
Suitability Level of School-Based Curriculum: An Analysis on
English Reading Material
Tini Mogea
1a
and Salaki Reynaldo Joshua
2b
1
English Education, Universitas Negeri Manado, Kampus Hasiru, Tondano, Indonesia
2
Electronics, Information and Communication Engineering, Kangwon National University,
Jungang-ro, Samcheok-si, Gangwon-do, Republic of Korea
Keywords: Wajar, Reading Texts, School-Based Curriculum, English Textbook.
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to analyze the reading materials contained in the WAJAR (Penunjang Wajib
Belajar) textbook published by Graha Pustaka and used for junior high school students with school-based
curricula, specifically to identify the genres of the reading materials and to explain the suitability of the
reading materials contained in the WAJAR textbook with school-based curricula (KTSP). With a
documentary study, the author used a descriptive and qualitative design. The reading texts in the WAJAR
textbook, which is used in junior high school with a school-based curriculum, are the source of data. The
textbook contains 11 different types of text as a result of the results. The WAJAR textbook contains a variety
of text types. Report text, descriptive text, analytical exposition, hortatory exposition, and procedure text are
all covered in the book.
The reading text contained within the textbook explicitly identifies all of the text's
generic structures. According to the findings, some language features are not used proportionally in the
reading text. In each text type, certain language features were missing. The reading text contains only two to
three of the five language features. Not all reading indicators are developed through textbook reading
activities. The calculated suitability level was only 65.21 percent (suitable enough), indicating that there is
still unsuitability in the WAJAR textbook. Some reading indicators are not included in the reading materials.
There are some missing sections that explain why the indicators are not fully elaborated and evaluated in the
WAJAR textbook's reading texts.
1 INTRODUCTION
Some teachers find it difficult to choose the best
textbook. Although many textbooks claim to be
curriculum compatible, there is no guarantee that the
textbook is relevant to the curriculum's standard
competencies (Tyas and Safitri 2019). A good
textbook contains lessons and exercises that can be
used as activities to help students master their
language skills. One of the most important language
skills is reading. It is an English skill that students
must master when learning the language. As a result,
if students want to master English, they must learn
reading as well as the other skills. Reading is a fluid
process in which readers combine information from
the text with their own prior knowledge to construct
meaning (Nunan 1999)
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4296-1785
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2163-4945
"reading can be viewed as a "interactive" process
between a reader and a text that leads to automaticity
or (reading fluency)". Reading is assumed to be a
non-passive skill because it requires so much practice
and exercise (Alyousef 2005). The readers'
comprehension improves based on how they work on
it. It means that as readers read more, their reading or
comprehension improves. Essentially, teaching
reading is the process of conveying or guiding
students to gain some important message and
meaning from written text. The majority of students
enjoy reading English-language written materials
such as books, novels, newspapers, articles, and texts.
Reading skills are developed in Junior High School
English lessons. The development of reading skills,
particularly in the analysis of various types of text, is
required in Junior High School English lessons.
Mogea, T. and Joshua, S.
Suitability Level of School-Based Curriculum: An Analysis on English Reading Material.
DOI: 10.5220/0012198200003738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Innovation in Education (ICoIE 4 2022) - Digital Era Education After the Pandemic, pages 175-190
ISBN: 978-989-758-669-9; ISSN: 2975-9676
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
175

Teachers should consider the learning materials
used in the classroom when teaching and learning
(Setyaningsih 2019). A textbook is one of the most
common types of learning materials. It is a type of
printed material that is necessary for teaching and
learning. A textbook (Ur 1996), is the primary
learning material that teachers and students typically
use. A textbook has numerous benefits in the teaching
and learning process (Gholami, Noordin, and Rafik-
Galea 2017). To enable students to learn English
materials, they require high-quality English
textbooks. They can improve their English skill
productivity by learning from quality textbooks.
There are different kinds of good books. First, the
textbook's contents should be relevant to the current
curriculum; it may be from the genre that should be
available in the textbook. The textbook's contents
correspond to the level of study as well. The second
category is a textbook, which should have an
appealing display to entice readers to read the book.
Furthermore, the textbook's language should be
corrected in context and situation. It means that the
language is free of ambiguity, allowing the reader to
understand it easily (You, Lee, and Craig 2019).
Some factors influence students' comprehension
of the text. These factors can be attributed to the
teacher, the students, the materials, or the media used
by the teacher. The first issue stems from the teacher.
The teacher does not pay attention to what students
require in terms of reading. The second issue stems
from the students. The students' command of the
English language remains limited. As a result, they
have difficulty deciphering the meanings of difficult
words (Noprianto and Purnawarman 2019). The
students are also unable to identify the main idea.
They can't find specific information in a text. As
evidenced by their behavior in class, the students lack
motivation to read. They are oblivious to the teacher's
explanation (Imamyartha et al. 2019)The materials
are the third issue. The materials used also play an
important role in dealing with the students' reading
comprehension. Materials are the foundation of the
knowledge that is passed on to students. In fact, the
majority of the material being taught was dull and
monotonous. As a result, the students were
uninterested in engaging with the material. As a
result, they would be unable to read well. The final
issue is the teacher's use of media. Another important
factor is the media. The materials taught can be
effectively delivered through media (Leong and
Ahmadi 2017).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 The Nature of Reading
Many definitions of reading can be found in various
sources. Reading is the act of converting written
symbols into corresponding sounds. Furthermore,
(Strang 1991) defines reading as more than just
seeing words clearly or correctly pronouncing printed
words; it also requires us to think, feel, and use our
imagination. For example, when we read a novel, we
must imagine how the character feels and how the
setting is in the story.(Grellet and Francoise 1981)
Reading, is an active skill that is demonstrated by eye
movements to recognize written symbols and, on
occasion, by pronouncing or reading aloud. While
reading, we are not only pronouncing the text but also
learning its meaning. Reading is a type of thinking in
this context (Cortina and Elder 2002). It means that
during the reading process, the brain reads in order to
associate knowledge and experience with the text.
People read for a variety of reasons and employ a
variety of strategies. In reality, people read to learn.
Furthermore, people read for pleasure. Some
strategies also follow people while they read. (Grellet
and Francoise 1981) divides reading into four goals
in his book: skimming, scanning, extensive reading,
and intensive reading. People quickly skim the text
for general information. Scanning is done by people
who read a text quickly in order to extract specific
information from it. Extensive reading is a difficult
activity in which people are required to read some
texts in order to gain more information, but the texts
used are usually chosen by the reader. In contrast to
extensive reading, intensive reading requires the
reader to read a number of short texts in order to
obtain specific information.
According to Jeremy Harmer (1983), a variety of
school-based curriculum exercises can be used to
achieve a number of reading objectives, including the
following:
a. Reading to confirm expectation
b. Reading to extract specific information
c. Reading for communicative tasks
d. Reading for general understanding
e. Reading for detail comprehension (information)
f. Reading for detail comprehension (function and
discourse)(Grabe 2022), on the other hand, believe
that reading purposes can be divided into seven
categories. They are as follows:
a. Reading to search for simple information
b. Reading to skim quickly
c. Reading to learn from text
d. Reading to integrate information
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
176

e. Reading to write
f. Reading to critique texts
g. Reading for general comprehension
2.2 Textbooks
A textbook is intended to meet and support the
educational needs of students. A textbook is best
viewed as a resource for achieving pre-determined
goals and objectives in terms of what learners require.
A suitable textbook should cover the necessary
indicators of a lesson learned by students. According
to (Cunningsworth 1995), textbooks play multiple
roles in ELT. A textbook can be any of the following:
1. a resource for presentation-related spoken and
written material.
2. a source of activities for learners to practice and
interact with.
3. A grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation
reference for students.
