
The Effect of Blended Learning and Digital Literacy on Students'
Reading Comprehension
Willy Satria
1a
, Ifan Iskandar
2b
and Ratna Dewanti
2c
1
Doctoral Students of Applied Linguistics, Universitas Negeri Jakarta, Indonesia
2
Lecturer of Applied Linguistics, Universitas Negeri Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Blended Learning Model, Digital Literacy, Flipped Classroom, a La Carte, Reading Comprehension, English
Text.
Abstract: Blended learning model and digital literacy is an interesting theme these days. There has recently been a lot
of research done on this theme, but not in relation to reading comprehension. It has a purpose to discover the
impact of the blended learning model and digital literacy on students’ for English reading comprehension
skill. The experimental method of a 2x2 ANOVA factorial design was based on second-year students in the
academic year of 2021-2022. Two instruments were used to collect data: a reading comprehension test
(multiple choice) and a digital literacy questionnaire. The data analysis used a two-way ANOVA with the F
test at a significance level of 0.05. The discoveries of this study are: 1) There was no significant difference
on reading comprehension between students who are taught using the flipped classroom and a la carte; 2)
There were significant differences between students with high digital literacy and students with low digital
literacy; and 3) There was no interaction effect between the blended learning model and digital literacy on
reading comprehension ability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Based on preliminary observations and the author's
experience in examining assignments and several
exam sheets of English education study programme
students at PGRI University of West Sumatra, some
problems are still worth reviewing both from the level
of reading comprehension and understanding of the
topic of the text being read. One of the results of the
reading comprehension test test found that out of a
total of 30 students who took the Advanced Reading
course obtained an average score of 62.4. Where the
average score obtained by students ranges from 60-
70.
The main difficulty experienced by students in
mastering reading comprehension skills is within the
students themselves. They have low enthusiasm and
motivation when faced with a lot of text. In line with
(Nanda & Azmi, 2020), conducting in-class research
at the University of Dharmas Indonesia, which states
that motivation is the main factor that becomes a
hurdle in learning reading comprehension so that
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9739-2359
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8078-3639
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8184-0321
students are not interested in reading and
concentrating on analysing the text. Furthermore, low
knowledge of the topic of the text being read. This is
in line with the findings of (Kikas, Silinskas,
Mädamürk, & Soodla, 2021) who stated that the texts
given were not familiar to students so they struggled
and spent a long time to understand one text that was
more than 10 sentences.
Continuing from the previous paragraph, the
researcher assumes that the blended learning can be
used as a solution in improving learners' English
reading comprehension skills. Where blended
learning is able to actively engage learners to think
creatively, self-learn and interactively which is the
key to learning itself. Apart from these reasons,
effective and efficient factors are one of the reasons
why this learning model was chosen. This is in line
with (Geng, Law, & Niu, 2019) which states that
learning with any kind of model and model will not
have a good and maximum impact if it is not used
appropriately and efficiently.
374
Satria, W., Iskandar, I. and Dewanti, R.
The Effect of Blended Learning and Digital Literacy on Students’ Reading Comprehension.
DOI: 10.5220/0012201400003738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Innovation in Education (ICoIE 4 2022) - Digital Era Education After the Pandemic, pages 374-380
ISBN: 978-989-758-669-9; ISSN: 2975-9676
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

As a study material, this research is based on 5
primary reference sources that are used as a
benchmark. Research conducted by: 1. (Muharlisiani,
2015) with the title “The Usage of Skype Messenger
on Blended Learning, Weblog and E-learning to
Improve Student’s Writing Ability of the Fourth
Semester in English Education Department, Faculty
of Language and Science” Wijaya Kusuma
University, 2. (Tang & Chaw, 2016) with the title
“Digital Literacy: A Prerequisite for Effective
Learning in a Blended Learning Environment”, 3.
