
A Low-Cost Sensors Study Measuring Exposure to Particulate
Matter in Mobility Situations
Marie-Laure Aix
a
, Mélaine Claitte and Dominique J. Bicout
b
Univ. Grenoble Alpes, CNRS, UMR 5525, VetAgro Sup, Grenoble INP, TIMC, 38000 Grenoble, France
Keywords: Low-Cost Sensor, PM
2.5
, Calibration, Mobility, Exposure Assessment.
Abstract: In 2013, the International Agency for Research on Cancer classified particulate matter (PM) as carcinogenic
to humans. It is therefore essential to measure PM concentrations to minimize the exposure of individuals.
Our objective was to investigate personal exposure to PM
2.5
(PM with diameter ≤ 2.5 µm) in Grenoble
(France) during commuting in different transportation modes: bike, walk, bus and tramway. PM
2.5
measurements were found to be the highest for bikes, followed by walk, bus, and tramway. In this study,
conducted in spring during low pollution levels of PM, exposure levels are greatly influenced by the time of
day. Pedestrian and cyclists’ exposure generally stayed under background reference values. Exposure in
public transportation was usually below reference values, but when background PM
2.5
levels went lower
(evening), levels registered in the tramway or bus reached those of the reference. Therefore, public transport
users could be less exposed than active commuters, except when ambient pollutant levels are low.
Environmental parameters like wind might be important in Grenoble, and it would be worthwhile to reproduce
this study at a time when wind speed is lower.
1 INTRODUCTION
Every year, it is estimated that outdoor air pollution
causes 7 million deaths around the world (Fuller et
al., 2022). Particulate matter (PM) is made of solid
compounds suspended in the air that are small enough
to be inhaled. Considered as the most dangerous form
of air pollution, PM can enter blood circulation, and
accumulate in numerous organs (Pryor, Cowley, &
Simonds, 2022). Therefore, it is important to assess
populations’ exposure to PM, which is generally done
by official reference monitoring stations. However,
more and more scientists state that stationary
monitoring stations are not always representative of
people’s exposure (Van den Bossche et al., 2015; F.
Yang et al., 2019). This might be related to the time
that people spend indoor and outdoor, in places where
the pollutant levels do not always equal to reference
values. Time spent in transportation could represent
up to 30% of the inhaled dose (Dons, Int Panis, Van
Poppel, Theunis, & Wets, 2012). According to Han et
al. (2021), personal exposure to PM
2.5
(PM with
diameter ≤ 2.5 µm) measured by portable sensors, is
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5366-2372
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0750-997X
significantly associated with an increase in
respiratory and systemic inflammatory biomarkers.
However, the associations are weaker when ambient
PM
2.5
concentrations, measured by fixed reference
stations, are used as an exposure proxy. Low-cost
sensors demonstrate good accuracy to measure
individual exposure to PM (Motlagh et al., 2021) and
can therefore be used for exposure studies, especially
during commuting. Few mobility studies involving
low-cost sensors have been performed, especially in
low-concentration situations. Many surveys take
place in Asia where pollution levels are usually
higher than in Europe. During 10 working days, we
conducted a field experiment to collect PM
measurements using four transportation modes
around Grenoble (France): bike, walk, bus, and
tramway. Our objective was to estimate personal
exposures to PM
2.5
with a low-cost sensor during
commuting in different modes. Another purpose was
to compare the so measured concentrations with
reference values. We wanted to know whether the
low-cost sensors could be used to assess differences
between transport modes and the time of day. In
32
Aix, M., Claitte, M. and Bicout, D.
A Low-Cost Sensors Study Measuring Exposure to Particulate Matter in Mobility Situations.
DOI: 10.5220/0011747600003399
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Sensor Networks (SENSORNETS 2023), pages 32-41
ISBN: 978-989-758-635-4; ISSN: 2184-4380
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

doing this, we hope to contribute to the exposure
literature using low-cost sensors.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Particulate Matter Sensor
2.1.1 Monitoring Devices
PM concentrations were measured using two
AirBeam2 (HabitatMap), which entail an optical
sensor (Plantower PMS7003). AirBeam2 are
inexpensive ($249) and measure concentrations of
PM
1
, PM
2.5
, PM
10
, temperature and relative humidity
(RH). They are connected to a smartphone via
Bluetooth and provide real time values to users. With
the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) sector (Das,
Ghosh, Chatterjee, & De, 2022; Y. Yang et al., 2022),
cheaper PM sensors are currently available on the
market. However, they often have to be assembled
with other components like microcontrollers or GPS
modules, and an IoT platform has to be set-up for data
visualisation. Designing a monitoring station,
assembling components and developing a data
visualisation tool are different steps which can be
time-consuming. HabitatMap already provides an
online platform (http://aircasting.org) for viewing and
downloading AirBeam2 data. Furthermore,
AirBeam2 are ready-to-use devices. South Coast Air
Quality Management District (2018) compared the
AirBeam2 PM
2.5
measurements to values given by
three Federal Equivalent Method instruments. They
observed very strong correlations in the laboratory
studies (R
2
> 0.99) and moderate to strong
correlations with different reference instruments from
the field (0.68 < R
2
< 0.79). More recently, Tong, Shi,
Shi, and Zhang (2022) found that Airbeam2
measurements correlated well with roadside official
monitoring stations. They also reported a good
agreement (R
2
= 0.67–0.89) between Airbeam2 local
measurements and the predictions from a model
involving satellite observations. AirBeam2 is already
calibrated by the manufacturer, but the calibration
equations do not account for RH (HabitatMap, 2022).
