
How to Select Quantum Compilers and Quantum Computers Before
Compilation
Marie Salm
a
, Johanna Barzen
b
, Frank Leymann
c
and Philipp Wundrack
d
University of Stuttgart, Institute of Architecture of Application Systems,
Universitätsstraße 38, Stuttgart, Germany
Keywords:
Quantum Computing, NISQ Analyzer, Decision Support, Machine Learning, Prediction.
Abstract:
Quantum computers might solve specific problems faster than classical computers in the future. But their
actual qubit numbers are small, and the error rates are high. However, quantum computers are already used in
various areas and a steadily increasing number is made available by cloud providers. To execute a quantum
circuit, it is mapped to the quantum computer’s hardware. The resulting compiled circuit strongly influences the
precision of the execution in terms of occurring errors caused by used qubits and quantum gates. Selecting an
optimal one is, therefore, essential. SDKs are used to implement circuits and differ in supported cloud providers
and programming languages. These differences complicate a change to other backends. In previous work, we
developed an automated framework to translate a given circuit and compile it on available quantum computers
using multiple compilers. The compilation results can be prioritized and executed. Nevertheless, the translation
and compilation with all compilers and quantum computers is resource-intensive and does not scale well with
further backends in the future. We, therefore, present an extension to automatically select suitable compiler and
quantum computer combinations based on the user’s needs, e.g., for short waiting times and precise results
based on past executions. To demonstrate and validate our approach, we show a prototype and case study.
1 INTRODUCTION
Quantum computing is often seen as a promising tech-
nology of the future (National Academies of Sciences,
Engineering, and Medicine, 2019). Several experi-
ments showed an advantage of quantum computers
compared to classical computers for specific prob-
lems (Arute et al., 2019; Zhong et al., 2020). However,
the current Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ)
computers suffer from high error rates and offer only
a small number of qubits for computation (Preskill,
2018). Nevertheless, quantum computers are already
applied in different fields, such as finance, chemistry,
and computer science (Bova et al., 2021).
Cloud providers such as IBMQ and Google of-
fer access to steadily growing numbers of quantum
computers, also called Quantum Processing Units
(QPUs) (LaRose, 2019; Leymann et al., 2020; Buluta
et al., 2011). However, users of a growing community
often have to wait until their computations are exe-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2180-250X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8397-7973
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9123-259X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7606-6936
cuted on available quantum computers as the access
is usually managed by the cloud providers using, e.g.,
queues or time slices to be booked (LaRose, 2019;
Vietz et al., 2021). Quantum computations for gate-
based quantum computers are described with quantum
circuits consisting of quantum gates and qubits, analo-
gous to classical circuits (Nielsen and Chuang, 2011).
Users implement quantum circuits by commonly us-
ing Software Development Kits (SDKs). Besides the
implementation, the SDKs also offer the compilation
for supported quantum computers and the subsequent
execution of circuits (LaRose, 2019). The compilation
with a quantum compiler is required to map the de-
signed qubits and gates of the circuit to the physical
qubits and gates of the specific quantum computer,
which is NP-hard (Siraichi et al., 2018; Leymann and
Barzen, 2020). Thereby, existing quantum computers
differ in the supported sets of gates, the qubit connec-
tivity, and the appearing error rates. The resulting com-
piled circuits, thus, differ between individual backends
and used compilation methods (Kharkov et al., 2022;
Salm et al., 2021). The number of required qubits, i.e.,
the width, the numbers of single- and multi-qubit gates,
and the number of sequentially executable gates, i.e.,
172
Salm, M., Barzen, J., Leymann, F. and Wundrack, P.
How to Select Quantum Compilers and Quantum Computers Before Compilation.
DOI: 10.5220/0011775300003488
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER 2023), pages 172-183
ISBN: 978-989-758-650-7; ISSN: 2184-5042
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

the depth of the compiled circuit, affects the quality,
i.e., the precision of the execution result (Leymann and
Barzen, 2020; Salm et al., 2020b): With each qubit and
gate further errors can be introduced to the computa-
tion leading to deviations from the actual result. Thus,
the circuits to be executed on today’s NISQ computers
should be as small as possible (Salm et al., 2020a).
In recent years, the number of SDKs has
grown (Gill et al., 2022). They differ in supported
cloud providers and, therefore, the set of accessible
quantum computers, programming languages to imple-
ment circuits, provided compilers, and gates (LaRose,
2019; Gill et al., 2022). This variety makes it difficult
for the user to select an SDK for developing quan-
tum circuits. It complicates solving specific problems
using quantum computers that are suitable for the re-
quirements of the user, such as short waiting times and
precise execution results (Salm et al., 2022a,b).
In previous work, we developed an automated
framework that translates quantum circuits into several
programming languages (Salm et al., 2021). It enables
the exchange of circuits between different SDKs and
allows access to quantum computers offered by various
cloud providers. The compilation with several com-
pilers on available quantum computers is supported
to select optimal compilation results. Furthermore,
the executability regarding occurring errors is exam-
ined (Salm et al., 2020a). The executable compilation
results can be prioritized based on the requirements of
the user to finally execute selected ones on the suitable
quantum computers (Salm et al., 2022a,b).
However, the translation into the required program-
ming languages of supported SDKs and the compi-
lation with their various compilers on the available
quantum computers is resource-intensive. Moreover,
it gets more difficult with the increasing amount of
upcoming SDKs, compilers, and quantum computers.
Therefore, the first research question we want to tackle
with this work is the following:
RQ 1: How can quantum compilers and quantum
computers be automatically selected before the
translation and compilation of a given input circuit
targeting precise execution results of the future?
We extend the framework to (i) analyze the user’s
initial input circuit and (ii) select compilers and quan-
tum computers before the translation and compilation
based on prior execution results. We use machine learn-
ing (ML) algorithms and involve the user’s needs for
the selection. The extension reduces the number of
resources and improves the scalability of our approach.
Our second research question is, thereby, as follows:
RQ 2: Which quantum circuit and quantum com-
puter metrics are important to predict the precision
of future execution results for a given input circuit
before its translation and compilation?
Therefore, we present a (iii) prototype of the frame-
work and a (iv) case study. We compare the perfor-
mance and precision of various implementations of
several ML algorithms and examine the influence of
the input circuit and quantum computer properties,
i.e., metrics. We further investigate the runtime of our
pre-selection, compilation, and analysis approach.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2
presents fundamentals about the selected ML algo-
rithms. Sect. 3 focuses on the extension of our ap-
proach. In Sect. 4, the system architecture and pro-
totype are presented and validated with a case study
in Sect. 5. Sect. 6 discusses limitations, and Sect. 7
presents related work. In Sect. 8, our paper is con-
cluded and future work is presented.
2 PREDICTING RESULTS
Selecting quantum computers and compilers for a non-
compiled input circuit aiming at precise executions
requires predicting the precision of future results for
the different combinations. For the prediction, met-
rics of prior executed circuits and the related quantum
computers, the precision of their results, and the in-
fluence of the compilers must be considered. Salm
et al. (2022a) and Weder et al. (2021) collected sev-
eral circuit metrics describing its size, the numbers of
single- and multi-qubit gates, and measurement opera-
tions. Collected quantum computer metrics consider
the average error rates and times of supported gates,
measurement errors, and the decoherence times T1 and
T2, i.e., how long a specific quantum state is stable be-
fore getting too erroneous and flipping to another state.
