
Mapping Task Types and Gameplay Categories in the Context of
Declarative Knowledge Training
B
´
er
´
enice Lemoine
a
, Pierre Laforcade
b
and S
´
ebastien George
c
LIUM Computer Science Laboratory, Le Mans Universit
´
e, Laval, France
Keywords:
Serious Game, Didactic, Design, Training, Declarative Knowledge, Gameplay.
Abstract:
Learning games for the training of declarative knowledge must offer learners a wide variety of game situ-
ations in order to keep them engaged. Designing such situations remains a challenge due to the inherent
entanglement of didactical objectives and gaming implementations. This article proposes to tackle the need
for mapping different training tasks to different gameplays in order to help the design of relevant gameplay-
oriented training situations. We identified an approach during the design of a Roguelite-oriented training game
for multiplication tables. This approach has been intentionally specified towards a genericity purpose by using
domain-independent task types and abstract gameplays. This article details the method we followed to identify
this approach and presents the resulting mappings when applied to our specific application context.
1 INTRODUCTION
This last decade, the design and use of learning games
has become a common practice (Codish and Ravid,
2015). However, most learning games fail to be seen
as real video games mostly because of their lack of
gameplay (i.e., fun elements that can be controlled,
decided and done by the players) (Prensky, 2005). Al-
though combining the fun of real game and educa-
tional content is not easy (Prensky, 2005), it is a key
component of a good learning game design. Com-
bining the two dimensions (i.e., game and education)
is difficult, primarily because there are multiple vari-
ables to consider. Moreover, these variables often de-
pend on the knowledge to be learned and the targeted
game genre.
Learning games targeting declarative knowledge
training require a deeper commitment from learners
as they are used regularly for repetitive training ses-
sions. This implies that the design of such learning
games must offer a wide variety of situations, game
mechanisms or gameplays. Designers then have to
deal with various stakes such as the dynamic genera-
tion of training sessions or the adaptation of these ses-
sions to take into account the different teachers and/or
learners’ needs or preferences. This also includes de-
signing how the variety of situations will be tackled.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7608-3223
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8498-2731
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0812-0712
Our research interest is about that challenge. We
focus on it by considering the design of varied game-
plays. These gameplays involve that the player-
learner makes the avatar, which he/she controls, in-
teract with the environments and objects in the game
to perform contextualized actions to answer the ques-
tion being asked. Because training games include
several domain-specific parameterized training tasks,
many gameplays have to be identified for each one of
them. Identifying how different training tasks can be
implemented using these different gameplay concepts
requires conceptualizing and addressing a transdisci-
plinary TEL (Technology Enhanced Learning) prob-
lem: how can didactic knowledge be mapped to dif-
ferent gameplays?
We encountered this challenge during the design
of a Roguelite oriented learning game to train the re-
tention of the multiplication tables. First, we iden-
tified an approach that involves addressing the chal-
lenge at a higher level of abstraction (task types in-
stead of domain-specific tasks and game categories
instead of practical gameplays). This allows for
a more generic and domain-independent approach.
Secondly, the main thrust of the approach is to use a
dedicated pivot to help identify the source (task types)
and target (gameplay categories) parameters whose
values will guide the elicitation of practical mappings.
This paper explains how we identified this approach
(method), what this approach consists in (proposal),
and which mappings are obtained in our context (ap-
264
Lemoine, B., Laforcade, P. and George, S.
Mapping Task Types and Gameplay Categories in the Context of Declarative Knowledge Training.
DOI: 10.5220/0011840100003470
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2023) - Volume 2, pages 264-275
ISBN: 978-989-758-641-5; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

plication). We assume that this approach is suffi-
ciently generic and reusable to contribute to help-
ing multidisciplinary design teams identify and map
gameplays for their domain-specific tasks (contribu-
tion).
In cognitive psychology, test-based learning rep-
resents the idea that the process of retrieving (i.e. re-
membering) concepts or facts increases their long-
term retention. While tests are mainly used as sum-
mative assessment tools, they can also be forma-
tive. Repeated retrieval (i.e., retrieval practice) is
one way to implement test-based learning, which has
been shown to improve long-term retention in re-
search (Roediger and Pyc, 2012; Brame and Biel,
2015). In addition, research also suggests that various
test formats enhance learning (i.e. the benefits are not
linked to a specific type of retrieval practice) (Brame
and Biel, 2015). In our work, training means pro-
viding the learner with different forms of questions
repeatedly, which is a form of retrieval practice.
The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2
presents our research context including our gaming
(Roguelite genre) and learning (training of multiplica-
tion facts) contexts as well as the mapping issue; Sec-
tion 3 draws current close research studies for tackling
this challenge; Section 4 details how the identification
of the mapping approach we propose has been con-
ducted; Section 5 presents the resulting approach and
its application in our specific context; Section 6 dis-
cusses the next challenges to overcome, mainly about
formalizing and exploiting the resulting mappings to
drive the generation of adapted training sessions.
2 RESEARCH CONTEXT
Our research interest is about generating effective and
engaging training sessions for the retention of declar-
ative knowledge. Declarative knowledge (i.e. knowl-
edge about facts, laws, statements, etc.) are known
to require repetition for encouraging their memoriza-
tion, generalization, and retention (Kim et al., 2013;
Roediger and Pyc, 2012). Our concern is about identi-
fying approaches, models, and processes helping mul-
tidisciplinary teams in designing learning games tar-
geting such training. Nevertheless, creating activities
combining fun and educational content is not an easy
job (Prensky, 2005). To that extent, Prensky pro-
posed a three steps process to create digital game-
based learning: “(1) Find or create a game with great
gameplay that will engage our audience, (2) Find the
learning activities and techniques that will teach what
is required (doing each with the other in mind), and
then (3) successfully blend the two”.
2.1 A RogueLite for Multiplication
Tables Training
As a first application domain, our research takes place
into the context of the AdapTABLES project
1
which
aims at designing and developing a learning game for
the training of multiplication tables. It implies the
design of a generator for providing game levels dur-
ing training sessions. It is worth notice that practic-
ing multiplication tables will complement classroom
learning (from the teacher’s point of view): learning
the tables, application in problem-solving, and gener-
alization are outside the scope of the learning game.
This project involves mathematical teachers and di-
dactic experts, as well as game designers and serious
game experts.
In addition, we studied different game genres in
order to identify those capable of keeping players en-
gaged while providing repetitive but various game-
plays. The Roguelite game genre meets these needs.
It is mainly characterized by procedural dungeon gen-
eration with randomized content, permanent death
(each avatar’s death implies for the player to start a
new playthrough), and limited retention of unlockable
game elements (characters, items, powerups, ...).
Had
`
es, Rogue Legacy, Binding of Isaac are well
known Roguelite video games. They also share a
dungeon-crawler approach: the player has to explore
dungeons made up of interconnected rooms where
actions take place. Therefore, Roguelite combines
all necessary prerequisites for training declarative
knowledge (i.e., generation → variety, repetition, and
it is a well-known and liked game genre). Briefly,
learners-players will get across successive generated
dungeon levels, wherein most of the rooms will chal-
lenge them to answer task-oriented questions.
2.2 Abstract Training Task Types
In an exploratory research, partially presented
in (Laforcade et al., 2022), a user group composed
of 2nd to 6th grade teachers and mathematics experts
has identified several tasks for training multiplication
tables, such as: complete a fact where the result is
missing, complete a fact where the operand is miss-
ing, decide if a fact is correct, identify the results of a
table. These tasks also embeds dedicated parameters
in order to drive which facts to consider, how to build
them and how to answer them.
