
Fake It, Mix It, Segment It:
Bridging the Domain Gap Between Lidar Sensors
Frederik Hasecke
1,2 a
, Pascal Colling
2 b
and Anton Kummert
1 c
1
Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of Wuppertal, Germany
2
Department of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Aptiv, Wuppertal, Germany
Keywords:
Lidar, Panoptic Segmentation, Semantic Segmentation, Domain Adaptation.
Abstract:
Lidar segmentation provides detailed information about the environment surrounding robots or autonomous
vehicles. Current state-of-the-art neural networks for lidar segmentation are tailored to specific datasets.
Changing the lidar sensor without retraining on a large annotated dataset from the new sensor results in a
significant decrease in performance due to a ”domain shift.” In this paper, we propose a new method for
adapting lidar data to different domains by recreating annotated panoptic lidar datasets in the structure of a
different lidar sensor. We minimize the domain gap by generating panoptic data from one domain in another
and combining it with partially labeled data from the target domain. Our method improves the SemanticKITTI
(Behley et al., 2019) to nuScenes (Caesar et al., 2020) domain adaptation performance by up to +51.5 mIoU
points, and the SemanticKITTI to nuScenes domain adaptation by up to +48.3 mIoU. We compare two state-
of-the-art methods for domain adaptation of lidar semantic segmentation to ours and demonstrate a significant
improvement of up to +21.2 mIoU over the previous best method. Furthermore we successfully train well
performing semantic segmentation networks for two entirely unlabeled datasets of the state-of-the-art lidar
sensors Velodyne Alpha Prime and InnovizTwo
1 INTRODUCTION
Lidar point cloud segmentation is essential for au-
tonomous vehicles and robots to make informed deci-
sions based on a complete understanding of the envi-
ronment. However, accurately segmenting lidar data
requires a large amount of labor-intensive human an-
notation (Behley et al., 2019; Fong et al., 2021), and
different lidar sensors and mounting positions make
it difficult to reuse annotated data for different appli-
cations. Current domain adaptation methods for li-
dar segmentation align geometric and feature statis-
tics at the data level (Alonso et al., 2020; Rochan
et al., 2022) and use specific adaptations at the model
level to reduce domain shift between datasets (Be
ˇ
si
´
c
et al., 2022; Corral-Soto et al., 2021). Our method
aligns different lidar domains exclusively at the data
level, using sensor-aware domain adaptation modules
and self- and semi-supervised data fusion methods.
We recreate source data in the structure of the target
sensor by combining point clouds into a static mesh
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6724-5649
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5599-1786
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0282-5087
Figure 1: We modified the lidar structure and class defi-
nitions of both datasets to be compatible in both domains.
Best viewed in color on a digital device.
and ray-tracing the mesh with a virtual target lidar,
as shown in figure 1. Furthermore, we use semi-
supervised and self-supervised techniques to further
reduce domain shift between datasets, enabling us to
train effective lidar segmentation networks.
Hasecke, F., Colling, P. and Kummert, A.
Fake It, Mix It, Segment It: Bridging the Domain Gap Between Lidar Sensors.
DOI: 10.5220/0011618500003411
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2023), pages 743-750
ISBN: 978-989-758-626-2; ISSN: 2184-4313
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
743

2 RELATED WORKS
Lidar segmentation has made significant progress in
recent years, with various approaches emerging to ad-
dress different challenges. Early methods focused on
foreground classification and clustering of individual
objects (Moosmann et al., 2009; Bogoslavskyi and
Stachniss, 2016), while more recent approaches have
used deep learning for point-wise semantic segmen-
tation from range image projection (Milioto et al.,
2019; Cortinhal et al., 2020) and voxel structures
(Tang et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2020; Hou et al., 2022;
Xu et al., 2021) as well as direct point-wise oper-
ations (Thomas et al., 2019). Some methods have
also combined lidar data with camera data for multi-
modal segmentation (Yan et al., 2022). The most
widely used datasets for lidar segmentation are the
SemanticKITTI (Behley et al., 2019) and nuScenes
(Caesar et al., 2020) datasets, which include point-
based semantic and panoptic segmentation labels. In
this work, we will consider these datasets and the lat-
est advances in lidar segmentation.
One approach for lidar domain adaptation is the
’simulation to real’ method, in which a computer pro-
gram simulates the sensor data to create a large pool
of annotated training data for a target sensor (Dosovit-
skiy et al., 2017). While this approach can generate a
large amount of data, it suffers from a ”domain shift”
when applied to real data, as simulated environments
are too smooth and clean compared to real recordings.
To address this issue, some researchers have proposed
data-level methods to adjust the appearance and spar-
sity of simulated point clouds to be more similar to
real recordings (Xiao et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2021),
or have added pseudo-labeled real data to simulated
data (Saltori et al., 2022). However, simulation envi-
ronments are also limited in the diversity of scenarios
they can create.
