
WSAM: Visual Explanations from Style Augmentation as Adversarial
Attacker and Their Influence in Image Classification
Felipe Moreno-Vera
1,∗ a
, Edgar Medina
2,∗
and Jorge Poco
1 b
1
Fundac¸
˜
ao Get
´
ulio Vargas, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
2
QualityMinds, Munich, Germany
Keywords:
Style Augmentation, Adversarial Attack, Understanding, Style, Convolutional Networks, Explanation,
Interpretability, Domain Adaptation, Image Classification, Model Explanation, Model Interpretation.
Abstract:
Currently, style augmentation is capturing attention due to convolutional neural networks (CNN) being
strongly biased toward recognizing textures rather than shapes. Most existing styling methods either per-
form a low-fidelity style transfer or a weak style representation in the embedding vector. This paper outlines
a style augmentation algorithm using stochastic-based sampling with noise addition for randomization im-
provement on a general linear transformation for style transfer. With our augmentation strategy, all models not
only present incredible robustness against image stylizing but also outperform all previous methods and sur-
pass the state-of-the-art performance for the STL-10 dataset. In addition, we present an analysis of the model
interpretations under different style variations. At the same time, we compare comprehensive experiments
demonstrating the performance when applied to deep neural architectures in training settings.
1 INTRODUCTION
Currently, deep learning neural nets require a large
amount of data, usually annotated, to increase the
generalization and obtain high performance. To deal
with this problem, methods for artificial data gen-
eration are performed to increase the training sam-
ples; this common learning strategy is called data
augmentation. In computer vision, data augmenta-
tion increases the number of images through pixel-
level processing and transformations. For supervised
tasks where labels are known, these operations per-
form label-preserving transformations controlled by
the probability of applying the operation and usually
a magnitude that intensifies the operation effects on
the image (Szegedy et al., 2016; Tanaka and Aranha,
2019). More recently, random erasing (DeVries and
Taylor, 2017) and GAN-based augmentation (Tanaka
and Aranha, 2019) improved the previous accuracy.
In contrast, recent advances in style transfer (Ghiasi
et al., 2017; Jackson et al., 2018) lead us to think
about the influence of applying random styling and
what deep networks learn from this.
Style augmentation is a technique that generates
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2477-9624
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9096-6287
∗
means equal contribution
variations from an original set of images changing
only the style information and keeping the main con-
tent. The style transformation applied to the image
changes the image’s pixel information, generating a
new diverse set of samples that follow the same orig-
inal distribution. In contrast, content information re-
mains equal (Ghiasi et al., 2017). However, original
style transfer techniques started with heavy compu-
tation to generate one stylized image. Experimen-
tally, augmenting the training set randomly shows a
new level of stochastic behavior, avoids overfitting in
a small dataset, and stabilizes performance on large
ones (Zheng et al., 2019). Nowadays, some can work
close to real-time performance while others can gen-
erate a batch of styles per image (Ghiasi et al., 2017;
Jackson et al., 2018).
In Interpretable Machine Learning (IML), specif-
ically in image-based models such as CNN, several
methods exist to interpret and explain predictions.
Usually, large and complex models like CNN are
called “black-box” due to their vast number of param-
eters (hidden layers). So, to know the information
shared through each layer, some methods were de-
veloped using information from layers and gradients
such as Saliency Maps (Simonyan et al., 2013), and
CAM-based methods (Zhou et al., 2016; Selvaraju
et al., 2017). These methods help explain complex
830
Moreno-Vera, F., Medina, E. and Poco, J.
WSAM: Visual Explanations from Style Augmentation as Adversarial Attacker and Their Influence in Image Classification.
DOI: 10.5220/0011795400003417
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2023) - Volume 5: VISAPP, pages
830-837
ISBN: 978-989-758-634-7; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

“black box” image-based models and identify essen-
tial features in each sample prediction. In our ap-
proach, we will use these model explainers to high-
light regions inside the input images to provide a vi-
sual interpretation of them.
In this work, we propose an augmentation strategy
based on traditional augmentation plus style trans-
formations. Besides, we implement new methods to
visualize, explain, and interpret the behavior of our
trained models. Also, we can understand which fea-
tures are activating based on the style augmentation
selected and study the influence of that style. Our
main contributions in the present work are summa-
rized as follows:
• We give an explanation of the successful augmen-
tation strategy based on interpretation methods.
• We propose a Style Activation Map (SAM),
Weighted Style Activation Map (WSAM), and
WSAM Variance to visualize and understand the
influence of style augmentation.
• We outperform previous results on the STL-10
dataset using traditional and style augmentations.
