
Concept for General Improvements in the Treatment of Femoral
Shaft Fractures with an Intramedullary Nail
Finn Siegel
1a
, Christian Buj
1b
, Ralf Schwanbeck
2c
, Andreas Petersik
2
, Ulrich Hoffmann
2
,
Jakob Kemper
2
, Frank Hildebrand
3
, Philipp Kobbe
3
, Jörg Eschweiler
3d
, Johannes Greven
3e
,
Ricarda Merfort
3
, Christian Freimann
4
, Astrid Schwaiger
4
and Frerk Müller-von Aschwege
1
1
OFFIS e.V. – Institute for Information Technology, Escherweg 2, Oldenburg, Germany
2
Stryker, Schönkirchen, Germany
3
Universitätsklinikum Aachen, Aachen, Germany
4
OnCare GmbH, München, Germany
Keywords: Femur Fracture, Intramedullary Nailing, Intraoperative, Malrotation, Rehabilitation, Medical Data Security.
Abstract: The gold standard for femoral shaft fracture treatment is intramedullary (IM) nailing. This principle has gained
acceptance because of the good fracture healing rate and the rapid return to full weight-bearing of the leg.
Nevertheless, a significant number of patients suffer from impairments in everyday life years after treatment.
This paper discusses various causes and presents possible solutions: a) Improving the IM nailing procedure
by developing a new intraoperative assistance system to precisely restore length and rotation angle of the
injured femur. b) Improving rehabilitation after IM nailing treatment, through home monitoring. c) Increasing
data safety, standardization, and centralization along the entire patient pathway, enabling analytics to
statistically verify improvements in IM nailing treatments.
1 INTRODUCTION
Thanks to modern medicine, a femoral shaft fracture
can be treated with few complications. Nevertheless,
20% of patients still suffer from after-effects three
years post-treatment, reducing their quality of life.
These include pain in the lower limbs or an altered
gait pattern. One identified cause is an incorrect
reconstruction of the rotation angle or length of the
femur during surgery. This relationship and possible
improvements are presented in more detail below.
Treatment Challenges
Intramedullary (IM) nailing is the most successful
treatment for a femur shaft fracture in adults, due to
high healing rates with low complication (Rommens
& Hessmann, 2015). During treatment with an IM
nail, the soft tissue is minimally affected, enabling
rapid healing (Fantry et al., 2015). In addition,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9319-4304
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5357-5516
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0925-929X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8477-4884
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2856-4804
interlocking with screws provides rotational and
longitudinal stability and thus ensuring the conditions
for an early return to full weight bearing and a high
likelihood of fracture union (Jaarsma & van Kampen,
2004; Paterno & Archdeacon, 2009). Nevertheless, it
is still a surgical procedure that carries risks, such as
infection or neurovascular injury. Another
disadvantage of the minimally invasive procedure is
the difficulty to ensure anatomical realignment under
direct vision, which leads to less control of rotation
and length compared to the classical method of plate
fixation (Jaarsma et al., 2004). Deviations from the
original position, greater than 5° in frontal or sagittal
plane, 15° in the axial plane and 2 cm in length, are
regarded to be deformities (Ricci et al., 2008). It
originates from a poor choice of nail entry point or
incorrect positioning of nail fixation during surgery.
The occurrence varies between 22.7 - 28% of the
cases (28% (Jaarsma & van Kampen, 2004), 26%
360
Siegel, F., Buj, C., Schwanbeck, R., Petersik, A., Hoffmann, U., Kemper, J., Hildebrand, F., Kobbe, P., Eschweiler, J., Greven, J., Merfort, R., Freimann, C., Schwaiger, A. and Aschwege, F.
Concept for General Improvements in the Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fractures with an Intramedullary Nail.
DOI: 10.5220/0011679100003414
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2023) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 360-367
ISBN: 978-989-758-631-6; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

(Strecker et al., 1996), 22.7% (Rommens &
Hessmann, 2015), 25% (Papachristos, 2019)). In
general, a not correctly reconstructed femur leads to
arthritis and pain of back, hip and knee, limping,
restrictions in range of motion and daily life. These
complications scale with the severity of the
malalignment. (Jaarsma & van Kampen, 2004;
Papachristos, 2019). In summary, developing a way
to correctly restore the rotation (also known as
(ante-) version or (ante-) torsion) and the length of the
femur, malalignments could be reduced and therefore
the patient’s quality of life improved. Common
techniques used by surgeons to correctly restore the
anteversion angle of the fractured femur are based on
determining the anteversion angle of the uninjured leg
at beginning of surgery. This angle is used as
reference for the injured leg. One well known method
to determine a reference for the anteversion is the
lesser trochanter method (Deshmukh et al., 1998).