Several approaches have been proposed for real-
to-real lidar domain adaptation, in which the source
domain data are real recordings of a different sen-
sor. These approaches include translation and re-
moval of lidar channels (Alonso et al., 2020), sum-
marization and mesh filling of point clouds (Langer
et al., 2020; Be
ˇ
si
´
c et al., 2022), surface completion
using Poisson surface reconstruction and ray tracing
(Yi et al., 2021), in-painting of sparse labels (Jiang
and Saripalli, 2021), and use of generative adversarial
networks (Corral-Soto et al., 2021) and range image
masking (Rochan et al., 2022) to make one dataset
look like another.
Previous domain adaptation approaches for lidar
semantic segmentation have been limited to specific
data structures (Rochan et al., 2022; Corral-Soto
et al., 2021) or have resulted in rough target point
clouds with limited details for precise segmentation
(Langer et al., 2020; Be
ˇ
si
´
c et al., 2022; Yi et al., 2021;
Jiang and Saripalli, 2021).
In this work, we propose a method that com-
bines unsupervised domain adaptation with fusion
techniques of self-supervised pseudo labels to achieve
competitive results in the target domain with minimal
annotations, thus improving upon the limitations of
previous approaches.
3 METHOD
We propose a data-centric method for panoptic lidar
domain adaptation that preserves the semantic and in-
stance labels of the source dataset. We recreate the
source datasets scene with the shape, range, and struc-
ture of any other lidar sensor as a 3D point cloud to
accommodate all types of segmentation networks and
facilitate training on the resulting data. We use se-
quences from the source dataset to create the static
underlying environment in the structure of the tar-
get sensor, then add dynamic objects to the static
scenes and reduce the domain shift between the gen-
erated data and real data of the target sensor. To
do this, we utilize small pools of annotated data or
pseudo-labeled data from previous inference itera-
tions of trained networks.
3.1 Non-Causal Data Collection
To generate a denser representation of real-world
scenes captured and annotated in our source dataset,
we summarize the points of sequential scenes. Both
the SemanticKITTI (Behley et al., 2019; Geiger et al.,
2012) and nuScenes (Caesar et al., 2020; Fong et al.,
2021) datasets provide ego-motion ground truth for
training and validation data. To prevent dynamic ob-
jects such as moving cars and pedestrians from ap-
pearing multiple times in the static point map, we re-
move all dynamic instances from the point scenes.
The resulting scene point clouds appear denser, but
the points are still zero-dimensional probes (as shown
in figure 2 b). To sub-select or ray-trace the scene
point cloud using the structure of the target lidar sen-
sors, we can use methods such as closest-point sam-
pling. However, these methods can introduce unre-
alistic representations, such as visible points behind
walls or other objects, due to the lack of direct oc-
clusions (Langer et al., 2020). Therefore, we decided
to fill these gaps with a mesh representation derived
from the scene point cloud.
ICPRAM 2023 - 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
744

Figure 2: We use the SemanticKITTI dataset (a), sum up all point clouds (b) create a mesh world (c) and retrace the lidar
structure of the VLP-32C (d) used in the nuScenes dataset as well as the InnovizTwo lidar sensor (e). Best viewed in color on
a digital device.
3.2 Lidar Mesh Creation
Recreating surface models from point clouds has been
studied for almost a century (Delaunay et al., 1934),
and various methods have been developed, includ-
ing alpha shapes (Edelsbrunner et al., 1983), trun-
cated signed distance functions (Curless and Levoy,
1996), and the Poisson surface reconstruction algo-
rithm (Kazhdan et al., 2006). We used the Open3D
(Zhou et al., 2018) implementation of the Poisson
surface reconstruction algorithm to recreate the scene
point cloud as a mesh object. For each mesh vertex
we took the 10 nearest neighbors in the original scene
point cloud via k-nearest neighbors sampling (Fix and
Hodges, 1989). We assigned the most frequent val-
ues for the class and instance labels. The intensity
value reflects the mean value of the 10 nearest origi-
nal points, with an inverse distance weighting.
3.3 Virtual Lidar Sampling
To recreate a point cloud from the mesh object in the
structure of the target lidar sensor, we used the ray-
casting method. We projected the mesh environment
from Cartesian to spherical coordinates, capturing a
depth image from the perspective of the lidar sensor
using a virtual orthographic camera. We adjusted the
camera’s location and rotation to match the sensor and
used a render resolution that is three times the lidar
resolution, which we then subsampled to the target
sensor’s resolution in order reduce discretization ef-
fects at longer range. We reformulated the depth, az-
imuth, and elevation angle values of each pixel into a
Cartesian coordinate system to obtain a pseudo lidar
point cloud in the structure of the target sensor, while
also assigning semantic, instance, and reflection val-
ues directly from the mesh model to the newly created
points. This allows us to recreate the structure of any
number of different lidar sensors using a single mesh
world as shown in figure 2.
