
Implemention of Humaniststic Learning Theory on the Independent
Learning Curiculum in Harapan Kita Kindergarten Sungai Liku
Pesisir
Yessi Rifmasari, Maifit Hendriani and Jamaris
Ilmu Pendidikan, Universitas Negeri Padang, Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: Implementation, Humanistic Learning Theory, Mardeka Curriculum, Tk.
Abstract: This study discusses the application of humanistic learning theory in Harapan Kita Kindergarten. The
curriculum has a very important role in achieving the direction and goals of education. The independent
learning curriculum is one of the approaches that can be used in early childhood education. Students in this
humanistic learning theory are considered as subjects who are free to determine the direction of their life.
Learners are fully responsible for themselves in the educational process (Faiz & Kurniawaty, 2020). The
concept of independent learning designed by the Ministry of Education and Culture is related to the humanistic
learning theory pioneered by Abraham Maslow. Education or teachers must be able to carry out the curriculum
used in schools so that the teaching and learning process can be carried out. The purpose of this study is to
see the effect of the implementation of humanistic learning theory on the Independent Curriculum, learning
is stimulated from an early age. The Independent Curriculum prioritizes the needs and interests of students
according to the definition of independence. Through the Independent Curriculum which includes
extracurricular activities, and the Pancasila Student Profile Strengthening Project. Humanistic learning is
learning that optimizes the potential of children as human beings. In their activities, children fulfill their basic
needs in self-actualization. In the learning activities it can be seen that the children at Harapan Kita
Kindergarten are actively involved in playing and the teacher facilitates learning according to the interests
and needs of the children.
1 INTRODUCTION
The independent curriculum is a curriculum
development policy issued by the Ministry of
Education and Culture for the recovery of student
learning in schools. The independent curriculum is
implemented from the levels of PAUD, SD, SMP,
SMA, SMK, Special Education and Equality. The
essence of an independent curriculum is independent
learning. Freedom to learn is a vision built on the
thoughts of Ki Hajar Dewantara, who stated that
independence is an educational goal as well as an
educational paradigm that needs to be understood by
all stakeholders (Purba et al., 2021).
Minister of Education and Culture No. 22 of 2020
concerning the Strategic Plan of the Ministry of
Education and Culture for 2020-2024, in terms of
pedagogy, it is stated that the Freedom to Learn
policy will move away from a standardized approach
towards a heterogeneous approach that is more
complete, enabling teachers and students to explore a
growing body of knowledge. Students are learning
leaders in the sense that they are the ones who make
teaching and learning activities meaningful, so that
learning will be adjusted to the level of ability of
students and supported by a variety of technologies
that provide a personal approach to the progress of
each student's learning, without neglecting the
importance of aspects of socialization and working in
groups to foster social solidarity and soft skills.
This policy leads to the concept that students can
explore their individual interests and talents. The
Independent Curriculum Policy at the PAUD level
gives students the freedom to be able to move freely
choosing the activities they are interested in through
playing. Playing for early childhood is learning.
Learning is a process to explore, reason, think
critically and find new things from what you do.
Playing meaningful and fun for early childhood aims
to develop the effectiveness and capacity of the
child's brain. Freedom in choosing activities
342
Rifmasari, Y., Hendriani, M. and Jamna, J.
Implemention of Humaniststic Learning Theory on the Independent Learning Curiculum in Harapan Kita Kindergarten Sungai Liku Pesisir.
DOI: 10.5220/0012200800003738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Innovation in Education (ICoIE 4 2022) - Digital Era Education After the Pandemic, pages 342-347
ISBN: 978-989-758-669-9; ISSN: 2975-9676
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
according to interests is in line with humanistic theory
which views humans as subjects who are free and
independent to determine the direction of their lives.
Students act as the main actors (student centers) who
interpret the process of their own learning experience.
The process of students understanding their own
potential is expected to be able to develop their
potential positively and minimize negative potential
(Thobroni, 2015).
