
Hard Spatio-Multi Temporal Attention Framework for Driver
Monitoring at Nighttime
Karam Abdullah
1,2 a
, Imen Jegham
3b
, Mohamed Ali Mahjoub
3c
and Anouar Ben Khalifa
3,4 d
1
Université De Sousse, ISITCOM, LATIS-Laboratory of Advanced Technology and Intelligent Systems, 4011, Sousse, Tunisia
2
University of Mosul, Collage of Education for Pure Science, Computer Science Department, Mosul, Iraq
3
Université De Sousse, Ecole Nationale d’Ingénieurs De Sousse, LATIS- Laboratory of Advanced Technology and
Intelligent Systems, 4023, Sousse, Tunisia
4
Université De Jendouba, Institut National Des Technologies et Des Sciences Du Kef, 7100, Le Kef, Tunisia
Keywords: Driver Monitoring, Nighttime, Spatio-multi-temporal Attention, Hard Attention, Deep Learning, Hybrid
Network.
Abstract: Driver distraction and inattention is recently reported to be the major factor in traffic crashes even with the
appearance of various advanced driver assistance systems. In fact, driver monitoring is a challenging vision-
based task due to the high number of issues present including the dynamic and cluttered background and high
in-vehicle actions similarities. This task becomes more and more complex at nighttime because of the low
illumination. In this paper, to efficiently recognize driver actions at nighttime, we unprecedentedly propose a
hard spatio-multi-temporal attention network that exclusively focuses on dynamic spatial information of the
driving scene and more specifically driver motion, then using a batch split unit only relevant temporal
information is considered in the classification. Experiments prove that our proposed approach achieves high
recognition accuracy compared to state-of-the art-methods on the unique realistic available dataset 3MDAD.
1 INTRODUCTION
The World Health Organization stated that driver
distraction is a key factor of traffic crashes. Driver
distraction is the main cause of this sudden outcome
as using a mobile phone increases the risk of injury
by 4 times, as well as sending text messages and even
using an embedded phone that is portable with the car
is unsafe when using and driving. Road traffic
accidents claim the lives of about 1.3 million people
annually (WHO, 2022). It has been shown that the
number of traffic crashes at nighttime is multiplied by
4 compared to daytime (Williams, 1985). Moreover,
the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
(NHTSA) declared in the fatality analysis data system
that 57% of car occupants are killed in collisions
between 06:00 p.m. and 06:00 a.m. compared to 41 %
during the daytime hours (NHTSA, 2017). Therefore,
analysing the driver’s action in realistic driving
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2517-873X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1531-438X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9946-0829
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8181-4684
settings at nighttime is one of the most important
tasks to reduce traffic crashes and save drivers,
passengers and pedestrians’ lives.
Driver distraction is defined as anything that
results in inattention or loss of focus while driving a
vehicle (Jegham, 2020). Generally, distraction
consists of a collection of manuals, visual, and
cognitive distractions (Alkinani, 2022): Manual
distraction occurs when driver removes his hands off
the wheel, visual distraction happens when driver
takes gazing away from the road, and cognitive
distraction occurs when the driver's attention is
absorbed to the point that they cannot focus anymore
on the act of driving, which can happen in several
situations such as when the driver is sleepy or speaks
on the phone, etc.
Recently, many Driver Action Recognition
(DAR) solution have been proposed by car
manufacturers that use many sensors, mainly cameras
Abdullah, K., Jegham, I., Mahjoub, M. and Ben Khalifa, A.
Hard Spatio-Multi Temporal Attention Framework for Driver Monitoring at Nighttime.
DOI: 10.5220/0011637400003411
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2023), pages 51-61
ISBN: 978-989-758-626-2; ISSN: 2184-4313
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
51

(Jegham, 2018) (Jegham, 2019) (Jegham, 2020).
They have archived good accuracy results. However,
there is no apparent progress in these systems for
nighttime vision. DAR is one of the most challenging
tasks in computer vision due to the large number of
issues present in this field including illumination
variation, high interclass similarity and cluttered and
dynamic background. This task become more
complex at nighttime with the presence of low
visibility issue.
DAR is closely related to the field of Human
Action Recognition (HAR), where classification
performance has dramatically improved thanks to the
development of deep learning techniques (Martin,
2019). Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models
perform accuracy more than hand-crafted features
when compared to one another (Khemchandani,
2016). Convolutional operations in CNN techniques
learn the features from input frames by employing
pre-trained models, which are then training new
models; these convolutional layers extract and learn
spatial features, which are used to train classification
models in classification tasks (Jegham, 2020). CNN
models such as the VGG (Simonyan, 2014), Inception
(Szegedy, 2016) and ResNet (Fu, 2019) are used to
learn spatial properties, these models are useful for
capturing spatial features, but they are not very
effective at capturing temporal information, which is
a critical aspect in obtaining temporal features for the
HAR in a video sequence and is not captured by these
models (Muhammad, 2021). For that, several
sequence-based methods have been proposed. These
methods can be categorized to 3 main types: 3DCNN,
multi-stream network and hybrid network (Jegham,
2020). This latter has proved efficiency with their low
complexity.