Figure 3: We combine our generated static scene (a) with
sampled target sensor (pseudo) ground truth data (b), that
we extract from cuboid labels or alternatively bounding
box predictions. We inject the instances into the generated
scenes to create dynamic lidar data (c) consisting of parts of
the source and the target domain.
3.4 Instance Injections
The method described above creates accurate repre-
sentations of the source data in the structure of the tar-
get data, but the generated scenes only represent the
static components of the source data. To fix this prob-
lem, we used a semi-supervised approach to bring dy-
namic objects back into the empty scenes. We applied
object detectors to the unlabeled target lidar data and
cut out the points within the box predictions, along
with their semantic and instance labels, and inserted
them into the empty, recreated segmentation scenes as
dynamic objects as shown in figure 3. Alternatively,
we can use the same method with ground truth cuboid
labels if they are available for the target data. This
has three benefits: dynamic objects are inserted back
into the static scene, the distribution of underrepre-
sented classes is adjusted to force our segmentation
networks to see them more often,and the gap between
the real and generated domains is narrowed by mixing
generated scene point clouds with real instance point
clouds. For the semi-supervised approaches in section
4.1 and 4.2, we used a subset of the provided bound-
ing box labels from the KITTI (Geiger et al., 2012)
and nuScenes (Caesar et al., 2020) datasets, respec-
tively, for injecting instances.
Fake It, Mix It, Segment It: Bridging the Domain Gap Between Lidar Sensors
745

3.5 Mixing Domains
Recently, multiple lidar augmentation methods have
been published that go beyond injecting single objects
into a scene to a complete mixture between two lidar
point clouds recorded at different positions and times.
Mix3D (Nekrasov et al., 2021) proposes the straight-
forward concatenation of two point clouds to break up
the context of certain classes and objects. A similar
approach in another study (Hasecke et al., 2022) kept
only parts of each point cloud according to their dis-
tance to the lidar sensor, creating a mixed point cloud
while maintaining the structure of the lidar sensor. We
based our domain mixing approach on the latter, com-
bining our synthetic generated scenes with a subset
of target lidar data, as shown in figure 4. By mix-
ing a small subset of real, annotated data of the tar-
get dataset with the generated scenes, both data pools
exhibit the same lidar characteristics and the blend-
ing increases the diversity of the overall dataset while
interpolating the two domains within a single point
cloud, reducing the domain shift between them. A
similar effect was noticed by the authors of another
study (Saltori et al., 2022), who found that merg-
ing patches of different domain sources pulls them
closer together in the total distribution. Our method
increases this pull effect due to the structure-aware
fusion of the different point clouds.
3.6 Pseudo Labels
The previous technique of pulling domains together to
reduce the shift between them can be applied in both
semi-supervised and unsupervised fashion. In the un-
supervised approach, we use a network trained on the
domain adapted data to create pseudo labels for un-
labeled data of the target domain. We then apply the
same methods as in the semi-supervised approach, us-
ing the pseudo labeled data instead of a small anno-
tated data pool. To reduce the influence of incorrect
labels, we remove all points with a probability lower
than 85%. Our reformulated fusion methods from
(Hasecke et al., 2022) have an advantage over other
pseudo label approaches as we do not produce empty
point clouds when removing uncertain regions, but
rather populate them with the complete scene point
clouds of our generated samples.
4 EXPERIMENTS
To demonstrate the effectiveness of our lidar domain
adaptation method, we used two open source datasets:
SemanticKITTI (Behley et al., 2019) and panoptic
nuScenes (Fong et al., 2021). These datasets use dif-
ferent lidar sensors mounted on different vehicles at
different heights, and record data on different conti-
nents, creating a large domain gap between both auto-
motive lidar segmentation datasets. We remapped the
classes in both datasets to a common set, as shown
in figure 5, in order to apply our domain adaptation
method and compare the performance between the
two datasets. Unfortunately, the use of different class
combinations prevents direct comparison with some
previous methods (Langer et al., 2020; Be
ˇ
si
´
c et al.,
2022) for lidar domain adaptation for segmentation,
so we only compare our method to (Corral-Soto et al.,
2021) and (Rochan et al., 2022).
4.1 nuScenes to SemanticKITTI
The nuScenes dataset includes panoptic lidar labels,
instance-wise attributes for dynamic objects, and ego-
motion ground truth. This allows us to remove dy-
namic objects from the lidar point clouds and com-
bine all the point clouds in a sequence using their
ego-motion. The dataset is divided into multiple sub-
sequences, each lasting 20 frames and acquired at a
rate of 2 Hz, for a total of 10 seconds. Our goal is
to recreate panoptic segmentation lidar data in the
structure of Velodyne HDL-64E lidar sensor data. We
achieve this by summing all point clouds in each se-
quence and creating a 3D mesh world using Poisson
surface reconstruction. We use the spherical projec-
tion of the 3D mesh to represent the recording struc-
ture of the target sensor with an orthographic cam-
era. We define a minimum and maximum vertical
and horizontal angle and image resolution to recre-
ate the static scenes in the lidar structure of the KITTI
(Geiger et al., 2012) dataset. Note that while the cre-
ated data includes panoptic labels, we only use the
semantic labels for our semantic segmentation exper-
iments.
