along the route, such as the ancient Great
Wall site, Huapi Ridge, etc. Guyuan Grass Skyline is
opened to traffic in 2019, starting from Pingdingbao
town, and ending at Zhangbei County.
2.2 Methods
The study adopts content analysis and uses ROST
CM6 to analyze high-frequency words and affective
analysis of online travelogues, to study the
characteristics of tourists' perceptions of the Grass
Skyline from the perspective of cognition and
emotion, and to explore the patterns between tourists'
perceptions and spatial changes of the scenic byway.
2.3 Data Collection
The study selected travelogues related to Grass
Skyline in Mafengwo and Ctrip website. The
principles for selecting the travelogues are as follows:
firstly, the travelogues have complete information
and a detailed description of the emotional
expression of the travel activities. Secondly, those
with obvious traces of copying are excluded.
Consequently, 175 travelogues published from
January 2020 to November 2021 were identified as
the study sample, with a total word count of 308,879.
2.4 Data Treatment and Analyses
The word separation function in ROST CM6 was
used to separate the 175 travelogues, and word
frequency analysis was performed. 100 high-
frequency words related to the topic were selected
according to word frequency and were categorized.
This paper studies the differences in tourists'
perceptions at different locations. The sentiment
analysis of ROST CM6 was conducted, and the
distributions of positive, negative, and neutral
sentiments were obtained. Then the study returned to
the travelogues to count the number of sentiments in
each scenic spot/section. It should be noted that the
study mainly focuses on the positive and negative
emotions of tourists because neutral emotions are
difficult to define.
Therefore, a graph of the
fluctuation of tourists' emotional tendencies was
drawn to analyze the spatial characteristics of
tourists' perception of the Grass Skyline from the
perspective of emotions.
3 RESULTS
3.1 High-Frequency Word Analysis
3.1.1 Word Frequency Analysis Results
100 high-frequency words related to the topic were
selected from the highest to the lowest word
frequency, as can be seen from Table 1, the high-
frequency words are mainly composed of nouns and
adjectives. High-frequency words such as
“Grasslands”, and “High speed” reflect the tourists'
deep perceptions of the Grass Skyline.
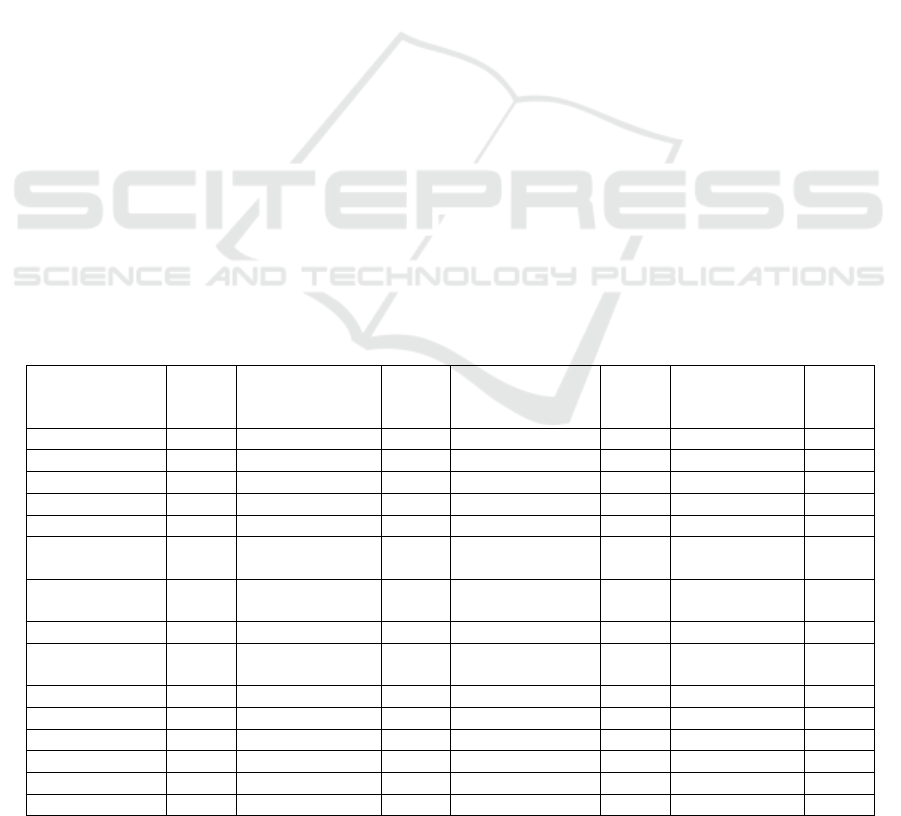
Table 1: Top 100 high-frequency words in the travelogues of Grass Skyline.
