
Randout-KD: Finetuning Foundation Models for Text Classification via
Random Noise and Knowledge Distillation
Pervaiz Iqbal Khan
1,2 a
, Andreas Dengel
1,2 b
and Sheraz Ahmed
1 c
1
German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), 67663 Kaiserslautern, Germany
2
Department of Computer Science, TU Kaiserslautern, 67663 Kaiserslautern, Germany
fi
Keywords:
Random Noise, Knowledge Distillation, Text Classification.
Abstract:
Finetuning foundation models effectively on downstream tasks is ongoing research. In this paper, we present
a finetuning method “Randout-KD” that enhances the performance of a student model for text classification.
We specifically propose a noise-injecting method in the representations of the transformer model during its
finetuning that works as regularization. Moreover, we integrate the knowledge distillation and noise injection
methods and show that combining these approaches boosts the baseline model performance. We evaluate the
proposed method on two datasets namely “CODA-19” and “RHMD” using PubMedBERT and RoBERTa
Large
as teacher models, and data2vec as a student model. Results show that the proposed approach improves the
accuracy up to 1.2% compared to the baseline methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Machine learning and deep learning methods have
been successfully applied to various natural language
processing (NLP) tasks such as question answering
(Wasim et al., 2019), named-entity-recognition (Zhao
et al., 2019), text summarization (Afzal et al., 2020),
text classification (Ibrahim et al., 2021), etc. The key
idea is to learn useful statistical representations for
the given piece of text before using it for the specific
task. Models built on the foundation of the Trans-
former model (Vaswani et al., 2017) have achieved
great success in NLP due to their ability of paralleliza-
tion and capability of learning long-range dependen-
cies. The original transformer model consists of en-
coder and decoder blocks where the encoder blocks
encode the representations for the given text data and
the decoder blocks decode the encoded representa-
tions. BERT (Devlin et al., 2018) is a transformer-
based model that takes the encoder part of the trans-
former model and is pre-trained on a huge amount of
unlabelled text data. It uses two proxy training objec-
tives, i.e., Masked Language Modeling (MLM) and
Next Sentence Prediction (NSP) to learn word rep-
resentations for a given text. In MLM some of the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1805-335X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6100-8255
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4239-6520
tokens are masked and BERT tries to predict the real
tokens for the masked tokens. In the NSP objective
function, two input sentences are given as input to
BERT and it predicts whether the second sentence
follows the first sentence or not. PubMedBERT (Gu
et al., 2021) is the model with similar architecture to
the BERT however, it is pre-trained on medical ab-
stracts from the PubMed dataset and full articles from
PubMedCentral. RoBERTa (Liu et al., 2019b) is the
extension of BERT that uses dynamic word masking
instead of static masking. Moreover, it uses more
training data compared to BERT. data2Vec (Baevski
et al., 2022) is another model that aims at the unifi-
cation of the different modalities such as image, text,
and speech with the same learning method. For the
NLP part, it uses the RoBERTa implementation as an
architecture but BERT masking strategy as an objec-
tive function. These pre-trained models also known
as foundation models (Bommasani et al., 2021) can
be finetuned on the downstream NLP tasks.
Effectively finetuning foundation models is an ac-
tive research topic (Zhang et al., 2020). Most of the
existing methods directly finetune these models on the
downstream tasks labeled dataset. However, some re-
search explores the effective finetuning method for
these models. Mixout (Lee et al., 2019) randomly
replaces some of the weights in the finetuned model
with the original weights from pre-trained models.
NoisyTune (Wu et al., 2022) adds a little random
Khan, P., Dengel, A. and Ahmed, S.
Randout-KD: Finetuning Foundation Models for Text Classification via Random Noise and Knowledge Distillation.
DOI: 10.5220/0011687800003393
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2023) - Volume 3, pages 457-465
ISBN: 978-989-758-623-1; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
457

noise to the parameters of the pretrained language
models (PLMs) before finetuning them.
Foundation models are large in size and often fine-
tuning them requires huge computation. To address
this challenge, various approaches such as model
pruning and knowledge distillation (KD) (Bucilua
et al., 2006; Hinton et al., 2015; Kim and Rush, 2016)
have been proposed in the literature. KD consists of a
teacher and a student model where the teacher model
is a large trained model and the student model con-
sists of the same or smaller model as compared to the
teacher model. The idea of the KD is to enable the
student model to “distill” knowledge from the teacher
model. KD forces the student model’s predictions to
match the predictions of the teacher model.
In this paper, we propose a method “Randout-
KD” to effectively finetune and improve the perfor-
mance of the student model. Concretely, our method
randomly injects noise into the hidden representa-
tions of various tokens while finetuning the student
model. We use data2vec as a student model whereas
RoBERTa and PubMedBERT as teacher models for
the two experimental settings. We evaluate our ap-
proach on two public datasets. Experiments results
show that our proposed method improves the perfor-
mance of the student model over the baseline model,
in terms of both F1-score and accuracy. The key con-
tributions of this paper are:
• We propose a new method of injecting random
noise into various tokens and their hidden repre-
sentations during finetuning of the model. The
proposed method improves the generalization of
the model.