4. a source of stimulation and ideas for classroom
language activities.
5. a syllabus where they reflect learning objectives
that have already been determined.
6. a resource for self-directed learning or work.
7. support for less experienced teachers who have
yet to gain confidence.
In most language programs, one of the
instructional materials is a textbook (Novianti,
Syihabuddin, and Rochyadi 2019)
2.3 Text Type
Text is an essential component of reading activities.
It appears in passages. In senior high school, students
learn nine different types of reading texts, according
to the curriculum: procedure text, narrative text,
banner, poster, pamphlet, report text, analytical
exposition, spoof text, and hortatory exposition. Here
are some explanations about those types of texts from
various sources (Anderson 1969):
a. Procedure Text
b. Narrative Text
c. Functional Text (Banner, Poster and Brochure)
d. Report Text
e. Analytical Exposition
f. Spoof Text
g. Hortatory Exposition
2.4 School-Based Curriculum (KTSP)
The curriculum is the most important aspect of the
teaching and learning process. A teacher should teach
his or her students according to the current curriculum
because it has been designed to meet the needs of the
students. According to Feez, "a curriculum is a
general statement of goals and outcomes, learning
arrangements, evaluation, and documentation relating
to the management of programs within an educational
institution."
In Indonesia, the school-based curriculum
(KTSP) is still being implemented. The KTSP is
designed to tailor education to the characteristics and
needs of individual schools (Hermuttaqien, Sata, and
Wadu 2019). It means that the school has been given
permission to create indicators based on the school's
characteristics and needs.
There are some operational references for
arranging KTSP in Education Regulation Number 20
for 2003:
a. focused on learners' potential, development,
needs, and interests; and their environment.
b. varied and integrated.
c. responsive to the development of science,
knowledge, technology, and art.
d. Comprehensive and ongoing
e. relevance to life's needs.
f. Lifelong learning is essential.
g. Keeping national and regional interests in
check.
According to (Ahiri 2007), KTSP is an
operational curriculum that is organized and carried
out by educational units and consists of educational
unit goals, the structure and content of KTSP, the
education calendar, and syllabuses, there are six
components of KTSP, which are as follows:
a. Vision and mission of school
b. Educational goal of school.
c. Educational calendar.
d. Syllabuses.
e. Lesson Plan.
f. Structure of Subject matter curriculum.
2.5 Related Studies
The curriculum is the most important aspect of
teaching and learning. A teacher must educate his or
her own students. Other researchers had previously
conducted a number of studies. They are as follows:
1) Syafniar and Rusda Ayu conducted a study titled
"The Analysis of the Reading Materials in English
AliveTextbook Based on School-Based Curriculum
for Second Grade Students of Senior High School"
(2014). According to the findings of this study, 85.7%
of the text-based curriculum in the textbook meets the
KTSP text-based curriculum, 87.5% of the reading
indicators meet the KTSP indicators, and 100% of
generic structures and linguistic features meet the
KTSP requirements. The reading material has a 93%
Suitability Level of School-Based Curriculum: An Analysis on English Reading Material
177

overall rating. It achieves excellent results in terms of
conformity level criteria.
2) (Syahbana and Pratama 2017) carried out a
study titled The Analysis of English Reading Texts
Based on National Character and Cultural Education
in the Tenth Grade Course Book at the Pamekasan
State Senior High School. This research is based on
the observation that many books, particularly reading
texts, contain inappropriate content. The author
discovered 13 values that were inserted in 17 reading
texts, but the rest were not; additionally, there were
several ways of reading texts to reflect values.
3) (Simanjuntak et al. 2021) carried out another
study titled "Content Analysis of the Student Book
"When English Rings a Bell" for Grade VIII Junior
High School. The purpose of this study is to compare
the cognitive and psychomotor domains of learning
between the materials in the student book "When
English Rings a Bell" for grade VIII junior high
school and the Core and Basic Competence in the
2013 Curriculum. According to the findings of this
study, there are 29 materials in the textbook that are
relevant to the cognitive domain, or approximately
78.37 percent; 4 materials that are partly relevant, or
approximately 10.81 percent; and 4 materials that are
irrelevant, or approximately 10.81 percent. In terms
of the textbook's relevance to the psychomotor
domain, there are 15 relevant materials, or
approximately 38.46 percent; 14 partially relevant
materials, or approximately 35.59 percent; and 10
irrelevant materials, or approximately 25.64 percent.
4) Erlangga published another study titled "An
Analysis of Reading Materials in Bright: An English
Course for Junior High School Students, Year VIII."
Ririn Pusparini's curriculum is based on the 2013
English Standard Curriculum (2014) The research
design for this study was descriptive qualitative
research. The data collection instrument is
observation in the form of checklists. Following an
examination, it was discovered that all chapters in the
first semester do not adequately cover the indicators
of cognitive aspects in the three basic competences.
Meanwhile, some of the reading materials are
unrelated to psychomotor aspects. After all, the
researcher contends that this textbook can still be
used because the materials are mostly relevant to the
2013 curriculum. This textbook can still be used to
assist teachers and students in the process of teaching
and learning, but it is not fully suitable for reading.
This study differs from previous studies in some
ways, such as the object of the study, method,
analyzing technique, and textbook, but it still has
some similarities. It means that this research is one-
of-a-kind, distinct, and original.
3 METHOD
3.1 Research Design
The purpose of this research was to examine the
reading material in the WAJAR (Penunjang Wajib
Belajar) textbook published by Graha Pustaka, which
is used for junior high school students in SMP Negeri
3 Ratahan with a school-based curriculum. The
author employed both descriptive and qualitative
design. Rather than numbers, qualitative research
focuses on describing phenomena through verbal
narratives and observations (Brown, R. N., 2014).
The author used a checklist of observations to back
up his description of the reading material. The data
would be analyzed descriptively rather than
statistically. The textbook is 112 pages long and
divided into three major chapters. Language skills are
presented separately in each chapter. The textbook
includes reading material for all chapters.
3.2 Source of Data
The data resource, according to Arikunto (2006), is
the subject from which the data can be obtained. The
reading texts found in WAJAR (Penunjang Wajib
Belajar), a textbook published by Graha Pustaka that
is used for junior high school students in SMP Negeri
3 Ratahan with school-based curriculum, are the
source of data in this study.
3.3 Data Collection
There were two kinds of data namely quantitative
data and qualitative data (Karnedi, Zaim 2021). The
writer used documentation studies to collect data.
Documentation study may refer to the technique of
gathering and analyzing documents used to collect
data, whereas a document is any communicable
material, particularly text in this study, used to
explain some attributes of an object, systems, or
procedures. To arrive at a conclusion, the qualitative
data, which is represented by words and sentences, is
categorized. The researcher follows three steps in
conducting this research:
1. Reading
The first step is to read WAJAR (Penunjang Wajib
Belajar), a textbook published by Graha Pustaka and
used by junior high school students at SMP Negeri 3
Ratahan who follow a school-based curriculum.
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
178

2. Identification
After reading the reading text in the English textbook,
the researcher will identify the school-based
curriculum of each text.
3. Classification
The classification process is the next step in this
research. The researcher in this case categorizes the
text based on its school-based curriculum. In order to
classify the text, the researcher created a table. The
researcher classifies the text based on its school-based
curriculum. The researcher created a table while
performing the classification. The data was numbered
in the first column. The second column contains the
name of the genre found in Graha Pustaka's WAJAR
(Penunjang Wajib Belajar) textbook, which is used
for junior high school students in SMP Negeri 3
Ratahan with school-based curriculum. The third
column contains the number or page of text.