The results on a quantum computer are compared to
the optimal results using histogram intersection (Swain
and Ballard, 1991) to measure the precision of an exe-
cution (Salm et al., 2022a,b): The considered circuit
is also executed on a quantum simulator without the
occurrence of errors. The received results of both back-
ends are often represented as histograms, and the his-
togram intersection is calculated by superimposing
them (Swain and Ballard, 1991). A histogram inter-
section value of 1 means total congruence, whereas 0
means total difference. ML algorithms can be used to
learn the dependencies between past histogram inter-
section values, quantum computer and circuit metric
values, and compilers. The actual input circuit and
data provided on the quantum computer used serve
How to Select Quantum Compilers and Quantum Computers Before Compilation
173

as input. The given data, except for the compilers, is
quantitative. The output is continuous and given for
the training data input, thus, the prediction is a super-
vised regression problem (Schuld et al., 2016; James
et al., 2021). The compilers are nominal categorical
data and must be converted into numerical data in a
pre-processing step using one-hot encoding (Cerda
et al., 2018). The categories, i.e., the
n
compilers are
represented by
n
distinct binary feature vectors with
n
dimensions. The vector of the
i
-th category has a 1 at
the
i
-th dimension, 0 elsewhere with 0
≤ i ≤ n
. Various
ML algorithms exist. We selected multiple linear re-
gression, Support Vector Regression (SVR), K-Nearest
Neighbors regression (KNN regression), and decision
trees as their implemented variants delivered the best
predictions in Sect. 5. Our plug-in-based system can
support further ML and encoding algorithms. For the
following, the predictors are our metric values and
compilers, responses are the histogram intersection
values, and observations are the sample data points.
2.1 Multiple Linear Regression
Multiple linear regression estimates the regression
coefficients of each predictor over all observations
such that the linear model suits well for the training
data (James et al., 2021). Thereby, predictors are as-
sumed to be linearly dependent on the observation. The
regression coefficient of a predictor describes the rela-
tionship between the predictor and the response. The
estimated coefficients can be applied to new predictors
to predict future responses.
2.2 Support Vector Regression
SVR bases on the Support Vector Machine
(SVM) (Vapnik, 1995) and is applicable for re-
gression problems (Awad and Khanna, 2015). SVR
forms a tube, serving as an error threshold around the
loss function to be estimated. Observations outside the
tube are punished, and those inside are ignored. The
goal of SVR is to find a minimal loss function with a
tube as flat as possible containing most of the given
data available for training.
2.3 K-Nearest Neighbors Regression
KNN regression is similar to KNN for classifica-
tion (James et al., 2021). For a new observation from
the test data, the
K
observations from the training data
closest to the new one are considered.
K
is given. The
response of the new observation is estimated by aver-
aging all given responses of the K observations.
2.4 Decision Trees
By repeatedly dividing predictors of the training data
into two non-overlapping regions, an upside-down
tree is built (De’ath and Fabricius, 2000; James et al.,
2021). The mean of all contained responses defines
each region (De’ath and Fabricius, 2000). Starting
from the root, the predictors are step-wise compared
with the splitting points of the related regions and as-
signed to the fitting region to predict an observation’s
response (James et al., 2021). At the bottom, the re-
sponse is determined as the mean value of the region.
3 APPROACH
To address RQ1, we present the extension of our ap-
proach from Salm et al. (2020a, 2021, 2022a,b) to
select quantum compilers and quantum computers be-
fore translating and compiling a given input circuit
based on prior execution results and the requirements
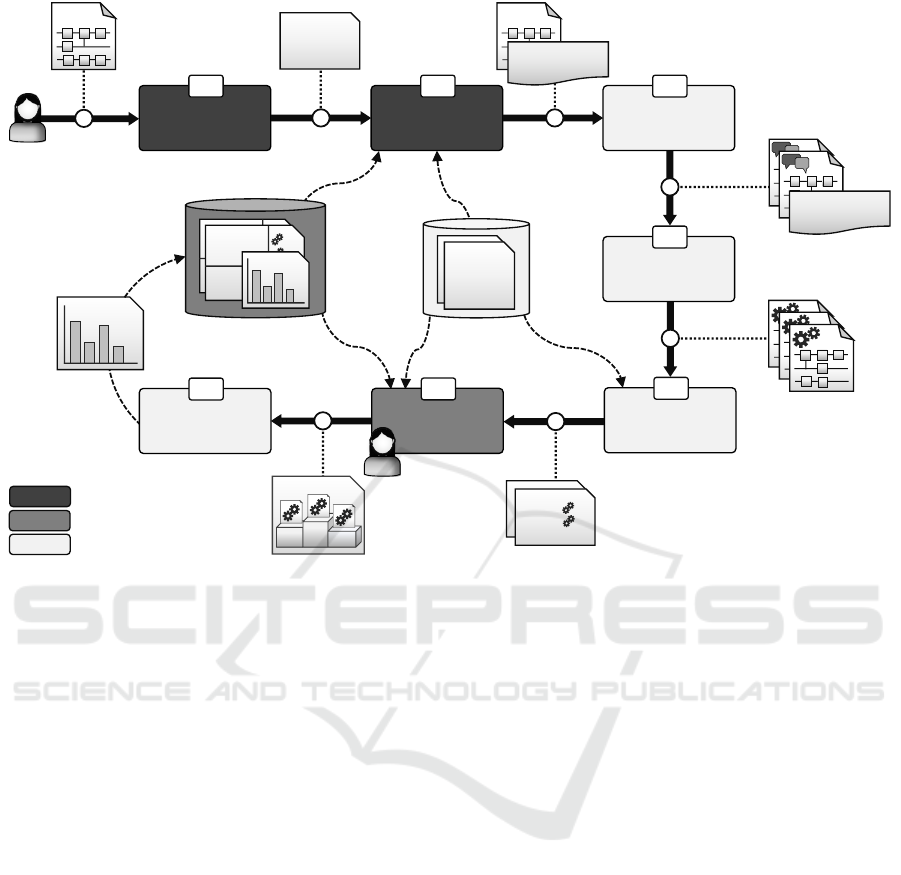
of the user, illustrated in Fig. 1.
3.1 Circuit Analysis
The input circuit of the user must be analyzed to select
available compilers and quantum computers based on
the user’s needs. In the (1) Circuit Analysis phase, the
user decides if they want to target precise execution
results, short waiting times until execution, or both in
combination. If the user desires a combination, they
can define the ratio between short waiting times and
precise execution results, e.g., 50:50 or 30:70. The
user can also specify a threshold how many compiled
circuits should at most be returned after compilation.
Afterward, the input circuit is analyzed based on the
circuit metrics collected by Salm et al. (2022a), such as
the number of operations, the number of single-qubit
gates, and the multi-qubit gate depth, i.e., the longest
path in the circuit only considering multi-qubit gates.
3.2 Compiler & QPU Pre-Selection
The analyzed metric values of the input circuit are
handed over to the (2) Compiler & QPU Pre-Selection
phase. In the first step, the actual data of available
quantum computers is requested from the provenance
system QProv (Weder et al., 2021). QProv collects and
stores current data and metric values of available quan-
tum computers, such as the average gate errors and
times, and the average decoherence times. If the user
requires short waiting times until the execution, the
actual waiting times, e.g., queue lengths of the quan-
tum computers, are considered (Salm et al., 2022a).