Alternatively, the anteversion angle can be measured
by using the inclination scale of the C-arm to measure
the C-arm angle between the positions required for
taking a true lateral image of the knee and a true
lateral image of the femoral head-neck junction
(Tornetta et al., 1995). Other possible methods for
assessing femoral rotation are the cortical step sign
method (Langer et al., 2010) and computer
tomography (CT) based navigation (Weil et al.,
2014). Although several different methods for
measuring anteversion exist none of the methods is
widely accepted. The fluoroscopy-based methods
significantly increase the number of necessary x-ray
images and the time needed for surgery (Deshmukh
et al., 1998; Tornetta et al., 1995). Additionally, these
methods have limited accuracy (Ju et al., 2021). The
cortical step sign method has limited value for
patients with comminuted fractures, and CT-based
navigation causes high costs and long setup time. In
conclusion, a widely accepted method to control for
anteversion and length of the femur is needed.
Rehabilitation
The following common impairments after IM nailing
are identified: Hip abduction and knee extensor
weakness, knee and hip pain, decreased hip
movement, decreased walking endurance, and gait
abnormalities, especially Trendelenburg gait pattern.
Rehabilitation focuses on reversing these through
physical exercises improving range of motion,
strength, weight bearing and gait. However, it is
described in literature that 20% of the patients could
not return to normality 3 years after surgery (Paterno
& Archdeacon, 2009; Noor, 2019). Therefore, it is
important to consider follow-up issues caused by
malrotation. Researchers found that up to 72% of a
present malrotation could be compensated (Jaarsma
et al., 2004). However, day-to-day monitoring of the
musculoskeletal system and its mobility is necessary
to assess individual stress caused by a given
malrotation. The collection and analysis of the
monitoring data can enable individual therapy
interventions, to improve patient’s healing in a
sustainable way. In addition, interventions can be
made comparable, and their success evaluated.
Lastly, new information about the compensation can
be gathered, for example when it sets in or how it
progresses. Physiotherapy could start directly at this
point and support with targeted training.
2 METHODS AND
PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Within the Secur-e-Health project (Secur-e-Health,
2021) the German subproject Smart Fracture Care
funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education
and Research (BMBF) is focusing on a new approach
for dealing with femur shaft fractures. The main
project goals are:
1. Improving the IM nailing procedure by
developing a new intraoperative assistance system
to precisely restore length and rotation angle of
the injured femur.
2. Improving rehabilitation after IM nailing
treatment, through home monitoring.
3. Increasing data safety, standardization, and
centralization along the entire patient pathway.
This will enable Big Data analytics to statistically
verify improvements in IM nailing treatments.
2.1 Intraoperative Assistance System
There is no widely accepted method controlling
anteversion and length of the femur shaft.
To address this issue, we propose a computer
aided surgery system that allows intraoperative
reconstruction of the 3D shape of the uninjured femur
using a small number of fluoroscopic images
recorded before surgery. The mirrored 3D shape is
used as a reference for restoring the rotation and
length of the injured femur.
