
Adoption of Intelligent Information Systems: An Approach to the
Colombian Context
Sofía Abadía
a
and Oscar Avila
b
Department of Systems and Computing Engineering, School of Engineering, Universidad de los Andes, Bogota, Colombia
Keywords: Intelligent Information Systems, Data Analytics, Adoption, Influencing Factors.
Abstract: Enterprise Information Systems (EIS) are widely used to support operational and tactical processes of
companies and have begun, in recent years, to be used at the strategic level to support decision-making
processes. To do so, new systems, known as intelligent EIS, integrate data analytics modules to provide the
necessary information and reports to make informed decisions. There are certain influencing factors for the
adoption of such systems, however, from a first analysis of the academic literature, it was found that research
works in the domain are very scarce and even more, there are no research works on the subject in Colombia.
Consequently, this article aims at identifying the relevant factors for the adoption of intelligent EIS based on
an analysis of the academic literature, and then structuring a focus group activity with 5 experts on the subject
to obtain a first approach to the adoption of this kind of systems for the Colombian context. As a preliminary
result, we found that in the Colombian industry the most important influencing factors include cost and IT
capabilities which differs from main factors identified in the revision of the international scholar literature.
1 INTRODUCTION
There is a wide variety of technological tools that
aims at providing support to the companies' business
processes. Some of the most important support tools
are Enterprise Information Systems (EIS) and data
analytics modules, which have become very popular
in recent years due to the large amount of data
produced by both companies and customers (el Kadiri
et al., 2016).
The use of EIS can bring great benefits to
companies due to the high impact they have on
business processes at both operational and tactical
levels. Usually, systems such as Enterprise Resource
Planning (ERP) or Customer Relationship
Management (CRM) contribute to register
transactional data generated in business processes such
as financial accounting, purchasing, operations or
sales, and in the realization of descriptive reports of the
company's situation based on historical information
(Kenneth C. Laudon & Jane P. Laudon, 2014).
On the other hand, data analytics tools allow a
characterization of both customers and the business
based on historical information (Sharda et al., 2015).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9388-5543
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7586-0353
By analysing the company's historical data, it is viable
to know its current situation, i.e., it is possible to
identify the failures that are occurring, as well as the
processes that are working correctly. In this manner,
the company's historical data can be used to develop
a predictive analysis, with which the company can
have an idea about the possible scenarios that may
arise both internally and in relation to customers, and
thus be able to identify new business opportunities. In
this way, data analytics makes it possible to determine
the changes that should be made in business processes
in order to improve the company's situation. (Sharda
et al., 2015)
In recent years, data analytics components have
begun to be integrated to EIS in order to support
processes at the strategic level, all thanks to advances
in analytics and business intelligence (Kenneth C.
Laudon & Jane P. Laudon, 2014). This allows
companies to profit of transactional data registered in
EIS for several strategic processes such as decision-
making, recommendations and analysis of customer
behaviour. To this end, today analytics can be
integrated to EIS through embedded modules that
collect all the information stored in the EIS and
Abadía, S. and Avila, O.
Adoption of Intelligent Information Systems: An Approach to the Colombian Context.
DOI: 10.5220/0011750300003467
In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2023) - Volume 1, pages 21-31
ISBN: 978-989-758-648-4; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
21

perform more accurate business analysis and reports
(Z. Sun et al., 2017). Other possibility is when the
organisation has analytics tools external to the
transactional EIS, in which case, the EIS collects data
from the different processes, and then there is an
external integration with the analytics tool (Sharda et
al., 2015). It is used when the EIS and the analytics
tools were implemented by different vendors or at
different times.
This new configuration of systems are called
intelligent EIS (Jenab et al., 2019), since they take
advantage of the organisation’s information in
internal sources and combine them with external
information to make business analysis using
techniques such as artificial intelligence, analytics
and business intelligence
(Jenab et al., 2019).
Companies can also have analytics tools external to
the transactional enterprise systems, in which case,
the enterprise system collects data from the different
processes, and these are transferred to the analytics
tool to be analysed.
The adoption of intelligent EIS brings great
advantages for businesses, as a correct data analysis
helps to identify new opportunities and,
consequently, create value. However, there is little
research literature found on the factors influencing
the adoption of such systems, and to understand if
they are implemented and adopted through embedded
analytics modules, or by implementing and
integrating external analytics tools. Moreover, in
Colombia, the documentation on the adoption of
technological tools including EIS and analytic
applications is quite scarce and, so far, there are no
academic publications that analyse such aspects.
To fulfil this lack we carry out a review of the
international research literature that aims at
determining the most significant factors in the
adoption of intelligent EIS and the type of impact they
have. Then we undertake a qualitative analysis for the
Colombian context from a focus group from experts
in the domain.
This paper is structured as follows: section 2
analyses the research literature in the domain. Section
3 describes the characteristics of the focus group and
synthesize the main results of this activity. Section 4
compares and discusses the results of both activities
to draw conclusions for the Colombian context.
Finally, section 5 describes conclusions.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The process of conducting the literature review is
divided into three main stages: (i) Planning: it focuses
on identifying the articles’ selection criteria and
defining a framework with review questions for the
evaluation of the articles. (ii) Realization: it consists
in searching and selecting academic articles based on
the fulfilment of the selection criteria and the
possibility of answering the review questions. (iii)
Synthesis and analysis: the review questions are
applied to each of the selected academic articles and
answered according to the information obtained.