The recent evolution of deep neural networks has
resulted in the widespread usage of visual attention
mechanism in a wide range of application disciplines
(Niu, 2021). The visual attention mechanism is
considered as a dynamic weight regulation process
based on image features (Guo, 2022). The main idea
behind this mechanism is to simulate the human
visual cognitive system of individuals to focus on the
main features in the images (Hassanin, 2022). In
general, visual attention aims to reduce the
computational complexity and thus reduce the time
spent executing the arithmetic operations (Vaswani,
2017). It can be split into 2 types based on the method
through which it generates attention: spatial attention
that aims to focus on a specific region space and
temporal attention that is defined as a dynamic time
selection technique. These types can be combined to
generate a hybrid attention mechanism (Hermann,
2015) (Guo, 2022) called spatio-temporal attention,
where spatial and temporal features are taken
advantage of and enhance the mechanism's
performance simultaneously (Liu, 2019). These
attention models can be also clustered in 2 main
categories (Sharma, 2015): soft and hard attention
models. Soft attention models treat the entire input
but dynamically weigh each part of this input, while
hard attention models bring hard decisions when
picking only relevant parts of the input data.
When driving at nighttime, many frames are not
useful for interpreting the scene because they are
repetitive, and have slight changes. Therefore, the
advantages gained from an entire chain are attrition
on the system, reduced performance wastes time, and
the system may fail to understand the meaning of the
graphic chain. Despite the presence of the recurrent
layer capable of capturing temporal information, it
must follow a method that reduces non useful features
(Xu, 2017). On another hand, some information of
driving scene is irrelevant as driver’s actions are
performed in a cluttered and dynamic scene.
Therefore, focusing attention on relevant spatial and
temporal information of the driving scene at
nighttime is required to recognize driver in-vehicle
actions in order to decrease dramatic traffic injures.
Inspired by the ability of humans to process image
sequences with high efficiency by paying attention
only on important information in a certain period, we
propose a hard spatio-temporal attention mechanism
to explain the night driving actions with high
accuracy. We depend on our recent work mechanism
to separate the driver's body from the rest of the car
environment using digital image processing
techniques by create a mask through which the
driver's movements are extracted and allows the
model to focus on the most prominent parts of driver
body features maps for spatial attention in the system.
On the other hand, for temporal attention, we
mapping different size of batches of features vectors
and use the LSTM-based convolutional attention
mechanism to select features frames from the input
images chain.
The main contributions of this paper can be listed
as follows:
• We designed a novel spatio-temporal attention
mechanism that captures the dynamic spatial
dependency by constructing a hard attention
technique on infrared images, uniquely retain relevant
driver information, and pass the features to temporal
attention to capture the action along a certain period
of time to get a correct and accurate classification.
• We developed for the first time a Batches Split
Unit (BSU) that computes alternative frames feature
ICPRAM 2023 - 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
52

numbers to address the issue of repeated frames and
ensure the highest possible accuracy in the minimum
time.
• Experiments on 3MDAD at nighttime datasets
prove that the suggested framework is more effective
when compared with certain other state-of-the-art
approaches.
2 RELATED WORKS
Over the last few years, several researchers have
relied on the technique of attention in their work (Xia,
2021) (Islam, 2021), because of the many advantages
that technology offers, including reducing the
complexity of computational operations and
optimizing the exploitation of the device’s resources.
Therefore, attention models have been widely used in
the classification of human actions and more
specifically driver actions.
2.1 Human Action Recognition
To develop a technique that allows taking into
account the spatial and temporal aspects, many
researchers have submitted several papers in this
regard because this technique provides a broad and
accurate understanding of human actions. Li et al. (Li,
2020) introduced a spatio-temporal attention
mechanism for the input feature maps at the frame
level and learn a sequence weights matrix via the
transform function, the source sequence of images is
usually too short for extracting variance information
between consecutive frames, especially when a
convolutional layer is applied to further reduce the
length, resulting in the loss of valuable information
for action recognition, they devise a temporal
attention function that first stretches the temporal
dimension using a deconvolutional layer to keep more
temporal information, then squeezes it with a
convolutional layer to keep the initial length for
further processing. Donahue et al. (Donahue, 2015)
have presented another approach to describe images
features and temporal information, which is a fusion
of CNN and RNN in a structure, the CNN algorithm
is employed image features, and the RNN algorithm
is also used to extract temporal data. In (Li, 2018), Li
et al. indicated that, when detecting actions in video,
the both spatial and temporal attention should be
considered, they proposed video action recognition
system called a unified spatio-temporal attention
networks, even sampling is used to break the video
into several video chunks, the spatial attention neural
cell is designed to generate attention distributions
across all local regions in order to identify action and
spatially aggregate these local features as a
representation of each video segment, the
representations of each video segment on several
modalities are then concatenated and successively fed
into an LSTM network to train temporal attention
using temporal, which diverts attention to the most
relevant video segments. In (Meng, 2019) Meng et al.
developed an interpretable spatial-temporal attention
mechanism, they proposed that the convolutional
features first attended throughout both spatially in
each frame and then temporally for the full video
sequence, in this case, the final effective
representation at time step is a spatial and temporal
weighted aggregate of convolution features across the
stream, as well as a hidden state from a previous time.
2.2 Driver Action Recognition
It has become necessary to develop new systems for
classifying driver actions to solve the driver
distraction problem at nighttime using deep learning
techniques, because these techniques provide a
powerful analysis of image situations, especially
when using spatial and temporal attention to obtain
the best interpretation of situations. Thus, in this field
Jegham et al. (Jegham, 2020) developed a technique
for recognizing driver in-vehicle actions, they
produced DSA, which is a hybrid deep network which
utilizes the depth modality to obtain helpful aspects
of RGB data in order to accurately classify driver
actions in realistic driving environments. Wang et al.
