
Comparing the Effect of Privacy and Non-Privacy Social Media Photo
Tools on Factors of Privacy Concern
Vanessa Bracamonte
1
, Sebastian Pape
2
and Sascha Loebner
2
1
KDDI Research, Inc., Saitama, Japan
2
Goethe University Frankfurt, Frankfurt am Main, Germany
Keywords:
Privacy Tools, Perceived Value of Information, Affect, Social Presence, Trust, Privacy Concern, User Study.
Abstract:
Research into privacy tools for social media content has found that although there is a positive attitude towards
these tools, there are also privacy concerns related to the user information involved. This privacy concern
towards privacy tools can be higher than for non-privacy tools of a similar type, but the reason for this differ-
ence is not clear. To address this, we conducted an online experiment to compare the effect of a privacy and
a non-privacy tool on antecedent factors of privacy concern (Perceived value of personal information, Social
presence, Affect and Trust) which are hypothesized to be affected by the different purpose of the tools. The
results show that participants had higher affect towards the privacy tool compared to the non-privacy tool. On
the other hand, the results also show that participants in the privacy tool group had a higher level of perception
of value of their personal information, that is, that the information provided to and inferred by the tool is valu-
able. Finally, both factors mediated a significant but opposing effect of the type of tool on privacy concern.
1 INTRODUCTION
Automated analysis of images has been proposed as
a way of protecting peoples’ privacy in a social me-
dia context (Korayem et al., 2016). In general terms,
these proposals work by analyzing the content of
users’ photos to detect whether the content reveals
private or sensitive information and potentially trans-
forming that content to anonymize it (Ilia et al., 2015;
Li et al., 2019; Hasan et al., 2020). Research has
identified that users worry about their data being col-
lected, sold, shared or misused, and about having their
privacy intruded upon by these privacy tools (Braca-
monte et al., 2021; Bracamonte et al., 2022). Al-
though in essence this type of privacy tool would
not be very different from a tool that analyzes users’
content for the purposes of enjoyment, research has
found that privacy concerns towards privacy tools can
be higher than towards tools that would also analyze
user data, but which have a non-privacy related pur-
pose (Bracamonte et al., 2022). This indicates that
the priming of the privacy tool has an effect on privacy
concerns, but it is unclear through which mechanisms
these effects are occurring.
We hypothesize that a number of factors may have
a different effect on privacy concern towards privacy
tools compared to non-privacy tools, and conduct an
online survey-based experiment comparing the per-
ception of two tools with similar characteristics but a
different purpose: a tool for privacy vs. a non-privacy
tool for enjoyment. In this paper, we evaluate possi-
ble constructs through which the positive and negative
perceptions may be influencing privacy concern: Per-
ceived value of personal information, Affect and Trust
towards the tool, and Social presence.
2 RELATED WORK
Research on perception towards privacy tools that
process personal data has identified that users have
privacy concerns towards these types of tools. (Bra-
camonte et al., 2022) conducted a study comparing
privacy and non-privacy tools for text and photos, and
found that these concerns can be higher than for sim-
ilar tools with a non-privacy related purpose. They
also found that similar themes are reported when ex-
plaining the reasons for privacy concern towards both
types of tools.
However, existing research has not evaluated
through which mechanism do privacy tools influence
privacy concerns differently than non-privacy tools.
Nevertheless, findings from user evaluation studies of
Bracamonte, V., Pape, S. and Loebner, S.
Comparing the Effect of Privacy and Non-Privacy Social Media Photo Tools on Factors of Privacy Concern.
DOI: 10.5220/0011784900003405
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2023), pages 669-676
ISBN: 978-989-758-624-8; ISSN: 2184-4356
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
669

privacy tools suggest some possibilities of variables
which may explain this difference.
2.1 Perceived Value of Information
Privacy tools can cause some users to become con-
cerned about how the tool itself may obtain value
from the data they collect. (Schaub et al., 2016)
found that users have reported concerns that privacy
tools could potentially profit from their personal in-
formation (Bracamonte et al., 2022) similarly found
that some users were concerned that a privacy tool
could profit from their information through advertis-
ing, sharing or selling of the data.
When users become aware that their personal in-
formation is valuable to third parties, this can cause
them to place a higher value on that information
(Spiekermann et al., 2012). (Danezis et al., 2005)
found that students increased their bids for the dis-
closure of their location information after learning
that there was a possible commercial interest in that
data. (Staiano et al., 2014) found that aggregated per-
sonal identifiable information, collected over a period
of time, was valued higher than individual points of
data , and it was hypothesized that the higher valua-
tion was due to the participants realizing that this data
revealed more information about their life.