2.1 Planning
For the selection of the most relevant academic
articles, a set of criteria is defined, which are:
adoption of an intelligent business system or an
analytics tool, explanation of the determining factors
on the adoption decision process and mention of the
factor’s impact type. All the articles that meet the
above criteria are considered potential articles for the
realization of the literature review. The evaluation
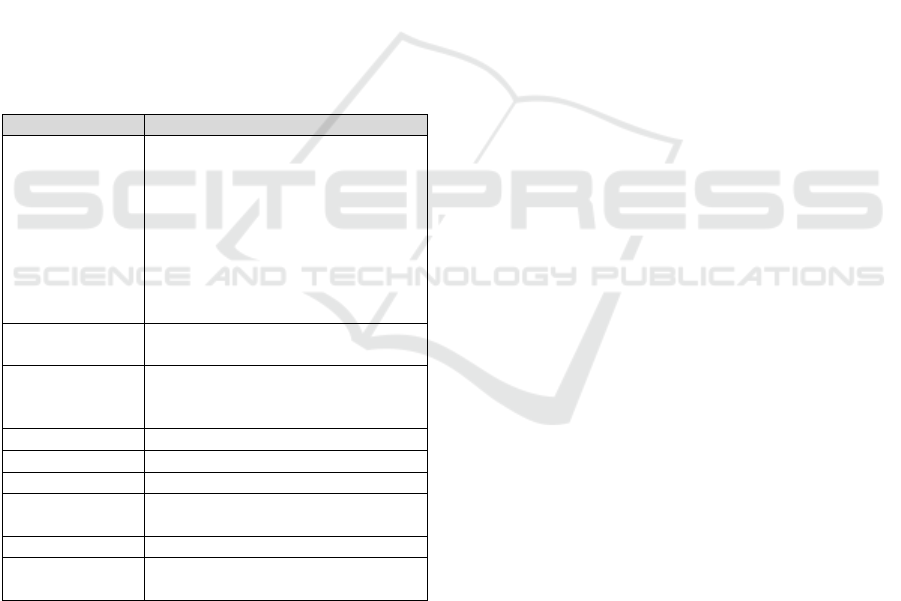
framework (see Table 1) is structured in terms of
three types of concepts, which are described below.
1. Category: these are the main key points to be
analysed in the articles.
2. Criterion: each category has a set of criteria that
help us evaluate the articles.
3. Research question: each criterion is associated
with a research question, which is used to
analyse the contribution of the article to the
defined criteria.
Table 1: Literature assessment framework.
Context cate
g
or
y
Size of the
company(ies)
What is the size of the
company(ies) studied in the
article?
Type of study Is it a qualitative or quantitative
stud
y
?
Analytics category
Type of EIS On what type of EIS is the adoption
anal
y
sis done in the article?
Component Is the adoption of an internal or
external analytics component
b
ein
g
anal
y
se
d
?
Adoption category
Method of study What method is used to study
ado
p
tion?
Factors What are the main factors
influencin
g
ado
p
tion?
Impact Do the identified factors positively
or negatively impact adoption?
Significance Do the identified factors have a
si
g
nificant effect or not?
ICEIS 2023 - 25th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
22

The context category is to clearly understand the
purpose of the research and the industrial context in
which it was carried out. The following criteria are
proposed: Size of the analysed company(ies), the
industrial sector to which the companies studied
belong and the type of study between qualitative and
quantitative. The analytical category seeks to
understand the type of tool studied in the article and
its relationship with EIS, the purpose is to identify if
the analytics tool is an internal module of the business
system or it is a completely separate tool. Finally, the
adoption category refers to the Study method, e.g.
Technology-Organization-Environment (TOE)
framework, the factors that according to the study
have an impact on the adoption decision, the impact
that each factor has on the decision to adopt the
technology (positive or negative) and the significance
that corresponds to the factors that are relevant to the
adoption process. A significant factor is a
determining factor in the decision to adopt a tool,
while a non-significant factor is not very relevant to
the process.
2.2 Realization
Having the selection criteria for the academic articles
ready, a keyword search is started. Scopus, a database
that indexes academic articles published in different
scientific journals, conference proceedings and book
chapters, among others, is used for this search.
As intelligent EIS can be implemented and
adopted through embedded analytics modules or by
implementing traditional EIS integrated with external
analytics tools, we used keywords aimed at searching
both possibilities. The query used for the search of
academic articles using defined keywords is
described as follows.
TITLE-ABS-KEY ((("intelligent enterprise
information systems" OR "intelligent enterprise
systems" OR "iEIS" OR "intelligent EIS" OR "I-
ERP" OR "intelligent ERP" OR "I-CRM" OR
"enterprise information systems" OR "enterprise
systems" OR "enterprise systems" OR "EIS" OR
"ERP" OR "CRM" ) AND ( "business intelligence"
OR "data analytics" OR "big data analytics" OR
"BDA" ) AND ( "technology adoption" OR
"technological adoption" OR "IT adoption" OR
"TOE" OR "DOI" OR "UTAUT2" OR "TRA" OR
"TAM" )) AND ( LIMIT-TO ( SUBHEARING ,
"COMP" ) ) AND ( LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2022 )
OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2021 ) OR LIMIT-TO
( PUBYEAR , 2020 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR ,
2019 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2018 ) OR
LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2017 ) OR LIMIT-TO (
PUBYEAR , 2016 ) ) )
At the beginning there were more than 200 results,
these results were downloaded to Excel with the
information of the source, the title and the summary.
Once in Excel, a first elimination was performed
according to the titles, with this filter the number of
articles went down to 46. Then another filter was
performed, this time with the summary of the articles,
which resulted in 24 articles. However, when the
reading and application of the evaluation framework
began, it was found that certain articles were not of
great relevance to the study, so they were eliminated,
thus ending up with 19 articles.
2.3 Synthesis and Analysis
Based on the application of the evaluation framework
to the set of articles, an analysis is presented
indicating the similarities and differences between the
articles and the conclusions reached.
