
Concept Explainability for Plant Diseases Classification
Jihen Amara
1 a
, Birgitta K
¨
onig-Ries
1,2 b
and Sheeba Samuel
1,2 c
1
Heinz Nixdorf Chair for Distributed Information Systems, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science,
Friedrich Schiller University Jena, Jena, Germany
2
Michael-Stifel-Center for Data-Driven and Simulation Science, Jena, Germany
Keywords:
Plant Disease Classification, Explainable Artificial Intelligence, Convolutional Neural Networks, Testing with
Concept Activation Vectors (TCAV).
Abstract:
Plant diseases remain a considerable threat to food security and agricultural sustainability. Rapid and early
identification of these diseases has become a significant concern motivating several studies to rely on the in-
creasing global digitalization and the recent advances in computer vision based on deep learning. In fact, plant
disease classification based on deep convolutional neural networks has shown impressive performance. How-
ever, these methods have yet to be adopted globally due to concerns regarding their robustness, transparency,
and the lack of explainability compared with their human experts counterparts. Methods such as saliency-
based approaches associating the network output to perturbations of the input pixels have been proposed to
give insights into these algorithms. Still, they are not easily comprehensible and not intuitive for human users
and are threatened by bias. In this work, we deploy a method called Testing with Concept Activation Vectors
(TCAV) that shifts the focus from pixels to user-defined concepts. To the best of our knowledge, our paper is
the first to employ this method in the field of plant disease classification. Important concepts such as color,
texture and disease related concepts were analyzed. The results suggest that concept-based explanation meth-
ods can significantly benefit automated plant disease identification.
1 INTRODUCTION
Plant diseases are important factors as they result in
serious reduction in quality and quantity of agricul-
tural products. Therefore, early detection and diag-
nosis of these diseases are important. In our prior
work, we built a deep learning model based on con-
volutional neural networks (CNN) to identify diseases
from images of plant leaves (Amara et al., 2017) au-
tomatically. While successful, this type of model is a
black-box predictor preventing the acquisition of any
explanation for the predictions. We believe that the
availability of an explainable model that can rapidly
and accurately identify and quantify plant diseases
would have a significant impact on scientific research
and smart crop production. Humans need to know
and understand about the detection, symptoms and
diagnosis process in addition to the high accuracy
of the plant disease classification models. Hence, it
is widely believed that coupling black-box models
with interpretability techniques would increase their
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3675-259X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2382-9722
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7981-8504
adoption in the industry, agriculture, healthcare, and
other high-stakes fields (Molnar, 2020). In this paper,
we define interpretability as the ability to explain or
present in understandable terms to a human, as sug-
gested by (Doshi-Velez and Kim, 2017). We will use
explainability and interpretability interchangeably in
the paper. This urgent need for model interpretabil-
ity led to a proliferation of proposed methods. These
methods, that we will review in Section 2, follow a
common strategy which is simply highlighting pixels
that were relevant for a certain class classification by
a neural network. However, they suffer from various
drawbacks. It has been shown that they are not as reli-
able as expected and are susceptible to human confir-
mation biases (Ghorbani et al., 2019). Consequently,
a new line of research has focused on producing ex-
planations in the form of high-level ”concepts” (Kim
et al., 2018). Hence, our goal in this work is to inves-
tigate the usefulness of these methods that focus on
producing semantic and human-understandable ex-
planations for our use case plant diseases classifica-
tion. We believe that semantics can enhance inter-
pretability in many areas. Instead of just displaying
numbers or saliency maps on image regions, these
246
Amara, J., König-Ries, B. and Samuel, S.
Concept Explainability for Plant Diseases Classification.