(Wang, 2019) presented an attentional convolutional
neural network that can recognize driving actions, the
network is made up of three modules: the basic
convolution module, the attention module, and the
classification module, the attention module has the
ability to reassign weights among both dimensions of
space and channel, allowing the weights from the
network to be transferred to the location with
discrimination, to improving the ability to distinguish
between different classes, the classification module is
responsible for completing recognition process. Li et
al. (Li, 2019) In their research, used spatial-temporal
graphs and genetic weighted algorithms to investigate
skeleton-based driver action detection. the driver's
body posture is initially determined using a process
of selective sampling of informative frames from a
video, which contains driver joints that have high
confidence ratings and joint position coordinates
produced through the pose estimation algorithm, they
employed the skeleton-based graphs in the spatial-
temporal fields to calculate the position of the driver's
joints, and these skeletons of the collected poses have
Hard Spatio-Multi Temporal Attention Framework for Driver Monitoring at Nighttime
53

been used as feeds to the Graphs Convolutional
Networks, the genetically-weighted algorithm is then
utilized to select joint points also with the best rating
of association and considerable placement change,
and they use the correlation between sensory input
and approaching driver behaviour to identify the
specific actions that the driver will take. Wharton et
al. (Wharton, 2019) present a framework that models
the small changes by utilizing spatiotemporal
attention as a modelling tool, the model is referred
seen as the Coarse Temporal Attention Network, or
CTA-Net, and it is comprised of a trainable glance
network with coarse temporal branches added by
zeroing in on a particular segment of a video, the aim
is to make it possible for the glimpse to "catch" high-
level temporal associations, such as "during,"
"before," and "after," amongst others.
Up to our knowledge, Abdullah et al. (Abdullah,
2022) proposed the first and only work for DAR at
nighttime. They suggested a multi-convolutional
stream for a hybrid network that efficiently classifies
drivers' activities in a low-visibility, they congested
driving scenario by effectively fusing multimodal data.
For that, in this paper, we introduce our Spatio-
temporal attention that gives each spatial region in
various frames attention weights that include both
temporal attention information and spatial attention
information to achieve an efficient classification at
nighttime.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
Our proposed approach handles image sequences of
variable length due to its non-parametric design; this
is a very important point to dealing with driver action
recognition because of an uncontrolled natural
environment issue. Our proposed framework consists
of the architecture illustrated in Figure 1 and
Algorithm 1, the spatio- multi temporal attention that
focuses attention on the components within the
images over time, and Figure 2 shows the specific
architecture of the temporal attention, which focuses
on the set of features resulting from the previous stage
during a certain period of time. The spatial features
map is divided by Batches Split Unit (BSU) lines 4-
14 in Algorithm 1, as shown in Figure 2, into M
pipeline, every pipeline has N batches, and every
batch has ‘k’ numbers of Feature Vector (FV) to
represent the features map for each frame to take
advantage of reducing the time spent on
implementation and reducing the consumption of
computer resources. The number of FV should not be
too large because that leads to a loss of useful content,
and also, it should not be too small because that leads
to less attention.
In this paper, we propose a Hard Spatio-Multi
Temporal Attention (HSMTA) architecture to
recognize driver actions at nighttime inside a vehicle
to give the greatest ability and accurately classify the
different series images by our system; we make use
of our recent work Hard Spatial Attention framework
(HSA), as a pre-processing step and extract spatial
feature map of input series images after passing
through the fine-tuned Inception v3 model.
Algorithm 1: Hard Spatio-Multi Temporal Attentio
n
Framework.
Require: IR test sequence: {I
i
}
Ensure: Classification result label: Z
1:𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝑖 ← 0: 𝑡 𝐝𝐨
2: 𝑆𝑝𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙_𝐹𝑒𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒𝑠_𝑀𝑎𝑝 ← 𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈𝑤
𝑥
𝑏;
3:𝐞𝐧𝐝 𝐟𝐨𝐫
4: 𝐶𝑜𝑚𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑩𝑺𝑼:
5: 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝑚 ← 1: 𝑝𝑖𝑝𝑒𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒 𝐝𝐨
6: 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝑛 ← 1: 𝑏𝑎𝑡𝑐ℎ 𝐝𝐨
7: 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝑘 ← 2… ..𝐹𝑉 𝐝𝐨
8: 𝐿𝑆
𝑆𝑖𝑔𝑚𝑜𝑖𝑑
𝑤
𝑥
𝑤
ℎ
𝑏
9: 𝐿𝑅
𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈
𝑤
𝐿𝑆
𝑤
ℎ
𝑏
10: 𝑅
𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈
𝑤
𝐿𝑅
𝑤
ℎ
𝑏
11: 𝑍𝑆𝑜𝑓𝑡𝑚𝑎𝑥R
12: 𝐞𝐧𝐝 𝐟𝐨𝐫
13: 𝐞𝐧𝐝 𝐟𝐨𝐫
14: 𝐞𝐧𝐝 𝐟𝐨𝐫
15:𝐫𝐞𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐧 𝑍
Figure 1: Architecture of HSMTA.
3.1 Pre-processing
Firstly, in Figure 3, we fine-tuned our model by the
Inception v3 network that pre-trained by “ImageNet”
(Deng, 2009) dataset. Then we used a hard spatial
attention methodology from our recent work to
extract 2048 features for the next step. The hard
spatial attention methodology consists of two
separate series of image processing units, the system
simultaneously generates a hard-attention image as
well as an LBP (Mattivi, 2009) (Nanni, 2012) image.