• We further combine noise injection with knowl-
edge distillation for finetuning models. We em-
pirically show that this combination improves the
student model’s performance as compared to the
separate usage of these two approaches.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section, we briefly discuss the prior work in
literature focusing on regularization techniques and
knowledge distillation in NLP tasks.
2.1 Regularization Methods in NLP
Dropout (Srivastava et al., 2014) has been used as an
effective technique to prevent overfitting while train-
ing large pre-trained models. This method randomly
drops neurons during the training of a neural network,
which prevents neurons from co-adapting and gener-
alizes well. This technique has also shown success
in the domain of NLP. (Lee et al., 2019) proposed
a method “mixout” to finetune large pre-trained lan-
guage models. While finetuning a pre-trained model
on the downstream task, mixout stochastically re-
placed the weights of the finetuning model with the
pre-trained weights. The authors showed the effec-
tiveness of this method on various NLP tasks. Noisy-
Tune (Wu et al., 2022) added noise to the model
parameters before finetuning the pre-trained models.
This method added different amounts of random noise
to different parameters of the model based on their
standard deviation. Some of the work (Kitada and Iy-
atomi, 2021; Zhu et al., 2019) added noise to the at-
tention weights of the transformer models. However,
their work focused on adversarial training. (Khan
et al., 2022b) added noise to the embedding matrix of
the various transformer models and showed their ef-
fectiveness on social media text classification. (Khan
et al., 2022a) added Gaussian noise to the hidden rep-
resentations of transformer models and showed that it
improved the model’s performance.
2.2 Knowledge Distillation in NLP
(Liu et al., 2019a) applied knowledge distillation to
the multi-task learning setting in the domain of natu-
ral language understanding (NLU). They used multi-
ple teacher models for the single student model and
showed that this approach improved performance on
7 out of 9 datasets. (Xu et al., 2020) applied self-
distillation as an effective finetuning method to im-
prove BERT generalization capability. They evalu-
ated their method on four text classification and two
natural language inference datasets and showed that
their method improved the performance on all the
datasets. (Zhou et al., 2022) presented a knowledge
distillation method where the teacher network learns
to better transfer its knowledge to the student network
by getting feedback from the student network during
training. (He et al., 2022) achieved the state-of-the-
art results for the Chinese word segmentation task us-
ing weighted self-distillation where the student model
learns from itself instead of a separate finetuned
teacher model. They also added a weight mechanism
that allowed the student network to gather knowledge
selectively from the teacher model based on the im-
portance of knowledge. (Liu et al., 2020) proposed
noisy self-distillation for the text summarizing task
where they added noise to both teacher and student
models. They used teacher dropout (Bul
`
o et al., 2016)
during the predictions of the teacher model whereas
experimented with various noise mechanisms for per-
turbing the input of the student model during training.
In this work, we present a new method that injects
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
458
noise into the representations of a model during its
finetuning. Moreover, we incorporate knowledge dis-
tillation and show that combining knowledge distilla-
tion with noise injection improves the performance of
the network as compared to the baseline models.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
In this section, first we describe the preliminaries of
the transformer models, and knowledge distillation.
Then we present how we combine these concepts to
propose our finetuning method.
3.1 Transformers
Let (X,Y ) be a dataset containing X number of
examples and their corresponding Y labels, where
each example x
i
∈ X consists of T tokens. Let
L
m
represent a pre-trained language model such
as RoBERTa, data2vec, or PubMedBERT. For any
given x
i
, L
m
gives an output sequence S
L
=
[s
L
CLS
,s
L
1
,s
L
2
,....,s
L
T
,s
L
SEP
] where L represents number
of layers in L
m
. [CLS] and [SEP] are special tokens
representing the end of the example xi, and separating
two examples respectively.
We finetune L
m
by adding the softmax classifier
at the top of the model that takes the sentence level
hidden representation s
L
CLS
and produces output as
follows:
p(y
c
|s
[CLS]
) = so f tmax(Ws
[CLS]
) c ∈ C (1)
where ‘C’ is the number of classes and W is the
weight matrix of the final layer learned during train-
ing, and s
[CLS]
represents the final representations of
the [CLS] token.
We train L
m
by minimizing the cross-entropy loss
given by the following equation:
L
CE
= −
1
N
N
∑
i=1
C
∑
c=1
y
i,c
log(p(y
i
,c|s
i
[CLS]
)) (2)
where s
i
[CLS]
is the final hidden representation for the
i-th training example in the batch and ‘N’ is the batch
size.
3.2 Randout
Let ‘η’ denotes the amount of random noise. We com-
pute η as follows:
η = U (min, max) − 0.5 (3)
where U(min, max) is the uniform noise ranging from
min to max. We further subtract 0.5 from the gener-
ated noise to reduce the amount of noise. Following
is the Pytorch-style code for generating the random
noise between 0 and 1 and then subtracting 0.5 from
it:
η = torch.rand([B, T,H]) − 0.5
where ‘B’ represents the batch size, and ‘T’ and ‘H’
represent the number of tokens and the number of hid-
den units to be perturbed for each token, respectively.