DOI: 10.5220/0011667900003417
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2023) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages
246-253
ISBN: 978-989-758-634-7; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

methods output explanations that are understandable
by humans and based on interpretable concepts. For
a diseased plant leaf, instead of outputting a single
probability (e.g., 90% probability of having the late
blight disease), this type of algorithm would, for ex-
ample, output ”high texture irregularity, high amount
of black, yellow and brown areas on top of the leaf”
etc. One of the methods that belong to this family
is Testing with Concept Activation Vectors (TCAV)
(Kim et al., 2018). This method tests the sensitivity
of a trained deep neural model to a defined concept of
interest. It also provides a global explanation for the
model. The central idea of TCAV is to evaluate how
responsive a CNN is to input patterns representing a
concept (e.g., color or texture) linked to the prediction
output of the CNN (e.g., the class ”late blight” dis-
ease). Therefore, in our work, interpretability refers
to a quantitative explanation of which plant disease
concepts are most important for accurate plant dis-
ease classification by CNNs. Our research contribu-
tions are summarized as follows. First, to the best
of our knowledge, this study is the first attempt at a
comprehensive understanding of what semantic con-
cepts the CNN learns during the plant disease diag-
noses. This is a critical issue for the vast prolifera-
tion of deep learning techniques in plant phenotyping
tasks. It can give insights about CNN models for plant
image analysis and help increase trust in such mod-
els. Second, we have presented a concept dataset that
can be used in the future to test concept methods with
plant disease image classification. The remainder of
this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents
related work on interpretability and its application to
plant disease classification, while Section 3 describes
the trained networks, the TCAV theory, and the uti-
lized datasets. Section 4 presents our experimental
results regarding prediction accuracy and model in-
terpretation. Finally, Section 5 depicts our conclusive
remarks and possible future work.
2 RELATED WORK
In recent years, there has been an increasing inter-
est in explainability and interpretability approaches to
deep learning. Two main sets of methods have been
proposed, which are saliency-based methods (Zeiler
and Fergus, 2014) and concept-based methods (Kim
et al., 2018; Zhou et al., 2018). The first is based on
simply highlighting relevant pixels for a certain class
classification by a neural network. Saliency-based
methods are also called feature attribution methods.
In the case of image classification, features are in-
put pixels, and such methods aim to give each pixel
a value that can be understood as the pixel’s rele-
vance to the image’s classification. Few works in the
literature focus on interpreting deep learning mod-
els for plant disease classification using saliency-
based methods. For example, different papers have
tried to apply these visualization methods and present
a comparison study when applied to plant diseases
(Brahimi et al., 2018; Toda and Okura, 2019; Kinger
and Kulkarni, 2021). Other works have focused on
using visualization methods to extract the descrip-
tion of plant diseases from trained CNN (Sladojevic
et al., 2016; Ballester et al., 2017). In addition, some
papers tried to present novel visualization methods
for plant disease classification (Ghosal et al., 2018;
Brahimi et al., 2019). These methods are beneficial
because they give visual explanations, making it easy
to see the critically highlighted pixels. However, these
methods are considered fragile and sensitive to ad-
versarial perturbation (Ghorbani et al., 2019). Other
work has shown how these methods could be highly
unreliable (Kindermans et al., 2019). Since these
methods create importance maps based on individ-
ual input samples, they provide only local interpre-
tations and cannot explain the network’s decisions on
a global scale (Lucieri et al., 2020). In addition, these
methods’ lack of expressiveness to users is an essen-
tial drawback. For instance, the importance of a single
pixel in the classification does not bring a meaningful
explanation, and it is also contrived by the number of
features (Molnar, 2020). Hence, concept-based ap-
proaches were proposed to address these limitations
(Zhou et al., 2018; Kim et al., 2018). Concepts can
be colors, objects, or abstract ideas. Users can define
these concepts without the need to train the network
on them. Hence, they are understandable by humans,
and they are not limited to the neural network feature
space. One of these methods is the TCAV approach,
which was proposed by (Kim et al., 2018). We will
describe this method in detail in the following section.
TCAV was successfully used with a different applica-
tion in the medical field (Lucieri et al., 2020). To our
knowledge, concept-based explanation methods have
not previously been explored for plant disease classi-
fication networks. Hence, in this work, we adopt the
TCAV method to the problem of plant disease classi-
fication. We also present a set of concepts that could
be used in this case.
Concept Explainability for Plant Diseases Classification
247

3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
3.1 Dataset and Networks for Plant
Diseases Classification
3.1.1 Datasets
The Plant Village dataset is a public repository that
contains 54,323 images of 14 crops and 38 different
types of plant diseases (Hughes et al., 2015). It has
been extensively used by the community of plant dis-
ease image classification. We used only images of
tomato leaves from this dataset to train the CNNs.
The total number of images is 18,160, divided into ten
classes (nine diseases and a healthy class). Finally,
the data was separated into three sets, containing 80%
of the data in the training set, and the remaining 20%
is divided equally between the testing and validation
sets. Figure 1 presents one example of each disease
class, and Table 1 summarizes our dataset.
Figure 1: Sample images from the Plant Village Dataset.
(a) Bacterial Spot, (b) Early Blight, (c) Healthy, (d) Late
Blight, (e) Leaf Mold, (f) Septoria Leaf Spot, (g) Spider
Mites, (h) Target Spot, (i) Mosaic Virus, and (j) Yellow Leaf
Curl Virus.