We conducted an ablation study to assess the im-
pact of each module in our method. We replaced
the original nuScenes data with the recreated lidar
frames, resulting in a performance increase from 19.1
mIoU to 30.7 mIoU. We then used the trained network
to generate pseudo labels for unlabeled data from
the target sensor and mixed them with our generated
frames, resulting in a total mIoU of 34.3. We further
increased the amount of semi-supervision by adding
the object detection cuboid labels from the original
3D object detection dataset (Geiger et al., 2012) with-
out using pseudo labels, resulting in a mIoU of 31.9.
Next, we fused the domains by sampling 100 frames
from the target domain, which is less than 0.5% of the
original dataset. This resulted in a significant perfor-
ICPRAM 2023 - 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
746
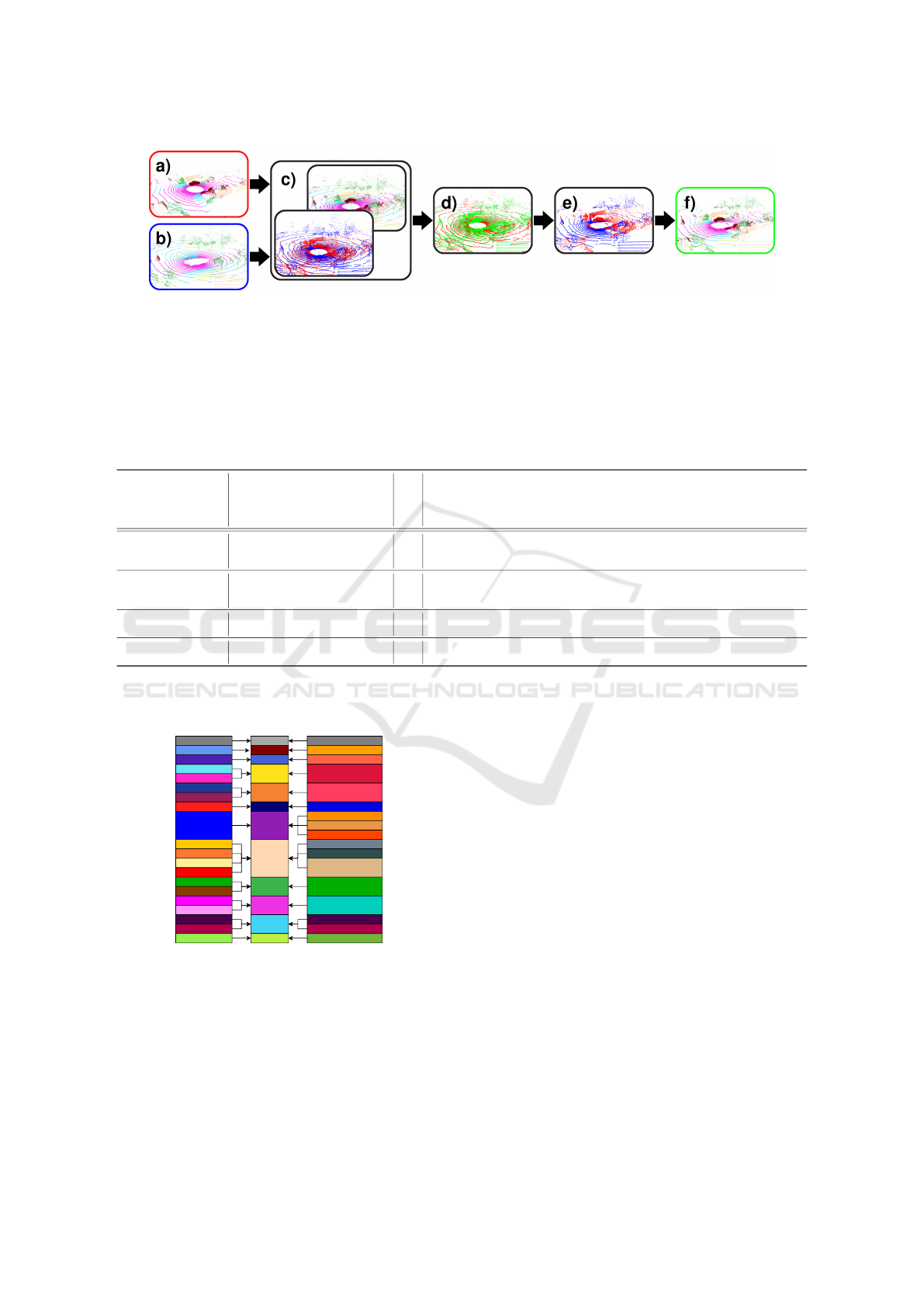
Figure 4: We combine a generated lidar scene (a) and a ground truth lidar frame (b) using point-wise range competition in the
range image domain (c & d). The resulting point cloud (e & f)contains both real and generated data, resulting in a structurally
intact point cloud. Note: the graph in this figure is adapted from (Hasecke et al., 2022) and is best viewed in color.