High-Frequency
Words
Words
Frequ
enc
y
High-Frequency
Words
Words
Frequ
enc
y
High-Frequency
Words
Words
Frequ
enc
y
High-
Frequency
Words
Words
Frequ
enc
y
Grass Skyline 1906 Route 127 Evening part
y
70 Weeken
d
52
Grasslands 741 Tri
p
125 Breakfast 69 Sea of flowers 52
Hua
p
i Rid
g
e 463 hi
g
hwa
y
123 Boss 67 Wildflowe
r
52
Wildfox rid
g
e 395 Chon
g
li 121 Ticket 66 Ulan 52
Zhangbei 391 Windmill 117 Camping 66 Road signs 51
Kilometre 351
Horseback
ridin
g
111 Potato 64 Green 51
Hotel 299
Beautiful
scener
y
104 Dine 64 Clean 51
Hi
g
h s
p
ee
d
272 Pla
y
104 Countr
y
63 Full ran
g
e 50
Entrance 257
Viewing
p
latfor
m
96 far away 63 China 50
Scener
y
201 Terrace 95 Camelot 63 Feature
d
50
View 201 Frien
d
94 Roads 60 Li
g
htnin
g
lake 49
Scenic s
p
ot 193 Curbside 92 Middle 58 Mano
r
49
Attraction 192 Rest 92 Par
k
58 Sight 49
East route 177 Chil
d
88 Forest 58 Holida
y
49
Hou
r
176 White clou
d
87 Ex
p
erience 56 Roast lamb 49
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
240
Drive 161 Bonfire 86 Direction 56 Vehicle 48
Roa
d
156 Along the wa
y
82 Nature 56 Summe
r
48
Navigation 156 Travel 82 Room 56 Landscape 48
Accommodatio
n
153 Blue sky 80 Appreciation 54 winding 48
Guyuan 142 Weather 80
The most
b
eautiful
54 Service area 47
Zhangjiakou 140 Traffic jam 79
National
highway
54 Best 47
West route 140 Beautiful 78 Swan Lake 54 Seven colors 47
Self-drive 138 Parkin
g