Table 1: The image numbers of each tomato disease class
in the Plant Village dataset.
Classes Number of Images
Bacterial Spot 2127
Early Blight 1000
Healthy 1591
Late Blight 1909
Leaf Mold 952
Septoria Leaf Spot 1771
Spider Mites 1676
Target Spot 1404
Mosaic Virus 373
Yellow Leaf Curl Virus 5357
Total 18,160
3.1.2 Models
In this work, we will focus on two widely used CNN
architectures: InceptionV3 (Szegedy et al., 2016) and
Vgg16 (Szegedy et al., 2015). We selected these
architectures due to their high use in the plant dis-
ease classification literature (Lee et al., 2020). To
train these networks, we took advantage of fine-tuned
transfer learning (Weiss et al., 2016), which is based
on transferring the knowledge gained from training
the models on a more significant dataset to a smaller
one. The models were created and loaded with pre-
trained weights on the ImageNet dataset (Deng et al.,
2009). In addition, excluding top layers was per-
formed by defining new layers on the top of the mod-
els. The altered top architecture consists of three
dense layers with corresponding dropout layers. For
training and optimizing the weights on the tomato dis-
ease dataset, we froze the first 51 convolutional layers
and made the rest trainable for InceptionV3, and we
unfroze the final convolutional layers of Vgg16 and
made them trainable. Training optimization was car-
ried out via stochastic gradient descent optimizer with
a learning rate of 0.0001 and momentum of 0.9. We
used a batch size of 20 and 20 epochs for training.
We use data augmentation techniques to increase the
dataset size in training while including different vari-
ations. These variations consist of transformations
such as random rotations, zooms, translations, shears,
and flips to the training data as we train. Both models
were implemented using Keras (Chollet, 2021), and
were saved for subsequent performance testing and
interpretability analysis. We experimented on a server
with a GPU that consists of two NVIDIA Tesla V100
with 128 GB of RAM.
3.2 Network Explanation Through
Concepts
This section will introduce a deep neural network ex-
planation method called Testing with CAV (TCAV).
TCAV requires three types of data samples: samples
representing particular plant disease concepts (con-
cept samples), samples known to be specific plant dis-
ease classes (disease-class samples), and samples se-
lected randomly to supervise the training quality (to
ensure the stability of the results). In contrast to the
original work (Kim et al., 2018), where random ex-
amples may by chance include the concept, we en-
sure that the selected set is strictly negative. Below is
a detailed description of TCAV theory and our study’s
used concepts.
3.2.1 TCAV Theory
To better understand the concepts used by the trained
CNN to classify images as either healthy or diseased
leaves, we use the concept activation vectors (CAVs)
method (Kim et al., 2018) defined as follows: Im-
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
248

portance of a ‘concept’ C (e.g., brown) to an image
class k (e.g., late blight) is found by taking the direc-
tional derivative of class predictions (for class k) at
each layer l of a CNN in the direction of (with respect
to) a CAV. Hence, a CAV, is a vector v
l
c
in the em-
bedding space of a CNN denoting the direction that
encodes the given concept C in the activation space of
a neural network layer l. To find CAV of a concept
C, we need to prepare two datasets: a concept dataset,
which represents C, and a random dataset that does
not contain the concept. A binary concept classifier
is trained to separate the activations generated by the
concept set from those generated by the random set
at a specific hidden layer l. The CAV v
l
c
is then de-
fined as the normal to the hyperplane separating the
two classes at a particular layer l. Finally, given an
image input x, we can measure its conceptual sensi-
tivity by computing the directional derivative S of the
prediction in the direction of the CAV v
l
c
for concept
C:
S
c,k,l
(x) = lim
ε→0
h
l,k
( f
l
(x) +εv
l
c
) − h
l,k
( f
l
(x))
ε
= ∇h
l,k
( f
l
(x)).v
l
c
(1)
where f
l
maps the input x to the activation vector
of the layer l and h
l,k
maps the activation vector to
the logit output of class k. Then, to measure the in-
fluence of a CAV on a class of input images, a metric
called TCAV score is computed. It employs the direc-
tional derivatives S
c,k,l
(x) to compute the contextual
sensitivity of a concept towards the whole inputs X
k
for class k. The TCAV score is given by:
TCAV
Q
c,k,l
=
x ∈ X
k
;S
c,k,l
(x) > 0
|
X
k
|
(2)
Hence, the TCAV score denotes the ratio of class k’s
inputs that are positively influenced by concept C.