When conducting research, the researcher
requires references that are relevant to the study. They
were there to help me analyze the data. The writer will
go through the following steps when gathering
references:
a. I'm searching the internet for any study-related
materials.
b. searching the library for books on the subject.
c. Looking through the library for any thesis
related to the study
A documentary study was used to collect data for
this study. The goal of this research was to obtain a
description of the relevance of the reading material in
the WAJAR (Penunjang Wajib Belajar) textbook
published by Graha Pustaka and used for junior high
school students in SMP Negeri 3 Ratahan with a
school-based curriculum. First, the researcher chose
reading material from the textbook. Second, the
writer analyzed the relevance of the reading material
in the textbook with the school-based curriculum in
terms of cognitive aspects and the relevance of the
school-based curriculum in terms of psychomotor
aspects using the available observation checklist.
Finally, the researcher examined and expanded on the
data and findings from both observation checklists.
3.4 Data Analysis
Following the collection of data, the following
procedures were used to identify the elements of the
reading passages in WAJAR (Penunjang Wajib
Belajar) published by Graha Pustaka based on the
elements of the textbook used for junior high school
students in SMP Negeri 3 Ratahan with school-based
curriculum:
1) Thoroughly read WAJAR (Penunjang Wajib
Belajar), a textbook published by Graha Pustaka, is
used for junior high school students at SMP Negeri 3
Ratahan who follow a school-based curriculum.
2) Identifying the school-based curriculum of the
reading materials in the textbook based on the data
deemed necessary.
3) Identifying the social function of the textbook's
reading materials based on the data identified as
necessary.
4) Identifying the generic structure of the reading
materials in the textbook based on the data designated
as necessary.
5) Using the characterized data, identify the language
features of the textbook's reading materials.
6) Linking the reading materials to KTSP or school-
based curriculum indicators.
4 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Text Type Analysis
WAJAR (Penunjang Wajib Belajar) textbook
published by Graha Pustaka contains five school-
based curriculums of text.
Table 1: Number of articles published in IJAL from 2011
to 2016.
Genre Text
Unit/
Pa
g
e
Report
Tracto
r
A tractor is an example of modern farm
machinery. Most farmers use it because it
is faster than a traditional one. Do you
have a tractor? Of course, it is difficult to
use if we never see or use it. Please pay
close attention as I demonstrate tractor
operation. Of course, the first step is to
prepare the solar fuel. Sit down and turn
on the tractor when it is ready on the land.
Accelerate and move the steer depending
on which land or soil you want to lose. Do
you understand what a plough is? Plowing
is also used to remove soil. It is a piece of
traditional farming equipment.
This is
how a plough is used. To begin, ensure
that your plough is ready to use. Make
sure the cows or buffaloes are ready to
pull the plow. Then, place them on the
land you intend to cultivate. The animals
will walk if you hit them, and the plow
will be ready to work. All you have to do
is hit and point.
3/ 91
Suitability Level of School-Based Curriculum: An Analysis on English Reading Material
179

Genre Text
Unit/
Pa
g
e
Parque Central Cemplex
The Parque Central Camplex towers are
twin 56-story structures. In Caracas,
Venezuela, the buildings are latticed. With
a height of 225 meters, the towers are the
tallest structures in the country (738 ft).
President Rafael Caldera authorized the
construction of the tallest building in Latin
America, as well as the italo-venezuelan
entrepreneurial spirit. Delfino primarily
used his "Constructora Delpre" to construct
the skyscraper complex. The east tower was
finished in 1979, and the west tower was
finished in 1984. The towers are named
after a green oasis in the heart of Caracas'
urban jungle, but they are still surrounded
b
y a vast complex of office buildings and
amenities. The inside view provides a
p
anoramic view of the city and the
surrounding mountains. However, in April
2003, both towers were surpassed in height
(by an estimated 5 m) by Mexico City's
Torre Mayar, making them no longer the
tallest buildings in Latin America, though
they remain the tallest in South America.
On February 14, 1982, high-rise firefighting
and rescue advocate Dan Goodwin scaled
the outside of the Parque Central Complex
at the invitation of Venezuelan television
company Venevisian. A fire broke out in
the east tower on October 17, 2004. The
incident caused damage to at least ten
floors. The fire began on the 34th floor and
spread to the 44th floor of the building.
These levels housed important government
offices.
An inquest was being held at the
time on the activities of these offices. ft.
suffered critical damage as efforts were
hampered due to low water pressure and a
lack of firefighting equipment. Military
helicopters attempted to douse the flames
with water from above. It was also feared
that the steel structure would be severely
damaged, causing it to collapse. As of May
2009, the east tower was still undergoing
major repairs as a result of fire damage.
The reopening is scheduled for the second
semester of 2009.
1/ 40
What is planet?
When the ancient Greeks studied the
heavens, they noticed points of light
moving back and forth against a
background of seemingly fixed stars. These
moving lights shone steadily, rather than
twinkling like the stars. The Greeks
referred to these celestial bodies as planets,
also known as "wanderers." Planets are
now understood to be bodies that, like the
1/ 45
Earth, revolve around a star known as the
sun. Planets do not emit their own light, but
rather receive it from the sun. Our solar
system contains nine planets that revolve
around our sun, in addition to the Earth.
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter,
Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto are in
order, moving a pi/3rd from the sun. The
first four planets are known as the inner
planets, and they are mostly solid. Mercury
is the smallest planet; Venus is visible as
the Evening Star in the western sky; and
Mars appears red to the naked eye. The
others are known as the "outer planets," and
the first four are thought to be solid, while
Pluto is thought to be solid. Jupiter is the
largest planet, about 1,000 times the size of
Earth, and has twelve satellites; Saturn has
three beautiful rings; Uranus has five
satellites, and Neptune has two; Pluto was
discovered in 1930. Other stars in space are
likely to have planets as well, but because
planets emit no light, we cannot detect them
with our current instruments.
Orangutan
Orangutans, also known as Pongo
p
ygmaeus, are primates. The orangutan
spends the majority of its time in trees. It
constructs a new treetop nest every evening.
They are threatened by habitat loss, and
p
oachers continue to kill, own, and export
orangutans. They can only be found on the
island of Borneo and in the northern corner
of the island of Sumatra. Orangutans have
rough, long, reddish-
b
rown fur. Male
orangutans are 95 cm (37 in) long and
weigh 77 kg (170 lb). Females are smaller,
standing about 78 cm (31 in) tall and
weighing only about 37 kg (81 lb). The
male has puffy cheeks and a hanging throat
p
ouch. This pouch contains air sacks that
aid in the production of a groan. The male
has puffy cheeks and a pouch hanging from
his throat. This pouch contains air sacks that
contribute to the production of a groaning,
b
ubbling call that can be heard for at least 1
km (0.6 mi). Fruit accounts for half of the
orangutan's diet, but they also consume
meat. Young leaves, soft inner bark,
termites, eggs, and, on rare occasions,
monkeys are consumed. A female will seek
out an adult male when she is ready to mate.
Orangutans are mammals, and fernales give
b
irth to a single child every four to eight
years. Orangutans have a gestation period
of just under nine months, which is nearly
identical to that of humans. Infants remain
extremely close to their mothers for the first
three years, until they no longer require
their mothers' milk.
3/
109
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
180

Genre Text
Unit/
Pa
g
e
Descri
ptive
Dolphins
Dolphins are marine mammals. They must
breathe air in order to survive. They
belong to the Delhinidae family. Dolphins
have velvety skin. Only newborn dolphins
have a few bristly hairs on their snouts.
The hair quickly falls out. They have a long
tail and a fin on top of their backs that
prevents them from rolling over. When
female dolphins dive deep, they have a
thick layer of fat under their skin to keep
them warm. Flippers are the dolphin's front
fins. They use them to make left and right
turns. Dolphins can reach lengths of 2 to 3
meters and weigh up to 75 kilograms.
