
Do Rules Still Rule? Comprehensive Evaluation of a Rule-Based
Question Generation System
Bernardo Leite
1,2 a
and Henrique Lopes Cardoso
1,2 b
1
Faculty of Engineering of the University of Porto (FEUP), Portugal
2
Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science Laboratory (LIACC), Portugal
Keywords:
Natural Language Processing, Question Generation, Evaluation.
Abstract:
The task of Question Generation (QG) has attracted the interest of the natural language processing community
in recent years. QG aims to automatically generate well-formed questions from an input (e.g., text), which
can be especially relevant for computer-supported educational platforms. Recent work relies on large-scale
question-answering (QA) datasets (in English) to train and build the QG systems. However, large-scale quality
QA datasets are not widely available for lower-resourced languages. In this respect, this research addresses
the task of QG in a lower-resourced language — Portuguese — using a traditional rule-based approach for
generating wh-questions. We perform a feasibility analysis of the approach through a comprehensive evalua-
tion supported by two studies: (1) comparing the similarity between machine-generated and human-authored
questions using automatic metrics, and (2) comparing the perceived quality of machine-generated questions
to those elaborated by humans. Although the results show that rule-based generated questions fall short
in quality compared to those authored by humans, they also suggest that a rule-based approach remains a
feasible alternative to neural-based techniques when these are not viable. The code is publicly available at
https://github.com/bernardoleite/question-generation-portuguese.
1 INTRODUCTION
Question Generation (QG) is the process of auto-
matically generating questions that are grammati-
cally and semantically correct from a variety of data
sources, including free text, raw data, and knowledge
bases (Rus et al., 2008). Question generation can be
helpful in education since it may be used to create
well-formed questions for quizzes and assessments,
test students’ knowledge, and encourage self-learning
(Heilman and Smith, 2010a).
Considering deep learning has made significant
progress, neural approaches have been used to tackle
the QG task (Pan et al., 2019). These neural tech-
niques have some challenges, including their de-
pendency on sizable and quality question-answering
(QA) datasets, which are scarce for lower-resourced
languages. A first attempt to solve this problem
might be to build new target language QA datasets
from scratch: collect paragraphs and question-answer
pairs manually written (human-authored) based on
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9054-9501
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1252-7515
Passage: Don Juan Rhode Island engasgou-se e um
sil
ˆ
encio total cobriu todo o parque naquela hora da
chegada da Primavera. english: Don Juan Rhode Island choked and a
silence covered the entire park at that hour of spring arrival.
Question: Quando
´
e que Don Juan Rhode Island se
engasgou e um sil
ˆ
encio total cobriu todo o parque? When
did Don Juan Rhode Island choke up and a total silence cover the entire park?
Passage: Al
´
em de tudo, o seu olhar j
´
a est
´
a de novo fixo
na
´
arvore onde a Andorinha pousara na v
´
espera. Besides
everything, his gaze is fixed again on the tree where the Swallow had landed the day
before.
Question: Onde
´
e que a Andorinha pousara na v
´
espera?
Where had the Swallow landed the day before?
Passage: Os dois tubar
˜
oes chegaram juntos, e, quando o
mais pr
´
oximo abriu a goela e enterrou as queixadas no
flanco prateado do peixe... The two sharks arrived together, and as the
closer one opened his gullet and buried his jaws in the silver flank of the fish...
Question: Como
´
e que os dois tubar
˜
oes chegaram? How
did the two sharks arrive?
Figure 1: Examples of rule-based generated questions.
the paragraphs. Naturally, this is time-consuming
and costly, requiring the collection of thousands of
question-answer pairs to fill the demands of train-
Leite, B. and Cardoso, H.
Do Rules Still Rule? Comprehensive Evaluation of a Rule-Based Question Generation System.
DOI: 10.5220/0011852100003470
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2023) - Volume 2, pages 27-38
ISBN: 978-989-758-641-5; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
27

ing such neural models. A second attempt to miti-
gate the problem would be to machine-translate QA
datasets mostly available in English. However, most
QA datasets have been built using open-domain re-
sources such as Wikipedia (Rajpurkar et al., 2016),
Baidu (He et al., 2018), and news articles (Trischler
et al., 2017). As a consequence, any model trained
on top of the translated data might present suitable
questions for a generic domain but will likely fail to
serve specific purposes (e.g., pedagogical goal, as it
is in this research). Of course, another problem with
translation is the eventual troubles arising from such
a process (Leite and Lopes Cardoso, 2022), e.g., the
translated questions may become meaningless.
This research investigates the feasibility of using
a traditional rule-based method for QG when neu-
ral approaches have evolved the state-of-the-art. The
QG framework was designed toward a specific ped-
agogical goal (Section 3). Generated questions fol-
low the WH-type format, i.e., those beginning with
the following interrogative terms: WHO, WHICH,
WHAT, WHERE, WHEN, WHAT, HOW, and WHY.
Some question examples can be observed in Figure 1.
The generation process takes into account five well-
established linguistic aspects: (1) syntactic informa-
tion, (2) semantic roles, (3) dependency labels, (4)
discourse connectors, and (5) relative pronouns & ad-
verbs. Our case study focuses on the (European) Por-
tuguese language. Nevertheless, the proposed method
can be generalized to any other language, including
English, if proper adaptations are performed, as we
will explain later (Section 6).
The proposed method is not novel per se since
it is based on the extensive literature on rule-based
QG. The main contribution of this paper is more on
the comprehensive evaluation of the rule-based QG
method. The referred evaluation process includes two
studies. In the former, we use automatic evaluation
metrics to indicate the similarity between 150 pairs
of machine-generated and human-authored questions.
