
A Holonic Multi-Agent Architecture For Smart Grids
Ihab Taleb
a
, Guillaume Guerard
b
, Fr
´
ed
´
eric Fauberteau
c
and Nga Nguyen
d
L
´
eonard de Vinci P
ˆ
ole Universitaire, Research Center, 92 916 Paris La D
´
efense, France
Keywords:
Smart Grid, Holarchy, Holon, Multi Agent System (MAS).
Abstract:
The global warming and the increase of fossil fuel prices make the minimization of energy generation an
important objective. Thus, smart grids are becoming more and more relevant in a context where we want to
regulate the demand according to the available energy. This regulation can be operated thanks to Demand Side
Management (DSM) tools. While different models and architectures have been developed for smart grids,
only few papers used holonic architectures. For this, we propose in this paper a holonic architecture for smart
grids. This type of architectures is relevant to smart grids as it allows the various actors in the grids to work
even in the cases of technical problems. Holons in the proposed model are composed of five interconnecting
agents that ensure flexibility on the various aspects. This model has been tested and has proven to work on
3 different scenarios. The first scenario simulates a grid in its healthy state. The second one simulates a
grid where a region can be disconnected from a blackout for example. The third one simulates a grid with
production mismanagement. Results show how the grid distributes the available energy depending on the
available production, priorities (if any) and the assurance of the distribution across the various requesting
holons.
1 INTRODUCTION
In 2015, 196 countries accepted the Paris Agreement
for limiting global climate change caused by global
warming to less than 2
o
C, by restricting the use of fos-
sil fuels (UNFCCC, 2021). In this context, the Euro-
pean Union funds projects to develop solutions reduc-
ing the production of greenhouse gases. For example,
the MAESHA project, in which the contributions of
this article are part, aims at decarbonizing the French
island of Mayotte.
In fact, energy production infrastructures are ma-
jor players in climate change. In first projects, electri-
cal production based on natural gas has proven to be
not the ideal solution. First, natural gas is a type of
fossil fuel, which means that its energy is still pollut-
ing. Second, as it is not available in all countries its
price can increase dramatically during transportation
problems whether they are caused by accidents or by
political conflicts.
Consequently, it is important to find other solu-
tions that can be easier to access and to manage. For
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2666-7631
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6773-221X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1169-8040
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3273-8272
these reasons, transition policies from fossils like coal
have been discussed in (Spencer et al., 2017) by sug-
gesting the increase of the integration of Renewable
Energy Sources (RESs) by encouraging governments
and people to install RES generators like Photovoltaic
(PV) panels. Although RESs are still costly compared
to other energy sources, the study in (Brockway et al.,
2019) estimates that the Return Of Investment (ROI)
will increase with time (more cost effective) and will
reach, in the near future, that of the fossil fuels. On
the other hand, one of the biggest challenges when
talking about RES is that it is difficult to control, as it
highly depends on weather parameters like sun radia-
tions, temperature, wind, etc. This challenge means
that the more RESs we have in the Electrical Grid
(EG) the harder it is to control energy generation.
As another challenge, the number of Electric Ve-
hicles (EVs) is increasing by the day, which means
higher demand to charge their batteries and higher
risks of serious problems in the grids like partial or
total blackouts (Green et al., 2011). However, with
a proper control over these EVs (delaying or advanc-
ing the charging process and discharging if needed),
it is possible to not only avoid blackouts, but to use
these batteries as a storage point to provide energy in
the peak hour. This method is called Vehicle to Grid
(V2G) (Hannan et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2013). Hav-
126
Taleb, I., Guerard, G., Fauberteau, F. and Nguyen, N.
A Holonic Multi-Agent Architecture For Smart Grids.
DOI: 10.5220/0011803300003393
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2023) - Volume 1, pages 126-134
ISBN: 978-989-758-623-1; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

ing the uncontrollable generation, and the control-
lable EVs charging and discharging, the only parame-
ter that we can manage in this case is the demand, by
a process called Demand Side Management (DSM).
DSM aims to delay, flatten or plan the demand and
use battery storage when the demand is higher than
the available energy (peak hours) (Kanakadhurga and
Prabaharan, 2022), and store the extra energy pro-
duced during high generation hours. Thus, in order
to benefit from DSM, there is a need to upgrade the
traditional EG to a Smart Grid (SG) that can allow for
smarter energy usage and routing.