The hard attention image is generated by a mask and
ICPRAM 2023 - 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
54

Figure 2: Temporal attention and Batches Split Unit (BSU)
of HSMTA.
then dropping it onto the erosion image in order to get
the most informative part of the image. Therefore, we
choose the formula that, H
i
can be represented out
using Equation (1):
𝐻
𝑀
𝐸
(1)
Thereby, M
i
is the mask image and E
i
is erosion
image.
3.2 Feature Extraction
Many works are based on deep learning to classify
actions based on VGG 16, VGG19 and ResNet, these
networks are used to extract the features map, and one
of the most important ones of these networks is
Inception v3, that we used as a base network. In our
work, we make modifications to Inception v3,
including removing the fully connected layer (FC
Layer) to exploit 2048 * N of FV for each action. The
Inception v3 algorithm is considered to be one of the
most effective deep learning algorithms. This
algorithm consists of 48 convolutional layers to
ensure that its results are accurate, it accurately
describes the activities that take place within the car
cabin while the driver is engaged in nighttime driving.
Figure 3 shows the spatial attention network for
feature extraction. It consists of input, a pre-trained
model of Inception v3, Flatten Layer, “ReLU”
nonlinear unit and the output features. The activation
of the gate is computed as Equation (2). Where
“x
input
” is the current input, “w
x
” is the learnable
parameter matrix and b is bias.
𝑥
𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈𝑤
𝑥
𝑏
(2)
Figure 3: Spatial attention network of HSMTA.
To improve the performance of a particular
algorithm, we use a loss function which is also called
a cost function. We often seek to reduce this value in
artificial neural networks. It is abbreviated as "Loss"
(Machine learning mastery, 2019).
Our project is a multiclass classification, so we
need a categorical cross-entropy loss function.
Thereby, it can be expressed by Equation (3)
(Knowledge Center, 2022).
𝐿𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝑦
.log ŷ
(3)
where s represents the number of scalar values
that are produced by the model, and “y
i
” represents
the value that corresponds to the target, “ŷ
i
” is the
scalar value in the model output. Because of the
minus sign, when the distributions are brought into
closer proximity with one another, the loss will be
reduced.
Hard Spatio-Multi Temporal Attention Framework for Driver Monitoring at Nighttime
55
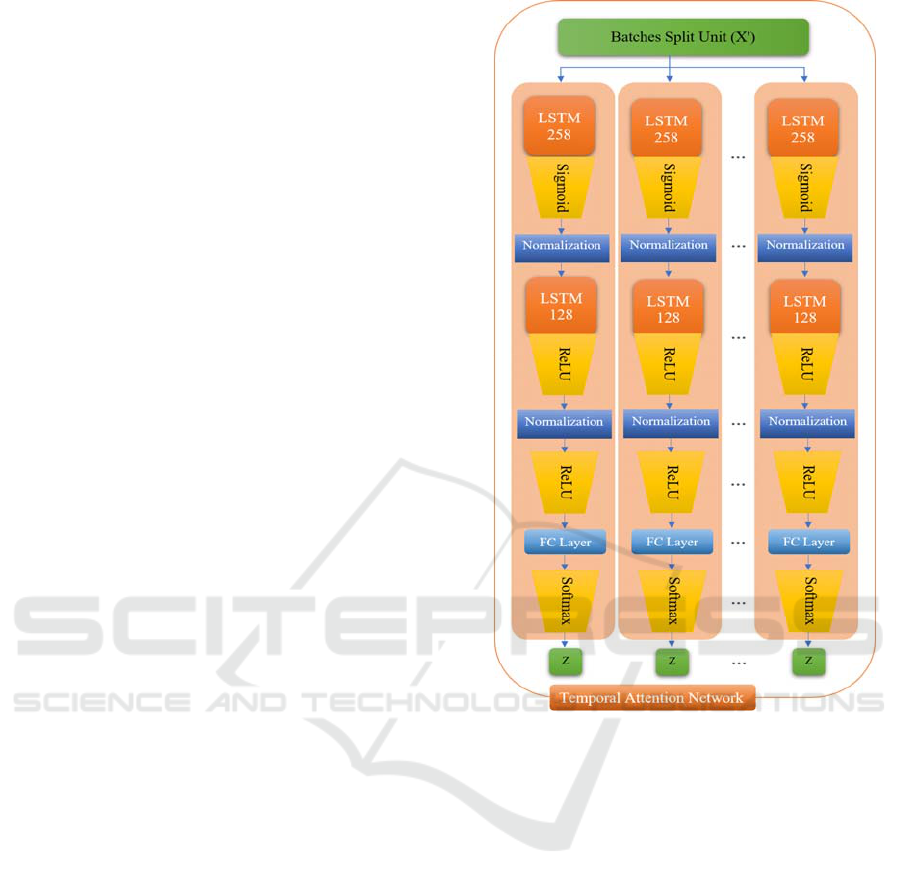
3.3 Classification
We proposed a novel multi-temporal attention
mechanism because we believe that the useful
information in explaining the human action of the
driver is in multiple frames. Batches contain a different
number of vectors and this size is pre-set by the
Batches Split Unit (BSU). Every Long-Short Time
Memory (LSTM) network (Hochreiter, 1997) (Graves,
2012), consist of four components: input gate, output
gate, forget gate and cell. The cell is able to remember
values over randomly long periods of time, and its
three gates are responsible for directing the flow of data
into a cell and out of it. LSTM is designed primarily
for time series processing and specifically to address
the issue of vanishing gradients (Siami-Namini, 2019).