We try to understand if the results align quantita-
tively with state-of-the-art neural approaches. Sec-
ond, we request human evaluators to assess the qual-
ity of 98 machine-generated and 97 human-authored
questions. The question quality is perceived here in
terms of well-formedness and answerability.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Sec-
tion 2 analyzes previous studies for QG methods and
evaluation strategies. In Section 3, we explain the pur-
pose behind the generated questions. In Section 4, we
present the generation pipeline for the QG framework.
In Section 5, we describe the comprehensive evalua-
tion. Finally, Section 6 covers the paper’s limitations
and Section 7 puts forward final remarks.
2 RELATED WORK
This section reviews related work for QG method-
ologies (Section 2.1) and evaluation procedures (Sec-
tion 2.2).
2.1 Question Generation Methods
Given the substantial breakthroughs in deep learn-
ing and large-scale question corpora, QG has taken
advantage of neural networks. Neural approaches
for QG are generally formulated as a sequence-to-
sequence (seq2seq) problem (Du et al., 2017). These
seq2seq approaches typically use an input text to
feed an RNN-based (Zhou et al., 2017; Guo et al.,
2018; Harrison and Walker, 2018) or transformer-
based (Chan and Fan, 2019; Wang et al., 2020a) en-
coder and generate questions about the text through
a decoder. Recent research has focused on improv-
ing natural language generation (NLG) techniques,
usually by incorporating pre-trained language models
into the seq2seq architecture. On a variety of NLG
tasks, including QG (Xiao et al., 2020; Wang et al.,
2020b; Yao et al., 2022), these pre-trained models
have demonstrated promising outcomes (Dong et al.,
2019).
This research focuses on rule-based methods,
which involve the use of crafted rules and significant
human effort to facilitate the conversion of declarative
sentences into interrogative ones. One critical part
of the rule-based QG pipeline is the linguistic aspect
of the input text required by the generation approach.
Three linguistics aspects are commonly considered in
the QG literature: syntactic (Liu et al., 2010; Heilman
and Smith, 2010a), semantic (Lindberg et al., 2013;
Mazidi and Nielsen, 2014), and dependency informa-
tion (Mazidi and Tarau, 2016a,b).
Although these linguistic aspects have already
been explored for Portuguese (Pirovani et al., 2017;
Leite et al., 2020; Ferreira et al., 2020), our research
considers two additional aspects that have not been
explored much (for English and other languages): dis-
course connectors (Agarwal et al., 2011) and relative
pronouns & adverbs (Khullar et al., 2018). The ex-
ploration and comparison between these linguistic as-
pects in the evaluation process is another contribution
of this paper.
2.2 Evaluation of Question Generation
Systems
There are mainly two methods typically employed in
the literature for assessing the performance of QG
systems: automatic and human evaluation.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
28

The idea behind automatic evaluation is to use
automatic metrics for outputting a similarity score
between machine-generated and gold-standard ques-
tions (typically human-authored). The standard met-
rics for computing these scores are BLEU (Papineni
et al., 2002), ROUGE (Lin, 2004), and METEOR
(Banerjee and Lavie, 2005).
The human evaluation consists in presenting a
sample of machine-generated and human-authored
questions to human reviewers, who evaluate the over-
all quality of each question based on defined metrics
(without knowing whether the question was gener-
ated or not). For this evaluation type, several met-
rics have been suggested over the past few years. In
fact, Kurdi et al. (2020) reported 27 distinct metrics
for assessing the quality of the questions and their
components. The most widely reported metrics are
well-formedness, acceptability, reliability, grammati-
cal correctness, fluency, semantic ambiguity, and an-
swerability.
While human-authored evaluation is highly val-
ued, it is usually costly and time-consuming. Whereas
automatic metrics are a quick and inexpensive form
of evaluation, they may not correlate well with ques-
tion quality (Callison-Burch et al., 2006; Liu et al.,
2016). For now, combining different existing evalu-
ation methods and allowing diversified perspectives
seems to be an appropriate strategy. For that rea-
son, this research undertakes a comprehensive eval-
uation of a rule-based QG framework supported by
automatic metrics and human judgments.
3 PURPOSE OF GENERATED
QUESTIONS
According to Kurdi et al. (2020), the primary reported
purpose for automatically generating questions in the
educational context is assessment. Other purposes in-
clude generic (with no particular focus on a specific
purpose), self-directed learning, self-study (or self-
assessment), learning support, tutoring, and providing
practice questions.
Our purpose is to provide quality practice ques-
tions for the benefit of the learners. Although our
comprehensive evaluation does not include an assess-
ment with actual students, we tried to ensure that the
QG framework is directed towards the target ped-
agogical goal: identify themes, main ideas, facts,
causes, and effects from text passages. This pedagog-
ical goal has been taken from the established essential
learning skills
1
for the Portuguese subject (consider-
1
https://www.dge.mec.pt/
ing middle school), which is the course that would fit
the proposed system.
The QG framework attempts to meet the peda-
gogical goal by incorporating five linguistic aspects
during the generation process. The first three are
based on three linguistic representation levels: syn-
tactic (PoS and NER), semantic, and dependency in-
formation. The other two focus on two particular lexi-
cal class targets: relative pronouns & adverbs and dis-
course connectors.
By using syntactic information, one can iden-
tify sequences containing information about enti-
ties (e.g., person and places), which are then used
(through transformation rules) to generate questions
about facts (e.g., Who discovered the Inca Empire in
South America?).
Regarding semantic information, one can go
deeper into sentence meaning, which is possible
by using semantic parsing. Questions concerning
modes/manners can be formulated (e.g., How does
Morning rub out each star?).