Regarding the criterion Type of EIS and
Components (see Table 1), the conclusions are
summarized in Table 2 and can be divided into 3
groups of papers. The first group of papers studies the
adoption of intelligent EIS, where 4 of them focus on
ERP adoption (Xu et al., 2017), (Nwankpa et al.,
2016), (Mayeh et al., 2016), (Elkhani et al., 2014), 3
of them on CRM adoption (Cruz-Jesus et al., 2019),
(Hasan Salah et al., 2019), (Ahani et al., 2017) and
one on EIS in general, but hosted in the cloud (Şener
et al., 2016). Although these papers refer to the
adoption of intelligent EIS, they do not provide
evidence of how they are integrated with internal or
external analytics modules or components.
The second group of papers ((Maroufkhani et al.,
2020), (Schüll & Maslan, 2018), (Park & Kim, 2021),
(Maroufkhani et al., 2022), (Angwar, 2018), (Khan &
Brock, 2017), (El-Haddadeh et al., 2021), (S. Sun et
al., 2018)) discuss the adoption of data analytics as
an external stand-alone tool that generates
information by using, among others, the
organisation’s internal transactional data sources.
Finally, in the third group, we identified two
subgroups. On the one hand papers dealing with the
adoption of analytics as an external component, but
mentioning explicitly that it is fed by data coming
from one or more EIS (Alaskar et al., 2021),
(Kyriakou et al., 2020) and on the other hand, articles
analysing the adoption of analytics as an internal
embedded module of an EIS (Junior et al., 2019).
Adoption of Intelligent Information Systems: An Approach to the Colombian Context
23

Table 2: Tool adopted.
Tool T
yp
e Article
Intelligent
EIS
ERP (Xu et al., 2017),
(Nwankpa et al., 2016),
(Mayeh et al., 2016),
(Elkhani et al., 2014)
CRM (Cruz-Jesus et al.,
2019), (Hasan Salah et
al., 2019), (Ahani et al.,
2017
)
EIS on clou
d
(Şener et al., 2016)
Stand-
alone data
analytics
External
component
(Maroufkhani et al.,
2020), (Schüll &
Maslan, 2018), (Park &
Kim, 2021),
(Maroufkhani et al.,
2022), (Angwar, 2018),
(Khan & Brock, 2017),
(El-Haddadeh et al.,
2021), (S. Sun et al.,
2018
)
EIS with
data
analytics
EIS powered
by an external
analytics
com
p
onent
(Alaskar et al., 2021),
(Kyriakou et al., 2020)
Internal
(embedded)
analytics
component in
ERP
(Junior et al., 2019)
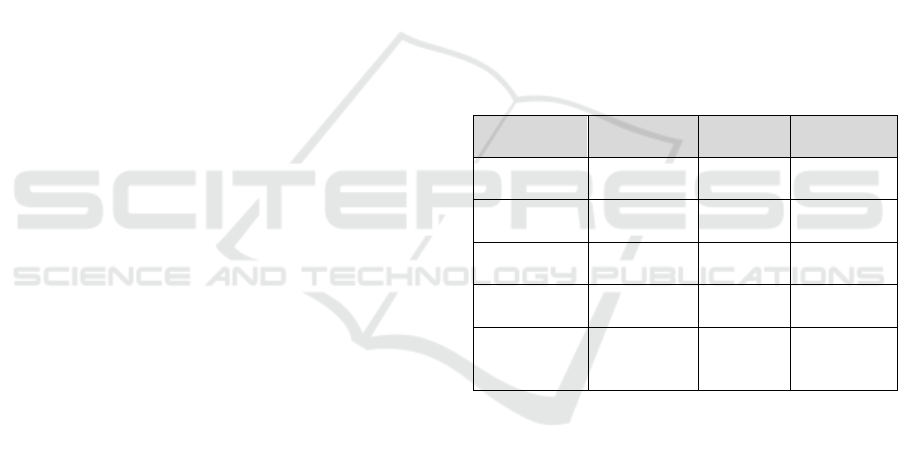
Regarding the question related to the criterion size
of the company(ies), Table 3 shows the articles for
which size is considered a relevant factor, the
relationship between the type of tool studied in the
article and the size of the companies, and the impact
and significance it has on each one.
As it can be seen in Table 3, for all the articles that
consider size as a factor to be taken into account, its
impact is positive, which means that the larger the
company, the more likely it is that the process of
adopting the tool can be initiated. However, there is
no unanimity regarding its significance, since one out
of 5 articles considers it a non-significant factor (S.
Sun et al., 2018).
When analysing the results by type of tool
adopted, in the case of intelligent EIS, even though in
(Şener et al., 2016) the company’s size is argued to
have a positive impact and be significant, making it a
relevant factor, the size of the companies
participating in this study is not presented. In the
remaining cases, (i.e., standalone data analytics and
EIS with data analytics) the articles study companies
of all size categories, namely, small, medium and
large.
Table 3: Company’s size as relevant factor vs type of tool.
Intelligent
EIS
Stand-alone
data analytics
EIS with
data
anal
y
tics
Size of
the
company
is
relevant
(Şener et
al., 2016):
positive
and
significant
(Angwar,
2018): positive
and significant
(Khan & Brock,
2017): positive
and significant
(S. Sun et al.,
2018): positive
and not
significant
(Kyriakou
et al.,
2020):
positive
and
significant
Regarding the criterion type of study, the vast
majority of cases conducted quantitative studies (see
Table 4) which usually began with an analysis of the
academic literature on the subject in order to identify
the significant factors for technology adoption.
Subsequently, a survey was developed and distributed
to the participating companies. Once the results were
obtained, a process of elimination of incomplete
surveys was carried out. Finally, different statistical
techniques, such as linear regression, were used to
determine the most significant factors.
