
Machine Learning for Cognitive BDI Agents: A Compact Survey
¨
Omer Ibrahim Erduran
a
Department of Computer Science, Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany
Keywords:
BDI Agent, Machine Learning, Agent-Oriented Programming, Cognitive Agents, Multi-Agent System.
Abstract:
The concept of Cognitive Agents has its roots in the early stages of Multi-Agent Systems research. At that time,
the understanding of the term Agent was referring to Software Agents with basic capabilities of perception
and action in a proper environment adding potential cognitive capabilities inside the agent architecture. A
fundamental drawback of the concept is the barrier of learning new capabilities since the full properties of
the agent are hard coded. Over the years, research in Agent-Oriented Programming has provided interesting
approaches with promising results in the interplay between Machine Learning methods and Cognitive Agents.
Such a combination is realized by an integration process of Machine Learning algorithms into the agent cycle
in the specific architecture. This survey is a review of combining both, Machine Learning and BDI Agents as
a selected form of Software Agent, including the applied concepts and architectures for different scenarios.
A categorization scheme named ML-COG is introduced to illustrate the integration perspectives for both
paradigms. The reviewed literature is then assigned to this scheme. Finally, a selection of relevant research
questions and research gaps is presented as worthwhile to be investigated.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the years, research in autonomous Agents and
Multi-agent Systems (MAS) has emerged as a multi-
disciplinary field with influences from a wide range of
related scientific fields (Cardoso and Ferrando, 2021).
Due to the recent advancement of Machine Learn-
ing (ML) algorithms, especially in Deep Learning,
the understanding of agency reflected by the term
Agent has gained a different meaning. This circum-
stance has been pointed out by Dignum & Dignum,
according to which the different understandings could
be fundamentally seen on the one side as a concept
or on the other side as a paradigm for autonomous
software systems (Dignum and Dignum, 2020). In
this regard, Shoham pointed out the fundamental shift
from Logic-based AI and Knowledge Representation
to ML and statistical algorithms (Shoham, 2015). In
a recently published viewpoint paper (Bordini et al.,
2020), a ”Cognitive era” is proclaimed and the con-
tribution of Agent-oriented Programming (AOP) to
future intelligent systems is investigated. Specifi-
cally, AOP is mentioned as an approach for the rapid
development of cognitive agents which are context-
sensitive. This means, that for a given scenario or
a task that has to be processed, software agents can
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1586-0228
be applied on large scale being extended or speci-
fied with capabilities for a given scenario, e.g. as au-
tonomous vehicle agents for transportation in Mobil-
ity or warehouse agents for sorting and packing goods
for deliveries. Since the goals and plans as well as the
predefined set of possible actions are usually imple-
mented into the architecture, the agent shows a robust
behavior in its corresponding environment. This cir-
cumstance represents a contrast to the learned behav-
ior in ML approaches. A main disadvantage of ML as
a decision-making component is the ”black-box” rep-
resentation, i.e. the insight into the underlying struc-
ture of the learning process can not be seen. That is
the reason why the behavior of a learning agent based
on Russel & Norvig, can not be explained thoroughly,
especially considering Sub-symbolic ML approaches
(Russell and Norvig, 2009). In Deep Reinforcement
Learning (DRL), the learning agent behavior leads to
actions, which are also difficult for humans to under-
stand
1
. Since independent research has been done
in the considered intersection over the years, this sur-
vey brings a significant amount of research together,
where the BDI architecture is added with ML meth-
1
Here, one can look at the well-known ”Move
37” of AlphaGo from DeepMind, mentioned in
https://www.deepmind.com/research/highlighted-
research/alphago, last access: 10/14/2022.
Erduran, Ö.
Machine Learning for Cognitive BDI Agents: A Compact Survey.
DOI: 10.5220/0011678100003393
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2023) - Volume 1, pages 257-268
ISBN: 978-989-758-623-1; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
257

ods, categorizing them according to the technical re-
alization as well as the considered ML methods. Fur-
thermore, the survey points out research areas in this
intersection worthwhile for deeper investigation. To
clarify the corresponding setting of the work handled,
we first explain the fundamentals which are consid-
ered in this survey. To structure the literature which
we investigate in this survey, we explain our approach
to set the research focus of this survey. As mentioned,
the integration of ML and AOP is the core research
intersection, where the works that have been done so
far, are represented in this survey. To the best of our
knowledge, this is the first survey, which explicitly
considers ML and AOP for the cognitive BDI agent
architecture. Moreover, it is an extended and updated
version of (Erduran, 2022) with additional relevant
literature covered as well as additional discussion
2
.
To sum up, this paper has the following contributions:
• a novel categorization scheme, ML-COG, is de-
veloped for assigning the surveyed literature,
• the papers addressing the question of integrating
BDI and ML are collected and surveyed,
• open challenges and research gaps are identified
and pointed out.
The remainder of this survey is structured as fol-
lows: Section 2 contains the preliminaries as well as a
distinction of the topic handled with other directions
to prevent misconceptions. The categorization ap-
proach of this survey is handled in section 2.3, where
ML-COG is described in particular. In the main part,
section 3, we examine the existing literature present-
ing different approaches to tackle the challenge of in-
tegrating ML and AOP and furthermore categorize
the considered works. After the categorization, we
present in section 4 the elaborated open challenges
and directions that are worthwhile for profound re-
search. Finally, we conclude our survey in section 5.
2 FUNDAMENTALS
A compact exposition of both paradigms ML and
AOP is presented in the following subsections focus-
ing on the main aspects. Furthermore, we go into
the distinction of the considered integration question
and Multi-Agent Learning (MAL) as a typical RL ap-
proach.
2
presented in the German National Workshop LWDA
2022
2.1 Machine Learning Algorithms
ML algorithms are data-driven, which means that for
specific learning behavior, the algorithm gets exposed
to a large data set. Here, the learning process can vary
according to the learning objective and what is more,
the setting. In principle, the relevant learning algo-
rithms can be subdivided into 3 categories: Super-
vised Learning (SL), Unsupervised Learning (UL),
and Reinforcement Learning (RL). They have been
investigated with respect to the integration into the
cognitive agent architecture (Hernandez et al., 2004b;
Rodrigues et al., 2022; Erduran et al., 2019). In SL,
the learning algorithm gets a proper training data set
to apply the learning process and therefore, learn-
ing a specific behavior
3
. After the training pro-
cess, the testing step examines the performance of the
learned behavior with a smaller sample from the data
set which is not considered during the training phase.
In contrast, UL considers learning algorithms that are
given the objective to find contextual structures in a
given data set. Thus, the learning algorithm does not
get information about the objective but has to find an
underlying structure to learn. In RL, a learning agent
is considered, that interacts in an environment to learn
and perform a specific behavior. Here, the agent itself
gets rewarded or punished for its actions in this envi-
ronment. Based on a reward function, the objective of
the agent is to maximize the reward which leads to a
specific behavior in the given environment.
ML for MAS is an extensive research field where
learning algorithms are examined in the multi-agent
setting. The research in this field gained recent pop-
ularity due to the advancement of Deep Neural Net-
works (Foerster et al., 2016). The first works for con-
sidering the multi-agent setting in ML set the focus
on RL, e.g. in Tuyls & Weiss, where an agent inter-
acts with its environment and learns by getting sen-
sor information and rewards (Tuyls and Weiss, 2012).
According to its definition, Multi-Agent Learning re-
sults when multiple agents collectively pursue a com-
mon learning goal or more broadly in situations where
a single learning agent is affected by several compo-
nents of other learning agents (Weiß, 1996). Whereas,
in this survey, we focus on integrating ML methods
for BDI agents. One can speak of Multi-Agent Learn-
ing when multiple learning-based BDI agents pursue
a common learning behavior. This is also a potential
future work in this research area, which will be inves-
tigated in section 4.
3
Here, proper means the suitable choice of a data set for
the learning objective.