The advantage of dependency information relies
on recognizing grammatical and functional relations
between words (e.g., the sentence’s subject is fol-
lowed by a copulative verb, indicating that the subject
is probably being characterized in some way), which
allows generating questions concerning the character-
ization of themes or ideas (e.g., How do you charac-
terize the first World War?).
As for the use of relative pronouns & adverbs,
they refer to nouns previously mentioned in the text.
As such, they identify connections between two con-
secutive parts of a sentence, allowing, for example,
to produce questions concerning results or effects
(e.g., What leads to the crossroads at the end of the
world?). Finally, discourse connects can, for instance,
indicate causalities connections between two or more
clauses, thus bringing out questions on causes (e.g.,
Why would the Portuguese be in numerical advan-
tage?).
In conclusion, the specificity of the type of infor-
mation provided by these linguistic aspects reinforces
our motivation behind the pedagogical goal: asking
about themes, main ideas, facts, causes, and effects
from text passages.
4 QUESTION GENERATION
FRAMEWORK
This section presents the generation pipeline within
the QG framework, including a description of each
aprendizagens-essenciais-ensino-basico
Do Rules Still Rule? Comprehensive Evaluation of a Rule-Based Question Generation System
29

step: pre-processing, sequence generation, search pat-
tern, and question formulation. Table 1 provides illus-
trative examples of the generation process according
to each approach step
2
and the five linguistic aspects
explored. We now describe each step.
4.1 Pre-Processing
The first state is pre-processing, in which the raw in-
put text is processed by employing the following NLP
techniques: segmentation (text is broken into sen-
tences); PoS tagging (morphological tag is assigned
to each word in a sentence); dependency parsing (as-
sign words with their grammatical and functional re-
lations); semantic role labeling (the process of assign-
ing semantic labels to words in a sentence); and NER
(named entities are identified in a sentence and clas-
sified according to their entity types). We use the
StanfordNLP (Qi et al., 2018) toolkit for all tasks, ex-
cept for NER and semantic role labeling. For NER,
we use the ner-re-pt model
3
, which has been trained
to identify the following entities: ABSTRACTION,
EVENT, THING, LOCAL, ORGANIZATION, PERSON,
TIME, VALUE, WORK OF ART, and OTHER. For se-
mantic role labeling, we use nlpnet
4
.
4.2 Sequence Generation
At this stage, a sequence is generated for each sen-
tence. Depending on the target linguistic aspect, the
sequence might include different information. For
syntactic information, all recognized entities are com-
bined with the PoS tags. For semantic information,
the sequence comprises the obtained semantic roles
from SRL. For dependency information, the sequence
is produced using the output of the dependency parser.
Regarding relative pronouns & adverbs, only PoS tags
are considered. Finally, for discourse connectors, the
sequence consists of two arguments (arg1 and arg2),
separated by a discourse connector. For instance, the
“because” connector separates the two arguments in
the example of Table 1.
4.3 Search Pattern
The search pattern phase finds patterns in the previ-
ously generated sequences. Regular expressions have
been manually defined for this purpose. The full list
of established regular expressions (and their descrip-
tion) is shown in Table 6. If a regular expression is
2
Since prep-processing is identical for all examples, it
is not represented in Table 1.
3
https://github.com/arop/ner-re-pt
4
https://pypi.org/project/nlpnet/
matched in the sequence, the sentence that originated
the sequence is considered a candidate for question
generation.
4.4 Question Formulation
In this stage, declarative-to-interrogative transforma-
tions are applied to candidate sentences. The appro-
priate interrogative term is introduced at the begin-
ning of the question wording. This interrogative term
is chosen based on the regular expression (see the reg-
ular expression’s descriptions in Table 6).
5 COMPREHENSIVE
EVALUATION
This section includes the performed comprehensive
evaluation, organized into two studies: (1) similar-
ity between machine-generated and human-authored
questions and (2) quality of machine-generated and
human-authored questions.
5.1 Study 1: Similarity Between
Machine-Generated and
Human-Authored Questions
5.1.1 Research Questions and Hypotheses
A standard method for evaluating QG systems is com-
paring machine-generated to human-authored ques-
tions using appropriate evaluation metrics. This study
aims to use automatic evaluation metrics as indica-
tors of the similarity between machine-generated and
human-authored questions. The rationale behind us-
ing these metrics is that they act as initial, inexpen-
sive and large-scale indicators of the similarity be-
tween human-authored and machine-generated ques-
tions. Therefore, we formulate the following research
question:
RQ1. Are rule-based generated questions similar
to those written by humans?
We hypothesize that rule-based generated ques-
tions are similar to those written by humans. We also
hypothesize that particular linguistic aspects explored
in the QG process produce generated questions closer
to those written by humans.
5.1.2 Procedure, Data and Participants
For addressing RQ1, we handle a manual QG process,
which can be summarized as follows:
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
30

Table 1: Illustrative examples for each step of the generation approach and linguistic aspect (best viewed in color). The blue
text represents the sequence part matched by the regular expression included in the question. The red text represents the part
not included in the question.
Syntactic
Example Sentence Francisco Pizarro descobriu o Imp
´
erio Inca na Am
´
erica do
Sul. english: Francisco Pizarro has discovered the Inca Empire in South America.
Sequence Generation per-per-verb-det-noun-noun-prep-loc-loc-loc-punct (NER combined with PoS)
Search Pattern per-verb|aux.*?punct
Question Formulation Quem Who + per-verb|aux.*?punct + ?
Generated Question Quem descobriu o Imp
´
erio Inca na Am
´
erica do
Sul? Who has discovered the Inca Empire in South America?
Semantic
Example Sentence Com um beijo, a Manh
˜
a apaga cada estrela enquanto prossegue a caminhada em
direc¸
˜
ao ao horizonte. With a kiss, the Morning rubs out each star as it continues its walk towards the horizon.