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
174
Depth 56
Width 5
... ...
Compiler & QPU
Pre-Selection
2
Circuit Analysis
1
Translation
3
Compilation
4
Compilation Result
Analysis
5
Prioritization
6
Execution
7
Compilers & QPUs
Translated Circuits,
Compiled Circuits
Circuit
Results
Measurement
t|ket⟩ + IBMQ_5
Qiskit + IBMQ_7
...
Compiled Circuits
Ranking of
1.
3.
2.
Depth 23
Width 5
... ...
t|ket⟩ + IBMQ_5
Qiskit + IBMQ_7
...
Prior Metric Values
& Measurement Results
Depth 32 52
Width 5 5
... ... ...
T1 0.02
T2 0.04
... ...
Depth 32 52
Width 5 5
... ... ...
T1 0.02
T2 0.04
... ...
Circuit Metric
Values
Circuit, QPUs &
Compilers
Compiled Circuit
Metric Values
= old components
= adapted components
= new components
QProv
Depth 56
Width 5
... ...
T1 0.02
IBMQ_5
T2 0.04
... ...
Figure 1: Automated selection, translation, compilation, and prioritization for quantum circuits. Extending Salm et al. (2022b).
Next, each entity of a quantum computer is multiplied
by each entity of a compiler that natively supports the
quantum computer. The overall sum defines the num-
ber of all possible quantum computer and compiler
combinations. Then, the resulting combinations are
sorted ascending based on the queue length and short-
ened by the threshold the user defined as the maximum
number of compilation results in Sect. 3.1.
If precise execution results are desired, the user
can choose between implementations of the ML al-
gorithms multiple linear regression, SVR, KNN re-
gression, and decision trees, described in Sect. 2, to
predict the precision of future results with the different
combinations. Decision trees are selected by default,
as they return the best results based on our case study,
see Sect. 5. The chosen ML algorithm accesses stored
metric values of all diverse input circuits executed in
the past, the used compilers, and the metric values of
the quantum computers on which they were executed.
Furthermore, the ML algorithm obtains the histogram
intersection values of the related past execution results.
If no prior data is available for learning, the (2) Com-
piler & QPU Pre-Selection phase targeting the desire
of precise execution results has to be skipped and all
available quantum computer and compiler combina-
tions are considered. In the other case, the prior metric
values and compilers serve as input, whereas the re-
lated histogram intersection values serve as a target to
train the ML algorithm, as described in Sect. 2. The
input values are normalized, and the objective is to
minimize the mean difference between the histogram
intersection values predicted by the ML algorithm and
the true histogram intersection values. The actual met-
ric values of the input circuit and the quantum com-
puters serve as input. The result is a list of predicted
histogram intersection values for the different quan-
tum computer and compiler combinations. It is sorted
descending by the histogram intersection values and
shortened by the threshold of the user from Sect. 3.1.
In the case the user requests estimations regarding
precise execution results and short waiting times, first,
the sorted lists regarding waiting times and precise
execution results are created separately, as described
previously, but not yet shortened. Instead, the common
Borda count method is used to combine the two sorted
lists (B ˛aczkiewicz et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2009): For
each list, the quantum computer and compiler combi-
nation in the first place gets
n −
1 points, in the sec-
ond place
n −
2 points, and so on, until the last place
gets 0 points, where
n
is the number of combinations.
Then, the received points for each combination are
summarized and based on the total points, a new list of
combinations in descending order is created. Suppose,
the user selected a ratio of precise execution results
and waiting times different to 50:50. In that case, the
assigned points for each combination on each list are
How to Select Quantum Compilers and Quantum Computers Before Compilation
175

multiplied by the related defined percentage (Russell,
2007). For example, the user has chosen a ratio of
70:30 for precise results and waiting times. The points
on the ordered list regarding precise results are multi-
plied by 0.7, whereas the points on the list for waiting
times are multiplied by 0.3 and then summed up as
described. Finally, the new combined and ordered list
of quantum computer and compiler combinations is
shortened by the user’s threshold.
3.3 Translation
For the previously selected compilers, it is checked
if the programming language that was used to im-
plement the given input circuit is supported by their
SDKs (Salm et al., 2021). If it is not the case, the
circuit is automatically translated into the required
formats in the (3) Translation phase.
3.4 Compilation
The translated quantum circuits and the list of selected
quantum compiler and quantum computer combina-
tions is input for the (4) Compilation phase (Salm et al.,
2020a, 2021). The selected compilers map the related
translated circuits to the selected quantum computers.
One circuit is also compiled on an available quantum
simulator to later calculate the execution result without
the appearance of errors (Salm et al., 2022a).
3.5 Compilation Result Analysis
In the (5) Compilation Result Analysis phase, the com-
piled circuits are again analyzed based on the metrics
collected by Salm et al. (2022a). Their structures and
sizes commonly change with the mapping to the hard-
ware. The compilation results are selected based on
evaluating their executability on the target quantum
computers, as shown by Salm et al. (2020a). QProv is
invoked to gain the required quantum computer data.
3.6 Prioritization
The minimized list of pre-selected and executable com-
pilation results with their related quantum computers
is presented to the user. As described by Salm et al.
(2022b), in the (6) Prioritization phase, the user can
prioritize the list based on their own or pre-defined
requirements, such as short waiting times and pre-
cise execution results. Based on the need for precise
future execution results, in comparison to Sect. 3.2,
the metric values of the remaining hardware-specific
compiled circuits ready to be executed are used to
calculate an accurate ranking. The metric values of
related quantum computers are received from QProv.
An optimizer calculates the relevance of the individual
metrics based on metric values and execution results
of prior compilation results and related quantum com-
puter data (Salm et al., 2022b). The resulting weights
determine the ranking via one of the supported multi-
criteria decision analysis methods (Salm et al., 2022a).
If the user requires a combination of short waiting
times and precise results, they can define the ratio
between both via weighted Borda count, described
in Sect. 3.1 and Sect. 3.2. The user can analyze the
sensitivity of the resulting ranking (Salm et al., 2022b).
3.7 Execution
In the (7) Execution phase, the user selects the priori-
tized compilation results to be executed (Salm et al.,
2020a). Besides executing the selected circuit on the
target quantum computer, one circuit is also executed
on a simulator if it offers enough resources for sim-
ulation. Suppose all execution results are received.
Then, the histogram intersection value is calculated
and stored with the compiler and the metric values of
the input circuit, the compiled circuit, and the quantum
computer for future selection and prioritization.
4 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE &
PROTOTYPE
This section shows the system architecture and proto-
type of the approach we presented in Sect. 3.