(Broadbent, 2017) with the title
“Comparing Online and Blended Learner's self-
regulated Learning strategies and Academic
performance”, and 4. (Kheirzadeh & Birgani, 2018)
with the title “Exploring the Effectiveness of Blended
Learning in Improving Reading Comprehension
among Iranian EFL Students”, and 5. (Alqahtani,
2019) with the title “The Usage of Edmodo: The
Impact on Learning and Students’ response”. The
variables studied by the researcher in order are about
1) blended learning, 2) digital literacy, 3) reading
comprehension. Furthermore, these three research
objects are included in the variables that will be
studied next.
So the researchers in this study conducted
experimental research to examine the effect of the
blended learning model using two classes
(Experiment class and control class) where each class
received different treatments. The experimental class
was treated with the flipped classroom model and the
control class was treated with the a la carte model,
although both types of models are contained in
blended learning.
Formulation problems of the research were posed
with these following research questions (Research
Question):
Is there a difference in reading comprehension of
students taught using the flipped classroom model
compared to students taught using the a la carte
model?
Is there a difference in reading comprehension
between students who have high digital literacy skills
and students who have low digital literacy skills?
Is there an interaction effect between the blended
learning model and digital literacy on students'
reading comprehension?
1.1 Theoretical Study
1.1.1 Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension is a complex process of
shaping the meaning in the text by interacting with it
through a combination of prior knowledge, past
experience, information in the text, the reader's own
stance (Pardo, 2004). In gaining good comprehension
it is possible for readers to question, interpret, and
evaluate what they read so that through reading they
can have the ability to build knowledge, improve
understanding, and ultimately change thinking
(Harvey & Goudvis, 2007).
There are various factors that play a role in
reading comprehension, namely; one of them is social
motivation so that readers not only think about what
they read but about what they learn and how it is
formed so that they are able to develop insights and
think more deeply and critically about the topic at
hand and the world around them.
In addition, culture can also play a role in
understanding a text based on the extent to which the
writer and reader match the culture embraced in the
text (Erten & Razi, 2009). The reader's cognitive
development can play a role in his/her ability to
understand the text by influencing his/her ability to
evaluate it in different ways. Not only do readers use
their skills, knowledge and cognition to comprehend
the text but the culture, goals and motivations they
bring to the text can also have an impact on their
comprehension. In addition, readers need a variety of
skills such as basic language skills, decoding skills,
and higher-order thinking skills to be able to connect
and understand texts. They also need to have different
types of knowledge including background knowledge
and content knowledge.
Readers need to be able to connect known
information with new information to learn and create
meaning.
Furthermore, the purpose of reading can also
influence or change the way readers understand a
particular text (Aarnoutse & Schellings, 2004).
Motivation can also influence the interest, purpose,
emotion or perseverance with which a reader
comprehends a text. More motivated readers will try
harder to understand and construct meaning from a
text by applying a wider range of strategies while less
motivated individuals tend to put in less effort and are
rarely able to create meaning as strongly as highly
motivated readers (Pardo, 2004). In line with Pardo,
skilful readers use thinking-while-reading strategies
to help them understand what they are reading
(Aarnoutse & Schellings, 2004).
Connecting what readers know with new
information is at the heart of learning and
comprehension. Skilled readers ask questions about
themselves, the author, and the text they are reading.
They do this before, during, and after reading the text.
They also draw conclusions during and after reading
The Effect of Blended Learning and Digital Literacy on Students’ Reading Comprehension
375
and distinguish important from less important ideas in
the text.
Skilled readers can synthesise information within
and across texts to create meaning. They can monitor
the adequacy of their understanding and correct
incomplete understanding (Harvey & Goudvis,
2007). Therefore, both young and adult readers alike
can benefit from comprehension strategy instruction
(Guthrie, 2004). However, proficient readers are able
to adapt strategies to suit their reading goals
(Aarnoutse & Schellings, 2004; Harvey & Goudvis,
2007).
