
Validity of Inquiry-Based Citizenship Learning Model in
Strengthening Student Social Concern at College
Hendrizal
1a
, Azwar Ananda
2b
and Maria Montessori
2c
1
Doctoral Program in Educational Sciences, Universitas Negeri Padang, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Social Sciences, Universitas Negeri Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: Citizenship Education, College, Inquiry-Based, Validity.
Abstract: This study aims to reveal the validity of the inquiry-based Citizenship Education Learning model to increase
students' social awareness in College. The Inquiry-based Citizenship Education Learning Model is a learning
model that provides opportunities for students to carry out scientific investigations, knowledge construction,
problem-solving experiences, instilling attitudes, collaboration, and communication. This research is research
and development using the ADDIE model. The instrument used was a questionnaire, and data were analyzed
descriptively based on the validation score sheet. The products are validated by pedagogy experts, civic
education experts, learning technology experts, and language experts. Observation results were analyzed with
the V Aiken formula. The analysis results show that the average value of Aiken's V is 0.78. The validity
results show that the Inquiry-based Citizenship Education learning model meets the valid criteria. These
findings indicate that the Inquiry-based Citizenship Education Learning Model is appropriate for use in
Citizenship Education learning to increase students' social awareness in College.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to Joyce, Weil & Calhoun (2016), a
lecturer must choose the learning model for character
education learning to be effective and efficient. The
learning model referred to includes the discovery
learning model, where the emphasis on this model
students are more active in finding learning
outcomes. At the same time, the lecturer plays an
active role in facilitating students to learn, the inquiry
learning model where the emphasis on this model is
that students learn to respond to learning. In contrast,
the lecturer plays an active role in facilitating students
learning, the problem-based learning model where the
emphasis on this model students play an active role in
solving problems. In contrast, lecturers play an active
role in facilitating students in solving problems, and
there are many other learning models.
While courses that emphasize character building
are Citizenship Education courses (Kautz & Working,
2013), Citizenship Education (often abbreviated as
Civics) is a field of study that discusses civic values.
Citizenship Education in several countries is one of
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-0510-2935
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3870-4348
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9712-0353
the subjects that can shape the personality and
character of students, and specifically there are six
countries in question, namely Australia, Hong Kong,
Japan, Taiwan, Thailand and the United States
(Morris et al., 2013). Citizenship Education
strategically increases national insight and the spirit
of nationalism (Soekarno & Mujiwati Sri, 2015).
Therefore, to strengthen the role of Citizenship
Education, the government in Indonesia requires
schools at every level of education to provide
Citizenship Education lessons, including at the
tertiary level (Komara, 2017). It is as stipulated in the
Law of the Republic of Indonesia Number 20 of 2003
concerning the National Education System article 37
paragraph (1), which reads, "Citizenship Education is
intended to form students into human beings who
have noble morals, believe in God and have a sense
of nationality and love for the motherland"
(Permendiknas, 2003).
Citizenship Education has been implemented and
developed worldwide, although using different terms
or names. These terms include civic education,
citizenship education and some even call democracy
140
Hendrizal, ., Ananda, A. and Montessori, M.
Validity of Inquiry-Based Citizenship Learning Model in Strengthening Student Social Concern at College.
DOI: 10.5220/0012197800003738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Innovation in Education (ICoIE 4 2022) - Digital Era Education After the Pandemic, pages 140-145
ISBN: 978-989-758-669-9; ISSN: 2975-9676
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

education. This Citizenship Education course has a
strategic role in preparing intelligent and responsible
citizens. A nation can be called a developed and
strong nation if the fundamental values that guide it
are indeed manifested or applied in people's daily
behavior. So that in the nation's life, there will be no
more deviations, abuses, colonialism, discrimination,
and other negative behaviors. The Indonesian nation
now seems to be in a position that is vulnerable to
various influences and problems. The existence of
Citizenship Education in tertiary institutions can help
build student character, especially in social care.