3.3 Knowledge Distillation
Knowledge Distillation (KD) consists of two models,
i.e., the teacher and the student model. The teacher
model is generally already finetuned. The student
model consists of equal or small architecture com-
pared to the teacher model. The student model jointly
learns from the training data and the teacher model by
making predictions closer to the teacher model.
Let T and S represent the teacher and student mod-
els respectively. Let f
T
and f
S
denote the functions
(transformer model in our case) of a teacher and stu-
dent model. We employ the softmax function to con-
vert the output logits of f
T
and f
S
into a probability
distribution as follows:
f
T
= f
S
=
exp(z
k
/t)
∑
C
c=1
exp(z
k
/t)
(4)
Here, z
k
is the k-th logit output of student and teacher
models, and t is the temperature parameter to smooth
the logit values. Then, we minimize the objective
function on training data given by the following equa-
tion:
L
KD
=
∑
x
i
∈X
l( f
T
(x
i
), f
S
(x
i
)) (5)
where l represents the Kullback-Leibler (KL) diver-
gence that calculates the difference between teacher
prediction given by f
T
and student prediction given
by f
S
. L
KD
denotes the total knowledge distillation
loss that is the sum of KL divergence distance for all
the examples.
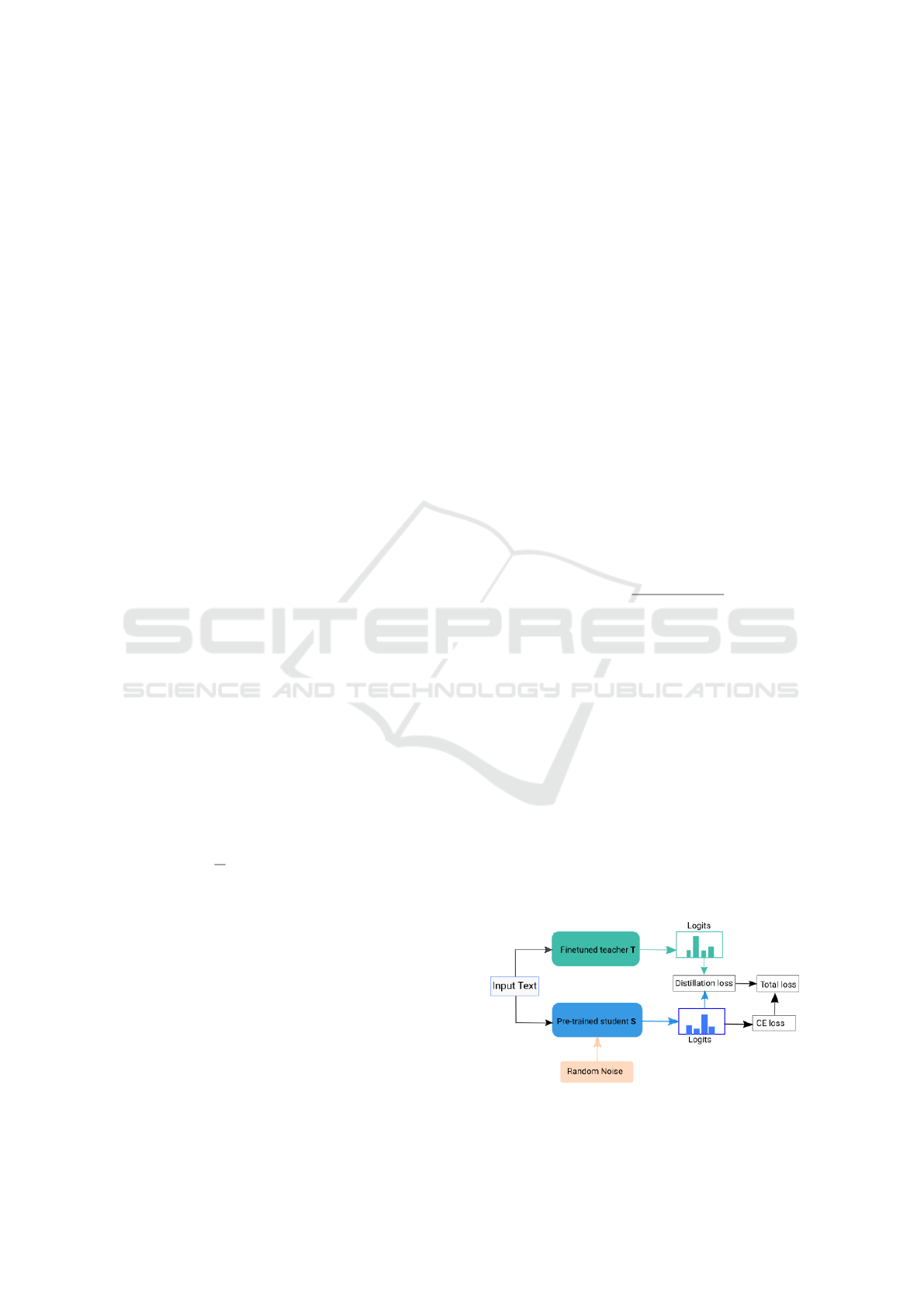
3.4 Randout-KD
Figure 1: Workflow of the proposed method “Randout-
KD”.