SG’s concepts have been defined as it is known
nowadays by (Amin and Wollenberg, 2005). It is the
new version that aims to upgrade EGs on the differ-
ent aspects : measurements, predictions, data registry
and analytics, control, and communication. It cov-
ers all grids’ problems and requirements starting from
consumers and producers to energy distribution and
blackouts handling. SGs improve the communica-
tion and the distributed control over the various ac-
tors (i.e., consumers, producers, storage facilities and
EVs) and integrate the new type of actors called pro-
sumers (Espe et al., 2018). Prosumers are consumers
that can produce all or part of their energy demand
using RES. An example of prosumers is a house hav-
ing PV panels where the energy produced can satisfy
or not the demands of this house depending on the
weather (sun radiation), or an EV having relatively
large battery storage where it can charge or discharge
depending on the available energy on both the grid’s
side and the EV’s side.
In order to use RESs, batteries and EVs to their
maximum potential, SGs require energy routing to
be bidirectional, to allow the users to act not only
as consumers, but also as producers whenever they
have sufficient energy production or storage during
peak hours (Ramchurn et al., 2012). However, to
reach the optimal performance for prosumers, it is im-
portant to have measurements and predictions for the
near future. Predictions help SG actors to make their
demands or offers to other actors ahead of time, al-
lowing the energy to be routed more effectively with
less loss and lower transmission costs, or to delay (if
needed) some of the demands before peak hours hap-
pen. Indeed, multiple deep learning methods have
been proposed to predict energy demands in a flexible
or reusable way. (Dudek et al., 2021; Huang et al.,
2022) proposed deep learning methods that can be
used to predict the demand in various regions. While
(Huang et al., 2022; Pallonetto et al., 2022) have pro-
posed deep learning models to predict on different
time ranges. (Taleb et al., 2022) proposed a flexible
deep learning method that ensures the flexibility on
both time ranges and region domains.
Different architectures and models for SGs have
been proposed. However, one architecture that has not
yet been sufficiently tested or defined in the domain
of SGs is the holonic architecture. Indeed, the goal of
this paper is to answer the suggestion made by (How-
ell et al., 2017) by proposing a holonic Smart grid
architecture. A holonic architecture is an architec-
ture defined by the aggregation of one universal entity
called holon. A holon is an entity that can work (by
itself) as a whole while at the same time, being part
of a larger entity of the same type (Mella, 2009). In a
holonic SG, a holon can be seen in such architecture
as the aggregation of multiple microgrids, while each
of them is also an aggregation of smaller microgrids
until we reach the level of houses or electric devices.
The proposed model simulates the behavior of holons
among the SG. Holons include various agents which
can be modified to simulate various scenarios. For
example, our model can include various energy prices
(flat prices, dynamic prices, carbon-based prices, etc.)
and energy management strategies (shifting, peak and
load reduction, peak clipping, valley filling, etc.) and
any technologies. Scenarios also includes all kinds of
disturbances on the grid, about its structure, its behav-
iors or external factors.
In this paper, a literature review of Holonic Multi-
Agent System (HMAS) and holons is given in Section
2. Section 3 describes the proposed model as both a
single holon model and as a holarchic model, as well
as discusses some of the possible decision and control
methods that can be applied to the proposed architec-
ture. In Section 4, the materials and methods used for
the simulations are discussed, as well as the three test
cases used on the proposed model. Conclusion and
future work are discussed in Section 5.
2 EXISTING MODELS AND GAPS
The idea of holons and holarchy (holons organized in
a hierarchical architecture) has been first introduced
with the book ”The Ghost in the Machine” written
by Arthur Koestler in 1967 (Koestler, 1967). (Ger-
ber et al., 1999) introduced the concept of HMASs
where one agent can be the aggregation of multiple
lower domain agents. The concept of HMASs has
then been applied to a diversity of domains like au-
tomation, manufacturing and transportation systems
(Mar
´
ık et al., 2013).
While different architectures have been defined
for SGs, the most interesting architectures are the
ones that are based on holarchies as they provide
more flexibility to the different actors of the grid (con-
A Holonic Multi-Agent Architecture For Smart Grids
127

sumers, producers, prosumers, storage facilities and
points of distribution) (Negeri et al., 2013), while at
the same time, benefiting from both the decentral-
ization of the decision and the top-down hierarchical
organization or surveillance. Indeed, (Ghorbani and
Unland, 2016) has proposed to compose the SG of
two layers: physical layer where all the connections
to all physical devices happen, and aggregation layer
where all holons from the first layer merge or aggre-
gate to form the SG. (Ansari et al., 2015) has defined
their SG based on low and medium voltages: a first
level designs smart homes and energy resources, than
the higher levels are for low voltage feeders, medium
voltage feeders, medium voltage substations, etc. up
to the highest level that contains the energy manage-
ment system holon that is responsible for managing
the whole system.