A privacy tool such as the one described in this pa-
per would work by detecting whether the information
contained in the users’ photos may be privacy sensi-
tive. Therefore, the tool itself assigns some meaning
to the content of the photo, which the users’ may not
have been aware of in advance. In doing so, the tool
may be indicating that the information in the photo
is something valuable to be protected. (Bracamonte
et al., 2022) found that users appear to be concerned
not only about the data collection aspect, but also
what the privacy tool could gain from the data. If
the photos are something to be protected, rather than
“normal” photos, then it is possible that users would
consider that data more valuable, to themselves or to
others who would profit from it. This could result in
an increased perception of the value of personal in-
formation, in comparison with tools that do not have
a privacy-enhancing purpose. The privacy tool’s in-
ference or prediction of the users’ content as (poten-
tially) privacy sensitive may increase the perception
of how valuable the content is, since the tools indi-
cates it needs to be protected.
2.2 Social Presence
Social presence has been investigated as an influence
on the positive perception of technology. (Gefen and
Straub, 2004) indicate that social presence can have
effect of perception in situations of interaction with
technology where there is typically no direct interac-
tion with a person. For example, the sense that others
are present helps increase factors such as perceived
trust (Gefen and Straub, 2004; Kim et al., 2013; Has-
sanein and Head, 2005) and benefit (Kim et al., 2013).
The effect of social presence is present in different
types of contexts of technology mediation, from web-
sites (Gefen and Straub, 2004) to automation tech-
nology such as robots (Kim et al., 2013), to varying
degrees. Much of the research has focused on the
effect of human images, but research by (Hassanein
and Head, 2005) has shown that interfaces that evoke
emotions such as fun or interest can also increase the
perception of social presence.
An utilitarian tool such a tool for privacy may not
have as much social presence, in the sense of posi-
tive human connection, in comparison with a tool for
enjoyment. In addition, (Oh et al., 2018) report that
social presence is not always correlated with positive
effects, and that its effects may depend on the context,
such as when a person is vulnerable. It is likely that
users would imagine different contexts for the use of
privacy vs. non-privacy tools. In a privacy context,
users may feel vulnerable and social presence could
represent a risk rather than a benefit.
2.3 Affect and Trust
It is also important to consider that not only negative
perceptions could affect privacy concern. A privacy
tool such as the one in the current study only dif-
fers from a non-privacy tool in its purpose, and be-
cause the purpose is privacy protection or enhance-
ment, which benefits the user, this may result in posi-
tive perception. (Dinev et al., 2015) indicate that pri-
vacy concerns are not only influenced by analytical
processes, but are also affected by dispositional atti-
tudes. Extraneous influences have an effect on privacy
concerns, and positive or negative feelings and heuris-
tics are also used used in order to decide and make pri-
vacy judgments about a particular technology. Users
have positive feelings towards privacy tools due to
their purpose of protection (Schaub et al., 2016; Bra-
camonte et al., 2021). Positive feelings, influenced by
the beneficial purpose of this type of tools, could also
work to reduce concerns. (Schaub et al., 2016) in-
dicated that users had a feeling of protection by the
privacy tool, and that this mitigated concerns related
ICISSP 2023 - 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
670

to tracking. (Bracamonte et al., 2022) found that the
purpose of the privacy tool was mentioned as one of
the reasons for having a lower level of privacy con-
cern, whereas there was no such reason for the non-
privacy tool. The privacy tool, which purpose is to
protect users, could increase positive feelings in users.
Positive feelings, or Affect, can be defined as
thought of as automatic responses associated with a
stimulus (Slovic et al., 2002). If we compare a privacy
and non-privacy tool, we can take the privacy purpose
of the former as a stimulus that primes users for a
type of reaction or response. Therefore, in their ini-
tial interaction with a privacy tool, positive perception
of the privacy tool brought by feelings of protection
may increase affect towards it, compared to a non-
privacy tool. Furthermore, (Finucane et al., 2000)
and (Slovic et al., 2002) indicate that overall affective
evaluation of an object can influence the risk judg-
ment related to that object. For example, (Kehr et al.,
2015) found that positive feelings towards a technol-
ogy medium can influence people’s privacy assess-
ment and can result in underestimating information
disclosure risks. Another factor which can automat-
ically affected by stimulus is trust (Lindgaard et al.,
2006). (Gefen and Straub, 2004) indicate that trust
plays an important role in the perception of technol-
ogy, and it is considered important for privacy tools
as well (Balebako et al., 2013; Coopamootoo, 2020;
Harborth et al., 2020).
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Questions
The objective of the paper is to evaluate the mech-
anism through which a privacy tool affects privacy
concern differently from a non-privacy tool, focusing
specifically on tools for the analysis and transforma-
tion of social media photos. We propose a number
of factors to test, and evaluate the following research
questions:
R1: Are the levels of Perceived value of informa-
tion, Social presence, Affect and Trust different when
viewing a privacy tool compared to viewing a non-
privacy tool?
