
Fine-Tuning Restricted Boltzmann Machines Using No-Boundary
Jellyfish
Douglas Rodrigues
a
, Gustavo Henrique de Rosa
b
, Kelton Augusto Pontara da Costa
c
,
Danilo Samuel Jodas
d
and Jo
˜
ao Paulo Papa
e
Department of Computing, S
˜
ao Paulo State University, Bauru, Brazil
Keywords:
Computing Methodologies, Reconstruction, Neural Networks, Bio-Inspired Approaches.
Abstract:
Metaheuristic algorithms present elegant solutions to many problems regardless of their domain. The Jellyfish
Search (JS) algorithm is inspired by how jellyfish searches for food in ocean currents and performs movements
within the swarm. In this work, we propose a new version of the JS algorithm called No-Boundary Jellyfish
Search (NBJS) to improve the convergence rate. The NBJS was applied to fine-tune a Restricted Boltzmann
Machine (RBM) in the context of image reconstruction. For validating the proposal, the experiments were
carried out on three public datasets to compare the performance of the NBJS algorithm with its original version
and two other metaheuristic algorithms. The results showed that proposed approach is viable, for it obtained
similar or even lower errors compared to models trained without fine-tuning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Metaheuristic algorithms have gained considerable
popularity in solving combinatorial problems that un-
til now were considered impractical due to high com-
putational costs. Problems like the traveling sales-
man (Wang et al., 2003; Hatamlou, 2018) and the
backpack problem (Hembecker et al., 2007) are just
a few examples where we employ metaheuristic algo-
rithms to find feasible solutions.
In machine learning, metaheuristic algorithms
have also played a notable role in improving the
model’s performance, especially in neural network
optimization. Kuremoto et al. (Kuremoto et al.,
2012) employed the Particle Swarm Optimization to
find the correct number of units and hyper-parameter
fine-tuning to the context of time series forecasting.
Moreover, Papa et al. (Papa et al., 2015) applied the
Harmony Search in the context of Bernoulli RBM’s
hyper-parameters fine-tuning. In the same context,
Papa et al. (Papa et al., 2016) applied the Harmony
Search to fine-tune Deep Belief Networks (DBN)
hyper-parameters. Later, Passos et al. (Passos et al.,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0594-3764
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6442-8343
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5458-3908
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0370-1211
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6494-7514
2019) compared six meta-heuristic algorithms to fine-
tune the hyper-parameters of an infinity RBM to the
context of automatic identification of Barrett’s esoph-
agus from endoscopic images of the lower esophagus.
The success achieved by metaheuristic algorithms
is because they are independent of the problem do-
main and can find near-optimal solutions in a rea-
sonable time. In addition, such algorithms can solve
non-linear, non-differentiable, and complex numeri-
cal optimization problems. However, the balance be-
tween exploration and exploitation behaviors is cru-
cial for such algorithms to perform well and avoid get-
ting stuck in local optima. Exploration is the search
for potential solutions in unexplored areas, while ex-
ploitation is the search for better neighboring solu-
tions in promising regions. In this fashion, Chou
and Truong (Chou and Truong, 2021) developed the
novel Jellyfish Search (JS) algorithm inspired by the
behavior of jellyfish’s motion inside the swarm and
the search for food in ocean currents. The algorithm
adopts a time control mechanism to balance the explo-
ration where the jellyfish follow the ocean currents in
search of food and the exploitation behavior in which
the jellyfish moves within the swarm.
In this context, the present work proposes a new
version of the JS algorithm called No-Boundary Jelly-
fish Search (NBJS) for fine-tuning RBM parameters.
Therefore, the main contributions of this work are:
Rodrigues, D., Henrique de Rosa, G., Pontara da Costa, K., Jodas, D. and Papa, J.
Fine-Tuning Restricted Boltzmann Machines Using No-Boundary Jellyfish.
DOI: 10.5220/0011643400003417
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2023) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages
65-73
ISBN: 978-989-758-634-7; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
65

• to introduce the NBJS and JS algorithm in the
context of optimizing RBM’s parameters for the
image reconstruction task; and
• to provide an in-depth comparative analysis be-
tween the JS algorithm and the Black Hole Al-
gorithm (BH) (Hatamlou, 2018) and Particle
Swarm Optimization (PSO) (Kennedy and Eber-
hart, 2001) algorithms in terms of effectiveness
and efficiency.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows: Section 2 presents some theoretical background
concerning Restricted Boltzmann Machines, JS and
NBJS algorithms, respectively, while Section 3 dis-
cusses the methodology employed in this work. Sec-
tion 4 presents the experimental results and Section 5
states conclusions and future works.
2 THEORETICAL FOUNDATION
In this section, we present a theoretical foundation
concerning Restricted Boltzmann Machines and Jel-
lyfish Search.
2.1 Restricted Boltzmann Machines
Restricted Boltzmann Machines (Ackley et al., 1988;
Hinton, 2012) are generative stochastic neural net-
works belonging to a class of energy-based models.
In such models, we have an energy value associated
with each state of the system. Basically, RBMs con-
sist of m neurons in the visible layer v = (v
1
, . . . , v
m
)
and n neurons in the hidden layer h = (h
1
, . . . , h
n
).
Thus, the probability of the system being in a certain
state is given by the Gibbs distribution:
p(v, h) =
1
Z
−E(v,h)
, (1)
where Z =
∑
v,h
e
−E(v,h)
is a partition function. The
energy function is described as follows:
E(v, h) = −
m
∑
i=1
a
i
v
i
−
n
∑
j=1
b
j
h
j
−
m
∑
i=1
n
∑
j=1
v
i
h
j
w
i j
, (2)
where W is the weight associated with the connection
of the neurons of the visible layer and the invisible
layer, and a and b represent the biases of visible and
hidden units, respectively.
In RBMs, connections between layers are bidirec-
tional, but connections between neurons belonging to
the same layer are not allowed. In this way, the states
of the visible and invisible layers are conditionally in-
dependent and can be described as follows:
p(v) =
m
∏
i
p(v
i
|h) and p(h) =
n
∏
j
p(h
j
|v). (3)
Essentially, training RBMs consists of minimizing
the expected log-likelihood for a training sample v,
given by:
argmin
W
E[−log p(v)]. (4)
We can compute the gradient of − log p(v) easily
as follows:
∂ − log p(v)
∂W
= E
h
h
∂E(v, h)
∂W
|v
i
− E
v,h
h
∂E(v, h)
∂W
i
, (5)
where the first term is responsible for increasing the
probability of the data and can be obtained through
conditional probabilities, and the second term is re-
sponsible for reducing the probability of samples gen-
erated by the model. Since this term corresponds to
an intractable problem, we can approximate it using
contrastive divergence training (Hinton, 2002).