Concerning holonic architecture, (Ferreira et al.,
2015) has introduced the concept of single holon
modeling where one type of holon can manage any-
thing from a physical device, to an apartment, build-
ing, to micro-grids. It also proposes the holon to be
multi-threaded, where each holon has a thread for
the negotiation with peers, a thread for the negotia-
tion with children, and a third thread for the local be-
haviours. (Abdel-Fattah et al., 2020) has discussed
the application of holonic SGs for self-healing appli-
cations, as well as the potential, the challenges and the
requirements for SGs in a holonic architecture. (Wal-
lis et al., 2020) has proposed a framework, based on
holonic architectures, that is composed of three parts:
historical data collection, prediction (FRODO, which
stands for Forecasting of Resources for Dynamic Op-
timization) and decision or strategy selection (OLAF,
which stands for Optimal Load and Energy Flow).
In the next sections we will discuss a new pro-
posed single holon model that is composed of multi-
ple agents. The main goal of this model is to provide
the highest possible flexibility in terms of the defini-
tion of the SG architecture, its reuse and blackouts
avoidance.
3 THE PROPOSED MODEL
A holon is the only component of a holonic architec-
ture. Thus, the more holons are flexible and perform-
ing, the better the model is. In this section we pro-
pose a holon that is composed of five interconnect-
ing main agents, namely: measurement agent, data
agent, prediction agent, control agent and communi-
cation agent. Figure 1 shows the agents of the holon
and their interactions.
3.1 A Holon Of Five Agents
The five agents of a holon are defined as follows:
Measurement Agent: is the agent responsible for
collecting data from physical devices: smart devices
that are IoT connected, sensors, smart meters. It is
the intermediary between the data agent (and all other
agents) and these devices.
Prediction Agent: is responsible to provide predic-
tions for future demands and/or generations depend-
ing on historical data provided by the data agent. It
implements the hybrid deep learning algorithm de-
scribed in (Taleb et al., 2022), which is able to make
flexible predictions on both time scale and spatial
scale. For the spatial scale, this method can provide
predictions on a whole island scale as well as on the
scale of a small group of buildings without the need of
any modifications in the method. On the other hand,
this method can also provide predictions on different
time ranges (real-time, daily and weekly predictions)
with minor changes in the preprocessing phase.
Data Agent: is the agent responsible for handling
data, storing these data and sending them to the pre-
diction agent. It is also responsible for storing predic-
tions made by prediction agent and to send them to
control agent depending on its requests.
Control Agent: is responsible for decision making,
it can be as simple as request-response in an Internet
of Energy (IoE) context as well as more sophisticated
algorithms implementing Evolutionary Game Theory
(EGT) or Q-learning. It takes its decision depending
on two flows of informations. The first is the predic-
tion data made by prediction agent and stored with
data agent. The second is the ensemble of requests
and/or offers sent from lower holons and the feed-
back received from the upper holon (in a holarchic
architecture).
Communication Agent: is the agent responsible
for the communications with other holons via their
respective communication agents, it uses the Agent
Communication Language (ACL) specifications for
the communications with other agents. It also ensures
that lower holons are in synchronization with its cur-
rent step.
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
128

Measurement
Agent
Prediction
Agent
Control Agent
Communication
Agent
Data Agent
Figure 1: The structure of the proposed holon, composed of
five interconnecting agents.
3.2 Holarchic Architecture
A holarchy or holarchic architecture is a holonic ar-
chitecture composed of holons organised in a hierar-
chical way. The concept of holarchy is similar to that
of a tree based architecture. However, the main differ-
ence between the two is that in a holarchy, the parts
are autonomous and able to operate independently,
while in a tree-based hierarchy, the parts are more de-
pendent on the whole and may not be able to function
on their own. The holarchic architecture is used in
this paper to provide flexibility in the functional as-
pect, the spatial aspect and the temporal aspect.
Holons should be able to work for any type of
actor in the SG whether it is a physical device, stor-
age facility, EV, or a micro-grid. Measurement agent
takes care of the communication with various types of
devices or smart meters while communication agent
takes care of communicating with other holons that
are either lower holons representing smaller micro-
grids or the upper holon representing the larger micro-
grid. This ensures the flow of data from both sides
(devices and/or other holons) to the control agent.