R2: Does the privacy tool have a different ef-
fect (compared to the non-privacy tool) on Privacy
concern through those variables? That is, do Per-
ceived value of information, Social presence, Affect
and Trust mediate the effect of the type of tool on Pri-
vacy concern?
3.2 Experiment Design
In order to answer the research questions, we de-
signed an experiment which consisted of a task for
participants to view, read a description and give their
opinion about an hypothetical app that would be used
to transform photos for uploading on social media.
We manipulated the type of tool that the participants
viewed: a privacy tool or a non-privacy tool for so-
cial media photos. The objective of this study was to
evaluate differences in perception that resulted from
the manipulation (priming), therefore, the privacy tool
was explicitly described as such. Participants viewed
the description and a mockup of only one type of app
(between-subjects design). After reading about the
app, the participants answered a questionnaire.
3.3 Task
We described to participants an hypothetical free,
third-party app for social media photos. For the pri-
vacy tool, the purpose was described as protecting pri-
vacy; for the non-privacy tool, the purpose was de-
scribed as enhancing the content for fun. The app
would hypothetically work by analyzing and detect-
ing the content in the users’ photos. We described
the type of information the app would detect from
the photos: private information for the privacy tool,
and information that could be enhanced with stickers
for the non-privacy tool. We then presented a non-
interactive mockup of the app interface which showed
how it would work. The mockups for each group had
the same general design, and only differed in their
message (“Privacy alert!” vs “Enhance it!”) and
the transformation performed on the photo (privacy-
enhancing vs non-privacy-enhancing).
After the mockup, we showed five additional
photo examples to the participants. The photos for
the examples were obtained from the COCO dataset
(Lin et al., 2014).
3.4 Measurement Items
We included items adapted from previous research to
measure Social presence (Gefen and Straub, 2004)
and Affect (Kehr et al., 2015). The items for mea-
suring Perceived value of information were developed
based on the single-item measurement from (Spieker-
mann et al., 2012), adapted to refer to personal infor-
mation provided by the user and personal information
generated by the tool. Privacy concern was measured
with the Mobile Users’ Information Privacy Concerns
(MUIPC) scale, which is comprised of the dimen-
sions of Perceived surveillance, Perceived intrusion
Comparing the Effect of Privacy and Non-Privacy Social Media Photo Tools on Factors of Privacy Concern
671

and Secondary use of personal information (Xu et al.,
2012). Trust was measured with 3 items adapted
from (Jarvenpaa et al., 1999). All questions had
a 7-point response scale, from Strongly disagree to
Strongly agree, with the exception of the Affect items.
To validate that the samples in each group were
comparable, we included questions on Prior pri-
vacy experience (Smith et al., 1996), Disposition to
value privacy (Xu et al., 2011), Information sensitiv-
ity (Dinev et al., 2013), as well as questions on the
participants’ age, gender (as an open text box (Spiel
et al., 2019)) and frequency of social media posting,
in general and for photos in particular. The question-
naire also included open-ended attention check ques-
tions, where we asked participants to answer briefly
about the app described.
3.5 Ethical Considerations
This study was exempt from review according to our
institution’s criteria for research of this type. Never-
theless, we provided a notice to inform potential par-
ticipants about the characteristics of the study. The
notice included a description of the purpose of the
survey, the approximate time to finish it and the task
that participants were expected to do (read a descrip-
tion and answer questions). The notice also explained
that the survey included attention questions, but that
we would not reject the participants’ answers based
only on these questions. However, we clarified that
we would reject duplicated answers or answers unre-
lated to the question asked.
We indicated that the survey was completely vol-
untary and that participants were free to decline to
participate, that we would not collect identifying in-
formation such as name, email or IP address, and that
the results would be used for academic purposes only.
We also indicated that the survey was limited to adults
who lived in the United States. Finally, we provided
the principal researcher’s name and email address in
case of any questions about the study. Participants
were asked to access the link to the survey itself if
they accepted to participate.
3.6 Participant Recruitment
We recruited participants by posting a task to answer
a survey on Amazon Mechanical Turk. We set the
qualifications for participation for workers from the
USA, who had a 99% rate of acceptance rate for their
tasks and who had worked on at least 5000 tasks. We
set the participant reward at US$2.5.
The survey ran on February 8-9, 2022. We ob-
tained 400 responses in total. We reviewed the an-
swers to all open-ended questions to identify cases
with multiple nonsensical answers or answers which
were completely unrelated to the questions. We iden-
tified 20 such responses, and rejected them. The
rest of the participants were rewarded, at a rate of
US$12.5/hour. The median response time was 12
minutes.
4 RESULTS
In this section, we describe the analysis method (PLS-
SEM) we used, then report the final sample character-
istics, the measurement model’s reliability and valid-
ity analysis results, and finally the results of the struc-
tural model analysis.