Randout-KD: Finetuning Foundation Models for Text Classification via Random Noise and Knowledge Distillation
459

Table 1: No. of layers and parameters for PLMs used or compared in this work.
Model # of Layers # of parameters
RoBERTa
Large
(Liu et al., 2019b) 24 355M
BERT
Large
(Devlin et al., 2018) 24 345M
data2vec
base
(Baevski et al., 2022) 12 125M
PubMedBERT
base
(Gu et al., 2021) 12 110M
SciBERT
base
(Beltagy et al., 2019) 12 110M
Our proposed method “Randout-KD” combines
knowledge distillation with noise injecting method
“Randout” to effectively finetune the student model.
Concretely, we first finetune a teacher model T on
a given dataset. Then we finetune a student model
S with the same or smaller architecture compared to
T . During finetuning of S, we freeze the model T
weights, and get its predictions for the given train-
ing examples in the form of probabilities, called as
soft-labels. Then, the objective function of the S
is to match its predicted probabilities similar to the
model T . To finetune S, we combine two objective
functions, i.e. standard cross-entropy (CE) loss and
Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence, where CE min-
imizes the classification loss and KL-divergence re-
duces the distance between predicted soft-labels of T
and S models. The overall loss function for training S
is as follows:
L = L
CE
+ λL
KD
(6)
where λ is the trade-off parameter between L
CE
and
L
KD
.
To generate the random noise, we utilize the
“Randout” method as discussed in subsection 3.2. For
every forward pass during the training of S, we gener-
ate a random noise of shape [B,T, H] and subtract 0.5
from it. Then we add the generated noise to the first
layer hidden representation of the model S as adding
noise in earlier layers has been effective (Khan et al.,
2022a).
Figure 1 shows the workflow of “Randout-KD”.
We evaluate Randout-KD on two datasets, and use
data2vec
base
as ‘S’ for both datasets. However, we
use two different models, i.e. RoBERTa
Large
and
PubMedBERT
base
as ‘T ’. Table 1 shows the no. of
layers and no. of parameters for some of the founda-
tion models relevant to this work.
4 EXPERIMENTS
In this section, we provide the training and datasets
detail we used for training and evaluating our pro-
posed method.
4.1 Datasets
To validate our proposed method, we used two differ-
ent multi-class classification datasets. The detail of
each dataset is as follows:
4.1.1 Reddit Health Mention Detection (RHMD)
RHMD dataset (Naseem et al., 2022b) consists of
10,015 Reddit posts. Every post in the dataset con-
tains one of the disease names from 15 categories,
i.e., addiction, allergy, Alzheimer’s, asthma, cancer,
cough, depression, migraine, PTSD, diabetes, OCD,
headache, fever, stroke, and heart attack. These dis-
ease words are used either as health mentions (HM),
non-health mentions (NHM), or figurative mentions
(FM). There are a total of 3, 360, 3,430, and 3,225
HM, NHM, and FM examples respectively, in the
dataset. We used 70%, 15%, and 15% train, valida-
tion, and test set split for experimentation.
4.1.2 CODA-19
CODA-19 dataset (Huang et al., 2020) consists of
10,966 abstracts related to COVID-19 research. Ex-
amples were extracted from these abstracts, and each
sample was labeled with one of the 5 sub-categories,
i.e., background, purpose, method, findings, and
“other”. We used the data split given with the origi-
nal dataset that consists of 137171, 15640, and 15475
train, validation, and test set examples, respectively.
4.2 Training Details
We finetuned teacher and student models with batch
sizes of {16, 32}. We used a learning rate of 1e
−5
and trained the teacher and student models for 15
epochs. We experimented with the trade-off param-
eter λ ∈ {0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8}, whereas we searched the
temperature parameter ‘t’ for knowledge distillation
in the span of {1.0, 2.0,3.0}. We set maximum se-
quence lengths of 100, and 215 for the CODA-19,
and RHMD datasets, respectively. We experimented
with adding noise to a various number of tokens
T ∈ {1,2,4, 8,16,32, 64}, and their hidden units H ∈
{1,2,4,8, 16,32, 64,128} for both datasets. We used
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
460
Table 2: Macro precision (P), recall (R), F1-scores (F1), and accuracy (acc) of teacher models on two datasets.
Dataset Model P R F1 acc
CODA-19 (Huang et al., 2020) PubMedBERT (Gu et al., 2021) 74.87 72.98 73.71 75.08
RHMD (Naseem et al., 2022b) RoBERTa (Liu et al., 2019b) 81.32 80.86 81.02 80.83
Table 3: Macro precision (P), recall (R), F1-scores (F1), and accuracy (acc) of baseline (data2vec) and proposed method.