On the other hand, holons are created and dis-
tributed on the various levels based on the regional
aspect, which means that the super holon on the very
first level (the highest level) will represent a whole
country or an island in the case of the simulation of
this paper. On the second level, each holon represents
a region or an actor of equivalent amount of power de-
mand or generation (e.g., a thermal power plant). The
third level represents villages or any equivalent actor
in terms of the amount of power traded (e.g., RES fa-
cility or a storage facility). the architecture can reach
down as much as needed depending on the decision
of the engineers that will apply this architecture until
it reaches the level of simple smart devices like heat-
ing devices. Holons continually check at each time
step to ensure if any physical devices or subholons
are connected to them respectively in order to provide
for them or from them the energy that is needed or
available. Holons also should also be able to provide
predictions on different regional scale whether it is a
large region or a small group of buildings or even a
small device. Holons in this paper are only connected
to their upper holon, to their lower holons, and to their
proper devices. In order to have a simpler and more
practical architecture, Holons do not communicate di-
rectly with other holons on the same level, but instead,
they wait for the feedback of their upper holon which
will have the broader information.
Moreover, holons should be able to work on dif-
ferent time ranges, depending on which level they are
in and with which type of physical actors and holons
they are dealing with. Data agent stores the data that
could be needed in the next steps for both predictions
and decision taking while prediction agent takes care
of providing predictions on multiple time ranges de-
pending on the needs of control agent.
Figure 2 shows an example of how a holarchy
looks like for the SG while Figure 3 shows a sequence
diagram for the five agents of a holon, with social
agents of its connected holons.
Figure 2: The holarchic architecture. In this image, we can
see that the holarchy is composed of three levels whereas it
can be extended to as many levels as needed.
3.3 Control Methods
In order to ensure an efficient routing and sharing of
energy across the grid, holons should be able to not
only take local decisions, but to negotiate by request-
ing or offering energy. They also should be able to
change their decisions (e.g., by delaying demands, or
stocking their offer for later use, etc.) depending on
the feedback of their upper holons. Indeed, different
methods can be applied to the negotiations and deci-
sion making for the control of the various holons on
the various levels. Also, these methods should follow
two specific steps in order to ensure the organization
of the communication of the different actors.
Local Decision: Each holon takes its decision
based on energy requests and offers of both its con-
A Holonic Multi-Agent Architecture For Smart Grids
129

Figure 3: The interaction between the various agents of the holon and the social agents of their connected holons (in this
diagram, we considered that the holon is connected to only 2 subholons while this number can be less or more in other cases).
nected actors and its subholons. Requests and of-
fers are decided, ahead of time, based on predictions.
These decisions can be taken using various algorithms
and methods, like IoE, EGT, optimization, etc.
• The IoE method, proposed in this paper, consists
of calculating, at each level, the request/offer ra-
tio. Based on this ratio, a holon decides whether
to demand or offer energy to its upper holon. This
process happens recursively in a bottom-up ap-
proach until it reaches the highest level holon, the
holon that is supposed to send its feedback. In
peak hours, if the generated energy cannot ful-
fill all the demands, upper holons feedback will
consist of the calculated ratio at the highest level,
which it turns will be the percentage to be de-
creased for each holon and at each level. In this
approach, negotiations can be as simple as one it-
eration of demand and response. Section 4 uses
this approach, tested on the proposed architecture,
in order to show the distribution of energy in dif-
ferent test scenarios.
• In EGT, demands and requests can be seen as
strategies, and each strategy is represented by its
own population. Populations evolve depending
on the feedback of the upper holon on multi-
step negotiations. EGT can be combined with Q-
Learning to update the payoff tables for players at
each time-step.
• In Optimization methods, requests and offers can
be seen as variables that can take positive or nega-
tive values. These variables can be updated de-
pending on the feedback of the upper holon at
each time-step. In Particle Swarm Optimization
(PSO), the feedback received can be considered
as the output of fitness function that is responsi-
ble to choose the particle with best fitness (in this
case, the best offer or demand).
Negotiations and Global Decision: In this step,
holons try to achieve a consensus with their upper
and lower holons. It is important to specify a max-
imum number of iterations and to stop whenever op-
timal values are reached. Simulated annealing is an
option to ensure the convergence of the grid.
4 SIMULATION AND RESULTS
The simulation has been made using JAVA as a pro-
gramming language and JAVA Agent DEvelopment
Framework (JADE) for the development of holons
and their composing agents. It exploits the IoE
method proposed in Section 3.3.