In the case of qualitative studies, the first step was
the same, the study of academic literature and
identification of the most important factors. Then, a
group of experts on the subject were surveyed to get
their opinion on the information collected and,
according to this, the factors were ordered from most
to least significant by means of techniques such as the
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), which is a multi-
criteria decision method (Şener et al., 2016).
However, no statistical analysis was performed at any
time.
Table 4: Type of study.
Type of
stud
y
Article
Quantitative
study
(Xu et al., 2017), (Cruz-Jesus et al.,
2019), (Kyriakou et al., 2020), (Junior et
al., 2019), (Alaskar et al., 2021),
(Nwankpa et al., 2016), (Maroufkhani et
al., 2020), (Ahani et al., 2017), (Schüll
& Maslan, 2018), (Mayeh et al., 2016),
(Park & Kim, 2021), (Maroufkhani et
al., 2022), (Angwar, 2018), (Khan &
Brock, 2017), (El-Haddadeh et al.,
2021), (Elkhani et al., 2014)
Qualitative
study
(Hasan Salah et al., 2019), (Şener et al.,
2016), (S. Sun et al., 2018)
With respect to the criterion method, as expected,
the Technology-Organization-Environment (TOE)
ICEIS 2023 - 25th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
24
framework is the most commonly used adoption
model, being used in 13 out of 19 articles (see Table
5). In addition, there are two more articles that made
use of variations of the TOE, namely, TOEP (Ahani
et al., 2017) and TOES (Angwar, 2018). Both study
the same three categories of the TOE, which are
Technology, Organization and Environment,
however, they add a new one. TOEP adds the
processes category because of its focus on the
company's business processes. TOES add the security
category which considers factors such as information
security and privacy. Regarding other methods, some
works use different adoption models simultaneously.
For instance, (Junior et al., 2019) uses TOE,
Diffusion of Innovations (DOI) and Inter-
organizational Relations (IOR) theory, (Hasan Salah
et al., 2019) uses TOE, DOI and Resource-based
View (RBV) and (S. Sun et al., 2018) uses TOE, DOI
and Institutional theory. The combination of methods
allowed researchers to have a broader view of
significant factors of adoption.
Table 5: Adoption models.
Ado
p
tion model Article
TOE (Xu et al., 2017), (Cruz-Jesus et al.,
2019), (Kyriakou et al., 2020),
(Junior et al., 2019), (Alaskar et al.,
2021), (Hasan Salah et al., 2019),
(Maroufkhani et al., 2020), (Schüll
& Maslan, 2018), (Park & Kim,
2021), (Maroufkhani et al., 2022),
(El-Haddadeh et al., 2021), (Şener et
al., 2016), (S. Sun et al., 2018)
DOI (Junior et al., 2019), (Hasan Salah et
al., 2019
)
,
(
S. Sun et al., 2018
)
Technology
Acceptance
Model (TAM)
(Mayeh et al., 2016), (Khan &
Brock, 2017), (Elkhani et al., 2014)
TOEP (Ahani et al., 2017)
TOES (Angwar, 2018)
IOR
(
Junior et al., 2019
)
Real Options
Theor
y
(Nwankpa et al., 2016)
RBV (Hasan Salah et al., 2019)
Institutional
theor
y
(S. Sun et al., 2018)
Concerning the factor criterion, this analysis is
characterized according to the adopted tools within 3
groups, namely, intelligent EIS, stand-alone data
analytics and EIS with data analytics. For this
analysis the information is gathered in Table 6 which
describes for each tool the factors influencing
adoption, as well as the impact (positive or negative)
and the significance level of each factor where S
stands for significant (i.e., it is a determining factor in
the decision to adopt a tool) and NS means non-
significant (i.e., it is not very relevant to the process).
According to Table 6 the most currently found
determining factor in the intelligent EIS group is
management support, which implies that the
management is involved in the EIS adoption process
(Xu et al., 2017), i.e., that it knows the competitive
advantages that can be provided by the technological
tool and is willing to accept its cost. This factor is
mentioned in 7 out of 8 articles and in all cases, it has
a positive impact that is significant.
Other important factors are described as follows.
Relative advantage relates to the increasing of
benefits that the new intelligent EIS can bring (Xu et
al., 2017). It has a positive impact that is considered
significant in all the articles. Competitive market
pressure concerns the pressure level a company feels
to implement a certain EIS due to market competition
(Xu et al., 2017). It is determined to have a positive
impact that is significant. Compatibility refers to the
degree of consistency between the EIS to be adopted
and the values, needs, experiences and practices of
the company (Xu et al., 2017). It also has a positive
impact which is significant. In the case of the factors
complexity and government policies, even though all
research works consider the former has a negative
influence and the later a positive one, there is no
consensus regarding their significance, as in both
cases, the same research work (Şener et al., 2016)
determines that these two factors are not significant.
This may be due to 2 reasons, the context and the type
of study: regarding the context, this work is the only
one that focuses on EIS in the cloud, which may
imply a change in the determinants, since the
complexity of deployment in this type of model does
not make its adoption easier or more difficult, and
possibly in the environment in which the analysis was
made, it is possible that government policies are
neutral regarding the adoption of cloud technologies.
Now, regarding the type of study, this article conducts
a qualitative study unlike articles (Xu et al., 2017),
(Hasan Salah et al., 2019) and (Ahani et al., 2017).
In the second’s group case, it is to say, the articles
dealing with stand-alone data analytics, the
determinants for the adoption of data analytics tools
are practically the same as for intelligent EIS, i.e., all
the EIS factors also appear in the data analytics list,
but 2 more factors are added: cost and organizational
readiness (see Table 6).
Adoption of Intelligent Information Systems: An Approach to the Colombian Context
25

Table 6: Factors for the three groups of tools.