In a perspective of genericity with other domain-
related declarative knowledge, we abstracted them
into 5 task types:
1
https://projets-lium.univ-lemans.fr/adaptables/
Mapping Task Types and Gameplay Categories in the Context of Declarative Knowledge Training
265
1. Completion 1: complete an incomplete fact that
has one missing element (e.g., 3×? = 15, 15 =
? × 5, 3 × 5 = ?);
2. Completion 2: complete an incomplete fact that
has two missing elements (e.g., ?×? = 15 with
a set of given choices [3, 6, 5, 10], ? × 5 = ? or
3×? = ? also with sets of given choices);
3. Reconstruction: replace, in the correct order, all
important elements of a fact (e.g., ?×? = ? with a
set of given choices [3, 6, 5, 10, 15]);
4. Identification: identify the correctness or incor-
rectness of one or several facts (e.g., 3 × 5 = 15,
true or false?);
5. (Non-)Membership Identification: identify the
elements that share or do not share a given prop-
erty (e.g., [3, 5, 9, 12, 14, 21] which are results of
the table 3?);
These task types do not claim to be exhaustive. They
only cover the specific multiplication tables tasks and
are expressed at a higher level of abstraction.
2.3 Abstract Gameplay Types
As mentioned by (Prensky, 2005), the main reason
for learning game failure is their lack of gameplay.
Therefore, we intend to provide a variety of possi-
ble gameplays. To that extent, informal interviews
were conducted with game designers to gather possi-
ble ideas which lead to the design of gameplay mock-
ups. A game prototype with a few gameplays was
created to test some ideas and collect some feedback.
One observation was made after the design of the
mock-ups: some gameplays seemed to belong to the
same category (e.g. breaking the pot wearing the an-
swer and opening the chest wearing the answer are
two similar ways of selecting an object). This ob-
servation followed the idea of the game classification
proposed by (Djaouti et al., 2008) which consists in
describing games through gameplay bricks (i.e., cat-
egories of actions that can be performed within the
games). Consequently, further reflexion led to the
definition of 5 categories of gameplay in our context
(as for the task types, these categories do not claim to
be exhaustive):
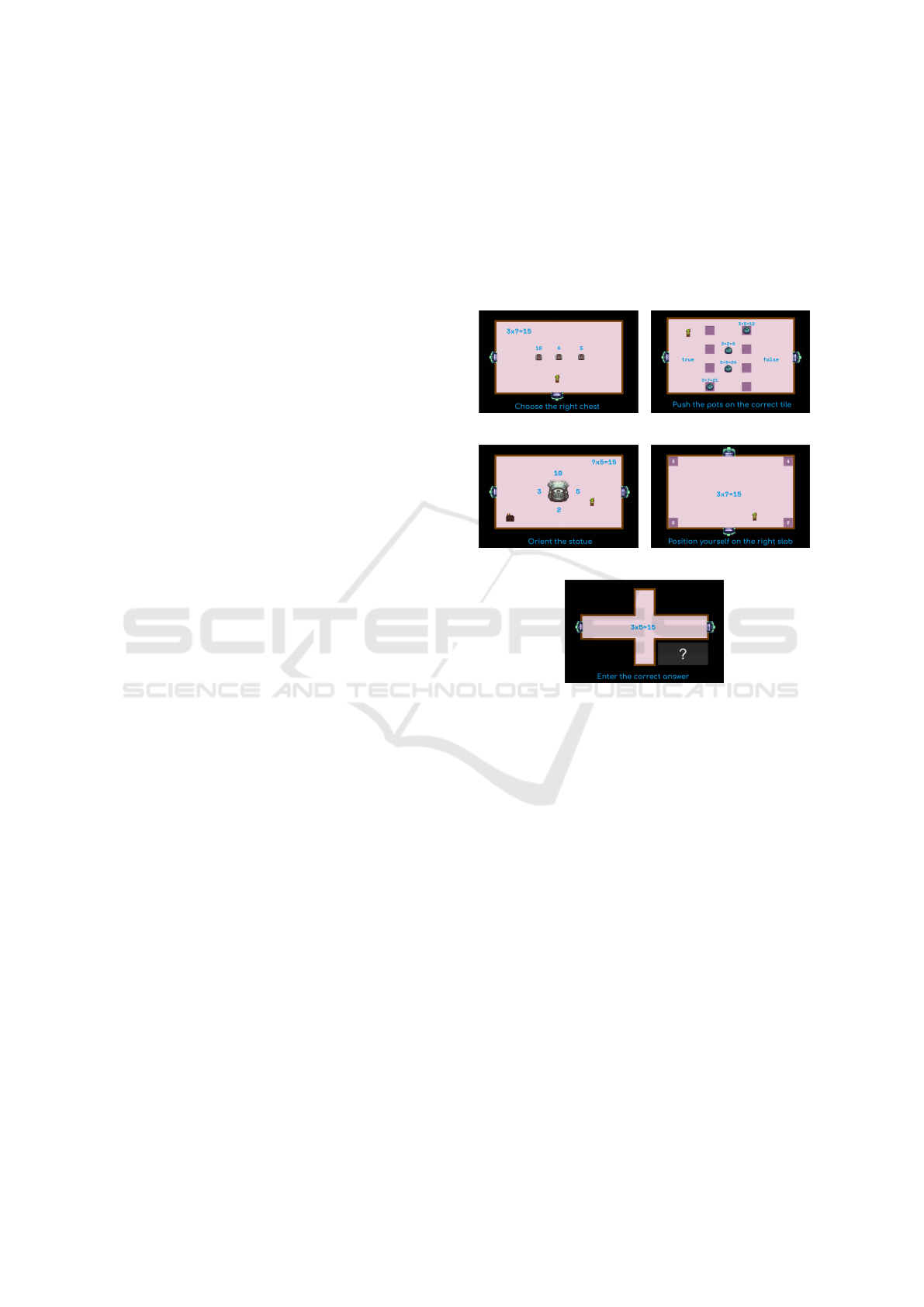
1. SELECT: select (e.g., touch, kill, break, open)
objects wearing the correct answers, through
avatar actions;
2. MOVE: correctly place objects at specific loca-
tions through avatar actions;
3. ORIENT: orient objects (e.g., rotate), through
avatar actions, towards the correct answer;
4. POSITION: move the avatar to the necessary po-
sitions for choosing or typing the correct answers;
5. DIRECT RESPONSE: no action is required
through the avatar, learners can directly type down
their answer by using an input device (e.g., enter
the correct answer through a keyboard).
Figure 1 presents a gameplay mock-up for each cate-
gory.
(a) SELECT example (b) MOVE example
(c) ORIENT example (d) POSITION example
(e) DIRECT RESPONSE
Figure 1: Example of mock-ups by gameplay categories.
2.4 Research Questions
Following Prensky’s process, our main question now
is: how to determine and specify the relationships be-
tween task types and game categories necessary to the
design of learning game activities? Indeed, know-
ing these relationships is important at design-time to
guide the identification of practical gameplays for ev-
ery specific tasks, and at run-time to drive the genera-
tion process. We assume that answering this question
at a higher level of abstraction (task types and abstract
gameplays) will allow these relationships to be reused
in different declarative knowledge contexts.
This research question (i.e., illustrated in Figure 2)
consists of answering more precisely to the follow-
ing questions: Which kinds of abstract gameplays are
suitable for which task types? Is the mapping system-
atic or conditional? If conditional, how to find these
conditions?
According to (Tchounikine et al., 2009), this is
typically a problem of research in TEL engineering
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
266

Figure 2: Our Research Question.
falling into the “elaborating powerful abstractions”
case where the problem must be addressed from a
transdisciplinary perspective.
Previous works have addressed the problem of re-
lationships identification between the educational and
game dimensions. The following section aims to po-
sition our work in relation to these existing works.