Additionally, the authors perform a statistical signif-
icance test of TCAV scores to make sure that only
meaningful CAV s are taken into account. They com-
pute multiple CAVs between concept images and a
batch of random images. In addition, they train ran-
dom CAVs where both concept set and random set are
random images. Then they perform a two-sided t-test
of the TCAV scores based on these multiple samples.
The resulting concept is considered significant for the
class prediction if they can reject the null hypothesis
of a TCAV score of 0.5. This helps to make sure that
concept CAVs and random CAVs are significantly dif-
ferent from each other. TCAV authors further perform
Bonferroni correction (p < α/m,m = 2) for multiple
comparisons between all concept-random pairs to re-
duce potential for false positives (incorrect rejection
of the null hypothesis, or a Type I error) to prevent
mistaking as significant a truly insignificant concept
(Kim et al., 2018). In our work, TCAV is imple-
mented using Keras rather than the original authors’
Tensorflow code (Kim et al., 2018).
3.2.2 Concepts Used for Analysis
Identification of plant diseases is commonly accom-
plished through visual inspection of the disease’s ef-
fect on the plant. This effect is considered a symptom
and could be detectable as a change of color or texture
of the leaf caused by the pathogen. In our work, we
would like to see if the CNN learned representation
of various concepts and those often used by plant dis-
eases experts are complementary. Hence, we choose
to test the concepts of color, texture, and late blight
disease pattern described below. Also, to show the
feasibility of this methodology and to have a general
disease pattern, we focus on one disease class: late
blight disease, which affects both potatoes and toma-
toes. The concepts used in this work to interpret the
deep classifiers are defined below in accordance with
the description in plant stress phenotyping literature
(Isleib, 2012).
Color Concepts. To train TCAV, we used colors
as concepts such as red, brown, blue, yellow, and
green. We wanted to test our trained models’ sensitiv-
ity to these colors especially green, brown, and yellow
which can present the difference between healthy and
diseased states. We will hence gain more comprehen-
sion of how our internal network behaves. Random
images used are grayscale images of diseased plant
leaves other than tomato. We produced 100 pictures
per color synthetically by generating the color chan-
nel randomly.
Describable Texture Dataset (DTD) Concepts
(Cimpoi et al., 2014). Texture is an essential part of
plant disease identification as it depicts more knowl-
edge of the infected leaf region. Infected leaves can
turn dry and present signs like crackedness, wrin-
kles, bumpiness, fibrousness, etc. Hence, this work
presents a dataset of texture concepts that could be
used with plant diseases and are also understandable
to humans. The dataset is extracted from the DTD
database (Cimpoi et al., 2014). DTD is a texture
database collected “in the wild” with semantic at-
tributes. It contains a list of 47 categories inspired
by human perception. The concepts concerning plant
diseases that we choose from DTD are: blotchy,
bumpy, cracked, fibrous, pitted and wrinkled. For
the TCAV experiment, we chose 100 images for each
concept category. For the random images, we selected
healthy images of leaves other than Tomato. Figure 2
presents some examples from the DTD categories.
Concept Explainability for Plant Diseases Classification
249

Figure 2: Concepts related to plant disease symptoms
extracted from DTD texture database (blotchy, bumpy,
cracked, pitted, fibrous, wrinkled) (Cimpoi et al., 2014).
Late Blight Disease Concepts. Late blight is a devas-
tating disease that can affect potato and tomato plants.
It is caused by the water mold Phytophthora infestans
(Britannica, 2020). The first symptoms of the disease
can start with light to dark green spots in the leaves,
which rapidly develop into large dark brown or black
lesions. Leaf lesions are also frequently surrounded
by a yellow chlorotic halo. Leaves can become dry
and shriveled, and crops can be severely damaged. In
our experiment, we use the images of potato leaves in-
fected by the late blight disease as a visual representa-
tion of the disease concept. These images will depict
the disease pattern that appears on the infected leaves.
It will help us test the network’s ability to learn the
representation of the disease independently from the
leaf shape or type. We used healthy leaves of plants
other than tomatoes and potatoes for the random im-
ages.
4 RESULTS AND ANALYZES
4.1 Network Training Results
This section will present the results of the models
evaluation on our dataset. Table 2 shows the found
results. The performance of the trained models is
evaluated using recall, precision, and accuracy met-
rics (Davis and Goadrich, 2006).
Table 2: Performance measures for pre-trained models
Vgg16 and InceptionV3.