Table 1: Ablation study of our domain adaptation method using the Cylinder3D network (Zhu et al., 2020) on the NuScenes to
SemanticKITTI dataset, with classes joined according to figure 5. ”GT Frames” denotes the addition of a small subset of 100
annotated target frames (0.5% of the training data), while ”GT Inst.” denotes the addition of cuboid detections as point-wise
labels. All Cylinder3D networks were trained from scratch with the same parameters for a fair evaluation. We compare our
method to the unsupervised domain adaptation method of (Rochan et al., 2022) and the semi-supervised domain adaptation
of (Corral-Soto et al., 2021), which uses 100 annotated target frames for training. The best results are shown in bold red,
and the second best in italic blue text.
Gen. Frames
Pseudo Labels
GT Inst.
GT Frames
mIoU
Car
Truck
Bicycle
Motorcycle
Pedestrian
OtherVehicle
Structure
Nature
Road
Ground
Terrain
Unsup. (Ours)
19.1 64.5 0.9 0.0 5.0 0.0 1.0 38.3 11.0 50.6 4.8 33.7
X 30.7 86.1 6.8 5.8 16.0 1.2 3.4 44.6 29.9 64.2 32.9 47.1
X X 34.3 88.8 3.0 1.0 16.9 0.3 1.0 49.3 42.5 74.0 51.2 49.3
Semi-Sup. (Ours)
X X 31.9 78.6 1.98 6.9 7.6 10.9 1.8 51.8 42.62 66.9 38.58 43.2
X X X 63.1 93.1 31.1 50.1 43.3 65.4 13.5 86.8 84.9 87.0 73.1 65.8
X X X X 67.4 94.0 50.8 58.2 51.9 71.6 13.9 88.3 85.8 88.2 75.3 67.0
(Rochan et al., 2022) 23.5 49.6 1.8 4.6 6.3 12.5 2.0 65.7 57.9 82.2 29.6 34.0
(Corral-Soto et al., 2021) X 46.2 87.3 27.6 29.2 26.9 34.6 24.4 61.7 46.4 70.3 52.3 47.4
Supervised
100 Frames X 49.0 91.2 1.6 8.1 2.6 30.1 6.0 83.3 85.3 88.3 73.3 69.6
Full Target Dataset † 75.8 96.5 84.7 62.3 53.7 70.2 53.2 89.5 86.0 91.0 79.2 67.3
† The target baseline mIoU is higher than reported by the original authors, as we are using the reduced joint class
set as shown in figure 5 and therefore eliminate some of the bad performing classes from the evaluation.
unlabeled noise
car
bicycle
truck
bicyclist
motorcycle
motorcyclist
person
other-vehicle
building
fence
pole
traffic-sign
vegetation
trunk
road
parking
sidewalk
other-ground
terrain
Outlier
vehicle.carCar
vehicle.truckTruck
vehicle.bicycle
Motorcycle vehicle.motorcycle
Bicycle
human.pedestrian
OtherVehicle
Pedestrian
vehicle.trailer
vehicle.construction
vehicle.bus
movable_object.barrier
movable_object.trafficcone
static.manmade
Nature
Structure
Road
Ground
Terrain
static.vegetation
flat.driveable_surface
flat.sidewalk
flat.other
flat.terrain
SemanticKITTI Panoptic nuScenes Ours
Figure 5: We remap the classes of both datasets used in this
work to match the different classes in joint categories, that
are present in both datasets for a uniform class label set.
mance increase to a mIoU of 63.1. The final version
of our semi-supervised method included all the pre-
viously mentioned components, as well as pseudo la-
bels derived from the previous network applied to un-
labeled target lidar data. Adding these pseudo labeled
point clouds as additional fusion point clouds resulted
in a final network performance of 67.4 mIoU, which is
89% of the segmentation quality of the same network
trained on the full target dataset (75.8 mIoU). For
comparison, we trained the same network on the 100
sampled frames of the target dataset used in our semi-
supervised approach, resulting in a mIoU of 49.0. As
shown in table 1, our domain adaptation, injection,
and fusion methods all significantly improve the final
segmentation quality.
We also compared our method to two state-of-
the-art lidar domain adaptation methods for seman-
tic segmentation. The first approach (Rochan et al.,
2022) is an unsupervised method that performs do-
main adaptation in the range image domain, achiev-
ing a reported mIoU of 23.5. The limited perfor-
mance of the network (Cortinhal et al., 2020) used
in (Rochan et al., 2022) may partly contribute to the
difference in performance between this method and
ours, which further highlights the advantage of our
domain adaptation approach, as it is not limited to net-
works for range images. The second work we com-
pare to is (Corral-Soto et al., 2021), which uses a
Fake It, Mix It, Segment It: Bridging the Domain Gap Between Lidar Sensors
747

semi-supervised approach with parts of the annotated
target dataset and domain adaptation, resulting in a
mIoU of 46.2 with the use of 100 annotated frames
of the target dataset. Their method with even 500 an-
notated frames only resulted in a performance of 53.6
mIoU. Our performance of 67.4 mIoU using only 100
ground truth frames demonstrates the effectiveness of
our domain fusion and injection methods in reducing
the ”domain shift” or ”gap” between the datasets.