Figure 4 illustrate a temporal attention network
consisting of a BSU, two LSTM networks, two
Normalization layer, a “ReLU” nonlinear unit
activation function, a fully connected layer and
“softmax” unit, this will play the important role in
temporal attention to extract features and actions
classify. The activation of the gates computed as
Equations (4-7). Where x' is the current input, w
x
, w
h
,
w
LS
, w
LR
is the learnable parameter matrices, b is bias
and h
t-1
it’s a hidden state of the previous time step.
𝐿𝑆
𝑆𝑖𝑔𝑚𝑜𝑖𝑑
𝑤
𝑥
𝑤
ℎ
𝑏
(4)
𝐿𝑅
𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈
𝑤
𝐿𝑆
𝑤
ℎ
𝑏
(5)
𝑅
𝑅𝑒𝐿𝑈
𝑤
𝐿𝑅
𝑤
ℎ
𝑏
(6)
𝑍𝑆𝑜𝑓𝑡𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑅
(7)
Accordingly, the new temporal attention of
HSMTA developed as illustrated above in Figure 2,
which is based on dividing the series of night image
feature vectors into a set of batches of variable size
starting from sequence “2” and ending with “N”.
Where the features are then sent to multiple LSTM
units to obtain the driver action.
4 EXPERIMENTAL AND
RESULTS
Experiments were carried out using HSMTA, by
applying the work to a group of nighttime driving
images of two different directions, the first from the
side view and the second from the front view.
4.1 Dataset
We used the only public realistic dataset recorded at
nighttime 3MDAD (Jegham, 2020). The HSMTA test
Figure 4: Temporal attention network of HSMTA.
on the 3MDAD dataset consists of 16 actions
beginning with “safe drive” and the rest of unsafe
driving at nighttime actions: “doing the hair and
makeup”, “ adjusting the radio”, “operating the GPS”,
“typing message with the right hand”, “typing the
message with left hand”, “ speaking phone with the
right hand”, “speaking phone with left hand”, “taking
a photo”, “talking to the passenger”, “ fatigue and
somnolence”, “singing and dancing”, “ drinking with
the right hand”, “ drinking with the left hand”, “going
behind” and “smoking”, they all refer to “Action1” to
“Action16” respectively as a 130,028 inside-vehicle
frames of 19 drivers.
4.2 Experimental Setup
Experiments were carried out on an ASUS laptop
TUF F15 Intel core i7-11370H processor with RAM
size of 40 GBDDR4 and 3200MHz. We work on
windows 10 as an operating system. The code written
by PYTHON 3.7 with Spyder IDE 4.2.5, we depend
ICPRAM 2023 - 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
56
on libraries like TensorFlow 2.6.0 and Keras 2.6.0.
The code was accomplished using a giant Nvidia
RTX 3070 graphics card with 8 GBDDR6. Using
ADAM optimizer, we believe the classification of
hyperparameter values is presented in Table (1). The
3MDAD The dataset is categorized into three
sections: the training data, validation data and the test
data. The training data accounts for 70% of the total
dataset, with the validation data accounting for 10%
and the test data is 20%.
Table 1: Hyper parameters values.
Parameter values
Epochs 100
Batch size 32
Learning rate 10
-4
Weight decay rate 10
-5
4.3 Evaluation of HSMTA Network
The choice of a Spatio-temporal attention period is of
great importance to the study of the effect of the time
factor on the process of Spatio-temporal attention in
the driver's behaviour by choosing the appropriate
timing to choose specific frames. This is because it is
possible that the important information for
classification may be in different frames and at
different time periods, as we mentioned earlier in this
work. We perform an empirical test on 10 different
periods to evaluate the results in terms of
classification accuracy as summarized in Table 2 for
the side view and Table 3 for the front view dataset.
It is noticeable from the results that the proposed
algorithm significantly reduces the time spent in the
implementation process by almost half and actually
gives a more accurate result. Because the time period
‘35’ experimentally obtained the highest accuracy in
the side view (80.37%), and front view (76.06%),
these results will be adopted in comparisons with the
rest of the competing algorithms.
Table 2: HSMTA Classification accuracy for side view.
Period HSMTA Time (ms)
2 72.34% 0.340
4 73.94% 0.266
10 75.75% 0.223
15 78.47% 0.211
20 78.07% 0.201
30 79.22% 0.190
35 80.37% 0.181
40 79.58% 0.175
50 79.08% 0.171
60 78.74% 0.168
Table 3: HSMTA Classification accuracy for front view.
Period HSMTA Time (ms)
2 61.74% 0.267
4 61.54% 0.208
10 65.43% 0.168
15 64.98% 0.161
20 68.49% 0159
30 70.05% 0.152
35 76.06% 0.150
40 66.45% 0.147
50 70.04% 0.144
60 63.11% 0.141
4.3.1 Quantitative Results
Table 4 illustrates in detail a comparison of HSMTA
accuracy in two views to the state-of-the-art
techniques. We compare the results of our model
HSMTA with other models which have attention
mechanisms using the same dataset (3MDAD)-(IR)
to ensure a fair evaluation for the models. It can be
seen that due to the use of Spatio-temporal attention,
HSMTA provided the highest performance than its
counterparts models DADCNet (Su, 2022) and our
previous work (HSA), in both side and front views.
The HSMTA classification accuracy results show
significant improvement over its competitors.