Tool Factors Im
p
Si
g
nific Article
Intelligent EIS
Management support + S
(Xu et al., 2017), (Cruz-Jesus et al., 2019),
(Nwankpa et al., 2016), (Hasan Salah et al., 2019),
(
Ahani et al., 2017
)
,
(
Elkhani et al., 2014
)
,
(
Şener et al., 2016
)
Relative advantage + S
(Xu et al., 2017), (Nwankpa et al., 2016),
(Hasan Salah et al., 2019), (Ahani et al., 2017), (Şener et al., 2016)
Competitive market
p
ressure
+ S
(Xu et al., 2017), (Cruz-Jesus et al., 2019), (Hasan Salah et al., 2019), (Ahani
et al., 2017), (Şener et al., 2016)
Compatibilit
y
+ S (Xu et al., 2017), (Hasan Salah et al., 2019), (Ahani et al., 2017)
Government policies +
S (Hasan Salah et al., 2019), (Ahani et al., 2017)
NS
(
Şener et al., 2016
)
Complexity
-
S
(
Xu et al., 2017
)
,
(
Hasan Salah et al., 2019
)
NS (Şener et al., 2016)
Expected benefits + S (Nwankpa et al., 2016), (Mayeh et al., 2016), (Elkhani et al., 2014)
IT capabilities + S (Cruz-Jesus et al., 2019), (Ahani et al., 2017)
IT infrastructure
/resources
+ S
(Hasan Salah et al., 2019), (Şener et al., 2016)
Securit
y
+ S (Hasan Salah et al., 2019), (Şener et al., 2016)
Size + S (Şener et al., 2016)
Stand-alone data analytics
Management support + S
(Maroufkhani et al., 2020), (Schüll & Maslan, 2018), (Park & Kim, 2021),
(Maroufkhani et al., 2022), (Angwar, 2018), (S. Sun et al., 2018)
Competitive market
pressure
+
S
(Maroufkhani et al., 2020), (Schüll & Maslan, 2018), (Angwar, 2018), (El-
Haddadeh et al., 2021
)
NS (S. Sun et al., 2018)
Compatibility
+
S (Maroufkhani et al., 2020), (Maroufkhani et al., 2022), (Angwar, 2018)
NS (Park & Kim, 2021), (S. Sun et al., 2018)
Complexity - S
(Maroufkhani et al., 2020), (Maroufkhani et al., 2022), (Angwar, 2018), (El-
Haddadeh et al., 2021), (S. Sun et al., 2018)
Organizational
readiness
+
S
(Maroufkhani et al., 2020), (Maroufkhani et al., 2022), (El-Haddadeh et al.,
2021
)
NS
(
An
g
war, 2018
)
Expected benefits + S (Park & Kim, 2021), (Khan & Brock, 2017), (El-Haddadeh et al., 2021)
Relative advantage + S (Maroufkhani et al., 2020), (Angwar, 2018), (S. Sun et al., 2018)
Government policies
+
S
(
Park & Kim, 2021
)
,
(
El-Haddadeh et al., 2021
)
,
(
S. Sun et al., 2018
)
-
(
Maroufkhani et al., 2020
)
Size
+
S
(
An
g
war, 2018
)
,
(
Khan & Brock, 2017
)
NS (S. Sun et al., 2018)
IT infrastructure /
resources
+ S
(Khan & Brock, 2017), (El-Haddadeh et al., 2021), (S. Sun et al., 2018)
IT ca
p
abilities + S
(
Schüll & Maslan, 2018
)
,
(
Park & Kim, 2021
)
Security and privacy
+
S
(Angwar, 2018)
- (Park & Kim, 2021), (S. Sun et al., 2018)
Cost - S (Park & Kim, 2021), (S. Sun et al., 2018)
EIS with data
analytics
Mana
g
ement su
pp
ort + S
(
Junior et al., 2019
)
,
(
Alaskar et al., 2021
)
Competitive market
p
ressure
+ S
(Junior et al., 2019), (Alaskar et al., 2021)
Com
p
atibilit
y
+ S
(
Junior et al., 2019
)
,
(
Alaskar et al., 2021
)
IT capabilities
+
S
(
K
y
riakou et al., 2020
)
NS
(
Junior et al., 2019
)
Expected benefits + S (Alaskar et al., 2021)
Relative advantage + S (Junior et al., 2019)
Size + S (Kyriakou et al., 2020)
Organizational readiness is the ability to make
available the technological, financial and human
resources necessary for the adoption of the analytics
technology (Angwar, 2018). Cost refers to the amount
ICEIS 2023 - 25th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
26
of money that needs to be invested to be able to adopt
an analytics technological tool which includes
acquisition cost, modifications to the company's
infrastructure, employee training and hiring new
personnel. The most mentioned factors for this group
are management support, competitive market
pressure and compatibility. When there is more
consensus in in the management support factor,
which is addressed in 6 out of 8 articles
Regarding negative impact factors, complexity
that is the degree of difficulty perceived by the
company when faced with a technological tool
(Angwar, 2018) is looked as significant and
mentioned in this way in 5 articles. It is worth to note
that, in this case, the size of the company can be
considered a determining factor, since it is mentioned
in 3 articles and is significant in 2 of them. In
addition, the impact is always positive, which means
that the larger the company, the easier the adoption.
Finally, for the third group, i.e., EIS with data
analytics, two papers study the adoption of an
external analytics component fed by EIS (Kyriakou et
al., 2020)(Alaskar et al., 2021), while one research
work studies the adoption of an internal embedded
analytics component in an ERP (Junior et al., 2019).
For this group the analysis shows that the most
determining factor is again management support,
followed by competitive market pressure,
compatibility and IT capabilities (see Table 6).