The Length Alignment Rotation (LAR) system
consists of a tablet computer with built-in frame
grabber and touch screen. The tablet computer is
placed in the sterile field close to the surgeon
allowing interaction with the LAR software. It also
obtains fluoroscopic images using a frame grabber
Concept for General Improvements in the Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fractures with an Intramedullary Nail
361
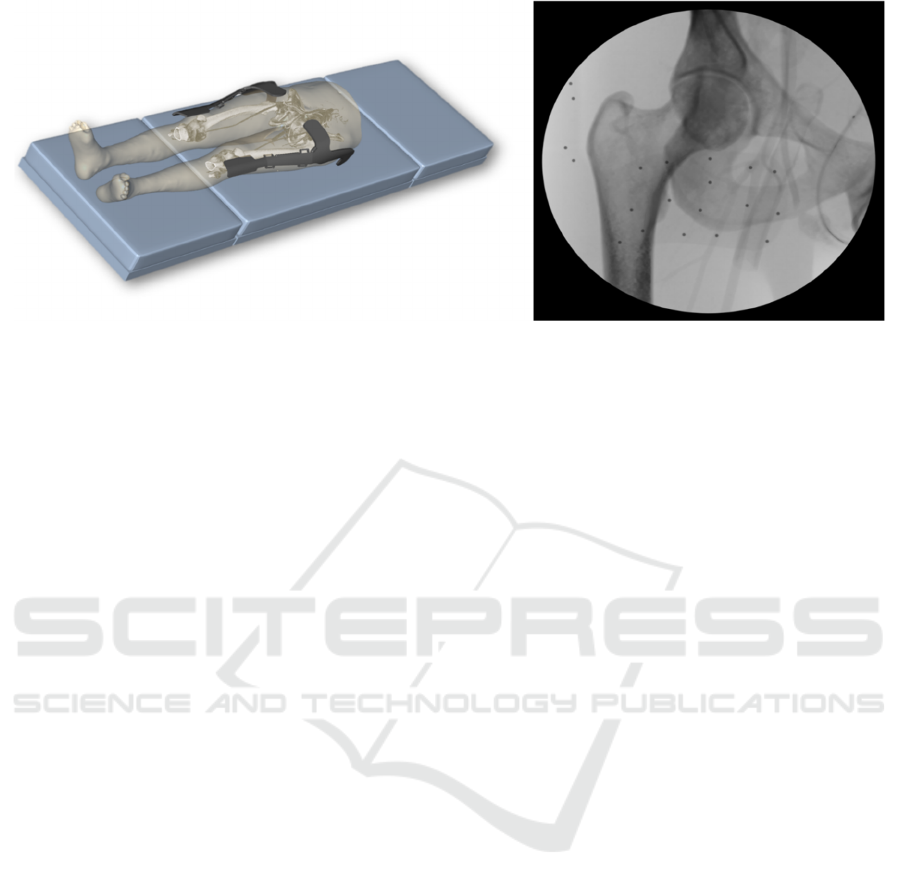
Figure 1: Placing (left) and radiographic image (right) of reference bodies attached to the patient, used for the LAR system.
and a connection to the C-arm. Additionally,
reference bodies are attached to the patient (see
Figure 1). These markers are based on polymer-
bodies with small, embedded steel beads. Using
computer vision software, the viewing orientation of
fluoroscopic images can be computed by analysing
the pattern of the projected beads in the image.
The reference Image is created at the beginning
of the surgery. The LAR system is used to compute
the 3D shape of the unaffected femur by the following
steps:
1. A reference body spanning the length of the femur
is placed on the unaffected limb.
2. Two fluoroscopic images of the proximal area of
the unaffected femur are taken.
3. Two fluoroscopic images of the distal area of the
unaffected femur are taken.
4. The LAR system computes a 3D approximation
of the unaffected femur from the images taken in
step 2 and 3.
For rotation and length control of the injured
femur, the approximation of the 3D shape of the
unaffected bone can be used as reference for the
injured bone. For this, the following workflow step
are required:
1. A reference body spanning the length of the femur
is placed on the affected limb.
2. Two fluoroscopic images of the proximal area of
the affected femur are taken.
3. The LAR system computes a 3D approximation
of the proximal part of the affected femur.
4. The mirrored 3D shape of the unaffected femur
is matched to the proximal part of the 3D shape of
the affected femur.
5. The contour and axes of the mirrored unaffected
femur will be presented as an overlay on top of the
fluoroscopic images of the affected femur. This
can be used as a reference by the surgeon (see
Figure 2).
6. Using two images of the distal area, the system
can also reconstruct the entire 3D shape of the
affected femur. Now angle and length of the
affected femur can be directly compared to the
unaffected femur (see Figure 2).