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Style Transfer
In the first neural algorithm (Gatys et al., 2015), a
content image and a style image are inputted to the
neural network to obtain an output image with the
original content but a new style. (Jing et al., 2017)
employed the Gram matrices to model textures by
encoding the correlations between convolutional fea-
tures from different layers. Previous style transfer
works (Ulyanov et al., 2017) improve the visual fi-
delity in which semantic structure was preserved for
images with higher resolution. In (Geirhos et al.,
2018) was concluded that neural networks have a
strong bias with texture. Although the initial de-
velopments generated exciting results compared to
the pioneer method, drawbacks such as weak texture
synthesis and high computational cost were present
(Ulyanov et al., 2017; Jing et al., 2017). More re-
cently, (Li et al., 2018; Ghiasi et al., 2017) solved the
problem by relying on arbitrary styles without retrain-
ing the neural model. Also, other techniques adjusted
a new parameter or inserted noise carefully to gener-
ate more style variations from one style input (Ghi-
asi et al., 2017; Kotovenko, Dmytro, adn Sanakoyeu,
Artsiom, and Lang, Sabine, and Ommer, 2019). Us-
ing these latter strategies, the first augmentation em-
ploying successfully style augmentation performing a
cross-domain classification task (Jackson et al., 2018)
follows the methodology adopted on (Ghiasi et al.,
2017), which uses an Inception-v3 (Szegedy et al.,
2015) architecture for the encoder and residual blocks
for the decoder networks. However, the latent space is
modified by a multivariate normal distribution which
changes the style embedding. Other contemporary
approaches (Zheng et al., 2019; Georgievski, 2019)
used style augmentation and reported exciting results
in classification tasks, specifically STL-10, CIFAR-
100, and Tiny-ImageNet-200 datasets. Other interest-
ing applications are extended to segmentation tasks
(Hesse et al., 2019; Gkitsas et al., 2019).
Based on this literature review, we used a neu-
ral transfer model following a trade-off between edge
preservation, flexibility to generate style variations,
time processing, and best visual fidelity under differ-
ent styles. We also compare our methodology to prior
approaches used for style augmentation.
2.2 Deep Network Explanations
Explaining a CNN is focused on analyzing the in-
formation passed through each layer inside the net-
work. Following this idea, several methods were pro-
posed to visualize and obtain a notion about which
features of a deep CNN were activated in one spe-
cific layer. In (Simonyan et al., 2013) (saliency maps)
showed the convolutional activations, (Zeiler and Fer-
gus, 2014) showed the impact of applying occlusion
to the input image. In other methods, they use the
gradients to visualize features and explain deep CNN
networks such as DeepLIFT (Shrikumar et al., 2017),
which computes scores for each feature; Integrated
Gradients (Sundararajan et al., 2017), which com-
putes features based on gradients; CAM (Zhou et al.,
2016), and Grad-CAM (Selvaraju et al., 2017) which
computes relevant regions using gradient and feature
maps. Each method identifies features with high and
strong activation representing the prediction for a spe-
cific predicted category.
Guided by this literature review, we propose a new
method called Style Activation Maps (SAM) based
on the Grad-CAM method applied to style augmen-
tation. We choose this one due to better behavior
and performance against adversarial attacks or noise-
adding techniques (Adebayo et al., 2018; Gilpin et al.,
2018). Our main goal is to understand and interpret
the impact of applying style augmentation in classifi-
cation tasks and analyze their influence.
WSAM: Visual Explanations from Style Augmentation as Adversarial Attacker and Their Influence in Image Classification
831

3 PROPOSED METHOD
In this section, we present theoretical formulation and
some interpretation methods used.
3.1 Style Augmentation
For our experiments, we used the same methodol-
ogy as (Jackson et al., 2018); we nevertheless used
a faster VGG-based network and added noise to di-
versify the style features. Specifically, we used an ar-
chitecture composed of a generalized form of a linear
transformation (Li et al., 2018). Also, we compare
with other related works (Jackson et al., 2018; Zheng
et al., 2019) that use neural style augmentation.
Formally, let C =
c
1
, c
2
, ..., c
j
, c
i
∈ R
N×M×C
be
the content image set and let Z =
z
1
, z
2
, ..., z
i
, z
i
∈
R
n
be the precomputed style embedding set from
S =
s
1
, s
2
, ..., s
i
, s
i
∈ R
N×M×C
, are used to feed
the styling algorithm to generate the output set O =
o
1
, o
2
, ..., o
j
, o
j
∈ R
N×M×C
. Moreover, we denote
zero-mean vectors c
j
∈ R
N×M×C
and z
i
∈ R
n
. Our
style strategy transfers elements z
i
from the style set
Z to a specific element from the content set C.