2.2 Jellyfish Search
Jellyfish Search was proposed by Chou and
Troung (Chou and Truong, 2021) inspired by how
jellyfishes live in waters of different temperatures
and depths. Let X = {x
1
, x
2
, . . . , x
m
} a population
of jellyfishes, such that x
i
∈ R
n
, ∀i = {1, 2, . . . , m}
represents the position of the i−th jellyfish in a
n−dimensional search space. The Jellyfish Search
is built on three fundamental rules: (i) a mechanism
called “time control” that controls the movement by
deciding whether the jellyfish will follow the ocean
current or will follow the swarm; (ii) jellyfishes are
preferentially attracted to places where the concen-
tration of food is higher; and (iii) the amount of food
available at a given location is defined by the location
and its corresponding objective function.
In the ocean current, there is a large amount of
food, making the jellyfish concentrate on it. The di-
rection of the ocean current is given as follows:
−−−→
trend = x
best
− β ∗ ε ∗ µ
µ
µ, (6)
where x
best
is the jellyfish with the best location, β > 0
is the distribution coefficient that controls the length
of the
−−−→
trend, ε ∈ U(0, 1), and µ
µ
µ ∈ R
n
is the mean lo-
cation of all jellyfishes.
Thus, the new location of each jellyfish is given
by:
x
t+1
= x
t
+ ϕ ∗
−−−→
trend, (7)
where ϕ ∈ U(0, 1).
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
66

As the ocean current temperature changes, jelly-
fishes switch ocean currents and form new swarms.
Over time, a swarm is formed with the jellyfish com-
ing together. The movements of a jellyfish within the
swarm can be (i) passive motions (type A) and (ii) ac-
tive motions (type B). The passive motion is described
as follows:
x
t+1
= x
t
+ η ∗ φ ∗ (U
b
− L
b
), (8)
where η > 0 is the motion coefficient, φ ∈ U(0, 1),
and U
b
∈ R
n
and L
b
∈ R
n
are the upper and lower
bound, respectively.
The active motion can be described as follows:
x
t+1
= x
t
+ (ψ ∗
−−→
step), (9)
where ψ ∈ U(0, 1) and step is defined by:
−−→
step =
(
x
j
− x
i
, if f (x
i
) ≥ f (x
j
)
x
i
− x
j
, otherwise
where f (.) denotes the fitness function.
The time control mechanism regulates jellyfish’s
movement and makes them change their behavior be-
tween following the ocean current or moving within
the swarm. The mechanism comprises a time con-
trol function c(t) and a constant C
0
. The time control
function c(t) can be obtained as follows:
c(t) =
1 −
t
T
∗ (2 ∗ λ − 1)
, (10)
where t is the current iteration, T is the total num-
ber of iterations, and λ ∈ U(0, 1). If c is greater
than C
0
, jellyfishes follow the ocean current; other-
wise, they move within the swarm. Also, the time
control mechanism is used to control the movement
performed by jellyfish within the swarm being Type
A if U(0, 1) ≥ (1 − c(t)) or Type B otherwise.
2.3 No-Boundary Jellyfish Search
In Type A movement, the jellyfish moves around its
location. The purpose of this work is to improve the
convergence rate by changing Equation 8, which is
responsible for the exploitation, as follows:
X
t+1
= X
t
+ η ∗ φ, (11)
where η > 0 is the motion coefficient, and φ ∈
U(0, 1). By removing the multiplicative factor (U
b
−
L
b
) from Equation 8, the magnitude of the motion
is reduced, making the jellyfish explores the region
around it with higher quality.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Experimental Setup
In this work, we proposed enhancing the RBM recon-
structive capacity by fine-tuning the parameters using
the No-Boundary Jellyfish Search algorithm. Briefly
speaking, we trained an RBM model with the follow-
ing hyper-parameter settings: the learning rate η =
0.1, weight decay λ = 0, and momentum ϕ = 0. For
the number of neurons in the hidden layer, we used
three different settings: n = 128, n = 256, and n = 512
represented by the symbols α, β, and γ, respectively.
Concerning the number of epochs, we have employed
T = 1, 10, 25, 50, 100 with mini-batches of size 128.
Also, the image sizes adopted were: 7 × 7, 14 × 14,
28 × 28.
After the model has been trained, the next step is
fine-tuning the parameters. In RBM, more specifi-
cally, if we look at Equation 2, we have the vector
a that represents the bias of the visible layer, and
the vector b that represents the bias of the invisible
layer. Finally, we have the matrix W that represents
the weights of all connections between the visible and
invisible layers. In the optimization task, we used two
different approaches: (i) selecting the best values for
the vector a, or (ii) selecting the best values for the
matrix W
1
.
Briefly explaining the process, the agents that
make up the meta-heuristic algorithm are initialized
with random values by the search space. At each it-
eration, the agents are evaluated in the search space.
In other words, for each evaluated agent, the RBM
model, previously trained, has its parameter (a or W)
replaced by the agent’s current position in the search
space. Then, this new model is validated using a vali-
dation set, and the Mean Square Error (MSE) is com-
puted. At the end of the optimization process, the
previously trained model will have its parameter re-
placed by the position of the best agent, i.e., the set of
parameters that minimizes the MSE in the validation
set.
2
Given the values that makeup a or W of the trained
model, the lower bound (lb) and upper bound (ub) of
the decision variables are given by:
lb = param − ∆ and ub = param + ∆, (12)
1
It was decided to optimize only the bias a and the
weight matrix W to test the proposal and then extend it to
other network parameters. As it is a new proposal, the be-
haviour of these experiments was not known.
2
Our source code is available at https://github.com/
gugarosa/rbm tuning.
Fine-Tuning Restricted Boltzmann Machines Using No-Boundary Jellyfish
67

where param means a or W, and ∆ = 0.1, 1.0. Fig-
ure 1 depicts the aforementioned methodology con-
cerning fine-tuning RBM’s parameters.
Initialize population
Replace the params by
the agent's position
Evaluating its validation
accuracy
Update population
Replace the params by
the agent's position
Return the optimized
model
TRAINING
TESTING
Meeting stop
criteria?
Evaluate the population
Yes
No
OPTIMIZATION
Figure 1: Pipeline of the optimization process.
3.2 Datasets
We employed three datasets, described as follows:
• MNIST dataset: it is composed of images of hand-
written digits. The original version contains a
training set with 60,000 images from digits ‘0’ to
‘9’, as well as a test set with 10,000 images.
• KMNIST dataset: it is composed of articles im-
ages. The dataset contains a training set of 60,000
examples and a test set of 10,000 examples.
• FMNIST dataset: it is composed of 70,000 images
of Japonese handwritten digits.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
This section presents the results regarding fine-tuning
RBM’s parameters over MNIST, FMNIST, and KM-
NIST datasets. We carried out the experimental
phase in two stages: (i) convergence analysis; and
(ii) reconstruction analysis. For statistical pursuits
and robust analysis, we used Wilcoxon’s signed-rank
test (Wilcoxon, 1945) adopting p = 0.05 on the re-
sults from 25 independent cross-validation runs. For
comparison purposes, besides No-Boundary Jellyfish
Search and Jellyfish Search algorithms, we also used
the Black Hole and Particle Swarm Optimization al-
gorithms available at Opytimizer library
3
. Thus, the
3
https://github.com/gugarosa/opytimizer.
results that compose this work are presented in terms
of mean and standard deviation. Notice that the best
results are highlighted in bold. Finally, we adopted 10
agents over 15 iterations for all techniques.