One of the main technical challenges in the LAR
system is the reconstruction of the 3D shape of the
femur from 2D fluoroscopic images. To compute the
3D shape of the femur, first the relative orientation of
the fluoroscopic images is computed using the
projections of the reference body beads in the
fluoroscopic images. A convolutional neural network
(CNN) for 3D segmentation is used to compute an
approximation of the proximal and distal femur shape
from the fluoroscopic images. The network
architecture used for this is similar to the architecture
described in (Milletari et al., 2016). The proximal and
distal approximation of the femur are fused into an
overall shape by fitting a 3D active shape model
(Cootes et al., 1995) to the distal and proximal
approximations.
An early version of the LAR system has been
tested in a cadaver lab on two specimen and in several
sawbone labs. The tests showed that the system can
be used to obtain a 3D reconstruction of a femur bone
from 2D images. The accuracy of the estimated
angles was ± 8 degree and ± 4 mm in length, when
compared to the ground truth obtained from a CT
scan. The objectives of further research are to
improve the workflow, to facilitate the work with
reference bodies and to enhance the robustness of the
3D reconstruction.
HEALTHINF 2023 - 16th International Conference on Health Informatics
362

Figure 2: Tablet computer showing the LAR system.
2.2 Rehabilitation Improvement
The healing process is determined either in sessions
with the physiotherapist or by patient self-reports. In
the first case, only a small insight into the treatment
progression is generated and not a continuous picture.
In the second case, documentation is often inaccurate
due to the patients’ tendency to misjudge themselves
(Komaris et al., 2022). Therefore, an objective,
continuous measurement method may be helpful to
obtain a more accurate picture of the patient’s healing
progress to further customize treatment. In addition,
such system could enable intercomparability,
allowing treatment methods to be compared. number.
2.2.1 Concept for Improvements
To overcome the difficulties described above, we
propose the usage of a sensor array, which can be
worn during rehabilitation in a wearable. Used for
this purpose are Force Sensing Resistors (FSRs),
inertial measurement units (IMUs) and
Electromyography (EMG) sensors. Collected data is
then processed and statements about the course of
healing can be made.
To improve individual treatment and to create the
possibility of easy intercomparability, the following
objectives are established:
a) Check for the common residual impairments after
IM nailing, hip abduction weakness, decreased
hip and knee movement, knee extensor weakness,
pain, gait abnormalities, decreased walking
endurance. If these are identified, targeted
countermeasures can be taken during
rehabilitation.
Since hip abduction and knee extension weakness
affect the patient’s gait pattern and daily routine,
they can be detected by combining a specific
questionnaire and a gait analysis. The range of
motion (ROM) can be measured allowing to
conclude about mobility. Which in turn allows
deductions about hip and knee joint movements.
Pain is a subjective perception and needs to be
assessed by questionnaires. Information about
changes in walking endurance can be obtained in
a trend analysis.
b) Collecting information about ROM and pain
tolerable load on the leg in everyday life. This
additional information can be used by the physical
therapist to customize exercises or to properly
assess the use of assistive devices.
c) A malrotation of the femur is followed by a
compensation mechanism of the body. This effect
is well known and documented, but information
about the onset of compensation is not yet
available. Continuous measurements could
provide further knowledge.
d) Visualization of the healing process. A visibly
positive progression could motivate the patient to
continue or even intensify the exercising and thus
accelerate the healing.
To meet these objectives (a-d), information about
the status of mobility, ROM, gait, activity,
malrotation, compensation, status of demanding
activity, pain, managing everyday life and the
before surgery state must be generated from
collected patient data. This will be accomplished
using wearable sensors as well as patient self -
assessments e.g., filling out questionnaires (about
pre-surgical status, pain and satisfaction with
healing).
2.2.2 Sensor Systems
In the following, three sensor systems (EMG, IMU
and FSR) proposed in chapter 2.2.1 for integration
into a wearable are described. After a functional
introduction, the data evaluation methods to generate
relevant information are described.