Sequence Generation mnr-a0-v-a1 (semantic labels)
Search Pattern mnr-a0-v-a1 (by coincidence, is equal to the generated sequence)
Question Formulation Como
´
e que How + mnr-a0-v-a1 + ?
Generated Question Como
´
e que a Manh
˜
a apaga cada estrela? How does Morning rub out each star?
Dependency
Example Sentence O ano de 1917 foi dif
´
ıcil para todos os belig-
erantes. The year of 1917 was difficult for all belligerents.
Sequence Generation det-nsubj-case-nmod-cop-root-case-det-det-obl-punct (dependency labels)
Search Pattern det-nsubj-case-nmod-cop-root.*?punct
Question Formulation Como caracteriza How do you characterize + det-nsubj-case-nmod-cop-root.*?punct + ?
Generated Question Como caracteriza o ano de 1917? How do you characterize the year of 1917?
Relative Pronouns and Adverbs
Example Sentence O Gato tomou a direc¸
˜
ao dos estreitos caminhos que con-
duzem
`
a encruzilhada do fim do mundo. The Cat took the di-
rection of the narrow paths which lead to the crossroads at the end of the world.
Sequence Generation det-noun-verb-det-noun-prep-adj-noun-pron-verb-
prep-noun-prep-noun-prep-noun-punct (PoS labels)
Search Pattern noun-pron.*?punct (pronoun must be relative)
Question Formulation O que
´
e que What + noun-pron.*?punct + ?
Generated Question O que
´
e que conduz
`
a encruzilhada do fim do
mundo? What leads to the crossroads at the end of the world?
Discourse Connectors
Example Sentence Os portugueses estariam em superioridade num
´
erica, porque as forc¸as ocupantes
tinham-se dispersado por Alc
´
acer e outras povoac¸
˜
oes. The Portuguese would be in
numerical advantage, because the occupying forces had dispersed throughout Alc
´
acer and other settlements.
Sequence Generation arg1-arg2 (arguments separated by the discourse connector)
Search Pattern arg1-arg2
Question Formulation Qual o motivo pelo qual Why + arg1-arg2 + ?
Generated Question Qual o motivo pelo qual os Portugueses estariam em supe-
rioridade num
´
erica? Why would the Portuguese be in numerical advantage?
1. Text collection: We choose 5 educational texts
from the Portuguese National Reading Plan
5
;
2. Automatic QG: We use the previous textbooks
to automatically generate all possible questions
through the rule-based QG framework;
5
https://www.pnl2027.gov.pt/np4/home
3. Sentence-Question sampling: After QG, we ran-
domly select a sample of 30 questions per linguis-
tic aspect and the sentences from which they were
generated. This results in 150 sentence-question
pairs;
4. Manual QG: We expose people 150 sampled sen-
tences (without the generated questions) and ask
Do Rules Still Rule? Comprehensive Evaluation of a Rule-Based Question Generation System
31

them to write questions about facts, themes, ideas,
causes, and effects;
5. Automatic evaluation: We use automatic evalua-
tion metrics to compare machine-generated ques-
tions with human-authored ones.
Ten Portuguese participants with a higher educa-
tion degree (from different fields) were involved in the
manual question generation process. All participants
participated pro-bono. Each person was instructed to
propose one or more questions from a set of 15 sen-
tences. As a guidance note to the participants, we re-
quested that the questions should target answers about
facts, themes, ideas, causes, and effects (to fulfill the
pedagogical goal).
In total, we acquired 419 human-authored ques-
tions, meaning that the participants have proposed an
average of 2.79 questions per sentence. The minimum
number of questions proposed per sentence was 1, and
the maximum was 8. The fact that we obtain multi-
ple human-authored questions per sentence is valu-
able when using automatic metrics for the evaluation
procedure. This is because several machine-generated
questions may be acceptable – by using a range of
possible human-authored questions, we increase the
chances that generated questions are properly eval-
uated (Rodrigues et al., 2022) when relying on the
usual BLEU-related metrics, which are based on lex-
ical similarity.
5.1.3 Automatic Evaluation Metrics
We use BLEU (Callison-Burch et al., 2006), ROUGE
(Lin, 2004) and BERTScore (Zhang et al., 2019) as
automatic evaluation metrics. BLEU is precision-
oriented: how many of the n-grams in the machine-
generated text were in the human written text. The n-
gram typically employed is 4 (and we also present it).
ROUGE is recall-oriented: how many n-grams in the
human-authored text appear in the machine-generated
text. We report a widely used variant of ROUGE,
called ROUGE
L
, which considers the longest com-
mon sequence between the machine-generated and
the human-authored text. Finally, BERTScore com-
putes a similarity value (using contextual embed-
dings) for each token in the machine-generated text
with each token in the human-authored text.
5.1.4 Results
Results for automatic evaluation are found in Table 2.
Given the fact that each participant has created, on
average, 3 questions for each sentence, we detail
our results when considering the “Worst” and “Best”
matches for the machine-generated questions. While
most datasets include a single gold question or report
the score on the best-matching gold question, the ob-
served differences highlight the importance of having
several reference questions. We observe that the abso-
lute improvement from “Worst” to “Best” ranges from
8.10 (BERTScore, Rel.) to 35.24 (ROUGE
L
, Dep.),
which is significant. We verified this significance by
performing the student’s t-test, where the p-value was
< .05 in both situations.
Overall, our BLEU 4 values range from ≈11 to
32. As for ROUGE
L
, they go from ≈21 to 53.