Dolphins hunt in large groups. A "pod" is a
group of dolphins. Fish, shrimp, and small
squid are among their favorite foods. They
live in saltwater oceans. When dolphins
hear or see a shirr nearby, they approach it
and follow it for several kilometers.
Dolphins can perform somersaults and
leaps out of the water. After watching other
dolphins perform, they sometimes invent
their own tricks and stunts. Dolphins are
extremely friendly and have never harmed
anyone. They are very amusing animals.
1/ 47
What is an Astronaut?
The term "astronaut" is derived from the
Greek words "astron," which means "star,"
and "nautes," which means "sailor."
Astronauts are people who pilot, navigate,
and fly spacecraft. Cosmonauts are Russian
"star-sailors," with "kosmos" being the
Greek word for "universe." In 1961, Yuri
Gagarin, a Russian, made the first space
flight. It lasted a little more than 89
minutes.
1/ 49
Proce
dure
Windsocks
To make a wind sock from a plastic bottle,
first cut the top and bottom of a two-liter
bottle to create a perfect cylinder. Then,
using a hole punch, make four evenly
spaced holes on top. Tie a 12-inch piece of
fishing line to each hole after that. Then,
connect all four to a large fishing swivel
snap. Sand the bottle and then paint it with
whatever design you want. When it's dry,
poke holes every inch around the perimeter.
Then, in each hole, tie a 3-foot piece of
ribbon. Colors can be varied or all the same.
Finally, hang up the phone and relax. The
words in the box may assist you in
comprehending the text.
2/ 59
How to Make Your Own Compost
Cornpost is the most nutrient-dense
fertilizer available. And with a little effort,
you can make it yourself. Compost is
made up of decomposing organic matter.
Compost can be made from leaves, grass,
2/ 62
decomposable kitchen scraps, and even
hair clippings. These materials are layered
with soil, manure, or a high-nitrogen
fertilizer in a container (or pile). Begin by
layering dry "brown" materials such as
wood, dried leaves, sawdust, or straw. Add
a layer of moist "green" materials from
your garden, such as grass cuttings, fruit
and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds,
eggshells, or prunings. Continue to add
layers, alternating "green" and "brown"
materials with soil and manure. According
to the recipe, the mixture should be kept
warm, wet (with a hose once a week to keep
the entire mixture moist), and aerated.
Every week or so, it will need to be turned
or mixed. If your compost isn't
decomposing, add chicken manure or bone
meal (for nitrogen). The compost will be
ready to use in your garden in 2-3 months!
When your compost is dark, combustible,
and resembles soil, it is ready. Mix compost
into the soil around existing plants once or
twice a year. Work into the soil liberally to
prepare new planting areas. spread around
the base of shrubs. Although compost can
be made in an open pile, using a bin will
yield faster results. A small kitchen
compost carrier can be hung on a cabinet
door or set on the counter. Larger yard bins
are now available for purchase everywhere.
There should be no use of animal
byproducts (meat scraps, grease, bones),
milk or dairy products, dog or cat
droppings, cardboard, or diseased plants.
Analy
tical
Expos
ition
Plastic
Plastic has now become an important part
of modern life. Most of the things around
us contain or are made of plastic. Our
blankets are made of nylon, a type of
plastic. The carpet is made of plastic. We
write with plastic ballpoints or pens. The
pans and pots we cook in, the toys our
children play with, and even the ears we
drive with all contain significant amounts
of plastic. Do you use a computer for work
or recreation? Some parts of your
computer are made of plastic. Plastics
have some advantages. They are relatively
inexpensive to produce. Some plastics are
as hard as stone and as strong as steel.
Some plastics are as clear as glass. They
are relatively inexpensive to manufacture.
Some plastics are as tough as steel and as
hard as stone. Some plastics have the
transparency of glass, the lightness of
wood, and the elasticity of rubber. Plastics
can be made in virtually any color and are
lightweight, waterproof, and chemically
resistant.
3/ 64
Suitability Level of School-Based Curriculum: An Analysis on English Reading Material
181
Genre Text
Unit/
Pa
g
e
What is the Significance of Rabbits'
Large Ears
A rabbit is a small, furry mammal with a
short tail and pointed ears. Rabbits live in
b
urrows in the ground. Each burrow is
home to a single family. The first fossils
associated with this family were discovered
in North America, but they can now be
found all over the world. The rabbit's ears
are large in comparison to its small body. A
rabbit is a weak and timid animal who is
constantly surrounded by enemies. As a
result, nature has endowed it with large
ears, allowing it to hear even the fun of a
drop sound. The large area of the ear
captures almost every sound wave
p
roduced in the air and transfers it to the
inner ear. This allows the rabbit to detect its
enemies and flee to safety zones in record
time. You've probably noticed that a rabbit
cleans its ears by licking its forepaws and
rubbing them over the surface of its ears. It
does this to keep its ears clean and to take
the natural oil that surrounds the ear surface
into its mouth. This oil is necessary for the
formation of vitamin D, which is required
for the growth of healthy bones. Rickets
will develop if the rabbit is not allowed to
develop this.
3/ 80
Rethinking Technology
Today we live in a modern world.
Technology allows people to present
everything easily and quickly. Unfor-
tunately, many things have become victims
of modernization. Our environment is one
of the victims. It receives a large number of
used items that are difficult to decompose.
There are environmental concerns because
used items take several years to decompose.
Millions of tons of trash are discarded every
day in major cities. The garbage can remain
there for days, months, or even years. It can
cause disease, an unpleasant odor, and an
unpleasant environment. All of these things
wreak havoc on our lives. Some beaches
now resemble garbage dumps. Rubbish
ends up on beaches far from the landfill
where it should be. The tide brings them to
the beach. The view of the beach
deteriorates dramatically. And perhaps
visitors are unable to keep the beach clean
b
y discarding broken sandals, shampoo
b
ottles, plastic packaging, glass bottles,
lunch boxes, and other items. The beach,
then, is not a healthy environment. At
home, people may be unaware that they are
using more energy than they require. They
can save energy by reducing their use of
motorcycles and turning off the electricity,
lights, television, and computer when they
3/ 93
are finished with them. When they use
electricity, they emit greenhouse gases
into the atmosphere.