4.1 Reconstruction Analysis
Table 1 presents the results obtained considering the
models trained in the training set and, later, evaluated
in the test set without any optimization. Such results
will serve as the baseline for comparison purposes
with the method proposed in this work. Tables 2, 3,
and 4 present the results concerning the MNIST, FM-
NIST, and KMNIST datasets, respectively.
To Facilitate and Guide Our Analysis in Under-
standing the Displayed Results, the Superscript
Markers Separate the Groups of Statistically Sim-
ilar Results. Starting with the MNIST dataset, the
first group is composed of α and 7 × 7 size images,
where the NBJS and JS showed MSE lower than the
baseline concerning the fine-tune W with ∆ = 1.0
considering 10 epochs of pre-training. In α group,
14 × 14 and 28 × 28 size images, the lowest errors
were achieved by the RBM trained conventionally
without fine-tuning.
Moreover, in β and γ groups, NBJS and JS reached
the lowest MSE to fine-tune W concerning 1 and
10 epochs of pre-training on 7 × 7 size images. In
both cases, the best result was achieved with ∆ = 1.0.
However, regarding the 14×14 size images belonging
to γ group, all the analyzed metaheuristics performed
statistically similar to the models without optimiza-
tion in the fine-tuning of a and W for ∆ = 0.1 and
∆ = 1.0. Furthermore, in the 28 × 28 size images, the
NBJS and JS performed similarly to the unoptimized
models in fine-tuning W with ∆ = 0.1.
Considering the FMNIST dataset, NBJS and JS
achieved the best results in the γ group for the fine-
tuning W with ∆ = 1.0 on the 7 × 7 size images. As
for the α group, in the 7 × 7 and 14 × 14 size im-
ages with ∆ = 0.1 and ∆ = 1.0, respectively, the NBJS
and JS had statistically similar results to the models
without optimization. Finally, for the γ group, in the
14×14 size images, the NBJS and JS had the smallest
errors considering the fine-tuning of W with ∆ = 0.1.
And in the 28 × 28 size images, for the fine-tuning of
a, all algorithms performed statistically similarly for
both ∆ configurations and ∆ = 0.1 in terms of fine-
tuning the W.
Finally, in the KMNIST dataset, in the 7 × 7 size
images, the PSO obtained the lowest MSE value in
the fine-tuning of the parameter a with ∆ = 1.0 for
the group α. In β and γ groups, the NBJS and the JS
obtained the lowest values of MSE in the fine-tuning
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
68

Table 1: Non-optimized models’ reconstruction errors over MNIST, FMNIST and KMNIST testing sets.
Models
MNIST FMNIST KMNIST
7 × 7 14 × 14 28×28 7 × 7 14 × 14 28 × 28 7 × 7 14 × 14 28 × 28
RBM-α
1
6.87 ± 0.03 24.23 ±0.15 87.66 ± 0.39 9.27 ± 0.03 35.11 ± 0.12 144.13 ± 0.71 10.83 ± 0.04 38.69 ± 0.13 160.92 ± 0.84
RBM-α
10
6.06 ± 0.02 17.39 ±0.05 65.13 ± 0.24 7.64 ± 0.05 26.81 ± 0.09 127.10 ± 0.83 9.70 ± 0.05 31.08 ± 0.11 136.14 ± 0.76
RBM-α
25
5.81 ± 0.02 16.41 ±0.07 62.71 ± 0.33 7.19 ± 0.04 25.81 ± 0.05
11
118.78 ± 1.37 9.39 ± 0.04 29.97 ± 0.11 134.41 ± 0.84
RBM-α
50
5.62 ± 0.05 15.99 ± 0.10
2
61.06 ± 0.38 7.06 ± 0.04
10
25.46 ± 0.06
11
110.92 ± 0.82 9.32 ± 0.03 29.69 ± 0.13
20
132.94 ± 1.27
21
RBM-α
100
5.52 ± 0.03 15.79 ± 0.07
2
59.21 ± 0.47
3
7.02 ± 0.04
10
25.24 ± 0.04
11
106.22 ± 0.62
12
9.27 ± 0.03 29.62 ± 0.11
20
130.80 ± 2.08
21
RBM-β
1
6.84 ± 0.04 21.65 ±0.07 67.13 ± 0.14 8.58 ± 0.03 30.88 ± 0.12 129.05 ± 0.59 10.47 ± 0.08 35.90 ± 0.12 134.16 ± 0.33
RBM-β
10
6.05 ± 0.04 15.90 ±0.05 42.30 ± 0.13 7.52 ± 0.01 25.46 ± 0.09 98.29 ± 0.26 9.59 ± 0.05 28.32 ± 0.05 93.06 ± 0.20
RBM-β
25
5.88 ± 0.02 14.92 ±0.04 37.11 ± 0.16 7.22 ± 0.03 24.81 ± 0.07 92.34 ± 0.21 9.37 ± 0.03 27.14 ± 0.08 85.26 ± 0.15
RBM-β
50
5.71 ± 0.03 14.39 ±0.05 35.02 ± 0.16 7.06 ± 0.02
13
24.49 ± 0.06 90.12 ± 0.26 9.29 ± 0.04 26.68 ± 0.06
23
82.53 ± 0.26
RBM-β
100
5.55 ± 0.04 14.10 ± 0.06
5
33.75 ± 0.12
6
7.02 ± 0.04
13
24.29 ± 0.08
14
88.85 ± 0.21
15
9.24 ± 0.02 26.40 ± 0.08
23
81.00 ± 0.18
24
RBM-γ
1
6.80 ± 0.20 20.16 ±0.16 55.37 ± 0.19 8.50 ± 0.07 27.46 ± 0.11 112.07 ± 0.51 10.53 ± 0.23 33.28 ± 0.22 111.28 ± 0.22
RBM-γ
10
6.06 ± 0.06 15.78 ± 0.05
8
32.67 ± 0.11
9
7.53 ± 0.06 25.27 ± 0.08 90.64 ±0.27
18
9.50 ± 0.08 27.36 ± 0.06 67.79 ± 0.12
RBM-γ
25
5.91 ± 0.04 14.84 ± 0.05
8
29.50 ± 0.06
9
7.26 ± 0.04 24.67 ± 0.07
17
87.27 ± 0.28
18
9.45 ± 0.08 26.50 ± 0.04 62.31 ± 0.08
RBM-γ
50
5.70 ± 0.05 14.35 ± 0.06
8
28.12 ± 0.04
9
7.08 ± 0.02 24.36 ± 0.11
17
85.76 ± 0.31
18
9.30 ± 0.04 26.06 ± 0.05
26
60.05 ± 0.10
RBM-γ
100
5.53 ± 0.04 14.03 ± 0.04
8
27.32 ± 0.04
9
7.01 ± 0.02 24.14 ± 0.06
17
84.43 ± 0.25
18
9.23 ± 0.05 25.81 ± 0.03
26
58.94 ± 0.07
27
Table 2: Optimized models’ reconstruction errors over MNIST testing set.