4.2 SemanticKITTI to nuScenes
To demonstrate the universality of our method, we
reversed the domain adaptation from the previous
section and used the training data from the Se-
manticKITTI dataset to create a fake panoptic seg-
mentation dataset for the lidar sensor of the nuScenes
dataset. We trained the Cylinder3D (Zhu et al., 2020)
semantic segmentation network on our fully unsu-
pervised method (using only generated frames and
pseudo labels) and our semi-supervised approach (us-
ing all modules from section 3). We compared these
approaches to fully supervised training on the source
and target datasets in table 2. The semantic segmen-
tation quality of the used network improved with each
additional component of our method.
Naive training on the SemanticKITTI data re-
sulted in a low performance of only 7.4 mIoU on
the nuScenes validation data. However, our unsuper-
vised domain adaptation improved the performance to
a mIoU of 29.2 which is slightly lower than the unsu-
pervised approach by (Rochan et al., 2022) with 34.5
mIoU. We believe the lower performance of our unsu-
pervised method on the nuScenes dataset compared to
the SemanticKITTI dataset is due to the very different
vertical aperture angles of the two lidar sensors. The
VLP-32C lidar sensor (nuScenes) has a larger ver-
tical opening angle and can ”see” up to ∼ 40.73 m
above the road surface, while the HDL-64E sensor
(SemanticKITTI) is limited to ∼ 3.48 m above the
ground. This large discrepancy impacts the perfor-
mance noticeably more for a point-wise domain adap-
tation than a range image variant.
Our best performing semi-supervised method uses
100 frames of the target dataset, which is 0.36% of the
original target training data, and reaches a final mIoU
of 58.9 using our pseudo label fusion, as shown in ta-
ble 2. The injection instances are sampled from the
same 100 frames to prevent data leakage. This en-
ables a performance of 85% compared to the network
trained on the fully labeled target dataset, which has
a mIoU of 69.5. Our semi-supervised method even
outperforms the fully supervised network on three out
of 11 classes. We compared our semi-supervised ap-
Figure 6: Inference Results of the Semantic Segmentation
Network Trained on NuScenes Data Recreated in the Struc-
ture of the Velodyne Alpha Prime Sensor.
proach to the state-of-the-art semi-supervised domain
adaptation method by (Corral-Soto et al., 2021). Our
semi-supervised approach (58.9 mIoU) significantly
improves the State of the Art compared to the pre-
vious best method of (Corral-Soto et al., 2021) with
a mIoU of 48.3, as well as their approach using 500
labeled frames (52.3 mIoU).
4.3 nuScenes to Velodyne Alpha Prime
We applied our domain adaptation method to the
training data of the nuScenes dataset to recreate an
annotated dataset for the high resolution lidar sensor
Velodyne Alpha Prime. We recorded multiple scenar-
ios in Wuppertal, Germany using this sensor to pro-
duce unlabeled automotive lidar data. The target li-
dar has a vertical resolution of 128 non-uniform li-
dar channels, 4 times the resolution of the nuScenes
lidar, and a horizontal resolution of 1800 points per
scan line, which results in twice the horizontal reso-
lution of the nuScenes lidar data. Additionally, the
range of the target sensor is increased from 200 m to
300 m. We took the same approach as in section 4.1
and summed up all points of a given scene to collect as
many original lidar measurements as possible. Due to
the lower resolution of the source lidar, the resulting
point cloud was comparably sparse. Using the mesh-
ing process from section 3.2, we connected the point
cloud to cover the entire visible surrounding. In addi-
tion to generating the point cloud, we applied two off-
the-shelf 3D bounding box algorithms (Lang et al.,
2019; Shi et al., 2020) to unlabeled target data from
the Velodyne Alpha Prime. As the bounding box de-
tection networks were not trained on this sensor, we
filtered out multiple false detections using a Kalman
filter (Kalman, 1960). We applied the method from
ICPRAM 2023 - 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
748

Table 2: Domain adaptation methods using the Cylinder3D network (Zhu et al., 2020) from the SemanticKITTI to NuScenes
dataset. All Cylinder3D networks were trained from scratch with the same parameters for a fair validation. We list the reported
IoU of the cited previous work. The best results are shown in bold red, and the second best in italic blue text.