Based on the results of the researchers'
observations in the preliminary study on students at
Bung Hatta University in Padang City, it appears: (1)
There are still students who do not want to help their
friends when they are in trouble, and this statement is
supported by the research results of Oktariani et al.
(2020) which states that students' social care attitudes
greatly influence the development of the student's
character. Social awareness that needs to be
developed is an attitude of respecting the opinions of
others and an attitude of caring about what other
people feel. Furthermore, there is also research by
Wahyuni & Reswita (2017) which states that the
emotional maturity of students will be stable if their
existence is appreciated and accepted by other
students, meaning that the attitudes and behavior of
students in the campus environment must show
mutual respect for one another. (2) Less concerned
with disaster-stricken areas (Soekarno & Mujiwati
Sri, 2015). (3) Lack of respect for the opinions of their
friends, and this statement is supported by the results
of research by Chang et al. (2019), which states that
students of different races tend to be less valued for
their opinions. This statement is also supported by the
results of research by Mwangi et al. (2018).
Likewise, the situation of students at Bung Hatta
University is motivated by various things, one of
which is the lack of students' understanding of the
1945 Constitution article 28F that every citizen has
freedom of expression (Republic of Indonesia, 1945),
lack of understanding students of the existence of a
plural Indonesian nation, namely different languages,
different religions, different ethnicities and races (Ali
Imron & Nugrahani, 2019) so that they are still bound
by idealism and maintain their respective egos
(Hefner, 2020). (4) Students are less involved in
community activities and are more likely to act
individually because they are preoccupied with
gadgets. This situation of students is supported by the
results of research by Schwartz et al. (2018) at
universities in the United States, which stated that
students tend to be more individual and do not want
to be involved in discussion groups on and off
campus. Students choose groups of friends who are
equal to their lives, while groups of students whose
economic level is at a low level, the average student
does not want to socialize. According to Rifat et al.
(2017) gadgets or information and communication
technology tools should be used by students to
accelerate social action and disseminate information
to their friends to do good (Pratiwi et al., 2019).
Students as social beings cannot live alone, but
need other people in various ways such as getting
along, doing assignments, helping each other, caring
for each other, working conscientiously and having
noble character (Wijaya et al., 2019). Students are
individual beings and social beings. Students as
individuals mean that each student has the right to
own personal property and adapts to the surrounding
environment. In contrast, students as social beings
mean that everyone cannot live alone but needs one
another (Lockwood, 2016). Students' social concern
will exist if they understand the values and meaning
of social care (Betzler, 2019). Caring is an attitude or
behavior of students that can be observed as actual
behavior in helping others who require help
(McElmeel, 2002). In fact, social care is a
participation or participation of students in building
relationships with the surrounding environment
(Kemendikbud Language Center, 2016). Social
concern is an attitude of openness with humans in
general which is shown by caring for every human
being who needs help (Bloom, 2017).
Forms of social care are (1) Concern for joy and
sorrow, meaning concern that arises without
differentiating between good and bad situations and
feeling what others feel. (2) Personal and shared
concern, meaning concern that arises because of
personal impulses in helping someone and also
concern that is carried out together in feeling what
others experience. (3) Urgent concerns, namely
concerns that are in the common interest that must be
prioritized for action (Tal Saban & Kirby, 2019).
Social concern will arise if students understand
the forms of concrete action in implementing social
care (Crowley & Fleury, 2019). This concept is based
on the cognitive domain. Namely, the lecturer
provides students with examples of cases in narrative
form. Students are encouraged to feel what other
people feel (affective), and finally, what is known and
felt is then manifested in the form of behavior (De
Vignemont & Jacob, 2012), including 1) if someone
asks for alms then they are willing to give it, 2) if
there are parents who need a seat on public
transportation then they are welcome to sit, (3) if a
friend is sick then come to visit, 4) if there is a dirty
room, they are moved to clean it even though it is not
on a picket schedule, 5) if someone experiences a
disaster, they collect funds as a form of social action
to ease the burden on others, 6) if a friend needs a pen
or something else, he is moved to help, 7) if someone
Validity of Inquiry-Based Citizenship Learning Model in Strengthening Student Social Concern at College
141

has an accident, they are moved to seek help (Bove,
2019).