Models
7 ×7 14 × 14 28 × 28
a W a W a W
∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0
BH-α
1
6.84 ±0.03 6.61 ±0.10 6.79 ±0.04 6.40 ± 0.20 24.19 ±0.14 23.98 ± 0.14 24.10 ± 0.17 24.34 ± 0.24 87.64 ±0.40 87.78 ±0.48 87.66 ±0.42 90.87± 0.83
JS-α
1
6.74 ±0.05 6.59 ±0.40 7.69 ±1.16 5.75 ± 1.19 23.79 ±0.15 24.98 ± 0.89 26.20 ± 1.71 32.59 ± 2.57 86.57 ±0.37 93.56 ±2.95 88.48 ±3.70 127.31 ± 23.45
NBJS-α
1
6.77 ±0.06 6.76 ±0.37 7.97 ±0.95 6.01 ± 0.74 23.85 ±0.14 24.88 ± 0.75 26.38 ± 2.21 31.34 ± 5.11 86.67 ±0.48 95.05 ±2.20 88.32 ±4.37 121.03 ± 17.06
PSO-α
1
6.83 ±0.03 6.26 ±0.14 6.69 ±0.05 6.40 ± 0.18 24.19 ±0.15 24.08 ± 0.20 24.05 ± 0.17 25.25 ± 0.50 87.66 ±0.37 88.14 ±0.39 87.77 ±0.42 96.91± 1.72
BH-α
10
6.04 ±0.02 5.89 ±0.04 5.99 ±0.02 5.76 ± 0.08 17.38 ±0.05 17.35 ± 0.07 17.36 ± 0.05 17.77 ± 0.17 65.14 ±0.25 65.29 ±0.25 65.15 ±0.24 67.14± 0.55
JS-α
10
6.02 ±0.02 6.04 ±0.22 6.38 ±0.44 5.23 ± 0.28
1
17.25 ±0.05 18.56± 0.27 17.18 ± 0.41 21.33 ±1.21 64.89 ± 0.28 69.97 ± 1.76 63.20 ± 0.62 78.68 ±5.02
NBJS-α
10
6.02 ±0.02 6.09 ±0.21 6.46 ±0.32 5.30 ± 0.64
1
17.27 ±0.07 18.66± 0.46 17.31 ± 0.34 20.44 ±2.13 64.87 ± 0.27 70.84 ± 0.78 62.96 ± 0.34 85.10 ±4.68
PSO-α
10
6.03 ±0.03 5.70 ±0.11 5.91 ±0.06 5.63 ± 0.19 17.38 ±0.05 17.43 ± 0.10 17.33 ± 0.08 18.56 ± 0.34 65.13 ±0.25 65.52 ±0.29 65.22 ±0.29 70.17± 0.86
BH-β
1
6.82 ±0.04 6.56 ±0.07 6.68 ±0.06 6.37 ± 0.15 21.63 ±0.06 21.50 ± 0.12 21.52 ± 0.09 22.05 ± 0.48 67.13 ±0.13 67.34 ±0.15 67.17 ±0.13 74.50± 1.02
JS-β
1
6.88 ±0.06 6.29 ±0.26 13.72 ±1.86 3.23 ±0.26
4
21.67 ±0.08 20.52± 0.60 26.98 ± 3.96 26.53 ±2.90 66.72 ± 0.11 69.03 ± 1.62 71.59± 13.32 137.08 ± 18.75
NBJS-β
1
6.86 ±0.07 6.18 ±0.26 10.48 ±3.64 3.32 ±0.33
4
21.64 ±0.10 20.58± 0.81 21.64 ± 3.38 27.02 ±1.77 66.73 ± 0.18 69.66 ± 2.01 69.96± 13.05 144.85 ± 19.50
PSO-β
1
6.80 ±0.04 6.22 ±0.12 6.45 ±0.08 6.40 ± 0.40 21.61 ±0.07 21.62 ± 0.11 21.50 ± 0.14 24.51 ± 0.75 67.14 ±0.15 67.61 ±0.18 67.37 ±0.21 86.40± 3.87
BH-β
10
6.04 ±0.04 5.87 ±0.05 5.92 ±0.04 5.57 ± 0.20 15.89 ±0.05 15.88 ± 0.06 15.84 ± 0.03 16.22 ± 0.17 42.30 ±0.12 42.49 ±0.14 42.40 ±0.12 47.76± 0.84
JS-β
10
6.07 ±0.04 5.62 ±0.23 7.10 ±1.34 3.22 ± 0.28
4
15.85 ±0.06 15.96± 0.34 19.18 ± 1.85 21.60 ±2.82 42.31 ± 0.17 43.53 ± 0.51 44.40 ± 4.96 100.76 ± 19.20
NBJS-β
10
6.07 ±0.06 5.65 ±0.18 7.03 ±1.26 3.20 ± 0.26
4
15.85 ±0.05 16.24± 0.32 17.09 ± 2.03 20.12 ±3.18 42.31 ± 0.17 43.72 ± 0.47 42.74 ± 3.38 109.93 ± 15.39
PSO-β
10
6.03 ±0.04 5.74 ±0.08 5.81 ±0.06 5.57 ± 0.41 15.90 ±0.05 15.97 ± 0.06 15.81 ± 0.10 17.33 ± 0.55 42.31 ±0.12 42.70 ±0.09 42.45 ±0.14 56.42± 1.82
BH-γ
1
6.77 ±0.20 6.56 ±0.22 6.50 ±0.16 6.32 ± 0.31 20.14 ±0.16 20.04 ± 0.14 19.98 ± 0.17 21.76 ± 0.58 55.37 ±0.20 55.50 ±0.20 55.44 ±0.16 64.56± 1.12
JS-γ
1
6.73 ±0.18 6.15 ±0.29 6.06 ±3.95 1.33 ± 0.06
7
20.02 ±0.16 18.98± 0.49 14.75 ± 0.52 14.25± 0.74
8
55.47 ±0.24 55.77 ±0.55 44.36 ±4.02 120.24 ± 11.78
NBJS-γ
1
6.75 ±0.18 6.08 ±0.19 4.95 ±0.33 1.36 ± 0.07
7
20.04 ±0.17 19.16± 0.47 14.84 ± 0.58 14.32± 0.64
8
55.45 ±0.20 56.05 ±0.60 229.20 ±301.12 128.76 ±18.63
PSO-γ
1
6.75 ±0.20 6.18 ±0.18 6.03 ±0.21 8.14 ± 0.79 20.13 ±0.14 20.09 ± 0.16 19.77 ± 0.22 28.28 ± 1.36 55.38 ±0.19 55.73 ±0.18 55.55 ±0.19 80.94± 5.25
BH-γ
10
6.04 ±0.06 5.90 ±0.04 5.79 ±0.08 5.52 ± 0.24 15.77± 0.06
8
15.78 ±0.04
8
15.58 ±0.07
8
16.05 ±0.52 32.67 ± 0.11 32.82 ± 0.10 32.78 ± 0.13 40.66 ±1.07
JS-γ
10
6.01 ±0.06 5.50 ±0.15 5.04 ±0.92 1.36 ± 0.10
7
15.72 ±0.05
8
15.65 ±0.23
8
14.01 ±2.58
8
15.72 ±1.34
8
32.63 ±0.10 33.33 ±0.19 32.84 ±9.23
9
108.16 ±14.30
NBJS-γ
10
6.01 ±0.06 5.49 ±0.14 4.98 ±0.95 1.34 ± 0.05
7
15.74 ±0.05
8
15.71 ±0.24
8
15.15 ±3.61
8
15.84 ±0.75
8
32.63 ±0.10 33.32 ±0.17 30.44 ±2.93
9
105.50 ±12.80
PSO-γ
10
6.03 ±0.06 5.64 ±0.12 5.51 ±0.11 6.34 ± 0.37 15.78± 0.06
8
15.82 ±0.07
8
15.42 ±0.08
8
18.14 ±0.70 32.68 ± 0.11 32.93 ± 0.11 32.88 ± 0.12 51.66 ±3.86
of the parameter W with ∆ = 1.0. In 14 × 14 size
images, NBJS and JS obtained similar results in opti-
mizing the parameter W with ∆ = 0.1 and ∆ = 1.0 to
the results obtained without optimization.