To evaluate the research questions of this study,
we used the partial least squares structural equation
modeling (PLS-SEM) method. In summary, the PLS-
SEM method consists of a series of steps from check-
ing the reliability of the measurement model (rela-
tionship between the measurement items and its cor-
responding construct), the reliability of the struc-
tural model (relationships between the constructs)
and finally obtaining the path coefficients (direct and
mediated) i.e. the relationships between the con-
structs (Hair et al., 2019).
We conducted the PLS-SEM analyses using the R
seminr package (Ray et al., 2022).
4.1 Sample Characteristics
The sample consisted of 380 cases. We first identi-
fied 22 multivariate outliers, using the Mahalanobis
distance (alpha = 0.001), and removed them. We
reviewed the answers to the attention questions, but
found none that could be considered incorrect. The
final sample for analysis consisted of 358 participant
responses, 179 in each group. The sample size ob-
tained was over the minimum for finding path coeffi-
cients of 0.11 - 0.2 with a 1% significance level and a
power of 80% with the PLS-SEM method (Hair et al.,
2021), according to guidelines based on the inverse
square root method for minimum sample size estima-
tion (Kock and Hadaya, 2018). The age mean was
41 years-old for both groups. The gender distribution
was 53% female / 48% male participants in the pri-
vacy tool group, and 56% female and 44% male in
the non-privacy tool group.
Mann-Whitney U tests indicated no significant
differences in age (W = 16124, p-value = 0.92) fre-
quency of social media posting, in general (W =
17594, p-value = 0.10) or photos in particular (W =
17446, p-value = 0.14), Prior privacy experience (W
ICISSP 2023 - 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
672

= 14904, p-value = 0.25), Disposition to value privacy
(W = 14960, p-value = 0.28) or Information sensitiv-
ity (W = 15230, p-value = 0.42) between groups.
4.2 Measurement Model
We first evaluated the reliability and validity of the
measurement model. The PLS-SEM method can
be used to evaluate multiple relationships simultane-
ously, so in addition to the relationships related to the
research questions, we also control for the effects of
constructs which have been validated in previous re-
search, such as the influence on Social presence on
Trust (Gefen and Straub, 2003), but we do not focus
on those in this paper.
An initial evaluation indicated that although all
other reliability indicators were satisfactory, the con-
structs of Perceived surveillance, Intrusion and Sec-
ondary use of personal information had low discrimi-
nant validity. These constructs are dimensions of Pri-
vacy concern (Xu et al., 2012), and therefore concep-
tually similar. Therefore, we modeled Privacy con-
cern as a higher-order construct and report the re-
sults of the evaluation of the higher-order measure-
ment model. We examined indicator reliability by
inspecting the values obtained by squaring the item
loadings, which are the correlation weights between
the construct and its indicators (measurement items).
All items had an indicator value (squared loading)
over the threshold of .708 (Hair et al., 2019).
To evaluate internal consistency reliability, which
is the association between indicators of the same con-
struct, we examined the Cronbach’s alpha and the
rhoA reliability coefficient (Dijkstra and Henseler,
2015). For all constructs, Cronbach’s alpha values
ranged from 0.932 - 0.973, and rhoA values ranged
from 0.932 - 0.973, which is higher than the satisfac-
tory minimum of 0.7 (Hair et al., 2021). Although re-
liability coefficient values were higher than the ideal
upper limit of 0.9, this is likely due to the use of es-
tablished scales.
Convergent validity, which is how much the con-
struct converges to explain indicator variance, was ex-
amined using the average variance extracted (AVE).
The AVE for all constructs had a value above the min-
imum level of 0.5 (Hair et al., 2019), on a range from
0.856 - 0.949. Finally, we examined the discriminant
validity, which is how much a construct is distinct
from other constructs, using the heterotrait–monotrait
(HTMT) ratio of correlations criterion. All values
were significantly lower than the threshold value of
0.9 (Hair et al., 2021).
4.3 Structural Model
After validating the measurement model, we assessed
the structural model. We first examined whether there
were collinearity issues (too high correlation between
constructs) in the structural model, by calculating the
variance inflation factor (VIF) values for the con-
structs. All VIF values were below the minimum
recommended of 3 (Hair et al., 2021), with values
ranging from 1.01 - 2.11. We then examined the R-
squared values, which measure the variance in a con-
struct explained by the predictors; values of 0.25 are
considered weak (Hair et al., 2019). Social presence
and Perceived value of information were the only con-
structs with a value lower than 0.25, but this is ex-
pected since the type of tool is their only predictor in
the model. All other values were above the moderate
threshold of 0.5 (Hair et al., 2019).