4.1 Materials and Methods
The model proposed in this paper has been tested
on the data of the island of Mayotte provided by the
MAESHA project.
Indeed, weather forecasts, holiday data and histor-
ical data of both energy demand and RES production
on 60 minutes granularity has been provided for the
simulation. The island has two thermal power plants,
one Biogas and various RES facilities. The simula-
tion is composed of 3 levels holarchy. The first level
consists of the super holon representing the whole is-
land. The second level represents the 17 regions of
the island. While it is possible to be defined in other
ways, in this simulation, second level holons have the
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
130
two thermal power plants, the Biogaz plant, and the
RES facilities each directly attached to the holon rep-
resenting their region. On the third level, holons rep-
resent the villages of each region. Mayotte has a to-
tal of 72 villages which means a total number of 72
holons on the third level. Third level holons start all
the energy demands, and their requests propagate to
second level holons. Second level holons gather the
data from third level holons and verify if their requests
can be satisfied in the local network of holons, other-
wise, they send their request to upper level holons un-
til they reach a point where their request is fulfilled or
until the request reaches the highest level with no suf-
ficient energy. In this case, the super holon will send
feedback about lowering the demands, this feedback
will then propagate back from higher levels to lower
levels until it reaches the lowest levels that are respon-
sible for the demands. Although it is not included in
this simulation, it is also possible to have storage fa-
cilities that can store energy (in this case they act like
consumers) and then to provide this energy (in this
case, they act like generators) in later times depending
on the need of the SG (depending on the feedback that
arrives from higher level holons). The architecture de-
fined in Section 3 has been tested in three scenarios.
Having the large number of holons in the island, it is
not possible to show the result of the simulation for
each holon. For this, The results of these three sce-
narios are provided for one specific holon (in Figure
4, 5, 6 and 7), showing the energy received by the
holon representing Handr
´
ema, which is a village in
the Bandraboua region. The reason for choosing this
village is that it belongs to a region having PV gen-
eration so that in case of a disconnection like in the
second case (Section 4.3), it can still demand energy
from its region’s holon. Any region or a village that
can either produce its own energy or demand energy
from connected holons should give a similar output as
in the second scenario. However, it is worth mention-
ing that if a holon or a group of holons got discon-
nected from the grid with zero-productions, they will
not be able to satisfy their demands as they have no
way for having energy.
4.2 Standard Scenario
The simulation in this scenario is the standard case
where all holons on the three levels, described in Sec-
tion 4.1, are properly connected and thermal produc-
tion is in its optimal production, which means that
all energy demands can be satisfied across the whole
grid. Energy requests, that could not be fulfilled lo-
cally, propagate from the third level (the lowest level)
to upper levels. When the highest level holon receives
all requests, it then sends its feedback ranging from 0
(no energy available) to 1 (energy demanded can be
fulfilled in full). Figure 4 shows that all the energy,
demanded by (Handr
´
ema), is received.
Figure 4: Energy received by a holon representing a village
on level 3, in the standard scenario where all the holons
across the whole grid are properly connected.
4.3 Disconnected Holon
The second scenario shows what happens to the en-
ergy received and consumed in the case if a discon-
nection happened between a holon in the second level
and its upper holon (the holon representing the whole
island). In fact, disconnection might happen for mul-
tiple reasons, but it is mostly because of technical
problems in transmission cables. In this scenario, re-
quests can propagate from villages only to one higher
level (i.e., only to their directly upper holon), namely
the holon representing the region Bandraboua. Ban-
draboua can no longer demand from the holon rep-
resenting the island because of the disconnection be-
tween them. Thus, the only energy that can be sent
to its lower holons is the energy produced locally in
this region. The upper holon has two choices: the first
choice (described in Section 4.3.1) is to give priority
to specified holons and give the rest of the energy to
the other holons, while the second choice (described
in Section 4.3.2) is to distribute the energy propor-
A Holonic Multi-Agent Architecture For Smart Grids
131

tionally to their demands (which means, as an exam-
ple, that the holon requesting 10% of the total demand
will receive 10% of the available energy).