Huang et al. (2022) found that the accuracy and bias
of the PM data reported by AirBeam2 sensors were
affected by rainy weather and high humidity
environments. Moreover, Zou, Clark, and May
(2021) suggested that there was a significant linear
relationship between RH and the relative response of
the low-cost PM sensors to the research-grade
instruments. Therefore, we calibrated the devices by
accounting for RH.
2.1.2 Calibration
The calibration process involved two steps (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Two steps calibration process.
• Step 1: Calibration of a Fixed Low-Cost
Sensor (“Gold Pod”) with a Reference Device
Before this study, we had already calibrated a low-
cost fixed station by collocating it with a Palas GmbH
200 (Reference) from Atmo Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
(Atmo AuRA) in Grenoble “Les Frênes” (Refer
Figure 4). This calibration was performed using a
random forest regression technique developed by
Schmitz et al. (2021) comparing this individual fixed
sensor with the reference station. This low-cost fixed
station, called “gold pod” used the same optical
sensor (PMS7003) than the mobile devices.
• Step 2: AirBeam2 Sensors Calibration with a
Fixed Low-Cost sensor (“gold Pod”)
Next, 44 days of calibration were performed from
September 20, 2022 to November 3, 2022 where the
two AirBeam2 were collocated close to the “gold
pod”. The two mobile devices were calibrated
independently: first, the AirBeam2 used by
experimenter 1 (“mob1”) and then the device used by
experimenter 2 (“mob2”). This was motivated by the
observation that mob2 was delivering concentrations
a bit higher than mob1. By using the nls() function
from RStudio 2022.07.1 (R Core Team, 2022) on
75% of the dataset, we applied the mechanistic
equation (Equation 1) involving relative humidity and
temperature for calibration:
PM
ଶ.ହ ୮
ൌ a b
మ.ఱ ౣౘ
൬
ଵାୢ
ౄ
ౣౘ
భబబషౄ
ౣౘ
൰
భ
య
c T
୫୭ୠ
(1)
where PM
2.5 gp
= PM
2.5
concentrations in µg/m
3
given
by the “gold pod”, PM
2.5 mob
= PM
2.5
concentrations
(µg/m
3
) measured with the AirBeam2, RH
mob
=
relative humidity in % determined by the AirBeam2,
T
mob
= temperature in °C given by the AirBeam2. For
A Low-Cost Sensors Study Measuring Exposure to Particulate Matter in Mobility Situations
33

mob1, we found a = 0.49, b = 0.91, c = 0.07 and d =
0.43. For mob2, we had a = -0.1, b = 0.86, c = 0.08
and d = 0.31. We then tested these two calibration
formulas on the remaining 25% dataset, and we found
the following performance indicators. For mob1, we
had RMSE = 0.62 µg/m
3
and R
2
= 0.96 and for mob2,
we found RMSE = 0.58 µg/m
3
and R
2
= 0.97. RMSE
(root mean square error) reflects the accuracy of the
model to predict actual PM
2.5
values, and R
2
(coefficient of determination) refers to the correlation
between the AirBeam2 values and the reference
concentrations. Based on this, we decided to continue
with these models as the indicators were good
compared to what is found in the literature (Blanco et
al., 2022; Haghbayan & Tashayo, 2021).
2.2 Sampling Design
2.2.1 Monitoring Routes
The study took place in Grenoble, the largest city in
the Alps, hosting around 450,000 inhabitants. Five
different monitoring sites were selected (Figure 2):
two wide streets (“Jaurès” and “Pain”) and two
narrow (also called “canyon”) streets surrounded by
higher buildings (“Grégoire” and “Blanchard”). We
also monitored PM when we commuted between
Blanchard and Grégoire (“Cross” route).
Figure 2: Monitoring routes used in the experiment.
Credits: © OpenStreetMap contributors.
2.2.2 Experimental Timings
Ground measurements were conducted from April 25,
2022 to May 12, 2022 during 10 working days
(Figure 3). Three different measurement sessions
were performed daily: a first session (S1, morning)
between 8:00 and 9:00, a second session (S2,
noontime) between 12:00 and 13:00 and a third
session (S3, afternoon) between 16:00 and 17:00.
Sometimes, for reasons related to the public transport
timetables, the sessions went slightly beyond the time
slots. Nine sessions were postponed because of rainy
conditions.
Two experimenters were involved in the study.
For each session, they had to travel the same routes in
parallel using different modes of transport: bike,
walk, bus or tramway (Appendix). Each site was
sampled for at least three days (Figure 3). On the days
when we studied Blanchard and Grégoire, we also
monitored PM while travelling in between the two
sites (“Cross” route). Jaurès was sampled four times
because this street, longer than the others, had many
potential biases (intersections, stores, idling cars) and
we thought it might be interesting to replicate the
measurements further.