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
258

Figure 1: The typical cognitive BDI cycle based on Deljoo
et al. (Deljoo et al., 2017).
2.2 BDI Agent Architecture
Autonomous Agents have been broadly investigated
in Distributed Artificial Intelligence (Chen et al.,
2022). Different applications, where agents come
into play, are among others ranging from Negotia-
tion mechanisms and Game Theory to Distributed
problem-solving. In AOP, we suppose an inter-
nal cognitive architecture based on the ”observation,
thought, act-cycle” that each considered cognitive
agent applies during processing in its environment
(Wooldridge, 2009). Starting from the fewer capa-
bilities of a reactive agent that only reacts to senses
from the environment, the more complex cognitive
architecture is usually represented by the Belief, De-
sire, Intention - in short BDI - architecture. The BDI
model is a goal-oriented practical reasoning system
and it has its roots in practical philosophy (Bratman,
2000). A pre-version of the BDI model is the Pro-
cedural Reasoning System (PRS). Bryson, for exam-
ple, presents learning for PRS and cognitive agents
based on the cognitive logical model of Marvin Min-
sky (Bryson, 2000; Minsky, 1991). Learning, there-
fore, has been the main challenge since the beginning
of cognitive reasoning systems development. In the
Agent literature, there exist multiple variations of the
BDI architecture, where one example is depicted in
Fig. 1. The agent observes information from the envi-
ronment, defining its Belief. The Desires are derived
from the beliefs, indicating the planned behavior of
the agent. For each desire, a sequence of Goals and
Plans as combinations, which are defined, come into
play. A single plan can contain multiple Actions. An
action is then executed by the agent in its environ-
ment and the beliefs are updated at the same time. A
more comprehensive survey that covers the BDI agent
architecture and its variations, is examined in (Silva
et al., 2020).
2.3 ML-COG Categorization Scheme
The integration of ML into the BDI architecture as
two distinct paradigms is the core area that we con-
sider in this survey. To provide a clear view of this
intersection with the corresponding published works,
we set up a categorization scheme. The rationale
for this scheme is based on a problem-solution or-
der since we focus on an integration problem, which
can be seen equally as an implementation problem
in AOP. Displayed as a cube structure, we present
the ML-COG cube (Figure 2) to classify the con-
sidered research. In its basic features, ML-COG
comprises three main dimensions. The first dimen-
sion, which is defined as the Cognitive Agent De-
velopment, is reflected on the y-axis. In this dimen-
sion, we distinguish between different agent devel-
opment approaches leaning on the fundamental lit-
erature of Multi-agent research based on Wooldridge
(Wooldridge, 2009). The development of cognitive
agent architecture ranges from a Single-agent (SA)
approach (Shoham, 1993), to a Multi-agent (MA) ap-
proach where the agents interact with each other (Bor-
dini et al., 2009). Both approaches are constricted
to BDI agents. In the second dimension, we accord-
ingly envisage the ML perspective, which is reflected
in the x-axis. Here, we differentiate between SL, UL
and RL. Since the core of this survey is the integra-
tion of both ML and AOP, we focus on adding both
dimensions together accordingly by investigating the
different taken approaches. As the third dimension
in the z-axis, the Integration Type denotes, in which
form both paradigms ML and AOP are deployed dur-
ing the architectural design and implementation phase
of intelligent agent systems. If the learning algorithm
is implemented into the BDI architecture influencing
its reasoning cycle, we consider it as Hard coded. If
the learning algorithm is modular i.e. represented as
an external component, it is called loosely coupled.
Consequently, a combination of both approaches is
called Hard & So f t
4
. Either in the architectural de-
sign or on the implementation level, there are different
approaches combining ML algorithms with the BDI
architecture. These approaches are discussed in sec-
tion 3. It is important to note that, we constrict the sur-
veyed literature mainly to the approaches, where ML
is considered for BDI agents. Thus, we have to ne-
glect prominent works where Learning is investigated
into other types of cognitive architectures, like SOAR
4
Another interesting scale representation distinguishing
between learned and hard-coded behavior is introduced by
Ricci, A. in his talk ”Agent Programming in the Cognitive
Era: A New Era for Agent Programming?”, EMAS 2021.
Machine Learning for Cognitive BDI Agents: A Compact Survey
259
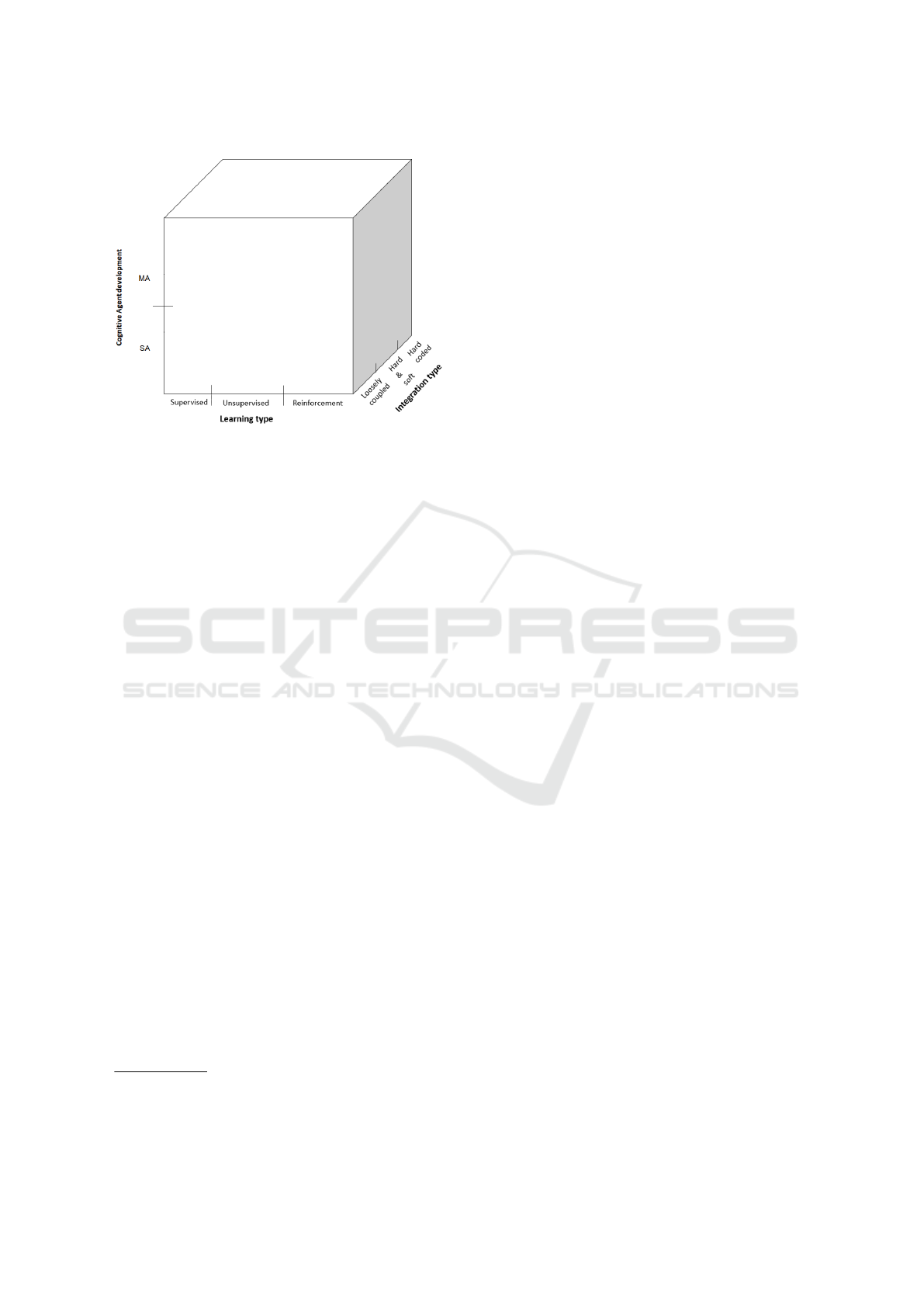
Figure 2: The proposed multidimensional ML-COG Cube.
or Act-R
5
. From this starting point, we went through
the publications cited in the considered works. Due to
space constraints, we consider specific representative
works for ML-COG. We also apologize to the authors
whose work we had to omit due to space constraints.