4.1 System Architecture
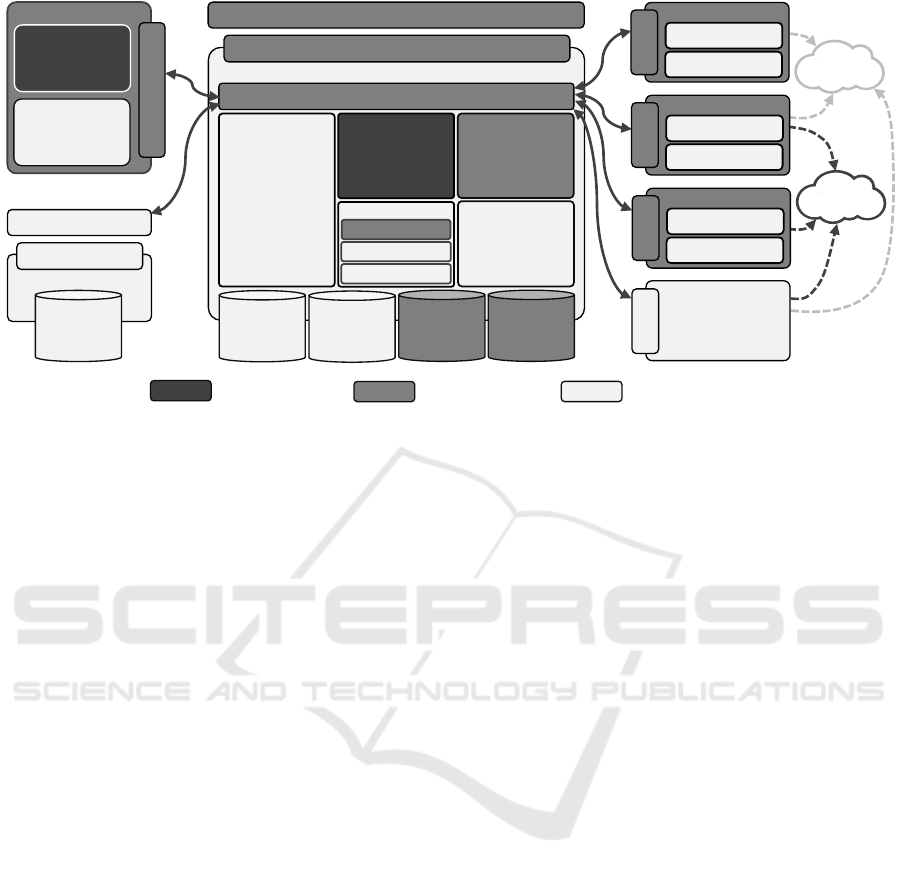
Fig. 2 presents the overall system architecture (Salm
et al., 2020a, 2021, 2022a,b). The Predict & Prio Ser-
vice on the top left of Fig. 2 contains the Prediction
Algorithms, i.e., ML algorithms, explained in Sect. 2,
to estimate future execution results of a given input cir-
cuit based on prior data, as described in Sect. 3.2. Fur-
thermore, it applies the weighted Borda count method
to combine the diverse requirements of the user. The
HTTP REST API of the Predict & Prio Service is
adapted to support these new features. The service
also supports different methods to prioritize compiled
circuits, as described in previous work. The Translator
component in the bottom left of Fig. 2 translates the
input circuit into the required programming languages
of the selected compilers. The NISQ Analyzer UI and
the HTTP REST API of the NISQ Analyzer, in the
middle of Fig. 2, are extended to support the user in
defining their needs for the pre-selection, compilation,
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
176
NISQ Analyzer
REST API
NISQ Analyzer UI
Connector
Rule Handler
Metrics,
Weights,
Rankings
Selector
Comp. Selector
QPU Selector
Impl. Selector
Performance
Extractor
Results
Algorithms,
Impl., SDKs
Selection
Rules
Rigetti
Forest Service
Quilc
Executor
REST API
QProv
REST API
pytket Service
t|ket⟩
Executor
REST API
IBMQ
REST API
Predict & Prio Service
Prioritization
Methods
Translator
REST API
Translator UI
Gate
Mappings
Transpiler
Executor
Qiskit Service
REST API
Prioritizer
Prediction
Algorithms
Pre-Selector
= old components
= adapted components
= new components
Figure 2: System architecture to select quantum computers and compilers. Extending Salm et al. (2022b).
prioritization, and execution of quantum computers.
The Pre-Selector coordinates the collection of the ac-
tual input circuit and quantum computer metric val-
ues by invoking QProv and the SDK Services (Fig. 2,
right). The SDK Services wrap supported SDKs and
uniformly offer their compilers and execution func-
tionalities. They are extended to enable the analysis
of non-compiled input circuits. The Pre-Selector also
collects prior input circuit and quantum computer met-
ric values and sends the data and the user’s specified
requirements to the Prediction Algorithms via the Con-
nector. The Compiler Selector invokes the Translator
if required, and afterward, the SDK Services contain-
ing the selected compilers with the quantum comput-
ers to be considered for compilation. The Prioritizer
coordinates the data collection and invocation of Pri-
oritization Methods to prioritize compiled circuits and
is extended to enable the user to specify the ratio for
weighted Borda count to combine pre-defined needs,
as explained in Sect. 3.6. The selected lists of compiler
and quantum computer combinations and the metric
values of the input circuit are stored in repositories.
The user initiates the analysis and selection pro-
cess by selecting the input circuit and defining their
requirements in the UI. The user selects between short
waiting times and precise execution results and defines
the ratio if both must be considered. Furthermore, they
choose the maximum number of returning compilation
results and, in the case of precise execution results, the
Prediction Algorithm. The Pre-Selector calls an SDK
Service that supports the programming language of the
input circuit over the Connector to analyze the input
circuit based on the defined metrics. Additionally, the
Pre-Selector invokes QProv to retrieve actual metric
values of available quantum computers. The compo-
nent also collects metric values of prior input circuits
and related quantum computers, corresponding his-
togram intersection values, and used compilers. The
data retrieved and the constraints set by the user are
sent to the Predict & Prio Service via the Connector.
If the user desires short waiting times, the num-
ber of available quantum computers is multiplied by
the number of compilers, as described in Sect. 3.2.
The list is sorted based on the actual queue length
and shortened by the user’s threshold. If precise ex-
ecution results are required, the selected Prediction
Algorithm is invoked to predict the precision of future
execution results for the different quantum computer
and compiler combinations based on the prior data.
The Prediction Algorithm returns a list of all combi-
nations sorted by the estimated histogram intersection
values, which is then shortened. If short waiting times
and precise execution results are desired, both lists
are calculated separately. Weighted Borda count is ap-
plied as described in Sect. 3, and the combined list
is shortened. The resulting list is returned to the Pre-
Selector and stored in a repository. The Pre-Selector
invokes the Compiler Selector that invokes the Trans-
lator if one of the selected compilers requires another
programming language. Afterward, the Compiler Se-
lector sends the circuits to be compiled and the name
of the target quantum computers to the SDK Services
of the selected compilers. The QPU Selector of the
NISQ Analyzer examines the executability of the re-
turned compilation results. The user can prioritize the
executable compilation results via the Prioritization
Methods described by Salm et al. (2022b). Finally,
the calculated ranking is shown to the user. The user
How to Select Quantum Compilers and Quantum Computers Before Compilation
177

selects which compilation results should be executed
with the Executors of the related SDK Services on the
target quantum computer in parallel with the simulator.
With the extensibility of our plug-in-based system, fur-
ther Prediction Algorithms, programming languages,
metrics, and SDK Services can be added.
4.2 Prototype
The NISQ Analyzer and QProv are implemented in
Java using the framework Spring Boot. The UIs are
implemented in TypeScript with Angular. The SDK
Services, the Translator, and the Predict & Prio Ser-
vice are implemented in Python using Flask. Imple-
mentation details of existing components can be read
in previous work (Salm et al., 2022b,a, 2021, 2020a).