Figure 3: Measurement campaign schedule.
Next, we analysed carefully the public transportation
schedules. A session example is reported in the
Appendix. The same document was used as a
roadmap by the experimenters for each session.
Reproducing measurements on the same street is
important to be representative (Van den Bossche et
al., 2015). Every day, each experimenter performed
at least 12 repetitions of the route.
2.3 Data Cleaning
In this paper, we decided to focus only on PM
2.5
analysis and on commuting times. We left PM
10
, PM
1
,
and results related to waiting times for further work.
SENSORNETS 2023 - 12th International Conference on Sensor Networks
34
Data were extracted via AirCasting application and
analysed with RStudio. We retrieved 214 comparison
trips where the two experimenters were travelling
along the same routes (428 trips in total, considering
both experimenters). PM sensors can be vulnerable to
inaccuracies resulting from drift, temperature,
humidity and other factors (Motlagh et al., 2021). As
both AirBeam2 were quite new, drift was not an issue,
but we blew compressed air through the intake of the
gold pod used for calibration as recommended by
Bathory, Dobo, Garami, Palotas, and Toth (2021). As
explained above, both AirBeam2 devices were
calibrated using formulas accounting for RH and
temperature. We also checked the presence of dust
with CAMS (Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring
Service) satellite data (retrieved 0.1° x 0.1° resolution
dust values from ENSEMBLE dataset (METEO
FRANCE, 2020) (‘analysis’ type)). Fortunately, no
dust event happened during the experiment period.
We removed outliers in the dataset because we had
peak events on trips, even inside public transports,
mainly because of smokers or idling cars. In public
transports, those peaks were often caused by door
openings. All outliers with more than 1.5 times the
interquartile range above the third quartile (Q3) or
less than 1.5 times the interquartile range below the
first quartile (Q1) were removed. Hourly background
reference PM
2.5
concentrations from Atmo AuRA
were collected through their Application
Programming Interface (https://api.atmo-aura.fr/).
For this study, we used the average from two
background reference stations (Les Frênes and Saint-
Martin d’Hères). Both references, placed at
approximately 3 km from the experimental sites, were
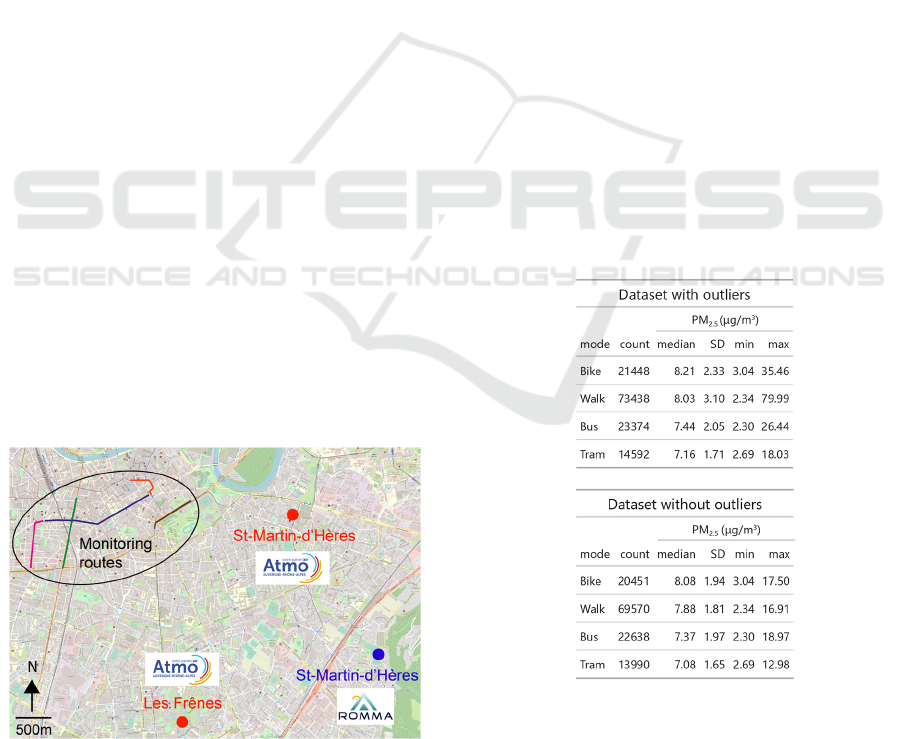
located in relatively open areas (Figure 4). For each
measurement made every second with our mobile
devices, we affected the corresponding hourly value
Figure 4: Location of the Atmo AuRA reference stations (in
red) and ROMMA meteorological station (in blue). Credits:
© OpenStreetMap contributors.
given by the reference stations. We also used
meteorological data from the Réseau d’Observation
Météo du Massif Alpin (ROMMA, 2022). Their
nearest weather station (GPS coordinates: latitude =
45.169°, longitude = 5.768°) was located around 3 km
from the collocation site (Figure 4). A Davis Vantage
Pro2 instrument registered all weather parameters.
Wind speed (km/h) corresponded to a 10-mn average,
with a measurement frequency of 2.5-3 s. We
checked that all data sources used the same time zone
(Europe/Paris).