2.4 Literature Collection Approach
The research question addressed in this survey is:
”How can Machine Learning be integrated into BDI
agents?”. We traced the citations on Google Scholar
using the following keywords in the specific order:
BDI Agent, Machine Learning, Integration. We re-
ceived 16.400 results and based on the first 5 re-
sults, i.e. (Singh et al., 2011), (Bordini et al., 2020),
(Heinze et al., 1999), (Bosello and Ricci, 2020), and
(Bosello, 2019) sorted by relevance, we traced the
literature which is cited inside these works and also
considered relevant literature that in turn cited these
works. The core contribution is made by authors
with approaches at the conceptual and implementa-
tion level. Based on this distinction, it can be said
that most of the work focuses on demonstrations as
preliminary results. As a reviewing strategy, we de-
cided to strictly include solely works that consider the
BDI agent architecture. Since there are different vari-
ations of it described in agent literature, we include
each of them. Therefore, we exclude other architec-
tural concepts. From the ML perspective, we focus
on works that can be categorized into the considered
three ML approaches explained in section 2.1. As a
result, we have a literature contingent that is suitable
for categorization.
5
Interested readers are referred to Broekens et al.
(Broekens et al., 2012), Nason & Laird (Nason and Laird,
2005) and Chong et al. (Chong et al., 2007).
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
Based on the approach explained in section 2.4, this
survey covers works that combine ML for AOP, espe-
cially considering the BDI architecture. The literature
collection is processed by selecting works where ML
approaches are applied to BDI agents, i.e. the learn-
ing algorithm is integrated into the BDI cycle. We
examined a plethora of works neglecting approaches,
where ML is though considered but not for BDI
agents. One work mentioned before is from Bordini
et al., where the literature is examined with respect
to Artificial Intelligence in general for BDI agents
(Bordini et al., 2020). The mentioned work considers
ML approaches but is not limited to. Whereas in this
survey, the focus solely lies on ML for BDI agents.
Based on the fact, that they cover a broader range of
the literature spectrum, they do not go into detail for
specifically mentioned works that are also subject to
this survey. In this survey, the ML paradigm and BDI
architecture are opposed, and thus, we explain the re-
lated literature in this more specific context consider-
ing the introduced categorization scheme. In section
4, we point out challenges concerning ML and AOP.
3.1 A General View
A unifying view of both fields MAS and ML is shown
in the survey of Stone & Veloso (Stone and Veloso,
1997), which points out learning opportunities for
MAS e.g. enabling actions of other agents. Suit-
able techniques, like Q-Learning in RL or Stigmergy-
based learning is mentioned. The latter is known in
MAS for efficient collaboration in teams with indirect
communication. Other possibilities for learning MAS
communication are mentioned e.g. using speech acts
or when and what to communicate. Furthermore,
knowing other agents’ internal states or sensory in-
puts is helpful for recursive modeling methods pre-
dicting the future actions of other agents. Following
the development of cognitive agent architectures like
BDI, the issue of lacking learning capabilities was re-
marked on in the early phase of BDI research. Weiss
addresses this issue in his work (Weiß, 1996) pointing
out different learning categories for MAS. He distin-
guishes between single-agent and interactive learning
and does not explicitly mention learning for BDI but
rather gives an overview of learning perspectives like
its purpose and goal. For a single agent, this means
the improvement of its skills and in MAS, coordi-
nation and communication stay at the center. Other
works containing a general view of this research in-
tersection are from Kudenko et al. (Kudenko et al.,
2003), Khalil et al. (Khalil et al., 2015) as well as
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
260

Sardinha et al. (Sardinha et al., 2004). The latter is
more focused on the software engineering process for
cognitive agents. Recent work pointing to the issue
is from Mascardi et al. (Mascardi et al., 2019) men-
tioning learning approaches for improving MAS sys-
tems design also in the software engineering process.
Here, an Action failure and Recovery mechanism is
introduced, where the BDI cycle is extended by an ac-
tion reconfiguration and learning module. This mod-
ule provides new action descriptions for plans, which
are annotated to deprecated actions leading to a ver-
ifiable BDI system. A verification approach of BDI
learning agents is crucial for monitoring learned be-
havior. However, the specific learning module is not
specified and the work progress is in a conceptual
phase. Based on the works mentioned in this sec-
tion, one can see the relevance of investigating ML
approaches for cognitive software agents, like BDI
systems. ML for Agent-based Modeling is reviewed
by Zhang et al. (Zhang et al., 2021). The differ-
ence to this work is, that we consider the relation
of the BDI architecture with ML techniques. Otter-
loo et al. (van Otterlo et al., 2003) investigate the
extension of ML for cognitive agents by introducing
the term Sapient Agent, which denotes the extension
of capabilities for learning and planning in cognitive
agents. Furthermore, the authors provide, opportuni-
ties for learning behavior in BDI agents emphasizing
goal and plan selection. In the thesis of Sioutis, the
question of integrating learning in cognitive agents is
investigated. Different hybrid systems are developed
and frameworks for developing cognitive agents are
therefore extended (Sioutis, 2006). In (Saadi et al.,
2020), different BDI reasoning processes are cov-
ered and several approaches for behavioral flexibility
in BDI agents are presented. However, the authors
do not explicitly investigate learning approaches. In
(Ricci, 2022), the author proposes a novel fundamen-
tal approach to designing cognitive agents with com-
ponents that are explicitly modeled and parts that are
learned by the agent.
3.2 BDI and Decision Trees
One of the first works mentioning ML approaches for
BDI agents explicitly is from Guerra-Hern
´
andez et
al.(Hernandez et al., 2004b; Hernandez et al., 2004a;
Hernandez et al., 2001) where the plan selection
process is investigated by applying logical Decision
Trees (DT). As a typical SL approach, this method is
integrated into the BDI cycle by adding the DT into
the interpreter of the agent, transforming the selected
plans into intentions. A DT is a classification model
which consists of nodes and leaves. In Fig.3, the
leaves are marked oval and contain values. The nodes
are marked rectangular and represent attributes of the
considered data set. The first node is called the root
of the tree and the leaves are terminal states usually
containing a weight to reflect the outcome of the cor-
responding result. For a new object from the data set,
which has to be classified, the root node is the start-
ing point and a path is followed until a certain leaf.
In general, DTs are learned top-down considering a
learning algorithm, like ID3. ID3 implements a re-
cursive partitioning algorithm for a set of classes and
discrete attribute values (Sammut and Webb, 2011).
Phung et al. (Phung et al., 2005) apply DTs for BDI
agents using a learning-based framework, where the
learning component is added to the BDI cycle. The
agent processes its past experience to adapt it to the
current behavior with respect to background knowl-
edge. The result of the learning algorithm is then
added to the beliefs of the agent. In the work of Airiau
et al. (Airiau et al., 2009), the BDI agent is inves-
tigated to learn from past experience by preventing
failed plan executions. In the initial step, the relation
of goals and plans is represented by means of a Goal-
plan Tree. A Goal-plan Tree contains the defined
goals and their corresponding plans of a BDI agent,
leading to a hierarchical tree structure with goals and
possible sub-plans. In the thesis of Singh (Singh,
2011), the plan selection step in the BDI cycle is tack-
led with different approaches. Multiple works related
to the author are therefore considered. The work of
Singh et al. (Singh et al., 2010b; Singh et al., 2010a)
build upon the previous paper (Airiau et al., 2009) and
add Context conditions for the plan selection process
in form of DTs. In common, a context condition is a
Boolean function that needs to be predetermined dur-
ing the implementation phase. It is attached to each
plan and describes the conditions and whether a plan
is useful to a corresponding goal in a specific situ-
ation. Focusing on the learned behavior, the DT is
built up for each considered plan in the agent’s library.