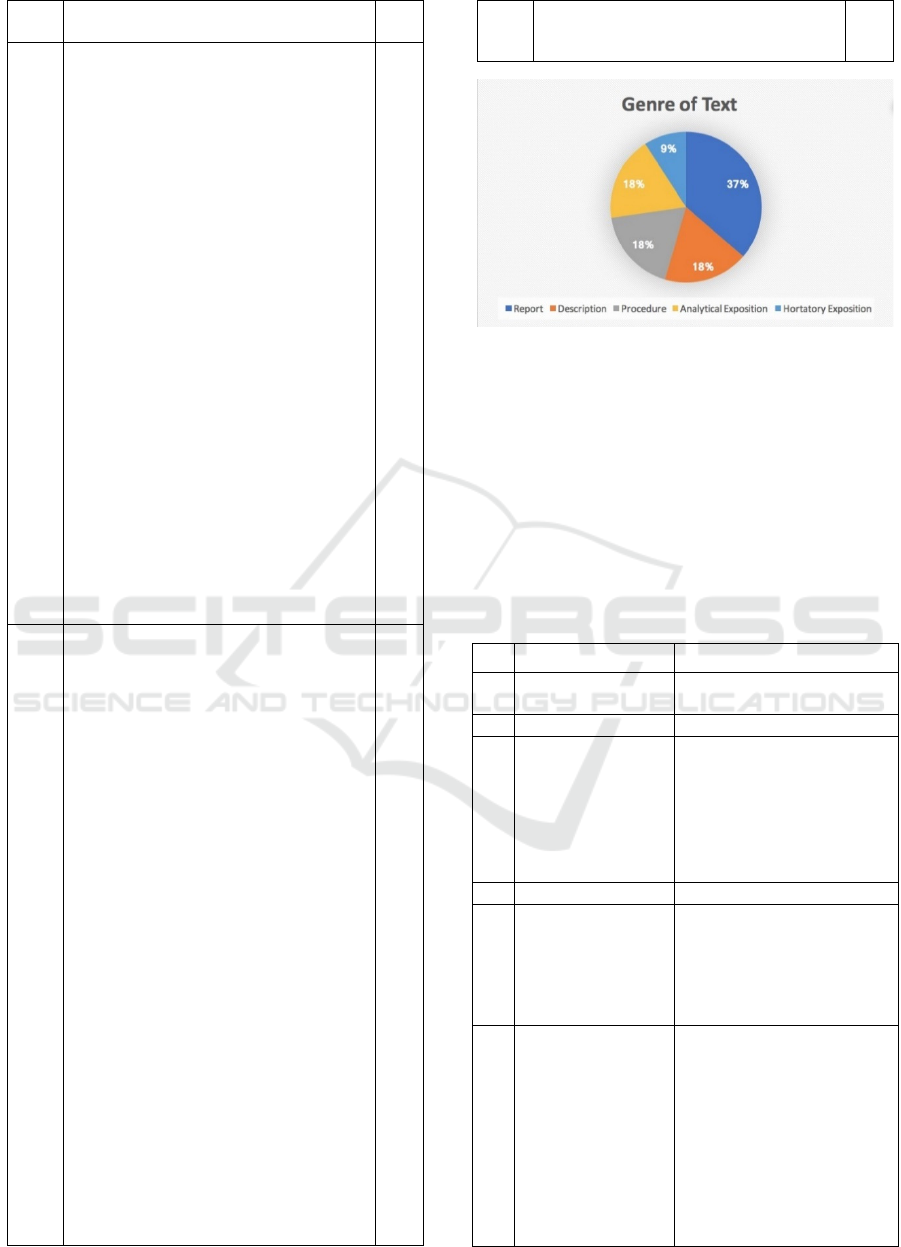
Figure 1: Genre of Text.
It is common knowledge that report text describes
how things are. A report may also refer to natural,
man-made, or social phenomena in our environment.
It describes something in general terms. A report also
describes the components, qualities, habits,
behaviors, or applications. The purpose of report text
is to describe how things are in our environment, with
reference to natural, man-made, and social
phenomena.
Table 2: Report Text Analysis.
No Title Unit/ Page
1 Parque Central
Cem
p
lex
Social Function
Describe the way
things are, with
reference to arrange
on natural,
manmade, and
social phenomena
in our environment.
The Parque Central Camplex
towers consist of twin 56-story
towers. The buildings are
lacated in Caracas, Venezuela.
The towers are the tallest
buildings in the country, with
a height of 225 m (738ft).
Generic Structure
General
Classification
The towers take their name
from the green refuge in the
heart of Caracas' urban jungle,
but are still in the midst of a
vast complex of office
b
uildings and amenities.
Description
The east tower was completed
in 1979 and the west tower in
1984. The towers take their
name from the green refuge in
the heart of Caracas' urban
jungle, but are still in the midst
of a vast complex of office
buildings and amenities. The
view from inside off ers
panoramic access to the city
and the surrounding
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
182
No Title Unit/ Page
mountains. However. in April
2003, both towers were
surpassed in height (by anly
5m) by Mexica City's Torre
Mayar, and thus are no longer
the tallest buildings in Latin
Arneriza, but still they remain
the tallest in South America.
Language Features
Past Tense
On February 14. 1982, high
rise firefighting and rescue
advocate, Dan Goodwin, at the
invitation of the Venezuelan
television company, Venevi-
sian, scaled the outside of the
Parque Central Complex.
Action Verb
On October 17. 2004. a fire
broke out in the east tower. At
least ten floors were damaged
in the incident. The fire started
on the 34th floor and flames
reached the 44th floor af the
building. These floors housed
key government offices.
Present Tense
The Parque Central Camplex
towers consist of twin 56-story
towers. The buildings are
lacated in Caracas, Venezuela.
The towers are the tallest
buildings in the country, with
a height of 225 m (738 ft).
2 Solar System
Social Function
Describe the way
things are, with
reference to arrange
on natural, man-
made, and social
phenomena in our
environment
Other stars in space probably
have planets also but, as
planets give off no light, we
cannot detect them with our
presentinstruments.
Generic Structure
General
Classification
When the ancient GreglSs
studied the heavens, they
observed points of light which
seemed to move back and
forth against the background
of apparently fixed stars.
Description
These moving lights shone
steadily and did not twinkle
like the stars. The Greeks
called these heavenly bodies
planets, m aning "wanderers".
We know now that the planets
are those bodies, like the earth,
which revolve around a star,
the sun. Planets do not give off
light of their own, but get their
light from the sun. Including
No Title Unit/ Page
the earth, there are nine planets
in our solar system that is
revolving around our sun. ln
sequence, moving a‘p/3y from
the sun, they are Mercury,
Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter,
Satum, Uranus, Neptune, and
PlutO.
Language Features
Present Tense
Including the earth, there are
nine planets in our solar
system that is revolving
around our sun. ln sequence,
moving a‘p/3y from the sun,
they are Mercury, Venus,
Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Satum,
Uranus, Neptune, and PlutO.
Adverbs
ln sequence, moving a‘p/3y
from the sun, they are
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars,
Jupiter, Satum, Uranus,
Neptune, and PlutO.
Past Tense
These moving lights shone
steadily and did not twinkle
like the stars. The Greeks
called these heavenly bodies
p
lanets, maning "wanderers".
3Oran
g
utan
Social Function
Describe the way
things are, with
reference to arrange
on natural,
manmade, and
social phenomena
in our environment
Orangutans or Pongo
pygmaeus belong to the
Primate order. The orangutan
spends most of its time in
trees. Each evening it builds a
new treetop nest. They are
endangered because of habitat
lost and poachers keep on
killing, owning, and exporting
orangutans.
Generic Structure
General
Classification
They only live on the island of
Borneo and in the northern
corner of the island of
Sumatra. Orangutans are
characterized by rough, long,
reddish-brown fur. Male
orangutans are about 95 cm
(37 in) in length and about 77
kg (170 Ib) in weight. Females
are smaller, reaching about 78
cm (31 in) in height and
weighing only about 37 kg (81
Ib). The male has puffy cheeks
and a hanging throatpouch.
This pouch contains air sacks
that help produce a groaning,
bubbling call, which can be
heard at least 1 km (0.6 mi)
away.
Suitability Level of School-Based Curriculum: An Analysis on English Reading Material
183
No Title Unit/ Page
Description
Half of the orangutan's diet
consists of fruit, but they
also.eat young leaves, soft
inner bark, termites, eggs, and
occasionally monkeys. When
a female is ready to mate, she
will seek out an adult male.
Orangutan are mammals;
fernales give birth to a single
infant about once every four to
eight years. The gestational
period for orangutans is just
under nine months, nearly the
same as in human beings.
Infants stay very close to their
mothers for the first three
years until they don't consume
their mother's milk.
Language Features
Present Tense
Orangutan are mammals;
fernales give birth to a
single infant about once every
four to eight years.
Adjective
Orangutans are characterized
by rough, long, reddish-brown
fur. Male orangutans are about
95 cm (37 in) in length and
about 77 kg (170 Ib) in weight.
Action verb
When a female is ready to
mate, she will seek out an adult
male. Orangutan are
mammals; fernales give birth
to a single infant about once
every four to eight years.
4 Tracto
r
Social Function
To describe how
something is
accomplished
through a sequence
of actions or steps.