The HSMTA recognition system has improved in
accuracy by 10% over the rest of the hybrid networks
recognition systems that follow other deep learning
methods without attention mechanisms, such as
MCSH (Abdullah, 2022) and hybrid networks LRCN
based on Inception v3, VGG19 and VGG16.
Table 4: HSMTA accuracy comparing to the-state-of-the-
art methods.
Side view
accuracy
Front view
accuracy
MCSH 69.62% 60.29%
LRCN
(
Ince
p
tion v3
)
60.82% 50.74%
LRCN
(
VGG19
)
64.53% 45.07%
LRCN (VGG16) 56.61% 45.02%
Attention-
b
ased methods
HSA 72.16% 61.33%
DADCNet 77.08% 75.51%
HSMTA 80.37% 76.06%
It is worth noting that the side view is always more
accurate than the front view due to the absence of a
viewer that cuts the scene, such as the steering wheel.
Experimentally, the implementation process was
carried out at various varying intervals in order to
capture as much information as possible from
different scenes without losing the understanding
required to explain the driver’s action inside the
Hard Spatio-Multi Temporal Attention Framework for Driver Monitoring at Nighttime
57

vehicle and reduce the cost of image processing to
understand the scene and increase accuracy in an
excellent manner.
4.3.2 Qualitative Results
The confusion matrices shown in Figure 6, Figure 7,
Figure 8 and Figure 9 illustrate the results cases of
HSMTA and LRCN (Inception V3), respectively.
Confusion was recorded between some of the driver's
actions due to the interference with the movements of
the driver's actions inside the car cabin space. Where
we have noticed that there is a remarkable similarity
in some of the images taken when performing actions
or moving from one place to another and returning to
the usual position within one action. This is the secret
of the workforce, due to giving the work the realistic
feature without modifications or revision of the
dataset. Figure 5 is an example of the transition from
action Frame “1” to action Frame “2” and then back
to an image similar to Frame “1”.
Figure 5: Illustration of front view frames similarity in one
in-vehicle action.
Experimentally, the proposed algorithm HSMTA
achieved promising results compared to other hybrid
deep learning algorithms, and the results can be
summarized through confusion matrices on the side
and front views; the proposed algorithm presented a
good percentage in the first action A1 "Safe driving",
but the result of the A1 the LRCN (Inception V3)
algorithm failed, On the other hand, the proposed
algorithm achieved classification accuracy in the side
view Figure 6 a rating of 100% in the A2 “doing hair
and makeup”, A3 “adjusting the radio”, A7 “speaking
in the phone by right hand”, A8 “speaking in the
phone by right hand” and A15 “reaching behind”, this
has never been achieved in any of the previous
literature, especially the hybrid deep learning
algorithms. For the front view Figure 7, the proposed
algorithm gave a complete classification except for
A9, “taking a photo”, while the LRCN (Inception v3)
algorithms gave different percentages with a miss-
classification in some actions as A1, A3, A6, A9, A11
and A16, see Figure 9. On the other hand, in the side
view as Figure 7, for A4, A5, and A6, the accuracy
rate was more than 80%. There is a misclassification
in A11 and A12 because the steering wheel has cut
off some parts of the driver's body, and the
background is not perfect, i.e., the occlusion problem
and other reasons are the similarities mentioned
earlier in this research. Generally, our method
HSMTA achieved a better accuracy rate in the side
view with an amount of 80%, and 76% for the front
view and was lower in the LRCN (Inception v3)
algorithm.
Figure 6: Confusion matrix of HSMTA for side view.
Figure 7: Confusion matrix of HSMTA for front view.
Figure 8: Confusion matrix of LRCN (Inception v3) for side
view.
In this paper, we put forward HSMTA, a hard
spatio-multi temporal attention network to recognize
in-vehicle driver action at nighttime in real-world
environments taking into consideration the time,
which proved the great progress appropriately in
ICPRAM 2023 - 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
58

Figure 9: Confusion matrix of LRCN (Inception v3) for
front view.
experimental results. Because we want to ensure that
our proposed method is as accurate and reliable as
possible, we run the HSMTA on the 3MDAD dataset
from both the side and front perspectives. We have
achieved an accuracy of more than 80%, which is the
highest percentage that has been achieved in the state-
of-the-art in both a realistic and uncontrolled setting.
5 DISCUSSIONS
Our proposed method HSMTA introduced a valuable
and important pictorial explanation of the driver's
nighttime actions that were not previously obtained in
the literature because we used several innovative
methods during the successive implementation stages
in a simplified manner, taking into account the
implementation times during the different stages.
There is still a problem in using the method in real-
time due to the presence of major challenges in the
hardware used in addition to the lack of public
abundant datasets in this field. The other challenge is
to treat it to a real database without making any
modifications to it.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we propose a novel hard spatio-multi
temporal attention network for driver action
recognition framework at nighttime. This is done
through the use of two successive techniques of
attention: spatial attention and temporal attention.
Whereas a previous work relied on Piece-wise linear
transformation function and LBP to create a mask by
extracting the most useful spatial features and then
mapping features by organizing them into batches of
different sizes to ensure harmony in the selection of
the numbers of features in each batch with the sizes
of the database to produce the highest accuracy in the
system, and indeed a much higher accuracy was
recorded in classifying the actions of night driving.
The HSMTA achieved an accuracy of up to 80.37
% in terms of classification on the multiview dataset
when viewed from the side and 76.06 % from the
front. In conclusion, the utilization of hybrid
networks that are equipped with a hard attention
mechanism yields a higher level of productivity when
we use a realistic 3MDAD database. Driver action
recognition systems still lack real-time treatments and
the ability to recognize multiple actions occurring at
the same time. For example, a driver might be
smoking and drinking coffee at the same time, and
other concurrent activities.