Humanistic theory encourages individual learning
where students can learn subject matter at their own
pace and in their own way of achieving goals.
Humanistic theory pays attention to individual
differences in the learning process. Personality
growth and individual development are a concern in
this theory (Aradea & Harapan, 2019). The main
concept in this humanistic learning theory is how
learning can humanize humans.
Humanistic learning is based on what is human
needs in everyday life. Humans are different from
other organisms and have physiological needs and
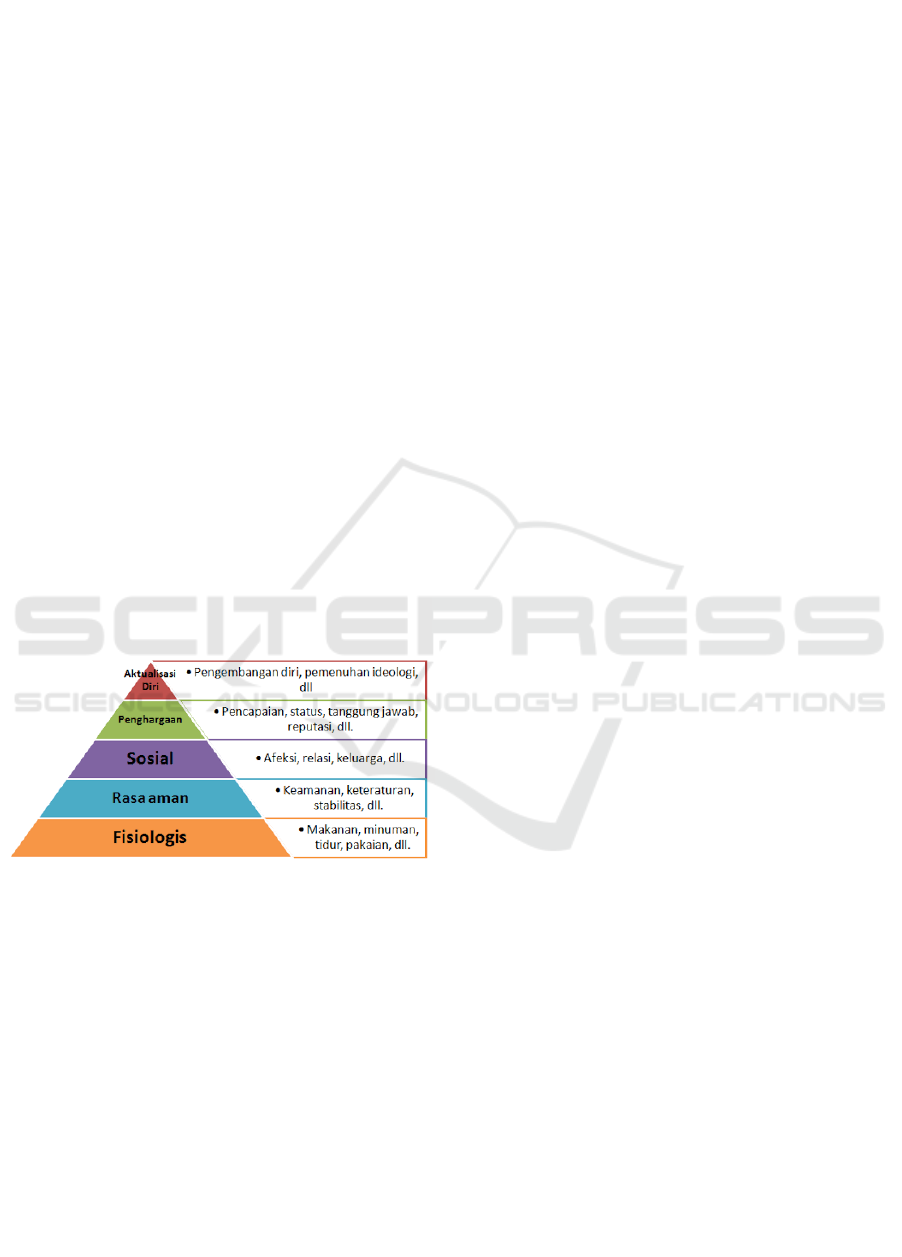
psychological needs. Maslow in Shahrawat and
Shahrawat (2017) put forward 5 (five) hierarchies of
human needs as basic needs that must be met by
humans in their lives. These human needs such as;
physiological needs, needs, safety, love, self-esteem,
and self-actualization.
