
Human Factors for Cybersecurity Awareness in a Remote Work
Environment
César Vásquez Flores
1
, Jose Gonzalez
2
, Miranda Kajtazi
3
, Joseph Bugeja
4
and Bahtijar Vogel
4
1
Adesso Sweden, Malmö, Sweden
2
Accelerated Growth, Malmö, Sweden
3
Department of Informatics, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
4
Department of Computer Science and Media Technology, Internet of Things and People Research Center (IOTAP),
Malmö University, Malmö, Sweden
{joseph.bugeja, bahtijar.vogel }@mau.se
Keywords: Cybersecurity, Trust, Human Factors, Awareness, Employees, Remote Work Environment.
Abstract: The conveniences of remote work are various, but a surge in cyberthreats has heavily affected the optimal
processes of organizations. As a result, employees' cybersecurity awareness was jeopardized, prompting
organizations to require improvement of cybersecurity processes at all levels. This paper explores which
cybersecurity aspects are more relevant and/or relatable for remote working employees. A qualitative
approach via interviews is used to collect experiences and perspectives from employees in different
organizations. The results show that human factors, such as trust in cybersecurity infrastructure, previous
practices, training, security fatigue, and improvements with gamification, are core to supporting the success
of a cybersecurity program in a remote work environment.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to PurpleSec's 2021 Cybersecurity Trends
Report
1
, cybercrime has increased by 600% since the
start of the worldwide pandemic. Meanwhile, a study
by Splunk
2
found that 36% of IT executives reported
an increase in security vulnerabilities due to the shift
to remote work. In this environment, there is a greater
likelihood of financial losses and business
interruptions. The question of “what aspects of
cybersecurity are critical for organizations that must
conduct remote operations?” remains critical.
The human factor is commonly recognized as a
major vulnerability that can be exploited by
cyberattacks (D’Arcy et al., 2009). This is
exacerbated by a lack of training and knowledge
about cybersecurity, which can lead to an increase in
data breaches, non-compliance with security policies,
and intentional or unintentional violations by users,
particularly employees (Rubenstein & Francis, 2008;
Vance et al., 2013). As a result, various regulations
and frameworks, such as those of the National
1
https://gcnsolutions.com/blog/2021-cybersecurity-trends
2
https://purplesec.us/resources/cyber-security-statistics/
Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the
International Organization for Standardization and
the International Electrotechnical Commission
(ISO/IEC 27001), and the General Data Protection
Regulation (GDPR), recommend implementations
that contribute to improved data protection within
organizations (NIST, 2022; ISO/IEC 27001, 2022;
GDPR, 2022).
One key practice that these regulations and
frameworks have in common is that of fostering
cybersecurity awareness and training (Chowdhury et
al., 2022). This practice comprises the effective
transmission of policies and practices to all
organizational levels (Siponen & Vance, 2010). But
two reasons prevent the organizations from achieving
success in this endeavor. First, there is often a lack of
engagement of participants/employees (Chowdhury
et al., 2022); and second, organizations are not fully
prepared to ensure that cybersecurity programs are
regulated on how employees should participate and
perform (D’Arcy et al., 2009; Kajtazi et al., 2018).
Engagement is based on different factors such as
608
Flores, C., Gonzalez, J., Kajtazi, M., Bugeja, J. and Vogel, B.
Human Factors for Cybersecurity Awareness in a Remote Work Environment.
DOI: 10.5220/0011746000003405
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2023), pages 608-616
ISBN: 978-989-758-624-8; ISSN: 2184-4356
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

cultural, motivational, learning preferences, and other
behavioral-related theories that explain compliance
and noncompliance behavior in organizations
(Chowdhury et al., 2022; Bulgurcu et al., 2010).
Moreover, organizations tend to find it rather
challenging to cope with all the different factors that
drive human behavior in organizations (D’Arcy et al.,
2009; Sadok et al., 2020). Understanding the human
factor in cybersecurity is one of the most important
aspects of changing people’s behavior and their
awareness for remote working employees.
2 CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 Cybersecurity and Remote Work
Remote work is described as organizational work that
is completed outside of the traditional organization's
physical location. Pranggono and Arabo (2021) stated
that in the UK, many organizations did not have a
procedure on how to build a remote workforce. The
authors also observed that only around 38% of
organizations had a security policy. Similarly, Naidoo
(2020) indicated that the most important priority for
organizations was to facilitate employees’ working
remotely in a short time. Consequently, the authors
emphasized that the organization did not have enough
time to build and deploy the correct security
safeguards.