Each tree, therefore, leads to a decision of whether the
plan will be successful or fail with a probability score.
A further extension of this work is from Singh et al.
(Singh et al., 2011), where plan selection consider-
ing changing dynamics is investigated. A confidence
measure function for the degree of Stability of Plans
is presented with respect to execution traces and the
environment of the agents. The resulting weights are
added to the plans denoting the success of being ap-
plied for a corresponding goal. Montagna et al. inves-
tigate the integration of symbolic and sub-symbolic
AI approaches and examples of integration are pre-
sented (Montagna et al., 2021). A learning module
as a separate system is developed that interacts with
Machine Learning for Cognitive BDI Agents: A Compact Survey
261

Figure 3: Example decision tree node with options and
weights based on (Hernandez et al., 2004b).
a BDI agent for the treatment of patient data based
on historical data. Here, the prediction model in the
learning module is trained offline before applying it to
the BDI agent. The learning module and the agent are
independent of each other and the learning module is
implemented in Python with asynchronous commu-
nication. They use DT, Linear Support Vector Clas-
sification, and Random Forests as ML prediction al-
gorithms. In (Nguyen and Wobcke, 2006), DTs are
integrated into the plan selection step inside a single
BDI agent for Smart Personal Assistants.
3.3 BDI and Reinforcement Learning
The thesis of Feliu (Feliu, 2013) considers the appli-
cation of RL for generating plans in BDI agents with-
out relying on earlier knowledge. The author covers
some related works concerning BDI and ML, which
are also objects of this survey. Related to this set-
ting, where RL is applied for BDI is the work from
Pereira et al. (Pereira et al., 2008). The work of Qi
& Bo-ying (Qi and Bo-ying, 2009) represents a com-
bination of RL and BDI for robot soccer simulation.
Here, RL is considered as a feedback process by us-
ing the Q-Learning algorithm for the simulation steps.
The learning algorithm is not integrated into the BDI
architecture but processes the outcome of the BDI
agent’s action. Another approach in the same setting
is presented by Wan et al. (Wan et al., 2018) where a
BDI agent is extended with Q-Learning in AOP lan-
guage AgentSpeak. More specifically, the plan library
is improved by the Q-Learning decision algorithm in
an uncertain environment. What they found out is,
that in state space exploration, which is the obligatory
step in RL, the communication of AgentSpeak slowed
down. For faster convergence, Deep Reinforcement
Learning seems to be a suitable approach. The lat-
ter is also mentioned in section 4. Action selection
based on rules is a challenge in this area which is
tackled by Broekens et al. (Broekens et al., 2012). In
this work, the authors use RL for the Rule Selection,
which slightly differs from the action selection pro-
cess. In the typical RL setting, the learned behavior
is the corresponding action. In this work, an internal
uninstantiated rule is selected during the learning pro-
cess. They consider the GOAL agent programming
language. The relevant components for learning are
reflected in the states, which are built up with a set of
rules for the agents and the number of active goals.
The considered state representation seems to be an
initial version for learning but is capable to deliver in-
teresting results for rule selection. The learning pro-
cess takes place inside the agent architecture. Initial
works of combining elements of the RL setting with
Partial Observability have been investigated by Rens
et al. (Rens et al., 2009). Here, the authors combine
the BDI architecture with the Partially Observable
Markov Decision Process (POMDP) plan approach
providing initial results by considering small exper-
imental settings. They argue in favor of a more com-
plex simulation environment. For this approach, Chen
et al. integrate the POMDP into the planning phase
of the BDI architecture by considering AgentSpeak
(Chen et al., 2014). Nair & Tambe also investigate the
concept of POMDP for the BDI paradigm (Nair and
Tambe, 2005). They consider Multi-agent teaming
by POMDP and Team-Oriented Programming. An-
other work concerning this specification is from Rens
& Moodley, where the reward-maximizing approach
of POMDP and the management of multiple goals
in BDI systems are combined (Rens and Moodley,
2017). These works open up opportunities for inves-
tigating RL and BDI in Multi-agent settings. Bosello
& Ricci extend the BDI architecture with RL. They
consider SARSA algorithm for the decision-making of
the agent (Bosello and Ricci, 2020). A Low-level
learning approach is represented in the BDI-FALCON
agent architecture, which is presented in Tan et al.
(Tan et al., 2011; Tan, 2004). At its lowest level, BDI-
FALCON contains a reactive learning module based
on Temporal Difference Learning (TD), an RL algo-
rithm that estimates a value function of state-action
pairs Q(s, a) that indicates the learning step of the
system. Two other modules contain the BDI-native
components like goals and plans which are sent to the
low-level RL environment. Karim et al. propose an
approach, where learning with a high level of abstrac-
tion by a BDI agent is connected to a low-level RL
environment, based on BDI-FALCON (Karim et al.,
2006a). Result in a hybrid architecture, the BDI agent
generates plans that are derived from the RL envi-
ronment. Norling integrates the Q-Learning algo-
rithm into the BDI cycle to learn rules for pathfind-
ing in a grid world (Norling, 2004). It is evaluated
in a simple grid environment. Subagdja & Sonenberg
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
262

also integrate the Q-Learning algorithm into the BDI
agent cycle (Subagdja and Sonenberg, 2005). They
introduce Meta-level plans which are considered for
monitoring the reasoning step and the executed plans.
Badica et al. apply several RL algorithms like TD-
Learning, Q-Learning and SARSA for BDI agents
(Badica et al., 2015; Badica et al., 2017). Consid-
ering a grid scenario, they define the agent’s actions
as well as specific states representing the correspond-
ing goals. Singh & Hindriks investigate in (Singh and
Hindriks, 2013) the Q-Learning algorithm for adap-
tive behaviors in autonomous BDI agents. Alvarez &
Noda consider Inverse RL for simulating pedestrian
behavior (Alvarez and Noda, 2018). Further works
that are worthwhile mentioning are from Araiza et
al. (Araiza-Illan et al., 2016) and Lee & Son (Lee
and Son, 2009), where Q-Learning is applied to a
BDI agent for evacuation scenarios. In (Lee and Son,
2009), Bayesian Belief Networks in combination with
Q-Learning as a RL method are applied for updating
the Belief of a BDI agent. In (Pulawski et al., 2021),
the authors provide an environment for BDI Multi-
agent training and application in uncertain and adver-
sarial environments. They apply two goal-based BDI
agents which are jointly trained with RL in an adver-
sarial manner. They extend the work of Bosello &
Ricci in a multi-agent grid-world setting. One agent
tries to achieve its goals which the other adversar-
ial agent tries to prevent. Zoelen et al.(Zoelen et al.,
2020) apply Q-Learning into BDI agents for learning
to communicate.
3.4 Alternative Approaches
Heinze et al. (Heinze et al., 1999) integrate a match-
ing algorithm called CLARET into the BDI architec-
ture. The BDI agent sends queries to the observation
component which contains the learning algorithm for
experience, recognition, and learning. Based on the
algorithm, which processes the data from the envi-
ronment, a resulting recognition pattern is sent to the
agent influencing its upcoming plans. The CLARET
algorithm processes an unknown segmented trajec-
tory which is compared with other known trajectories
in the Memory component. This leads to an informed
plan selection of the BDI agent with respect to pre-
vious experiences. A rather distinct approach from
the previous sections is made by Norling in (Norling,
2001), where the BDI cycle is extended by a psycho-
logical method called Recognition-primed Decision
Making (RPDM) leading to real-time agent behavior
adaptation. Having its roots in naturalistic decision-
making, RPDM enables the agent to distinguish be-
tween different situations. This ability leads to dif-
ferent action selections and evaluations of applicable
goals and plans. Learning in the planning phase is
tackled by Karim et al. (Karim et al., 2006b). A hy-
brid architecture is presented, which combines a BDI
plan extracting component with a generic learning
component for a high level of abstraction. Consider-
ing a low-level monitoring system, called Plan Gener-
ation Sub-system, the learning process arises by con-
necting a priori data as clues to corresponding goals.