Humanistic learning theory is a theory that aims to
humanize humans. Parties who are humanized in the
narrow sense are teachers and students. Teachers give
freedom to their students in choosing what they learn
according to their needs (Nasution, 2020; Nursikin,
2016; M Yusuf & Arfiansyah, 2021). Students in this
humanistic learning theory are considered as subjects
who are free to determine the direction of their lives.
Students are fully responsible for themselves in the
educational process (Faiz & Kurniawaty, 2020).
Students can develop critical and creative thinking
skills through meaningful learning. The concept of
independent learning designed by the Ministry of
Education and Culture seems to be related to the
humanistic learning theory that was pioneered by
Abraham Maslow long ago. Of course, this
relationship needs to be analyzed by means of a
supporting literature review for the two topics in
order to find common threads from these two hats.
The concept of independent learning that liberates the
minds of teachers and students is expected to be able
to humanize humans and become a place for students
to develop critical, innovative and creative thinking.
Based on the description of the background that has
been previously described, the problem at the heart of
this study is how the concept of independent learning
is designed by the Ministry of Education and Culture,
how is the theory of humanistic learning, and how is
the concept of independent learning in the perspective
of humanistic learning theory.
2 METHOD
The type of research used in this study is the research
method used is a qualitative descriptive method.
According to Sugiyono (2016) the qualitative
research method is a method used to examine the
condition of natural objects where the researcher is
the key instrument. According to Nazir (2014)
descriptive research examines the status of human
groups, objects, conditions, systems of thought or
current events with the aim of making systematic,
factual and accurate descriptive of the facts studied.
According to Nana Syaodih Sukmadinata (2011: 73),
qualitative descriptive research is intended to
describe and illustrate existing phenomena, both
natural and human-made, which pay more attention
to characteristics, quality, interrelationships between
activities. Data collection techniques used are
observation, interviews and literature/documentation
studies.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
According to Mulyasa (2012: 16) early childhood is
the first stage which is critical and crucial in the
process of growth and development of human
existence. Early childhood is a period of personality
development that will shape how children will live
their next life. The "golden age" is referred to as
childhood. "Golden Age is a very meaningful age for
children's lives in the future," claims Windayani
(2021:1). It serves as a basis for teaching children
how to develop a variety of cognitive, motor,
linguistic, social and other skills. Law No. 20 of 2003
concerning the national education system provides a
statement where early childhood is a coaching effort
for children aged birth to six years who use
Implemention of Humaniststic Learning Theory on the Independent Learning Curiculum in Harapan Kita Kindergarten Sungai Liku Pesisir
343

educational stimuli to increase physical and spiritual
development so that children are ready to continue on
to an advanced level of education. Early childhood is
defined by Windayani (2021: 3) as between the ages
of 0 and 8 years, shown in instructional programs in
kindergartens, family daycare facilities, private and
public preschools, kindergartens, and elementary
schools.
According to Syamsu (2007, 141) The uniqueness
of human attributes, especially those related to free
choice and self-development capacity, is highlighted
by humanistic theory, which can be understood as a
theoretical direction. According to the idea of
humanistic learning, students can reach their full
potential by making people like them more.