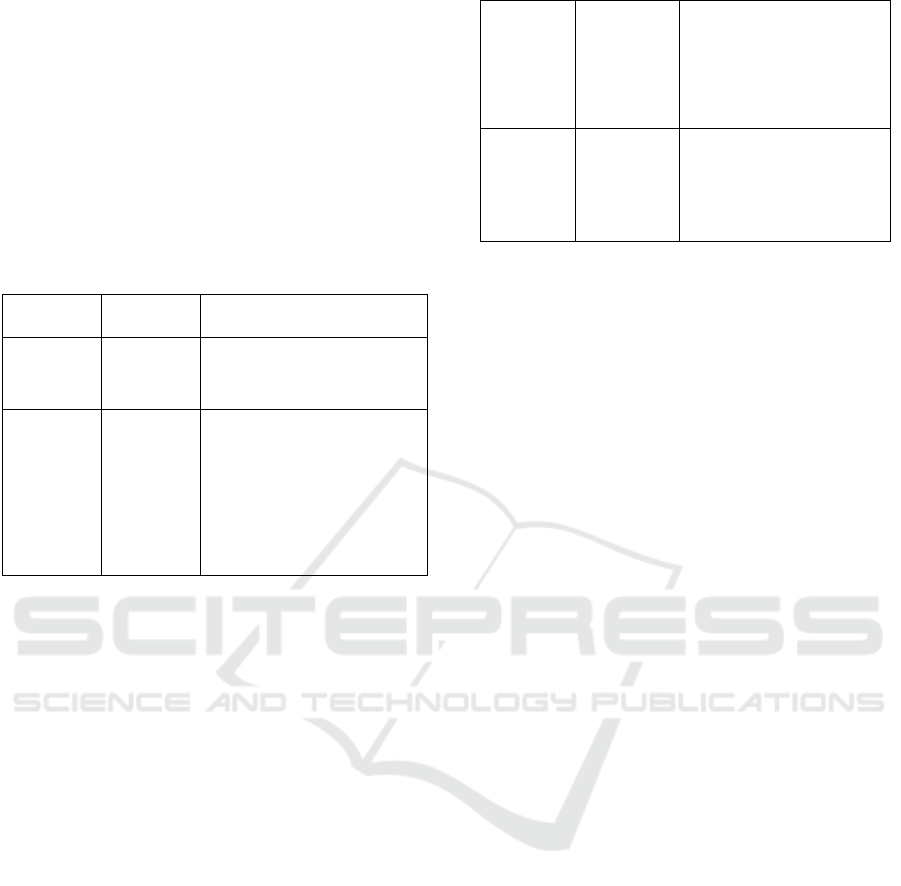
Online
Percentage
Learning
Type
Description
0% Tradisional
( T a t a p M u k a )
Learning with On-lin
e
posted content not delivered i
n
writing or verbally
1 sampai
29%
Facilitated
Web
Learning to use we
b
facilities to facilitate somethin
g
very important in face-to-fac
e
learning. By using Learnin
g
Management System (LMS) o
r
web pages, for example: t
o
upload syllabus, material
s
q
uizzes, exams.
1.1.2 Blended Learning
Blended learning is a combination of two learning
models consisting of face to face classes and
information technology (e-learning) as written by
(Garrison & Kanuka, 2004). Added by (Jachin &
Usagawa, 2017), blended learning refers to learning
activities that combine aspects of on-line and face-to-
face learning. Furthermore, there are several aspects
of information technology such as web-based
learning, mobile learning, video streaming,
asynchronous and synchronous audio communication
combined with face-to-face learning (Graham, 2005).
(Bonk & Graham, 2009) added that blended learning
is a combination of different training media
(technologies, activities, types of activities) used to
form an optimum training programme for specific
learners. The term blended means that training is
delivered in a traditional educator-led manner
supplemented by other electronic formats.
The difference between blended learning and e
learning is the percentage of online media used in the
learning or training. (Allen & Seaman, 2011)
formulated the percentage of the learning model
based on the use of online media used as follows:
30 sampai
79%
Pembelajara
n
bauran
(Blended
Learning)
Learning with a face-
to-face system. The
proportion of online content
and substance using online
and face-to-face
discussions is balanced.
80+% Online
Learning
It is learning that is
mostly or even entirely
online. This type of
learning does not utilise
face-to-face meetings at all.