Method mIoU Car Truck Bicycle Motorcycle Pedestrian OtherVehicle Structure Nature Road Ground Terrain
No Domain Adaption 7.4 3.7 0.3 0.0 0.1 0.1 0.5 18.2 0.1 11.3 1.2 0.1
Unsupervised (Ours) 29.2 72.3 0.0 0.0 0.3 0.1 4.8 59.3 38.5 77.8 25.9 42.1
Semi-supervised (Ours) 58.9 78.0 57.0 14.1 53.6 51.9 39.1 79.9 77.0 91.0 52.3 53.9
Unsupervised (Rochan et al., 2022) 34.5 54.4 15.8 3.0 1.9 27.7 7.6 65.7 57.9 82.2 29.6 34.0
100 Target Frames + (Corral-Soto et al., 2021) 48.3 69.0 37.7 5.5 9.4 45.4 23.5 69.0 74.7 78.8 56.1 61.8
100 Target Frames 46.3 70.3 27.1 2.0 0.1 40.3 14.7 78.1 76.0 90.7 52.1 58.0
Full Target Dataset† 69.5 80.0 61.7 11.9 38.0 72.1 34.2 82.6 81.4 94.0 63.7 60.7
† The target baseline mIoU is lower than reported by the original authors, as we are training from scratch.
Figure 7: Inference Results of the Semantic Segmentation
Network Trained on SemanticKITTI Data Recreated in the
Structure of the InnovizTwo Sensor.
section 3.4 to sample and inject the lidar points in-
side the detected cuboids as semantic instances into
our generated training data pool. Qualitative results
of the trained semantic segmentation network can be
seen in figure 6. Unfortunately, we are unable to pro-
vide a quantitative evaluation as there is no openly
available semantic or panoptic segmentation dataset
for the Velodyne Alpha Prime sensor.
4.4 SemanticKITTI to InnovizTwo
We applied our method to one more dataset without
segmentation labels with an entirely different lidar
sensor to demonstrate the methods domain adapta-
tion capability. The InnovizTwo is a high resolution
directional lidar sensor with a limited aperture angle
(120
◦
×40
◦
) and a range of up to 300 m. It has a much
higher point density in the given direction than the
Velodyne Alpha Prime. We used the InnovizTwo data,
provided for a self-supervised object detection chal-
lenge (Innoviz and NVIDIA, 2022), to adapt from a
low resolution, low range, 360
◦
rotating lidar sensor
to a high resolution directional lidar. We used the pro-
vided cuboid labels of 100 annotated frames to de-
fine point-wise instances for our semi-supervised do-
main adaptation. The results of our trained SalsaNext
(Cortinhal et al., 2020) semantic segmentation model
for the InnovizTwo data can be seen in figure 7.
5 CONCLUSION
We have developed a method to recreate annotated
lidar data in the structure of different lidar sensors.
Our throughout evaluation demonstrated, that the pro-
posed method improves semantic segmentation via
domain adaption up to +21.2 mIoU compared to the
current State of the Art. We conducted an extensive
ablation study to show the influence of each module
in our domain adaption for reducing the domain gap
between generated and real data. Our method oper-
ates solely at the data level and can be used with any
lidar semantic segmentation model. In the future, we
plan to apply our method to panoptic segmentation
networks and 3D bounding box detectors.
REFERENCES
Alonso, I. et al. (2020). Domain adaptation in lidar seman-
tic segmentation by aligning class distributions. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2010.12239.
Behley, J. et al. (2019). Semantickitti: A dataset for seman-
tic scene understanding of lidar sequences. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference
on Computer Vision, pages 9297–9307.
Be
ˇ
si
´
c, B. et al. (2022). Unsupervised domain adaptation
for lidar panoptic segmentation. IEEE Robotics and
Automation Letters, 7(2):3404–3411.
Bogoslavskyi, I. and Stachniss, C. (2016). Fast range
image-based segmentation of sparse 3d laser scans
for online operation. In 2016 IEEE/RSJ International
Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS),
pages 163–169. IEEE.
Caesar, H. et al. (2020). nuscenes: A multimodal dataset for
autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
conference on computer vision and pattern recogni-
tion, pages 11621–11631.
Contributors, M. (2020). MMDetection3D: OpenMMLab
next-generation platform for general 3D object detec-
tion. https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection3d.
Corral-Soto, E. R. et al. (2021). Lidar few-shot domain
adaptation via integrated cyclegan and 3d object de-
Fake It, Mix It, Segment It: Bridging the Domain Gap Between Lidar Sensors
749

tector with joint learning delay. In 2021 IEEE In-
ternational Conference on Robotics and Automation
(ICRA), pages 13099–13105. IEEE.
Cortinhal, T. et al. (2020). Salsanext: Fast, uncertainty-
aware semantic segmentation of lidar point clouds. In
International Symposium on Visual Computing, pages
207–222. Springer.
Curless, B. and Levoy, M. (1996). A volumetric method for
building complex models from range images. In Pro-
ceedings of the 23rd annual conference on Computer
graphics and interactive techniques, pages 303–312.
Delaunay, B. et al. (1934). Sur la sphere vide. Izv. Akad.