3 RELATED WORK &
POSITIONNING
Several existing works have focused on determining
the relationships between educational elements and
game elements. A pioneer is (Prensky, 2005), who
proposed compatible game genres (e.g., action, role-
play, adventure) with knowledge to be learned (e.g.,
facts, skills, judgement, behavior) and learning activ-
ities (e.g., questions, experiments, observation). An
extension to this work, consisting of adding a relation
to the learning styles (i.e., activists, reflectors, theo-
rists, and pragmatists) of (Chong et al., 2005) has
been proposed by (Rapeepisarn et al., 2008). Like
wise, (Sherry, 2010) defined relationships between
some game genres and the 6 levels of Bloom’s tax-
onomy (Bloom, 1956). Similarly, (Gosper and Mc-
Neill, 2012) proposed a framework to support the in-
tegration of technology in education. This framework
defines relationships between learning outcomes (e.g.
acquisition of basic facts, automation of skills and
concepts), learning processes (e.g. memorization,
analogical reasoning, proceduralization), assessment
(e.g. self-assessment, peer assessment) and game
genres. Although these works are very interesting for
the general design of learning games, the identified re-
lationships are not usable at a specification stage for
guiding the definition of practical gameplays.
Some work attempts to provide relationships at a
specification level. (Dondi and Moretti, 2007) linked
learning objectives (e.g., memorization/repetition/ re-
tention), knowledge types (e.g., factual knowledge),
and game genres to high-level features that games
should possess (e.g., presence of content engine, as-
sessment engine). However, these high-level features
do not describe how the relationships are to be imple-
mented in practice.
Other works offer a framework to specify rela-
tionships (i.e., either for analyzing existing games
or conceiving one). The LM-GM framework (Lim
et al., 2013) supports the transition from learning ob-
jectives/practices to game elements through a con-
cept called Serious Game Mechanic (SGM). It defines
learning mechanics and game mechanics and uses
SGM to associate both concepts. However, the pre-
sented mechanics are high-level ones (e.g., guidance,
collaboration, explore) and the relationships are not
meant to be implemented as such. Furthermore, (Hall
et al., 2014) proposed a framework to guide the de-
signer in specifying the transition from learning con-
tent to core-gameplay. It is composed of 5 categories
(i.e., goal, choice, action, rules, feedback) in which a
series of questions need to be answered from a real-
world and a game-world perspective. However, the
framework is more oriented towards the general de-
sign of the game rather than its implementation.
In conclusion, existing approaches are more ori-
ented towards defining relationships for analysis pur-
poses or to assist in the high-level design of games
rather than specifying relationships for low-level de-
sign purposes. Indeed, they address specific learning
targets or the contexts of specific game genres, as we
do. In our context, we seek to propose an approach
to specify relationships between declarative knowl-
edge training tasks and gameplays from the Roguelite
genre. These relations need to respect one condition:
their specification must allow their implementation.
It is well known that the training and evaluation
of declarative knowledge is done through question-
naires/quizzes. Moreover, numerical quizzes, com-
pared to paper ones, allow for user interactions that
are closer to the ones we can found into basic train-
ing games (for example a multiplication table training
games where correct answers make the avatar run-
ning faster or jumping to higher platforms). There-
fore, using exercises types from quizzes formats as a
pivot (i.e., a way to close the gap between task types
for declarative knowledge training and gameplay cat-
egories) seemed interesting in particular because the
use of existing content is a way to reduce subjectivity.
Therefore, our work intends to propose a systematic
mapping approach based on the use of quizzes exer-
cises types as a pivot. The next sections present the
development of our approach, followed by the pro-
posed approach and an application example.
Mapping Task Types and Gameplay Categories in the Context of Declarative Knowledge Training
267

4 APPROACH DESIGN
Several steps were necessary to the elaboration of our
mapping approach. At first, we conducted an anal-
ysis of quizzes design formats to define the types of
existing exercises (i.e., our pivot), after which the fol-
lowing questions appeared: (1) How can we draw a
parallel between the types of tasks and the exercises
identified? (2) How can we draw a parallel between
the gameplay categories and the exercises identified?
As previously mentioned, the interactions offered by
each quiz exercise are closer to games’ interactions.
Moreover, every concept (i.e., task types, gameplay
categories, and exercises) are characterized by their
possible response modalities (e.g., enter one answer,
choose between X propositions). Therefore, our sec-
ond step consisted in using the exercises types to iden-
tify possible criteria and parameters in order to spec-
ify the task types and gameplay categories and ease
the identification of the mappings. The last step con-
sisted in using these parameters values (from both
task types and gameplay categories perspectives) to
compare and identify matches.
4.1 Identification of the Pivot
Foremost, we analyzed the proposed exercises types
of 6 formats, mostly extracted from Learning Man-
agement Systems (LMS), allowing the creation of nu-
merical questionnaires/quizzes:
• the eponymous and proprietary format from the
itsLearning (#1) LMS;
• GIFT (#2) a markup language for describing tests
that is associated to the Moodle LMS;
• Performance Matters Assessment and Analytics
(#3) format associated to the PowerSchool LMS;
• NetQuizzPro (#4) a software allowing the creation
of questionnaire;
• QTI (Question & Test Interoperability specifica-
tion) (#5) from the IMS global learning consor-
tium that defines a standard format to exchange
and store assessment content;
• Tactileo - Maskott (#6) format associated to the
French pedagogical platform of the same name.
This analysis lead us to the definition of 12 dif-
ferent types of exercises useful for declarative knowl-
edge (i.e., only exercises for which the verification of
the results can be automatized). Mainly the analysis
consisted of a comparison of the exercises in terms
of what they allow. Exercises (of different format)
that shared the same type of statement, the same num-
ber of desired answers and for which the interaction
of answers was similar have been merged to com-
pose a single exercise type. Furthermore, some for-
mats combine several exercises into one (i.e. mul-
tiple choice and answers were merged in the format
of itsLearning). In these cases, we considered them
to be two independent exercises. Moreover, the pos-
sibility of having intruders (i.e., elements not to be
associated) was something asked by domain experts,
however, none of the “Associate” type of exercise an-
alyzed from the formats offer that possibility. There-
fore, it was considered as a possibility in our type of
this exercise definition. The final types of exercises
defined are:
• Alternative: choosing one answer between 2 op-
tions;
• Multiple choice: choosing one answer between X
(i.e., X ⩾ 2) options;
• Multiple responses: choosing Y (i.e., zero or
more) answers between X (i.e., X ⩾ 2) options;
• Short answer: enter the correct answer. Multiple
form of answers can be accepted, e.g., for exam-
ple, How much is 3 times 5? as two possible an-
swers, which are 15 and fifteen;
• Fill-in-the-blanks: enter for each gap of a text the
wanted “short” answer;
• Fill-in-the-blanks choices: choose for each gap of
a text the correct answer from a list. Each gap can
have an associated list of options, or one list can
be associated to all gaps;
• Reconstruction: reassemble, in the correct order,
each significant element of an information;
• Associate—Group: associate elements from a list
or multiple lists together. The association can be
done by pairs, or not. The elements can be asso-
ciated with zero to several other ones;
• Order: replace a set of information in the correct
order;
• Graphic choice: point or locate X (i.e., X ⩾ 1)
elements on a picture.
• Graphic identification: write the correct label for
each area-to-complete of a picture;
• Graphic association: associate the correct labels
to X areas of a picture.