Pranggono and Arabo (2021) stated that in a lot of
cases, employees used their home systems to perform
their jobs. These systems were secured by the
employer, but due to this new infrastructure, it created
a clear security concern. According to Alexander and
Jaffer (2021), existing safeguards such as the Virtual
Private Network (VPN) and other organizational
tools still contain vulnerabilities. The literature
suggests an inherent vulnerability in the current
remote work practices. In addition, there is a clear
increase in dependency on technology from
organizations (Naidoo, 2020), which has not been
overseen by cybercriminals, and the number of
cybercrimes has been observed to have grown
significantly. Naidoo (2020) also observed that
emotional factors can be an important factor in users’
compliance with security policies. It is important to
mention that these attacks are not necessarily new;
they have just been repeatedly exploited in this era.
Malware, including phishing or ransomware, DDoS,
and misinformation, for example, are among the most
commonly used cyberattacks during the COVID-19
era.
Furthermore, according to the Center for the
Protection of National Infrastructure (CPNI, 2020),
the complexity of remote work can be used to
generate insider threat attacks. This is because of
multiple factors: oversight from management, an
unfamiliar environment, stress, and poor screening
processes when adding new employees to the
organization.
The success of malware and phishing emails, for
example, resides in attackers using current relevant
information, in this case related to the pandemic, and
using it to attract users with their malicious software
(Naidoo, 2020). Furthermore, as observed by
Pranggono and Arabo (2021), DDoS attacks focused
on infrastructure and organizations that were
vulnerable or overwhelmed during the pandemic.
As an example of these organizations, Pranggono
and Arabo (2021) claimed that the internet or
healthcare providers were the targets. The reason for
this, according to their study, is that this type of
organization’s focus was set on other priorities than
cybersecurity, opening a window for vulnerability.
Ultimately, we see that users’ increased engagement
with technology left the door open for vulnerabilities
to be exploited by criminals.
As a result of this work environment change, it is
worthwhile considering aspects that go beyond
cybersecurity, which may affect its successful
implementation. Galanti et al. (2021) stated that
remote work presents some personal challenges for
users. First, family conflict that impacts work.
Second, social isolation, and third, the distracting
environment that users may be in. The importance of
this is that, as stated previously, emotional factors
may affect cybersecurity compliance on the part of
the users. In addition, envisioning a return to a
previous work environment and IT settings would not
be appropriate, but the new working conditions rather
give organizations an opportunity to explore different
options. Kane et al. (2021) observed that
organizations can take advantage of the effectiveness
of remote work. The authors suggested a hybrid
model that can provide the flexibility needed in a post
pandemic reality.
2.2 Employees’ Cybersecurity
Learning Process
Employees at all levels of an organization must be
aware of their responsibilities to protect the resources
they interact with. To implement a holistic
cybersecurity program, frameworks such as NIST
and ISO/IEC 27001 include the concepts of
awareness and training in their handbooks and guides
Human Factors for Cybersecurity Awareness in a Remote Work Environment
609

(NIST, 2022; ISO/IEC 27001, 2022). Awareness and
training are needed for any organization to secure
itself against cyberattacks. In this paper, we explain
these elements following the structure introduced by
Wilson and Hash (2003, p.8) who proposed the
learning continuum process, based on three
components: awareness, training, and education.
2.3 Cybersecurity Awareness
Awareness is the capacity of individuals to identify a
security concern and be able to respond adequately to
it when a risky event occurs (Wilson & Hash, 2003).
Previous investigations, books and reports in the
literature have defined in detail the concept and
mentioned aspects that could help to increase
awareness in organizations (Bada et al., 2015;
Stallings & Brown, 2018; Siponen, 2000). The
motivation of these studies was driven by different
objectives, such as the reduction of user-related
faults, the maximization of the efficiency of the
security procedures, and the compliance with
regulations (Siponen, 2000; Stallings & Brown,
2018).
Scholars in the field show that the intention to
provide people with information about existing risks
and recommended behaviors is one part of the
process, but not the entire process (Siponen, 2000;
Bada et al., 2015). In addition, the motivational aspect
is an important element considering that the final
objective of an awareness campaign is to modify the
employees’ behavior and attitudes (Siponen, 2000).
From an employee perspective, this requires different
steps, such as perceiving that the content is relevant,
then accepting how they should respond, and finally
being responsible to follow the advice despite the
existence of other demands (Bada et al., 2015). An
essential aspect is to design an awareness program
that “support the business needs of the organization
and be relevant to the organization’s culture and
information technology architecture” (Bowen et al.,
2006, p.31). One interesting observation obtained
from these studies is the influence of the motivational
factor in the success of awareness programs.