According to humanistic learning theory, learning is
successful when the learner is aware of his
environment and himself. Students must strive
throughout the learning process to gradually achieve
self-actualization. The purpose of this learning theory
is to understand learning activities from the side of
the actor not from the observer. Kartono and Gulo
(1987: 207) provide a statement where humanistic
psychology is a realm of psychology that places a
strong emphasis on treating individuals as whole
beings, emphasizing subjective awareness,
investigating significant human challenges, and
improving human life processes. According to Saam
(2010: 60), humanistic theory holds that individual
behavior is influenced by the way he views himself
and his environment, as well as by internal factors.
From a humanistic point of view, educators must
consider students' needs for affection. According to
the humanistic learning philosophy, students are more
compassionate, individual, and student-focused.
Dalyono (2007: 43) that the problem of how people
get influence and direction by the personal goals they
give to their own experiences is the essence of
humanistic psychology. Teachers in humanistic
schools believe that the preparation and presentation
of course material must take into account the
emotions and interests of students. According to
Sadulloh (2006: 173), humanistic psychology places
great emphasis on one's freedom of choice,
sensitivity, and personal accountability. Humanistic
psychology emphasizes individual accomplishments,
motivations, emotions, and desires, as its themes
suggest. Individual self-actualization, according to
this view, is the goal of education.
To achieve humanist education, learning patterns
or cultures should be applied in schools. This pattern
is an educational pattern that is positive and has
humanist values, such as a democratic education
pattern, an education pattern that pays attention to the
uniqueness of students in learning, an education
pattern that maintains harmonious relations between
school members, both between students and students,
teachers with teachers, as well as teachers with
students (Suswanto et al., 2015). The learning
principle in the Independent Curriculum is through
differentiated learning, namely the variety of services
from a review of differences in the characteristics of
students. Differentiated learning is learning that
accommodates, serves, and recognizes the diversity
of students in learning according to students'
readiness, interests, and learning preferences
(Tomlinson, Moon, Imbeau, 2015). Every learner has
various kinds of differences in abilities, experience,
talents, interests, language, culture, way of learning,
and many other differences. The learning process
needs to pay attention to the differences in students
and provide services that suit the needs of their
students. Providing services that are adjusted to the
level of readiness, interest and learning profile of
students (learning styles) is a form of liberating
students in learning. Freedom to learn means that
students are not required to be the same in all respects
as others. Each individual has their own space for
movement according to their characteristics and
needs. The freedom of movement to carry out
learning is in line with humanistic theories that lead
to humanizing humans. The direction of independent
learning for students is focused on how each
individual is influenced and guided by himself related
to his experiences. Independent learning provides
opportunities for students to obtain meaningful
learning. According to Ausubel (in Thobroni, 2015)
learning is said to be meaningful if the information
that students will learn is arranged according to the
cognitive structure that students have, so that students
can associate new information with their cognitive
structure.
The Independent Curriculum is an option or
alternative for schools depending on how well the
readiness of each school is in its implementation. This
shows that schools are not forced to use the Self
Curriculum in the part of their education program that
is not yet enrolled in a driving school. When it comes
to carrying out the curriculum and achieving its goals,
the teacher plays an important and vital role. The
ability to carry out and succeed in the teaching and
learning process using the curriculum used in schools
is a requirement for an educator. The success of
implementing the ongoing curriculum will be
measured by the teacher's ability to carry out the
curriculum. Whether the curriculum is used in
educational settings depends on the teacher's
knowledge and ability to understand the relevant
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
344

curriculum. According to Minister Nadiem, teachers
must first introduce children to the importance of
freedom of thought. According to Nadiem, learning
occurs as a result of the process of combining teacher
competencies at all levels with the existing
curriculum and basic competencies.