1.1.3 Digital Literacy
The term digital literacy was first expressed by
(Gilster, 1997) in his book entitled Digital Literacy,
where digital literacy is defined as an attitude to
understand and use information in various forms from
a very wide range of sources accessed through
computer devices. Later, the term developed as stated
by (Bawden, 2001) who stated that digital literacy is
rooted in computer literacy and information literacy.
Furthermore, (Hague & Payton, 2010) explains
digital literacy as an attitude to create and share
information in different modes and formats; which
aims to create, collaborate and communicate
effectively and understand how and when digital
technology should be used to support the process.
Then (Paul, 2017) explains the definition of Digital
Literacy as an attitude towards the field of science to
use remote technological devices for various
purposes.
In line with the description above, the American
Library Association adds that digital literacy is an
attitude of using information and communication
technology to search, evaluate, create, and
communicate information, which requires both
cognitive and technical skills. Finally, according to
(Culture, 2017) digital literacy is the knowledge and
skills to use digital media, communication tools, or
networks to find, evaluate, use, create information,
and utilise it in a healthy, wise, intelligent, careful,
appropriate, and law-abiding manner in order to
foster communication and interaction in everyday
life. In conclusion, from some of the definitions
above, it can be concluded that digital literacy is the
ability to find, understand, evaluate, create and
communicate digital information in various formats
from various sources when presented through
information technology.
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
376
2 METHODOLOGY
The research based on an experimental method with
a 2X2 factorial design to test the hypothesis to prove
the existence of a causal relationship between the two.
The design can be seen in the following table:
Table 1: Factorial Design 2x2.
Treatmen
t
Attribute
Blended Learning
Model (A)
Experimental
Group
(Flipped
Classroom) A1
Control
Group
(A La
Carte) A2
Digital
Literacy (B)
High Digital
Letacy (B1)
A1B1 A2B1
Low Digital
Letacy (B2)
A1B2 A2B2
The population of this study were students of the
English education study programme who took
Advanced Reading courses in the odd semester of the
2021-2022 academic year consisting of classes A, B
and C. Two (2) classes consisting of 30 students for
each class were taken deliberately to represent the
population. Later two (2) classes consisting of 30
students for each class were taken deliberately to
represent the population. Then these two classes will
be divided into experimental classes and control
classes using coins. The experimental class will get
treatment where students in the group are taught using
the flipped classroom model and the control class will
get treatment by being taught using the a la carte
model.
Data Collection Technique Researchers used 2
(two) instruments, namely reading comprehension
tests and digital literacy questionnaires that had gone
through validity and reliability tests first. Completion
of the instrument in the form of a questionnaire is
carried out at a time before the implementation of the
treatment, then the reading comprehension test is
given after the students get treatment. The data
collected were then statistically analysed using a two-
way analysis of variance (ANOVA)
technique with a significance level of 0.05.
However, before the data from the hypothesis test
results are carried out, normality test and
homogeneity test are carried out as prerequisite tests.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION
3.1 Data Description
The data obtained from the results of the research
design include students' ability to understand reading
texts in English after being taught using the flipped
classroom and a la carte models that have high digital
literacy.