The metaheuristic algorithms, especially the
NBJS algorithm, obtained errors similar to or lower
than the models’ errors without fine-tuning. The num-
ber of functions evaluated during an iteration in a
metaheuristic algorithm is equivalent to the number of
agents. Furthermore, the computational cost to eval-
uate the objective function is just replacing the posi-
tions of each agent in the RBM weight matrix. For
Fine-Tuning Restricted Boltzmann Machines Using No-Boundary Jellyfish
69

Table 3: Optimized models’ reconstruction errors over FMNIST testing set.
Models
7 ×7 14 × 14 28 × 28
a W a W a W
∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0
BH-α
1
9.25 ±0.03 9.16 ±0.04 9.21 ± 0.05 9.12 ± 0.08 35.10± 0.12 34.93 ± 0.15 35.01± 0.10 35.16 ± 0.12 144.12 ±0.70 144.24 ± 0.70 143.98 ±0.68 146.43 ± 0.74
JS-α
1
9.24 ±0.05 9.17 ±0.13 8.24 ± 0.04 9.65 ± 0.89 34.98± 0.13 35.48 ± 0.41 31.81± 0.18 40.11 ± 2.39 143.87 ±0.69 147.08 ± 1.75 132.62 ±1.77 165.04 ± 13.06
NBJS-α
1
9.23 ±0.04 9.22 ±0.20 8.21 ± 0.05 10.06 ± 0.83 34.98 ± 0.13 35.46 ± 0.47 31.95 ±0.32 43.06 ± 2.35 143.83 ± 0.69 147.63 ± 1.42 132.79 ± 2.13 170.35 ± 22.75
PSO-α
1
9.24 ±0.04 9.10 ±0.09 9.15 ± 0.07 9.11 ± 0.22 35.08 ± 0.12 35.07 ± 0.20 34.93 ±0.18 36.62 ± 0.50 144.09 ± 0.68 144.65 ± 0.72 144.11 ± 0.60 151.48 ± 1.79
BH-α
10
7.63 ±0.04 7.58 ±0.04 7.58 ± 0.05 7.48 ± 0.08 26.80 ± 0.09 26.78 ± 0.09 26.75 ±0.10 27.28 ± 0.29 127.10 ± 0.83 127.19 ± 0.79 126.96 ± 0.82 128.57 ± 1.16
JS-α
10
7.60 ±0.04 7.67 ±0.07 7.00 ±0.04
10
8.02 ±0.48 26.75 ±0.10 27.56 ±0.20 25.21 ±0.27
11
31.74 ±2.49 126.84 ± 0.82 128.96 ±0.80 115.30± 0.74 135.76 ± 4.26
NBJS-α
10
7.60 ±0.04 7.67 ±0.07 6.99 ±0.03
10
8.39 ±0.29 26.74 ±0.10 27.52 ±0.19 25.22 ±0.40
11
33.67 ±3.28 126.87 ± 0.83 128.93 ±1.01 115.35± 0.81 138.35 ± 6.82
PSO-α
10
7.63 ±0.05 7.60 ±0.05 7.58 ± 0.05 7.72 ± 0.10 26.79 ± 0.09 26.93 ± 0.11 26.74 ±0.11 28.55 ± 0.43 127.06 ± 0.85 127.49 ± 0.90 126.98 ± 0.79 131.47 ± 1.18
BH-β
1
8.57 ±0.03 8.49 ±0.03 8.50 ± 0.03 8.53 ± 0.23 30.86 ± 0.12 30.79 ± 0.15 30.74 ±0.13 31.73 ± 0.45 129.04 ± 0.57 129.16 ± 0.60 128.92 ± 0.56 134.28 ± 1.34
JS-β
1
8.54 ±0.03 8.49 ±0.13 8.02 ± 0.51 8.47 ± 0.45 30.84 ± 0.12 31.16 ± 0.28 28.26 ±1.51 42.48 ± 3.28 128.48 ± 0.53 130.94 ± 0.81 111.57 ± 3.72 187.45 ± 26.21
NBJS-β
1
8.53 ±0.03 8.51 ±0.05 7.89 ± 0.56 8.09 ± 0.46 30.84 ± 0.12 31.09 ± 0.17 27.60 ±0.64 43.96 ± 3.35 128.48 ± 0.52 130.41 ± 0.85 115.17 ± 7.33 194.65 ± 27.40
PSO-β
1
8.56 ±0.03 8.47 ±0.06 8.44 ± 0.06 8.73 ± 0.28 30.85 ± 0.13 30.92 ± 0.17 30.69 ±0.18 33.59 ± 0.69 129.03 ± 0.61 129.51 ± 0.69 129.05 ± 0.63 144.27 ± 2.77
BH-β
10
7.51 ±0.01 7.47 ±0.03 7.46 ± 0.04 7.41 ± 0.08 25.45 ± 0.09 25.42 ± 0.11 25.37 ±0.11 26.73 ± 0.32 98.29 ± 0.26 98.44 ± 0.31 98.27 ± 0.32 105.35 ± 0.78
JS-β
10
7.49 ±0.01 7.57 ±0.06 8.25 ± 1.40 7.61 ± 0.40 25.35 ± 0.09 25.87 ± 0.15 30.44 ±6.31 36.18 ± 2.72 97.70 ± 0.26 98.23 ± 0.47 96.97 ± 7.86 169.09 ± 18.54
NBJS-β
10
7.49 ±0.01 7.59 ±0.08 8.42 ± 1.12 7.82 ± 0.42 25.34 ± 0.09 25.88 ± 0.22 32.60 ±4.79 37.60 ± 4.40 97.68 ± 0.26 98.28 ± 0.40 97.68 ±10.17 148.84 ± 15.41
PSO-β
10
7.51 ±0.02 7.50 ±0.04 7.39 ± 0.04 7.57 ± 0.17 25.45 ± 0.09 25.49 ± 0.10 25.36 ±0.08 29.04 ± 0.58 98.29 ± 0.27 98.79 ± 0.32 98.39 ± 0.18 114.54 ± 2.19
BH-γ
1