Technology can be used as a tool by educators to
facilitate the educational process. In addition,
students can also explore more knowledge and carry
out different learning processes. Learning in class can
be made more fun by implementing technology-based
learning innovations. In the current digitalization era,
almost all access to information and materials can be
found in cyberspace, both accessing pages and
applications. The Ministry of Education and Culture
is very aware of the current needs, because by
utilizing technology it can reach and distribute
policies more broadly, as well as optimize the
implementation of the Merdeka curriculum through a
differentiated learning process. During differentiated
learning, there must be classrooms that support an
environment where everyone in class is welcomed
and accepted, everyone respects each other, students
feel as safe as possible in their class
Teaching to achieve student success. There is a
real sense of equality by students. teachers and
students work together to succeed. Ulamoliddinova
2019: 321). The use of technology can be a teacher's
choice to carry out differentiation learning in the
classroom. According to, Li and Atkins in Genevieve
Marie Johnson (2010) note that exposure to
computers during the preschool years is associated
with the next child's school readiness which greatly
influences children's development. Kumtepe (2006)
observed that computer literate children assessed by
their teachers suggested that children's social skills
were higher than children who were less computer
proficient. According to Fischer and Gillespie in
Sharon A. (2004). Explaining the results of their
research in the Head Start class, showing that
programs in computers such as (1) computer software
can encourage children to explore and go beyond
their thinking, (2) computers are just another option
in class, (3) computers are a bridge for children to
think abstractly, and (4) computer technology can
stimulate behavior among children.
Humanistic psychology is the product of many
people and the synthesis of various ideas, especially
existential and phenomenological ideas. Humanistic
psychology is part of the universal humanistic
movement, which also includes social sciences,
education, biology, and the philosophy of science,
and is an expression of a larger view of the world.
According to Brewster Smith (1969), he was a
member of a larger movement that aspired to create a
human science that was also aimed at humans and
promised to be fair to human humanity. According to
humanistic thought, education must begin with the
aim of making human beings more like themselves.
Therefore, compared to learning psychology,
humanistic learning theory has a more abstract nature
and is more closely related to the study of philosophy,
personality theory, and psychotherapy. Content
learned from the learning process itself is a major
topic in humanistic theory. This learning theory
focuses more on educational ideas that help create the
perfect person and the best possible learning
environment. In other words, unlike other learning
theories, this theory is more concerned with the idea
of learning in the most ideal conditions than
understanding the actual learning process. This
humanistic notion can be observed in action in
Ausubel's learning strategy. According to his
understanding of learning, which is also part of this
cognitive school, learning is a meaningful integration.
Acquired knowledge is integrated with previous
knowledge and linked to newly learned topics.
Absorption of new knowledge on the existing
cognitive structure of learners depends on motivation
and desire on their part, therefore motivational factors
and emotional experiences are very decisive in the
learning process. According to humanistic theory,
any learning method can be applied as long as its goal
is to humanize humans, which includes maximizing
self-actualization, self-understanding, and self-
realization of learners.
The goal of humanism is in line with the goal of
designing the independent learning program, which is
to humanize humans (Yamin & Syahrir, 2020).
Teachers and students are free to determine learning
methods, methods, objectives, materials, and
assessment techniques as long as they are in
accordance with the goals set by the curriculum.
Teachers freely translate the curriculum according to
their wishes and creativity. The teacher determines
how to learn together with their students. There is
freedom of thought in this independent learning.
Teachers and students can actualize themselves
optimally so that the learning process takes place in a
meaningful and meaningful way. Understanding that
each student has differences is learning that is very
appropriate to the needs of students. That's why in
humanistic theory it is conveyed that teachers should
not blame students for a student's mistake before the
teacher conducts a further review regarding whether
the needs of students as human beings have been
fulfilled or not. Learning can be done anywhere both
in the classroom and outside the classroom. Learning
Implemention of Humaniststic Learning Theory on the Independent Learning Curiculum in Harapan Kita Kindergarten Sungai Liku Pesisir
345

becomes meaningful if learning can be done by
providing direct experience to students and in
accordance with the needs of students. Students are
not limited in exploring the environment with a full
sense of security so that students can maximize self-
actualization. Individual learning on the concept of
independent learning is in accordance with
humanistic theory where students learn according to
their abilities without being anxious compared to
other students. The role of the teacher here is as a
mover, moving weak students to become more
understanding by obtaining more training and
learning and moving students who already understand
competence to become richer with knowledge.