InceptionV3 Vgg16
Accuracy 0.92 0.98
Precision 0.93 0.98
Recall 0.92 0.98
F1-score 0.92 0.98
As shown in Table 2, Vgg16 and InceptionV3
trained on the Tomato disease dataset have achieved
good results with a predominance from Vgg16
achieving an accuracy of 98% compared to Incep-
tionV3 with an accuracy of 92%.
4.2 TCAV Experiments Result
We will concentrate on the quantitative evaluation of
the TCAV score. The TCAV score quantifies a given
concept’s positive or negative influence on a specific
target class. For InceptionV3, in each experiment,
TCAV scores were computed within 9 layers (mixed3,
mixed5 to mixed9), which are the concatenation lay-
ers at the end of each inception module. The num-
bers denotes the location depth of a layer in the net-
work. This can help us see how different network
depths affected the final classification. For Vgg16,
TCAV scores were computed within three layers (flat-
ten, dense, and dense 1). We tested the final layers
added on top of the model, which go from the shal-
lowest (flatten) to the deepest (dense 1). We train
CAVs on the activations extracted from these chosen
layers.
4.2.1 Importance of Colors Concepts
Figure 3: TCAV scores for color concepts red, brown,
blue, yellow and green in InceptionV3 with layers mixed
3, mixed 5, mixed 6, mixed 7, mixed 8 and mixed 9.
Figure 4: TCAV scores for color concepts red, brown, blue,
yellow and green in Vgg16 with layers dense 1, dense and
flatten.
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
250
Results for InceptionV3 are shown in Figure 3, where
we tested layers mixed 3, mixed 5, mixed 6, mixed
7, mixed 8, and mixed 9. The layers that should be
chosen for testing are those who passed the statistical
testing (t-test) mentioned above successfully for most
of the concepts. In consistency with plant diseases ex-
perts description (Isleib, 2012) we found that brown
and yellow were both significant for identifying late
blight disease, with TCAV scores as high as 0.83 for
brown in mixed 9 and 0.64 for yellow in mixed 6.
Also, green was significant in layer mixed 6 with a
TCAV score of 0.69. In contrast, the rest of the col-
ors were less important. The bars marked by a star
‘*’ indicate TCAV scores that did not pass the sta-
tistical testing. For Vgg16 (Figure 4), the important
color concepts captured by the model were green and
brown. To our surprise, it seems red was also crucial
for the model in classifying the disease. Green had a
TCAV score of 1 for the three tested layers dense 1,
dense, and flatten. While brown had TCAV scores of
0.9 and 0.87 for the dense and flatten layers. More-
over, red had TCAV scores of 1 and 0.9 for layers
dense 1 and dense. Hence, even though Vgg16 had