Moreover, an organization which will start the
implementation of awareness should conduct a needs
assessment to determine the status and justify the
allocation of resources for this endeavor (Wilson &
Hash, 2003). Because of this, different roles must be
involved. Some of them are organizational leaders,
whose role is critical in promoting full compliance;
security personnel, who are experts with extensive
knowledge of best practices and policies; system
users, who perform routine business operations; and
others (Wilson & Hash, 2003). The main challenge of
this approach is that a complete assessment of needs
often requires a hefty commitment from different
actors inside an organization. These actors must also
have certain roles, which are sometimes nonexistent
in some structures (Sadok et al., 2020). Additionally,
it could be interpreted that only the security personnel
are responsible for this task. However, managers need
to play a more effective role that is decisive (Soomro
et al., 2016). For that reason, some organizations
could be obligated to realize trade-offs or abbreviated
ways during the implementation which can lead to
lack of success.
Once the assessment is completed, the application
of the methods must be executed. Wilson and Hash
(2003) listed different tools and elements in their
wide-ranging study. In terms of content, topics such
as password management, email security, laptop
security while traveling, software license restriction
issues, and desktop security are possible options to be
included. The final decision to include one item or not
is based on a discussion that considers the
organizational context. Regarding the sources of
material, several themes could be combined or
introduced one at a time in each material, depending
on what skills need to be transmitted to the audience
(Wilson & Hash, 2003). For instance, e-mail
advisories, security websites, periodicals,
conferences, posters, flyers, courses, and seminars are
possible options to expose the information to the
employees (Wilson & Hash, 2003; Stallings &
Brown, 2018).
One positive aspect to also consider in the current
analysis of employee awareness is that today more
people are aware of security risks. Their constant
interaction with digital products motivates them to
proactively look for better personal protection
(Öğütçü et al., 2016). This could be a positive factor
for increasing the success of future awareness
programs.
Stallings and Brown (2018) highlighted that it is
relevant for organizations to share a security
awareness policy document with their employees.
This has three main objectives. First, to communicate
the requirement to employees to participate in the
awareness program on a mandatory basis. Second, to
inform that every employee will have enough time to
be part of the activities. Third, to clearly state who is
responsible for the management of awareness
activities.
While the positive aspects of awareness have been
constantly stated in previous publications, some of
them also analyzed the reasons that could potentially
prevent the success of cybersecurity awareness
ICISSP 2023 - 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
610

endeavors (Bada et al., 2015). It is possible to see
cases of employees violating security policies even
though they have received some security preparation
(Kajtazi et al., 2018; Sadok et al., 2020). Kajtazi et al.
(2018) conducted an insightful study with more than
500 participants of two banks in Europe. The insights
showed that employees usually give more importance
to the completion of a work task than to a possible
exposition of confidential information (Kajtazi et al.,
2018).
This is supported by the idea that the immediate
benefit achieved with this specific task has a greater
priority than the avoidance of a future security cost.
(Kajtazi et al., 2018). Another relevant study
performed by Parsons et al. (2014) stated that
employers could feel confident that an improvement
in employees’ knowledge about security rules will
have a beneficial impact on their attitude. However,
the results helped to conclude that generic courses do
not influence the attitude as expected and therefore
training should be better contextualized (Parsons et
al., 2014).
2.4 Cybersecurity Training
Training is focused on teaching specific and
necessary security skills to employees depending on
the role they perform (Wilson & Hash, 2003). It is
relevant to state that the content of a training is
designed based on security basics and literacy
material, with tailored training based on the needs of
each group of people inside the organization (Wilson
& Hash, 2003; Bowen et al., 2006). For instance,
training must be different for a System Administrator
than for a Project Manager due to the different tasks
they realize, and the security knowledge required.
Additionally, recent papers have explained the
positive results obtained when employees’ learning
preferences are also considered in the design of
training (Chowdhury et al., 2022; Pattinson et al.,
2018).
Initially, a review of the various techniques used
to deliver training material is beneficial in
understanding the various options. Wilson and Hash
(2003) recommended that when opting for a
technology for training, aspects such as “ease of use,
scalability, accountability, and broad base of industry
support” must be evaluated (Wilson & Hash, 2003,
p.34). This is supported by the fact that organizations
are involved in an ever-changing environment where
the ability to adapt and expand their training with
continuous updates is perceived as a clear advantage.