As a reminder, these types of exercises aim at dealing
with declarative knowledge in general, not just mul-
tiplication tables. Therefore, some exercises offer a
more visual approach that could be useful, for exam-
ple, in the context of geographical facts. An overview
of which format allows for which exercises is pre-
sented in Table 1.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
268
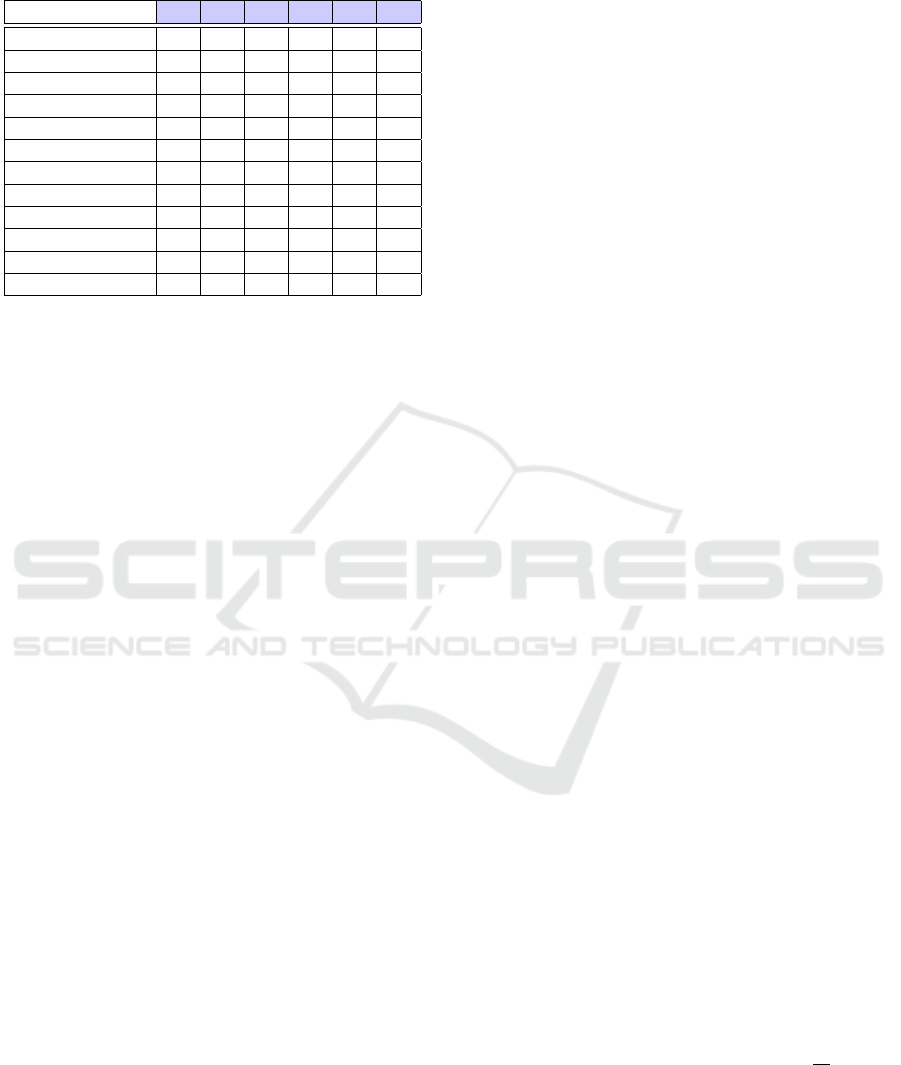
Table 1: Exercises by quiz format (✓ present; ✗ absent;
— present but incomplete).
#1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6
Alternative ✓ — — ✗ ✗ ✗
Multiple Choice ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
Multiple Resp. ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
Short Answer ✗ ✓ ✓ ✗ ✓ ✓
Fill-in ✓ — ✓ ✓ ✗ ✓
Fill-in Choice ✓ — ✗ ✓ ✓ ✓
Reconstruction ✗ ✗ ✗ ✓ ✗ ✗
Association — — — — — —
Order ✓ ✗ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
G. Choice — ✗ — ✗ ✓ —
G. Identification ✗ ✗ ✗ ✓ ✗ ✗
G. Association ✗ ✗ ✗ — ✓ ✓
These exercises are characterized by several pa-
rameters, such as: their interactions, their response
modality (i.e., input or choice), their statement type
(i.e., format of the question asked), the number of an-
swers desired, and the number of propositions pre-
sented (i.e. if the response modality of a concrete
task of this type is “Choice”). Through our analy-
sis, 6 types of interactions were identified: Select Y
From X (i.e., the learner must select Y answers from
a set of X values); Y (Select 1 from X
1
to X
Y
) (i.e,
the learner must make a selection of one answer from
each set of proposals); a variant is Y (Select 1 from X)
(i.e, the learner must select Y answers, one by one,
from a set of proposals.); Write X (i.e., the learner as
to enter X answers); Order X (i.e., the learner must
order X elements correctly); Point X or Locate X (i.e.,
the learner must point X elements on a picture or lo-
cate them); Match Y with X 1-to-1 or Match Y with X
(i.e., the learner must associate elements from Y with
those from X by pairs or not). In addition, 3 types
of statement were found: 1) classic statement (i.e.,
simple text question), 2) graphic statement (i.e., text
question accompanied by an image), and 3) To fill-in
statement (i.e., question separating textual elements
with other types of elements such as answer boxes).
Table 2 presents the exercises through their character-
ization. It is important to note that none of the formats
allows for all possible forms of exercise.
4.2 Mapping Task Types to Game
Categories
Now that the pivot is specified, the remaining ques-
tions are: How to match (1) task types to exercises,
and (2) game categories to exercises? The main idea
is to use some of the parameters that characterize each
concept (i.e. task types, gameplay categories and ex-
ercises) to map them.
Task Type to Exercises
Task types are characterized by several parameters,
which are: the number of facts targeted by the task,
the types of statements allowed for such a task, the re-
sponse modalities, the number of desired responses,
and the number of propositions presented (i.e., if the
response modality of a concrete task of this type is
“Choice”). For example, the Completion 1 type is
characterized as follows: one fact is targeted, all state-
ment types are allowed (i.e., classic, graphic and To
fill-in), both response modalities can be used (i.e., in-
put and choice), only one response is desired and at
least 2 propositions must be presented if the modality
equals Choice.
Nevertheless, the assignment of parameter values
is not an easy task. At first sight, it could seem
possible to carry out a task of the Completion 2
type through the response modality Input. However,
presenting a statement in the context of declarative
knowledge, such as “?×? = 12”, does not give enough
information about the fact to work with (i.e., is it 3×4
or 6 × 2). As another example, for a Completion 2
task, it is possible to choose one or two answers. This
depends on how the choices are presented. If the set
of propositions represents numbers, such as [3, 5, 7,
4], two answers must be chosen. However, if each
proposition is presented as a multiplication (without
the result), such as [3 × 4; 4 × 5; 6 × 3], then only one
answer is required. Table 3 presents the task types
through their characterization. Thus, except for the
interactions, task types and exercises are character-
ized by the same parameters.
Consequently, the mapping consists in comparing
the shared parameter’s values between task types and
exercises. For examples, Completion 1 corresponds to
Short answer because the specification of Short an-
swer, i.e., {number of facts = 1; type of statement
= classic; modality = input; number of desired an-
swers = 1}, is a possible configuration of a concrete
task of the type Completion 1 (i.e., the parameter val-
ues are included into those of the type Completion 1).
This gives questions such as “What times 5 equals
15?” and “What does 3 times 5 equal?”. Comple-
tion 1 also corresponds to Fill-in-the-blanks choices
exercise specified as {number of facts = 1; type of
statement = to fill-in; modality = choice; number
of desired answers = [1 − ∞]; number of choices =
[2 − ∞]}. This gives questions such as “ times 5
equals 15”.
Thanks to these mappings, each task type can also
be described by its possible interactions (i.e., the in-
teractions of the exercises corresponding to the task
type considering the number of requested answers).