State-of-the-art QG values (using seq2seq models) for
BLEU 4 and ROUGE
L
present ≈12 to 25 and 32 to 53
ranges, respectively, considering the SQuAD dataset
(Rajpurkar et al., 2016) for English (see Table 7 from
Zhang et al. (2021)). Regarding BERTScore, our val-
ues range from ≈75 to 90. State-of-the-art QG val-
ues (using seq2seq models) for BERTScore present a
range of 85 to 91 values, considering the HotpotQA
dataset (Yang et al., 2018) for English (see Table 1
from Ji et al. (2022)). So, although the compari-
son conditions are slightly different (distinct dataset
and language), our results for automatic metrics align
quantitatively with those obtained using recent ap-
proaches.
Finally, the generated questions underlying the
linguistic aspect of dependency information yields
consistently better results for all settings (except for
ROUGE
L
, “Worst”). In contrast, the linguistic aspect
of relative pronouns & adverbs yields consistently
worst results for all settings (except for ROUGE
L
,
“Best”). We do not find any clear trend for the re-
maining linguistic aspects explored.
Table 2: Automatic evaluation results (0-100) for BLEU 4,
ROUGE
L
and BERTScore. Bold is applied to the best value
obtained in each column.
BLEU 4 ROUGE
L
BERTScore
Aspect Nr. Worst Best Worst Best Worst Best
Syn. 30 8.61 27.39 17.80 47.16 75.10 83.39
Sem. 30 8.28 30.33 19.76 51.16 77.40 85.54
Dep. 30 14.09 43.64 25.99 61.23 80.98 90.38
Rel. 30 7.52 25.46 14.90 48.44 74.75 82.85
Disc. 30 13.10 35.06 26.91 57.69 75.67 85.30
Overall 150 10.79 32.33 21.07 53.14 76.78 85.49
5.1.5 Discussion of the Results
The first study’s results imply that rule-based ques-
tions are similar to those written by humans in terms
of automatic evaluation metrics. We found that the
obtained scores are quantitatively aligned with those
obtained in the literature. Additionally, the results
reinforce the importance of producing multiple ref-
erence questions for the source text. This allows
considering the varied formulations that a generated
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
32

question may take, which significantly impacts the re-
sults. Although this study provided an initial indica-
tion of the similarity between machine-generated and
human-authored questions, the quality aspect of the
questions still needs to be addressed. We do this in
study 2.
5.2 Study 2: Quality of
Machine-Generated and
Human-Authored Questions
5.2.1 Research Questions and Hypotheses
This study aims to manually evaluate the quality of
machine-generated and human-authored questions. In
this respect, Zhang and VanLehn (2016) concluded
that human-authored biology questions are compa-
rable to those generated by a machine, using expert
ratings on 5-point scales (e.g., fluency, ambiguity,
depth). In turn, Heilman and Smith (2010b) col-
lected human judgments on one “goodness” scale of
machine-generated factual questions without compar-
ing them to human-authored ones.
Our study is based on the one conducted by
Chinkina et al. (2020). The authors performed a
crowdsourcing study and showed that machine-
generated questions (for supporting computer-
assisted language teaching) are comparable to those
written by humans, considering two important
aspects: well-formedness and answerability. Intu-
itively, a question is well-formed when there are no
syntactical, grammar, or spelling mistakes, while it
is answerable when there is an undoubtedly unique
answer. Accordingly, we formulate our second
research question:
RQ2. Are rule-based generated questions com-
parable to those written by humans in terms of well-
formedness and answerability?
We hypothesize that machine-generated and
human-authored questions are comparable, consider-
ing these two aspects under analysis. Additionally, we
also tried to find out if humans can effectively distin-
guish a generated question from a question written by
a human. Therefore, we formulate our third research
question:
RQ3. How well can humans distinguish questions
generated by a machine from those written by a per-
son?
5.2.2 Procedure, Data and Participants
For addressing RQ2 and RQ3, we request a new group
of participants to look at both machine-generated and
human-authored questions and rate them according to
well-formedness, answerability, and distinguishabil-
ity (Is this question human or machine-generated?)
measures.
The questions to be judged are the BLEU 4 “Best”
150 pairs from study 1. More specifically, 150
machine-generated questions and the corresponding
most similar 150 human-authored questions, consid-
ering BLEU 4. So, there are 150 machine-generated
questions, both well and ill-formed, and 150 human-
authored questions, presumed to be well-written. We
mixed machine-generated and human-authored ques-
tions in an evaluation set and requested 30 Portuguese
participants with higher education (from different
fields) to rate and distinguish them. All participants
participated pro-bono, and each one of them rated
between 15 and 30 questions. Each question, either
machine-generated or human-authored, was assessed
according to the following inquiry:
• Well-formedness – How well-formed is this ques-
tion item? [5-point Likert scale];
• Answerability – How many answers does the
question have? [One answer; Two or more an-
swers since the question is ambiguous; None
since the question is badly formulated; None since
the answer is not in the excerpt;]
• Distinguishability - Do you believe this question
was written by a person or generated by a com-
puter? [Person; Computer; I am not sure].
We ensure that each rated question has been as-
sessed by at least 3 participants. In the end, we col-
lected 645 responses corresponding to 98 machine-
generated and 97 human-written questions (a total of
195).