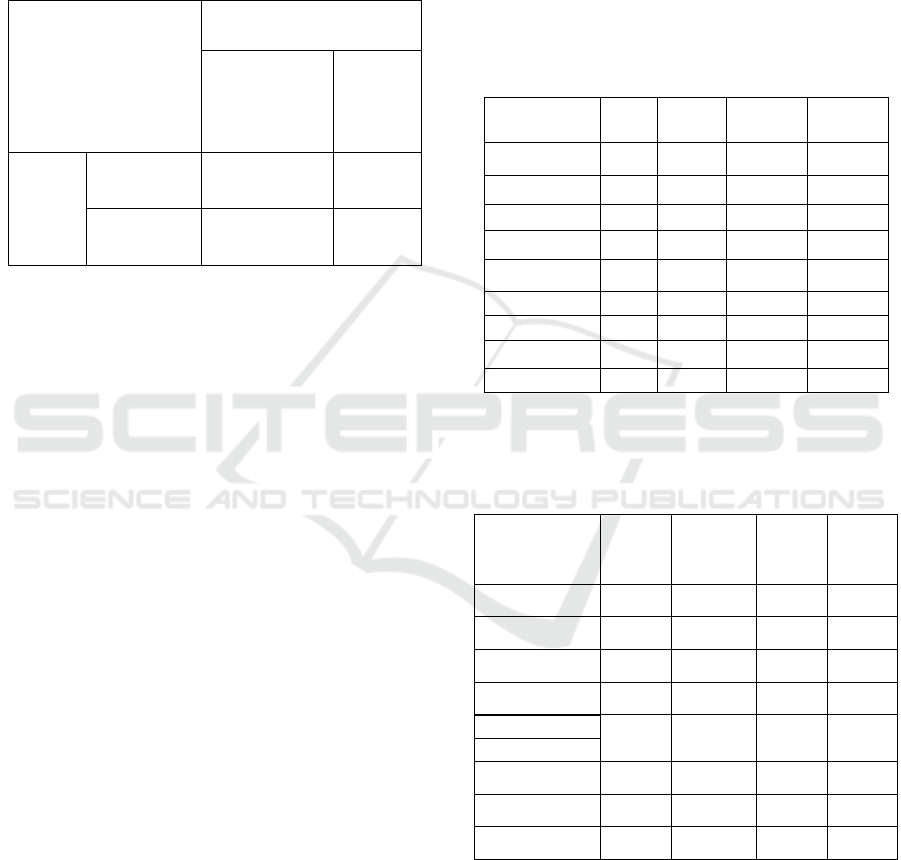
Table 2: Summary of Group Description Data.
MPB
(A1)
MPT
(A2)
SLDT
(B1)
SLDR
(B2)
N Valid 16 16 16 16
Missing 0 0 0 0
Mean 21 17,44 18,88 19,56
Median 21 17,5 21 20
Std Deviation 3,33 3,69 4,20 4,53
Variance 11,07 13,6 17,65 20,55
Mode 21 22 21 20
Highest 27 22 23 27
Lowes
t
14 8 8 13
The following table also shown the sub-group’s
descriptive data summary.
Table 3: Summary of Sub-Group Description Data.
MPB-
SLDT
(A1B1)
MPT-
SLDT
(A2B1)
MPB-
SLDR
(A1B2)
MPT-
SLDR
(A2B2)
N
Vali
d
8 8 8 8
Missing
0 0 0 0
Mean
20,25 17,50 21,75 17,38
Median
21 17,5 21 17,5
Std Deviation
Lowes
t
14
2,76 4,60 5,95 2,83
Variance 7,64 21,14 35,43 8,00
Mode 21 22 21 18
Highes
t
23 22 27 22
This test is conducted to determine whether the
data from each group comes from a normally
distributed population or not. It is expected that the
sample of 60 people consisting of 2 groups of students
must be normally distributed.
A summary of the results of the normality test
calculation is in the table below.