3 RESULTS
3.1 Descriptive Statistics
Collected PM
2.5
data are summarized in Table 1.
More measurements were performed on walking
mode because, in order to replicate the experiment
and use public transportation again, we had to walk
back to the starting point. This was especially true on
routes where public transport was only running in one
direction. The number of measurements made on foot
were also higher because walking the road segment
took longer than cycling, taking the bus or tramway.
Table 1: Descriptive statistics on PM
2.5
concentrations and
number of measurements (count) performed in different
commuting modes.
More outliers were identified for walking (5.3%) than
for cycling (4.6%), tramway (4.1%) or bus (3.1%).
Walkers are generally more exposed to PM coming
from smokers, restaurants or bakeries. In addition,
they are close to idling cars. When leaving outliers in
A Low-Cost Sensors Study Measuring Exposure to Particulate Matter in Mobility Situations
35
the dataset, cyclists were more exposed (median: 8.2
µg/m
3
) than walkers (median: 8 µg/m
3
), followed by
buses (median: 7.4 µg/m
3
) and tramway (median: 7.2
µg/m
3
). Compared with cyclists, pedestrians were
2.2% less exposed, bus users 9.4% less and tramway
commuters 12.8% less. When removing outliers, the
exposure ranking proved to be the same. Cyclists
were more exposed (median value of 8.1 µg/m
3
) than
walkers (median: 7.9 µg/m
3
), followed by bus users
(median: 7.4 µg/m
3
) and tramway (median: 7.1
µg/m
3
). Compared to cyclists, walkers were 2.4%
less exposed, bus commuters 8.6% less and tramway
users 12.2% less. Qiu and Cao (2020) also found that
walkers were more exposed than bus commuters.
Peng et al. (2021) and Wang et al. (2021) found the
same exposure ranking (bike>walk>bus). They used
a PMS3003 device, similar to PMS7003. According
to Shen and Gao (2019), cyclists and pedestrians can
be directly exposed to other local particle emissions
along the road, which probably results in elevated PM
concentrations in specific areas and times. In a study
taking place in Nantes (France), Muresan and
François (2018) stated that public transport users
would accumulate 4–11 times less PM in their lungs
than nearby pedestrians walking the same route. We
decided to pursue all further analyses after having
removed outliers in our dataset.
3.2 Comparison Between Travel Modes
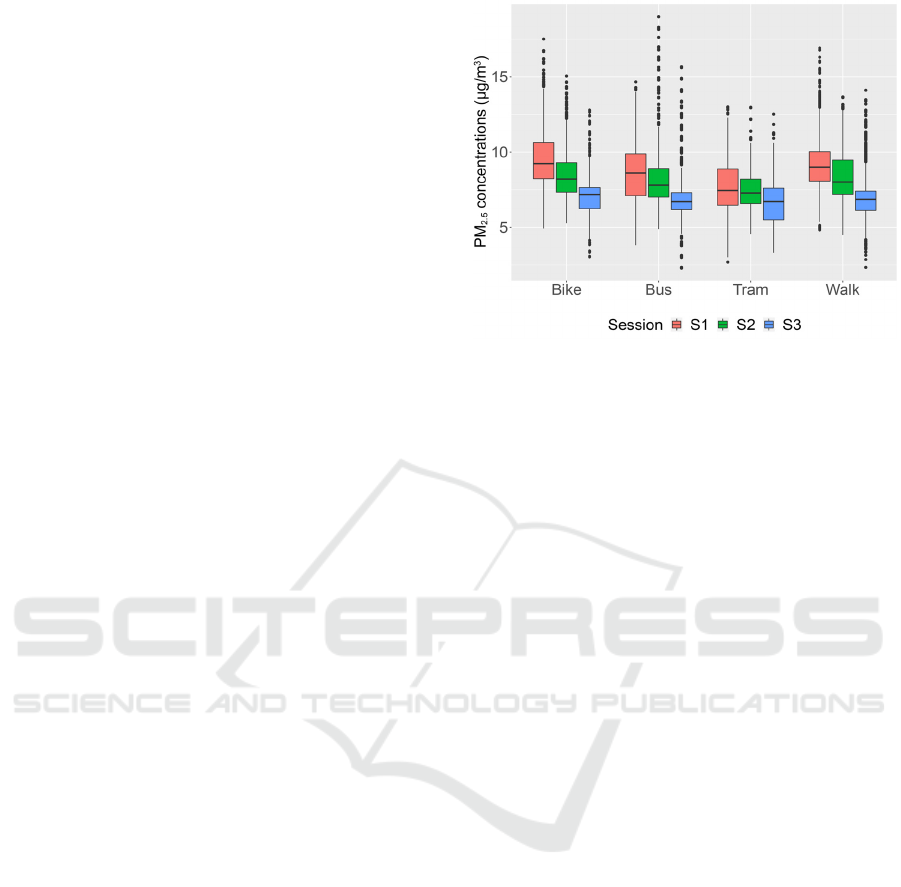
Exposure levels are greatly influenced by the time of
day (Figure 5). The morning session (S1) showed
higher PM
2.5
concentrations, followed by the
noontime (S2) and the afternoon session (S3).