Tractor is an example of
modern farming equipments.
It is used for most of farmers
because it is faster than
traditional one. Can you use a
tractor?
Generic Structure
Transatinal Signal
After 2-3 months,
Action Verbs
Keep adding, Add, Mix
Sprea
d
Reiteration
When the tractor is ready on
the land, sit down and switch
the power on. And then, turn
on the gas and move the steer
depends to the land/soil which
you want to lose. Do you know
plough? Plough is used to lose
the soil, too. It is one of the
traditional farming equipment.
And this is the way how to use
plough. Firstly, make sure that
your plough is ready to work.
Don't forget to prepare the
animals of cows or buffaloes
No Title Unit/ Page
to pull the plough. Then, take
them on the land which you
want to cultivate. When you
hit the animals, they will walk
and the plough is ready to
work. You only hit and give
the direction.
Language Features
Connectives
Firstly, and, then
Action Verbs
Turn on, take, sit down.
The generic structures of report text are general
classification and description. The WAJAR text book
only explains the types of generic structure; the
definition of the types of generic structure in the
report text is not explained. A descriptive text is one
that is written to describe a specific person, place, or
thing. The descriptive text's schematic structure is
divided into two parts: identification and description.
Aside from its schematic structure, descriptive text
has its own linguistic characteristics. Linguistic
characteristics of descriptive text include the use of
specific participants, writing in the present tense,
linking verbs, adjectives, and the use of relational and
material processes.
Table 3: Descriptive Text Analysis.
No Title Unit / Page
1Dol
p
hins
Social Function
To describe a
particular
person, place
or thin
g
.
Dolphins are sea mammals. They
have to breathe air or they will
die. They are members of the
Delhinidae family.
Generic
Structure
Identification
Only baby dolphins are born with
a few bristly hairs on their snouts.
The hairs soon fall out. They have
a long tail and fin on the top of
their backs keeps the dolphin
from rolling over. The female
dolphins have a thick layer of fat
under their skin to keep them
warm when they dive very deep.
Description
The dolphin's front fins are called
flippers. They use them to turn
left and right. Dolphins grow
from 2 to 3 meters long and
weight up to 75 kilograms.
Dolphins hunt together in a
group. A group of dolphins is
called a pod. They eat fish,
shrimps and small squid. They
live in salt water oceans. When
dolphins hear or see a shirr close
b
ythe
y
go nea
r
it and follow it
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
184
No Title Unit / Page
from many kilometers. Dolphins
can leap out of the water and do
somersaults. Sometimes they
invent their own tricks and stunts
after watching other dolphins
perform. Dolphins are very
friendly to people and have never
harmed anyone. They are very
p
layful animals.
Language
Feature
Adjective
The female dolphins have a thick
layer of fat under their skin to
keep them warm when they dive
very deep.
Present Tense
Dolphins hunt together in a
group. A group of dolphins is
called a pod. They eat fish,
shrimps and small squid. They
live in salt water oceans.
Material
Process
The dolphin's front fins are called
flippers. They use them to turn
left and right. Dolphins grow
from 2 to 3 meters long and
weight up to 75 kilograms.
2 What is an
Astronaut?
Social Function
To describe a
particular
person, place or
thing.
The word "astronaut" comes from
the Greek, "astron", meaning
"star" and "nautes" meaning
"sailor". Astronaut are the men
and women who pilot, navigate
and fly in spacecraft Russian
"star- sailors " are called
cosmonauts, "kosmos " being the
Greek for "universe". The first
space flight in 1961 by the
Russian, Yuri Gagarin. It lasted
just over 89 minutes.
Generic
Structure
Identification
Astronaut are the men and women
who pilot, navigate and fly in
spacecraft Russian "star-sailors "
are called cosmonauts, "kosmos "
b
eing the Greek for "universe".
Description
l the first space flight in 1961 by
the Russian, Yuri Gagarin. it
lasted just over 89 minutes. The
word "astronaut" comes from the
Greek, "astron", meaning "star"
and "nautes" meaning "sailor".
Language
Features
Present Tense
Astronaut are the men and women
who pilot, navigate and fly in
spacecraft Russian "star- sailors "
are called cosmonauts, "kosmos "
b
eing the Greek for "universe".
No Title Unit / Page
Adjective
The first space flight in 1961 by
the Russian, Yuri Gagarin. it
lasted just over 89 minutes.
It is discovered that language features are not used
proportionally in the reading texts contained in the
WAJAR textbook.
A procedure is a set of activities, tasks, steps,
decisions, calculations, and other processes that,
when carried out in the order specified by procedures,
result in the desired result, product, or outcome. A
procedure text type's purpose is to explain how
something can be done. A procedure is a method of
describing how something is done through a series of
actions or steps (Depdiknas, 2003:49). A procedure is
a series of steps that demonstrate how to accomplish
certain objectives. The most basic procedure is a brief
series of simple imperative clauses centered on well-
known action verbs and commonplace objects.
Language learners face increased difficulty as
procedures become more specialized and technical.
The steps may include constraints that must be met in
order to successfully carry out the instructions.
Simple constraints can be expressed as conditions of
manner or place, such as carefully, close to the edge.
Conditional clauses can be used to express more
complex constraints, such as "if the metal is cool"
(Feez and Joyce, 1989: 87–88). (1) goal; (2)
materials; and (3) steps are the elements of procedure
text. Furthermore, the steps for creating a procedure
are as follows: (1) begin with a statement of the
purpose and importance of the specific task; (2)
present a step-by-step description of "how to
proceed;" and (3) express the steps in the procedure
in a simple and clear format, ensuring that it is correct
and complete (Depdiknas 2003).
Table 4: Procedure Text Analysis.
No Title Unit / Page
1 Windsocks
Social Function
To describe how
something is
accomplished
through a sequence
of actions or ste
p
s
To make a wind sock out of
a plastic bottle first you
need to cut the top and the
bottom cff a two litre bottle,
to have a
p
erfect c
y
linder.
Generic Structure
Goal To make a wind sock out of
a plastic bottle first you
need to cut the top and the
bottom cff a two litre bottle,
to have a
p
erfect c
y
linder.
Material To make a wind sock out
of a plastic bottle first you
Suitability Level of School-Based Curriculum: An Analysis on English Reading Material
185
No Title Unit / Page
need to cut the top and the
bottom cff a two litre
bottle, to have a perfect
c
y
linde
r
.
Steps Then,
p
unch 4 holes (with a
hole punch) spaced evenly
on top. After that, tie a 12-
inch piece of fishing line to
each hole. Next, attach all
four to a large swivel snap
used in fishing. Sand the
bottle and paint with paints
any design you wish. When
it is dry, punch holes evety
an inch around the bottom.
Then, tie a 3-foot piece of
ribbon in each hole. Vary
your colours or make them
all the same. Finally, hang
up and enjoy.
Language Features
Transitional
Signals
After th a t, Next, Then,
Finally,
Action Verb Tie, hang up, sand, etc.
2
How to make own
compost
Social Function
To describe how
something is
accomplished
through a sequence
of actions or steps
Compost is the richest
fertilizer you can use. And
you can make it yourself
with a littleeffort. Compost
consists of decaying
organic material. Things
like leaves, grass,
decomposable kitchen
scraps, even hair clippings
can be used to make
compost.
Generic Structure
Goal Larger bins for your yard
are available for purchase
everywhere now. Things
NOT to use: ashes from the
barbeque, animal by-
products (meat scraps,
grease, bones), milk or
dairy products, dog or cat
droppings, cardboard,
diseased plants.
Material These materials are layered
in a container (or pile) with
soil and manure or a high-
nitrogen fertilizer.mer Start
with a layer of dry "brown"
materials, like wood
c2.1.125, dried leaves,
sawdust, or straw.