The Effect of Blended Learning and Digital Literacy on Students’ Reading Comprehension
377
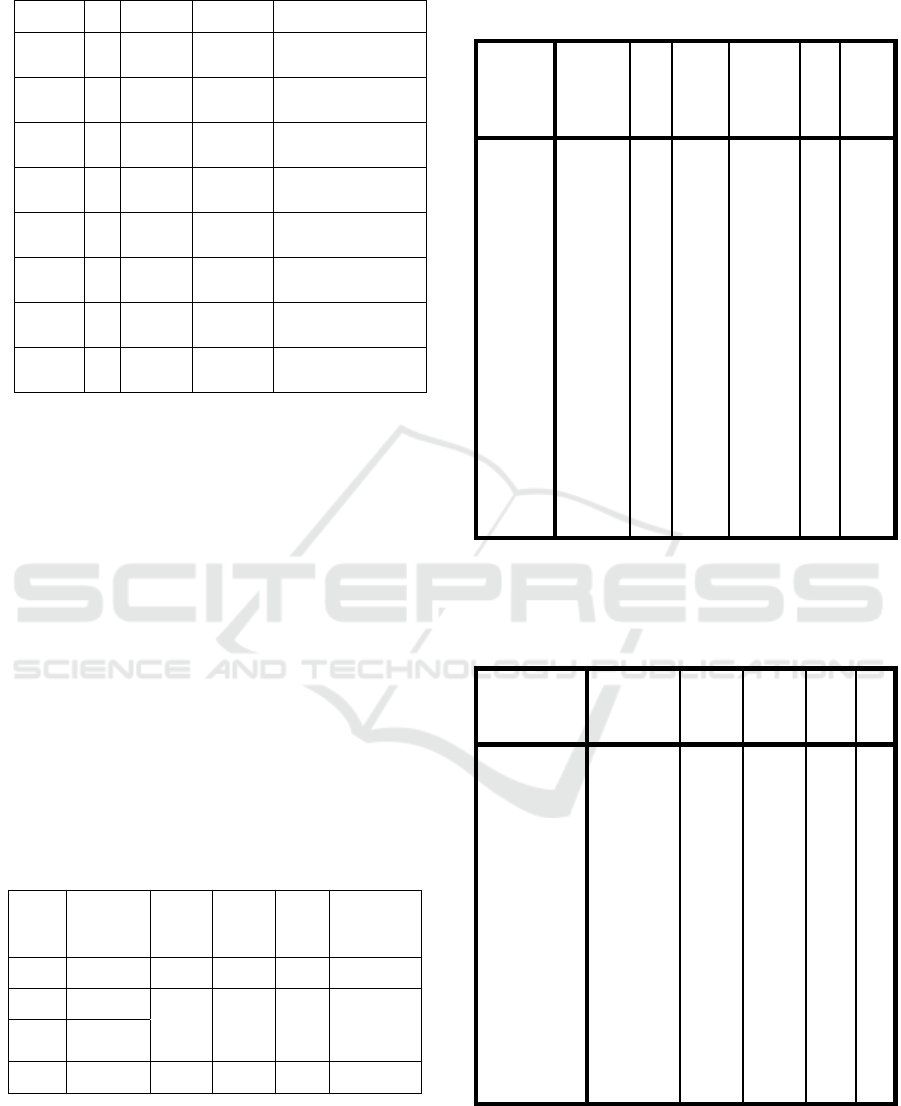
Table 4: Summary of Normality Test Calculation Results.
Group
N
L
coun
t
L
table Keterangan
A
1 14 0,1635 0,227
N
ormally
Distribute
d
A
2 14 0,1239 0,227
N
ormally
Distribute
d
B
1 14 0,1590 0,227
N
ormally
Distribute
d
B
2 14 0,0924 0,227
N
ormally
Distribute
d
A
1
B
1 7 0,1679 0,300
N
ormally
Distribute
d
A
2
B
1 7 0,1861 0,300
N
ormally
Distribute
d
A
1
B
2 7 0,2143 0,300
N
ormally
Distribute
d
A
2
B
2 7 0,1214 0,300
N
ormally
Distribute
d
From the table above, it is known that tested for
normality that the reading comprehension scores of all
groups of students tested for normality by the Liliefors
test give the value of L0 or the observation value of
Liliefors is smaller than the Ltabel or the critical value
of L at the significance level α = 0.05 with n = 7, the
value of Lt = 0.300 and n = 14, the value of Lt = 0.227.
Thus it can be concluded that all reading
comprehension scores of all sub-populations in this
study come from a normally distributed population. In
the appendix, it can be seen from the detail regarding
of the results from the normality test.
Homogeneity Test
F-test
From the calculation, the value of Fcount =
1.89 and the value of Ftable = 2.58 at the
significance level α = 0.05 and dk1 = 13 and dk2 = 13
so that H0 is accepted
Table 5: Summary of Homogeneity Test Results.