78 Distance 54 Wind Powe
r
46
Farmhouse 135 Chec
k
-in 73 E
p
idemic 53 Performances 46
Dam 127 Exit 70 Taste 52 Circle line 46
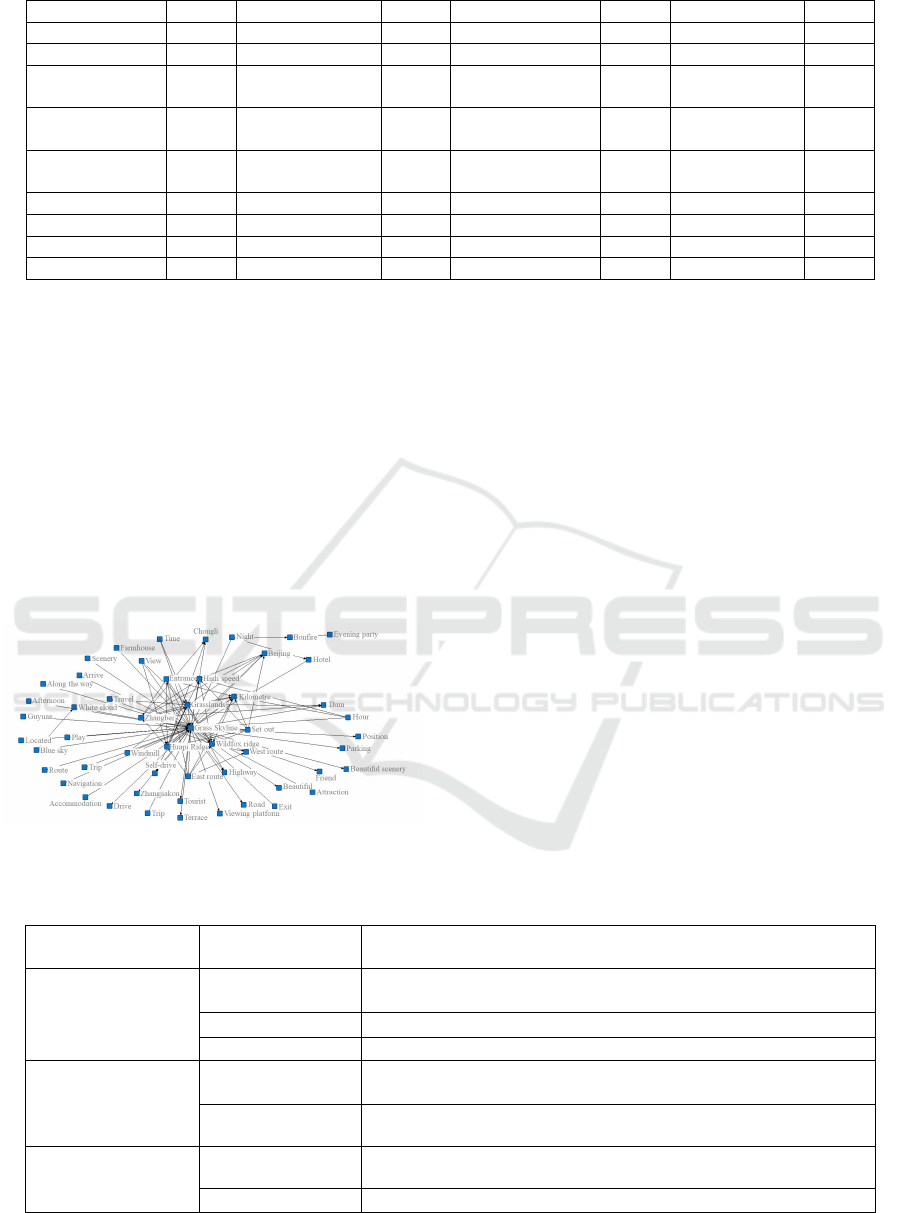
3.1.2 Semantic Network Analysis Results
The semantic network diagram of the Grass Skyline
travelogues was obtained by using Net Draw (Figure
1). The structure shows a three-circle structure of
“core—sub-core—periphery”. Firstly, “Grass
Skyline”, “Grassland” and “Wildfox ridge”
constitute the core image of Grass Skyline. Secondly,
“High speed” and “Highway” show the direct tourists’
perception, and the Grass Skyline has been attracting
tourists with its charming natural landscape. Third
and lastly, “Blue sky”, “Farmhouse”, and “Bonfire”
from the outer circle, suggest that these also represent
the characteristics of tourists’ perception.
Figure 1: The semantic network structure.
According to the previous study(Zhong 2015,
Yan et al. 2021), the study divided the feature words
derived into three categories. The First is tourism
attraction represented by grassland and viewing
platform, etc. Secondly, tourism supporting facilities
with accommodation and highway as representative
words. Thirdly, public environment and services with
weather and navigation as representative words. As a
whole, figure 1 shows the most profound features of
tourists’ perception, which can be summarized as
tourism and transportation on the scenic byway.