Nauk SSSR, Otdelenie Matematicheskii i Estestven-
nyka Nauk, 7(793-800):1–2.
Dosovitskiy, A. et al. (2017). CARLA: An open urban driv-
ing simulator. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Con-
ference on Robot Learning, pages 1–16.
Edelsbrunner, H. et al. (1983). On the shape of a set of
points in the plane. IEEE Transactions on information
theory, 29(4):551–559.
Fix, E. and Hodges, J. L. (1989). Discriminatory analy-
sis. nonparametric discrimination: Consistency prop-
erties. International Statistical Review/Revue Interna-
tionale de Statistique, 57(3):238–247.
Fong, W. et al. (2021). Panoptic nuscenes: A large-scale
benchmark for lidar panoptic segmentation and track-
ing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.03805.
Geiger, A. et al. (2012). Are we ready for Autonomous
Driving? The KITTI Vision Benchmark Suite. In
Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR), pages 3354–3361.
Hasecke, F. et al. (2022). What can be seen is what you get:
Structure aware point cloud augmentation. In 2022
IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), pages 594–
599. IEEE.
Hou, Y. et al. (2022). Point-to-voxel knowledge distillation
for lidar semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of
the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pages 8479–8488.
Innoviz and NVIDIA (2022). Eccv workshop on 3d percep-
tion for autonomous driving: The lidar self-supervised
learning challenge: Learning from a limited amount
of high-resolution lidar data. https://innoviz.tech/
eccv-challenge. Accessed: 2022-09-15.
Jiang, P. and Saripalli, S. (2021). Lidarnet: A boundary-
aware domain adaptation model for point cloud se-
mantic segmentation. In 2021 IEEE International
Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA),
pages 2457–2464. IEEE.
Kalman, R. E. (1960). A new approach to linear filtering
and prediction problems.
Kazhdan, M. et al. (2006). Poisson surface reconstruction.
In Proceedings of the fourth Eurographics symposium
on Geometry processing, volume 7.
Lang, A. H. et al. (2019). Pointpillars: Fast encoders for
object detection from point clouds. In Proceedings
of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and
pattern recognition, pages 12697–12705.
Langer, F. et al. (2020). Domain transfer for semantic seg-
mentation of lidar data using deep neural networks. In
2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelli-
gent Robots and Systems (IROS), pages 8263–8270.
Milioto, A. et al. (2019). Rangenet++: Fast and accurate
lidar semantic segmentation. In 2019 IEEE/RSJ In-
ternational Conference on Intelligent Robots and Sys-
tems (IROS), pages 4213–4220. IEEE.
Moosmann, F. et al. (2009). Segmentation of 3d lidar data
in non-flat urban environments using a local convexity
criterion. In 2009 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Sympo-
sium, pages 215–220. IEEE.
Nekrasov, A. et al. (2021). Mix3D: Out-of-Context Data
Augmentation for 3D Scenes. In International Con-
ference on 3D Vision (3DV).
Rochan, M. et al. (2022). Unsupervised domain adaptation
in lidar semantic segmentation with self-supervision
and gated adapters. In 2022 International Conference
on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages 2649–
2655. IEEE.
Saltori, C. et al. (2022). Cosmix: Compositional semantic
mix for domain adaptation in 3d lidar segmentation.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.09778.
Shi, S. et al. (2020). From points to parts: 3d object de-
tection from point cloud with part-aware and part-
aggregation network. IEEE transactions on pattern
analysis and machine intelligence, 43(8):2647–2664.
Tang, H. et al. (2020). Searching efficient 3d architec-
tures with sparse point-voxel convolution. In Euro-
pean conference on computer vision, pages 685–702.
Thomas, H. et al. (2019). Kpconv: Flexible and deformable
convolution for point clouds. In Proceedings of the
IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,
pages 6411–6420.
Xiao, A. et al. (2022). Transfer learning from synthetic to
real lidar point cloud for semantic segmentation. In
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial In-
telligence, volume 36, pages 2795–2803.
Xu, J. et al. (2021). Rpvnet: A deep and efficient range-
point-voxel fusion network for lidar point cloud seg-
mentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Interna-
tional Conference on Computer Vision, pages 16024–
16033.
Yan, X. et al. (2022). 2dpass: 2d priors assisted seman-
tic segmentation on lidar point clouds. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2207.04397.
Yi, L. et al. (2021). Complete & label: A domain adapta-
tion approach to semantic segmentation of lidar point
clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference
on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages
15363–15373.
Zhao, S. et al. (2021). epointda: An end-to-end simulation-
to-real domain adaptation framework for lidar point
cloud segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Con-
ference on Artificial Intelligence, volume 35, pages
3500–3509.
Zhou, Q.-Y. et al. (2018). Open3D: A modern library for
3D data processing. arXiv:1801.09847.
Zhu, X. et al. (2020). Cylindrical and asymmetrical 3d
convolution networks for lidar segmentation. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2011.10033.
ICPRAM 2023 - 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
750