better classification performance than InceptionV3,
the latter was better at capturing color concepts simi-
lar to those used by experts to classify plant diseases.
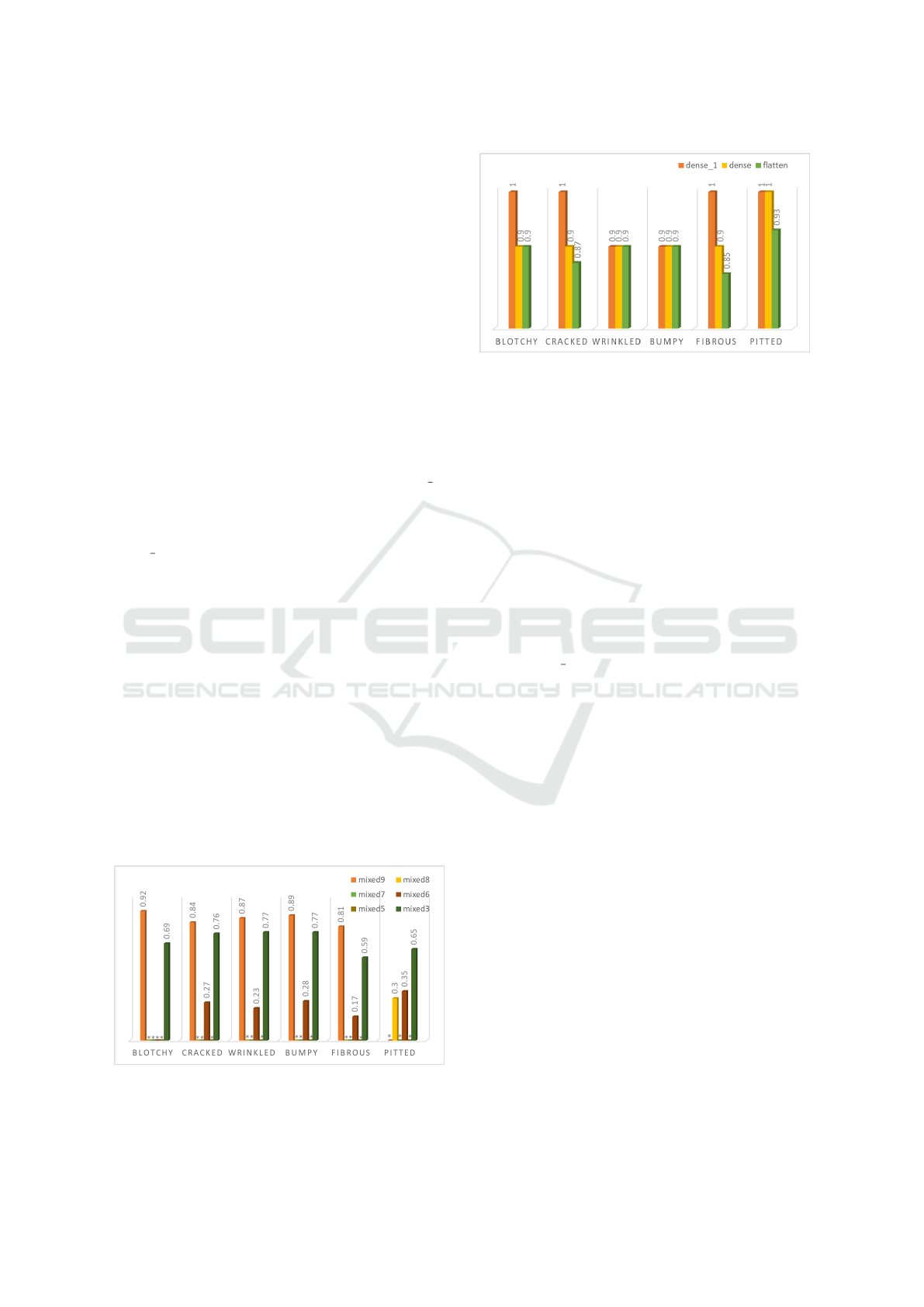
4.2.2 Importance of Describable Texture
Dataset (DTD) Concepts
To show our trained models’ sensitivity to textures re-
lated to plant disease symptoms, we experiment on a
texture recognition dataset (DTD). As shown in Fig-
ure 5 and Figure 6, we got a good insight into what
texture concepts exactly were important for Incep-
tionV3 and Vgg16 when looking to identify a plant
disease. TCAV scores show that concepts such as
blotchy, cracked, wrinkled, bumpy, fibrous, and pit-
ted are highly relevant to the late blight disease class.
In the case of InceptionV3 (Figure 5), we found that
Figure 5: Conceptual importance (TCAV scores) of DTD
concepts blotchy, cracked, wrinkled, bumpy, fibrous, pitted
in InceptionV3.
Figure 6: Conceptual importance (TCAV scores) of DTD
concepts blotchy, cracked, wrinkled, bumpy, fibrous, pitted
in Vgg16.
the layers that could capture these important texture
concepts were mixed 3 and 9, while for the rest of the
layers, TCAV scores were insignificant. This finding
can raise the possibility that some layers can be omit-
ted and consequently reduce the parameters needed
for the network training. Especially in the case of
plant disease classification, where mobile phones can
be used for such tasks, reducing the number of net-
work parameters is exceptionally beneficial for mem-
ory and calculation efficiency. In the other case, re-
sults show that Vgg16 (Figure 6) is sensitive to all
the DTD concepts compared to InceptionV3. TCAV
scores were as high as 1 and 0.9 for the tested layers
dense, dense 1, and flatten, which indicate the sen-
sitivity of these layers to such concepts when classi-
fying late blight disease. In the case of our training
set, images are about a single leaf in a uniform back-
ground, which makes recognizing the change of tex-
tures on the leaf sufficient to solve the task of plant
disease classification. Hence, the results show that
different texture detectors emerge, which explains
why the texture concepts dominate in the tested lay-
ers especially in the case of Vgg16. This discov-
ery is consistent with the former qualitative finding
from (Toda and Okura, 2019) where feature visual-
ization methods showed that the model focused on
learning the visual cues (textutre) of the disease le-
sions rather than objects or shapes. Hence, TCAV
permit for quantitative confirmation of this previous
qualitative discovery. Results look very much as ex-
pected and are aligned with the description in plant
stress phenotyping literature (Isleib, 2012).