The prototypical implementation of our approach is
available open-source (University of Stuttgart, 2023b).
To support prediction algorithms, we use the
Python library scikit-learn
1
, which offers various ML
algorithms (Pedregosa et al., 2011). We tested all ML
algorithm implementations for regression of scikit-
learn available when the paper was written. The list
of all considered ML algorithm implementations and
applied settings can be viewed online (University of
Stuttgart, 2023c). We integrated the best performing
implementations from Sect. 5 which are different vari-
ants of the ML algorithms explained in Sect. 2: Our
prototype supports TheilSenRegressor (TSR) as a vari-
ant of multiple linear regression. We offer KNeigh-
borsRegressor (KNNR) as KNN regression. We sup-
port NuSVR as an implementation of SVR. Addition-
ally, the prototype offers ExtraTreesRegressor (ETR),
GradientBoostingRegressor (GBR), RandomForestRe-
gressor (RFR), and HistGradientBoostingRegressor
(HGBR), which are variants that combine multiple
decision trees. We implemented DecisionTreeRegres-
sor (DTR) for simple decision trees. Thereby, we con-
sidered every implementation stand-alone, with Ad-
aBoostRegressor (ABR) (Freund and Schapire, 1997),
and BaggingRegressor (BR) (Breiman, 1996). ABR
is a meta-estimator that applies the given regression
algorithm several times on the data set and slightly
adjusts the settings based on the latest estimation (Fre-
und and Schapire, 1997). Also, BR is a meta-estimator
whereby the regression algorithm to be considered is
applied several times on random subsets of the data,
and the outcomes are combined to form a single pre-
diction (Breiman, 1996). For the one-hot encoding of
the compilers, described in Sect. 2, we support the
OneHotEncoder implementation of scikit-learn.
1
https://scikit-learn.org
5 CASE STUDY
This section summarizes the case study of the approach
from Sect. 3. We compare the supported ML algorithm
implementations from Sect. 4.2 regarding their perfor-
mance of predicting histogram intersection values for
different quantum computer and compiler combina-
tions. Then, we analyze the quantum computer and
input circuits metrics and the compilers to investigate
their influence on the precision of execution results, an-
swering RQ2. Furthermore, we examine the precision
of the implementations and investigate the runtime of
the pre-selection, compilation, and analysis process.
An example of a predicted ranking of quantum com-
puter and compiler combinations regarding precise
execution results and short waiting times with a ra-
tio of 70:30 using weighted Borda count and ETR is
shown online (University of Stuttgart, 2023a).
The basis of our evaluation is the data set created
by Salm et al. (2022b). We compiled 52 input circuits
with the t
|
ket
⟩
compiler (Sivarajah et al., 2020) and
the Qiskit Transpiler (Aleksandrowicz et al., 2019) us-
ing the highest circuit optimization level (Salm et al.,
2022b). We considered the free accessible ibmq_lima,
ibmq_quito, ibmq_belem, and ibmq_bogota as target 5-
qubit quantum computers of the cloud provider IBMQ
and the ibmq_qasm_simulator to compute the his-
togram intersection values. The circuit set contains
three algorithmic circuits from Salm et al. (2022a), and
generated randomized Clifford gate circuits, where the
non-erroneous results are equal to the initial states,
such that a simulator is not required for histogram in-
tersection (Magesan et al., 2012; Salm et al., 2022b).
The randomized circuits have widths between three
and five qubits and depths between 11 and 355 single-
and two-qubit gates (Salm et al., 2022b). The data set
can be seen online (University of Stuttgart, 2023a). It
contains 229 samples, i.e., compiled circuits that were
successfully executed, and 16 features, listed in Fig. 4.
5.1 Performance of ML Algorithms
To evaluate the performance of the considered ML
algorithm implementations from Sect. 4.2, we use the
well-known
k
-fold cross-validation and split the data
set randomly into five folds, i.e.,
k
= 5, of similar
size (James et al., 2021). We control the splitting such
that compilation and execution results of the same
input circuit are part of the same fold to simulate the
handling of circuits that haven’t been considered yet;
thus, a more realistic scenario. The first fold is the test
set, whereas the
k −
1 other folds build the training
set. Then, the often-used mean error is calculated due
to its easy interpretability (Willmott and Matsuura,
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
178
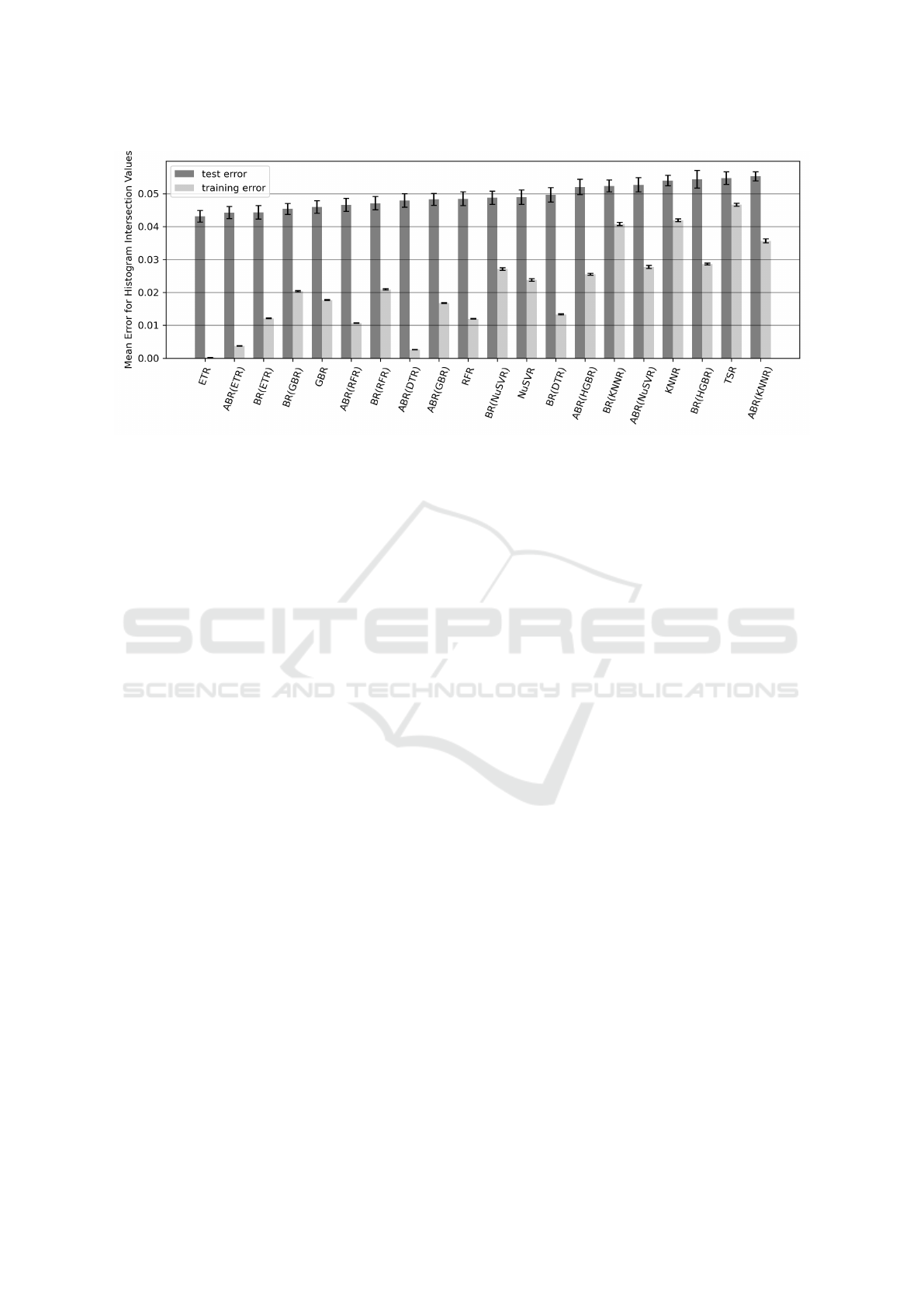
Figure 3: Mean error of the 20 best supported ML algorithm implementations.