This can be seen as a plan generation step. Lokuge
& Alahakoon extend the BDI cycle with learning in
the planning phase (Lokuge and Alahakoon, 2007).
Adding a Knowledge Acquisition Module (KAM) to
the BDI reasoning module, a hybrid BDI model is de-
veloped for the application of vessel berthing. The
adaptive planning is processed by KAM, which also
contains a trained neural network for the learning pro-
cess. Thus, a dynamic plan selection is provided
leading to intention commitments. Rodriguez et al.
integrate a Deep Neural Network into the BDI rea-
soning cycle for decision-making (Rodrigues et al.,
2022). They define agents as a Multi-context Sys-
tem, which provides representation and exchange of
information in heterogeneous agents. Another work,
where Neural Nets are applied is from Ahmed et
al. (Ahmed et al., 2020). In this work, stock mar-
ket prediction is tackled by considering Single- and
Multi-Layer Perceptrons and integrating them into the
BDI architecture. Further works with alternative ap-
proaches for learning are in (Honarvar and Ghasem-
Aghaee, 2009), where a Neural Network is integrated
into the BDI agent architecture for checking the ethics
of taken actions of an agent and in (Shi and Xu, 2009),
where Fuzzy Logic is considered for self-learning
agents and external learning. Xu et al. consider Be-
lief Inference Networks for BDI agents in Cloud Com-
puting applications (Xu et al., 2012). The thesis of
Ramirez (Luna Ramirez, 2019; Luna Ramirez and
Fasli, 2017), investigates plan selection with inten-
tional learning. Males et al. present an extension of
the BDI agent by adding Deep Neural Networks for
face detection and trajectory memory. The agents are
described in modal logic. The paper delivers prelim-
inary quantitative results concerning the performance
of BDI agents with extended Deep Neural Networks
for detecting faces in video sequences (Male
ˇ
s et al.,
2019). A further work, that applies Neural Networks
combining BDI agents is from (Buettner and Baum-
gartl, 2019) in the domain of crisis management and
route recognition. In (Chen et al., 2013), the authors
apply Bayesian Networks for the belief component of
a BDI agent to interpret mental states in the deliber-
ation phase. In (Verbeet et al., 2019), a Deep Neu-
ral Network for object detection is applied, which in-
Machine Learning for Cognitive BDI Agents: A Compact Survey
263

teracts with a BDI agent in a warehouse domain. In
(Chaouche et al., 2015), the plan selection step is in-
vestigated considering learning from past actions.
3.5 Literature Categorization Overview
In Table 1, we have listed a selection of the research
works handled in this survey and classified them with
respect to the ML-COG dimensions sorted by the
ML approach and neglecting mentioned other surveys
in the previous section. For the sake of clarity, we
set up the columns reflecting the dimensions of ML-
COG. In addition, the last column Objective contains
the contribution objective of the corresponding work.
Note, that we have left out the works, where learn-
ing approaches are not explicitly implemented or ex-
ecuted
6
. For future research in this area, the open
research challenges are explained in Section 4.
4 OPEN RESEARCH
CHALLENGES
The research done so far in the intersection of ML
and AOP provides many different applications, where
some of which have been elaborated on in the previ-
ous section. Since the categorization process follows
the presented dimensions, we point out the following
application areas, which are picked due to their tech-
nical proximity as well as based on the contributions
and potential limitations in the investigated literature.
Therefore, we list the following areas for future re-
search:
1. Communication protocols
2. Cognitive decision-making and learned behavior
3. Goal-level learning
4. Environment interaction
The overall aim is to provide a high level of ab-
straction with the usage of learning-based compo-
nents. The areas 1 and 2 are intentionally formulated
each with two extremes, indicating the different ap-
proaches to agent development in the programming
phase. The first area ranges from predefined com-
munication languages like AgentSpeak (Bordini et al.,
2007) which is considered in a MAS over to emergent
communication in learning-based agents interacting
with each other. Current research in emergent com-
munication provides RL algorithms in Multi-agent
settings to encourage agents to communicate with
6
A ”?” entry denotes, that the implementation type is
not clearly classifiable.
each other based on single and collective rewards
(Noukhovitch et al., 2021). This area is important, es-
pecially in MAS where reliable communication leads
to efficient coordination and cooperation. In Table 1,
one can see that nearly all works focus on the single-
agent setting. The shift to MAS is therefore a cru-
cial step in inspecting the behavior of BDI learning
agents interacting with each other. A combination of
learning-based communication with initial rules rep-
resents such a combination approach. The advan-
tage overall is a better explainable learned behav-
ior and thus the corresponding actions of the agents
(Broekens et al., 2010). In the second area, we dis-
tinguish rather different agent types which are com-
monly considered in MAS as it is presented by Russel
& Norvig in (Russell and Norvig, 2009). Decision-
making is the essential step an agent processes to
reach their goals successfully. The research in MAL
based on RL algorithms has already covered a broad
range of settings starting from single-agent settings to
MAS settings with different applications (Gronauer
and Diepold, 2022). Here, we see future work in
the MAS settings based on cognitive decision-making
based on the BDI architecture. Works covered in
this survey already provide solutions for the single-
agent setting (Bosello and Ricci, 2020; Tan et al.,
2011). One observation of this survey is that there
is scarce relevant work so far, considering the Multi-
agent setting with multiple BDI agents and Learn-
ing approaches. As a third area, we see learning at
goal-level as a novel approach to connecting ML and
BDI. In the surveyed literature, learning at the plan
level is predominantly tackled by different works. In
this case, sub-symbolic learning methods, like Neural
Networks, could be therefore considered. The fourth
area is concerned with the environment of the agents.
Since the focus in the research intersection of ML and
AOP lies in the agent architecture, experimental eval-
uations are rather processed in lower complexity en-
vironments leading to initial results. A more com-
plex simulation environment with an application sce-
nario for learning-based cognitive agents is a feasi-
ble approach for evaluating large-scale MAS behav-
ior in the mentioned intersection. In RL, where the
environment is crucial for testing the agent’s behavior
and thus the learning algorithm, there exists a plethora
of suitable environments for RL algorithms (Metelli,
2022). For the research in this survey, an example
worthwhile to mention is the simulation environment
MATSim, which is an agent-based traffic simulation
environment (W Axhausen et al., 2016). For this en-
vironment, there exists an approach to transforming
it into an RL-suitable environment (Khaidem et al.,
2020). Further work by Singh et al. investigates
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
264

Table 1: Overview of selected surveyed literature based on ML-COG.