Different techniques for implementing trainings
are classic, but also newly developed (Wilson and
Hash, 2003; Chowdhury et al., 2022; Pattinson et al.,
2018). Techniques such as interactive video training,
web-based training, computer-based training, onsite,
instructor-led training, and personalized training
allow for the incorporation of multiple techniques
into a single session as part of an organization's
cybersecurity program. With that in mind, Furnell et
al. (2002) conducted a study about a company which
implemented their own security training tool. One
aspect of this innovative tool was that information
about the suitability and the associated impact of each
security issue was shared with the participant (Furnell
et al., 2002). Also, they were able to see a message
explaining each possible decision they were able to
make with teaching purposes. This demonstrated a
good example of how different techniques could be
adapted and tailored to specific needs.
A relevant aspect of personalized training was
highlighted by Pattinson et al. (2018) who concluded
that the extent to which training is associated with the
participant’s learning preference is more important
than the frequency of the training. This could be a
strong reason to always consider personalized
training as one of the most effective options.
However, from a practical perspective, it would be
impossible to tailor the training based on each
individual characteristic. For that reason, a viable
option is to design different training based on certain
divisions inside the organization such as business
teams or groups (Pattinson et al., 2018).
Finally, it is important to note that nowadays, an
organization does not need to design exclusive
content for this endeavor, which is sometimes
complicated due to the probable absence of a specific
security area in the organization (Sadok et al., 2020).
Furnell et al. (2002) argued that, especially for small
organizations, this task is difficult to approach due to
a lack of expertise. On this note, Gartner (2021b)
published a report containing several options of
vendors offering computer-based training. Some
offer the option of a free knowledge check, and many
of them can be accessed as Software as Service
(SaaS) solutions.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This qualitative empirical study based on purposive
sampling had the following criteria for choosing
employees as respondents:
- Employees who use technology to perform their
daily jobs.
Human Factors for Cybersecurity Awareness in a Remote Work Environment
611

- Their organizations must have a cybersecurity
awareness and training program.
- Employees must have received cybersecurity
training before the pandemic.
- The organizations must have offered
cybersecurity training for remote working
employees.
- Their job routine has changed due to the
pandemic in terms of remote work.
- Participants must have relevant years of
experience.
In terms of business sectors, IT, Financial
Technology, and Business Process Outsourcing
(BPO) were taken into consideration, and also
regarded as information intensive organizations
(Kajtazi et al., 2018). These have been identified as
industries where cybersecurity implementation plays
an important factor. Further, the assumption is that
some behavioral theories could be perceived in a
different way by employees in different industries
(Bulgurcu et al., 2010).
The employees considered were identified in the
professional networks of the first two authors of this
paper. Once a participant confirmed the precondition
requirements, a brief explanation of the paper
objective was shared to ensure that they felt
comfortable and open to us.
The locations of our participants were Peru, the
USA, and Guatemala. A primary reason for choosing
such locations is that there was reportedly an increase
in the number of cyberattacks in those regions
(Statista, 2022). The requirement for participants to
have relevant years of experience led us to identify a
number of employees within senior roles that would
have a more mature perspective in terms of work
experience as well as could comprehend better the
pre- and during- pandemic cybersecurity efforts of
their organizations. Table 1 below shows relevant
information about the participants, such as the
organization, industry, role, country, and years of
industry experience.
Interviews were conducted remotely due to the
geographical location of participants. The first two
authors conducted one pilot interview (PR1), then
followed with five interviews (R1, R2, R3, R4, and
R5). While PR1 was useful to fine-tune the guide for
actual interviews, we retained the results of PR1 as
changes to the interview guide were not substantial
enough to re-direct the discussion in another way. In
fact, PR1 showed the robustness of our interview
guide.
Table 1: Participant details.
No. Industry Role Country Experience Duration
PR1 IT
Software
Engineer
Peru 8 yrs 33 mins
R1
Financial
Technology
Risk
Manage
r
Guatemala 14 yrs 48 mins
R2 IT
Project
Manager
Peru 15 yrs 43 mins
R3 IT
Operations
Manager
Guatemala 13 yrs 37 mins
R4
Business
Process
Outsourcing
(BPO)
Program
Manager
USA 15 yrs 51 mins
R5 IT
Project
Manage
r
Guatemala 25 yrs 33 mins
The questions for the interview guide were based
on the themes identified and presented in the
conceptual framework (cf. Section 2), we present the
full version in Vasquez and Gonzalez (2022). In this
paper we categorized the data and findings based on
themes identified in the conceptual framework.