Electromyography (EMG) can be used to measure
the onset of a muscle activation. Surface electrodes
can measure the electronical potential differences,
which are due to the activation of muscles. The EMG-
signal changes in amplitude and frequency depending
on the induced motion (Wang et al., 2021). The
following information must be determined from the
recorded sensor data:
Rotation: A gait pattern is created by the interaction
of several muscles. In case of deformed bones in the
lower limbs, gait pattern changes and therefore the
activity of the muscles. The change can be measured
externally with the help of EMG sensors. Since the
Concept for General Improvements in the Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fractures with an Intramedullary Nail
363

sensors are to be worn above the knee, the vastus
medialis and the vastus lateralis seem to be suitable
muscles for such measurements. Mohammad &
Elsais, 2020 found significant negative correlations
between hip internal rotation angle and EMG activity
for the gluteus maximus and vastus medialis
obliquus. Significant positive correlations were
observed between hip internal rotation angle and
EMG activity for the vastus lateralis obliquus
(Mohammad & Elsais, 2020). Those findings indicate
that the EMG measurement could be used to draw
conclusions about malrotation. A study to determine
this relationship is being planned.
Load and Muscle Strength: The load on the leg
influences the muscle force required for walking.
E.g., if the patient uses a walker, less load is placed
on one leg and less muscle force is required. Since
musculoskeletal electrical activity correlates with
muscle force, EMG sensors are useful for detecting
different loads. In fact, and Mokri et al., 2022 showed
that neuromuscular activation is a major contributor
to muscle strength (Mokri et al., 2022). However, the
research also showed that a direct model cannot be
created because muscle force also depends on muscle
volume, fiber length, and velocity (Roberts &
Gabaldon, 2008), which means that EMG
calculations can only be used as an indicator of the
healing process. For example, if the EMG detects an
increase in activity, improvement can be assumed.
Calculating absolute load values remains a challenge.
To gain more insight, a study will be conducted to
examine different loads and corresponding EMG
signals.
Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) are available in
small sizes and for a low cost. They can be used to
obtain position and orientation. It usually consists of
an accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer. We
propose wearing at least two sensors. The following
information must be determined from the recorded
sensor data:
ROM: At least two sensors are needed to determine
a joint angle, quantifying the ROM. If the sensor axes
are perfectly aligned with the object axes the joint
angle can be computed by integrating the difference
of both angular rates (Seel et al., 2014). The
positioning of the sensors will be supported by
wearables, but it cannot be guaranteed, that the
positioning accuracy will repeatedly be sufficient. To
overcome this issue a joint is considered as a hinge
joint and therefore creating constraints allowing the
position and direction vector of the knee to be
determined. Concluding, only the individual
orientation of the sensors is required, directly
resulting in an accurate flexion/extension angle
(Favre et al., 2008). Seel et al., 2014 could achieve an
accuracy of 3° when measuring the knee joint (Seel et
al., 2014). This concept is suitable to be integrated in
the wearable.
Activity: Information on the patient’s activity can be
derived from the calculations of ROM, e.g., step
count. Another important aspect that should be
sensorially detected is the performance of
physiotherapeutic exercises in the home environment.
Komaris et al., 2022 have already presented a
working concept in which exercise sequences are
recorded and processed during supervised training
(Komaris et al., 2022). These recordings can now be
compared to home training, identifying exercises and
detecting changes in execution.
Gait: Insights into Gait irregularities are an indicator
for the healing process. To put as little additional
strain on the patient as possible, the aim is to use a
unilateral sensor fitting. This limits the ability to
detect gait differences based on lateral differences.
However, it is still possible to observe the change of
spatio-temporal gait parameters unilaterally (Shahar
& Agmon, 2021), allowing conclusions to be drawn
about gait irregularities. From this, e.g.,
Trendelenburg gait could be detected, a study is
planned to gain further insight.
Pressure sensors are one of the simplest methods to
measure the force under the foot while walking. In
example, Force Sensing Resistors (FSRs), are
suitable for this purpose. These consist of a
conductive polymer between two electrodes. If a
force is applied from outside, its conductive
properties change along with the resistance between
the electrodes. This change correlates with the
applied force (Abdul Razak et al., 2012). The
following objectives are to be measured:
Load: The load can be estimated, by real-time
pressure sensors worn inside the shoe sole. After a
calibration with the help of a scale, a threshold value
can be set, which is considered as a limit for the load
of the leg. This can be used to provide direct feedback
for the patient to assist in loading the leg accordingly.
In addition, the data shows the objective course of the
tolerable load allowing for exercises to be adapted
accordingly. Bril et al., 2016 showed the possible
usage of such threshold to directly support the patient
(Bril et al., 2016).
HEALTHINF 2023 - 16th International Conference on Health Informatics
364

Figure 3: Concept of digital patient pathway.