The VGG (“r41”) architecture, denoted as M(.),
maps R
N×M×C
→ R
N
1
×M
1
×F
. and a non-linear func-
tion φ(.) maps R
N
1
×M
1
×F
1
→ R
n
, where N
1
< N,
M
1
< M and F
1
> F. Also, we denote C(.), U(.) as the
compress and uncompress CNN-based networks from
the original paper (Li et al., 2018). φ(.) embeds the
input image to an embedding vector that contains the
semantic information of the image. More concisely,
we use this non-linear function to map the original
image to an embedding vector as shown in Eq. 1 for
the content image and Eq. 2 for the style image. In
our implementation, the function φ(.) employs a CNN
whose output is used to compute the covariance ma-
trix and feed it to a fully-connected layer.
Since we use an architecture based on linear trans-
formations, which is generalized from previous ap-
proaches (Ghiasi et al., 2017), the transformation
matrix T sets and preserves the feature affinity of
the content image (determined by the covariance
matrix of the content and the style). This is ex-
pressed in Eq. 3. In our implementation, we pre-
computed the style vectors and saved all textures in
memory; thereby, our modifications are described in
Eq. 4 and 5.
φ
c
= φ
1
(V GG(c
j
)) (1)
φ
s
= φ
2
(V GG(s
i
)) (2)
T = φ
c
φ
T
c
φ
s
φ
T
s
(3)
In our implementation, we precompute the style
vector and save all textures in memory; thereby, our
modifications are expressed in Eq. 4 and 5.
T = φ
c
φ
T
c
(αφ
c
φ
T
c
+ (1 − α) ˆz
i
) (4)
o
i
= U(T C(c
j
)) + (α)µ
c
i
+ (1 − α)µ
z
i
(5)
Where α is the interpolation hyper-parameter
which controls the strength of the style transfer simi-
larly to (Jackson et al., 2018), and ˆz
i
, defined in Eq. 6,
is the embedding vector of the style set with a noise
addition for style randomization.
ˆz
i
∼ z
i
+ N (µ
i
, σ
2
i
) (6)
As argued in prior methodologies, minor vari-
ations increase the randomization in the process;
thereby, we apply noise instead of using a sampling
strategy similar to applying a Gaussian noise in the
latent space of generative networks during the train-
ing. In particular, we set this noise source as a mul-
tivariate normal distribution which means covariance
scales and shifts z
i
into the embedding space. This is
also useful for understanding the randomization pro-
cess and the influence of the latent space.
3.2 Model Interpretation
In this work, we propose a new method Style Activa-
tion Map based on Grad-CAM to visualize the pre-
dictions and the highlighting regions with the most
representative activated features from styled images.
To do this, we extract from the penultimate layer the
A
k
∈ R
u×v
feature maps of width u and height v, with
each element indexed by i,j. So A
k
i, j
refers to the ac-
tivation at location (i, j) of the feature map A
k
. We
apply the GlobalAveragePooling (GAP) technique to
the feature maps to get the neuron importance weights
defined in Eq. 7.
δ
c
k
=
GAP
z }| {
1
Z
∑
i
∑
j
∂y
c
∂A
k
i j
|{z}
grad-backprop
(7)
Where δ
c
k
represents the neuron importance
weights, c is the class, Z = u × v the size of the im-
age, k is the k-th feature map, A
k
i j
is the feature map,
y
c
the score for class c, and
∂y
c
∂A
k
i j
is the gradient vec-
tor obtained via back-propagation. Next, we calcu-
late the corresponding activation maps for each pre-
diction using Eq. 7. From this point, we propose a
new technique to visualize the highlighted regions in
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
832

stylization and their variations. We present two meth-
ods: the Style Activation Map (SAM) defined as the
relevant highlighted regions of the different styles in
predictions and the Weighted Style Activation Map
(WSAM) defined as the weighted sum of all styles
applied in all samples per class.