Based on the above, Citizenship Education
lecturers have an essential role in facilitating students
recognize and understand forms of social care so that
students have high awareness and concern in feeling
what other students and the general public feel (Matto
& Bennion, 2017; Jaber et al., 2018). In order for
learning objectives to be easily achieved, a lecturer
must adopt a learning model or can also develop an
Inquiry learning model that will be used during the
learning process (Mulyana et al., 2018). One of the
learning failures is not achieved effectively and
efficiently when lecturers are still bound by
conventional learning methods, namely still bound by
lecture teaching methods, where the learning process
is still dominated by lecturers so that students sit
quietly listening to the lecturer's lectures
(Margunayasa et al., 2019 ). Research by education
experts says that conventional teaching methods are
no longer effectively applied (Bagus et al., 2020).
Lecturers must have creativity in choosing a suitable
learning model so that students are more active in the
learning process (Walker & Warfa, 2017).
Based on the problem regarding the level of social
awareness of students who are still lacking,
Citizenship Education lecturers need to change their
learning model from conventional to student-
centered. The learning model that will be developed
in this study is the Inquiry learning model to increase
the social care values of students at Bung Hatta
University.
2 METHODS
The research conducted was design research using the
ADDIE model of development study type. The
development study is at the prototype stage, namely
product validation. The components of the Inquiry-
based Citizenship Education Model learning model
validity include content, construction, and language.
The validity assessment of Inquiry-based Citizenship
Education Model carried out by experts who are
experienced in their fields. Before evaluating the
validity of Inquiry-based Citizenship Education
Model, the validity of the instrument used is tested
first. The questionnaire that was filled in by the expert
review was analyzed to determine the validity of the
instrument. A valid instrument is used to assess the
validity of Inquiry-based Citizenship Education
Model. Furthermore, the questionnaire that was filled
in by experts was then analyzed to determine the
validity of the developed Inquiry-based Citizenship
Education Model. Validity analysis uses a Likert
scale with steps (a) Giving a score for each answer;
strongly agree (4), agree (3), disagree (2), and
strongly disagree (1), (b) Adding up the total score of
each expert review for all indicators, (c) Providing
validity values using the Aiken's V formula:
(1)
with: s = r - lo, lo = the lowest validity score (in
this case = 1), c = the highest validity score (in this
case = 4), r = the number given by the expert review.
Validity categories can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1: Validity Category.
Value Category
≥ 0.60 Valid
< 0.60 Valid Invalid
Based on Table 1, it can be seen that the criteria
of the agreement value of the validity obtained. This
validity is done using Aiken’s V formula and is
categorized into two values: valid and invalid. The
Inquiry-based Citizenship Education Model
instrument and the learning model developed are
valid when the value obtained exceeds or equals 0.6.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The validity of the Inquiry-based Citizenship
Education Model learning model begins with the
development stage, namely designing an Inquiry-
based Citizenship Education Model learning model in
the form of a draft guide containing background,
concepts, and characteristics of the model comprising
syntax, principles of reaction, social systems, support
systems, instructional effect, and nurturant impact.
This draft refers to the results of the analysis at the
preliminary research stage that has been carried out.
This draft first carried out a self-evaluation to check
for errors in design, to get relevant product criteria
and based on science, consistency, and have the
expected practicality. After that, this draft was asked
for opinions from four lecturers of Universitas Negeri
Padang and Universitas Bung Hatta to provide input
so that a prototype of the Inquiry-based Citizenship
Education Model learning model was obtained, which
would be validated by experts in the related field.
Details of the results of the validity are explained as
follows.