3.2 Tourists’ Perception Analysis
Results
3.2.1 Cognitive Appraisal Analysis Results
Combining the semantic network structure and the
relevant study(Zhong 2015), the study divides
tourists' cognitive dimensions of the Grass Skyline
from three perspectives: tourism attraction, tourism
supporting facilities, and public environment and
services (Table 2).
Table 2: Tourists' cognition appraisal of Grass Skyline.
Cognitive
dimensions
Specific entries Examples of high-frequency words (frequency)
Tourism attraction
Natural Resources
Grassland(741), Huapi Ridge (463), Wildfox Ridge(395),
Guyuan(142), Terrace(95)
Human Resources Windmill(117)、Viewing platform(96)、Park(58)、Manor(49)
Tourism Activities Drive(138), Horseback riding(111), Camping(66)
Tourism Supporting
Facilities
Transportation
Grass Skyline(1906), High speed(272), East route(177), Self-
drive(161), West route(140)
Accommodation
Hotel(299), Accommodation(153), Farmhouse(135), Evening
p
arty(70)
Public Environment
and Services
Public
Environment
Scenery(201), Scenic spot(193), Dam(127), Weather(80)
Public Services On the road(156), Navigation(156), Trip(125), Boss(67)
Research on Tourists’ Perception of Scenic Byways Based on Text Big Data: Taking Grass Skyline as an Example
241

Tourism attraction includes natural resources,
human resources, tourism activities, etc. Grass
Skyline gathers a variety of natural landscapes such
as grasslands, forests, and lakes, and also has various
types of human landscapes such as windmills and
parks, etc. The “Huapi ridge” and “Wildfox ridge” as
the iconic landscape of the Grass Skyline, so tourists
have a strong psychological identity. “Camping” and
“Tenting” are high-frequency words related to
tourism activities, which provide tourists with a
variety of choices.
Tourism supporting facilities include
transportation and accommodation. “High speed”
and “Self-drive” indicate that tourists mainly choose
self-driving tours to travel the Grass Skyline. And
“Hotel” and “Farmhouse” can reflect the tourists'
cognitive appraisal of accommodation and catering.
Public environment and services involve public
environment and public services. Tourists'
perceptions are mainly reflected in the landscape,
weather, climate, itinerary, etc.
3.2.2 Emotional Tendency Analysis Results
The study obtained the tourists' emotional tendency
(Table 3). The positive emotions are mainly the
praise of the environment of the scenic byway, such
as the words “Beautiful” and “Appreciation”.
Neutral emotions are words related to the expression
of geographical information, such as “Chongli”.
Negative emotions account for a small proportion.
Table 3 shows that tourists' emotional evaluation
is mainly positive and neutral. Positive and neutral
emotions of visitors accounted for 54.86% and 31.59%
respectively. The percentage of negative emotions of
visitors to the Grass Skyline reached 13.54%.
Table 3: Tourists' Sentiment Analysis.
Category Proportion Strength Proportion
Positive
Emotions
54.86%
General (0 ~
10)
26.57%
Moderate (10 ~
20)
14.75%
Height (above
20)
13.54%
Neutral
Emotions
31.59% / /
Negative
Emotions
13.54%
General (-10 ~
0)
10.57%
Moderate (-20
~ -10)
1.77%
Height (below
-20)
0.51%
A graph of the fluctuation of tourists' emotional
tendency was drawn (Figure 2). Figure 2 shows that
the positive emotions of tourists during the Grass
Skyline tour were higher than the negative emotions.
Figure 2: The tourists' emotional tendency in scenic spots/road sections.