4.2.3 Importance of Late Blight Disease
Concepts
To assess the importance of the late blight concept
for both InceptionV3 and Vgg16 when classifying the
disease, we experimented with images of potato with
late blight disease and healthy images of tomato. In-
Concept Explainability for Plant Diseases Classification
251

Figure 7: Conceptual importance (TCAV scores) of late
blight disease concept in InceptionV3.
Figure 8: Conceptual importance (TCAV scores) of late
blight disease concept in Vgg16.
terestingly, from Figure 7 we can see that, for the In-
ceptionV3, the late blight concepts contribute posi-
tively to the tomato late blight disease class. While
the healthy concepts don’t have any significant con-
tribution. To our surprise, this was the opposite for
Vgg16 (Figure 8) where the late blight concepts did
not play a role. A possible explanation for these re-
sults may be the fact that the network did not focus on
disease regions but crop-specific characteristics such
as leaf shape and also for the fact that InceptionV3 is
a deeper network than Vgg16 which helped in captur-
ing better the concepts. These findings further support
the idea of training models with common diseases re-
gardless of crop type for more generalizability (Lee
et al., 2020). Also, it shows that regardless of the
accuracy that indicates a good learning performance,
DL models could inherently learn or fail to learn rep-
resentations from the data which an expert might con-
sider important (Isleib, 2012). This enforces the im-
portance of including explainability in the deep learn-
ing workflow.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The influence of artificial intelligence in modern agri-
culture is increasing with the incorporation of new
technologies such as machine learning and robotics to
boost crop abundance and quality. Plant pathologists
are starting to use deep learning techniques to help
in disease classification, surveillance, and manage-
ment. However, they have yet to be adopted globally
due to concerns regarding robustness, transparency,
and lack of explainability compared with their hu-
man experts counterparts. Hence, in our work, we
adopted a concept-based explanation method called
TCAV for plant disease classification to gain more in-
sights into the model and which concepts affect its
decisions. Based on transfer learning techniques, we
have trained two famous networks, Vgg16 and Incep-
tionV3. Important concepts such as color, texture,
and concept-related disease were analyzed. Our re-
sults show that deep learning based models can learn
and use similar disease-related concepts for predic-
tion as plant pathologists use. Nevertheless, the study
could be extended to grant a more comprehensive in-
terpretation of the TCAV scores for this particular use
case. It would be great to exploit more granular la-
beling of disease concepts and explore more disease
classes to draw further insight into the model’s classi-
fication mechanism and to give better validation of its
decisions. Future work could incorporate plant dis-
ease datasets from the field with real background, and
then, we can use TCAV to ensure the model is un-
biased towards the background. Also, finding a way
to define concepts automatically could simplify the
process by eliminating the necessity for manual an-
notations and could allow revealing new knowledge
for plant disease experts or unexpected biases from
the network. We would also like to investigate ways
of adding semantics through context and Knowledge
Graphs into TCAV.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Chiheb Karray for helpful dis-
cussions. We thank the German Academic Exchange
Service (DAAD) for supporting the work of Jihen
Amara and the Carl Zeiss Foundation for the financial
support of the project “A Virtual Werkstatt for Digiti-
zation in the Sciences (K3)” within the scope of the
program line “Breakthroughs: Exploring Intelligent
Systems for Digitization”- explore the basics, use ap-
plications”. The computational experiments were per-
formed on resources of Friedrich Schiller University
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
252

Jena supported in part by DFG grants INST 275/334-
1 FUGG and INST 275/363-1 FUGG.
REFERENCES
Amara, J., Bouaziz, B., Algergawy, A., et al. (2017). A deep
learning-based approach for banana leaf diseases clas-
sification. In BTW (workshops), volume 266, pages
79–88.
Ballester, P., Correa, U. B., Birck, M., and Araujo, R.
(2017). Assessing the performance of convolutional
neural networks on classifying disorders in apple tree
leaves. In Latin American Workshop on Computa-
tional Neuroscience, pages 31–38. Springer.
Brahimi, M., Arsenovic, M., Laraba, S., Sladojevic, S.,
Boukhalfa, K., and Moussaoui, A. (2018). Deep learn-
ing for plant diseases: detection and saliency map vi-
sualisation. In Human and machine learning, pages
93–117. Springer.
Brahimi, M., Mahmoudi, S., Boukhalfa, K., and Mous-
saoui, A. (2019). Deep interpretable architecture for
plant diseases classification. In 2019 Signal Process-
ing: Algorithms, Architectures, Arrangements, and
Applications (SPA), pages 111–116. IEEE.