5.2.3 Results
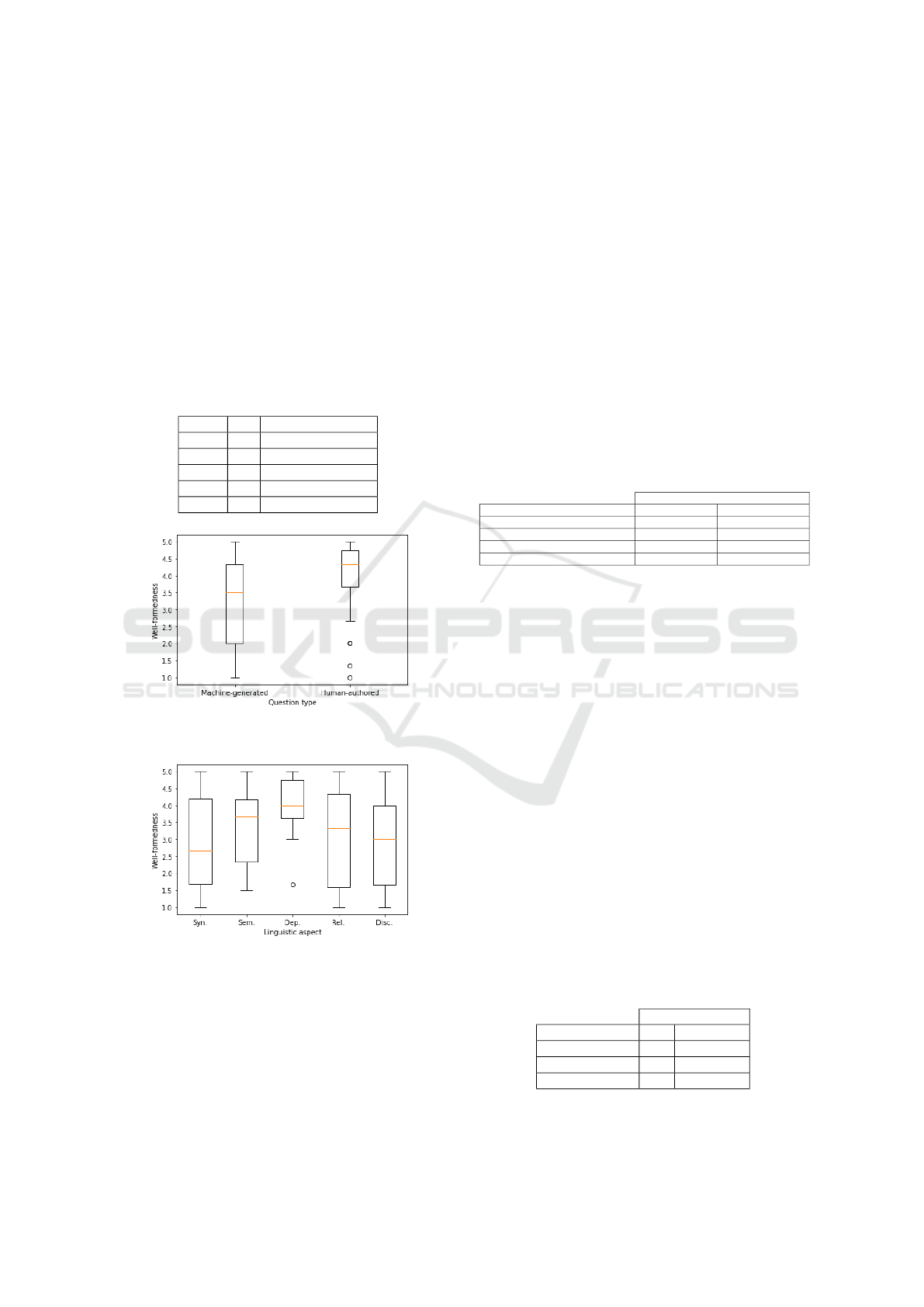
On the well-formedness scale, the means are 4.12
±.86 for human-authored and 3.24 ±1.32 for
machine-generated questions. The detailed values per
linguistic aspect are shown in Table 3. For better ob-
servation of the locality and dispersion values, we
present the boxplots in Figures 2 and 3. To inves-
tigate whether the difference in ratings between all
machine-generated and all human-authored questions
is statistically significant, we perform student’s t-test.
We find that the referred differences are statistically
significant for well-formedness, and the effect size
is large: t
1
= -5.52, p
1
< .05, Cohen’s d
1
= -0.79.
One exception is the questions generated by explor-
ing the dependency information. If we consider only
these questions for performing the same test, we find
that the differences are not statistically significant: t
2
= -.38, p
2
= .70, Cohen’s d
2
= -0.09. These val-
ues indicate that human-authored questions present
Do Rules Still Rule? Comprehensive Evaluation of a Rule-Based Question Generation System
33
higher quality than machine-generated ones, except
those generated using dependency information that
seems to capture more of the linguistic characteristics
of the human-authored questions. It should be noted
that although human-authored questions are of higher
quality than machine-generated ones in terms of well-
formedness, the mean of machine-generated ques-
tions is still above the scale’s average (≥2.5). Also,
human-authored questions fall short of the expected
well-formedness mean value for questions elaborated
by humans (we would expect it to be between 4.5 and
5).
Table 3: Mean results on the well-formedness scale, con-
sidering machine-generated questions.
Aspect Nr. Well-formedness (1-5)
Syn. 26 2.87 ±1.36
Sem. 15 3.25 ±1.19
Dep. 20 4.04 ±.89
Rel. 16 3.13 ±1.51
Disc. 21 3.04 ±1.34
Figure 2: Locality and dispersion well-formedness values
for machine-generated and human-authored questions.
Figure 3: Locality and dispersion well-formedness values
for each linguistic aspect (machine-generated questions).
Regarding answerability, Table 4 shows a contin-
gency matrix representing the relation between ques-
tion provenance (human or machine) and the partic-
ipants’ judgment. Given the non-ordinal options for
assessing answerability, we rely on majority voting
for each question under evaluation. Of the 195 ques-
tions evaluated, 183 had a majority agreement, 7 had
a tie, and 5 had a total disagreement. In the table, we
represent only the questions with majority agreement.