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
142
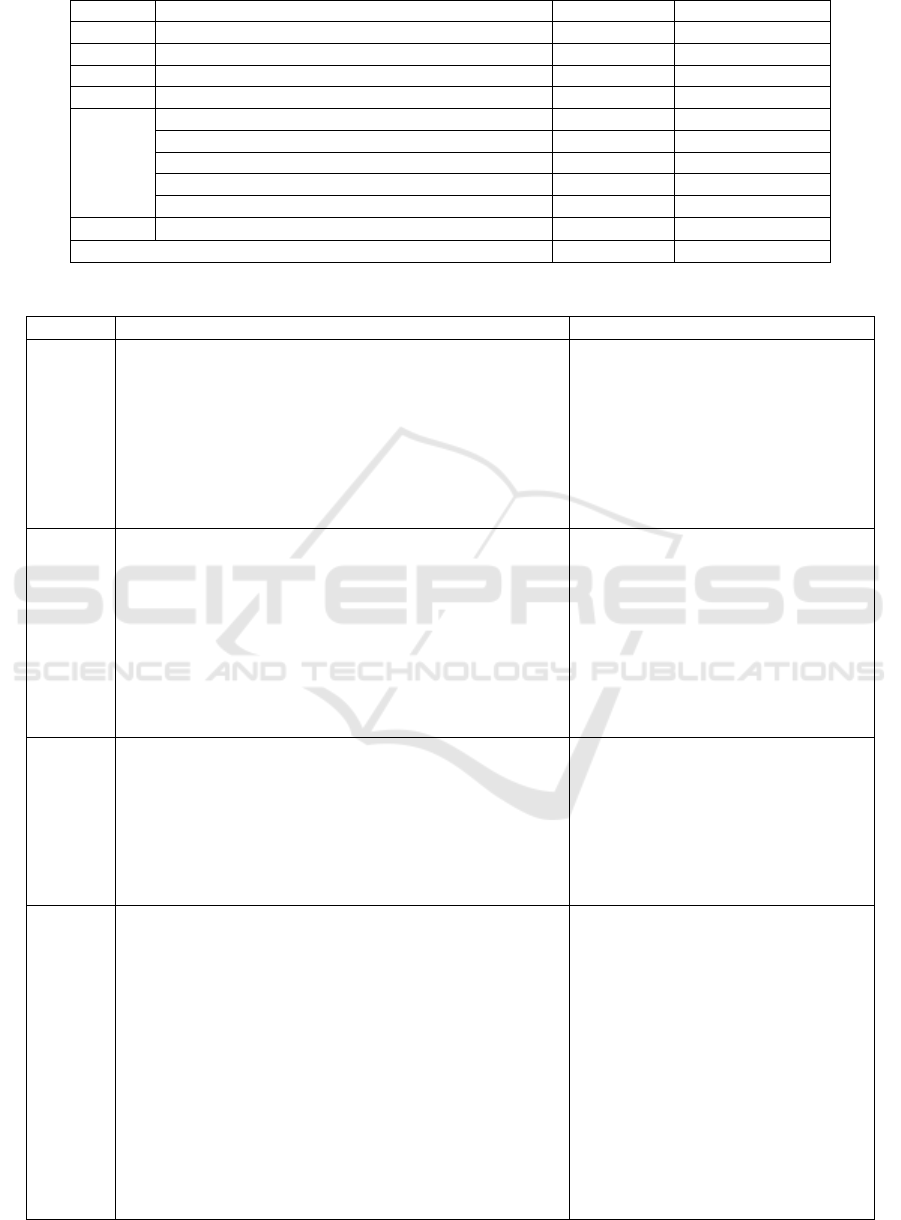
Table 2: Summary of the Book Validation Results of the Inquiry-Based Civics Learning Model.
No Rated Aspect Aiken-V Categor
y
1 Book Format 0.80 High
2 Lin
g
uistics 0.77 Hi
g
h
3 Rational Model 0.77 Hi
g
h
4 Su
pp
ortin
g
Theor
y
0.77 Hi
g
h
a. Syntax 0.81 Very High
b
. Social Syste
m
0.78 High
c. Principle of Reaction 0.71 High
d. Su
pp
ort S
y
stem 0.75 Hi
g
h
e. Interactional and Accom
p
animent Im
p
acts 0.80 Hi
g
h
6 Implementation in Learning 0.85 Very High
Avera
g
e 0.78 Hi
g
h
Table 3: Validator Suggestions.