Britannica, T. (2020). Editors of encyclopaedia. Argon.
Encyclopedia Britannica.
Chollet, F. (2021). Deep learning with Python. Simon and
Schuster.
Cimpoi, M., Maji, S., Kokkinos, I., Mohamed, S., and
Vedaldi, A. (2014). Describing textures in the wild.
In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer
vision and pattern recognition, pages 3606–3613.
Davis, J. and Goadrich, M. (2006). The relationship be-
tween precision-recall and roc curves. In Proceed-
ings of the 23rd international conference on Machine
learning, pages 233–240.
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., and Fei-
Fei, L. (2009). Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical
image database. In 2009 IEEE conference on com-
puter vision and pattern recognition, pages 248–255.
Ieee.
Doshi-Velez, F. and Kim, B. (2017). Towards a rigorous sci-
ence of interpretable machine learning. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1702.08608.
Ghorbani, A., Abid, A., and Zou, J. (2019). Interpretation
of neural networks is fragile. In Proceedings of the
AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, volume 33,
pages 3681–3688.
Ghosal, S., Blystone, D., Singh, A. K., Ganapathysubrama-
nian, B., Singh, A., and Sarkar, S. (2018). An explain-
able deep machine vision framework for plant stress
phenotyping. Proceedings of the National Academy
of Sciences, 115(18):4613–4618.
Hughes, D., Salath
´
e, M., et al. (2015). An open access
repository of images on plant health to enable the
development of mobile disease diagnostics. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1511.08060.
Isleib, J. (2012). Signs and symptoms of plant disease: Is
it fungal, viral or bacterial. Michigan State University
Extension.
Kim, B., Wattenberg, M., Gilmer, J., Cai, C., Wexler, J.,
Viegas, F., et al. (2018). Interpretability beyond fea-
ture attribution: Quantitative testing with concept ac-
tivation vectors (tcav). In International conference on
machine learning, pages 2668–2677. PMLR.
Kindermans, P.-J., Hooker, S., Adebayo, J., Alber, M.,
Sch
¨
utt, K. T., D
¨
ahne, S., Erhan, D., and Kim, B.
(2019). The (un) reliability of saliency methods. In
Explainable AI: Interpreting, Explaining and Visual-
izing Deep Learning, pages 267–280. Springer.
Kinger, S. and Kulkarni, V. (2021). Explainable ai for deep
learning based disease detection. In 2021 Thirteenth
International Conference on Contemporary Comput-
ing (IC3-2021), pages 209–216.
Lee, S. H., Go
¨
eau, H., Bonnet, P., and Joly, A. (2020). New
perspectives on plant disease characterization based
on deep learning. Computers and Electronics in Agri-
culture, 170:105220.
Lucieri, A., Bajwa, M. N., Braun, S. A., Malik, M. I., Den-
gel, A., and Ahmed, S. (2020). On interpretability of
deep learning based skin lesion classifiers using con-
cept activation vectors. In 2020 international joint
conference on neural networks (IJCNN), pages 1–10.
IEEE.
Molnar, C. (2020). Interpretable machine learning. Lulu.
com.
Sladojevic, S., Arsenovic, M., Anderla, A., Culibrk, D., and
Stefanovic, D. (2016). Deep neural networks based
recognition of plant diseases by leaf image classifi-
cation. Computational intelligence and neuroscience,
2016.
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S.,
Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., and Rabi-
novich, A. (2015). Going deeper with convolutions.
In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer
vision and pattern recognition, pages 1–9.
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., and Wo-
jna, Z. (2016). Rethinking the inception architecture
for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE con-
ference on computer vision and pattern recognition,
pages 2818–2826.
Toda, Y. and Okura, F. (2019). How convolutional neural
networks diagnose plant disease. Plant Phenomics,
2019.
Weiss, K., Khoshgoftaar, T. M., and Wang, D. (2016).
A survey of transfer learning. Journal of Big data,
3(1):1–40.
Zeiler, M. D. and Fergus, R. (2014). Visualizing and under-
standing convolutional networks. In European confer-
ence on computer vision, pages 818–833. Springer.
Zhou, B., Sun, Y., Bau, D., and Torralba, A. (2018). Inter-
pretable basis decomposition for visual explanation.
In Proceedings of the European Conference on Com-
puter Vision (ECCV), pages 119–134.
Concept Explainability for Plant Diseases Classification
253