Work SA/MA Learning Integration Objective
(Heinze et al., 1999) SA CLARET (SL) Loosely coupled Plan recognition
(Hernandez et al., 2004b) SA/MA Decision Tree (SL) Hard Plan execution
(Phung et al., 2005) SA Decision Tree (SL) Hard & Soft Experience learning
(Nguyen and Wobcke, 2006) SA Decision Tree (SL) (?) Plan selection
(Airiau et al., 2009) SA Decision Tree (SL) Hard Plan selection
(Singh et al., 2010a) SA Decision Tree (SL) Hard Plan selection
(Singh et al., 2010b) SA Decision Tree (SL) Hard Plan selection
(Singh et al., 2011) SA Decision Tree (SL) Hard Plan selection
(Faccin and Nunes, 2015) SA SL Hard Plan selection
(Ahmed et al., 2020) SA Decision Tree (SL) (?) Decision making
(Montagna et al., 2021) SA Decision Tree, Linear SVC, Random Forest (SL) Loosely Coupled Decision making
(Norling, 2004) SA RPDM (UL)/Q-Learning (RL) (?) Decision making
(Subagdja and Sonenberg, 2005) SA Q-Learning (RL) Hard Learning plans & actions
(Karim et al., 2006a) SA RL Loosely coupled Plan execution
(Karim et al., 2006b) SA RL Loosely coupled Plan execution
(Qi and Bo-ying, 2009) SA/MA Q-Learning (RL) Hard & Soft Decision making
(Lee and Son, 2009) SA/MA Bayesian Belief Network, Q-Learning (RL) Hard & Soft Decision making
(Tan et al., 2011) SA TD-Learning (RL) Loosely coupled Plan selection
(Broekens et al., 2012) SA Model-based (RL) Hard Rule selection
(Feliu, 2013) SA Q-Learning (RL) Hard & Soft Plan generation
(Singh and Hindriks, 2013) SA Q-Learning (RL) Hard & Soft RL-BDI agent
(Badica et al., 2015) SA TD-Learning (RL) Hard RL-BDI agent
(Badica et al., 2017) SA Q-Learning & SARSA (RL) Hard RL-BDI agent
(Wan et al., 2018) SA Q-Learning (RL) Hard RL-BDI agent
(Alvarez and Noda, 2018) SA/MA Inverse RL Loosely Coupled Decision making
(Bosello and Ricci, 2020) SA SARSA (RL) Hard & Soft RL-BDI agent
(Pulawski et al., 2021) SA/MA RL Hard & Soft RL-BDI agent
(Norling, 2001) SA RPDM (UL) (?) Decision making
(Lokuge and Alahakoon, 2007) SA KAM (UL) Hard & Soft Intention selection
(Honarvar and Ghasem-Aghaee, 2009) SA Deep Neural Network (UL) Loosely Coupled Action detection
(Xu et al., 2012) SA/MA Belief Inference Network (SL/UL) (?) Belief reasoning
(Male
ˇ
s et al., 2019) SA/MA Deep Neural Network (SL/UL) Hard Decision making
(Rodrigues et al., 2022) SA Deep Neural Network (UL) Hard & Soft Decision making
the integration of BDI agents for MATSim (Padgham
et al., 2014). Since connecting BDI agents into com-
plex simulation environments is a challenging task,
adding learning algorithms in the BDI cycle on top
is not been studied extensively. Therefore, we see a
need for further research concerning this component
(Erduran et al., 2022).
5 CONCLUSION
Learning methods in MAS differ from the traditional
ML process since the autonomous and flexible behav-
ior of the agents is considered, which are furthermore
interacting in a complex and dynamic environment.
This survey aims to get in the lane at the intersection
of ML and AOP by comprising the relevant work done
in the field, especially in the last two decades. In ML
research, the term Agent is predominantly considered
as a concept rather than an existing instance with ex-
plicitly developed cognitive capabilities as it is in soft-
ware agents (Dignum and Dignum, 2020). Such a
form of disambiguation also influences the contex-
tual understanding of our work. In spite of the fact
that this intersection is based on different approaches,
cognitive software agents have not been considered
sufficiently in ML research and therefore represent a
relevant direction for future research. The analysis of
such an integration process will lead to better insight
into the functioning of learned behaviors in a cogni-
tive framework. The presented open issues are suit-
able entry points for further investigation. This work
is resulted due to the detailed viewpoint in (Bordini
et al., 2020) as well as the survey concerning the BDI
architecture (Silva et al., 2020), and therefore delivers
an overview for thriving future research in the consid-
ered area.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank Mirjam Minor for giv-
ing helpful advice throughout the survey process.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, M., Sriram, A., and Singh, S. (2020). Short Term
Firm-Specific Stock Forecasting with BDI Frame-
work. Computational Economics, 55(3):745–778.
Airiau, S., Padgham, L., Sardina, S., and Sen, S. (2009). En-
hancing the Adaptation of BDI Agents Using Learn-
Machine Learning for Cognitive BDI Agents: A Compact Survey
265

ing Techniques. International Journal of Agent Tech-
nologies and Systems, 1(2):1–18.
Alvarez, N. and Noda, I. (2018). Inverse Reinforcement
Learning with BDI Agents for Pedestrian Behavior
Simulation. JSAI.
Araiza-Illan, D., Pipe, A. G., and Eder, K. (2016). Intel-
ligent Agent-Based Stimulation for Testing Robotic
Software in Human-Robot Interactions. In Proceed-
ings of the 3rd Workshop on MORSE ’16, pages 9–16,
Leipzig, Germany. ACM Press.
Badica, A., Badica, C., Ivanovic, M., and Mitrovic, D.
(2015). An Approach of Temporal Difference Learn-
ing Using Agent-Oriented Programming. In 20th In-
ternational Conference on Control Systems and Com-
puter Science, pages 735–742. IEEE.
Badica, C., Becheru, A., and Felton, S. (2017). Integration
of jason reinforcement learning agents into an inter-
active application. In 2017 19th International Sympo-
sium on Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scien-
tific Computing (SYNASC), pages 361–368.
Bordini, R. H., Dastani, M., Dix, J., and El Fal-
lah Seghrouchni, A., editors (2009). Multi-Agent
Programming: : Languages, Tools and Applications.
Springer US.
Bordini, R. H., El Fallah Seghrouchni, A., Hindriks, K., Lo-
gan, B., and Ricci, A. (2020). Agent programming
in the cognitive era. Autonomous Agents and Multi-
Agent Systems, 34(2).
Bordini, R. H., H
¨
ubner, J. F., and Wooldridge, M. (2007).
Programming multi-agent systems in AgentSpeak us-
ing Jason. John Wiley & Sons.
Bosello, M. (2019). Integrating BDI and Reinforcement
Learning: the Case Study of Autonomous Driving.
Thesis.
Bosello, M. and Ricci, A. (2020). From Programming
Agents to Educating Agents – A Jason-Based Frame-
work for Integrating Learning in the Development of
Cognitive Agents. In Engineering Multi-Agent Sys-
tems, volume 12058, pages 175–194. Springer Inter-
national Publishing, Cham.
Bratman, M. (2000). Intention, plans, and practical reason.
CSLI, Stanford, Calif.
Broekens, J., Harbers, M., Hindriks, K., Bosch, K. v. d.,
Jonker, C., and Meyer, J.-J. (2010). Do you get it?
user-evaluated explainable bdi agents. In German
Conference on Multiagent System Technologies, pages
28–39. Springer.
Broekens, J., Hindriks, K., and Wiggers, P. (2012). Re-
inforcement Learning as Heuristic for Action-Rule
Preferences. In Collier, R., Dix, J., and Nov
´
ak,
P., editors, Programming Multi-Agent Systems, vol-
ume 6599, pages 25–40. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,
Berlin, Heidelberg.
Bryson, J. (2000). Cross-paradigm analysis of autonomous
agent architecture. Journal of Experimental & Theo-
retical Artificial Intelligence, 12(2):165–189.
Buettner, R. and Baumgartl, H. (2019). A highly effective
deep learning based escape route recognition module
for autonomous robots in crisis and emergency situa-
tions. HICSS, page 8.
Cardoso, R. C. and Ferrando, A. (2021). A review of agent-
based programming for multi-agent systems. Comput-
ers, 10(2):16.
Chaouche, A.-C., El Fallah Seghrouchni, A., Ili
´
e, J.-M.,
and Sa
¨
ıdouni, D. E. (2015). Improving the Con-
textual Selection of BDI Plans by Incorporating Sit-
uated Experiments. In Chbeir, R., Manolopoulos,
Y., Maglogiannis, I., and Alhajj, R., editors, Artifi-
cial Intelligence Applications and Innovations, vol-
ume 458, pages 266–281. Springer International Pub-
lishing, Cham.