4 ANALYSIS AND RESULTS
COVID-19 brought a new work dynamic that led to
increased cybersecurity concerns. Based on our
results from the interviews, we can infer that the
majority of individuals in an organization today are
aware of the importance of cybersecurity with regard
to the human component, including its role, behavior,
and awareness aspects. We discuss details from our
results in the following sections by mapping their
relation to our conceptual framework and related
studies that influenced its composition.
4.1 Cybersecurity and Remote Work
Studies like that of Arabo (2021) have suggested that
many organizations do not have an established
procedure for having a remote workforce. However,
most of our interviewees stated that a practice of
working remotely was in place within their
organizations for specific employees. Further, the
same interviewees stated that there was a lack of
proper infrastructure or control in a remote work
environment which would then cast doubt on the
security practices the organizations had before the
pandemic. This important notice needs to be
addressed within the governance the company has for
ICISSP 2023 - 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
612

such premature measures. In some organizations, the
inability to effectively scale-up and secure the already
in place practice of remote work needs to be improved
through governance measures. The literature has also
been vocal about the emotional factors within remote
work mixed with the pandemic and how they can
affect compliance with cybersecurity policies
(Naidoo, 2020). There are three factors we identified
through our interviewees. First, there is a lack of
bonding among team members. Second, there is
difficulty separating work from personal life due to
increased work hours. Third, there is difficulty
getting support for IT within the remote work context.
As a result, if security practices can be improved
along with increased employee support, the safety of
a hybrid work environment is possible; however, not
without focusing on such important cues that the
employees signaled.
4.2 Cyberthreats in a Remote Work
Environment
In terms of cyberthreats in the remote work
environment, an increase of attacks during the
pandemic (Naidoo, 2020) has been noticeable. This
supports our interviewees’ perceptions, who also
witnessed that the most common threat in their
remote work was phishing emails. In addition, even
when they were not categorized as insider threats by
our interviewees, all of them stated that employees
used company equipment and network for activities
unrelated to their job, a practice that continued
similarly in pre-pandemic times.
4.3 Cybersecurity Governance
Across all interviewees and their views on
cybersecurity governance, we saw a strong support of
the literature which states that one of the most
effective tools for managing the employee side of an
organization are policies, frameworks, and best
practices for technical and non-technical users (Guo
et al., 2021; NIST, 2022). Our respondents
demonstrated a general understanding of the policies
in place within their organization. One respondent
even shared a security framework they use, which
serves as further evidence of the effectiveness of
these methods for communicating cybersecurity
information and practices to employees.
4.4 Cybersecurity Training
The personalization aspect as a possibility to improve
training was an important point raised, which
promoted an interesting discussion during the
interviews. The interviewees were not only positive
about this aspect; they also acknowledged the fact
that personalized training could increase the sense of
identity of the employees. Such personalization could
also prevent overloading them with unnecessary
concepts in a training which can be performed based
on the access level of each employee. Recent studies
on personalization and training in the organizational
context have only been implemented by a few
organizations so far (Chowdhury et al., 2022;
Pattinson et al., 2018). The findings demonstrated a
good employees’ perception about personalization,
and yet there is little empirical research about its
implementation in organizations. For that reason, we
recommend ‘personalization aspect’ as a worthwhile
focus of study that might contribute to improving
training experiences in the future.
4.5 Employees’ Behavior
Our respondents confirmed that the behavior of some
employees is positively modified after the security
training. Specifically, they mentioned that they feel
engaged because they are aware of the possible risks
they can encounter (Bulgurcu et al., 2010). We
emphasize that our respondents have an accumulated
level of experience which may influence the
predisposition to modify their behavior. In terms of
deterrence and neutralization, scholars have stated
that if a sanction is clearly communicated by the
organization, an employee may be restrained from
realizing a security flaw (Straub & Wekle, 1998;
Willison & Warkentin, 2013). Even though, one of
the employees mentioned that there are legal
consequences for policy violation, the majority
referred to other reasons. In particular, a possible loss
of company prestige and a leak of customer
information were pointed out as causes. This could be
interpreted as a strong connection between the
employee and organizational assets. Therefore, the
deterrence effect is achieved through a more organic
way where sanctions are not the main reason to follow
the guidelines. The main conclusion obtained was
that the interviewees in a critical situation will avoid
breaking a cybersecurity policy. The interviewees
talked about re-evaluation, escalation, and
negotiation as first options before deciding not to
follow a cybersecurity policy. Furthermore, our
interviewees also confirmed that some employees
feel that this occurred through the description of some
events that they or their colleagues experienced. In
the first instance, none of them said directly that they
felt overwhelmed. However, they had an
Human Factors for Cybersecurity Awareness in a Remote Work Environment
613
understanding that the difficulties new employees
experience when they first see a cybersecurity policy
are not to be taken lightly. According to the literature,
more employees have a higher level of awareness and
general cybersecurity knowledge in today’s context
because their personal experience with technology
encourages them to learn more about the topic
(Öğütçü et al., 2016). According to our interviewees,
they all cover their work web camera, but not on their
personal devices. Furthermore, some organizations
have already implemented a physical restriction in the
devices to ensure that the camera is disabled by
default. This finding shows that awareness and risks
differ between individual practices on personal
devices with that of the organizational practices and
work-related devices.