The structural model included the experiment
groups as a dichotomous variable (1 for the pri-
vacy tool and 0 for the non-privacy tool). We con-
ducted a bootstrapping procedure with 10,000 sam-
ples (Sarstedt et al., 2016) to calculate the path signif-
icance. Statistical significance criteria in this case is
determined by the bootstrapped standardized t statis-
tic (Hair et al., 2021): above 3.291 corresponds to sig-
nificant at 0.1% probability of error (alpha = 0.001) ;
above 2.576, to significant at 1% (alpha = 0.01), and
above 1.96, to significant at 5% (alpha = 0.05) (two-
tailed). These are represented in the tables with * for
significant at 5%, ** for 1%, and *** for 0.1%.
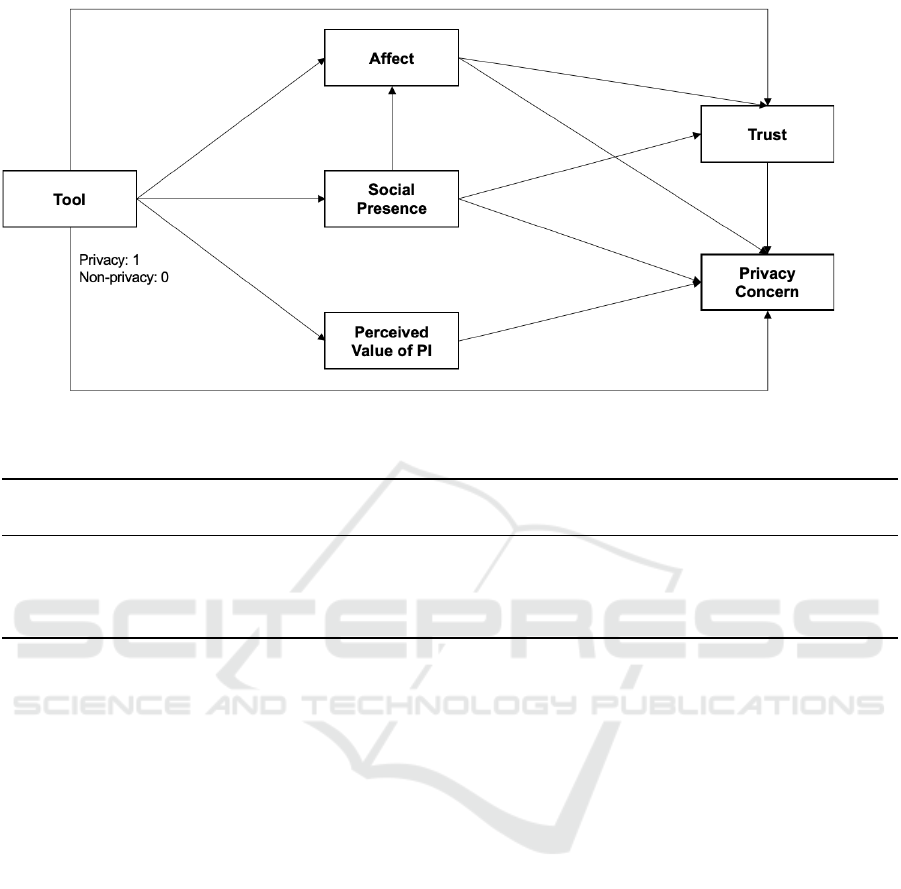
Figure 1 shows the representation of those results.
The results, specifically the direct paths from the vari-
able representing the tool, answer the first research
question (R1) of whether the level of the factors is
different for the privacy tool compared to the non-
privacy tool group. The results show that Perceived
value of information and Affect were significantly
higher for the privacy tool. On the other hand, Social
presence, Trust and also Privacy concern itself were
not significantly different between the two groups.
Although they are not the focus of this study, we ob-
serve from the results that other direct relationships
between constructs were significantly different. How-
ever, one interesting result is that Social presence in-
creases Privacy concern, but also increases Affect and
Trust.
We then examined the mediated effects on Pri-
vacy concern (Table 1) to answer the second research
question (R2). The results show that there was a sig-
nificant indirect effect of the privacy tool on Privacy
concern (compared to the non-privacy tool) through
Perceived value of information, which resulted in an
increase of Privacy concern. There was also a signif-
Comparing the Effect of Privacy and Non-Privacy Social Media Photo Tools on Factors of Privacy Concern
673
𝛽
= 0.216***
95%CI [0.137,0.296]
𝛽 = 0.177***
95%CI [0.074,0.275]
𝛽
= -0.07
95%CI [-0.176,0.035]
𝛽 = 0.004
95%CI [-0.075,0.083]
𝛽
= 0.026
95%CI [-0.051,0.103]
𝛽 = 0.488***
95%CI [0.372,0.596]
𝛽
= -0.216***
95%CI [-0.312,-0.117]
𝛽 = 0.336***
95%CI [0.255,0.421]
𝛽
= 0.602***
95%CI [0.526,0.673]
𝛽
= 0.23***
95%CI [0.114,0.348]
𝛽 = 0.19***
95%CI [0.097,0.278]
𝛽 = -0.596***
95%CI [-0.693,-0.491]
Figure 1: Results of the PLS-SEM analysis.