4.3.1 Holon Prioritization
In this case the disconnected holon representing the
region Bandraboua gives the priority to the holon
representing the village Handr
´
ema which means that
this holon will receive all energy that it needs and the
other holons will only receive what is left. Figure 5
shows the received energy for Handr
´
ema on hourly
basis. At the beginning of the simulation at time-step
0, the energy received starts at zero in the first hour as
the connection between the holon (Handr
´
ema) and
its upper holon (Bandraboua) is not yet established
and it is to be established in this time-step. The en-
ergy received then increases and decreases depending
on the PV energy produced, which is directly corre-
lated to the sun radiations. This explains the zeros re-
ceived between hours 15 and 25 and after 39 which
indicate night-time hours. While this seems like a
problem, it can still be a solution to avoid total or
partial blackouts. The energy received between time-
steps 3 and 13 and 28 and 38 are equal to the energy
demand which means that during these time-steps,
energy production has exceeded energy demand (for
Handr
´
ema, the prioritized village) and thus, the other
villages can share the energy produced that is left. Al-
though this is not included in the current simulation,
it is worth mentioning that the energy received during
day-time can then be stored in batteries in order to
be used depending on predefined priorities through-
out the day.
4.3.2 No Priorities Given
In this case, the disconnected holon will not give any
priority to any holon and will instead give the energy
proportionally to what has been demanded in total.
Figure 6 shows the amount of energy received by the
holon representing Handr
´
ema. The results in this fig-
ure show that the specified holon never receives a suf-
ficient amount of energy because the total demand is
higher than the PV generation.
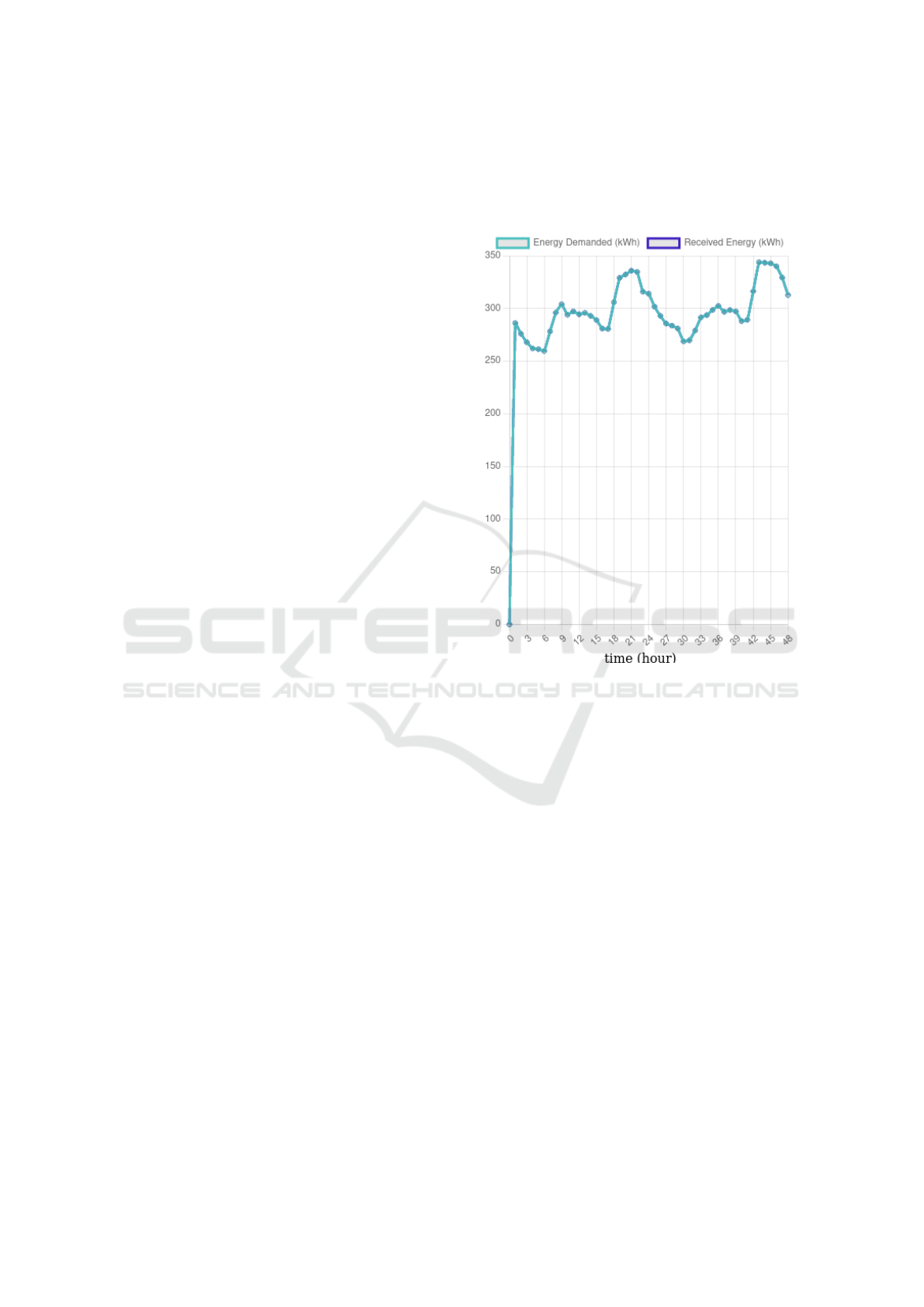
4.4 Disconnected Plant
In 2023, the thermal power station of Badamiers is
scheduled to be at the end of its life. Thus, the is-
land will be then using only one power plant which
means less energy generation. For this, this test sce-
nario consists in using only the other thermal power
plant (located in Koungou), the biogas station, and
the PV generation. In a similar way to above, when-
Figure 5: Energy received by a holon representing a priori-
tized village on level 3, in a scenario where its upper holon
is disconnected from the grid and the only energy available
is the energy produced locally in the region.