Group Variance
Join
t
Varian
ce
X
2
coun
t
X
2
tab
el
Conclusion
A1B1 4,57
A1B2 4,95
6,64 3,15 7,82 Homogen
A2B1 3,90
A2B2 13,14
3.2 Research Hypothesis Testing
By using the two-way ANOVA table, the analysis
results are obtained as in the table below:
Table 6: Analysis of Variance Result Using SPSS. Tests of
Between-Subjects Effects Dependent Variable : Reading
Comprehension.
Source
Type III
Sum of
Squares
df
Mean
Squar
e
F
Sig.
Partia
l Eta
Squar
ed
Correcte
d Model
72.000
a
3
2
4.000 1.756 .182 .180
Intercep
t
10.108.0
00
1
1
0108.
000
7
39.610 .000 .969
Learning
Model
.571
1
.571 .042 .840 .002
Digital
Literacy
69.143
1
6
9.143 5.059 .034 .174
Learning
Model &
Digital
Literac
y
2.286
1
2.286 .167 .686 .007
Erro
r
328.000 24
1
3.667
Total 10.508.0
00
28
Correcte
d Total
400.000 27
R Squared = ,180 (Adjusted R Squared = ,078)
Tests of Between-Subjects Effects
Dependent Variable: Reading Comprehension
Source Type III
Sum of
Squares
df
Mean
Square
F
Sig.
Corrected
Model
110.594
a
3
36.865 2.860 .055
Intercept
11819.531
1
11819.
531
917.0
68
.000
Learning
Model
101.531
1
101.53
1
7.878 .009
Digital
Literac
y
3.781
1
3.781 .293 .592
Learning
Model &
Digital
Literac
y
5.281
1
5.281 .410 .527
Erro
r
360.875 28 12.888
Total
12291.000 32
Corrected
Total
471.469 31
R Squared = ,235 (Adjusted R Squared = ,153)
Figure 1: Interaction Test Plot.
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
378

Further discussion of the results of testing the
research hypothesis is as follows:
First Hypothesis: There is no difference in
students' ability in reading comprehension using
English between those who learn with the flipped
classroom model and those who learn with the a la
carte model.
Second Hypothesis: There is a difference in
reading comprehension between students that have a
decent digital literacy skill and students with the low
digital literacy skill.
Third Hypothesis: Lack of acknowledgement
between learning model and digital literacy on
students' reading comprehension.
4 CONCLUSION
The findings that have been stated in the results of data
processing can be summarised that the reading
comprehension of English texts in the group of
students taught using the flipped classroom model is
not significantly better than the group of students
taught using the a la carte model. Then the results of
the English text reading comprehension test for
students who have different digital literacy taught
using the same model have different results. Finally,
there was no interaction between the blended learning
model (flipped classroom model, a la carte model)
and digital literacy (high digital literacy, low digital
literacy) on reading comprehension.
REFERENCES
Aarnoutse, C., & Schellings, G. (2004). Learning Reading
Strategies by Triggering Reading Motivation.
Educational Studies, (December 2003).
https://doi.org/10.1080/0305569032000159688
Allen, I. E., & Seaman, J. (2011). Going the Distance.
Newburyport: Sloan Consortium. Diambil dari
http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED529948.pdf
Alqahtani, A. S. (2019). The Use of Edmodo: Its Impact on
Learning and Students’ Attitudes toward It. Journal of
Information Technology Education: Research, 18, 319–
330. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.28945/4389
Bawden, D. (2001). Information and Digital Literacies: A
Review of Concepts. Journal of Documentation, 57(2),
218–259. Diambil dari https://doi.org/10.1108/
EUM0000000007083
Bonk, C. J., & Graham, C. R. (2009). Handbook of Blended
Learning: Global Perspective, Local Designs. San
Franscisco: Pfeiffer Publishing. Diambil dari
http://curtbonk.com/toc_section_intros2.pdf
Broadbent, J. (2017). Comparing online and blended
learner ’ s self-regulated learning strategies and
academic performance. The Internet and Higher
Education, 33(January 2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.iheduc.2017.01.004
Erten, I. H., & Razi, S. (2009). The effects of cultural
familiarity on reading comprehension.