Individual success is largely determined by the
individual himself. Therefore, Rogers in Rachmahana
(2018) said that learning in humanistic learning
theory should not be excessively dependent on
anything by a student. Students recognize themselves,
know their weaknesses and strengths so they can get
the best way they choose to acquire the knowledge
demanded by the curriculum. Assessment on
humanistic theory is also in line with the concept of
independent learning where assessment is not only
carried out on results but also on the learning process.
Assessment also should not ignore aspects of the
attitudes that become the personality of students.
Assessment is not the only decision in determining
whether the learner is achieving or not. Assessment
must be carried out thoroughly and there is no ranking
system which causes a lot of anxiety for students and
parents of students. The ranking system will only
create gaps that lead to teacher subjectivity in
assessing individual students. In the process of
liberating students in thinking, a driving teacher is
needed who of course has gained freedom of thought.
Teachers need to guide and direct their students in
recognizing individual students so that students can
make the right decisions in determining how to learn
(BPK Penabur, 2020; Rezeki, 2020; Wijayanti,
2020). Teachers are no longer burdened with
administrative tasks so that teachers have more time
to explore the potential of themselves and their
students. The teacher is also not burdened with
making a lesson plan with many pages which can
make the teacher frustrated and tiring. Free learning
frees important figures in education, namely teachers
and students. Freedom of thought which is very
important is pursued first (Bentri & Hidayati, 2020;
Faizah, 2020; Manalu, 2020).
The independent learning curriculum is one of the
approaches that can be used in early childhood
education. Different teachers view the Independent
Curriculum differently. The notion that the
Independent Curriculum prioritizes the needs and
interests of students is in line with the definition of
independence. The New Paradigm Independent
Curriculum aims to develop students to become
lifelong learners through learning. An important
feature of the Pancasila Student Profile includes
lifelong learners. Through the Independent
Curriculum which includes extracurricular programs,
and the Pancasila Student Profile Strengthening
Project, the learning process with a new paradigm is
carried out in PAUD. Meanwhile, there are
extracurricular programs other than PAUD. This is in
line with the characteristics of PAUD learning which
believe that every child has a distinctive appearance
and has the potential for both strengths and
weaknesses. Supriano's assertion, Director General of
GTK, that the curriculum concept gives schools
independence to interpret the basic competences of
the curriculum itself and become an assessment for
each school, supports the PAUD teacher's perception
that an independent curriculum is a dynamic
curriculum. The evolution of an increasingly
sophisticated and dynamic era is the cause of
curriculum adjustments. The curriculum is adaptive
and dynamic, constantly changing by taking into
account the characteristics of students and building
competencies according to their current and future
needs. One option in the effort to restore learning for
educational units is the Independent Curriculum. The
findings indicate that instructors are more inventive
learners because of the Self-Curriculum. The function
of the curriculum for teachers, aims to assist students
in learning. Teachers are now more creative and
flexible in designing their activities to achieve
student-centered learning goals thanks to the
Pancasila Student Profile Strengthening Project
activities. Teachers can concentrate on improving
learning outcomes in early childhood through the
Independent Curriculum. Learning outcomes in
PAUD based on Ministerial Decree 033/H/KR/2022
include identification, basic literacy skills, arithmetic,
science, technology, engineering, and art. They also
incorporate religious and ethical principles.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
The implementation of Independent Curriculum as
proclaimed by the Minister of Education and Culture
becomes means of improvement and development
sustainable education unit especially the students and
educators. This can be seen from the concept and the
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
346

advantages of independent curriculum, the
implementation of independent curriculum through
teacher’s teaching module as well implementation in
learning. Humanistic learning is a learning theory that
treats students as active participants in the learning
process. The idea of a humanistic learning process
that pays attention to what is needed and interests of
students is a fundamental idea in the field of
education. Teachers are more inventive in class due
to Self Curriculum. The goal of a teacher's curriculum
is to direct student learning. Teachers are now more
creative and flexible in designing their activities to
achieve student-centered learning goals thanks to the
Pancasila Student Profile Strengthening Project
activities. Teachers can concentrate on improving
learning outcomes in early childhood through the
Independent Curriculum. According to Ministerial
Decree 033/H/KR/2022, learning outcomes for
PAUD must cover identification, basic literacy skills,
mathematics, science, technology, engineering, and
arts. These results are consistent with instructors
stimulating play and offering carefully planned
learning through stimulation in carefully planned
situations to maximize the potential of young
children. The idea behind incorporating early
childhood education into the curriculum calls for
convenience for practitioners and the general public.