4.6 Cybersecurity Program’s
Continuous Improvement
The main insight identified through our interviewees
is that gamification plays a central role. It is looked at
as a beneficial tool to increase the engagement of
employees in cybersecurity programs, especially if
many of them are young or in entry-level positions.
This finding is solid because one of the participants
confirmed to us that the actual implementation of
gamification in their company is indeed helping them.
Further research focused on the use of gamification
as a method to increase the success of a cybersecurity
program would be beneficial. Our respondents also
considered that, for improving a cybersecurity
program, the use of gamification is not only an option
but a solution. Gamification can enhance the user
experience of the process and motivate participants
based on possible rewards. It is appropriate
particularly for groups of employees, such as young
talent or those at entry-level positions who are
familiar with game techniques. Its inclusion in a
cybersecurity program could be a crucial factor.
4.7 Summary of Results
Our results are organized on the basis of identified
themes in our conceptual framework in Table 2. We
also highlight the identified aspects as relevant and/or
relatable by mapping the findings from our
interviewees. An aspect is considered relevant,
because it is a necessary condition to distinguish the
aspect when it is appropriate and contemporary to the
context of the employees, and/or relatable, when
there is a connection or engagement with a topic,
particularly from the employees’ perspective. Our
results also emphasize the importance of
understanding the human factor in cybersecurity.
Human factors have been researched extensively, but
our findings further underscore the importance of
prioritizing them for implementing effective
cybersecurity safeguards in the long run.
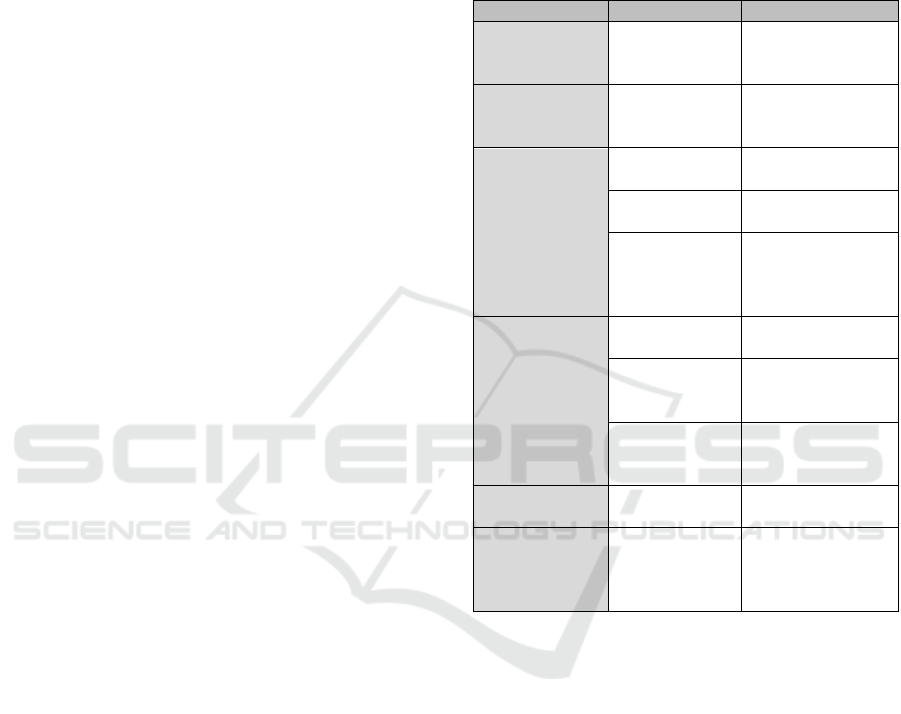
Table 2: Results from the interview study.