We denote the SAM of a styled image with style
σ, style intensity α, and class c by I
c
α,σ
. Where α is
the style intensity used, σ is the style used. Also, we
have the k-th feature activation maps A
k
∈ R
u×v
, and
their class score y
c
for class c:
SAM
c
α,σ
= ReLU(
∑
k
δ
c
k
A
k
α,σ
) (8)
We apply the ReLU function to the weighted lin-
ear combination of the feature maps A
k
because we
are only interested in features with a positive influ-
ence. Then, we use this result to obtain the WSAM
doing a weighted mean of SAM
c
α,σ
and their predic-
tions y
c
α,σ
using all styles and all intensities. We de-
fine Ω as the product of total styles and total intensi-
ties evaluated, so we have:
W SAM
c
=
1
Ω
∑
α
∑
σ
y
c
α,σ
× SAM
c
α,σ
(9)
Once we calculate W SAM
c
in eq. 9 we will calcu-
late the total variance region of m samples to identify
the most significant styles features for the classifier:
W SAM
c
variance
=
1
Z × m
m
∑
i
(W SAM
c
i
− y
c
i
× I
c
i
)
2
(10)
Where I
c
i
is the i-th input sample stylized with
α = 1.0 (no style), Z = u × v the image size, and their
class score y
c
i
for the class c. Our metric shows the
highlighted region variance between an image and its
styles with different αs.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
We perform our experiments using the STL-10
(96 × 96) dataset, where samples are distributed in
5,000 and 8,000 labeled data for training and test-
ing, respectively. We disregard the 100,000 un-
labeled data for all our experiments. Besides,
all experiments were performed using five differ-
ent networks with high performance, such as Xcep-
tion (Chollet, 2016), InceptionV3-299 (Szegedy
et al., 2015), InceptionV4 (Szegedy et al., 2016),
WideResNet-96 (Zagoruyko and Komodakis, 2016),
and WideResNet-101 (Kabir et al., 2020). We
also compare our results with other state-of-the-
art style augmentation like SWWAE (Zhao et al.,
(a)
1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0
(b)
Figure 1: (a) Visualization using t-SNE, samples with their
style augmentation. (b) Different styles with variations of
the parameter α from 1.0 (no stylization) to 0.0 (style aug-
mentation) on images.
2015), Exemplar Convnet (Dosovitskiy et al., 2014),
IIC (Ji et al., 2018), Ensemble (Thoma, 2017),
WideResNet+cutout (DeVries and Taylor, 2017), In-
ceptionV3 (Jackson et al., 2018), and STADA (Zheng
et al., 2019).
4.1 Style Augmentation
First, we explore the effects of style augmentation
through t-SNE visualization of images after apply-
ing the styler network to a subset of the test set Fig-
ure 1a; we note some clusters of original images and
their styles separate a bit of distance such as truck and
horse. In Figure 1b, we performed some styles us-
ing some α values to find the best balance between
style and content information as described above in
Eq. 5. However, we emphasize the difference between
traditional augmentation and the classical technique
WSAM: Visual Explanations from Style Augmentation as Adversarial Attacker and Their Influence in Image Classification
833

like rotation, mirroring, cutout (DeVries and Taylor,
2017), etc. With style augmentation, we increase the
number of samples using about 80 000 styles and
sampling for style intensity. Figure 1b shows differ-
ent styles and different α values (style intensity) from
0.0 to 1.0 by steps of 0.2.
Images with augmentation strategies for train-
ing deep models include traditional augmentations,
cutouts, and our style augmentation method using a
lower style effect (α = 0.7). At this point, we can
consider style augmentation as a noise-adding tech-
nique or adversarial attacker due to the style distor-
tion, which makes images more challenging to repre-
sent and be associated with the correct class.
4.2 Training Models
For experiments, we define four learning strategies,
which are composed of no augmentation (None or
N/A), traditional augmentation (Trad), style augmen-
tation (SA), and both (Trad+SA) for each model. In
Table 1, we present the quantitative comparisons be-
tween the state-of-the-art methods in style augmen-
tation using styling and architectures for the STL-10
dataset; the Extra column means additional data is
used to train that model, Trad column means tradi-
tional augmentation plus cutout, and Style column in-
dicates our style augmentation.
We note that in all cases, style augmentation helps
to improve results. Besides, we found that models
with higher input resolution reached higher accuracy
after applying the styling method shown in Figure 2a.
Experiments on different input sizes support this af-
firmation (Chollet, 2016).
Furthermore, in Figure 2b, we analyze the influ-
ence of style additions to a subset of the test set com-
posed of 100 samples (10 samples per class), com-
puting their average accuracy in each point on axis X
consisting of an overall 20,000 random styles, these
styles were sorted following from greater to lower ac-
curacy. Note that the accuracy of the model trained
without style augmentation decreased drastically for
some styles. In contrast, the use of styles in training
becomes the same architecture more robust to strong
variations without losing accuracy.