Suggestion
Related to the implementation of the independent
curriculum, the sustainable monitoring and coaching
by the centraland local government can be done in
accordance concept that has been developed so that
there is education equity, achievement of the goals of
national education and reinforcement of the profile of
Pancasila student.
REFERENCES
Darsono, Max. 2001. Belajar dan Pembelajaran.
Semarang: IKIP Semarang Press
Kartono, K dan Gulo, D. 1987. Kamus Psikologi. Bandung:
CV Pionir Jaya.
Mulyasa. 2012. Manajemen Pendidikan Karakter. Jakarta:
PT Bumi Aksara
Purwo, Bambang Kaswanti. 1989. (ed.).PELLBA 2:
Pertemuan Linguistik Lembaga Bahasa Atma Jaya.
Jakarta: Lembaga Bahasa Unika Atma Jaya.
Kartono, K dan Gulo, D. 1987. Kamus Psikologi. Bandung:
CV Pionir Jaya.
Saam, Zulfan dan Wahyuni, Sri. 2012. Psikologi
Keperawatan. Jakarta: Rajawali Pers.
Sadulloh, Uyoh. 2006. Pengantar Filsafat Pendidikan.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Soemanto, Wasty.1998. Psikologi Pendidikan. Jakarta: PT.
RajaGrafindo Persada
Sudarsono, Kamus. 1993. Filsafat dan Psikologi. Jakarta:
Rineka Cipta.
Uno, Hamzah B.2006. Orientasi Baru Dalam Psikologi
Perkembangan. Jakarta: Bumi aksara
Windayani. 2021. Teori Dan Aplikasi Pendidikan Anak
Usia Dini. Aceh: Yayasan Penerbit Muhammad Zaini
Yaswinda. 2019. Model Pembelajaran Sains Berbasis
Multisensory Ekologi (PSB MUGI) Bagi Anak Usia
Dini. Jawa Barat: Edu Publisher
Zuriah, Nurul.2006. Metodologi Penelitian Sosial dan
Pendidikan Teori-Aplikasi. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Sudarsono, Kamus. 1993. Filsafat dan Psikologi. Jakarta:
Rineka Cipta.
Uno, Hamzah B.2006. Orientasi Baru Dalam Psikologi
Perkembangan. Jakarta: Bumi aksara
Windayani. 2021. Teori Dan Aplikasi Pendidikan Anak
Usia Dini. Aceh: Yayasan Penerbit Muhammad Zaini
Yaswinda. 2019. Model Pembelajaran Sains Berbasis
Multisensory Ekologi (PSB MUGI) Bagi Anak Usia
Dini. Jawa Barat: Edu Publisher
Zuriah, Nurul.2006. Metodologi Penelitian Sosial dan
Pendidikan Teori-Aplikasi. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Implemention of Humaniststic Learning Theory on the Independent Learning Curiculum in Harapan Kita Kindergarten Sungai Liku Pesisir
347