Validator Suggestions and Feedback Repair Efforts
Validator
1
- It should also be linked to 21st-century competencies,
namely the 4C formula: Critical thinking, Collaboration,
Communication, and Creativity.
- Confirm whose expert constructivism theory is used.
- It is necessary to emphasize what the indicators of student
activity are
- There are still words found that are not operational
- All principles are written in operational language, not
theoretical lan
g
ua
g
e
- Added to the rational model of the
4C formula
- Using John Piaget's theory of
constructivism
- Reinforcing student activity
indicators in model book
- Operationalize the words in the
model book
Validator
2
- The book's construction needs to improve its layout so it
does not seem too congested.
- We recommend selecting the color of the image with a
background or writing with a contrasting background.
- There are several tables that are not given a number and
name should be completed For the model structure, there
are 3 main activities, namely: planning, implementing and
evaluating activity, of which there are only two in the
book, namely implementing and evaluating. We
recommend that you add a planning structure to it.
- Fixed book layout
- Changed the color and text on the
cover page
- Completing the numbering table in
the model book
- Changed the model structure chart
Validator
3
- Numbering according to the rules of scientific writing
- Please pay attention to writing sentences and adjust them
to the rules of Indonesian grammar
- There are still sentences not according to SPOK
- Must be consistent in font size and type of writing used
- Citation of source names, please correct
- Writing words/foreign language in italics
- Adjust numbering based on
scientific rules
- Correct sentences that are not
appropriate
- Consistent font sizes and fonts used
- Fixed quoting
- Check and revise foreign language
writing and italics
Validator
4
- Cover design to make it even more attractive
- Double-check typing errors
- Re-check several sentences in the book so that readers can
easily understand them.
- Clarify the difference in syntax between the original model
and the developed model.
- Check back the supporting theory for a more complete
- Improved the description of the model component
elements
- Check the suitability of the bibliography and citations
- Clarify Supporting Theory
- The rational model needs to be clarified from the
curriculum aspect, the characteristics of higher education
students, the material, social conditions, etc.
- Revised the cover design by
changing the color and background
- Fixed typing error
- Fixed sentences in the book
- Details the difference between the
original syntax and the developed
model syntax
- Delete and add appropriate
supporting theories
- Fixed model components
- Check and revise the bibliography
- Revise the rational model based on
curriculum aspects, characteristics of
higher education students, material,
social conditions, etc.
Validity of Inquiry-Based Citizenship Learning Model in Strengthening Student Social Concern at College
143

3.1 Results of Instrument Validity
The instrument to validate the prototype of the
Inquiry-based Citizenship Education Model learning
model was assessed first by three experts using the
instrument validity assessment sheet. The
components of the instrument validity assessment
include the suitability of the statement with the
instrument grid, the instrument can reveal the quality
of the content, language, and the construction of the
Inquiry-based Citizenship Education Model learning
model, and the instrument is straightforward to use.
The results obtained from the assessment of this
validity instrument were 0.83. The average validity
value (Aiken’s Values) of the Inquiry-based
Citizenship Education Model learning model
instrument from experts is more significant than 0.6
in the valid category. Thus, the instrument of the
validity of the Inquiry-based Citizenship Education
Model learning model can validate the Inquiry-based
Citizenship Education Model.
3.2 Results of the Inquiry-Based
Citizenship Education Model
Five experts in their field logically validate the
prototype of the Inquiry-based Citizenship Education
Model, while the results of these experts are shown in
Table 2.