Steps Add a layer of moist
"green"materials, such as
No Title Unit / Page
grass cuttings, fruit and
vegetable scraps, coffee
grounds, eggshells, or
pruning from your garden.
Keep adding layers,
alternating quot; green" &
"brown" materials with a
layer of soil and manure.
per the mixture should be
kept warm and wet (water
with a hose once a week to
keep entire mixture moist),
and aerated. lt will need to
be turned, or mixed, every
week or so. Add chicken
manure or bone meal (for
nitrogen) if your compost is
not decaying. After 2-3
months, the compost willbe
ready to use in your garden!
Your compost is ready
when it is dark and
c_airiably, and looks like
soil. Mix compost into soil
around existing plants once
or twice a year. Prepare new
planting areas by working
liberally into soil. Spread
around the base of shrubs.
Although compost can be
made in an open pile, you'll
get faster results if you use
a bin. Asmall Kitchen
Compost Carrier can hang
on the cupboard door or
even sit on your kitchen
counter.
Language Features
Transitional
Signals
After 2-3 months,
Action Verbs Keep adding, Add, Mix,
Sprea
d
It is discovered that language features are not used
proportionally in the reading texts contained in the
WAJAR textbook.
One of the argumentative essays is Analytical
Exposition. Horatory exposition differs from
analytical exposition. Analytical is used to persuade
readers to care about a particular case. Meanwhile,
hortatory exposition is meant to persuade readers that
something should or should not be true. As a result,
the text in WAJAR (PENUNJANG PROGRAM
WAJIB BELAJAR) is meant to persuade the reader
that "something is true," rather than "to recommend
an action." As a result, the text in WAJAR
(PENUNJANG PROGRAM WAJIB BELAJAR) is
analytical. The language function of analytical
exposition is to persuade the reader or listener that
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
186

something is true. It can also be used to analyze or
explain "how and why." As a result, it is sometimes
referred to as a persuasive text.
Table 5: Analytical Exposition Analysis.
No Title Unit / Page
1 Plastics
Social Function
To persuade the
readers to be
concerned with one
case.
Today plastic have become
important part in modern life.
Most of the things around us
contain plastic, or are made of
plastics. Our blankets are
made of nylon, kind of
p
lastics.
Generic Structure
Thesis Statement
The carpet is made of plastic.
The ballpoints or pens we
write with are made of
plastics. The pans and pots we
use to cook with, the toys the
children play with, even the
ears people drive, all have
important
plastic
components. Do you work or
play with a computer? Some
components of your computer
are made of plastics.
Arguments
Plastics have made some
advantages. They are relative
cheap to produce. Some
plastics are made hard as stone
and strong as steel. Some
plastics are produce
transparent as glass, light as
wood and elastic as rubber.
Reiteration
Plastics also produced in
almost any colours they are
lightweight, waterproof and
chemical resistant.
Language Features
Adjective
Important, transparent,
chemical.
General and
abstract noun
Ballpoint, toys, adventage,
waterproof, etc.
2
What is the
Significance of
Rabbits' Lar
g
e Ears
Social Function
To persuade the
readers to be
concerned with one
case
A rabbit is a small furry
mammal with a short tail and
pointed ears. Rabbits live in
burrows in the ground.
Generic Structure
Thesis Statement
Each burrow is the home of a
single family. The first fossils
which can be attributed to this
No Title Unit / Page
family came from North
America but now they are
found in every part of the
world. Compared to its small
body rabbit has large-sized
ears.
Arguments
A rabbit is a weak and timid
animal and is always
surrounded by many enemies.
Therefore, nature has gifted it
with large ears to help it to hear
even the fun of drop sound.
The large area of the ear
catches almost every sound
wave produced in the air and
transfers them into the inner
ear. This makes the rabbit to
detect its enemies in time and
run to safety zones
Reiteration
This oil is important in forming
vitamin D which is necessary
for the growth of healthy
bones. If the rabbit is not
allowed to form this, it will
develop rickets.
Language Features
General and
Abstract Nouns
growth, family, ear, rabbit
It is discovered that language features are not used
proportionally in the reading texts contained in the
WAJAR textbook.
The purpose of hortatory exposition text is to
persuade readers that something should or should not
be said or done.
The generic structure of hortatory exposition texts
is: Thesis, 2. Arguments, and 3. Recommendation,
and the dominant language features are: a. the use of
the simple present tense; b. the use of modals; c. the
use of action verbs; d. the use of thinking verbs; e. the
use of adverbs; f. the use of adjectives; g. the use of
technical terms; h.
Table 6: Hortatory Exposition Analysis.
No Title Unit / Page
1 Rethinking
Technolo
gy
Social Function
Persuading the
readers that
something should or
should not be the
case or be done.
We face a modem life today.
Technology really helps
people presenting everything
easily and fast.
Unfortunately, there are
many things become victims
of the modernization.
Generic Structure
Thesis Statement Our environment is one of the
Suitability Level of School-Based Curriculum: An Analysis on English Reading Material
187

No Title Unit / Page
victims. It receives many
used things that can not
decompose easily. There are
environmental problems then
because the used things need
several
y
ears to decom
p
ose.
Arguments
Everyday in big cities
millions of tones of rubbish is
sent to rubbish damp. The
rubbish stays there for days,
months, even years. It can
create diseases, unpleasant
smell and uncomfortable
scenery. All of these disturb
our life.
Recommendation
At home, sometimes people
don't realize that they spend
more energy than they need.
Exactly they can save their
use of energy by cutting the
use of motorbikes, switch off
the electricity, the lights, the
television, and computer
when they have finished using
them. Whenever they use
electricity they put
g
reenhouse
g
ases into the air.
Lan
g
ua
g
e Features
Thingking Verbs
Realize
Present Tense
Nowadays some beaches
look like rubbish dumps.
Rubbish arrives on beaches
far from the lace where the
rubbish should be. The sea
tide brin
g
s them to the beach.
4.2 Suitability Between Reading Texts
and School-Based Curriculum
(KTSP)
The researcher compares the suitability of reading
materials and curriculum aspects by relating the
reading texts to the indicators used and analyzing
their consistency.
Table 7: Suitability Analysis.
No Indicators
Description in
Readin
g
Material
1
M
engidentifikasi makna
gagasan dalam teks
berbentuk procedure dan
re
p
ort
A
nswer the following
questions based on
the monologue in task
3 above!
(
60
)
2 Mengidentifikasi berbagai
informasi
yang terdapat dalam teks
berbentuk
p
rocedure dan
Complete the
dialogues with
suitable expression!
(60)
No Indicators
Description in
Readin
g
Material
report
3
M
engidentifikasi tujuan
komunikatif teks berbentuk
p
rocedure/re
p
ort
-
4 Mengidentifikasi langkah
retorika Dalam teks
berbentuk
procedure/report
Your teacher will
read the procedure
text of how to make a
compost. Listen to
him/her carefully and
answer these
following questions
based on the text of
dialogue above! (62)
5 Membaca nyaring
-
6 Mengidentifikasi informasi
yang berhubungan dengan
bacaan tentang prosedu
r
Questions above!
7
Menjawab pertanyaan-
pertanyaan berdasarkan
bacaan
Questions above!
8 Membuat ringkasan
-
9
Menulis essay berbentuk
procedure / report
Read the text again
and answer the
following questions!
(67)
10
M
enyusun kalimat acak
menjadi teks yang padu
berbentuk procedure/report
Your teacher will
read the text
completely and fill in
the blank space! (71)
11
M
engidentifikasi makna
dalam teks monolog
berbentuk narrative/re
p
ort
-
12
M
engidentifikasi tujuan
komunikatif dan langkah
retorik teks monolog
berbentuk narrative/re
p
ort
-
13
M
engidentifikasi ciri
Kebahasaan teks
narrative/re
p
ort
-
14
Mengidentifikasi berbagai
informasi dalam teks
monolog berbentuk
narative/re
p
ort
-
15
M
enangkap informasi
spesifik yang ada pada teks
descriptif.