5 STYLE ACTIVATION MAPS
VISUALIZATION
Once our training step was finished, we evaluated
and understood the stylization behavior in our mod-
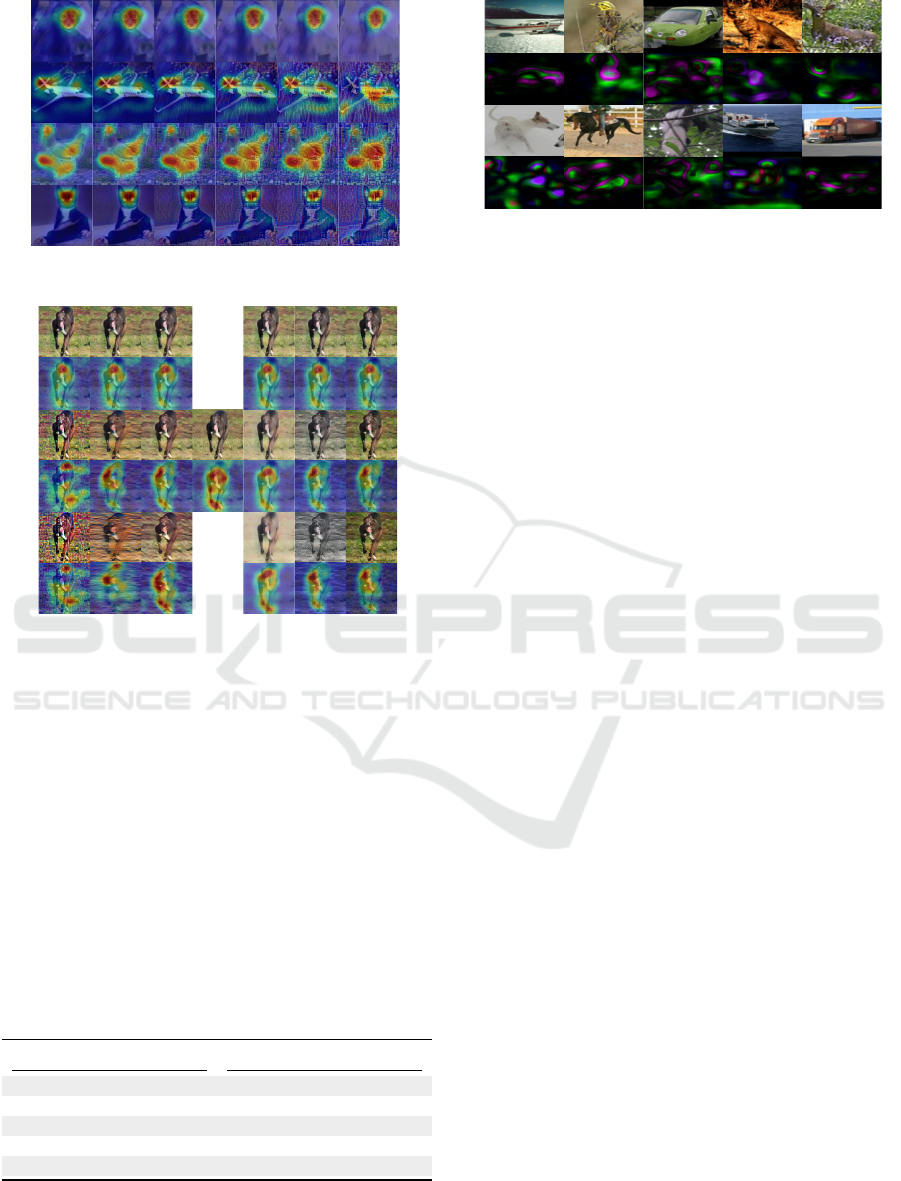
els. First, in Figure 3a, we show how our Style Acti-
vation Map works. Each row is the model, and each
Table 1: Accuracy comparison of data augmentation meth-
ods in STL-10 (
∗
) indicates results performed by us.
Network Extra Trad Style Acc
SWWAE ✓ ✓ 74.33
Exempla Conv ✓ ✓ 75.40
IIC ✓ ✓ 88.80
Baseline ✓ 75.67
Ensemble ✓ 77.62
STADA
∗
✓ ✓ 75.31
InceptionV3-299
∗
✓ ✓ 80.80
Xception-96
∗
✓ ✓ 82.67
Xception-128
∗
✓ ✓ 85.11
73.37
✓ 86.19
✓ 74.89
Xception-256*
✓ ✓ 86.85
79.17
✓ 86.49
✓ 80.52
InceptionV4-299*
✓ ✓ 88.18
77.28
✓ 87.26
✓ 83.58
WideResNet-96*
(WRN)
✓ ✓ 88.83
87.83
✓ 88.23
✓ 92.23
WideResNet-101*
(WRN)
✓ ✓ 94.67
column is the learning strategy using no augmentation
(N/A), using only style augmentation (SA), using tra-
ditional augmentation plus cutout (Trad), and using
both (Trad+SA). We take a random sample with no
style (α = 1) to calculate their SAM (style activation
map) for each model and each augmentation strategy.