Of all transport modes combined, S1 PM
2.5
median was 12.9% higher than S2, while S2 median
was 15.3% higher than S3. In the tramway, diurnal
variations seem to be reduced compared to other
modes. deSouza, Lu, Kinney, and Zheng (2021) also
found that time of day (evening/morning) had an
influence. In their ANOVA analysis, travel mode
explained 9% of the variability in PM
2.5
concentrations
whereas time of day explained 8%
variability.
All sessions considered, cyclists are the most
exposed commuters. Abbass, Kumar, and El-Gendy
(2021) studied morning and evening PM
2.5
peaks. In
their work, daily exposure patterns when walking or
cycling looked similar, whereas microbus
concentrations behaved differently, and cycling
resulted in exposure to the highest average PM
2.5
concentrations.
Figure 5: Boxplots of PM
2.5
concentrations by
transport mode. Upper
and
lower whiskers show the
ranges of 5% to 95%, the central dark lines indicate
the median. The bars outside the box represent 1.5
times the interquartile range, and circles are outliers.
Per session, we observe the same PM
2.5
exposure
ranking (bike > walk > bus > tramway) but, during
S3, the levels measured in the bus get close to those
measured in the tramway. When PM
2.5
levels are high
(S1), the differences between the transport modes are
important, but when the levels are low, during the
afternoon (S3), the differences become less
pronounced. This suggests that when PM levels are
low, public transports no longer play a “protective”
role against PM
2.5
. In addition, relative differences
between sessions are lower in the tramway than in the
other transportation modes. This could mean that
levels in the tramway are less influenced by
background concentrations, which are higher in the
morning.
3.3 Comparison with Reference Value
One of the objectives of this study was to compare the
PM
2.5
values measured by the mobile sensors with
those returned by the reference stations. The graph
below (Figure 6) shows PM
2.5
levels measured by the
mobile devices and the corresponding background
reference levels. The hours marked in bold are the
times when we carried out the most PM
2.5
measurements. As an example, the 10 am
measurements were those that we were unable to
perform as planned between 8 and 9 am. As this rarely
happened, we got fewer observations for those extra
hours.
In general, PM
2.5
levels given by the mobile
sensors were lower than values given by background
SENSORNETS 2023 - 12th International Conference on Sensor Networks
36

Figure 6: Comparison between values measured by mobile devices and reference values. The 9 o'clock boxplot corresponds
to the values measured by mobile sensors between 8 and 9 am. The hours in bold are the ones where we had the more
measurements taken by mobile devices.
stations, especially when considering hours when the
counts were the highest (9, 13, and 17). This could
come from microscale PM
2.5
variations, as PM
2.5
at
the local scale could be affected by different factors.
This was surprising that measured PM
2.5
values were
lower than reference values, because we were in a
traffic situation and the reference stations are located
in a background environment. Both reference
stations, situated in opened areas, could be exposed to
more PM
2.5
which would be covered by the dense and
high buildings of the city centre where experiments
took place. The AirBeam2 calibration could also be
an explanation. The ideal way to perform a calibration
would have been to collocate our mobile devices
directly with the reference station, without using a
gold pod as an intermediary. It is also important to
note that the calibration with the reference was
performed at an hourly scale, and we had to apply it
to values given at a fine scale (seconds). Knowing the
RMSE related to step 1 calibration (Refer Figure 1),
we could expect a maximal error of 0.7 µg/m
3
. The
average difference between reference and mobile
values during S1 and S2 (considering 9, 13 and 17
o’clock timings) was about 1.1 µg/m
3
. Therefore, the
calibration error alone could most probably not
explain the observed difference. Motlagh et al. (2021)
used low-cost sensors to measure PM
2.5
in Helsinki
and saw that roadside measurements were higher than
reference values. But during spring or summer, the
pollution levels in the train, bus or tramway were well
below the ambient reference pollution levels. They
attributed this to the fact that the transport fleet in
Helsinki was quite modern and the indoor air heavily
filtered. This should be the case for tramways in
Grenoble. However, older buses might remain in
operation, and the practice of using conditioned air
depends on the weather and the driver. It would have
been interesting to know if the air was filtered in the
different buses and trams we used. Han et al (2021)
also used low-cost sensors and observed that personal
PM
2.5
levels were consistently lower than ambient
concentrations. The Center for Advancing Research
in Transportation Emissions, Energy, and Health
(2019) measured exposure of urban cyclists in Atlanta
(United States) with a PMS5003. They concluded that
few segments recorded air quality worse than the
A Low-Cost Sensors Study Measuring Exposure to Particulate Matter in Mobility Situations
37

background concentration. During most of the routes,
riders experienced a better air quality than the one
registered at the monitoring location.
In our study, wind could be an important factor
determining PM
2.5
levels. We observed that wind
speed values were increasing starting from 10 am
(Figures 7 and 8). The relief around Grenoble could
contribute to this phenomenon.
Figure 7: Wind speed values during the experiment.
Figure 8: Average wind speed values between April 25,
2022 and May 12, 2022.