Chen, J., Lang, J., Amato, C., and Zhao, D., editors
(2022). Distributed Artificial Intelligence - Third In-
ternational Conference, DAI 2021, Shanghai, China,
December 17-18, 2021, Proceedings, volume 13170
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer.
Chen, Y., Bauters, K., Liu, W., Hong, J., McAreavey,
K., Godo, L., and Sierra, C. (2014). Agentspeak+:
Agentspeak with probabilistic planning. Proc. of
CIMA, pages 15–20.
Chen, Y., Hong, J., Liu, W., Godo, L., Sierra, C., and
Loughlin, M. (2013). Incorporating PGMs into a BDI
Architecture. In Boella, G., Elkind, E., Savarimuthu,
B. T. R., Dignum, F., and Purvis, M. K., edi-
tors, PRIMA: Principles and Practice of Multi-Agent
Systems, pages 54–69, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Chong, H.-Q., Tan, A.-H., and Ng, G.-W. (2007). Inte-
grated cognitive architectures: a survey. Artificial In-
telligence Review, 28(2):103–130.
Deljoo, A., van Engers, T. M., Gommans, L., de Laat, C. T.,
et al. (2017). What is going on: Utility-based plan
selection in bdi agents. In AAAI Workshops.
Dignum, V. and Dignum, F. (2020). Agents are dead. long
live agents! In Proceedings of the 19th International
Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent
Systems, pages 1701–1705.
Erduran,
¨
O. I. (2022). Machine Learning algorithms for
cognitive and autonomous BDI Agents. In Reuss, P.,
editor, LWDA 2022 Workshop: FGWM 2022. ceur-ws,
Hildesheim, Germany.
Erduran,
¨
O. I., Mauri, M., and Minor, M. (2022). Negotia-
tion in ride-hailing between cooperating bdi agents. In
Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on
Agents and Artificial Intelligence - Volume 1, pages
425–432. INSTICC, SciTePress.
Erduran,
¨
O. I., Minor, M., Hedrich, L., Tarraf, A., Ruehl,
F., and Schroth, H. (2019). Multi-agent Learning for
Energy-Aware Placement of Autonomous Vehicles.
In 18th IEEE International Conference On Machine
Learning And Applications (ICMLA), pages 1671–
1678, Boca Raton, FL, USA. IEEE.
Faccin, J. and Nunes, I. (2015). Bdi-agent plan selec-
tion based on prediction of plan outcomes. In 2015
IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web In-
telligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (WI-IAT),
volume 2, pages 166–173.
Feliu, J. (2013). Use of Reinforcement Learning for Plan
Generation in Belief-Desire-Intention (BDI) Agent
Systems. PhD thesis, University of Rhode Island,
Kingston, RI.
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
266

Foerster, J., Assael, I. A., De Freitas, N., and Whiteson, S.
(2016). Learning to communicate with deep multi-
agent reinforcement learning. Advances in neural in-
formation processing systems.
Gronauer, S. and Diepold, K. (2022). Multi-agent deep re-
inforcement learning: a survey. Artificial Intelligence
Review, 55(2):895–943.
Heinze, C., Goss, S., and Pearce, A. (1999). Plan recog-
nition in military simulation: Incorporating machine
learning with intelligent agents. In Proceedings of
IJCAI-99 Workshop on Team Behaviour and Plan
Recognition, pages 53–64. Citeseer.
Hernandez, A., El Fallah-Seghrouchni, A., and Soldano, H.
(2004a). Distributed learning in intentional bdi multi-
agent systems. In Proceedings of the Fifth Mexican
International Conference in Computer Science, 2004.
ENC 2004., pages 225–232.
Hernandez, A. G., El Fallah-Seghrouchni, A., and Soldano,
H. (2004b). Learning in BDI Multi-agent Systems. In
Dix, J. and Leite, J., editors, Computational Logic in
Multi-Agent Systems, volume 3259, pages 218–233.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Hernandez, A. G., Seghrouchni, A. E.-F., and Soldano, H.
(2001). Bdi multiagent learning based on first-order
induction of logical decision trees. In Intelligent Agent
Technology: Research and Development, pages 160–
169. World Scientific.
Honarvar, A. R. and Ghasem-Aghaee, N. (2009). An arti-
ficial neural network approach for creating an ethical
artificial agent. In 2009 IEEE International Sympo-
sium on Computational Intelligence in Robotics and
Automation - (CIRA), pages 290–295.
Karim, S., Sonenberg, L., and Tan, A.-H. (2006a). A Hy-
brid Architecture Combining Reactive Plan Execution
and Reactive Learning. In PRICAI 2006: Trends in
Artificial Intelligence, volume 4099, pages 200–211.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Karim, S., Subagdja, B., and Sonenberg, L. (2006b). Plans
as Products of Learning. In 2006 IEEE/WIC/ACM In-
ternational Conference on Intelligent Agent Technol-
ogy, pages 139–145, Hong Kong, China. IEEE.
Khaidem, L., Luca, M., Yang, F., Anand, A., Lepri, B., and
Dong, W. (2020). Optimizing transportation dynamics
at a city-scale using a reinforcement learning frame-
work. IEEE Access, 8:171528–171541.
Khalil, K. M., Abdel-Aziz, M., Nazmy, T. T., and Salem,
A.-B. M. (2015). Machine Learning Algorithms for
Multi-Agent Systems. In Proceedings of the IPAC,
pages 1–5, Batna Algeria. ACM.
Kudenko, D., Kazakov, D., and Alonso, E. (2003). Machine
learning for agents and multi-agent systems. In Intel-
ligent Agent Software Engineering, pages 1–26. IGI
Global.
Lee, S. and Son, Y.-J. (2009). Dynamic Learning in Hu-
man Decision Behavior for Evacuation Scenarios un-
der BDI Framework. INFORMS Simulation Society
Research Workshop, Catonsville, MD, page 5.
Lokuge, P. and Alahakoon, D. (2007). Improving the adapt-
ability in automated vessel scheduling in container
ports using intelligent software agents. European
Journal of Operational Research, 177(3):1985–2015.
Luna Ramirez, W. A. (2019). Plan Acquisition Through In-
tentional Learning in BDI Multi-Agent Systems. PhD
thesis, University of Essex.
Luna Ramirez, W. A. and Fasli, M. (2017). Plan Acquisi-
tion in a BDI Agent Framework Through Intentional
Learning. In Berndt, J. O., Petta, P., and Unland,
R., editors, Multiagent System Technologies, volume
10413, pages 167–186. Springer International Pub-
lishing, Cham. Series Title: Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science.
Male
ˇ
s, L., Mar
ˇ
ceti
´
c, D., and Ribari
´
c, S. (2019). A multi-
agent dynamic system for robust multi-face tracking.
Expert Systems with Applications, 126:246–264.
Mascardi, V., Weyns, D., and Ricci, A. (2019). Engineering
Multi-Agent Systems: State of Affairs and the Road
Ahead. ACM SIGSOFT Software Engineering Notes,
44(1):18–28.
Metelli, A. M. (2022). Configurable environments in rein-
forcement learning: An overview. Special Topics in
Information Technology, pages 101–113.
Minsky, M. (1991). Logical Versus Analogical or Symbolic
Versus Connectionist or Neat Versus Scruffy. In AI
Magazine Volume 12 Number 2, pages 34–51.
Montagna, S., Mariani, S., and Gamberini, E. (2021). Aug-
menting BDI Agency with a Cognitive Service: Ar-
chitecture and Validation in Healthcare Domain. Jour-
nal of Medical Systems, 45(12):103.
Nair, R. and Tambe, M. (2005). Hybrid BDI-POMDP
Framework for Multiagent Teaming. Journal of Ar-
tificial Intelligence Research, 23:367–420.