Choose the correct
answer by crossing
a, b, c,or d (48)
16 Mengidentifikasi makna
dan gagasan dalam teks
descriptive.
Read the text below
and answer the
questions! (49)
17
M
engidentifikasi aspe
k
-
aspek yg ada pada teks
descriptive
Find a text about
natural objects. Then
analyze the
followings (54)
18
Merespon wacana
monolog analytical
ex
p
osition
-
19
M
elakukan monolog
berbentuk analytical
ex
p
osition
Read the text below
aloud! (64)
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
188
No Indicators
Description in
Readin
g
Material
20
Menganalisis fungsi
sosial, struktur teks, dan
unsur kebahasaan dari
teks eksposisi hortatori
tentang topik yang hangat
dibicarakan umum, sesuai
dengan konteks
p
en
gg
unaann
y
a.
What is the main
idea? (80)
21
Memahami fungsi sosial
dari teks eksposisi
hortatori memahami
struktur teks eksposisi
hortator
y
Answer these
questions based on
the text! (65)
22
M
emahami unsur
kebahasaan teks eksposisi
hortatory
Make five
conditional sentences
about our
environment. Do it
in a group! (64)
23
Menjelaskan fungsi
sosial, struktur teks, dan
unsur kebahasaan teks
eks
p
osisi hortator
y
Answer these
following questions
based on the text!
(94)
5 CONCLUSION
After conducting research on the WAJAR textbook,
the researcher comes to the following conclusions: 1)
The WAJAR textbook contains a variety of school-
based curriculum texts. Report text, descriptive text,
analytical exposition, hortatory exposition, and
procedure text are all covered in the book. The
reading text contained within the textbook explicitly
identifies all of the text's generic structures. The first
conclusion pertains to the WAJAR textbook's
contents. There are some points to consider when
dealing with aspects of the textbook's content.
These points are the conformity of reading
materials and curriculum, the types of genres found
in reading materials, the arrangement of reading
materials based on level of difficulty, reading tasks
given to develop students' abilities, reading materials
that support life skills, and reading materials that
consider gender, religion, race, and SARA. Except for
the conformity between reading materials and
curriculum, the WAJAR textbook had already met all
of the content requirements.
2) According to the findings, some language
features are not used in proportion in the reading text.
In each text type, certain language features were
missing. The reading text contains only two to three
of the five language features.
(3) Not all reading indicators are developed
through the textbook's reading activities. Some
reading indicators are not included in the first
semester's reading materials. The calculated
suitability level was only 65.21 percent (suitable
enough), indicating that there is still unsuitability in
the WAJAR textbook.
REFERENCES
Ahiri, J. 2007. Hubungan gaya kepemimpinan dan konsep
diri dengan akuntabilitas kepsek. Gema Pendidikan, 14
(2).
Akbar S., Mochammad R., Adhi P. 2017. The analysis of
english reading texts based on national character and
cultural education on course book for the tenth grade at
the state of senior high school in pamekasan. Jurnal
Bahasa dan Sastra, Vol. 11, No.1.
Alyousef, H.S. 2005. Teaching Reading Comprehension to
ESL/EFL Learners. The Reading Matrix Vol.5, No. 2.
Anderson. 1969. Efficient Reading. London: Mc Graw-Hill
Book Company
Anderson, Lorin W. & Krathwohl, David R. 2001. A
Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing: a
Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy. New York: Longman
Publishing
Arikunto, Suharsimi,2006. Prosedur Penelitian Suatu
Pendekatan Praktik, Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 6th Ed.
Brown, R. N., Carducci, R., & Kuby, C. R. (2014).
Disrupting Qualitative Inquiry. Peter Lang Publishing
Incorporated.
Cortina J. and Janet E. 2005. Opening Doors;
Understanding College Reading, New York: McGraw
Hill Company.
Cunningsworth, Allan. 1995. Choosing Your Coursebook,
Oxford: Macmillan Education, p. 7.
Dian S. 2015. Content analysis of student book“when
english rings a bell” for grade viii junior high school. A
Final Project in Universitas Negeri Semarang.
E. Mulyasa. 2006. Kurikulum yang di sempurnakan.
Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Fardani, Wahjuningsih E., Sundari S., Hudori R. F., & Arya
B. 2019. The efficacy of 4Cs-based reading to foster
21st-century learning competencies. Indonesian
Journal of Applied Linguistics UPI. Vol.9, No.2.
Gholami R., Noordin N., & Galea S. R. 2017. A Thorough
Scrutiny of ELT Textbook Evaluations: A Review
Inquiry. International Journal of Education & Literacy
Studies (IJELS), Vol. 5, No.3.
Grabe, William Frederika L. Stoller. 2002. Teaching and
Researching Reading, Edinburgh: Pearson Education.
Grellet, Françoise. 1981. Developing Reading Skills: A
Practical Guide to Reading Comprehension Exercises.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Harmer, Jeremy. 1983. The Practice of English Language
Teaching, New York: Longman.
Hermuttaqien B. P. F., Sata H. R., & Wadu L. B. 2019.
Perbandingan Pembelajaran PPKn Pada Implementasi
KTSP dan Kurikulum 2013 Di Sekolah Menengah
Pertama (SMP). Jurnal Inspirasi Pendidikan, Vol. 9,
No.1.
Suitability Level of School-Based Curriculum: An Analysis on English Reading Material
189

Leong L. M., & Ahmadi S. M. 2017. An Analysis of Factors
Influencing Learners’ English Speaking Skill.
International Journal of Research in English Education,
Vol. 2, Issue 1.
Noprianto E., Punawarman P. 2019. EFL students’
vocabulary learning strategies and their affixes
knowledge. Journal of Language and Linguistic
Studies, Vol.15, No.1
Novianti R., Syihabuddin S., Rochyadi E. 2019.
Phonology-based reading instruction to improve
dyslexic students’ early reading ability. Indonesian
Journal of Applied Linguistics UPI. Vol.9, No.2.
Nunan, David. 1999. Second Language Teaching and
Learning. Boston: Heinle and Heinle.
Pardiyono. 2007. Pasti Bisa! Teaching Genre-Based
Writing.Yogyakarta: ANDI.
Ririn Pusparini. 2014. A study on the relevance of materials
in english textbook “bright” for seventh graders of
junior high school published by erlangga to 2013
curriculum. Jurnal Mahasiswa Unesa, Vol.2, No.2.
Strang, Ruth. 1991. The Improvement of Reading, (New
York: McGraw Hill Company,), p. 1.
Safitri M., Tyas P. A. 2019. An Analysis of English
Textbook Entitled "Bahasa Inggris SMA/MA
SMK/MAK Kelas X". Journal of English Educators
Society UMS, Vol.4. No.1.
Setyaningsih E. 2019. Bringing critical literacy into tertiary
EFL reading class. Indonesian Journal of Applied
Linguistics UPI. Vol.9, No.2.
Syafniar, Rusda Ayu. 2014. The Analysis of The Reading
Materials in “English Alive” Textbook Based on
School-based Curriculum for Second Grade Students of
Senior High School. Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic
University. Jakarta.
Tomlison, Brian. 2001. Material Development. In centre.
UR, Penny A Course in Language Teaching: Practice and
Theory, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,
1996), p.138.
You J., Lee H., & Craig C. J. 2019. Remaking textbook
policy: analysis of national curriculum alignment in
Korean school textbooks. Asia Pacific Journal of
Education, Vol.39, Issue 1.
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
190