Based on the validation sheets collected from the
validators, all validators stated that model books and
learning tools for the Inquiry-Based Civics Learning
Model were in an Outstanding category. All
validators agree that the model can be used with
minor revisions, meaning that all aspects assessed are
at acceptable criteria, so they do not require
significant revisions and re-validation. The results of
each validator above show that the Inquiry-based
Citizenship Education Model has an average validity
(Aiken’s Values) of 0.78 and can be used in Civic
Education learning with minor revisions. The revision
is related to the suggestions the experts provided, as
seen in Table 3.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the process and results of the study, it is
concluded that the design of the Inquiry-based
Citizenship Education Model of students' Civic
Education in university is valid in terms of content,
construct, and language with an average validity
value (Aiken’s Values) of 0.78. It means that the
Inquiry-based Citizenship Education Model can be
applied on Civic Education in university.
REFERENCES
Bagus, I., Putra, A., Gusti, N., Putu, A., & Santika, L.
(2020). Simulation-based learning compared with
conventional methods in procedural skill. 14(2), 86–91.
https://doi.org/10.15562/ijbs.v14i2.268.
Betzler, M. (2019). The relational value of empathy.
International Journal of Philosophical Studies, 27(2),
136–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/09672559.2019.1598
081.
Bloom, P. (2017). Empathy and its discontents. Trends in
Cognitive Sciences, 21(1), 24–31. https://doi.org/10.
1016/j.tics.2016.11.004.
Bove, L. L. (2019). Empathy for service: benefits,
unintended consequences, and future research agenda.
Journal of Services Marketing., 33(1), 31–43.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JSM-10-2018-0289.
Chang, J., Wang, S. W., Mancini, C., McGrath-Mahrer, B.,
& de Jesus, S. O. (2019). The complexity of cultural
mismatch in higher education: Norms affecting first-
generation college students’ coping and help-seeking
behaviors. Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority
Psychology, 26(3), 280–294. https://doi.org/10
.1037/cdp0000311.
Chesser, S., Murrah, W., & Forbes, S. A. (2020). Impact of
personality on the choice of instructional delivery and
students’ performance. American Journal of Distance
Education, 34(3), 211–223. https://doi.org/10.
1080/08923647.2019.1705116.
Crowley, C., & Fleury, A. (2019). Educating for empathy:
Literacy learning and civic engagement. Michigan
Reading Journal, 51(2), 13.
De Vignemont, F., & Jacob, P. (2012). What is it like to feel
another’s pain? Philosophy of Science, 79(2), 295–316.
https://doi.org/10.1086/664742.
Hefner, R. W. (2020). Islam and covenantal pluralism in
Indonesia: A critical juncture analysis. Review of Faith
and International Affairs, 18(2), 1–17.
https://doi.org/10.1080/15570274.2020.1753946.
Jaber, L. Z., Southerland, S., & Dake, F. (2018). Cultivating
epistemic empathy in preservice teacher education.
Teaching and Teacher Education, 72, 13–23.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2018.02.009.
Joyce, B., Weil, M., & Calhoun, E. (2016). Models of
teaching: Model-model pengajaran. Yogyakarta:
Pustaka Pelajar.
Kautz, J. J. H. T., & Working. (2013). Fostering and
measuring skills: Interventions that improve character
and cognition.
Kemendikbud. (2018). Permendikbud RI No. 20 Tahun
2018 tentang Penguatan Pendidikan Karakter pada
Satuan Pendidikan Formal. 8–12.
Kemendikbud. (2020). Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan dan
Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia Nomor 7 tentang
Pendirian, Pembubaran dan Pencabutan Izin
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
144

Perguruan Tinggi.
Komara, E. (2017). Curriculum and civic education
teaching in Indonesia. Educare, 10(1), 23–32.
http://journals.mindamas.com/index.php/educare/articl
e/view/929.
Lockwood, P. L. (2016). The anatomy of empathy:
Vicarious experience and disorders of social cognition.
Behavioural Brain Research, 311, 255–266.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.05.048.
Margunayasa, I. G., Dantes, N., Marhaeni, A. A. I. N., &
Suastra, I. W. (2019). The effect of guided inquiry
learning and cognitive style on science learning
achievement. International Journal of Instruction,
12(1), 737–750. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2019.121
47a.