Nason, S. and Laird, J. E. (2005). Soar-RL: integrating rein-
forcement learning with Soar. Cognitive Systems Re-
search, 6(1):51–59.
Nguyen, A. and Wobcke, W. (2006). An Adaptive Plan-
Based Dialogue Agent: Integrating Learning into a
BDI Architecture. AAMAS, page 786–788.
Norling, E. (2001). Learning to notice: Adaptive models of
human operators. In Second International Workshop
on Learning Agents. Citeseer.
Norling, E. (2004). Folk psychology for human mod-
elling: Extending the bdi paradigm. In Proceedings of
the Third International Joint Conference on AAMAS-
Volume 1, pages 202–209.
Noukhovitch, M., LaCroix, T., Lazaridou, A., and
Courville, A. (2021). Emergent communication under
competition. In AAMAS Proceedings, page 974–982,
UK. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents
and Multiagent Systems.
Padgham, L., Nagel, K., Singh, D., and Chen, Q. (2014). In-
tegrating BDI agents into a MATSim simulation. IOS
Press, pages 681–686.
Pereira, D. R., Goncalves, L. V., and Dimuro, G. P. (2008).
Constructing BDI Plans from Optimal POMDP Poli-
cies, with an Application to AgentSpeak Program-
ming. Conferencia Latinoamericana de Informatica,
CLEI.
Phung, T., Winikoff, M., and Padgham, L. (2005). Learn-
ing Within the BDI Framework: An Empirical Analy-
Machine Learning for Cognitive BDI Agents: A Compact Survey
267

sis. In Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and
Engineering Systems, volume 3683, pages 282–288.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Pulawski, S., Dam, H. K., and Ghose, A. (2021). BDI-Dojo:
developing robust BDI agents in evolving adversarial
environments. In 2021 IEEE (ACSOS-C), pages 257–
262, DC, USA. IEEE.
Qi, G. and Bo-ying, W. (2009). Study and Application
of Reinforcement Learning in Cooperative Strategy of
the Robot Soccer Based on BDI Model. International
Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 6(2):15.
Rens, G., Ferrein, A., and Van Der Poel, E. (2009). A
BDI Agent Architecture for a POMDP Planner. 9th
International Symposium on Logical Formalization of
Commonsense Reasoning: Commonsense.
Rens, G. and Moodley, D. (2017). A hybrid POMDP-BDI
agent architecture with online stochastic planning and
plan caching. Cognitive Systems Research, 43:1–20.
Ricci, A. (2022). ”Go to the Children”: Rethinking Intel-
ligent Agent Design and Programming in a Develop-
mental Learning Perspective. AAMAS.
Rodrigues, R., Silveira, R. A., and Santiago, R. D. (2022).
A Mediator Agent based on Multi-Context System
and Information Retrieval. ICAART 2022.
Russell, S. J. and Norvig, P. (2009). Artificial Intelligence:
a modern approach. Pearson, 3 edition.
Saadi, A., Maamri, R., and Sahnoun, Z. (2020). Behavioral
flexibility in Belief-Desire- Intention (BDI) architec-
tures. Multiagent and Grid Systems, 16(4):343–377.
Sammut, C. and Webb, G. I. (2011). Encyclopedia of Ma-
chine Learning. Springer Publishing Company, Incor-
porated, 1st edition.
Sardinha, J. A. R. P., Noya, R. C., Milidiu, R. L., and de Lu-
cena, C. J. P. (2004). Engineering machine learning
techniques into multi-agent systems. PUC.
Shi, Y. and Xu, H. (2009). Research on the bdi-agent learn-
ing model based on dynamic fuzzy logic. In 2009 In-
ternational Conference on Computational Intelligence
and Software Engineering, pages 1–6.
Shoham, Y. (1993). Agent-oriented programming. Artificial
Intelligence, 60(1):51–92.
Shoham, Y. (2015). Why knowledge representation matters.
Communications of the ACM, 59(1):47–49.
Silva, L. d., Meneguzzi, F., and Logan, B. (2020). BDI
Agent Architectures: A Survey. In Proceedings of
IJCAI, pages 4914–4921, Yokohama, Japan.
Singh, D. (2011). Learning plan selection for BDI agent
systems. PhD thesis, RMIT University.
Singh, D. and Hindriks, K. V. (2013). Learning to Im-
prove Agent Behaviours in GOAL. In Programming
Multi-Agent Systems, volume 7837, pages 158–173.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Singh, D., Sardina, S., and Padgham, L. (2010a). Ex-
tending BDI plan selection to incorporate learning
from experience. Robotics and Autonomous Systems,
58(9):1067–1075.
Singh, D., Sardina, S., Padgham, L., and Airiau, S. (2010b).
Learning Context Conditions for BDI Plan Selection.
AAMAS.
Singh, D., Sardina, S., Padgham, L., and James, G. (2011).
Integrating learning into a bdi agent for environments
with changing dynamics. In Twenty-Second IJCAI.
Sioutis, C. (2006). Reasoning and learning for intelligent
agents. PhD thesis, University of South Australia
Adelaide.
Stone, P. and Veloso, M. (1997). Multiagent Systems: A
Survey from a Machine Learning Perspective:. Tech-
nical report, Defense Technical Information Center,
Fort Belvoir, VA.
Subagdja, B. and Sonenberg, L. (2005). Learning plans
with patterns of actions in bounded-rational agents.
Springer-Verlag, page 30–36.
Tan, A.-H. (2004). Falcon: a fusion architecture for learn-
ing, cognition, and navigation. In 2004 IEEE Interna-
tional Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE),
volume 4, pages 3297–3302 vol.4.
Tan, A.-H., Ong, Y.-S., and Tapanuj, A. (2011). A hybrid
agent architecture integrating desire, intention and re-
inforcement learning. Expert Systems with Applica-
tions, 38(7).
Tuyls, K. and Weiss, G. (2012). Multiagent Learning: Ba-
sics, Challenges, and Prospects. AI Magazine, 33(3).
van Otterlo, M., Wiering, M., Dastani, M., and Meyer,
J.-J. (2003). A Characterization of Sapient Agents.
IEMC - Managing Technologically Driven Organiza-
tions: The Human Side of Innovation and Change.
Verbeet, R., Rieder, M., and Kies, M. (2019). Realization
of a Cooperative Human-Robot-Picking by a Learning
Multi-Robot-System Using BDI-Agents. SSRN Elec-
tronic Journal.
W Axhausen, K., Horni, A., and Nagel, K. (2016). The
multi-agent transport simulation MATSim. Ubiquity
Press.
Wan, Q., Liu, W., Xu, L., and Guo, J. (2018). Extend-
ing the BDI Model with Q-learning in Uncertain En-
vironment. In International Conference on Algo-
rithms, Computing and Artificial Intelligence, pages
1–6, Sanya China. ACM.
Weiß, G. (1996). Adaptation and learning in multi-agent
systems: Some remarks and a bibliography. In Adap-
tion and Learning in Multi-Agent Systems, volume
1042, pages 1–21. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Wooldridge, M. J. (2009). An introduction to multiagent
systems. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, U.K, 2nd ed
edition.
Xu, L., Tan, G., Zhang, X., and Zhou, J. (2012). A bdi
agent-based approach for cloud application autonomic
management. In 4th IEEE International Conference
on Cloud Computing Technology and Science Pro-
ceedings, pages 574–577.
Zhang, W., Valencia, A., and Chang, N.-B. (2021). Syn-
ergistic integration between machine learning and
agent-based modeling: A multidisciplinary review.
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning
Systems.
Zoelen, E. M. v., Cremers, A., Dignum, F. P., Diggelen,
J. v., and Peeters, M. M. (2020). Learning to commu-
nicate proactively in human-agent teaming. In PAAMS
Proceedings, pages 238–249. Springer.
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
268