Table 1: Mediation effects results: standardized coefficients and significance.
X Mediator(s) Original
Est
Bootstrap
Mean
Bootstrap
SD
T Stat. 95% CI Signif.
Tool Value 0.059 0.06 0.02 3.034 [ 0.023, 0.1 ] **
Tool SocialPresence −0.013 −0.013 0.011 −1.193 [ −0.037, 0.006]
Tool Affect −0.047 −0.047 0.014 −3.376 [ −0.077, −0.022] ***
Tool Trust −0.002 −0.003 0.024 −0.086 [ −0.051, 0.043]
icant mediated effect on Privacy concern through Af-
fect which resulted in a decrease of Privacy concern.
In line with the direct effect results, neither Trust nor
Social presence significantly mediate the effect of the
privacy tool on Privacy concern.
5 DISCUSSION
The results of the analysis indicate that privacy con-
cern towards a privacy tool is affected through an in-
crease of the perception of value of the information
that the user gives the tool and the value of the infor-
mation the tool infers from the photos, and through
Affect and Trust towards the privacy tool, which is
higher in comparison to the non-privacy tool. How-
ever, these variables have opposing effects on privacy
concern. Affect decreased Privacy concern and acted
as a mediator of the positive effect of Social pres-
ence on Privacy concern. In the opposite direction,
an increased Perception of the value of personal in-
formation increased Privacy concern towards the tool,
and countered the previously described effect. In this
study, the result was that the overall effect the privacy
tool on privacy concern (compared to the non-privacy
tool) was not significant (unlike the findings by (Bra-
camonte et al., 2022)), as these two opposing effects
canceled each other out.
We consider that the fact that users report a higher
a level of Perceived value of information represents
an interesting problem for privacy tools of the type
we focus on in this study. We can assume that the
provider of a such a tool would naturally want to em-
phasize the privacy protection aspect, and this may
increase a positive attitude towards the tool. On the
other hand, by emphasizing protection the providing
may also be emphasizing the value of the data that is
to be protected. Once that is established, users may be
able to more easily imagine what would be the nega-
tive consequences of losing control of that data. An-
other possibility is that the provider could emphasize
other aspects of the privacy tool besides the protection
itself, in order to increase affect towards it.
Finally, although the results showed that the pri-
vacy tool did not significantly increase or decrease
perception of Social presence compared to the non-
privacy tools, Social presence directly increased Pri-
vacy concern and at the same time increased positive
perceptions (Affect and Trust). This might indicate
that a variable not included in this study may be me-
diating the effect of Social presence on Privacy Con-
cern. Future research should validate empirically val-
ICISSP 2023 - 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
674

idate these effects, since research has shown that the
effect of Social presence can depend on the context of
use of a technology (Phelan et al., 2016; Zhang and
Xu, 2016; Mozafari et al., 2021).
5.1 Limitations
First, we used a non-interactive app mockup for the
experiment. This decreases the realism of the situ-
ation for participants, who are not risking their pri-
vate information. Second, we only evaluated a lim-
ited set of variables that affect Privacy concern in this
experiment. The results show that these variables ex-
plained Privacy Concern with an R-squared = 0.538
(moderate). Nevertheless, we acknowledge that there
could be other variables which could also explain a
difference in perception of these two types of tools.
Third, we recruited Amazon Mechanical Turk work-
ers for the experiment. Although research has found
that these workers have a higher sensitivity to pri-
vacy issues (Kang et al., 2014), there is also evidence
that privacy-related related knowledge matches the
US population to some extent (Redmiles et al., 2019).
Nevertheless, the results might not generalize to other
populations.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Previous research has found evidence of a higher level
of privacy concern towards privacy tools compared to
similar tools with a non-privacy purpose. In this pa-
per, we explore the mechanisms that might explain
this difference in privacy concern. We found that pri-
vacy tools increased the Perception of value of per-
sonal information, and that this variable mediated an
increase of Privacy concern caused by the privacy
tool. We also found that the privacy tool increases Af-
fect compared to the non-privacy tool, and that Affect
along with Trust mediate a decrease of Privacy con-
cern. In our study, these effects appeared to cancel
each other out, resulting in an overall non-significant
effect of the privacy tool on Privacy concern, com-
pared to the non-privacy tool. Finally, we found no
significant differences in the level of Trust and Social
presence between the privacy and non-privacy tools,
although these two variables had an effect on Privacy
concern.
In future research, we plan to empirically exam-
ine how privacy tools affect the perception of value of
information, and how this perception affects privacy
concern in turn.