Mobility: Step frequency can be investigated to
derive information about the patient’s mobility. Since
steps are recognizable in recorded pressure data, a
Fast Fourier Transformation can provide information
about the step frequency. Also, classifying pressure
patterns while being active can help to differentiate
events such as stair climbing. Chakraborty & Dendou
were able to detect whether a patient was climbing up
or down stairs, with an accuracy of 100%
(Chakraborty & Dendou, 2014). Implemented in this
approach, it could provide additional information
about healing progress.
2.2.3 Overall Sensor Concept
A concept, to achieve the above-mentioned goals has
been created. It is based on a sensor set built into
wearables and a data collection unit. The wearable
will hold multiple sensors (FSR, IMU, EMG) while
keeping the additional burden on the patient to a
minimum. E.g., the sensors must be easy to place and
remain stable to ensure measurement reliability. To
meet these requirements, the sensors are divided into
two systems. System A is used on the thigh and holds
the EMG sensors and a single IMU sensor. It is
designed as a bandage, starting just below the knee,
and extending 15 cm above. A hole at the position of
the patella helps the patient to position it. System B is
built into the shoe and holds the pressure sensors and
a single IMU sensor. Because it is firmly installed in
the sole, it cannot be applied incorrectly or slip during
examination. To gather data from system A and B, a
gateway is needed that automatically connects to the
wearable and receives, encrypts, and forwards the
collected data to a server. The server stores, processes
and evaluates the data.
2.3 Digital Patient Pathway
The success of a treatment is influenced by many
factors, e.g., concomitant diseases, nail types, nail
techniques and interlocking methods. Thus, the
choice of the most suitable method for an individual
patient becomes a challenge. Additionally, there are
issues with data flow and accessibility, as not all
stakeholders, such as treating specialists, have access
to all the data generated during the treatment process.
Leading to two main problems, to be solved by
improved data handling. On the one hand, a concept
has to be developed, which allows to conduct studies
on the success of different treatment methods. On the
other hand, the availability of patient information as
a basis for individual treatment must be enhanced.
For an improved individual outcome patient
data is digitalised and stored in a centralized entity,
making the entire patient pathway traceable, see
Figure 4. A cloud (1) provides the ability to
automatically collect patient data and to process it
generating further information, cf., section 2.2.
This concept ensures security by providing a
REST API (2) and de- and encrypting data traffic.
Additionally, data will be standardized generating
comparability. Authentication and authorization
management is used to ensure that only the patient
can view, and share collected data.
Neither patient nor medical specialist is in need to
always be able to view all stored data. This creates the
need for an interface between the data cloud (1) and
the user (4). In Germany, the introduction of the
electronic patient record (ePA) has created a basis for
solving such issue (Bundesminesterium für
Gesundheit, 2021). For our proposed concept, the
principle is abstracted, which allows to build a
demonstrator on a known base while being
compatible with other concepts of electronic patient
Concept for General Improvements in the Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fractures with an Intramedullary Nail
365

data storage. The myoncare application, an approved
medical product, is used in this case (Oncare GmbH,
2022). It offers a communication platform for
healthcare providers and patients in a way that
information on health status, exercise videos,
questionnaires or educational sheets can be
exchanged directly between specialist and patient.
The platform can be connected to the central cloud (1)
via an interface. Thus, the patient’s healing process
can be monitored continuously, creating a basis for
improved individual outcome.
To enable further research, the data stored in the
cloud (1) can be utilized. With the patient’s consent,
the data is anonymized, standardized and made
accessible, providing the opportunity to evaluate the
success of different treatment methods in patient
cohorts.
3 CONCLUSION AND
DISCUSSION
LAR System
The LAR system is a good alternative to existing
techniques for intraoperatively measuring femoral
anteversion angle and length. Compared to existing
solutions the proposed system is designed to save
radiation, time, costs while increasing accuracy.
Initial experiments have had promising results and
have shown that the overall system design is
viable. Future work will concentrate on streamlining
the workflow and the handling of reference bodies to
make the system more usable. Additionally, the
algorithms for 3D reconstruction from 2D
fluoroscopic images will be made more accurate and
robust.