ever the produced energy is not sufficient, thermal en-
ergy gets distributed to every village proportionally
to the population of the village. Figure 7 shows the
energy received for the holon of Handr
´
ema. In this
figure, the energy received from thermal power plants
is around 280 kW·h all the time. The result shows that
between time-step 2 and 7, and time-step 29 and 32,
the received energy meets the energy demand because
the amount requested is below the available amount
of energy. On the other hand, during the time-steps
between 8-13, 16-17 and 33-38, the energy requested
was completely fulfilled because of the energy gen-
erated additionally to the thermal energy. For all the
other time-steps, energy demands were not fully sat-
isfied because of the lack of energy.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we proposed a holonic smart grid ar-
chitecture following the concept of single holon mod-
elling, where holons represent geographical zones
starting from houses and buildings up to islands or
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
132

Figure 6: Energy received by a holon representing a village
on level 3, in a scenario where its upper holon is discon-
nected from the grid and the only energy available is the en-
ergy produced locally in the region and no village has any
priority.
countries as a whole thanks to its flexibility on the
regional, spatial and functional aspects. We have dis-
cussed the components (agents) of this holon, the in-
teractions between the agents in the same holon, and
between the various connected holons as well as some
of the methods that can be applied to this architecture.
We then applied this architecture to the French island
of Mayotte, forming 3 levels holarchy. The first level
consists of the highest holon which represents the is-
land as a whole. The second level represents the 17
regions of the island and the third level (the lowest
level in the holarchy) is composed of 72 holons. Each
of these holons is connected to its respective upper
holon. We then tested this holarchy on three test sce-
narios. The first one is a standard scenario where the
energy flow and the connection between holons are as
supposed to be. The second scenario is a disconnec-
tion scenario where a holon is disconnected from the
main grid and it has to deal with the energy that it has
without going into a blackout. This scenario has been
tested on two cases. The first case is a priority case
where we give the priority to a specific holon where
the second case is a no-priority case where all holons
have the same level of priority and have to share the
Figure 7: Energy received by a holon representing a village
on level 3, in a scenario where only one thermal power plant
is operating.
available energy. The third scenario is a test where
a thermal power plant is disconnected from the grid.
The simulations have proven this architecture to be
flexible and effective in both the standard scenario
and the scenario where a micro-grid can get discon-
nected from the main grid. Finally, this paper has fo-
cused mainly on the proposition of this new architec-
ture, its feasibility and its flexibility in all aspects. In
future works, more sophisticated methods and algo-
rithms will be implemented to this architecture, while
introducing the concepts of delays, storage, priorities
in more details, the formation of virtual power plants
and the negotiations with other holons in multiple it-
erations before taking decisions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This project has received funding from the European
Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation pro-
gramme under grant agreement No. 957843.
A Holonic Multi-Agent Architecture For Smart Grids
133

REFERENCES
Abdel-Fattah, M., Kohler, H., Rotenberger, P., and Scholer,
L. (2020). A review of the holonic architecture for
the smart grids and the self-healing application. pages
1–6.
Amin, S. M. and Wollenberg, B. F. (2005). Toward a smart
grid: power delivery for the 21st century. IEEE power
and energy magazine, 3(5):34–41.
Ansari, J., Kazemi, A., and Gholami, A. (2015). Holonic
structure: A state-of-the-art control architecture based
on multi-agent systems for optimal reactive power dis-
patch in smart grids. IET Generation, Transmission &
Distribution, 9.