The positive emotion of tourists is divided into
two levels: 50% < Q < 65% and 65% ≤ Q < 80%. The
scenic spots/road sections within the second level can
be called the peak experience points/sections. The
peak experience sites are richer in resources and
relatively well supplied with products and activities,
which can bring diverse tourism perceptions and
attractions to visitors. Only East Route 1 belongs to
the peak experience section, and the positive visitor
sentiment of this section is only 65.14%. Tourists
gained a better perception in this section, mainly
because most of them followed the recommended
route of the Grass Skyline, entering from the west
entrance. Entering the Grass Skyline from Wildfox
Ridge was better perceived by tourists, and tourists'
sense of novelty was satisfied.
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
242

Negative emotions arise mainly in Zhongdu
Primitive Grassland Resort, Huaqian Valley, Dakang
Manor, East Route 2. There are several main reasons.
The first is traffic congestion. Most of the tourists are
following the route initially recommended by the
Grass Skyline for touring. It leads to congestion, and
traffic jams directly make tourists have negative
emotions. Secondly, the quality of food and
accommodation can directly affect the perceived
characteristics of tourists. Thirdly, weather
conditions affect the quality of tourists' perceptions.
Fourthly, tourists usually start from Wildfox Ridge to
tour the Grass Skyline. And it leads to tourists' visual
fatigue in East Route 2.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The perceptual characteristics of tourists' perceptions
of the Grass Skyline are studied from the perspective
of cognition and emotion, and the pattern between
tourists' perceptions and spatial characteristics of the
scenic byway is analyzed. The study drew the
following conclusions:
The tourist perception shows diversified
characteristics, and the characteristic is in a “core-
sub-core-periphery” structure, with “Grass Skyline”
as the core extending outward. Tourists' perceptions
can be divided into three categories: tourism
attractions represented by terraces, tourism
supporting facilities represented by high speed, and
public environment and services represented by
navigation.
Tourists' emotional evaluation of the Grass
Skyline is mainly positive and neutral. It was found
that the percentage of tourists' positive emotions was
higher than the percentage of negative emotions. In
addition, the tourists' positive emotions were divided
into two levels. Tourists generated strong positive
emotions, that is due to the richness of resources,
sufficient supply of the activities. The reasons for
negative emotions were traffic congestion, poor
quality of food and accommodation, bad weather
conditions, and tourists' visual fatigue.
The Grass Skyline needs to be constructed and
managed according to the local conditions of the
scenic byway. Firstly, the Grass Skyline needs to
introduce different tourist routes that meet tourists'
differentiated needs. Secondly, Grass Skyline can use
the resource to create diversified products and
activities, while improving the quality of tourism
services, to better solve the problem of tourist dining
and accommodation.
REFERENCES
Eby D. W., Molnar L. J. (2002). Importance of scenic
byways in route choice: A survey of driving tourists in
the United States. J. Transportation research part A:
Policy and practice. 36, 95-106.
Fang Q. (2019). Research on Self-driving Experience of
National First Scenic Byway-Based on Web Text and
Photo Analysis. D. Beijing Jiaotong University.
Hallo J. C., Manning R. E. (2009). Transportation and
recreation: a case study of visitors driving for pleasure
at Acadia National Park. J. Journal of Transport
Geography. 17, 491-499.
Yan M. F., Liang Y. L., Liu X. H. (2021). Research on
tourists’ perception of scenic avenue based on web text
analysis: Taking National First Scenic Byway as an
example. J. Hubei Agricultural Sciences. 60, 191-195.
Yu Q., Fan X., Liu Z. M., et al. (2006). On the Principle
and Application of Scenic Byways Abroad. J. Tourism
Tribune. 5, 91-95.
Zhang Y. G., Chen X., Yu R. Z. (2020). The logic
transformation of the scenic byway system to the linear
experience space transformation. J. Journal of Natural
Resources. 35, 284-296.
Zhong L. N. (2015). A Reconstruction of Destinations'
Perception Structure Based on the Context and
Complex Network Analysis. J. Tourism Tribune. 30,
88-95.
Research on Tourists’ Perception of Scenic Byways Based on Text Big Data: Taking Grass Skyline as an Example
243