2005; Yildiz et al., 2017). Each fold is iteratively the
first fold. The mean error of all iterations is averaged.
This procedure is repeated ten times and the training
is repeated 50 times for each implementation. The
standard error of the mean (SEM) is determined by
calculating the variance of the 50 results divided by
the root of 50 (Altman and Bland, 2005).
Fig. 3 presents the mean error over the 50 repeti-
tions for the 20 best implementations based on our test
and training data setup. The error bar represents the
SEM. The performance and the execution times of all
implementations can be viewed online (University of
Stuttgart, 2023a). A slight decrease in the implemen-
tations’ performances regarding the test data can be
seen. ETR and ETR in combination with ABR and BR
deliver the smallest test errors on average, followed
by GBR, RFR, and DTR. Their predicted histogram
intersection values on the test data are on average be-
tween 0.04 and 0.05 above or below the actual values.
Thus, the decision tree variants deliver the best his-
togram intersection value estimations. NuSVR with
BR is in the eleventh place in the middle, followed
by its stand-alone variant. KNNR with BR is in the
fifteenth place with a mean error over 0.05. Multiple
linear regression implemented with TSR seems to be
one of the worst-performing ML algorithms in our case
study regarding the test error. Nevertheless, especially
in the first places of Fig. 3, the mean training error is
by far smaller than the related test error, also known as
overfitting (James et al., 2021). Overfitting means that
the ML algorithm implementations in the first place
are less flexible and learn patterns that do not occur in
the test data compared to the implementations in the
second half of the ranking, where the training error is
much higher. The SEM seem to be in a similar range
in Fig. 3 compared over the different implementations.
5.2 Influence of Metrics
To investigate the influence of the individual metrics,
we apply the permutation feature importance method
of scikit-learn (Breiman, 2001). We also consider the
one-hot encoded compilers to examine their impact
on the predictions. Thereby, an ML algorithm imple-
mentation learns on a data set where for an individual
feature, i.e., our metrics and compilers, its value is
replaced randomly by another given value of this fea-
ture in the data set. The method dissolves the feature’s
dependency on the response, and the estimation’s de-
terioration represents the feature’s influence. The pro-
cess is executed ten times for each feature. Then, we
repeat the overall procedure ten times and calculate
the average distance to the non-disturbed response.
Fig. 4 presents the individual importance’s dis-
tribution and mean of all features calculated with
the 20 best-performing ML algorithm implementa-
tions of Sect. 5.1. Some of the tested implementations
of Sect. 4.2 failed with the application of feature impor-
tance and returned invalid results. The list of results
of all implementations is shown online (University
of Stuttgart, 2023a). It seems that the t
|
ket
⟩
compiler
has, in general, more influence on predicting precise
execution results than the Qiskit Transpiler. The cir-
cuit metrics width, depth, and multi-qubit gate depth
influence the prediction models similarly. Also, the
comparatively more important total number of opera-
tions and the number of single-qubit gates are similar
in their influence. Whereby the total number of opera-
tions can slightly have higher importance. The number
of measurement operations follows with a difference
of 0.1 less mean importance. The most influencing
metric in Fig. 4 seems to be the number of multi-qubit
gates, whose importance is also stated by other work
How to Select Quantum Compilers and Quantum Computers Before Compilation
179

Figure 4: Feature importance measured by the 20 best-performing ML algorithm implementations.
because of their high error rates (Sivarajah et al., 2020;
Salm et al., 2022b). The influence of the quantum com-
puter metrics is relatively low, with values smaller than
0.05, compared to the metrics for non-compiled input
circuits. The single-qubit gate time, thereby, has the
smallest importance equal to 0.
5.3 Precision of Pre-Selection
We examine the precision of the best-performing im-
plementations of Sect. 5.1 by step-wise decreasing the
threshold of the maximum number of compiler and
quantum computer combinations to be returned, as de-
scribed in Sect. 3. Thereby, we analyze if the combina-
tion with the most precise real histogram intersection
value is in the returned set. As presented in Sect. 5.1,
we apply ten times 5-fold cross-validation. Fig. 5
shows the probability of returning the best combination
dependent on the percentage of removed combinations
using the five best-performing implementations. The
precision of the 20 best-performing implementations
can be found online (University of Stuttgart, 2023a).
By removing 50% of all possible combinations within
the Compiler & QPU Pre-Selection phase (Sect. 3.2),
the best combination is kept with a probability of over
80%. Removing 90% of all combinations keeps the
best combination with over 50% probability. The dif-
ferent variants of ETR show a higher precision com-
pared to BR(GBR) and GBR.
5.4 Runtime Analysis
We investigate how much the pre-selection approach
reduces the runtime of our framework with the re-
quirement of precise executions applying the best-
performing implementation ABR(ETR). Thus, we
measure the overall runtime of the phases Circuit Anal-
Figure 5: Precision of the five best-performing ML algorithm
implementations for different thresholds.
ysis, Compiler & QPU Pre-Selection, Compilation,
and Compilation Result Analysis, described in Sect. 3.
Based on the precision shown in Fig. 5, we set thresh-
olds such that 0%, 50%, 70%, and 90% of all possible
compiler and quantum computer combinations are re-
moved for three different circuits. As a first attempt,
we considered an algorithmic implementation with
three qubits (Gr3) and a depth of 14 and two random-
ized circuits with four (RC4) and five (RC5) qubits
and depths of 85 and 77. We used the t
|
ket
⟩
compiler
and the Qiskit Transpiler with six quantum computers
of IBMQ, resulting in 12 combinations in addition to
one compiler and simulator combination. All circuit
and quantum computer metric values can be seen on-
line (University of Stuttgart, 2023a). We repeat the
process for each circuit and threshold combination ten
times and calculate the median, as shown in Table 1.
The framework was executed on a MacBook Pro
running Ventura 13.1 with a 2,4 GHz Quad-Core Intel
Core i5 processor and 16 GB of RAM.
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
180

Table 1: Median runtimes of our approach removing various
percentages of compiler-QPU-combinations (in seconds).
Circuit 0% 50% 70% 90%
Gr3 84.34 51.72 42.01 31.56
RC4 108.80 63.05 51.49 39.32
RC5 109.81 65.65 54.39 42.88
Table 1 shows that setting the threshold such that
50% of all possible combinations are removed during
pre-selection reduces the median runtime by around
40%. Removing 70% compared to 50% reduces the
runtime by an additional 18%. Lowering the full set
by 90% such that one compiler and quantum computer
as well as one simulator combination remains, reduces
the overall runtime by around 62%. Compiling circuits
with higher depths seems to require more runtime.