Matto, E. C., & Bennion, E. A. (2017). Teaching civic
engagement across the disciplines. PS: Political
Science & Politics (Vol. 50, Issue 04).
https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049096517001706.
McElmeel, S. L. (2002). Character education: A book
guide for teachers, librarians, and parents.
Mulyana, S., Rusdi, R., & Vivanti, D. (2018). The effect of
guided inquiry learning model and scientific
performance on student learning outcomes. Indonesian
Journal of Science and Education, 2(1), 105.
https://doi.org/10.31002/ijose.v2i1.596.
Mwangi, C. A. G., Thelamour, B., Ezeofor, I., & Carpenter,
A. (2018). “The Black elephant in the room”: Black
students contextualizing campus racial climate within
US racial climate. Journal of College Student
Development, 59(4), 456–474. https://doi.org/10.1353/
csd.2018.0042.
Oktariani, O., Munir, A., & Aziz, A. (2020). Hubungan self
efficacy dan dukungan sosial teman sebaya dengan self
regulated learning pada mahasiswa Universitas Potensi
Utama Medan. Tabularasa: Jurnal Ilmiah Magister
Psikologi, 2(1), 26–33. https://doi.org/10.31289/
tabularasa.v2i1.284.
Permendiknas. (2003). Undang-Undang Republik
Indonesia Nomor 20 Tahun 2003 tentang Sistem
Pendidikan Nasional. In Depdiknas (Vol. 1, Issue
January, pp. 21–30).
Pratiwi, A., Meytri, D. I., & Patriana, O. (2019). Analisis
dampak penggunaan teknologi terhadap lingkungan
sosial mahasiswa Fakultas Ilmu Komputer. POSITIF:
Jurnal Sistem dan Teknologi Informasi, 5(1), 8.
https://doi.org/10.31961/positif.v5i1.668.
Republik Indonesia. (1945). Undang-Undang Dasar 1945.
1–12. https://doi.org/10.31227/osf.io/498dh.
Rifat, M. R., Chen, J., & Toyama, K. (2017). Money, god,
and SMS: Explorations in supporting social action
through a Bangladeshi mosque. In Proceedings of the
2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing
Systems, 5941–5953. https://doi.org/10.1145/30254
53.3025960.
Schwartz, S. E. O., Kanchewa, S. S., Rhodes, J. E., Gowdy,
G., Stark, A. M., Horn, J. P., Parnes, M., & Spencer, R.
(2018). “I am struggling with this. Can you help me
out?”: Examining impacts and processes of a social
capital intervention for first-generation college
students. American Journal of Community Psychology,
61(1–2), 166–178. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajcp.12206.
Soekarno, B., & Mujiwati Sri, E. (2015). Peningkatan nilai
kepedulian sosial melalui modifikasi model
pembelajaran konsiderasi pada mahasiswa tingkat I
Program Studi PGSD FKIP Universitas Nusantara
PGRI Kediri. Jurnal Pendidikan Karakter, 26, 35–36.
Tal Saban, M., & Kirby, A. (2019). Empathy, social
relationship and co-occurrence in young adults with
DCD. Human Movement Science, 63(November 2018),
62–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2018.11.005.
Wahyuni, S., & Reswita, R. (2017). Hubungan kematangan
emosional terhadap kemampuan bersosialisasi
mahasiswa PG-PAUD FKIP UNILAK. Lectura: Jurnal
Pendidikan, 8(2).
Walker, L., & Warfa, A. R. M. (2017). Process-oriented
guided inquiry learning (POGIL®) marginally affects
student achievement measures but substantially
increases the odds of passing a course. PLoS ONE,
12(10), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.
pone.0186203.
Wijaya, T., Elihami, E., & Ibrahim, I. (2019). Student and
faculty of engagement in nonformal education. Edukasi
Non Formal, 3(3).
Validity of Inquiry-Based Citizenship Learning Model in Strengthening Student Social Concern at College
145