Dataset Model P R F1 acc
CODA-19 (Huang et al., 2020)
data2vec (Baevski et al., 2022) 72.74 71.12 71.52 73.27
Randout-KD (proposed) 71.79 73.18 72.35 73.82
RHMD (Naseem et al., 2022b)
data2vec (Baevski et al., 2022) 78.59 78.36 78.09 78.17
Randout-KD (proposed) 79.35 79.50 79.37 79.37
early stopping to prevent overfitting and then evalu-
ated the trained models with the best validation ac-
curacy on the test set. We trained Randout-KD on
NVIDIA V100 GPU.
5 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
In Table 2 and Table 3, we present the results of
teacher models and our proposed method along with
the baseline method, respectively. For the CODA-
19 dataset, our proposed method improves the F1
score by 0.83% over the baseline method, whereas it
improves accuracy by 0.57%. This improvement in
the F1-score is due to the increase in recall of 2.8%.
However, precision drops by 0.95%. For the RHMD
dataset, accuracy gains the performance increase of
1.2% whereas precision, recall, and F1-score increase
by 0.76%, 1.14%, and 1.28%, respectively.
Table 4 presents the class-wise results for the
baseline, “Randout-KD”, and some of the existing
work, i.e., (Huang et al., 2020) on CODA-19 dataset.
As compared to the baseline, our proposed method
improves the F1-score for all 5 classes. However, pre-
cision improves for 3 out of 5 classes. Similarly, recall
also improves for 3 out of 5 classes. Table 5 shows
the class-wise results for the baseline and “Randout-
KD” on the RHMD dataset. Our proposed method
improves F1-scores over the baseline by 1.38%, 2.1%,
and 0.34% for FM, NHM, and HM classes, respec-
tively. For FM and HM classes, precision increases
by 2.21%, and 3.91%, respectively. However, it de-
creases by 3.83% for NHM class. Recall increases
by 0.41%, and 6.6% for the FM and NHM classes,
respectively, however, it decreases by 3.57% for the
HM class.
(Huang et al., 2020) finetuned SciBERT(Beltagy
et al., 2019) on CODA-19 dataset that gave an ac-
curacy of 74.9%. On the other hand, the PubMed-
BERT model we finetuned as a teacher and our pro-
posed method “Randout-KD” achieved an accuracy
of 75.08%, and 73.82%, respectively. Although SciB-
ERT and PubMedBERT models have a smaller num-
ber of parameters than data2vec that we finetune in
our proposed method, unlike data2vec, these models
are pre-trained on the domain-specific scientific liter-
ature.
On the RHMD dataset, we performed 10-fold
cross-validation to compare our approach with the
state-of-the-art (SOTA) results. We chose the best val-
idation set hyperparameters to train the 10-fold cross-
validation method. “Randout-KD” achieved an aver-
age of 79.93%, 79.93%, and 79.80% precision, recall,
and F1-score, respectively, for 3-class classification
settings. On the other hand, (Naseem et al., 2022a)
had 71% precision, recall, and F1-score. Although
(Naseem et al., 2022b) method had the highest pre-
cision, recall, and F1 score of 81%, their finetuned
BERT
Large
that has 24 layers, and 345M parameters.
On the other hand, we utilized data2vec in “Randout-
KD” that has 12 layers and 124M parameters, there-
fore (Naseem et al., 2022b), and “Randout-KD”are
not comparable directly. Moreover, in this paper, we
aimed to show that our method improves the capa-
bility of the baseline model. We plot the confusion
matrix of our proposed method for both datasets in
Figure 2.