Wearable
Analysis of sensor data allows each of the objectives
described in section 2.2.1 to be addressed. The home
exercise will be monitored objectively, a continuous
picture of the healing process will be drawn, different
treatment methods will be comparable. This will be
an important improvement because, to our
knowledge, there is no universal standard for
rehabilitation after IM nailing. Further studies on the
concept in terms of feasibility and usability need to be
conducted.
Digital Patient Pathway
Limitations, identified in section 2.3, concerning the
data handling, can be improved with the proposed
idea. All information about the patient’s history will
be available for each treating specialist. In addition,
the data will be automatically processed so that
patient and specialist receive a comprehensive
overview of the treatment. In addition, treatment
methods can be compared and evaluated as data from
multiple patients is available. Big data analyses, for
example, can then be carried out. The addition of the
myoncare application enables to process all data in a
user-friendly way, while maintaining a certified
standard. Since the data handling concept is
abstracted from the established ePA, our proposed
concept is exchangeable and additionally transferable
into the ePA or other patient data management
concepts. Aspects of data privacy and security remain
to be discussed before the proposed concept can be
integrated into everyday clinical practice.
The proposed concept of a secure medical data
repository that facilitates both individual outcome
and further research is highly consistent with the
goals of the Secur-e-Health (ITEA) project.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was founded by the German Federal
Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (FKZ:
01IS21085).
We would like to thank Mrs. Rütten and Mr.
Schifflers for their consultative support.
REFERENCES
Abdul Razak, A. H., Zayegh, A., Begg, R. K., & Wahab, Y.
(2012). Foot Plantar Pressure Measurement System: A
Review. Sensors, 12(7), 9884–9912. https://doi.org/
10.3390/s120709884.
Bril, A. T., David, V., Scherer, M., Jagos, H., Kafka, P., &
Sabo, A. (2016). Development of a Wearable Live-
feedback System to Support Partial Weight-bearing
While Recovering From Lower Extremity Injuries.
Procedia Engineering, 147, 157–162. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.206.
Bundesminesterium für Gesundheit (2021). Die
elektronische Patientenakte (ePA). https://www.bundes
gesundheitsministerium.de/elektronische-
patientenakte.html. Accessed 28.09.2022.
Chakraborty, G., & Dendou, T. (2014). Analysis of Foot-
pressure Data to Classify Mobility Pattern.
International Journal on Smart Sensing and Intelligent
Systems, 7(5), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.21307/ijssis-
2019-119.
Cootes, T. F., Taylor, C. J., Cooper, D. H., & Graham, J.
(1995). Active Shape Models-Their Training and
Application. Computer Vision and Image
HEALTHINF 2023 - 16th International Conference on Health Informatics
366

Understanding, 61(1), 38–59. https://doi.org/10.1006/
cviu.1995.1004.
Deshmukh, R. G., Lou, K. K., Neo, C. B., Yew, K. S.,
Rozman, I., & George, J. (1998). A technique to obtain
correct rotational alignment during closed locked
intramedullary nailing of the femur. Injury, 29(3), 207–
210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1383(97)00182-4.
Fantry, A. J., Elia, G., Vopat, B. G., & Daniels, A. H. (2015).
Distal femoral complications following antegrade
intramedullary nail placement. Orthop Rev (Pavia),
7(1). https://doi.org/10.4081/or.2015.5820.
Favre, J., Jolles, B. M., Aissaoui, R., & Aminian, K. (2008).
Ambulatory measurement of 3D knee joint angle.
Journal of Biomechanics, 41(5), 1029–1035.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2007.12.003.
Jaarsma, R. L., Ongkiehong, B. F., Grüneberg, C.,
Verdonschot, N., Duysens, J., & van Kampen, A.
(2004). Compensation for rotational malalignment after
intramedullary nailing for femoral shaft fractures.
Injury, 35(12), 1270–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016
/j.injury.2004.01.016.
Jaarsma, R. L., & van Kampen, A. (2004). Rotational
malalignment after fractures of the femur. The Journal
of Bone and Joint Surgery. British volume, 86-B(8),
1100–1104. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-
620X.86B8.15663.
Ju, B., Moon, Y. J., & Lee, K.-B. (2021). Use of Lesser
Trochanter Profile as a Rotational Alignment Guide in
Intramedullary Nailing for Femoral Shaft Fracture.
Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 103(22), e89.
https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.21.00105.