From this, we see how both Trad and Trad+SA help
the models to focus on the plane instead other regions
like no augmentation (N/A). Also, it is important to
highlight that the better the prediction, the more ac-
curate the region in the object (in this case, a plane).
On the other hand, using the best model
WideResNet-101, we use the same random sample
(a plane) to test the different learning strategies us-
ing the same style but varying the α parameter. Let’s
say, in this case, we will use as input the stylized sam-
ple. In Figure 3b, we show the influence of image
stylization. Each row means learning strategy N/A,
SA, Trad, and Trad+SA. So, each column implies that
the styled input sample by α value varies from 1.0
(no intensity/style) to 0.0 (more intensity) before be-
ing evaluated by each network. We saw that a styled
image tested in a model which does not use SA gets
too bad results, but this did not happen in the model
trained with SA. Also, the SAM-relevant regions in
styled models tend to be constant along the α varia-
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
834

(a)
(b)
Figure 2: (a) Influence of the application of styles on a sub-
set of the test set. (b) Comparison of WideResNet-101 ro-
bustness under style augmentation setting during training.
Accuracy vs. style transfer (α = 0.5) for a subset of the test
set.
tions.
In Figure 4a, we show different samples, styles,
and α values. We show the influence of style in ran-
dom samples with random styles; we note that some
styles exist which don’t help to improve prediction.
Otherwise, it gets worse. From this result, we say
some styles can influence positively, negatively, or
do not impact the input image. In addition, this re-
sult shows how the relevant regions for the network
change depending on the style, and these two results
are shown in Figure 4b, also improving or not the con-
fidence of the prediction.
6 DISCUSSIONS
We train, test, and visualize the impact of the style
augmentation varying both α values (from 0.0 to 1.0
in steps of 0.2) and learning strategies (N/A, SA,
Trad, and Trad+SA) using the STL-10 dataset. We
InceptionV4-299
InceptionV3-299
Xception-256
Xception-96
WideResNet-101
N/A
SA Trad Trad+SA
(a)
Trad
Trad+SA
SA
N/A
0.00.20.40.60.81.0
0.8106289 0.75712097 0.7257931 0.635738 0.36989683 0.34148487
0.7895591 0.34183666 0.42409673 0.57569075 0.4494388 0.66490185
0.98092914 0.9881363 0.98781824 0.974838 0.92511356 0.8637477
0.30903456 0.57933134 0.7311614 0.8176371 0.577271 0.4265946
(b)
Figure 3: Comparing SAM results: (a) We compare
SAM from different models (rows) using the augmentations
strategies: None, Trad, SA, and Trad+SA (columns). (b)
We compare SAM of the WideResNet-101 trained using
N/A, Trad, SA, and Trad+SA tested on the same image and
style but varying the style intensity α as input.
achieve high performance and the best result with
WideResNet-101. We show the behavior of the style
augmentation technique proposed (see Figure 1a and
Figure 1b). We identify that some styles perturb the
images more than others using the same sample, like
adding noise. Also, we argue that by using larger
input sizes and removing some complex styles, we
probably remove the negative impacts on training (see
Figure 2a. Furthermore, our experiments showed in-
teresting robustness to styles when styling is included
in the training (see Figure 2b). Nonetheless, we also
observed that the accuracy of models with Trad de-
creased drastically for some styles. Additionally, we
found that some textures are more challenging to per-
form a style transfer using cutting-edge networks.
We explored more deeply the effects of particu-
lar styles and their influence on training and testing.