8.49 ±0.07 8.39 ±0.05 8.33 ± 0.07 8.58 ± 0.46 27.45 ± 0.11 27.38 ± 0.10 27.39 ±0.11 30.86 ± 0.51 112.05 ± 0.50 112.19 ± 0.44 112.07 ± 0.48 123.33 ± 1.97
JS-γ
1
8.41 ±0.07 8.27 ±0.13 6.29 ± 0.41 4.93± 0.21
16
27.21 ±0.11 27.72 ±0.18 33.45± 30.77 35.29 ± 1.60 111.48 ± 0.51 113.08 ± 0.40 134.08 ± 17.21 198.84 ±5.65
NBJS-γ
1
8.41 ±0.06 8.37 ±0.12 8.76 ± 7.39 7.51 ± 7.83 27.20 ± 0.11 27.77 ± 0.19 42.75 ± 41.22 34.99 ±1.05 111.49 ± 0.51 113.03 ±0.53 93.77 ± 0.98 197.88 ± 10.55
PSO-γ
1
8.48 ±0.07 8.39 ±0.10 8.12 ± 0.05 9.54 ± 0.57 27.45 ± 0.11 27.51 ± 0.14 27.52 ±0.14 35.83 ± 1.48 112.06 ± 0.50 112.56 ± 0.54 112.32 ± 0.52 138.71 ± 5.22
BH-γ
10
7.53 ±0.06 7.47 ±0.07 7.38 ± 0.05 7.36 ± 0.26 25.26 ± 0.09 25.25 ± 0.09 25.15 ±0.07 26.79 ± 0.37 90.64 ±0.28
18
90.82 ±0.27
18
90.63 ±0.31
18
106.06 ±1.75
JS-γ
10
7.48 ±0.06 7.50 ±0.11 6.06 ± 0.31 4.94± 0.18
16
25.07 ±0.08 25.59 ±0.22 22.42 ± 2.93
17
33.11 ±3.73 89.84± 0.29
18
90.04 ±0.82
18
95.40 ±27.45
18
172.91 ±21.13
NBJS-γ
10
7.48 ±0.06 7.56 ±0.09 6.20 ± 0.44 5.14± 0.22
16
25.06 ±0.08 25.75 ±0.19 22.18 ± 1.21
17
33.54 ±2.34 89.82± 0.26
18
90.45 ±0.34
18
84.27 ±14.87
18
174.66 ±23.89
PSO-γ
10
7.52 ±0.06 7.51 ±0.07 7.29 ± 0.09 8.04 ± 0.38 25.26 ± 0.08 25.36 ± 0.14 25.20 ±0.13 29.29 ± 0.88 90.62 ±0.28
18
91.15 ±0.20
18
91.01 ±0.39
18
122.89 ±4.74
Table 4: Optimized models’ reconstruction errors over KMNIST testing set.
Models
7 ×7 14 ×14 28 ×28
a W a W a W
∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 0
0
0.
.
.1
1
1 ∆
∆
∆ =
=
= 1
1
1.
.
.0
0
0
BH-α
1
10.79 ±0.04 10.39 ± 0.06 10.78± 0.05 10.64 ± 0.14 38.64 ±0.13 38.37 ± 0.16 38.63 ±0.13 38.91 ±0.20 160.84 ± 0.83 160.72 ± 0.89 160.89 ± 0.79 163.86 ± 0.94
JS-α
1
10.67 ±0.05 9.95 ± 0.97 11.08± 0.62 10.03 ± 0.59 37.73 ±0.14 41.33 ± 1.00 41.01 ±2.18 43.36 ±2.42 157.35 ± 0.80 169.78 ±10.02 163.12 ±6.24 187.36 ±13.69
NBJS-α
1
10.67 ±0.08 9.67 ± 1.00 11.29± 0.84 9.81 ± 0.30 37.73± 0.12 40.78 ± 1.99 41.12± 1.85 43.93 ± 2.18 157.36± 0.80 167.97 ± 7.81 167.66 ± 6.19 195.96 ± 13.55
PSO-α
1
10.75 ±0.07 9.83 ± 0.40 10.77± 0.05 10.55 ± 0.32 38.58 ±0.15 38.52 ± 0.41 38.62 ±0.13 40.18 ±0.49 160.81 ± 0.84 161.40 ± 1.04 160.94 ± 0.81 169.29 ± 2.05
BH-α
10
9.67 ±0.05 9.35 ±0.10 9.66 ±0.04 9.46 ± 0.11 31.06± 0.10 30.91 ± 0.18 31.02± 0.10 31.32 ± 0.15 136.11± 0.78 136.20 ± 0.71 136.10 ±0.80 138.14 ± 0.90
JS-α
10
9.57 ±0.04 9.93 ±0.41 9.89 ±0.33 9.40 ± 0.43 30.68± 0.09 33.34 ± 0.90 31.23± 0.21 37.01 ± 1.57 134.45± 0.73 141.08 ± 4.49 135.96 ±1.24 163.67 ± 9.29
NBJS-α
10
9.57 ±0.05 9.74 ±0.65 9.99 ±0.33 9.38 ± 0.35 30.68± 0.09 32.89 ± 1.33 31.27± 0.31 36.51 ± 2.08 134.35± 0.70 140.70 ± 3.12 135.79 ±1.12 157.81 ± 5.66
PSO-α
10
9.64 ±0.04 8.95 ± 0.22
19
9.62 ±0.04 9.45 ± 0.17 31.05± 0.10 30.92 ± 0.22 31.03± 0.10 32.58 ± 0.32 136.15± 0.76 136.51 ± 0.80 136.22 ±0.81 141.95 ± 1.28
BH-β
1
10.44 ±0.08 10.09 ± 0.10 10.30± 0.08 10.28 ± 0.34 35.87 ±0.12 35.51 ± 0.10 35.82 ±0.12 36.29 ±0.31 134.15 ± 0.36 134.22 ± 0.38 134.27 ± 0.37 142.67 ± 1.36
JS-β
1
10.38 ±0.08 8.71 ± 0.60 7.82 ±1.24 5.97 ± 0.18
22
35.76 ±0.22 32.49 ± 2.51 36.78 ±2.72 41.26 ±1.86 131.93 ± 0.25 132.90 ± 7.55 130.76 ± 9.51 210.66 ± 7.30
NBJS-β
1
10.35 ±0.09 9.19 ± 0.62 7.82 ±0.94 5.85 ± 0.31
22
35.61 ±0.20 33.86 ± 1.74 36.61 ±2.47 41.30 ±1.43 131.85 ± 0.33 138.13 ± 3.98 127.59 ± 7.77 207.93 ±14.93