However, there is a discrepancy regarding the
significance of the latter, since in (Kyriakou et al.,
2020) it is considered a significant factor and in
article (Junior et al., 2019) it is not. It is worth to note
that here complexity is not considered by any of the
articles and size is only mentioned in article
(Kyriakou et al., 2020), so it is not possible to reach a
conclusion of their importance in the process of
adopting enterprise systems with embedded data
analytics modules. On the other hand, management
support, competitive market pressure and
compatibility are once again determining factors, as
in the case of adoption of enterprise systems and
stand-alone data analytics.
3 ADOPTION OF INTELLIGENT
EIS IN COLOMBIA
This section is intended to carry out a first approach
to the identification of the determining factors for the
adoption of intelligent EIS in the context of the
Colombian industry. To collect information, a focus
group is conducted. The results of the literature
review will be used as a basis to guide this activity.
3.1 Focus Group
The objective of the focus group is to determine if the
determinants identified in the literature review are
also determinants in the context of the Colombian
industry or if discrepancies are found.
For the focus group, 5 professionals were selected
to participate in this activity considering their work
experience in the field of data analytics and enterprise
information systems. They have knowledge in the
different EIS and data analytics tools available in the
market. The group is composed of men and women
between 35- and 65-years old working in private
sector companies, in the IT department or as IT
consultants. The information on the participants'
current position, their companies’ size and the
industry sector to which they belong is presented as
follows:
Table 7: General information of the participants.
Participant Current
p
osition
Company
size
Industrial
secto
r
P1:
Partici
p
ant 1
IT Manager Medium Consulting
P2:
Participant 2
BI Architect Large Technology
P3:
Participant 3
Product
Manage
r
Large Technology
P4:
Partici
p
ant 4
Expert
En
g
inee
r
Large Technology
P5:
Participant 5
Independent
BI
Consultant
Large Financial
This activity lasts approximately one hour, during
which the participants discussed among themselves
and answered the researcher's questions. The focus
group questions are semi-structured, that is, there are
some basic questions, and the researcher can add
questions according to the evolution of the
discussion. The used questions are presented below:
• Does your company currently use an EIS?
• Does your company currently use a data
analytics tool?
• Is the analytics tool external or is it a module
embedded in the EIS? Who is your supplier?
• During the literature review phase, we identified
factors influencing the adoption of intelligent EIS.
How would you prioritise these factors, from the least
to the most significant?
• Why do you rank them this way? Would you
add any other factors?
Adoption of Intelligent Information Systems: An Approach to the Colombian Context
27

The first questions were asked with the objective
of gathering general information about the type of
EIS and analytics tool that has been implemented in
the participants' companies, while the subsequent
questions aimed at generating a discussion about the
determining factors for the adoption of data analytics
in companies of the Colombian industry.
The focus group was conducted virtually and
recorded considering confidentiality criteria. During
the session, participants had the right to ask to be
identified by their name or a pseudonym. All
transcribed fragments were anonymized. The
recording of the session is securely stored in a private
folder in the cloud to which only the researchers have
access. All these norms were presented to the
participants in a written informed consent, which was
signed by them prior to the session.
3.2 Synthesis
We present the synthesis of the answers for each of
the questions as follows.
Does your company currently use an EIS?
In most cases, the participants' companies do not
use a single EIS, but a combination of several tools
within which the transactions associated with their
business processes are registered. It means that in
most of the cases they do not have an integrated EIS
for all areas of the business.
In the case of participant 1, his company manages
the different business processes separately and with
different tools, for example, it uses one of the leading
ERP systems in the market for financial processes,
however, the main system in which they run most of
their processes was custom developed. On the other
hand, the organisation of participant 2 works with
multiple internal systems, from which information is
collected. The information is also collected from
different sources such as JSON or CSV files and
applications, and then a data warehouse is assembled.
Does your company currently use a data analytics
tool?
All participants' companies have one or more
analytics tools and different analytics strategies. In
general, companies use third parties' analytics tools
and data science techniques implemented in-house.
The only exception to this is participant 4's company,
which works exclusively with one of the leading
cloud computing services companies in the market.
Regarding techniques implemented in-house, 3 of
the 5 participants (Participant 2, Participant 3 and
Participant 5) mention that in their companies data
science is performed internally, with which they can
obtain a better knowledge of their clients.
Specifically, it is mentioned that in the company of
Participant 2 an information analysis system was
created based on a data warehouse in which the
collected data is stored and, once all the data is there,
a commercial BI tool is used to create reports on the
processes. On the other hand, participant 3's company
has developed its own algorithms for demand
forecasting. Finally, participant 5 indicates that they
develop "in situ" algorithms in Python for predictive
analytics through linear regression models,
classification, decision trees and correlation between
variables. These algorithms are invoked then by a
commercial BI tool for performing business
intelligence processes.
How would you prioritise adoption influencing
factors, from the least significant to the most
significant?
Regarding the relevance of factors identified in
the literature review, it was not possible to reach a
final/total consensus in the group, since viewpoints
were divided between organisational and
technological factors. However, cost is a common
factor among all, being always placed among the first
places. Likewise, management support, complexity,
competitive market pressure and IT capabilities are
important for the participants. The reasoning for such
results is presented below:
• Cost: companies can contract cloud services
specifically for what they need and thus reduce
costs, however, if a company wants accurate
analytics process it must develop robust tools,
which comes with a high cost. Additionally, the
cost of hiring expert personnel must also be
taken into account.
• Management support: it is important for the
management to know exactly the objective of
analytics tools and be aware of the benefits that
can be gained from them. In this way, they will
be willing to assume the cost of adoption and
staff training.
• Complexity: many of the tools available in the
market may be difficult to handle at the
beginning, which would imply a great expense
in staff training. For this reason, it is important
to maintain the level of complexity not too
high.
• Competitive pressure from the market: if a
company starts to offer a better service to
customers, other companies must start to
innovate in order not to be left behind, in the
words of one of the participants "those who do
not move, die".