As an example, the Short answer exercise type asks
Mapping Task Types and Gameplay Categories in the Context of Declarative Knowledge Training
269
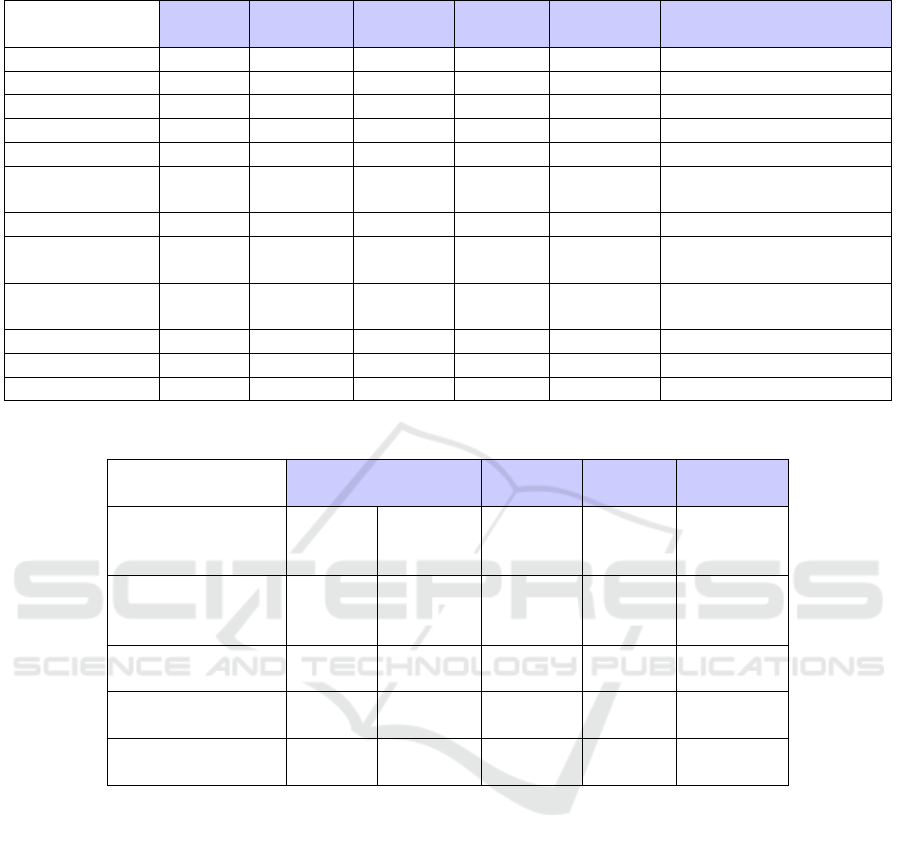
Table 2: Characterization of the exercises.
Number Statement Response Number Number of
of Facts Types Modality Answers Choices
Interactions
Alternative 1 Classic Choice 1 2 Select 1 from 2
Multiple Choice 1 Classic Choice 1 2 to ∞ Select 1 from X
Multiple Resp. 1 Classic Choice 0 to ∞ 2 to ∞ Select Y from X
Short Answer 1 Classic Input 1 0 Write 1
Fill-in 1 To fill-in Input 1 to ∞ 0 Write Y
Fill-in Choice 1 To fill-in Choice 1 to ∞ 2 to ∞
Y (Select 1 from X)
Y (Select 1 from X
1
to X
Y
)
Reconstruction 1 To fill-in Choice 2 to ∞ 2 to ∞ Match Y with X 1-to-1
Association 2 to ∞ Classic Choice 2 to ∞ 4 to ∞
Match Y with X 1-to-1
Match Y with X
Order 2 to ∞
Classic
Choice 1 to ∞ 2 to ∞ Order Y
Graphic
G. Choice 1 to ∞ Graphic Choice 1 to ∞ 2 to ∞ Point Y or Locate Y
G. Identification 1 to ∞ Graphic Input 1 to ∞ 0 Write Y
G. Association 1 to ∞ Graphic Choice 1 to ∞ 1 to ∞ Match Y with X 1-to-1
Table 3: Characterization of the task types.
Number Statement Response Number Number of
of Facts Types Modality Answers Choices
Completion 1 1
Classic
1Graphic
Input 0
To fill-in
Choice 2 to ∞
Completion 2 1
Classic
Choice 1 or 2 2 to ∞Graphic
To fill-in
Reconstruction 1
Graphic
Choice 2 to ∞ 2 to ∞
To fill-in
Identification 1 to ∞ Classic
Input
1 to ∞
0
Choice 2 to ∞
(Non-)Membership
1 to ∞
Classic Input
2 to ∞
0
Identification Graphic Choice 2 to ∞
the learner to write down one short answer to a tex-
tual question. Thus, its interaction parameter as for
value Write 1. A task of the Completion 1 type could
ask questions such as “What does 3 times 5 equal?”,
leaving the learner to write down 15. Therefore, Com-
pletion 1 has Write 1 for possible interaction. As a
result of all mappings, Completion 1 can be achieved
through the following interactions: Select 1 from X
(i.e., X ∈ [2, ∞]), Write Y (i.e., Y is the number of
wanted answer therefore Y = 1), Y (Select 1 from X),
Point Y or Locate Y, Match Y with X 1-to-1.
Gameplay Categories to Exercises
Each game category represents gameplays that are
similar in terms of the actions to be performed, such
as opening the right chest, choosing the right pot,
passing through the right bridge which belong to the
SELECT category. Therefore, the common parame-
ters of these gameplays (e.g., number of facts interro-
gated, number of possible answers) represent those of
the category itself.
After analysis, we characterized these categories
by the following parameters: the interactions, the re-
sponse modality (i.e., input or choice), the statement
type (i.e., format of the question asked), the number of
facts targeted, the number of answers desired, and the
number of propositions presented (i.e., if the response
modality of a concrete task of this type is “Choice”).
These parameters are quite similar to those used for
the exercises. They represent a minimal and relevant
set of parameters that allow us to discriminate the dif-
ferent categories and gameplays. As an example, the
SELECT category is characterized as follows: 1 to
many facts can be targeted, both classic and to fill-in
statement types are allowed, choice is the only possi-
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
270

ble response modality, 1 to many answers can be de-
sired, and two interactions (i.e., Select Y from X, and
Y (Select 1 from X
1
to X
Y
)) are possible.
However, during the characterization phase, we
realized that the possible interactions and the type
of statement changed depending on whether one or
more responses were desired. Therefore, in order to
simplify the mappings, each category allowing one to
multiple possible responses was divided into two sub-
categories: single (i.e., only one possible response)
and multiple (i.e., 2 to many possible responses).
As a result, our 5 categories turned into 9. Ta-
ble 4 presents the gameplay categories through their
characterization. Afterwards, the mapping consisted
in directly comparing the parameter’s values.
Task Type to Gameplay Categories
From there, we disposed of all the necessary informa-
tion to answer our main question: Which task type are
suitable for which gameplay categories? What are the
conditions?
The final step consisted in comparing the task
types and categories on the basis of their parameter
values (i.e. comparing Table 3 with Table 4). During
that step, we observed that 2 parameters represented
mapping conditions based on their values: the type
of statement and the response modality. Therefore,
the obtained relationships are quadruplet composed
as follows: (<task type>, <statement type>,
<response modality>, (<category1>, <category2>,
. . . )). Each task type can have from 1 to 6 associated
relationships.
In conclusion, this section has presented the pro-
cess followed to map the task types for declarative
knowledge training to gameplay categories for the
Roguelite video game genre. The next section will
present the results obtained.
5 RESULTS
The presented work led to two contributions: (1) an
approach to map designers’ own task types to their
own categories of gameplays, and (2) mappings be-
tween our own task types with our gameplay cate-
gories.