PSO-β
1
10.39 ±0.10 9.62 ± 0.25 10.10± 0.15 10.77 ± 0.63 35.84 ±0.15 35.69 ± 0.26 35.82 ±0.14 38.29 ±0.73 134.12 ± 0.36 134.81 ± 0.43 134.46 ± 0.33 156.26 ± 2.89
BH-β
10
9.56 ±0.06 9.30 ±0.09 9.48 ±0.07 9.18 ± 0.20 28.31± 0.05 28.24 ± 0.11 28.25± 0.06 28.66 ± 0.27 93.07 ± 0.19 93.29 ± 0.26 93.21 ±0.23 100.22 ± 0.53
JS-β
10
9.47 ±0.08 8.24 ±0.33 10.91± 3.10 6.33 ± 0.30
22
28.05 ±0.08 27.73 ± 1.24 29.52 ±2.46 35.11 ±3.76 92.31± 0.19 96.76 ±1.75 95.27± 6.74 163.08 ±17.29
NBJS-β
10
9.47 ±0.06 8.60 ±0.39 12.12± 1.94 6.21 ± 0.28
22
28.07 ±0.06 28.80 ± 0.84 29.54 ±1.73 35.54 ±2.09 92.36± 0.23 95.20 ±2.44 92.72± 3.55 156.13 ±16.53
PSO-β
10
9.55 ±0.06 8.86 ±0.28 9.34 ±0.06 9.14 ± 0.46 28.28± 0.04 28.35 ± 0.08 28.26± 0.06 29.75 ± 0.32 93.08 ± 0.20 93.55 ± 0.26 93.37 ±0.23 113.23 ± 3.14
BH-γ
1
10.49 ±0.22 10.15 ± 0.21 10.22± 0.23 10.61 ± 0.39 33.25 ±0.22 33.00 ± 0.18 33.07 ±0.28 36.83 ±1.18 111.27 ± 0.21 111.54 ± 0.26 111.36 ± 0.22 125.93 ± 2.04
JS-γ
1
10.29 ±0.21 8.98 ± 0.40 21.64 ± 16.16 2.44 ±0.13
25
32.60 ±0.20 29.99 ± 1.48 88.35 ±63.59 25.24 ± 0.98
26
110.24 ±0.19 109.04 ± 2.61 93.20 ± 1.65 170.98 ± 8.96
NBJS-γ
1
10.26 ±0.20 9.06 ± 0.48 15.91 ± 14.59 2.40 ±0.10
25
32.59 ±0.21 29.74 ± 1.30 88.26 ±63.68 24.91 ± 0.52
26
110.28 ±0.28 108.66 ± 3.07 92.72 ± 1.09 172.70 ± 7.76
PSO-γ
1
10.45 ±0.21 9.57 ± 0.37 9.79 ±0.24 11.74 ±0.91 33.21 ± 0.19 33.09 ± 0.23 33.03 ± 0.32 43.82 ± 2.57 111.27± 0.21 112.02 ± 0.35 111.62 ±0.30 152.02 ± 6.70
BH-γ
10
9.47 ±0.09 9.22 ±0.09 9.27 ±0.08 9.49 ± 0.37 27.35± 0.07 27.32 ± 0.15 27.20± 0.07 28.01 ± 0.51 67.79 ± 0.12 68.02 ± 0.23 68.03 ±0.14 85.81 ±2.42
JS-γ
10
9.27 ±0.08 8.08 ±0.31 6.73 ±0.80 2.61 ± 0.14
25
27.14 ±0.09 25.82 ± 0.86 24.08 ± 1.48
26
25.98 ±1.54 67.79± 0.14 68.96 ±0.72 225.91 ± 267.00 151.86 ± 15.73
NBJS-γ
10
9.27 ±0.08 8.28 ±0.33 6.32 ±0.13 2.59 ± 0.11
25
27.15 ±0.06 26.05 ± 0.93 25.14 ± 2.45
26
25.67 ±1.08 67.77± 0.14 68.82 ±0.64 280.13 ± 286.32 161.23 ± 8.41
PSO-γ
10
9.45 ±0.08 8.87 ±0.19 9.03 ±0.05 10.94 ±1.02 27.34 ± 0.05 27.37 ±0.11 26.97 ± 0.10 30.73 ±1.23 67.80± 0.14 68.39 ±0.26 68.36± 0.16 115.01 ± 7.53
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
70
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0.0
2.5
5.0
7.5
10.0
12.5
15.0
17.5
20.0
Error
Delta: 0.1
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
Error
Delta: 0.1
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
10
20
30
40
Error
Delta: 0.1
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
(a) (b) (c)
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
10
20
30
40
Error
Delta: 1.0
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
10
20
30
40
Error
Delta: 1.0
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
10
20
30
40
Error
Delta: 1.0
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
(d) (e) (f)
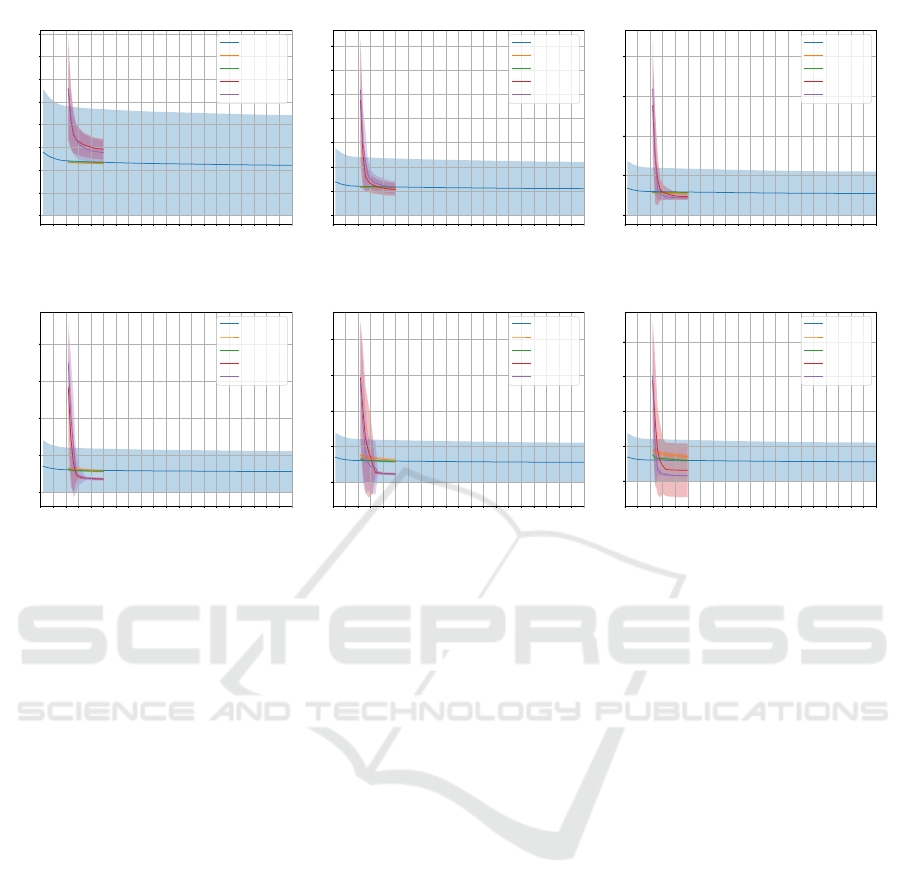
Figure 2: Convergence comparison on MNIST dataset regarding 7 × 7 size images: (a) 128, (b) 256, and (c) 512 hidden
neurons with ∆ = 0.1, and (d) 128, (e) 256, and (c) 512 hidden neurons with ∆ = 1.0.
the assumption that an iteration of the metaheuristic
algorithms and an epoch in RBM training are equiva-
lent, the metaheuristic algorithms achieved similar or
lower errors with the need for a smaller number of
epochs.