6 DISCUSSION
Our case study in Sect. 5 only covers 5-qubit quan-
tum computers and, besides randomized circuits, only
a few algorithmic circuits which are closer to real-
world applications (Salm et al., 2022b). The first at-
tempt of analyzing the runtime reduction with our pre-
selection approach does not include the Translation
phase from Sect. 3.3. Nevertheless, it shows that the
extension reduces the computation time of our frame-
work by up to 62% and we want to examine the run-
time more extensive in the future. The pre-selection of
quantum computer and compiler combinations is only
possible if histogram intersection values of prior input
circuits are available. However, the ML algorithms can
learn on the data of various input circuits and are not
dependent on past results of the same circuit. Translat-
ing a circuit can change its size because gates that are
not supported by the target compiler and SDK must
be replaced by subroutines of supported gates, increas-
ing the total number (Leymann and Barzen, 2020).
The translated circuit could cause more errors and less
precise execution results. An additional selection step
could be added after the translation phase in Sect. 3.3.
However, another selection could also increase the risk
of sorting out quantum computer and compiler combi-
nations that may have led to precise execution results.
No monetary metrics are considered, but further met-
rics can be supported by our framework.
7 RELATED WORK
Selecting suitable resources for a given use case is
a common problem in various areas, such as cloud
computing. For example, Sáez et al. (2014) and Sáez
et al. (2016) propose approaches of a decision support
system guiding the user to distribute their applications
to multiple clouds. Their target is to choose and con-
figure cloud services based on changing workloads
and requirements. Peddi (2016) present a survey about
resource allocation methods for the cloud. The study
suggests ML to predict required resources based on
given prior data. Islam et al. (2012) propose a pre-
diction framework to enable the automated scaling
of resources regarding future workload using linear
regression and error correction neural networks. The
work of Verma et al. (2016) presents a framework
that predicts and allocates resources for multi-tenant
systems in the cloud using several ML algorithms.
However, the presented approaches do not consider
resource prediction in the field of quantum computing.
Several approaches exist that compare the perfor-
mance of quantum compilers on different quantum
computers (Sivarajah et al., 2020; Amy and Gheorghiu,
2020; Mills et al., 2021). Kharkov et al. (2022) present
a framework to enable the automated benchmarking
of various compilers. The work of Proctor et al. (2022)
presents benchmarks to enable predicting whether a
circuit is executable on a certain quantum computer
based on collected error rates. However, none of these
works propose the automated selection of compilers
and quantum computers based on prior data and a
given input circuit before the compilation. Quetschlich
et al. (2022) present a framework that automatically
selects the best combination of quantum technologies,
quantum computers, compilers, and compiler settings
based on a given input circuit using ML algorithms.
They evaluate the execution result precision by consid-
ering the gate fidelity and measurement fidelity of the
available gates and qubits. Nevertheless, they do not
support the automated collection of up-to-date quan-
tum computer data (Weder et al., 2021) and do not
provide automated translation, SDK handling, and ex-
ecution for the input circuit. They also do not enable
the user to specify their own requirements and, e.g.,
besides precise execution results, support considering
short waiting times to a certain extent.
8 CONCLUSION
We presented an extension of our approach that auto-
matically selects quantum computers and compilers
for a given circuit before the translation and compila-
tion, supporting resource-saving and scalability. The
user can choose short waiting times until execution,
precise future execution results, or define a ratio con-
sidering a combination of both as a selection objective.
How to Select Quantum Compilers and Quantum Computers Before Compilation
181

To answer RQ1, we use ML to predict the precision of
future execution results based on executions of other
input circuits in the past. We reported a case study that
compared the prediction performance and precision
of various ML algorithm implementations. To answer
RQ2, we examined the influence on the execution re-
sults’ precision in dependence to the compilers and the
metrics for quantum computers and input circuits, iden-
tified by Salm et al. (2022a). The case study presented
that, especially, the number of multi-qubit gates has
strong influence, even regarding non-compiled circuits.
We showed a first attempt to analyze the runtime reduc-
tion of our framework with our pre-selection extension
and measured a time saving of up to 62%.
In the future, we want to expand our sample data
by considering further quantum computers and various
input circuits. We plan to extend the runtime analysis
of our framework by including the translation process
and considering additional quantum circuits. Further-
more, we plan to support additional SDK Services
and examine further metrics to estimate the precision
of executions on today’s NISQ computers. We also
want to enable an estimation of monetary aspects to
further support the user in selecting compiled circuits
and quantum computers based on their needs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially funded by the BMWK project
PlanQK(01MK20005N).
REFERENCES
Aleksandrowicz, G. et al. (2019). Qiskit: An Open-source
Framework for Quantum Computing.
Altman, D. G. and Bland, J. M. (2005). Standard deviations
and standard errors. Bmj, 331(7521):903.
Amy, M. and Gheorghiu, V. (2020). staq—a full-stack quan-
tum processing toolkit. Quantum Science and Technol-
ogy, 5(3):034016.
Arute, F. et al. (2019). Quantum supremacy using a
programmable superconducting processor. Nature,
574(7779):505–510.
Awad, M. and Khanna, R. (2015). Support Vector Regression,
pages 67–80. Apress, Berkeley, CA.
Bova, F., Goldfarb, A., and Melko, R. G. (2021). Commer-
cial applications of quantum computing. EPJ quantum
technology, 8(1):2.
Breiman, L. (1996). Bagging predictors. Machine Learning,
24(2):123–140.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine learning,
45(1):5–32.
Buluta, I., Ashhab, S., and Nori, F. (2011). Natural and
artificial atoms for quantum computation. Reports on
Progress in Physics, 74(10):104401.
B ˛aczkiewicz, A., Kizielewicz, B., Shekhovtsov, A., W ˛atrób-
ski, J., and Sałabun, W. (2021). Methodical Aspects
of MCDM Based E-Commerce Recommender Sys-
tem. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic
Commerce Research, 16(6):2192–2229.
Cerda, P., Varoquaux, G., and Kégl, B. (2018). Similarity En-
coding for Learning with Dirty Categorical Variables.
Mach. Learn., 107(8–10):1477–1494.
De’ath, G. and Fabricius, K. E. (2000). Classification and
regression trees: A powerful yet simple technique for
ecological data analysis. Ecology, 81(11):3178–3192.
Freund, Y. and Schapire, R. E. (1997). A Decision-Theoretic
Generalization of On-Line Learning and an Applica-
tion to Boosting. Journal of Computer and System
Sciences, 55(1):119–139.
Gill, S. S. et al. (2022). Quantum computing: A taxon-
omy, systematic review and future directions. Software:
Practice and Experience, 52(1):66–114.
Islam, S., Keung, J., Lee, K., and Liu, A. (2012). Empirical
prediction models for adaptive resource provisioning
in the cloud. Future Generation Computer Systems,
28(1):155–162.
James, G., Witten, D., Hastie, T., and Tibshirani, R. (2021).
Linear Regression, pages 59–128. Springer US, New
York, NY.