5.1 A Mapping Approach
Our proposal consists of a two to five-steps approach,
illustrated in Figure 3. The initial steps are to:
Figure 3: Proposed Mapping Approach.
1. abstract the concrete tasks by using the types of
tasks presented (e.g. a task “associate the right
date with the historical event” becomes complete
a fact with a missing element) or by creating new
task types;
2. associate the gameplay to one of the categories
presented or to a new category.
From here, four states are possible: new task types
and categories have been created, only new task types
have been created, only new gameplay categories
have been created, or nothing has been created. De-
pending on the condition, the instructions below must
be followed:
1. If new task types and new gameplay categories
were created:
(a) The first step is to characterize the task types
using the six parameters defined above (i.e.,
number of facts, types of statements, response
modalities, number of desired responses, num-
ber of propositions, and interactions). In a sub-
step, the mapping between task types and quiz
exercises (see Table 2) must be done to define
the values of the interactions parameter.
(b) The second step is to characterize the gameplay
categories using the same parameters.
(c) Finally, the last step is to compare both tables
(i.e., characterization) through their values. As
Mapping Task Types and Gameplay Categories in the Context of Declarative Knowledge Training
271
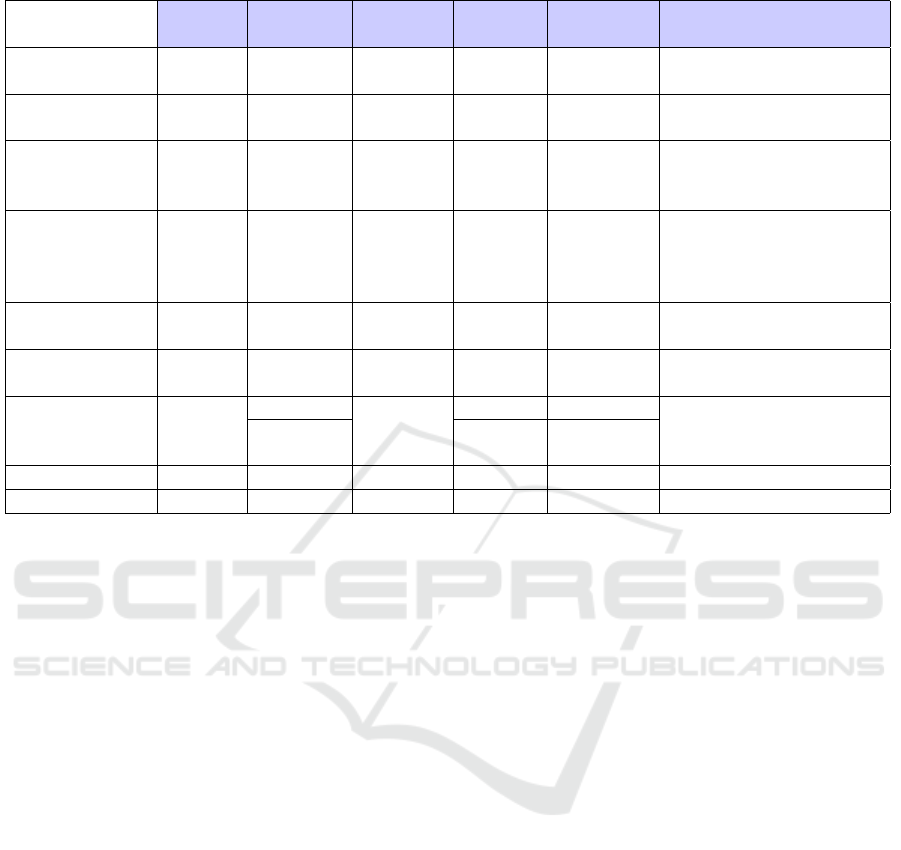
Table 4: Characterization of the gameplay categories ((S) = Single; (M) = Multiple).
Number Statement Response Number Number of
of Facts Types Modality Answers Choices
Interactions
SELECT (S) 1
Classic
Choice 1 2 to ∞ Select 1 from X
To fill-in
SELECT (M) 1 to ∞
Classic
Choice 2 to ∞ 2 to ∞
Select Y from X
To fill-in Y (Select 1 from X
1
to X
Y
)
MOVE (S) 1
Classic
Choice 1 2 to ∞
Select 1 from X
Graphic Point 1 or Locate 1
To fill-in Match 1 with 1
MOVE (M) 1 to ∞ Choice 2 to ∞ 2 to ∞
Match Y with X
Classic
Point Y or Locate Y
Graphic
Select Y from X
To fill-in
Y (Select 1 from X
1
to X
Y
)
ORIENT (S) 1
Classic
Choice 1 2 to ∞ Select 1 from X
To fill-in
ORIENT (M) 1 to ∞
Classic
Choice 2 to ∞ 2 to ∞
Y (Select 1 from X
1
to X
Y
)
To fill-in Y (Select 1 from X)
POSITION (S) 1
To fill-in
1
Input 0
Classic
Select 1 from X
Graphic
Choice 2 to ∞ Point 1 or Locate 1
POSITION (M) 1 Graphic Input 2 to ∞ 0 Write Y
DIRECT RESP. 1 Classic Input 1 0 Write 1
a reminder, the values of the Statement Type
and the Response Modality parameters are pos-
sible conditions of the relations.
2. If only new task types were created, then realize
step 1a and step 1c.
3. If only new gameplay categories were created,
then realize step 1b and step 1c.
4. If no new elements have been created, the work is
already done, cf. Figure 4.
Let’s take as example a task type T1 characterizes
as such {number of facts = 1; type of statement =
classic; modality = input or choice; number of de-
sired answers = 1}, and a gameplay category C1 =
{number of facts = [1 − ∞]; type of statement = clas-
sic or to fill-in; modality = choice; number of desired
answers = [1 − ∞]}. In this case, only one relation-
ship would result: (T1, Classic, Choice, C1).
5.2 Resulting Mappings
As a result of the process presented in section 3, sev-
eral conditional relationships were identified between
each task type and the gameplay categories.
These relationships are presented in Figure 4. If
the categories do not have (S) or (M), it means that
both are present.
For example, the task type Identification has two
relationships: (Identification, Classic, Input, (Position
(S), DIRECT RESPONSE)) and (Identification, Clas-
sic, Choice, (SELECTION (S,M), MOVE (S,M), ORI-
ENT (S,M)).
6 DISCUSSION & FURTHER
WORK
This section discusses the limitations of our work,
presents an experiment to validate some mappings,
and outlines a way to model the identified relation-
ships.
6.1 Extension of the Resulting
Mappings and Genericity
Our approach revealed some limits. First, due to the
non-exhaustiveness of our task types, all possible ex-
ercise types are not covered (i.e., this is the case of
Order). It is mainly due to our method: we intended
to start with a very first domain context while ab-
stracting tasks types and gameplay categories. It is a
very first step towards proposing a complete domain-
independent and generic approach.