Theme Human facto
r
Consideration
Cybersecurity
and remote
wor
k
Emotional
factors
Relatable (R1, R4,
R5)
Cyberthreats in
a remote work
environment
Exposure to
cyberthreats
Relevant
(R2,R3,R4,R5)
Cybersecurity
governance
Previous
Practices
Relevant
(R2,R4,R5)
New employee
engagement
Relevant (R1,R4)
Trust in
cybersecurity
practices and
infrastructure
Relevant and
relatable
(R1,R2,R3,R4,R5)
Cybersecurity
training
Language Relatable (R2,
R4
)
Training
delivery
techni
q
ue
Relevant and
relatable (R1, R2,
R3, R4, R5
)
Content
according to
the role
Relatable (R1, R2,
R4, R5)
Employees’
b
ehavio
r
Security
Fati
g
ue
Relevant (R1, R2,
R4
)
Cybersecurity
program’s
continuous
improvement
Gamification Relevant and
relatable (R1, R2,
R4, R5)
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper aimed to present core cybersecurity
awareness aspects that are particularly relevant and/or
relatable for remote working employees. We
presented a conceptual framework, which identified
that vulnerabilities in cybersecurity associated with
the remote work environment are numerous and
should not be neglected, but rather emphasized. We
categorized our results based on the identified themes
in our conceptual framework and mapped them to the
role of the human factor, their behavior, and
awareness aspects. We identified certain aspects as
relevant and/or relatable to the context of remote
employees. An aspect was considered relevant if it
was important and appropriate for the current
situation, and relatable if it connected or engaged the
employees with the topic from their perspective.
ICISSP 2023 - 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
614

Some aspects were identified as both relevant and
relatable. In general, we found out that employees’
awareness plays a vital role in supporting the
cybersecurity strategy among organizations and that
there is a strong relationship between awareness and
training among the employees’ perspectives. The
result is not particularly different from previous
studies conducted pre-pandemic, but it is an
important finding to highlight that cybersecurity
measures from a training perspective are highlighted
as vital in forced remote working contexts. Likewise,
since remote working is a trend to be pursued by
various organizations in the long run, a focus on the
perspective of employees in terms of awareness
within this context is important.
One of the key conclusions of this research is that
emotional factors, trust in cybersecurity
infrastructure, previous practices, training, security
fatigue, and improvements with gamification are core
to supporting the success of a cybersecurity program
in a remote work environment. We also found out that
trust in cybersecurity practices and infrastructures is
becoming an important building block for remote
workers, especially when autonomous technology
becomes more prevalent. As such, trust and
trustworthiness in cybersecurity are aspects that we
aim to address in our future work.
REFERENCES
Alexander, K. B., & Jaffer, J. N. (2021). COVID-19 and the
Cyber Challenge. The Cyber Defense Review, 6(2), 17-
28.
Bada, M., Sasse, A. & Nurse, J. R. C. (2015). Cyber
Security Awareness Campaigns: Why Do They Fail to
Change Behavior? International Conference on Cyber
Security for Sustainable Society
Bowen, P., Hash, J. & Wilson, M. (2006). Information
Security Handbook: A Guide for Managers, NIST
Special Publication 800-100
Bulgurcu, B., Cavusoglu, H. & Benbasat, I. (2010).
Information Security Policy Compliance: An Empirical
Study of Rationality-Based Beliefs and Information
Security Awareness, MIS Quarterly.
Chowdhury, N., Katsikas, S. & Gkioulos, V. (2022).
Modelling Effective Cybersecurity Training
Frameworks: A Delphi Method-Based Study,
Computers and Security, vol. 113.
CPNI (2020) Personnel Security Guidance on Remote
Working – A Good Practice Guide
D’Arcy, J., Hovav, A. & Galletta, D. (2009). User
Awareness of Security Countermeasures and Its Impact
on Information Systems Misuse: A Deterrence
Approach, Information Systems Research, vol. 20, no.
1, pp.79–98.
Furnell, S. M., Gennatou, M. & Dowland, P. S. (2002). A
Prototype Tool for Information Security Awareness and
Training, Logistics Information Management, vol. 15,
no. 5/6, pp.352–357.
Galanti, T., Guidetti, G., Mazzei, E., Zappalà, S., &
Toscano, F. (2021). Work from home during the
COVID-19 outbreak: The impact on employees’
remote work productivity, engagement, and stress.
Journal of occupational and environmental medicine,
63(7), e426.