5.1 Analysis of Noise Amount and
Trade-off Parameter
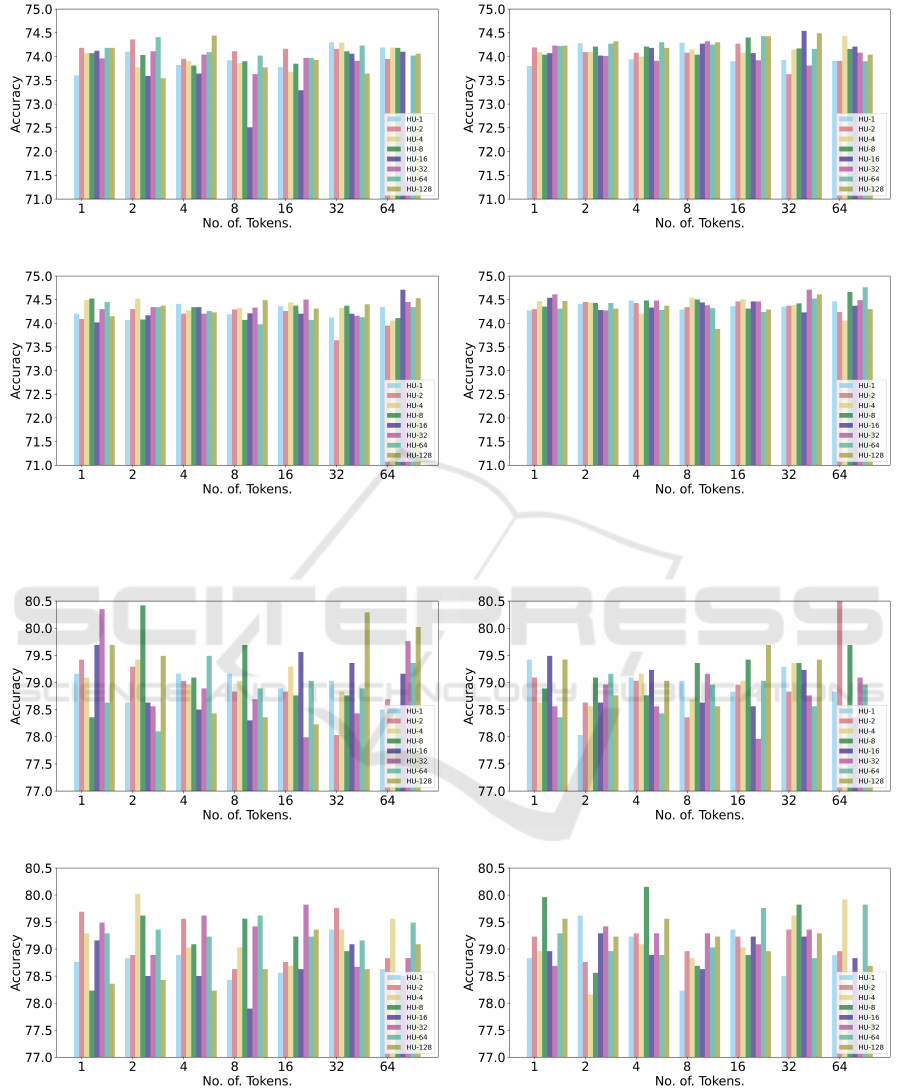
In Figure 3, we plot the impact on the accuracy of the
CODA-19 validation dataset with the variation of the
amount of noise and the trade-off parameter λ. The
plot shows that higher values of λ increase the vali-
dation set accuracy. One possible reason for this can
be the finetuning of PubMedBERT as a teacher model
on this dataset. As PubMedBERT was pretrained on a
large corpus of text related to medical literature, and
the CODA-19 also consists of health-related text ex-
tracted from abstracts, the teacher model better trans-
fers knowledge to the student. Plots show that, for
Randout-KD: Finetuning Foundation Models for Text Classification via Random Noise and Knowledge Distillation
461

Table 4: Class-wise results for the (Baevski et al., 2022), data2vec (baseline) and Randout-KD on CODA-19 dataset.
Model
Background Purpose Method Finding Other
P R F1 P R F1 P R F1 P R F1 P R F1
SVM (Huang et al., 2020) 65.80 70.30 68.00 62.10 44.6 51.90 61.5 49.5 54.9 69.7 72.9 71.2 72.9 69.9 71.4
RF (Huang et al., 2020) 67.1 63.2 65.1 69.6 36.5 47.9 71.6 35.0 47.1 63.0 78.7 69.9 67.4 74.2 70.6
MNB-count (Huang et al., 2020) 65.4 71.4 68.3 54.9 51.4 53.1 57.0 58.5 57.7 71.1 69.1 70.1 82.4 42.5 56.1
MNB-tfidf (Huang et al., 2020) 65.5 68.3 66.9 67.3 39.1 49.5 64.0 46.9 54.1 66.1 75.4 70.4 75.7 38.3 50.8
CNN (Huang et al., 2020) 64.9 70.6 67.6 61.2 51.2 55.7 59.6 56.2 57.9 72.6 70.2 71.4 74.3 79.5 76.8
LSTM (Huang et al., 2020) 65.5 70.6 68.0 70.0 46.4 55.8 63.4 50.8 56.4 70.0 72.4 71.1 68.2 77.0 72.3
BERT (Huang et al., 2020) 71.9 75.9 73.8 58.5 63.9 61.1 68.0 61.2 64.4 77.7 75.2 76.4 77.3 87.4 82.0
SciBERT (Huang et al., 2020) 73.3 76.8 75.0 61.6 63.6 62.6 71.5 63.6 67.3 78.3 77.5 77.9 79.4 85.2 82.2
data2vec (Baevski et al., 2022) 69.50 78.40 73.69 65.96 57.12 61.22 73.85 56.63 64.11 76.66 75.39 76.02 77.70 88.07 82.56
Randout-KD (proposed) 71.06 77.97 74.35 61.54 62.97 62.25 68.87 62.24 65.39 78.76 74.49 76.57 78.73 88.25 83.22
Table 5: Class-wise results for the data2vec (baseline) and Randout-KD on RHMD dataset.