Consequently, other domains than multiplication
tables have to be considered to cover, and refine if
necessary, our proposal. It is also possible that the
current task types have to be modified or extended
to cover all exercise types. In particular, we are cur-
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
272
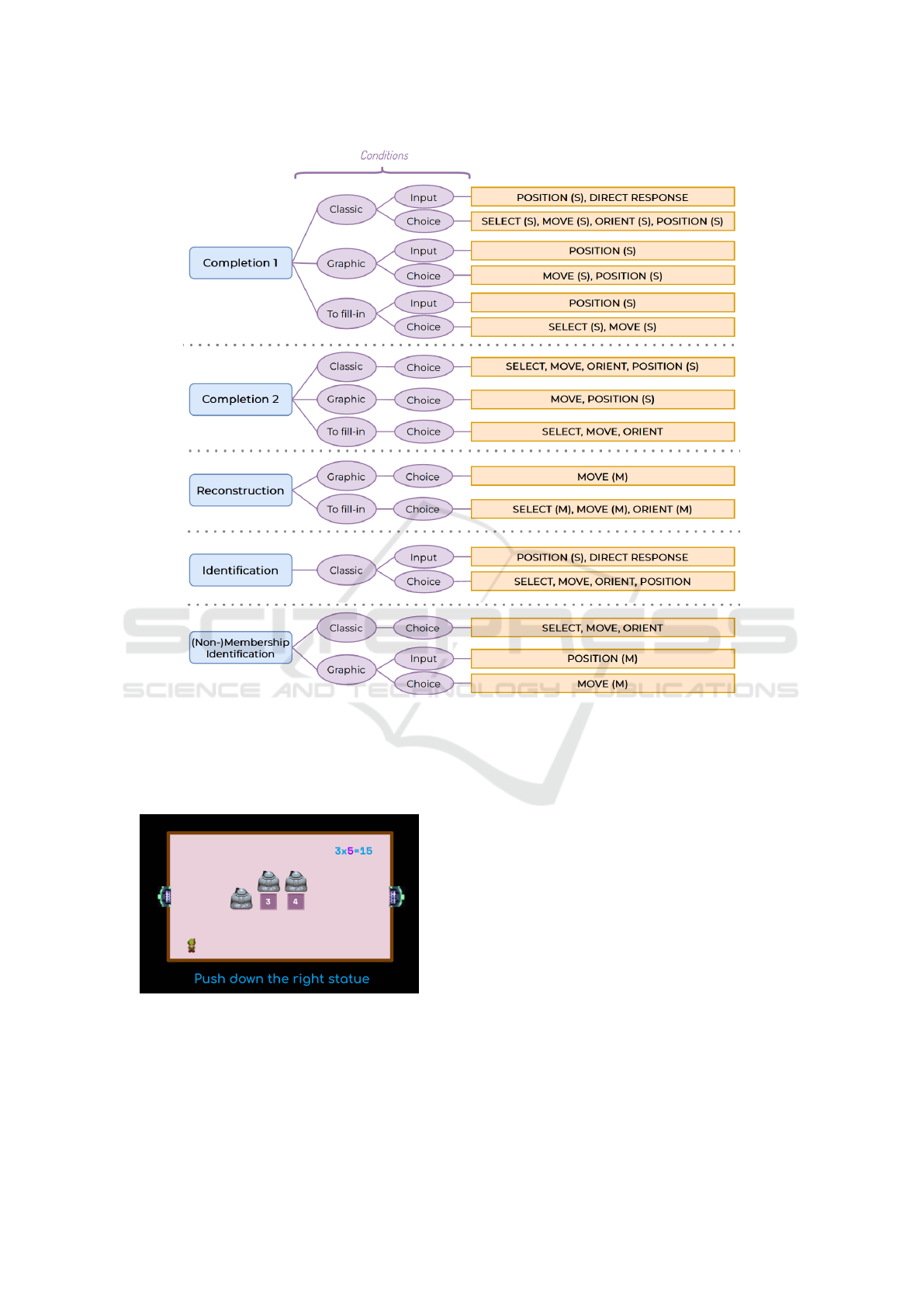
Figure 4: Conditional relations between task types and gameplay categories.
rently studying a second domain, consisting in the his-
tory and geography declarative knowledge necessary
to obtain the French diploma “Dipl
ˆ
ome National du
Brevet” (present in the 9th grade).
Figure 5: Second solution example.
6.2 Validation of the Mappings
In order to gather feedbacks on the gameplay mock-
ups (i.e., to identify relevant gameplays and game el-
ements), we proposed to the members (≈ 10 persons)
of the user group (of the project AdapTABLES) a
survey presenting possible gameplays for each type
of task. This experimentation was also an opportu-
nity to validate some mappings (i.e., the relations for
which the categories have existing gameplay mock-
ups). As the experiment is situated in the context
of multiplication tables, none of the mappings with
the condition “Graphic” are evaluated here. How-
ever, since mock-ups of each compatible categories
for each task types were created, other mappings are
evaluated here. Let’s take the example of a gameplay
consisting in selecting the right pot among several
pots bearing propositions (i.e., SELECT with Choice)
to answer a textual question of the type “3×? = 15”
(i.e., Completion 1). If this gameplay is validated by
the survey, then so is the relationship (Completion 1,
Classic, Choice, SELECT).
According to the first results, the mappings pre-
sented seem relevant. Negative comments are gener-
ally related to the lack of precision of some informa-
Mapping Task Types and Gameplay Categories in the Context of Declarative Knowledge Training
273
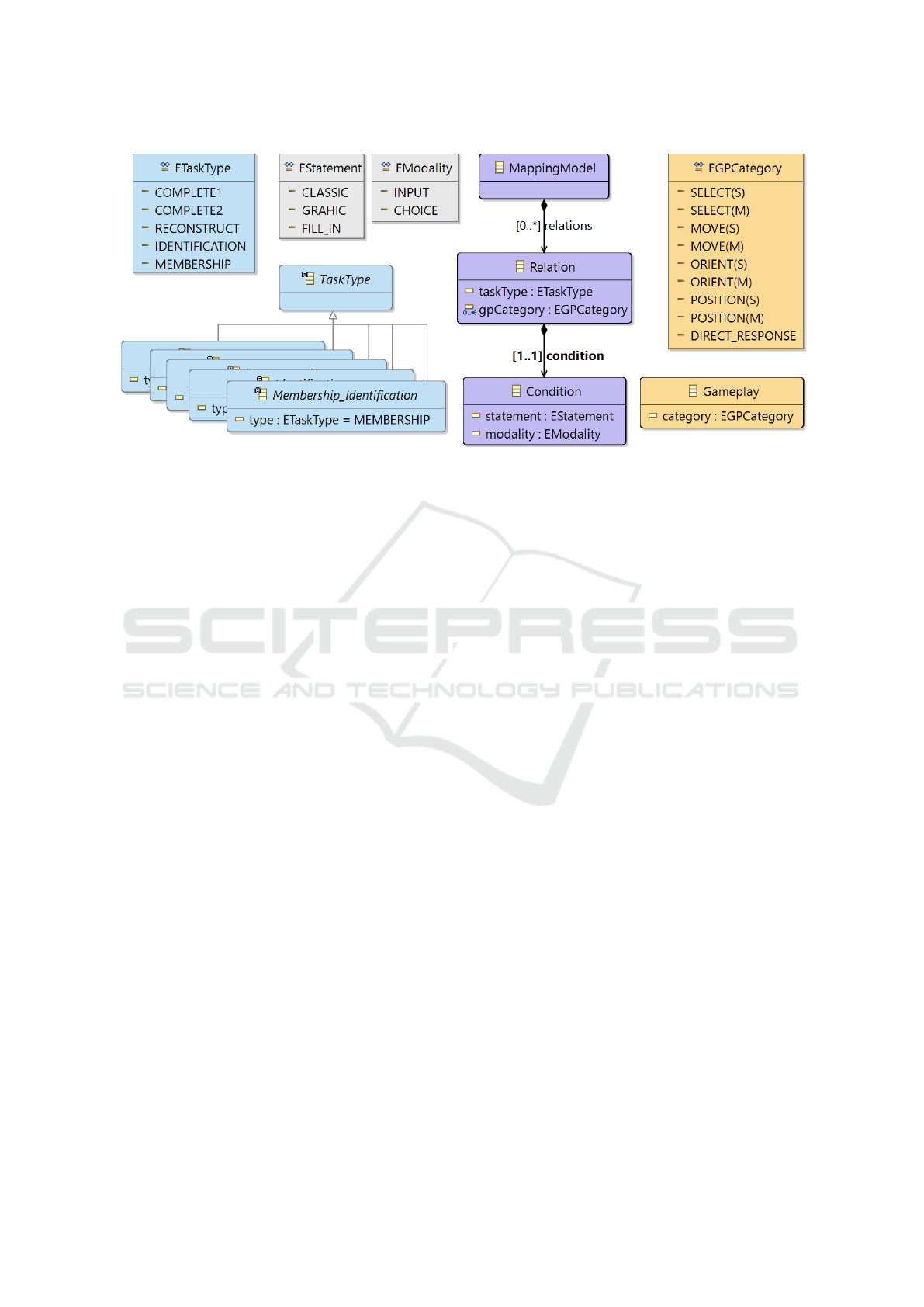
Figure 6: Example of EMF Ecore Modelling for relationships, task types and gameplays.