Gartner. (2021b). Security Awareness Computer-Based
Training Reviews and Ratings. Available online:
https://www.gartner.com/reviews/market/security-awa
reness-computer-based-training [Accessed 9 April
2022]
GDPR. (2022). General Data Protection Regulation,
Available online: https://gdpr-info.eu/ [Accessed 30
March 2022]
Guo, H., Wei, M., Huang, P., & Chekole, E. G. (2021).
Enhance Enterprise Security through Implementing
ISO/IEC 27001 Standard. In 2021 IEEE International
Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and
Informatics (SOLI) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
ISO/IEC 27001. (2022). Information Security
Management, Available online: https://www.iso.org/
isoiec-27001-information-security.html [Accessed 30
March 2022]
Kajtazi, M., Cavusoglu, H., Benbasat, I. & Haftor, D.
(2018). Escalation of Commitment as an Antecedent to
Noncompliance with Information Security Policy,
Information and Computer Security, vol. 26, no. 2,
pp.171–193.
Kane G., Nanda, R., Phillips, A., Copulsky, J. (2021)
Redesigning the Post-Pandemic Workplace. MIT Sloan
Management Review.
Naidoo, R. (2020). A multi-level influence model of
COVID-19 themed cybercrime. European Journal of
Information Systems, 29(3), 306-321.
NIST. (2022). Cybersecurity Framework, Available online:
https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework [Accessed 28
March 2022]
Öğütçü, G., Testik, Ö. M. & Chouseinoglou, O. (2016).
Analysis of Personal Information Security Behavior
and Awareness, Computers and Security, vol. 56,
pp.83–93.
Parsons, K., McCormac, A., Butavicius, M., Pattinson, M.,
& Jerram, C. (2014). Determining Employee
Awareness Using the Human Aspects of Information
Security Questionnaire (HAIS-Q), Computers and
Security, vol. 42, pp.165–176
Pattinson, M., Butavicius, M., Ciccarello, B., Lillie, M.,
Parsons, K., Calic, D. & Mccormac, A. (2018).
Adapting Cyber-Security Training to Your Employees,
Proceedings of the Twelfth International Symposium
on Human Aspects of Information Security &
Assurance (HAISA 2018).
Pimple, K. D. (2002). Six domains of research ethics.
Science and engineering ethics, 8(2), 191-205.
Human Factors for Cybersecurity Awareness in a Remote Work Environment
615

Pranggono, B., & Arabo, A. (2021). COVID‐19 pandemic
cybersecurity issues. Internet Technology Letters, 4(2),
e247.
Pranggono, B., & Arabo, A. (2021). COVID‐19 pandemic
cybersecurity issues. Internet Technology Letters, 4(2),
e247.
Rubenstein, S., & Francis, T. (2008). Are your medical
records at risk? Wall Street Journal—Eastern Edition,
251(100), D1–D2
Sadok, M., Alter, S., & Bednar, P. (2020). It Is Not My Job:
Exploring the Disconnect between Corporate Security
Policies and Actual Security Practices in SMEs,
Information and Computer Security, vol. 28, no. 3,
pp.467–483.
Siponen, M. T. (2000). A conceptual foundation for
organizational information security awareness.
Information management & computer security.
Soomro, Z. A., Shah, M. H. & Ahmed, J. (2016).
Information Security Management Needs More
Holistic Approach: A Literature Review, International
Journal of Information Management, vol. 36, no. 2,
pp.215–225
Stallings, W., and Brown, L. (2018): Computer Security:
Principles and Practice. 4th Ed, Global Ed. Pearson
Education Limited, Harlow, United Kingdom
Statista (2020) Annual change in incidence of computer
viruses in Latin America and the Caribbean from
January to March 2020. Available online:
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1117225/computer-
virus-latin-america/ [Accessed 5 May 2022]
Straub, D. W., & Welke, R. J. (1998). Coping with Systems
Risk: Security Planning Models for Management
Decision Making, MIS Quarterly, vol. 22, no. 4,
pp.441–469
Vance, A., Lowry, P. B., & Eggett, D. (2013). Using
accountability to reduce access policy violations in
information systems. Journal of Management
Information Systems, 29(4), 263–290.
Vasquez, C., & Gonzalez, J. (2022). Cybersecurity
engagement in a remote work environment. Master’s
Thesis, Lund University.
Willison, R., & Warkentin, M. (2013). Beyond Deterrence:
An Expanded View of Employee Computer Abuse,
MIS Quarterly.
Wilson, M. & Hash, J. (2003). Building an Information
Technology Security Awareness and Training Program,
NIST Special Publication 800-50.
ICISSP 2023 - 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
616