Model FM NHM HM
data2vec (Baevski et al., 2022) 78.71 86.36 82.36 83.29 67.76 74.73 73.77 80.95 77.19
Randout-KD (proposed) 80.92 86.77 83.74 79.46 74.36 76.83 77.68 77.38 77.53
(a) The normalized confusion matrix for CODA-19 dataset. (b) The normalized confusion matrix for RHMD dataset.
Figure 2: The normalized confusion matrix plots for both the datasets evaluated on Randout-KD method.
λ = 0.2, injecting noise to 28 hidden representations
of 4 tokens gives the highest accuracy, whereas for
λ = 0.4, adding noise to 16 hidden representations
of 32 tokens gives the highest accuracy score. Injec-
tion of noise into 16 hidden representations of 64 to-
kens gives the highest accuracy for λ = 0.6, however,
adding noise into 64 hidden representations of 64 to-
kens gives the highest accuracy for λ = 0.8, which is
also the best accuracy among all the settings. Figure
4 visualizes accuracy change by changing the values
of λ and noise for the RHMD dataset. Plots show
that λ = 0.2 and λ = 0.4 gives better accuracy val-
ues as compared to λ = 0.6 and λ = 0.8. The rea-
son might be, both teacher and student models share
similar architecture and pre-training data. Therefore,
higher values of λ do not enable the teacher model
to teach the student model much different knowledge.
Overall, adding noise to the 2 hidden representations
of 64 tokens with λ = 0.4 gives the best validation
accuracy for the RHMD dataset.
5.2 Effectiveness of Proposed Method
In Table 6, we show the effectiveness of our pro-
posed method. For the CODA-19 dataset, we first
drop the “Randout” component from the “Randout-
KD” that drops accuracy by 0.2%. Then, we keep the
“Randout” component and drop the “KD” component
that also drops accuracy by 0.2%. However, drop-
ping both components that correspond to the base-
line method, decreases accuracy by 0.55%. For the
RHMD dataset, dropping the “Randout” component
and keeping only the “KD” component drops accu-
racy significantly by 3.06% which results in accuracy
even lower than the baseline method. Dropping the
“KD” component and keeping the “Randout” compo-
nent reduces accuracy by 0.47%. It shows that using
“Randout” and “KD” separately decreases the per-
formance over the baseline method. However, com-
bining both “Randout” and “KD” components boost
the model’s performance. During all these settings,
we use the same hyperparameters such as batch size,
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
462
(a) λ = 0.2. (b) λ = 0.4.
(c) λ = 0.6. (d) λ = 0.8.
Figure 3: Accuracy plots of the validation set for CODA-19 dataset. ‘HU’ stands for the no. of hidden units in which noise is
added, whereas ‘λ’ controls the weight between cross-entropy and knowledge distillation losses.
(a) λ = 0.2. (b) λ = 0.4.
(c) λ = 0.6. (d) λ = 0.8.
Figure 4: Accuracy plots of the validation set for RHMD dataset. ‘HU’ stands for the no. of hidden units in which noise is
added, whereas ‘λ’ controls the weight between cross-entropy and knowledge distillation losses.
Randout-KD: Finetuning Foundation Models for Text Classification via Random Noise and Knowledge Distillation
463
Table 6: Accuracy scores on two datasets showing the effectiveness of Randout-KD. The baseline model is data2vec (Baevski
et al., 2022).
Dataset Baseline Randout KD Randout-KD
CODA-19 (Huang et al., 2020) 73.27 73.62 73.62 73.82
RHMD (Naseem et al., 2022a) 78.17 78.90 76.31 79.37
learning rate, no. of epochs, etc., for a fair compari-
son.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we presented a method called “Randout-
KD” to finetune foundation models. We proposed
a new noise injection method and combined it with
knowledge distillation. During finetuning of the stu-
dent model, we stochastically replaced the hidden
representations units of various tokens with random
noise. We evaluated the suggested method on two
multi-class text classification datasets. Our presented
approach improved the model’s performance on both
datasets compared to the baseline models. We shall
explore this method with variants of knowledge dis-
tillation in future work.
REFERENCES
Afzal, M., Alam, F., Malik, K. M., Malik, G. M., et al.
(2020). Clinical context–aware biomedical text sum-
marization using deep neural network: model devel-
opment and validation. Journal of medical Internet
research, 22(10):e19810.
Baevski, A., Hsu, W.-N., Xu, Q., Babu, A., Gu, J., and Auli,
M. (2022). Data2vec: A general framework for self-
supervised learning in speech, vision and language.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.03555.
Beltagy, I., Lo, K., and Cohan, A. (2019). Scibert: A
pretrained language model for scientific text. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1903.10676.
Bommasani, R., Hudson, D. A., Adeli, E., Altman, R.,
Arora, S., von Arx, S., Bernstein, M. S., Bohg, J.,
Bosselut, A., Brunskill, E., et al. (2021). On the
opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2108.07258.
Bucilua, C., Caruana, R., and Niculescu-Mizil, A. (2006).
Model compression. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM
SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge dis-
covery and data mining, pages 535–541.
Bul
`
o, S. R., Porzi, L., and Kontschieder, P. (2016). Dropout
distillation. In International Conference on Machine
Learning, pages 99–107. PMLR.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova, K.