tion or to didactic problems. For example, MOVE-
type gameplays requiring objects to be placed in the
correct answer areas were rejected because the ob-
jects would hide the answers, thus impacting learn-
ers’ thinking. The issue is not related to the mechan-
ics (i.e., moving objects to predefined areas), but a
cognitive one that can be corrected. A basic solution
would be to display the value above the selected ob-
ject. An alternative would be to display the chosen
value in the statement at the right position using a dif-
ferent color. Figure 5 illustrates the latter solution:
the statue pushed on the left tile hides the associated
’5’ value, but this value appears now in purple in the
room’s statement.
Furthermore, the mock-ups of the ORIENT game
have received mixed reviews. This is due to the fact
that the object chosen to be oriented (i.e., directing the
light of a streetlamp) lacks cognitive meaning. There-
fore, other mock-ups should be proposed to properly
assess the relationships associated with the ORIENT
category.
6.3 Modelling the Mappings
As mentioned earlier, our overall goal is to build a
generator of Roguelite oriented learning game activi-
ties for declarative knowledge training.
The originality of our overall work is the use of
Model-Driven Engineering (MDE) (Kent, 2002) tools
and principles to design the generator. The idea is to
specify all the information (domain-dependent tasks,
task types, game categories, gameplays, game ele-
ments and relationships) in different, interconnected
models that are consistent with a dedicated meta-
model that we are also specifying. Therefore, each
generation could be considered as a model transfor-
mation according to MDE.
Figure 6 proposes a first insight of the part of this
metamodel focusing on the mapping structure defined
in this article. The resulting mappings will be speci-
fied as a model in conformance with this metamodel
extract. The domain-dependant tasks, as well as the
specification of the concrete gameplays, and their im-
plementations into game elements, are not depicted
in the figure. As an overview of the mapping process
followed at runtime, here are the main steps starting
from a given identified domain-dependent task:
1. get the associated task type;
2. collect all relations from the mapping model that
are related to this task type;
3. restrict the collected relations to those whose as-
sociated condition is satisfied by comparing the
statement and modality values of the condition to
those of the original task;
4. collect the gameplay categories of the remaining
relations.
The generation algorithm will then handle fur-
ther steps such as selecting the gameplays implement-
ing these game categories, filtering them according
to other information (e.g. which gameplays are un-
locked and available for this learner-player), instanti-
ating the game elements composing the chosen game-
play, etc.
7 CONCLUSION
To conclude, this paper introduced an approach to
map task types for declarative knowledge training to
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
274

Roguelite oriented gameplay categories. The origi-
nality of this work lies on two points. Firstly, the pro-
posed approach is based on the use of a pivot (i.e.,
exercises in the form of questionnaires). Secondly, it
is oriented towards automating the design of learning
game activities (i.e., generation) and therefore speci-
fies fine-grained relationships.
In the future, we plan to: (1) continue the analy-
sis of the second application domain in order to have
generic task types with declarative knowledge; (2) fo-
cus on specifying gameplays in terms of game ele-
ments; and (3) model relationships (and other con-
cepts) to implement a first version of the generator.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank all the members of the user group (teachers
and didactics experts) as well as the game designers
without whom our research would not be successful.
REFERENCES
Bloom, B. S. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives:
The classification of educational goals. Cognitive do-
main.
Brame, C. J. and Biel, R. (2015). Test-Enhanced Learning:
The Potential for Testing to Promote Greater Learning
in Undergraduate Science Courses. CBE—Life Sci-
ences Education, 14(2).
Chong, Y., Wong, M., and Thomson Fredrik, E. (2005). The
impact of learning styles on the effectiveness of digital
games in education. In Proceedings of the Symposium
on Information Technology in Education, KDU Col-
lege, Patailing Java, Malaysia.
Codish, D. and Ravid, G. (2015). Detecting playfulness
in educational gamification through behavior patterns.
IBM Journal of Research and Development, 59(6):1–
14.
Djaouti, D., Alvarez, J., Jessel, J.-P., Methel, G., and
Molinier, P. (2008). A Gameplay Definition through
Videogame Classification. International Journal of
Computer Games Technology, pages 1–7.
Dondi, C. and Moretti, M. (2007). A methodological pro-
posal for learning games selection and quality assess-
ment. British Journal of Educational Technology,
38(3):502–512.
Gosper, M. and McNeill, M. (2012). Implementing game-
based learning: The MAPLET framework as a guide
to learner-centred design and assessment. In As-
sessment in Game-Based Learning, pages 217–233.
Springer, Springer Nature, United States.
Hall, J. V., Wyeth, P. A., and Johnson, D. (2014). Instruc-
tional objectives to core-gameplay: A serious game
design technique. In Proceedings of the First ACM
SIGCHI Annual Symposium on Computer-human In-
teraction in Play, pages 121–130, Toronto Ontario
Canada. ACM.
Kent, S. (2002). Model Driven Engineering. In Integrated
Formal Methods, pages 286–298. Springer Berlin Hei-
delberg.
Kim, J. W., Ritter, F. E., and Koubek, R. J. (2013). An inte-
grated theory for improved skill acquisition and reten-
tion in the three stages of learning. Theoretical Issues
in Ergonomics Science, 14(1):22–37.
Laforcade, P., Mottier, E., Jolivet, S., and Lemoine, B.
(2022). Expressing adaptations to take into account
in generator-based exercisers: An exploratory study
about multiplication facts. In 14th International Con-
ference on Computer Supported Education, Online
Streaming, France.
Lim, T., Carvalho, M. B., Bellotti, F., Arnab, S., de Fre-
itas, S., Louchart, S., Suttie, N., Berta, R., and Gloria,
A. D. (2013). The LM-GM framework for Serious
Games Analysis. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh.
Prensky, M. (2005). Computer Games and Learning: Dig-
ital Game-Based Learning. Handbook of Computer
Game Studies.
Rapeepisarn, K., Wong, K. W., Fung, C. C., and Khine,
M. S. (2008). The Relationship between Game Gen-
res, Learning Techniques and Learning Styles in Ed-
ucational Computer Games. In Technologies for E-
Learning and Digital Entertainment, volume 5093,
pages 497–508. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Roediger, H. L. and Pyc, M. A. (2012). Inexpensive
techniques to improve education: Applying cognitive
psychology to enhance educational practice. Jour-
nal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition,
1(4):242–248.
Sherry, J. L. (2010). Matching computer game genres to
educational outcomes. In Teaching and Learning with
Technology, pages 234–246. Routledge.
Tchounikine, P., Mørch, A. I., and Bannon, L. J. (2009).
A Computer Science Perspective on Technology-
Enhanced Learning Research. In Technology-
Enhanced Learning, pages 275–288. Springer Nether-
lands, Dordrecht.
Mapping Task Types and Gameplay Categories in the Context of Declarative Knowledge Training
275