Interestingly, we observed that bus and tramway
had levels close to the reference during S3 (Refer
Figure 6). When PM levels in Grenoble were high,
public transports provided an important advantage,
but when PM levels were lower, close to their
minimum, public transportation systems did not seem
to offer this benefit any longer. Wang et al. (2021)
also performed three daily measurement sessions
(morning/noon/afternoon). Their GRIMM instrument
showed that at lower pollutant levels, the
concentrations registered in the bus were higher than
the background levels. When pollutants levels were
higher (noontime), the difference between inside and
outside got larger, as in our study. They also observed
lower levels of PM
2.5
compared to the reference when
the pollutant levels were higher. Furthermore, by
using a similar low-cost sensor (PMS3003), they
found as well that when PM
2.5
levels were lower, the
difference between reference levels and bus carriage
levels was lower.
4 CONCLUSIONS
During this spring experiment, performed in 2022 at
low pollutant levels, cyclists were more exposed than
pedestrians, bus users and tramway commuters. This
ranking was the same whether we removed outliers or
not. We counted more outliers for walking than for
cycling, tramway or bus.
When comparing exposure values to reference
stations measurements: (1) pedestrian and cyclists’
exposure generally stayed under background values,
(2) public transportation systems were under
reference values at 9 or 13 o’clock but when PM
levels went lower, levels reached those of the
reference value. Public transport users could be less
exposed than commuters using active modes, except
when ambient PM levels are low.
The time of day seems to influence exposure more
than mode of transport, with a gradual concentration
decrease throughout the day. Environmental
parameters like wind might play a role in Grenoble. It
would be interesting to reproduce this work during
another season when wind speed is lower.
In the future, we will perform an inhalation dose
calculation on the same dataset in order to consider
breathing rate differences among commuting modes.
In Grenoble, about 15% of the working population
cycles to work (Agence de la Transition Écologique,
2015), which makes the problem of PM exposure
more acute. However, we must emphasize that
cycling helps prevent many chronic diseases and
brings environmental benefits.
REFERENCES
Abbass, R. A., Kumar, P., & El-Gendy, A. (2021). Fine
particulate matter exposure in four transport modes of
Greater Cairo. Science of The Total Environment, 791,
148104. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148104
Agence de la Transition Écologique. (2015). La mobilité
durable de Grenoble Alpes Métropole. Retrieved from
https://territoireengagetransitionecologique.ademe.fr/
metropole-de-grenoble-met-en-place-un-systeme-de-
mobilite-durable-1-2-2/
Bathory, C., Dobo, Z., Garami, A., Palotas, A., & Toth, P.
(2021). Low-cost monitoring of atmospheric PM-
development and testing. Journal of Environmental
SENSORNETS 2023 - 12th International Conference on Sensor Networks
38

Management, 304, 114158. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.jenvman.2021.114158
Blanco, M. N., Gassett, A., Gould, T., Doubleday, A.,
Slager, D. L., Austin, E., Sheppard, L. (2022).
Characterization of Annual Average Traffic-Related
Air Pollution Concentrations in the Greater Seattle Area
from a Year-Long Mobile Monitoring Campaign.
Environmental Science & Technology, 56(16), 11460-
11472. doi:10.1021/acs.est.2c01077
Center for Advancing Research in Transportation
Emissions, Energy, and Health. (2019). Measuring
Temporal and Spatial Exposure of Urban Cyclists to
Air Pollutants Using an Instrumented Bike (Report No.
GT-01-09). Retrieved from https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/
view/dot/56809
Das, P., Ghosh, S., Chatterjee, S., & De, S. (2022). A Low
Cost Outdoor Air Pollution Monitoring Device With
Power Controlled Built-In PM Sensor. IEEE Sensors
Journal, 22(13), 13682-13695. doi:10.1109/jsen.
2022.3175821
deSouza, P., Lu, R., Kinney, P., & Zheng, S. (2021).
Exposures to multiple air pollutants while commuting:
Evidence from Zhengzhou, China. Atmospheric
Environment, 247, 118168. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.
2020.118168
Dons, E., Int Panis, L., Van Poppel, M., Theunis, J., &
Wets, G. (2012). Personal exposure to Black Carbon in
transport microenvironments. Atmospheric Environ-
ment, 55, 392-398. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.
03.020
Fuller, R., Landrigan, P. J., Balakrishnan, K., Bathan, G.,
Bose-O'Reilly, S., Brauer, M., Yan, C. (2022).
Pollution and health: a progress update. The Lancet
Planetary Health, 6(6), e535–e547. doi: https://
doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(22)00090-0
HabitatMap. (2022). AirBeam3 Technical Specifications,
Operation & Performance. Retrieved from https://
www.habitatmap.org/blog/airbeam3-technical-specifi
cations-operation-performance
Haghbayan, S., & Tashayo, B. (2021). Integrating ground-
based air quality monitoring stations with mobile sensor
units to improve the accuracy of PM
2.5
concentration
modeling. Scientific - Research Quarterly of
Geographical Data (SEPEHR), 29(116), 45-58.
doi:10.22131/sepehr.2021.242859
Han, Y., Chatzidiakou, L., Yan, L., Chen, W., Zhang, H.,
Krause, A., . . . Kelly, F. J. (2021). Difference in
ambient-personal exposure to PM
2.5
and its
inflammatory effect in local residents in urban and peri-
urban Beijing, China: results of the AIRLESS project.