Kharkov, Y., Ivanova, A., Mikhantiev, E., and Kotelnikov, A.
(2022). Arline Benchmarks: Automated Benchmarking
Platform for Quantum Compilers.
LaRose, R. (2019). Overview and Comparison of Gate Level
Quantum Software Platforms. Quantum, 3:130.
Leymann, F. and Barzen, J. (2020). The bitter truth about
gate-based quantum algorithms in the NISQ era. Quan-
tum Science and Technology, 5(4):1–28.
Leymann, F., Barzen, J., Falkenthal, M., Vietz, D., Weder,
B., and Wild, K. (2020). Quantum in the Cloud:
Application Potentials and Research Opportunities.
In Proceedings of the 10
th
International Conference
on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER
2020), pages 9–24. SciTePress.
Magesan, E. et al. (2012). Efficient measurement of quantum
gate error by interleaved randomized benchmarking.
Phys. Rev. Lett., 109:080505.
Mills, D., Sivarajah, S., Scholten, T. L., and Duncan, R.
(2021). Application-motivated, holistic benchmarking
of a full quantum computing stack.
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine
(2019). Quantum Computing: Progress and Prospects.
The National Academies Press.
Nielsen, M. A. and Chuang, I. L. (2011). Quantum Computa-
tion and Quantum Information. Cambridge University
Press, 10th edition.
Peddi, P. (2016). Comparative study on cloud optimized
resource and prediction using machine learning algo-
rithm. ISSN: 2455, 6300:88–94.
Pedregosa, F. et al. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine Learning
in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
12:2825–2830.
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
182

Preskill, J. (2018). Quantum Computing in the NISQ era
and beyond. Quantum, 2:79.
Proctor, T., Rudinger, K., Young, K., Nielsen, E., and Blume-
Kohout, R. (2022). Measuring the capabilities of quan-
tum computers. Nature Physics, 18(1):75–79.
Quetschlich, N., Burgholzer, L., and Wille, R. (2022). Pre-
dicting Good Quantum Circuit Compilation Options.
Russell, N. (2007). Complexity of control of Borda count
elections.
Sáez, S. G., Andrikopoulos, V., and Leymann, F. (2016).
Consolidation of Performance and Workload Models
in Evolving Cloud Application Topologies. In Proceed-
ings of the 6th International Conference on Cloud Com-
puting and Service Science (CLOSER 2016), pages
160–169, Rome, Italy. SciTePress.
Salm, M., Barzen, J., Breitenbücher, U., Leymann, F., Weder,
B., and Wild, K. (2020a). The NISQ Analyzer: Au-
tomating the Selection of Quantum Computers for
Quantum Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 14th Sym-
posium and Summer School on Service-Oriented Com-
puting (SummerSOC 2020), pages 66–85. Springer In-
ternational Publishing.
Salm, M., Barzen, J., Leymann, F., and Weder, B. (2020b).
About a Criterion of Successfully Executing a Circuit
in the NISQ Era: What
wd ≪
1
/ε
eff
Really Means. In
Proceedings of the 1st ACM SIGSOFT International
Workshop on Architectures and Paradigms for Engi-
neering Quantum Software (APEQS 2020), pages 10–
13. ACM.
Salm, M., Barzen, J., Leymann, F., and Weder, B. (2022a).
Prioritization of Compiled Quantum Circuits for Differ-
ent Quantum Computers. In Proceedings of the 2022
IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis,
Evolution and Reengineering (SANER 2022), pages
1258–1265. IEEE.
Salm, M., Barzen, J., Leymann, F., Weder, B., and Wild,
K. (2021). Automating the Comparison of Quantum
Compilers for Quantum Circuits. In Proceedings of
the 15
th
Symposium and Summer School on Service-
Oriented Computing (SummerSOC 2021), pages 64–80.
Springer International Publishing.
Salm, M., Barzen, J., Leymann, F., and Wundrack, P. (2022b).
Optimizing the Prioritization of Compiled Quantum
Circuits by Machine Learning Approaches. In Pro-
ceedings of the 16
th
Symposium and Summer School
on Service-Oriented Computing (SummerSOC 2022),
pages 161–181. Springer.
Schuld, M., Sinayskiy, I., and Petruccione, F. (2016). Predic-
tion by linear regression on a quantum computer. Phys.
Rev. A, 94:022342.
Siraichi, M. Y., Santos, V. F. d., Collange, S., and Quin-
tão Pereira, F. M. (2018). Qubit Allocation. In CGO
2018 - International Symposium on Code Generation
and Optimization, pages 1–12.
Sivarajah, S., Dilkes, S., Cowtan, A., Simmons, W., Edging-
ton, A., and Duncan, R. (2020). t
|
ket
⟩
: A retargetable
compiler for NISQ devices. Quantum Science and
Technology, 6.
Swain, M. J. and Ballard, D. H. (1991). Color indexing.
International Journal of Computer Vision, 7(1):11–32.
Sáez, S. G., Andrikopoulos, V., Leymann, F., and Strauch,
S. (2014). Towards dynamic application distribution
support for performance optimization in the cloud. In
2014 IEEE 7th International Conference on Cloud
Computing, pages 248–255.
University of Stuttgart (2023a). Case Study.
https://github.com/UST-QuAntiL/nisq-analyzer-
content/tree/paper/pre-selection/pre-selection/Case-
Study.
University of Stuttgart (2023b). Content Reposi-
tory. https://github.com/UST-QuAntiL/nisq-analyzer-
content/tree/paper/pre-selection/pre-selection.
University of Stuttgart (2023c). ML Algorithm Imple-
mentations. https://github.com/UST-QuAntiL/nisq-
analyzer-content/tree/paper/pre-selection/pre-
selection/Prediction-Algorithms.
Vapnik, V. N. (1995). The Nature of Statistical Learning
Theory. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Verma, M., Gangadharan, G. R., Narendra, N. C., Vadla-
mani, R., Inamdar, V., Ramachandran, L., Calheiros,
R. N., and Buyya, R. (2016). Dynamic resource de-
mand prediction and allocation in multi-tenant service
clouds. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and
Experience, 28(17):4429–4442.
Vietz, D., Barzen, J., Leymann, F., and Wild, K. (2021).
On Decision Support for Quantum Application De-
velopers: Categorization, Comparison, and Analysis
of Existing Technologies. In Computational Science
– ICCS 2021, pages 127–141. Springer International
Publishing.
Wang, J.-J., Jing, Y.-Y., Zhang, C.-F., and Zhao, J.-H. (2009).
Review on multi-criteria decision analysis aid in sus-
tainable energy decision-making. Renewable and Sus-
tainable Energy Reviews, 13(9):2263–2278.
Weder, B., Barzen, J., Leymann, F., Salm, M., and Wild,
K. (2021). QProv: A provenance system for quantum
computing. IET QuantumCommunication, 2(4):171–
181.
Willmott, C. J. and Matsuura, K. (2005). Advantages of the
mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square
error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance.
Climate research, 30(1):79–82.
Yildiz, B., Bilbao, J., and Sproul, A. (2017). A review and
analysis of regression and machine learning models
on commercial building electricity load forecasting.
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 73:1104–
1122.
Zhong, H.-S. et al. (2020). Quantum computational advan-
tage using photons. Science.
How to Select Quantum Compilers and Quantum Computers Before Compilation
183