In Figure 3a, we present how style made a model
more robust thanks to the different intensities of α,
which behaves as noise but does not apply to every-
one. Specifically, we took the case of the plane eval-
uated in Figure 3b. We got a low accuracy (0.341%)
with higher style intensity (α = 0.0). Otherwise, we
got the highest accuracy (0.988%) with α = 0.8. Fur-
thermore, experiment results suggested that the best
WSAM: Visual Explanations from Style Augmentation as Adversarial Attacker and Their Influence in Image Classification
835
0.00.20.40.60.81.0
0.99995816
0.9999819 0.9999918 0.9999763 0.99991345 0.99970275
0.8106289 0.75712097 0.7257931 0.635738 0.36989683 0.34148487
0.999388340.9935370.98700040.982297240.952903750.8190598
0.99021720.99181550.997581360.986474040.965263070.91495544
(a)
0.7488983
0.4972404
0.4703555
1020
Original
0.0
0.5
0.9
0.702322
0.4094997
0.6379028
76300100
0.4877583
78020
0.5292392
6050
0.4534032
0.4564208
0.4865795
8050
0.3266519
0.4833863
0.4037483
0.4244615
0.3844772
0.4011378
0.4777342
0.4797770
(b)
Figure 4: Comparing SAM results: (a) WideResNet-101
SAM results using different values for α, different styles,
and different samples. (b) WideResNet-101 SAM results
show the negative impact styles (3 on the left side), positive
impact styles (3 on the right side), and no style evaluated
for α = (0, 0.5, 0.9) to one input image (middle).
fit for α could be between 0.3 and 0.8, similar re-
sults were found in (Jackson et al., 2018). In Fig-
ure 4a, we note that some styles have no effects, and
for others, the network learns how to classify images
correctly with higher intensities (noise). Also, style
strengthens the correlation between predictions and
styled features activation maps (see Figure 4b).
Table 2: Results of the total WSAM variance sorted for each
class in STL-10 after normalization.
W SAM
variance
Category W SAM
variance
Category
airplane 0.107 horse 0.269
truck 0.129 bird 0.316
deer 0.175 dog 0.338
cat 0.193 monkey 0.380
car 0.228 ship 0.456
We now calculate the WSAM variance and
WSAM for each class sample, using all styles and
Figure 5: Results after calculating the WSAM for each class
sample, varying styles, and α as defined in Eq. 9. We can
see the total variance of the relevant region after stylization.
αs. In Table 2, we present the WSAM variance of
all SAMs. Besides, in Figure 5, we show the result of
WSAM for one sample per class. These results give
us an idea about the impact of applying 79 424 styles
with different α intensities during the training phase
and how the network learns to deal with those noisy
samples (styled images), helping the robustness of the
model. Finally, These results allow us to understand
the influence of style augmentation in image classi-
fication. We can say that style augmentation can be
used as a noise adder or adversarial attacker, making
our model more robust against adversarial attacks.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this work, we define a metric to explain by ex-
perimentation the behavior, the impact, and how
the style augmentation may impact getting better re-
sults in the classification tasks. This metric is com-
posed of three main outputs: Style Activation Map
(SAM), Weighted Style Activation Map (WSAM),
and W S AM
variance
; this last one measures the vari-
ance of the regions of relevant features in styled
samples. We outperform the state-of-the-art with-
out extra data in style augmentation accuracy with
WideResNet-101 trained on the STL-10 dataset; be-
sides, our method gives robustness to input variations.
From results and experiments, style augmentation has
an impact on the model, and this impact can be visu-
alized through SAM regions generated. We conclude
that styles may modify and perturb different features
from the input images (as an adversarial attacker),
thus causing another set of images with slight vari-
ations in the distribution or becoming outliers mak-
ing that prediction fail. In future directions, we will
extend this study to more complex models with a
higher number of parameters (like transformers) and
higher images size like ImageNet and explain how
style could influence their internal behavior. Also, we
VISAPP 2023 - 18th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
836

propose to understand more deeply which features are
selected to be preserved in each style and which dis-
tortion they could generate through the network lay-
ers.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Carlos Chagas Filho
Foundation for Research Support of Rio de Janeiro
State (FAPERJ)-Brazil (grant #E-26/201.424/2021),
S
˜
ao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)-Brazil
(grant #2021/07012-0), and the School of Ap-
plied Mathematics at Fundac¸
˜
ao Getulio Vargas
(FGV/EMAp). Any opinions, findings, conclusions,
or recommendations expressed in this material are
those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the
views of the FAPESP, FAPERJ, or FGV.
REFERENCES
Adebayo, J., Gilmer, J., Muelly, M., Goodfellow, I., Hardt,
M., and Kim, B. (2018). Sanity checks for saliency
maps.
Chollet, F. (2016). Xception: Deep Learning with Depth-
wise Separable Convolutions.
DeVries, T. and Taylor, G. W. (2017). Improved Regulariza-
tion of Convolutional Neural Networks with Cutout.
Dosovitskiy, A., Fischer, P., Springenberg, J. T., Riedmiller,
M., and Brox, T. (2014). Discriminative Unsupervised
Feature Learning with Exemplar Convolutional Neu-
ral Networks.
Gatys, L. A., Ecker, A. S., and Bethge, M. (2015). A Neural
Algorithm of Artistic Style.