(2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional trans-
formers for language understanding. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1810.04805.
Gu, Y., Tinn, R., Cheng, H., Lucas, M., Usuyama,
N., Liu, X., Naumann, T., Gao, J., and Poon,
H. (2021). Domain-specific language model pre-
training for biomedical natural language process-
ing. ACM Transactions on Computing for Healthcare
(HEALTH), 3(1):1–23.
He, R., Cai, S., Ming, Z., and Zhang, J. (2022). Weighted
self distillation for chinese word segmentation. In
Findings of the Association for Computational Lin-
guistics: ACL 2022, pages 1757–1770.
Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., Dean, J., et al. (2015). Distilling
the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1503.02531, 2(7).
Huang, T.-H., Huang, C.-Y., Ding, C.-K. C., Hsu, Y.-C.,
and Giles, C. L. (2020). Coda-19: Using a non-expert
crowd to annotate research aspects on 10,000+ ab-
stracts in the covid-19 open research dataset. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2005.02367.
Ibrahim, M. A., Khan, M. U. G., Mehmood, F., Asim,
M. N., and Mahmood, W. (2021). Ghs-net a generic
hybridized shallow neural network for multi-label
biomedical text classification. Journal of biomedical
informatics, 116:103699.
Khan, P. I., Razzak, I., Dengel, A., and Ahmed, S. (2022a).
A novel approach to train diverse types of language
models for health mention classification of tweets.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.06337.
Khan, P. I., Siddiqui, S. A., Razzak, I., Dengel, A., and
Ahmed, S. (2022b). Improving health mention classi-
fication of social media content using contrastive ad-
versarial training. IEEE Access, 10:87900–87910.
Kim, Y. and Rush, A. M. (2016). Sequence-level knowledge
distillation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.07947.
Kitada, S. and Iyatomi, H. (2021). Attention meets pertur-
bations: Robust and interpretable attention with ad-
versarial training. IEEE Access, 9:92974–92985.
Lee, C., Cho, K., and Kang, W. (2019). Mixout: Effective
regularization to finetune large-scale pretrained lan-
guage models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.11299.
Liu, X., He, P., Chen, W., and Gao, J. (2019a). Improv-
ing multi-task deep neural networks via knowledge
distillation for natural language understanding. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1904.09482.
Liu, Y., Ott, M., Goyal, N., Du, J., Joshi, M., Chen, D.,
Levy, O., Lewis, M., Zettlemoyer, L., and Stoyanov,
V. (2019b). Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pre-
training approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692.
Liu, Y., Shen, S., and Lapata, M. (2020). Noisy self-
knowledge distillation for text summarization. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2009.07032.
Naseem, U., Khushi, M., Kim, J., and Dunn, A. G. (2022a).
Rhmd: A real-world dataset for health mention clas-
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
464

sification on reddit. IEEE Transactions on Computa-
tional Social Systems.
Naseem, U., Kim, J., Khushi, M., and Dunn, A. G. (2022b).
Identification of disease or symptom terms in reddit to
improve health mention classification. In Proceedings
of the ACM Web Conference 2022, pages 2573–2581.
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I.,
and Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: a simple way
to prevent neural networks from overfitting. The jour-
nal of machine learning research, 15(1):1929–1958.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones,
L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, L. u., and Polosukhin,
I. (2017). Attention is all you need. In Guyon,
I., Luxburg, U. V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fer-
gus, R., Vishwanathan, S., and Garnett, R., editors,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
volume 30. Curran Associates, Inc.
Wasim, M., Asim, M. N., Khan, M. U. G., and Mahmood,
W. (2019). Multi-label biomedical question classifi-
cation for lexical answer type prediction. Journal of
biomedical informatics, 93:103143.
Wu, C., Wu, F., Qi, T., Huang, Y., and Xie, X. (2022).
Noisytune: A little noise can help you finetune
pretrained language models better. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2202.12024.
Xu, Y., Qiu, X., Zhou, L., and Huang, X. (2020). Improving
bert fine-tuning via self-ensemble and self-distillation.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.10345.
Zhang, T., Wu, F., Katiyar, A., Weinberger, K. Q., and Artzi,
Y. (2020). Revisiting few-sample bert fine-tuning.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.05987.
Zhao, S., Liu, T., Zhao, S., and Wang, F. (2019). A neural
multi-task learning framework to jointly model med-
ical named entity recognition and normalization. In
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial In-
telligence, volume 33, pages 817–824.
Zhou, W., Xu, C., and McAuley, J. (2022). Bert learns to
teach: Knowledge distillation with meta learning. In
Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long
Papers), pages 7037–7049.
Zhu, C., Cheng, Y., Gan, Z., Sun, S., Goldstein, T., and
Liu, J. (2019). Freelb: Enhanced adversarial train-
ing for natural language understanding. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1909.11764.
Randout-KD: Finetuning Foundation Models for Text Classification via Random Noise and Knowledge Distillation
465