Faraday Discussions, 226, 569-583. doi:10.1039
/d0fd00097c
Huang, J., Kwan, M. P., Cai, J., Song, W., Yu, C., Kan, Z.,
& Yim, S. H. (2022). Field Evaluation and Calibration
of Low-Cost Air Pollution Sensors for Environmental
Exposure Research. Sensors (Basel), 22(6), 2381. doi:
https://doi.org/10.3390/s22062381
METEO FRANCE, Institut National de l'Environnement
Industriel et des Risques (Ineris), Aarhus University,
Norwegian Meteorological Institute (MET Norway),
Jülich Institut für Energie- und Klimaforschung (IEK),
Institute of Environmental Protection – National
Research Institute (IEP-NRI), Koninklijk Nederlands
Meteorologisch Instituut (KNMI), Nederlandse
Organisatie voor toegepast-natuurwetenschappelijk
onderzoek (TNO), Swedish Meteorological and
Hydrological Institute (SMHI), Finnish Meteorological
Institute (FMI). (2020). CAMS European air quality
forecasts, ENSEMBLE data. Copernicus Atmosphere
Monitoring Service (CAMS) Atmosphere Data Store
(ADS). [dataset]. Retrieved from: https://ads.atmo
sphere.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/cams-europe-
air-quality-forecasts?tab=overview
Motlagh, N. H., Zaidan, M. A., Fung, P. L., Lagerspetz, E.,
Aula, K., Varjonen, S., Tarkoma, S. (2021). Transit
pollution exposure monitoring using low-cost wearable
sensors. Transportation Research Part D: Transport
and Environment, 98. doi:10.1016/j.trd.2021.102981
Muresan, B., & François, D. (2018). Air quality in tramway
and high-level service buses: A mixed
experimental/modeling approach to estimating users'
exposure. Transportation Research Part D: Transport
and Environment, 65, 244-263. doi:10.1016/j.trd.
2018.09.005
Peng, L., Shen, Y., Gao, W., Zhou, J., Pan, L., Kan, H., &
Cai, J. (2021). Personal exposure to PM
2.5
in five
commuting modes under hazy and non-hazy conditions.
Environmental Pollution, 289, 117823. doi:10.
1016/j.envpol.2021.117823
Pryor, J. T., Cowley, L. O., & Simonds, S. E. (2022). The
Physiological Effects of Air Pollution: Particulate
Matter, Physiology and Disease. Frontiers in Public
Health, 10, 882569. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.882569
Qiu, Z., & Cao, H. (2020). Commuter exposure to
particulate matter in urban public transportation of
Xi'an, China. Journal of Environmental Health Science
and Engineering, 18(2), 451-462. doi:10.1007/s40201-
020-00473-0
R Core Team. (2022). R: A language and environment for
statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing, Vienna, Austria. Retrieved from: https://
www.R-project.org/
Réseau d'Observation Météo du Massif Alpin. (2022).
Données Station de Saint-Martin-d’Hères [Members
dataset]. Retrieved from: https://romma.fr/
Schmitz, S., Towers, S., Villena, G., Caseiro, A., Wegener,
R., Klemp, D., Von Schneidemesser, E. (2021).
Unravelling a black box: An open-source methodology
for the field calibration of small air quality sensors.
Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 4, 7221–7241.
doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-2020-489
Shen, J., & Gao, Z. (2019). Commuter exposure to
particulate matters in four common transportation
modes in Nanjing. Building and Environment, 156,
156-170. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.04.018
South Coast Air Quality Management District. (2018).
Field Evaluation - AirBeam2 PM Sensor, AQ-SPEC.
Retrieved from http://www.aqmd.gov/docs/default-
source/aq-spec/summary/habitatmap-airbeam2---sum
mary-report.pdf?sfvrsn=16
A Low-Cost Sensors Study Measuring Exposure to Particulate Matter in Mobility Situations
39

Tong, C., Shi, Z., Shi, W., & Zhang, A. (2022). Estimation
of On-Road PM
2.5
Distributions by Combining Satellite
Top-of-Atmosphere With Microscale Geographic
Predictors for Healthy Route Planning. Geohealth, 6(9),
e2022GH000669. doi:10.1029/2022GH000669
Van den Bossche, J., Peters, J., Verwaeren, J.,
Botteldooren, D., Theunis, J., & De Baets, B. (2015).
Mobile monitoring for mapping spatial variation in
urban air quality: Development and validation of a
methodology based on an extensive dataset.
Atmospheric Environment, 105, 148-161. doi:10.