REFERENCES
Abdullah, K., Jegham, I., Khalifa, A. B., & Mahjoub, M. A.
(2022, May). A Multi-Convolutional Stream for Hybrid
network for Driver Action Recognition at Nighttime.
In 2022 8th International. DOI: 10.1109/
CoDIT55151.2022.9804013
Alkinani, M. H., Khan, W. Z., Arshad, Q., & Raza, M.
(2022). HSDDD: A Hybrid Scheme for the Detection
of Distracted Driving through Fusion of Deep Learning
and Handcrafted Features. Sensors, 22(5), 1864.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051864
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L. J., Li, K., & Fei-Fei,
L. (2009, June). Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical
image database. In 2009 IEEE conference on computer
vision and pattern recognition (pp. 248-255). Ieee. DOI:
10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848
Donahue, J., Anne Hendricks, L., Guadarrama, S.,
Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan, S., Saenko, K., & Darrell,
T. (2015). Long-term recurrent convolutional networks
for visual recognition and description. In Proceedings
of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition (pp. 2625-2634). https://openaccess.thecvf.
com/content_cvpr_2015/papers/Donahue_Long-Term_
Recurrent_Convolutional_2015_CVPR_paper.pdf
Fu, Y., Wang, X., Wei, Y., & Huang, T. (2019, July). Sta:
Spatial-temporal attention for large-scale video-based
person re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI
conference on artificial intelligence (Vol. 33,
No. 01, pp. 8287-8294). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1609/
aaai.v33i01.33018287
Graves, A. (2012). Long short-term memory. Supervised
sequence labelling with recurrent neural networks, 37-
45. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24797-2_2
Guo, M. H., Xu, T. X., Liu, J. J., Liu, Z. N., Jiang, P. T.,
Mu, T. J., ... & Hu, S. M. (2022). Attention mechanisms
in computer vision: A survey. Computational Visual
Media, 1-38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-022-
0271-y
Hassanin, M., Anwar, S., Radwan, I., Khan, F. S., & Mian,
A. (2022). Visual Attention Methods in Deep Learning:
Hard Spatio-Multi Temporal Attention Framework for Driver Monitoring at Nighttime
59

An In-Depth Survey. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2204.07756.https://arxiv.org/pdf/2204.07756.pdf
Hermann, K. M., Kocisky, T., Grefenstette, E., Espeholt,
L., Kay, W., Suleyman, M., & Blunsom, P. (2015).
Teaching machines to read and comprehend. Advances
in neural information processing systems, 28.
https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2015/file/afdec70
05cc9f14302cd0474fd0f3c96-Paper.pdf
Hochreiter, S., & Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural computation, 9(8), 1735-1780. DOI:
10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Islam, A., Long, C., & Radke, R. (2021, May). A hybrid
attention mechanism for weakly-supervised temporal
action localization. In Proceedings of the AAAI
Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 35, No. 2,
pp. 1637-1645). https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/
article/download/16256/16063
Jegham, I., Ben Khalifa, A., Alouani, I., & Mahjoub, M. A.
(2019, September). Mdad: A multimodal and multiview
in-vehicle driver action dataset. In International
Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and
Patterns (pp. 518-529). Springer, Cham. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29888-3_42
Jegham, I., Khalifa, A. B., Alouani, I., & Mahjoub, M. A.
(2018, December). Safe driving: Driver action
recognition using SURF keypoints. In 2018 30th
International Conference on Microelectronics (ICM)
(pp. 60-63). IEEE. DOI: 10.1109/ICM.2018.8704009
Jegham, I., Khalifa, A. B., Alouani, I., & Mahjoub, M. A.
(2020). Soft spatial attention-based multimodal driver
action recognition using deep learning. IEEE Sensors
Journal, 21(2), 1918-1925. DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.
3019258
Jegham, I., Khalifa, A. B., Alouani, I., & Mahjoub, M. A.
(2020). A novel public dataset for multimodal
multiview and multispectral driver distraction analysis:
3MDAD. Signal Processing: Image Communication,
88, 115960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2020.
115960
Khemchandani, R., & Sharma, S. (2016). Robust least
squares twin support vector machine for human activity
recognition. Applied Soft Computing, 47, 33-46.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.05.025
Knowledge Center, “Categorical crossentropy” 2022,
last accessed 1/08/2022. [Online]. Available:
https://peltarion.com/knowledge-center/documentation/
modeling-view/build-an-ai-model/loss-functions/
categorical-crossentropy
Li, D., Yao, T., Duan, L. Y., Mei, T., & Rui, Y. (2018).
Unified spatio-temporal attention networks for action
recognition in videos. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia,
21(2), 416-428. DOI: 10.1109/TMM.2018.
Li, J., Liu, X., Zhang, W., Zhang, M., Song, J., & Sebe, N.
(2020). Spatio-temporal attention networks for action
recognition and detection. IEEE Transactions on
Multimedia, 22(11), 2990-3001. DOI: 10.1109/
TMM.2020.2965434
Li, P., Lu, M., Zhang, Z., Shan, D., & Yang, Y. (2019,
October). A novel spatial-temporal graph for skeleton-
based driver action recognition. In 2019 IEEE
Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC)
(pp. 3243-3248). IEEE. DOI: 10.1109/ITSC.2019.