Brockway, P. E., Owen, A., Brand-Correa, L. I., and Hardt,
L. (2019). Estimation of global final-stage energy-
return-on-investment for fossil fuels with compari-
son to renewable energy sources. Nature Energy,
4(7):612–621.
Dudek, G., Pełka, P., and Smyl, S. (2021). A hybrid resid-
ual dilated lstm and exponential smoothing model for
midterm electric load forecasting. IEEE Transactions
on Neural Networks and Learning Systems.
Espe, E., Potdar, V., and Chang, E. (2018). Prosumer com-
munities and relationships in smart grids: A litera-
ture review, evolution and future directions. Energies,
11(10).
Ferreira, A.,
ˆ
Angela Ferreira, Cardin, O., and Leit
˜
ao, P.
(2015). Extension of holonic paradigm to smart grids.
IFAC-PapersOnLine, 48(3):1099–1104. 15th IFAC
Symposium onInformation Control Problems inMan-
ufacturing.
Gerber, C., Siekmann, J., and Vierke, G. (1999). Holonic
multi-agent systems.
Ghorbani, S. and Unland, R. (2016). A holonic multi-agent
control system for networks of micro-grids. In Klusch,
M., Unland, R., Shehory, O., Pokahr, A., and Ahrndt,
S., editors, Multiagent System Technologies, pages
231–238, Cham. Springer International Publishing.
Green, R. C., Wang, L., and Alam, M. (2011). The im-
pact of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles on distribution
networks: A review and outlook. Renewable and Sus-
tainable Energy Reviews, 15(1):544–553.
Hannan, M., Mollik, M., Al-Shetwi, A. Q., Rahman, S.,
Mansor, M., Begum, R., Muttaqi, K., and Dong, Z.
(2022). Vehicle to grid connected technologies and
charging strategies: Operation, control, issues and
recommendations. Journal of Cleaner Production,
339:130587.
Howell, S., Rezgui, Y., Hippolyte, J.-L., Jayan, B., and Li,
H. (2017). Towards the next generation of smart grids:
Semantic and holonic multi-agent management of dis-
tributed energy resources. Renewable and Sustainable
Energy Reviews, 77:193–214.
Huang, Y., Hasan, N., Deng, C., and Bao, Y. (2022). Mul-
tivariate empirical mode decomposition based hybrid
model for day-ahead peak load forecasting. Energy,
239:122245.
Kanakadhurga, D. and Prabaharan, N. (2022). Demand side
management in microgrid: A critical review of key
issues and recent trends. Renewable and Sustainable
Energy Reviews, 156:111915.
Koestler, A. (1967). The Ghost in the Machine. Macmillan.
Liu, C., Chau, K. T., Wu, D., and Gao, S. (2013). Opportu-
nities and challenges of vehicle-to-home, vehicle-to-
vehicle, and vehicle-to-grid technologies. Proceed-
ings of the IEEE, 101(11):2409–2427.
Mar
´
ık, V., Lastra, J. M., and Skobelev, P. (2013). Indus-
trial applications of holonic and multi-agent systems.
In Proceedings of Ll” DEXA International Workshop.
Springer.
Mella, P. (2009). The Holonic Revolution Holons, Hol-
archies and Holonic Networks. The Ghost in the Pro-
duction Machine.
Negeri, E., Baken, N., and Popov, M. (2013). Holonic archi-
tecture of the smart grid. Smart Grid and Renewable
Energy, 04:202–212.
Pallonetto, F., Jin, C., and Mangina, E. (2022). Forecast
electricity demand in commercial building with ma-
chine learning models to enable demand response pro-
grams. Energy and AI, 7:100121.
Ramchurn, S., Vytelingum, P., Rogers, A., and Jennings,
N. (2012). Putting the ’Smarts’ into the Smart Grid:
A Grand Challenge for Artificial Intelligence. Com-
munications of The ACM - CACM, 55:86–97.
Spencer, T., Berghmans, N., and Sartor, O. (2017). Coal
transitions in China’s power sector: A plant-level as-
sessment of stranded assets and retirement pathways.
Coal transitions, 12/17:21.
Taleb, I., Guerard, G., Fauberteau, F., and Nguyen, N.
(2022). A flexible deep learning method for energy
forecasting. Energies, 15(11).
UNFCCC (2021). The Paris Agreement | UN-
FCCC. https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-
paris-agreement/the-paris-agreement.
Wallis, A., Hauke, S., Egert, R., and M
¨
uhlh
¨
auser, M.
(2020). A framework for strategy selection of atomic
entities in the holonic smart grid.
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
134