• IT capabilities: it is important for a company to
have expert staff in data analysis and with the
ICEIS 2023 - 25th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
28

necessary knowledge on the use of the tool
adopted, otherwise data analytics processes
will not be performed correctly and faithful.
For certain participants, the fact that there are
analytics tools available in the cloud makes some
factors not so decisive when looking for their
adoption. These factors are:
• Security and privacy: cloud service providers
guarantee the confidentiality, integrity and
availability of customer information, so
security and privacy take a back seat.
• IT infrastructure: it is not necessary to have a large
number of on-premise servers and facilities
because the data can be stored on cloud servers.
One of the most debated factors by the
participants is the size of the company, as for some
the size is related to the available resources of the
organization, which means that a small company, for
example, could not have the necessary resources to
acquire an analytics tool. On the other hand, other
participants argue that for smaller companies,
analytics may be the only differentiator that allows
them to increase their competitiveness and thus grow.
4 DISCUSSION
From the analysis of the literature review and the
focus group, it is possible to determine that there are
both coincidences and discrepancies regarding the
adoption of data analytics tools and strategies. At this
point it is important to note that the literature review
is a study of international literature, while the focus
group is based on the Colombian context, so it is
reasonable to find certain differences.
First, concerning the integration of EIS and
analytics tools and the parallelism in their adoption
we discuss as follows both perspectives. Regarding
the literature review perspective, the search and
selection process of articles on EIS integrated with
data analytics, only 2 articles were obtained in which
the data analytics components were fed by the
company EIS (Alaskar et al., 2021), (Kyriakou et al.,
2020) and one in which the data analytics component
was embedded in the EIS (Junior et al., 2019) (see
Table 2). In the case of the 8 articles that talk about
the adoption of intelligent EIS, the relationship that
these could have with other systems or analytics
components was not clearly mentioned, and authors
addressed the capabilities of such systems to generate
specific reports using analytics technics.
Concerning Colombian context perspective, all
participants mentioned their companies have multiple
EIS that are not integrated and register data generated
independently for each process. As a consequence,
they do not have centralized information for all the
areas of the business, but only have access to isolated
data for each process. However, once the data has
been successfully stored, the business intelligence
process begins, in which analytical tools are used to
generate knowledge from this data, so that the current
situation of the company as a whole can be
understood, and informed decisions can be made.
According to these conclusions from the literature
and the focus group, we can say that the adoption of
a centralized EIS and the adoption of a data analytics
tool are not necessarily linked. Companies can adopt
an EIS with data analytics modules embedded if this
system is the only one to be used across the entire
enterprise, otherwise the reports generated by the
analytics process would not be completely accurate,
as the enterprise system would not have access to all
enterprise data, but only to some areas of the business.
Otherwise, in most of the cases the process of
adoption of EIS and data analytics tools are
independent so that links between both adoption
processes and integration between both types of tools
are not strictly mentioned nor addressed.
Second, between the literature review and the
focus group, the determinants for the adoption of
independent data analytics tools vary. Table 8 shows
the most frequently identified factors in both the
literature review and the focus group. From this, it can
be seen that 3 of the 5 factors are determinants in both
cases (management support, competitive market
pressure and complexity), however, the other 2 are in
each case completely different.
Table 8: Literature review vs focus group factors.
Factor
Literature
review
Focus group
Management
su
pp
ort
X X
Com
p
atibilit
y
X
Complexity X X
Competitive
market
p
ressure
X X
Expected benefits X
IT Capabilities X
Cost X
From the analysis of the literature review, it is
found that the factor with the least relevance when
adopting a data analytics tool is cost, which is only
mentioned in 2 articles, (Park & Kim, 2021) and (S.
Sun et al., 2018). However, it was the most
determining factor in the focus group because the
participants agreed that the cost of a robust analytics
Adoption of Intelligent Information Systems: An Approach to the Colombian Context
29

tool can be quite high. Regarding IT capabilities and
skills of employees, in the case of the Colombian
context it is a relevant factor because of the shortage
of professional profiles in the country with experience
in this field, even though in the literature review it
was not identified as an influencing factor.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this document an extensive analysis of the main
factors that can affect the process of adoption of
intelligent EIS in companies is made, as well as a first
approach to this topic focused on the Colombian
industry. In order to carry out this analysis,
techniques such as a literature review and a focus
group are used. Regarding the literature review, an
evaluation framework is created to analyse the
selected set of academic articles. Each article is
evaluated according to 3 categories: research context,
type of data analytics studied and adoption process.
Through the analysis of the academic articles, it is
possible to identify the determining factors for the
adoption of intelligent EIS.
To get a first approach on the subject to the
Colombian context, a focus group is conducted with
5 experts on the subject of EIS and data analytics. The
focus group is intended to identify the main
characteristics of intelligent EIS in Colombian
companies as well as the main factors influencing
their adoption.
Based on the analysis of both the literature review
and the focus group, a comparison is made to
determine the similarities and differences that exist
between them. Through this comparison, it was found
that there are three factors that are determinant in both
cases and two that are different. On the one hand the
common factors are: management support,
competitive market pressure and complexity. On the
other hand, specific factors for the literature review
are compatibility and expected benefits, while
specific factor for the Colombian companies from the
focus group are cost and the company's IT capabilities
and skills.
Concerning the limitation of our study, it is worth
bearing in mind that the results of the focus group is
a first approach to the topic, since the participation of
5 experts is not enough to determine the process of
adoption of intelligent EIS to the whole Colombian
context. As future work, the information collected
through this study can be used to design additional
collection tools such a surveys’ questionnaires in
order to carry out a representative analysis of
quantitative nature.
REFERENCES
Ahani, A., Rahim, N. Z. A., & Nilashi, M. (2017).