REFERENCES
Balebako, R., Jung, J., Lu, W., Cranor, L. F., and Nguyen,
C. (2013). ”Little Brothers Watching You”: Raising
awareness of data leaks on smartphones. In Proceed-
ings of the Ninth Symposium on Usable Privacy and
Security, SOUPS ’13, pages 1–11. Association for
Computing Machinery.
Bracamonte, V., Pape, S., and Loebner, S. (2022). “All apps
do this”: Comparing privacy concerns towards privacy
tools and non-privacy tools for social media content.
Proc. Priv. Enhancing Technol., 2022(3).
Bracamonte, V., Tesfay, W. B., and Kiyomoto, S. (2021).
Towards Exploring User Perception of a Privacy Sen-
sitive Information Detection Tool. In 7th International
Conference on Information Systems Security and Pri-
vacy.
Coopamootoo, K. P. (2020). Usage Patterns of Privacy-
Enhancing Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2020
ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Commu-
nications Security, CCS ’20, pages 1371–1390. Asso-
ciation for Computing Machinery.
Danezis, G., Lewis, S., and Anderson, R. (2005). How
much is location privacy worth. In In Proceedings of
the Workshop on the Economics of Information Secu-
rity Series (WEIS.
Dijkstra, T. K. and Henseler, J. (2015). Consistent Par-
tial Least Squares Path Modeling. MIS Quarterly,
39(2):297–316.
Dinev, T., McConnell, A. R., and Smith, H. J. (2015).
Research Commentary—Informing Privacy Research
Through Information Systems, Psychology, and Be-
havioral Economics: Thinking Outside the “APCO”
Box. Information Systems Research, 26(4):639–655.
Dinev, T., Xu, H., Smith, J. H., and Hart, P. (2013). Informa-
tion privacy and correlates: An empirical attempt to
bridge and distinguish privacy-related concepts. Euro-
pean Journal of Information Systems, 22(3):295–316.
Finucane, M. L., Alhakami, A., Slovic, P., and Johnson,
S. M. (2000). The affect heuristic in judgments of
risks and benefits. Journal of behavioral decision
making, 13(1):1–17.
Gefen, D. and Straub, D. (2003). Managing user trust in
B2C e-services. e-Service, 2(2):7–24.
Gefen, D. and Straub, D. (2004). Consumer trust in B2C
e-Commerce and the importance of social presence:
Experiments in e-Products and e-Services. Omega,
32:407–424.
Hair, J., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., Sarstedt, M., Danks, N.,
and Ray, S. (2021). Partial Least Squares Structural
Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: A Workbook.
Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., and Ringle, C. M.
(2019). When to use and how to report the results of
PLS-SEM. European business review.
Harborth, D., Pape, S., and Rannenberg, K. (2020). Ex-
plaining the technology use behavior of privacy-
enhancing technologies: The case of tor and Jon-
Donym. Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Tech-
nologies (PoPETs), 2020(2):111–128.
Comparing the Effect of Privacy and Non-Privacy Social Media Photo Tools on Factors of Privacy Concern
675

Hasan, R., Crandall, D., Fritz, M., and Kapadia, A. (2020).
Automatically Detecting Bystanders in Photos to Re-
duce Privacy Risks. In 2020 IEEE Symposium on Se-
curity and Privacy (SP), pages 318–335.
Hassanein, K. and Head, M. (2005). The impact of infusing
social presence in the web interface: An investigation
across product types. International Journal of Elec-
tronic Commerce, 10(2):31–55.
Ilia, P., Polakis, I., Athanasopoulos, E., Maggi, F., and Ioan-
nidis, S. (2015). Face/off: Preventing privacy leak-
age from photos in social networks. In Proceedings of
the 22nd ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and
Communications Security, pages 781–792.
Jarvenpaa, S. L., Tractinsky, N., and Saarinen, L. (1999).
Consumer Trust in an Internet Store: A Cross-Cultural
Validation. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communi-
cation, 5(2):JCMC526.
Kang, R., Brown, S., Dabbish, L., and Kiesler, S. (2014).
Privacy Attitudes of Mechanical Turk Workers and the
U.S. Public. In 10th Symposium On Usable Privacy
and Security ({SOUPS} 2014), pages 37–49.
Kehr, F., Kowatsch, T., Wentzel, D., and Fleisch, E. (2015).
Blissfully ignorant: The effects of general privacy
concerns, general institutional trust, and affect in the
privacy calculus: Privacy calculus: Dispositions and
affect. Information Systems Journal, 25(6):607–635.
Kim, K. J., Park, E., and Sundar, S. S. (2013). Caregiving
role in human–robot interaction: A study of the medi-
ating effects of perceived benefit and social presence.
Computers in Human Behavior, 29(4):1799–1806.