Reading in Foreign Language, 21(1), 60–77. Diambil dari
https://nflrc.hawaii.edu/rfl/April2009/articles/erten.pdf
Garrison, D. R., & Kanuka, H. (2004). Blended learning :
Uncovering its transformative potential in higher
education. Internet and Higher Education, 7, 95–105.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2004.02.001
Geng, S., Law, K. M. Y., & Niu, B. (2019). Investigating
Self-directed Learning and Technology Readiness in
Blending Learning Environment. Internasional Journal
of Educational Technology in Higher Education.
https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0147
-0
Gilster, P. (1997). Digital Literacy. New York: John Wiley &
Sons Inc.
Graham, C. R. (2005). The Handbook of Blended Learning.
San Franscisco: Pfeiffer Publishing. Diambil dari
http://www.publicationshare.com/c1-Charles-Graham-
BYU--Definitions-of- Blended.pdf
Guthrie, J. T. (2004). Teaching for Literacy Engagement.
Journal of Literacy Research, 36(1), 1– 30.
https://doi.org/10.1207%2Fs15548430jlr3601_2
Hague, C., & Payton, S. (2010). Digital literacy across the
curriculum a Futurelab handbook. Bristol: Futurelab
Innovation in Education. Diambil dari
www.futurelab.org.uk/projects/digital-participation
Harvey, S., & Goudvis, A. (2007). Strategies That Work:
Teaching Comprehension for Understanding and
Enggagement (2 ed.). Portland: Etenhouse Publisher.
Jachin, N., & Usagawa, T. (2017). Potential Impact of
Blended Learning on Teacher Education in Mongolia.
Creative Education, 8, 1481–1494.
https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2017.89104
Kebudayaan, K. P. dan. (2017). Panduan Gerakan Literasi
Nasional. (Atmazaki, N. B. V. Ali, W. Mulidan,
Miftahussururi, N. Hanifah, M. N. Nento, … L. A.
Mayani, Ed.). Jakarrta Timur: Kementrian
Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. Diambil dari http://gln.
kemdikbud.go.id/glnsite/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/
panduan-gln.pdf
Kheirzadeh, S., & Birgani, M. B. (2018). Exploring the
Effectiveness of Blended Learning in Improving
Reading Comprehension among Iranian EFL Students.
Journal of Applied Linguistics and Language
Reasearch, 5(1), 106–120.
Kikas, E., Silinskas, G., Mädamürk, K., & Soodla, P.
(2021). Effects of Prior Knowledge on Comprehending
Text About Learning Strategies, 6(October), 1–15.
https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2021.766589
Muharlisiani, L. T. (2015). Using Skype Messenger on
Blended Learning, Weblog and E-learning to Improve
Students’ Writing Ability of Student Fourth Semester
English Education Department Faculty of Language
and Science Wijaya Kusuma University. In TEFLIN
International Conference. Bali.
The Effect of Blended Learning and Digital Literacy on Students’ Reading Comprehension
379

Nanda, D. W., & Azmi, K. (2020). Poor reading
comprehension issue in EFL classroom among
Indonesian secondary school students: Scrutinizing the
causes, impacts and possible solutions. Englisia:
Journal of Language, Education, and Humanities, 8(1).
https://doi.org/10.22373/ej.v8i1.6771
Pardo, L. S. (2004). What Every Teacher Needs to Know
About Comprehension. The Reading Teacher, 58(3),
272–280. https://doi.org/10.1598/RT.58.3.5
Paul, C. M. (2017). Encyclopedia of Information Science
and Technology, Fourth Edition, (July).
https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-7659-4.ch002
Tang, C. M., & Chaw, L. Y. (2016). Digital Literacy: A
Prerequisite for Effective Learning in a Blended
Learning Environment ? Electronic Journal of E-
learning, 14(1), 54–65. http://files.eric.ed.gov/full
text/EJ1099109.pdf
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
380