Forecasting social CRM adoption in SMEs: A
combined SEM-neural network method. Computers in
Human Behavior, 75, 560–578. https://doi.org/10.10
16/j.chb.2017.05.032
Alaskar, T. H., Mezghani, K., & Alsadi, A. K. (2021).
Examining the adoption of Big data analytics in supply
chain management under competitive pressure:
evidence from Saudi Arabia. Journal of Decision
Systems, 30(2–3), 300–320. https://doi.org/10.1080/
12460125.2020.1859714
Angwar, H. (2018). Understanding the determinants of big
data adoption in India: An analysis of the
manufacturing and services sectors. Information
Resources Management Journal, 31(4), 1–22.
https://doi.org/10.4018/IRMJ.2018100101
Cruz-Jesus, F., Pinheiro, A., & Oliveira, T. (2019).
Understanding CRM adoption stages: empirical
analysis building on the TOE framework. Computers in
Industry, 109, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.
2019.03.007
el Kadiri, S., Grabot, B., Thoben, K. D., Hribernik, K.,
Emmanouilidis, C., von Cieminski, G., & Kiritsis, D.
(2016). Current trends on ICT technologies for
enterprise information systems. Computers in Industry,
79, 14–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2015.06.
008
El-Haddadeh, R., Osmani, M., Hindi, N., & Fadlalla, A.
(2021). Value creation for realising the sustainable
development goals: Fostering organisational adoption
of big data analytics. Journal of Business Research,
131, 402–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.
10.066
Elkhani, N., Soltani, S., & Ahmad, M. N. (2014). The
effects of transformational leadership and ERP system
self-efficacy on ERP system usage. Journal of
Enterprise Information Management, 27(6), 759–785.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-06-2013-0031
Hasan Salah, O., Yusof, Z. M., & Mohamed, H. (2019). A
Conceptual Framework Of Crm Adoption Among
Palestinian SMES 1. Journal of Theoretical and
Applied Information Technology, 97(8). www.jatit.org
Jenab, K., Staub, S., Moslehpour, S., & Wu, C. (2019).
Company performance improvement by quality based
intelligent-ERP. Decision Science Letters, 8(2), 151–
162. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.dsl.2018.7.003
Junior, C. H., Oliveira, T., & Yanaze, M. (2019). The
adoption stages (Evaluation, Adoption, and
Routinisation) of ERP systems with business analytics
functionality in the context of farms. Computers and
Electronics in Agriculture, 156, 334–348.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.11.028
Kenneth C. Laudon, & Jane P. Laudon. (2014).
Management Information Systems Managing the
Digital Firm (13th ed.). Pearson.
Khan, H. U., & Brock, V. F. (2017). Are enterprises ready
for big data analytics? A survey-based approach.
International Journal of Business Information Systems,
ICEIS 2023 - 25th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
30

25(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijbis.2017.100044
08
Kyriakou, N., Loukis, E., & Chatzianastasiadis, M. M.
(2020). Enterprise Systems, ICT Capabilities and
Business Analytics Adoption – An Empirical
Investigation. Lecture Notes in Business Information
Processing, 402, 433–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-
3-030-63396-7_29
Maroufkhani, P., Iranmanesh, M., & Ghobakhloo, M.
(2022). Determinants of big data analytics adoption in
small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Industrial
Management and Data Systems.
https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-11-2021-0695
Maroufkhani, P., Wan Ismail, W. K., & Ghobakhloo, M.
(2020). Big data analytics adoption model for small and
medium enterprises. Journal of Science and
Technology Policy Management, 11(2), 171–201.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JSTPM-02-2020-0018
Mayeh, M., Ramayah, T., & Mishra, A. (2016). The role of
absorptive capacity, communication and trust in ERP
adoption. Journal of Systems and Software, 119, 58–69.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.05.025
Nwankpa, J. K., Roumani, Y., & Roumani, Y. F. (2016).
Exploring ERP-enabled technology adoption: A real
options perspective. Communications of the
Association for Information Systems, 39(1), 529–555.
https://doi.org/10.17705/1cais.03924
Park, J. H., & Kim, Y. B. (2021). Factors Activating Big
Data Adoption by Korean Firms. Journal of Computer
Information Systems, 61(3), 285–293. https://doi.org/
10.1080/08874417.2019.1631133
Schüll, A., & Maslan, N. (2018). On the adoption of big
data analytics: Interdependencies of contextual factors.
ICEIS 2018 - Proceedings of the 20th International
Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, 1, 425–
431. https://doi.org/10.5220/0006759904250431
Şener, U., Gökalp, E., & Erhan Eren, P. (2016). Cloud-
based enterprise information systems: Determinants of
adoption in the context of organizations. Communica-
tions in Computer and Information Science, 639, 53–
66. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46254-7_5
Sharda, Ramesh., Delen, Dursun., & Turban, E. (2015).
Business intelligence and analytics: systems for
decision support (10th ed.). Pearson.
Sun, S., Cegielski, C. G., Jia, L., & Hall, D. J. (2018).
Understanding the Factors Affecting the Organizational
Adoption of Big Data. In Journal of Computer
Information Systems (Vol. 58, Issue 3, pp. 193–203).
Taylor and Francis Inc. https://doi.org/10.1080/0887
4417.2016.1222891
Sun, Z., Strang, K., & Firmin, S. (2017). Business analytics-
based enterprise information systems. Journal of
Computer Information Systems, 57(2), 169–178.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08874417.2016.1183977
Xu, W., Ou, P., & Fan, W. (2017). Antecedents of ERP
assimilation and its impact on ERP value: A TOE-based
model and empirical test. Information Systems
Frontiers, 19(1), 13–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/
s10796-015-9583-0
Adoption of Intelligent Information Systems: An Approach to the Colombian Context
31