Kock, N. and Hadaya, P. (2018). Minimum sample size
estimation in PLS-SEM: The inverse square root and
gamma-exponential methods. Information systems
journal, 28(1):227–261.
Korayem, M., Templeman, R., Chen, D., Crandall, D., and
Kapadia, A. (2016). Enhancing Lifelogging Privacy
by Detecting Screens. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI
Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems,
CHI ’16, pages 4309–4314, New York, NY, USA. As-
sociation for Computing Machinery.
Li, F., Sun, Z., Li, A., Niu, B., Li, H., and Cao, G. (2019).
HideMe: Privacy-Preserving Photo Sharing on Social
Networks. In IEEE INFOCOM 2019 - IEEE Confer-
ence on Computer Communications, pages 154–162.
Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ra-
manan, D., Doll
´
ar, P., and Zitnick, C. L. (2014). Mi-
crosoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Fleet,
D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., and Tuytelaars, T., edi-
tors, Computer Vision – ECCV 2014, Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 740–755. Springer Inter-
national Publishing.
Lindgaard, G., Fernandes, G., Dudek, C., and Brown, J.
(2006). Attention web designers: You have 50 mil-
liseconds to make a good first impression! Behaviour
& information technology, 25(2):115–126.
Mozafari, N., Weiger, W., and Hammerschmidt, M. (2021).
That’s so Embarrassing! When Not to Design for So-
cial Presence in Human-Chatbot Interactions.
Oh, C. S., Bailenson, J. N., and Welch, G. F. (2018). A Sys-
tematic Review of Social Presence: Definition, An-
tecedents, and Implications. Frontiers in Robotics and
AI, 5.
Phelan, C., Lampe, C., and Resnick, P. (2016). It’s Creepy,
But it Doesn’t Bother Me. In Proceedings of the 2016
CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Sys-
tems, pages 5240–5251. Association for Computing
Machinery.
Ray, S., Danks, N. P., Valdez, A. C., Estrada, J. M. V., Uan-
horo, J., Nakayama, J., Koyan, L., Burbach, L., Bejar,
A. H. C., and Adler, S. (2022). Seminr: Building and
Estimating Structural Equation Models.
Redmiles, E. M., Kross, S., and Mazurek, M. L. (2019).
How well do my results generalize? comparing secu-
rity and privacy survey results from mturk, web, and
telephone samples. In 2019 IEEE Symposium on Se-
curity and Privacy (SP), pages 1326–1343.
Sarstedt, M., Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., Thiele, K. O., and
Gudergan, S. P. (2016). Estimation issues with PLS
and CBSEM: Where the bias lies! Journal of Business
Research, 69(10):3998–4010.
Schaub, F., Marella, A., Kalvani, P., Ur, B., Pan, C., Forney,
E., and Cranor, L. F. (2016). Watching Them Watch-
ing Me: Browser Extensions Impact on User Privacy
Awareness and Concern. In Proceedings 2016 Work-
shop on Usable Security. Internet Society.
Slovic, P., Finucane, M., Peters, E., and MacGregor, D. G.
(2002). Rational actors or rational fools: Implications
of the affect heuristic for behavioral economics. The
Journal of Socio-Economics, 31(4):329–342.
Smith, H. J., Milberg, S. J., and Burke, S. J. (1996).
Information Privacy: Measuring Individuals’ Con-
cerns about Organizational Practices. MIS Quarterly,
20(2):167–196.
Spiekermann, S., Korunovska, J., and Bauer, C. (2012).
Psychology of ownership and asset defense: Why
people value their personal information beyond pri-
vacy. Available at SSRN 2148886.
Spiel, K., Haimson, O. L., and Lottridge, D. (2019). How
to do better with gender on surveys: A guide for HCI
researchers. Interactions, 26(4):62–65.
Staiano, J., Oliver, N., Lepri, B., de Oliveira, R., Caraviello,
M., and Sebe, N. (2014). Money walks: A human-
centric study on the economics of personal mobile
data. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM International
Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Com-
puting, pages 583–594. ACM.
Xu, H., Dinev, T., Smith, J., and Hart, P. (2011). Infor-
mation Privacy Concerns: Linking Individual Percep-
tions with Institutional Privacy Assurances. Journal
of the Association for Information Systems, 12(12).
Xu, H., Gupta, S., Rosson, M., and Carroll, J. (2012). Mea-
suring Mobile Users’ Concerns for Information Pri-
vacy. In ICIS.
Zhang, B. and Xu, H. (2016). Privacy Nudges for Mo-
bile Applications: Effects on the Creepiness Emotion
and Privacy Attitudes. In Proceedings of the 19th
ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Coopera-
tive Work & Social Computing, CSCW ’16, pages
1676–1690. Association for Computing Machinery.
ICISSP 2023 - 9th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
676