Geirhos, R., Rubisch, P., Michaelis, C., Bethge, M., Wich-
mann, F. A., and Brendel, W. (2018). ImageNet-
trained CNNs are biased towards texture; increasing
shape bias improves accuracy and robustness.
Georgievski, B. (2019). Image Augmentation with Neural
Style Transfer. pages 212–224.
Ghiasi, G., Lee, H., Kudlur, M., Dumoulin, V., and Shlens,
J. (2017). Exploring the structure of a real-time, arbi-
trary neural artistic stylization network.
Gilpin, L. H., Bau, D., Yuan, B. Z., Bajwa, A., Specter, M.,
and Kagal, L. (2018). Explaining explanations: An
overview of interpretability of machine learning.
Gkitsas, V., Karakottas, A., Zioulis, N., Zarpalas, D., and
Daras, P. (2019). Restyling Data: Application to Un-
supervised Domain Adaptation.
Hesse, L. S., Kuling, G., Veta, M., and Martel, A. L. (2019).
Intensity augmentation for domain transfer of whole
breast segmentation in MRI.
Jackson, P. T., Atapour-Abarghouei, A., Bonner, S.,
Breckon, T., and Obara, B. (2018). Style Augmen-
tation: Data Augmentation via Style Randomization.
Ji, X., Henriques, J. F., and Vedaldi, A. (2018). Invariant
Information Clustering for Unsupervised Image Clas-
sification and Segmentation.
Jing, Y., Yang, Y., Feng, Z., Ye, J., Yu, Y., and Song, M.
(2017). Neural Style Transfer: A Review.
Kabir, H. M. D., Abdar, M., Jalali, S. M. J., Khosravi, A.,
Atiya, A. F., Nahavandi, S., and Srinivasan, D. (2020).
Spinalnet: Deep neural network with gradual input.
Kotovenko, Dmytro, adn Sanakoyeu, Artsiom, and Lang,
Sabine, and Ommer, B. (2019). Content and Style
Disentanglement for Artistic Style Transfer.
Li, X., Liu, S., Kautz, J., and Yang, M.-H. (2018). Learn-
ing Linear Transformations for Fast Arbitrary Style
Transfer.
Selvaraju, R. R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R.,
Parikh, D., and Batra, D. (2017). Grad-cam: Visual
explanations from deep networks via gradient-based
localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Computer Vision, pages 618–626.
Shrikumar, A., Greenside, P., and Kundaje, A. (2017).
Learning important features through propagating ac-
tivation differences. In Proceedings of the 34th In-
ternational Conference on Machine Learning-Volume
70, pages 3145–3153. JMLR. org.
Simonyan, K., Vedaldi, A., and Zisserman, A. (2013).
Deep inside convolutional networks: Visualising im-
age classification models and saliency maps.
Sundararajan, M., Taly, A., and Yan, Q. (2017). Axiomatic
attribution for deep networks. In Proceedings of the
34th International Conference on Machine Learning-
Volume 70, pages 3319–3328. JMLR. org.
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., Vanhoucke, V., and Alemi, A.
(2016). Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Im-
pact of Residual Connections on Learning.
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., and Wojna,
Z. (2015). Rethinking the Inception Architecture for
Computer Vision.
Tanaka, F. H. K. d. S. and Aranha, C. (2019). Data Aug-
mentation Using GANs.
Thoma, M. (2017). Analysis and Optimization of Convolu-
tional Neural Network Architectures.
Ulyanov, D., Vedaldi, A., and Lempitsky, V. (2017). Im-
proved Texture Networks: Maximizing Quality and
Diversity in Feed-forward Stylization and Texture
Synthesis.
Zagoruyko, S. and Komodakis, N. (2016). Wide Residual
Networks.
Zeiler, M. D. and Fergus, R. (2014). Visualizing and under-
standing convolutional networks. In European confer-
ence on computer vision, pages 818–833. Springer.
Zhao, J., Mathieu, M., Goroshin, R., and LeCun, Y. (2015).
Stacked What-Where Auto-encoders.
Zheng, X., Chalasani, T., Ghosal, K., Lutz, S., and Smolic,
A. (2019). STaDA: Style Transfer as Data Augmenta-
tion.
Zhou, B., Khosla, A., Lapedriza, A., Oliva, A., and Tor-
ralba, A. (2016). Learning deep features for discrim-
inative localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE con-
ference on computer vision and pattern recognition,
pages 2921–2929.
WSAM: Visual Explanations from Style Augmentation as Adversarial Attacker and Their Influence in Image Classification
837