Komaris, D.-S., Tarfali, G., O’Flynn, B., & Tedesco, S.
(2022). Unsupervised IMU-based evaluation of at-
home exercise programmes: a feasibility study. BMC
Sports Sci Med Rehabil, 14(1), 28. https://doi.org/
10.1186/s13102-022-00417-1.
Langer, J. S., Gardner, M. J., & Ricci, W. M. (2010). The
Cortical Step Sign as a Tool for Assessing and
Correcting Rotational Deformity in Femoral Shaft
Fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 24(2), 82–
88. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181b66f96.
Milletari, F., Navab, N., & Ahmadi, S.-A. (2016). V-Net:
Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric
Medical Image Segmentation. https://doi.org/10.48550/
ARXIV.1606.04797.
Mohammad, W. S., & Elsais, W. M. (2020). Association
Between Hip Rotation and Activation of the Quadriceps
and Gluteus Maximus in Male Runners. Orthopaedic
Journal of Sports Medicine, 8(11), 232596712096280.
https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967120962802.
Mokri, C., Bamdad, M., & Abolghasemi, V. (2022). Muscle
force estimation from lower limb EMG signals using
novel optimised machine learning techniques. Med Biol
Eng Comput, 60
(3), 683–699. https://doi.org/10.1007/
s11517-021-02466-z.
Noor, M. (2019). Rehabilitation following intramedullary
nailing of femoral shaft fracture: a case report, 8.
Oncare GmbH (2022). myoncare. https://www.myoncare.
com/.
Papachristos, I. V. (2019). Complications of Femoral
Intramedullary Nailing: What should the Surgeon
Remember? EC, 7.
Paterno, M. V., & Archdeacon, M. T. (2009). Is There a
Standard Rehabilitation Protocol After Femoral
Intramedullary Nailing? Journal of Orthopaedic
Trauma, 23(Supplement 5), S39‐S46. https://doi.org/
10.1097/BOT.0b013e31819f27c2.
Ricci, W. M., Schwappach, J., Tucker, M., Coupe, K.,
Brandt, A., Sanders, R., & Leighton, R. (2008).
Trochanteric versus Piriformis Entry Portal for the
Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fractures. Journal of
Orthopaedic Trauma, 22(Supplement 3), S9‐S13.
https://doi.org/10.1097/01.bot.0000248472.53154.14.
Roberts, T. J., & Gabaldon, A. M. (2008). Interpreting
muscle function from EMG: lessons learned from direct
measurements of muscle force. Integrative and
Comparative Biology, 48(2), 312–320. https://doi.org/
10.1093/icb/icn056.
Rommens, P. M., & Hessmann, M. H. (Eds.) (2015).
Intramedullary Nailing. London: Springer London.
Secur-e-Health (2021). Secur-e-Health. https://itea4.org/
project/secur-e-health.html. Accessed 2021.
Seel, T., Raisch, J., & Schauer, T. (2014). IMU-Based Joint
Angle Measurement for Gait Analysis, 19.
Shahar, R. T., & Agmon, M. (2021). Gait Analysis Using
Accelerometry Data from a Single Smartphone:
Agreement and Consistency between a Smartphone
Application and Gold-Standard Gait Analysis System.
Sensors, 21(22), 7497. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227
497.
Strecker, W., Suger, G., & Kinzl, L. (1996). [Local
complications of intramedullary nailing]. Orthopade,
25(3), 274–291.
Tornetta, P., Ritz, G., & Kantor, A. (1995). Femoral
Torsion after Interlocked Nailing of Unstable Femoral
Fractures. The Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection,
and Critical Care, 38(2), 213–219. https://doi.org/
10.1097/00005373-199502000-00011.
Wang, J., Dai, Y., & Si, X. (2021). Analysis and
Recognition of Human Lower Limb Motions Based on
Electromyography (EMG) Signals. Electronics, 10(20),
2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202473.
Weil, Y. A., Greenberg, A., Khoury, A., Mosheiff, R., &
Liebergall, M. (2014). Computerized Navigation for
Length and Rotation Control in Femoral Fractures: A
Preliminary Clinical Study. J Orthop Trauma, 28(2), 7.
Concept for General Improvements in the Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fractures with an Intramedullary Nail
367