The results show that most human-authored and
machine-generated questions are considered to con-
tain one unique answer. Given that a single answer
is an ideal scenario, this is a good indicator of the
answerability of machine-generated questions. How-
ever, there are 20 questions where the participants
considered the answer to be non-existent because the
question was badly formulated. Also, there are a
few remaining cases affecting both types of questions
where participants consider that the question has two
or more answers because it is ambiguous (2 cases), or
it has no answer — not found in the excerpt (9 cases).
In these cases, there is nearly a tie between machine-
generated and human-authored questions.
Table 4: Relations between question provenance and partic-
ipants’ judgment on the answerability.
Question provenance
Responses Human-authored Machine-generated
One answer 84 65
Two or more answers (ambiguous) 1 1
None (badly formulated question) 3 20
None (answer not in the excerpt) 5 4
On distinguishability, Table 5 shows the con-
tingency matrix representing the relation between
question provenance and the participants’ judg-
ment. In 645 responses, the participants correctly
judged HA questions as human-authored in 118
cases (36.5%), while they mistakenly judged HA
as machine-generated in 114 cases (35.3%). Also,
there are 91 (28.2%) cases where participants present
doubts about whether a HA question is human or
machine-generated. On the other hand, the partic-
ipants correctly judged MG questions as machine-
generated in 192 cases (59.6%), while they mistak-
enly judged MG as human-generated in 76 cases
(23.6%). They present doubts about whether a MG
question is human or machine-generated in 54 cases
(16.8%). These results show that the participants cor-
rectly identified most of the HA questions as human-
authored and most of the MG questions as machine-
generated. Another viewpoint is that there are 130
cases(40.4%) where participants have doubts or incor-
rectly judge MG questions as human-authored.
Table 5: Responses in distinguishing human-authored and
machine-generated questions.
Question provenance
Responses HA MG
Human-authored 118 76
Doubt 91 54
Machine-generated 114 192
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
34

5.2.4 Discussion of the Results
The results of the second study imply that the rule-
based questions are comparable to those written by
humans concerning well-formedness when explor-
ing dependency information as a linguistic aspect.
Questions generated by exploring other linguistic as-
pects fall considerably short of those generated by
humans. Still, the mean well-formedness value of
machine-generated questions is above the scale’s av-
erage value. Regarding answerability, except when
machine-generated questions are badly formulated,
they are comparable to those authored by humans.
Finally, the results of the second study also imply
that humans cannot distinguish (or present doubts)
machine-generated from human-authored questions
in over half of the cases (51.9%). This means that
machine-generated questions successfully captured
some linguistic features of human-authored ques-
tions.
6 LIMITATIONS, CHALLENGES
AND CONSIDERATIONS
This study has both limitations and challenges:
• Language-dependence: Although the study is
conditioned to the Portuguese language, we ar-
gue that the framework is adaptable to other lan-
guages. For instance, we use custom regular ex-
pressions for finding patterns (Section 4.3) along
source sentences. While we had a logical foun-
dation (as described in Table 6) for assembling
the expressions based on our language knowl-
edge, someone who intends to apply the same
technique should start by building custom regular
expressions for the chosen language. We recom-
mend starting with something as simple as the first
proposed expression, where a subject is followed
by the verb (denoting some action performed by
the subject), and then experimenting with vari-
ants consequential to the linguistic characteristics
of the studied language. Finally, we recommend
a similar strategy for question formulation (Sec-
tion 4.4), where declarative-to-interrogative trans-
formations are needed. The transformation pro-
cedure should consider the language’s particular-
ities, e.g., subject-verb inversion, proper interrog-
ative terms, or punctuation.
• Educational usefulness of the questions: Al-
though we aim to generate educationally relevant
questions for which we attempt to meet the peda-
gogical goal (as explained in Section 3), we do not
include an assessment with actual students. Thus,
this study does not provide evidence of the ques-
tions’ educational utility in a real setting.
• Reliability of automatic evaluation metrics:
Callison-Burch et al. (2006) and Liu et al. (2016)
have shown that these metrics may not correlate
well with fluency, coherence or adequacy, since
they essentially compute the n-gram similarity be-
tween the reference and generated text (for BLEU
and ROUGE). This is why we report the metrics
only as an initial measure of similarity in Study 1
and do not attempt to correlate with the quality of
the questions.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we present a rule-based QG framework
for generating Portuguese wh-questions. This frame-
work can be adapted to other languages if proper
adaptations are carried out. We perform a compre-
hensive evaluation for assessing the feasibility of the
QG approach, supported by two studies. In the for-
mer, we find that machine-generated questions are as
similar to human-authored questions as in prior work,
in terms of lexical and semantic similarity metrics.
In the second study, we find that machine-generated
questions are comparable to those written by humans
concerning well-formedness when exploring depen-
dency information as a linguistic aspect. We argue
that a QG rule-based approach may still be a feasi-
ble alternative to neural-based techniques when these
are not viable. For example, when quality QA data is
unavailable or machine translation falls short, a com-
mon situation for lower-resourced languages. For fu-
ture work, we intend to employ an assessment with
actual students since the QG framework was designed
toward a specific pedagogical goal.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank the 10 participants who voluntar-
ily participated in study 1. The authors also thank
the 30 participants who voluntarily participated in
study 2. This work was financially supported by
Base Funding - UIDB/00027/2020 of the Artificial
Intelligence and Computer Science Laboratory (LI-
ACC) funded by national funds through FCT/MCTES
(PIDDAC). Bernardo Leite is supported by a PhD
studentship (reference 2021.05432.BD), funded by
Fundac¸
˜
ao para a Ci
ˆ
encia e a Tecnologia (FCT).