8916929
Liu, Q., Che, X., & Bie, M. (2019). R-STAN: Residual
spatial-temporal attention network for action
recognition. IEEE Access, 7, 82246-82255. DOI:
10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923651
Machine learning mastery, “Loss and Loss Functions for
Training Deep Learning Neural Networks”, 2019, last
accessed 8/08/2022. [Online]. Available:
https://machinelearningmastery.com/loss-and-loss-
functions-for-training-deep-learning-neural-networks/
Martin, M., Roitberg, A., Haurilet, M., Horne, M., Reiß, S.,
Voit, M., & Stiefelhagen, R. (2019). Drive&act: A
multi-modal dataset for fine-grained driver behavior
recognition in autonomous vehicles. In Proceedings of
the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer
Vision (pp. 2801-2810).
Mattivi, R., & Shao, L. (2009, September). Human action
recognition using LBP-TOP as sparse spatio-temporal
feature descriptor. In International Conference on
Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns (pp. 740-
747). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/
10.1007/978-3-642-03767-2_90
Meng, L., Zhao, B., Chang, B., Huang, G., Sun, W., Tung,
F., & Sigal, L. (2019). Interpretable spatio-temporal
attention for video action recognition. In Proceedings of
the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer
Vision Workshops (pp. 0-0). https://openaccess.
thecvf.com/content_ICCVW_2019/papers/HVU/Meng
_Interpretable_Spatio-Temporal_Attention_for_Video
_Action_Recognition_ICCVW_2019_paper.pdf
Muhammad, K., Ullah, A., Imran, A. S., Sajjad, M., Kiran,
M. S., Sannino, G., & de Albuquerque, V. H. C. (2021).
Human action recognition using attention-based LSTM
network with dilated CNN features. Future Generation
Computer Systems, 125, 820-830. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.future.2021.06.045
Nanni, L., Lumini, A., & Brahnam, S. (2012). Survey on
LBP based texture descriptors for image classification.
Expert Systems with Applications, 39(3), 3634-3641.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.09.054
NHTSA, “Trafic tech Technology Transfer Series” 2017,
last accessed 07/10/2022 [Online]. Available:
https://www.nhtsa.gov/sites/nhtsa.gov/files/documents
/812396_ttnighttimeseatbeltwa_0.pdf
Niu, Z., Zhong, G., & Yu, H. (2021). A review on the
attention mechanism of deep learning.
Neurocomputing, 452, 48-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.neucom.2021.03.091
Sharma, S., Kiros, R., & Salakhutdinov, R. (2015). Action
recognition using visual attention. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1511.04119. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.
org/abs/1511.04119
Siami-Namini, S., Tavakoli, N., & Namin, A. S. (2019,
December). The performance of LSTM and BiLSTM in
forecasting time series. In 2019 IEEE International
Conference on Big Data (Big Data) (pp. 3285-3292).
IEEE. DOI: 10.1109/BigData47090.2019.9005997.
DOI: 10.1109/BigData47090.2019.9005997
ICPRAM 2023 - 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
60

Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep
convolutional networks for large-scale image
recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556.
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556
Su, L., Sun, C., Cao, D., & Khajepour, A. (2022). Efficient
Driver Anomaly Detection via Conditional Temporal
Proposal and Classification Network. IEEE
Transactions on Computational Social Systems. DOI:
10.1109/TCSS.2022. 3158480
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., & Wojna,
Z. (2016). Rethinking the inception architecture for
computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE
conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
(pp. 2818-2826). https://www.cv-foundation.org/
openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/papers/Szegedy_Rethi
nking_the_Inception_CVPR_2016_paper.pdf
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones,
L., Gomez, A. N., ... & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention
is all you need. Advances in neural information
processing systems, 30. https://proceedings.neurips
.cc/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a84
5aa-Paper.pdf
Wang, W., Lu, X., Zhang, P., Xie, H., & Zeng, W. (2019,
November). Driver action recognition based on
attention mechanism. In 2019 6th International
Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI) (pp.
1255-1259). IEEE. DOI: 10.1109/ICSAI48974.2019.
9010589
Wharton, Z., Behera, A., Liu, Y., & Bessis, N. (2021).
Coarse temporal attention network (cta-net) for driver's
activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
Winter Conference on Applications of Computer
Vision (pp. 1279-1289). https://openaccess.
thecvf.com/content/WACV2021/papers/Wharton_Coars
e_Temporal_Attention_Network_CTA-Net_for_Drivers
_Activity_Recognition_WACV_2021_paper.pdf
WHO, “Road traffic injuries,” 2022, last accessed
20/06/2022 [Online]. Available: https://www.who.
int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/road-traffic-injuries
Williams, A. F. (1985). Nighttime driving and fatal crash
involvement of teenagers. Accident Analysis &
Prevention, 17(1), 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-
4575(85)90002-8.
Xia, L., & Li, Z. (2021). A new method of abnormal
behavior detection using LSTM network with temporal
attention mechanism. The Journal of Supercomputing,
77(4), 3223-3241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-
03391-y
Xu, S., Cheng, Y., Gu, K., Yang, Y., Chang, S., & Zhou, P.
(2017). Jointly attentive spatial-temporal pooling
networks for video-based person re-identification. In
Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on
computer vision (pp. 4733-4742). https://openaccess.
thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2017/papers/Xu_Jointly_A
ttentive_Spatial-Temporal_ICCV_2017_paper.pdf.
Hard Spatio-Multi Temporal Attention Framework for Driver Monitoring at Nighttime
61