4.2 Convergence Analysis
Figures 2, 3, and 4 illustrate a comparison among
NBJS, JS, BH, and PSO convergence on MNIST, FM-
NIST, and KMNIST datasets for optimizing W pa-
rameter regarding 7×7 size images considering two ∆
configurations and 128, 256, and 512 hidden neurons,
respectively. In all cases in Figures 2, 3, and 4, the al-
gorithms obtained convergence similar to or superior
to the RBM convergence using 100 training epochs.
It is also noteworthy that the JS and NBJS techniques
surpassed the convergence of PSO and BH in all con-
figurations except for 128 hidden neurons as it can be
seen in Figures 2a, 3a, and 4a. It is worth mentioning
that the performance of all algorithms when ∆ = 1.0
in the MNIST dataset was shown to outperform when
∆ = 0.1.
However, a decreasing trend in the convergence of
JS and NBJS techniques, concerning images of size
7 × 7, can be observed in Figures 2a and 2b consider-
ing MNIST dataset, all configurations except for the
one shown in Figure 3d considering FMNIST dataset,
and, finally Figures 4a and 4b considering KMNIST
dataset.
5 CONCLUSION
This paper addressed increasing the reconstructability
of the RBM using metaheuristic optimization. The
idea is to pre-train an RBM model and fine-tune both
the a bias and the W connection weights to minimize
the mean square error. Experiments were performed
on the MNIST, FMNIST, and KMNIST datasets with
three different image size settings: 7×7, 14×14, and
28 × 28.
The reported results demonstrated the feasibility
of using metaheuristic algorithms to fine-tune con-
nection weights. The NBJS algorithm achieved er-
rors up to four times smaller than the baseline in
7 × 7. Fine-tuning the a parameter showed no sig-
nificant influence on the models. Assuming that the
iterations of the metaheuristic algorithms are compu-
tationally equivalent to the computational cost of the
RBM training epochs, one can conclude that the meta-
heuristic algorithms achieve errors similar to or lower
than those of the RBM, requiring a lower number of
iterations.
Fine-Tuning Restricted Boltzmann Machines Using No-Boundary Jellyfish
71

0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
5
10
15
20
Error
Delta: 0.1
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Error
Delta: 0.1
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Error
Delta: 0.1
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
(a) (b) (c)
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Error
Delta: 1.0
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Error
Delta: 1.0
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Error
Delta: 1.0
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
(d) (e) (f)
Figure 3: Convergence comparison on FMNIST dataset regarding 7 × 7 size images: (a) 128, (b) 256, and (c) 512 hidden
neurons with ∆ = 0.1, and (d) 128, (e) 256, and (c) 512 hidden neurons with ∆ = 1.0.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
5
10
15
20
25
Error
Delta: 0.1
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
Error
Delta: 0.1
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
10
20
30
40
Error
Delta: 0.1
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
(a) (b) (c)
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
10
20
30
40
Error
Delta: 1.0
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
10
20
30
40
Error
Delta: 1.0
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Iteration
0
10
20
30
40
Error
Delta: 1.0
Baseline
PSO
BH
JS
NBJS
(d) (e) (f)
Figure 4: Convergence comparison on KMNIST dataset regarding 7 × 7 size images: (a) 128, (b) 256, and (c) 512 hidden
neurons with ∆ = 0.1, and (d) 128, (e) 256, and (c) 512 hidden neurons with ∆ = 1.0.
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
72

Regarding future work, we intend to test the per-
formance of the fine-tuning in the bias of the invisible
layer b or even fine-tune the parameters simultane-
ously, e.g. a and b.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are grateful to FAPESP grants
#2013/07375-0, #2014/12236-1, #2019/07665-4,
#2019/18287-0, #2019/02205-5 and, #2021/05516-1,
and CNPq grants 308529/2021-9 and 427968/2018-6.
REFERENCES
Ackley, D., Hinton, G., and Sejnowski, T. J. (1988). A
learning algorithm for boltzmann machines. In Waltz,
D. and Feldman, J., editors, Connectionist Models and
Their Implications: Readings from Cognitive Science,
pages 285–307. Ablex Publishing Corp., Norwood,
NJ, USA.
Chou, J.-S. and Truong, D.-N. (2021). A novel metaheuris-
tic optimizer inspired by behavior of jellyfish in ocean.
Applied Mathematics and Computation, 389:125535.
Hatamlou, A. (2018). Solving travelling salesman problem
using black hole algorithm. Soft Computing, 22:8167–
8175.
Hembecker, F., Lopes, H. S., and Godoy, W. (2007). Par-
ticle swarm optimization for the multidimensional
knapsack problem. In Beliczynski, B., Dzielinski,
A., Iwanowski, M., and Ribeiro, B., editors, Adaptive
and Natural Computing Algorithms, pages 358–365,
Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Hinton, G. E. (2002). Training products of experts by min-
imizing contrastive divergence. Neural Computation,
14(8):1771–1800.
Hinton, G. E. (2012). A practical guide to training restricted
Boltzmann machines. In Montavon, G., Orr, G., and
Muller, K.-R., editors, Neural Networks: Tricks of the
Trade, volume 7700 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 599–619. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Kennedy, J. and Eberhart, R. C. (2001). Swarm Intelli-
gence. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Fran-
cisco, USA.
Kuremoto, T., Kimura, S., Kobayashi, K., and Obayashi,
M. (2012). Time series forecasting using restricted
boltzmann machine. In International Conference on
Intelligent Computing, pages 17–22. Springer.
Papa, J. P., Rosa, G. H., Costa, K. A. P., Marana, A. N.,
Scheirer, W., and Cox, D. D. (2015). On the model
selection of bernoulli restricted boltzmann machines
through harmony search. In Proceedings of the
Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference,
pages 1449–1450, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Papa, J. P., Scheirer, W., and Cox, D. D. (2016). Fine-tuning
deep belief networks using harmony search. Applied
Soft Computing, 46:875–885.
Passos, L. A., de Souza Jr, L. A., Mendel, R., Ebigbo, A.,
Probst, A., Messmann, H., Palm, C., and Papa, J. P.
(2019). Barrett’s esophagus analysis using infinity re-
stricted Boltzmann machines. Journal of Visual Com-
munication and Image Representation.
Wang, K.-P., Huang, L., Zhou, C.-G., and Pang, W. (2003).
Particle swarm optimization for traveling salesman
problem. In Proceedings of the 2003 International
Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics
(IEEE Cat. No.03EX693), volume 3, pages 1583–
1585.
Wilcoxon, F. (1945). Individual comparisons by ranking
methods. Biometrics Bulletin, 1(6):80–83.
Fine-Tuning Restricted Boltzmann Machines Using No-Boundary Jellyfish
73