1016/j.atmosenv.2015.01.017
Wang, W.-C. V., Lung, S.-C. C., Liu, C.-H., Wen, T.-Y. J.,
Hu, S.-C., & Chen, L.-J. (2021). Evaluation and
Application of a Novel Low-Cost Wearable Sensing
Device in Assessing Real-Time PM
2.5
Exposure in
Major Asian Transportation Modes. Atmosphere, 12(2).
doi:10.3390/atmos12020270
Yang, F., Lau, C. F., Tong, V. W. T., Zhang, K. K.,
Westerdahl, D., Ng, S., & Ning, Z. (2019). Assessment
of personal integrated exposure to fine particulate
matter of urban residents in Hong Kong. Journal of the
Air & Waste Management Association, 69(1), 47-57.
doi:10.1080/10962247.2018.1507953
Yang, Y., Wang, H., Jiang, R., Guo, X., Cheng, J., & Chen,
Y. (2022). A Review of IoT-Enabled Mobile
Healthcare: Technologies, Challenges, and Future
Trends. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 9(12), 9478-
9502. doi:10.1109/jiot.2022.3144400
Zou, Y., Clark, J. D., & May, A. A. (2021). A systematic
investigation on the effects of temperature and relative
humidity on the performance of eight low-cost particle
sensors and devices. Journal of Aerosol Science, 152.
doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2020.105715
ABBREVIATIONS
Acronym Definition
ANOVA Anal
y
sis of variance
Atmo AuRA Atmo Auver
g
ne-Rhône-Alpes
CAMS Copernicus Atmosphere Monitorin
g
Service
IoT Internet of Thin
g
s
mob1 AirBeam2 used b
y
experimenter 1
mob2 AirBeam2 used b
y
experimenter 2
PM Particulate matte
r
PM
1
Particulate matter with aerod
y
namic diameter ≤ 1
µm
PM
2.5
Particulate matter with aerod
y
namic diameter ≤ 2.5
µm
PM
10
Particulate matter with aerod
y
namic diameter ≤ 10
µm
R
2
Coefficient of determination
RH Relative humidit
y
RMSE Root mean square erro
r
ROMMA Réseau d’Observation Météo du Massif Alpin
SENSORNETS 2023 - 12th International Conference on Sensor Networks
40
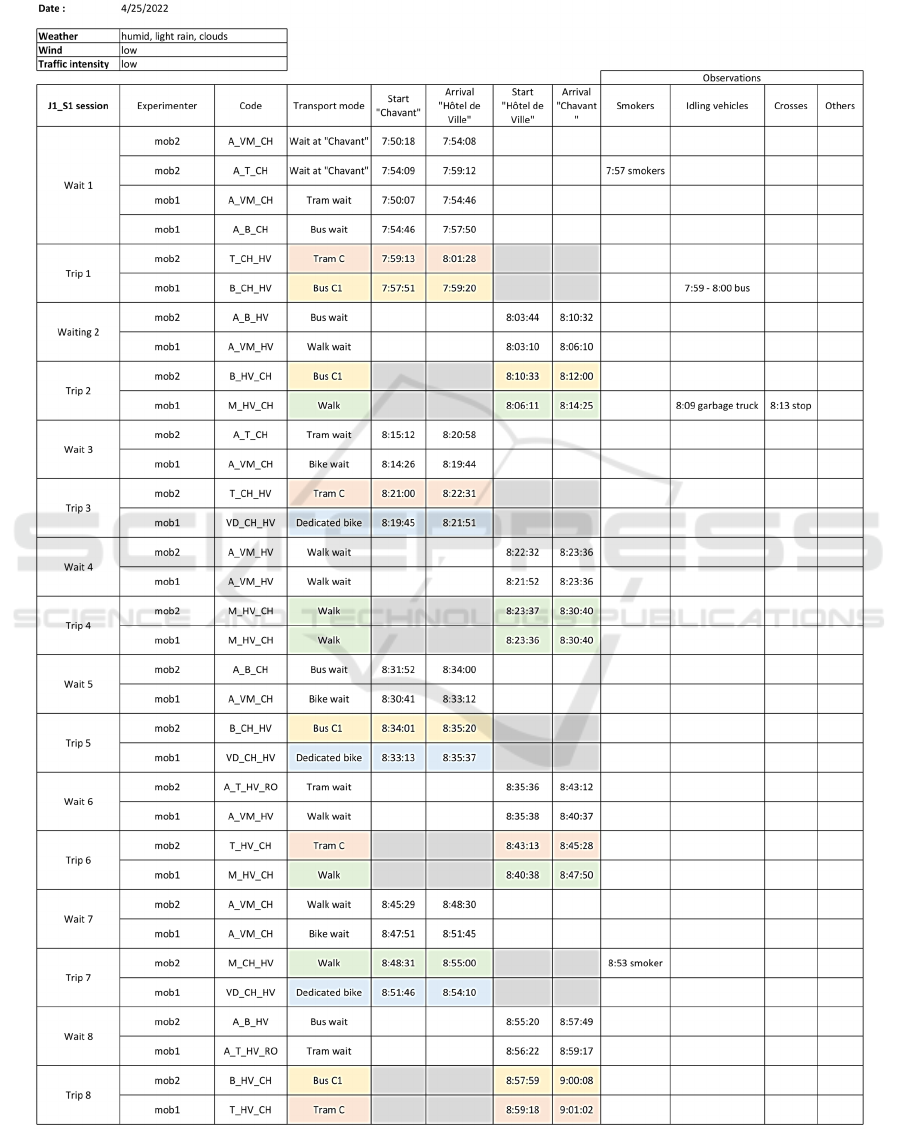
APPENDIX
Example of a measurement session
A Low-Cost Sensors Study Measuring Exposure to Particulate Matter in Mobility Situations
41