Do Rules Still Rule? Comprehensive Evaluation of a Rule-Based Question Generation System
35

Table 6: All explored regular expressions (used for SEARCH PATTERN in QG framework) and corresponding description.
Syntactic
Regular Expression Description
per-verb|aux.*?punct This expression tries to find information regarding a person. The first element is a
person-type entity, followed by a main or auxiliary verb. Interrogative term: WHO
per-conj-per-verb|aux.*?punct This expression tries to find information about two people. The first ele-
ment is a person-type entity, followed by a conjunction and another person-
type. A main or auxiliary verb follows. Interrogative term: WHICH PERSON
org|event-verb|aux.*?punct This expression tries to find information regarding events. The first element
is an organization-type or event-type entity, followed by a main or auxil-
iary verb. Interrogative terms: WHICH ORGANIZATION or WHICH EVENT
time|loc-verb|aux.*?punct This expression tries to find information regarding time or loca-
tions. The first element is a time-type or location-type entity, followed
by a main or auxiliary verb. Interrogative terms: WHEN or WHERE
per-verb|aux.*?loc-punct This expression tries to find relationships between people and places.
The first element is a person-type entity, followed by a main or auxiliary
verb. A location-type entity is also included. Interrogative term: WHERE
val-verb|aux.*?punct The first element is a value-type entity, followed by a main or auxiliary verb. If there is a
match within this expression, we perform disambiguation to assess whether val is a nu-
merical or percentage value. Interrogative terms: WHAT NUMBER or WHAT PERCENTAGE
Semantic
Regular Expression Description
mnr-a0-v-a1 The first element is a manner (mnr), followed by an agent (a0)
who performs a certain action (v and a1). Interrogative term: HOW
a0-v-a1-mnr The first element is an agent (a0) who is performing some action
(v and a1) with a specific manner (mnr). Interrogative term: HOW
tmp-a0-v-a1 The first element is a time expression (tmp), followed by an agent (a0)
who performs a certain action (v and a1). Interrogative term: WHEN
a0-v-tmp The first element is an agent (a0), who is performing some ac-
tion (v) in a given time space (tmp). Interrogative term: WHEN
a0-v-loc The first element is an agent (a0), who is performing some ac-
tion (v) in a given location (loc). Interrogative term: WHERE
a0-v-a1-loc The first element is an agent (a0), who is performing some ac-
tion (v and a1) in a given location (loc). Interrogative term: WHERE
loc-v-a1 The first element is a location (loc), followed by an ac-
tion being performed (v and a1). Interrogative term: WHERE
Dependency
Regular Expression Description
det-nsubj-cop-root.*?punct After the determinant, the subject (nsubj) is followed by a copulative verb (cop) and an
adjective (root). This expression informs that there is a subject being characterized in some
way, expressed in the adjective (root). Interrogative term: HOW DO YOU CHARACTERIZE
det-nsubj-cop-advmod-root.*?punct After the determinant, the subject (nsubj) is followed by a copulative verb
(cop). After the copulative verb, an adverb (advmod) and an adjective (root).
This expression informs that there is a subject being characterized in some
way. The correct answer (for the requested characterization) will be the ad-
verb plus adjective. Interrogative term: HOW DO YOU CHARACTERIZE
det-nsubj-case-nmod-cop-root.*?punct This expression identifies a characteristic/attribute (nsubj) from a per-
son/object/number (nmod) that is being characterized in some way (cop
+ root). The correct answer (for the requested characterization) will be
the adjective (root). Interrogative term: HOW DO YOU CHARACTERIZE
det-nsubj.*?root-xcomp After the determinant, the subject (nsubj) is described through a cer-
tain action with a verb (root) followed by an adjective (xcomp). The cor-
rect answer will be the adjective (xcomp). Interrogative term: HOW
det-nsubj.*?root-advmod-xcomp After the determinant, the subject (nsubj) is described through a certain action with
a verb (root) followed by an adverb (advmod) and an adjective (xcomp). The correct
answer will be the adverb and adjective (advmod + xcomp). Interrogative term: HOW
det-nsubj-root-det-obj.*?punct This expression identifies the syntactic function of direct complement (as
denominated from the Portuguese language). With this syntactic func-
tion, there is an indication of the subject (nsubj) on which the action ex-
pressed by the verb (root) falls directly (obj). Interrogative term: WHAT
Relative Pronouns and Adverbs
Regular Expression Description
noun-pron.*?punct (pron must be WHICH) The relative pronoun refers to the noun which is said to be an an-
tecedent of the relative pronoun. Interrogative term: WHAT
noun-adv.*?punct (adv must be WHERE) The relative adverb refers to the noun which is said to be an an-
tecedent of the relative adverb. Interrogative term: WHERE
Discourse Connectors
Regular Expression Description
arg1-arg2 (separated by connector BECAUSE) Two arguments are obtained using the discourse con-
nector as a separator. Interrogative term: WHY
arg1-arg2 (separated by connector WHEN) Two arguments are obtained using the discourse con-
nector as a separator. Interrogative term: WHEN
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
36

REFERENCES
Agarwal, M., Shah, R., and Mannem, P. (2011). Auto-
matic question generation using discourse cues. In
Proceedings of the Sixth Workshop on Innovative Use
of NLP for Building Educational Applications, pages
1–9, Portland, Oregon. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Banerjee, S. and Lavie, A. (2005). METEOR: An Auto-
matic Metric for MT Evaluation with Improved Cor-
relation with Human Judgments. In Proceedings of
the ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evalu-
ation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Sum-
marization, pages 65–72, Ann Arbor, Michigan. ACL.
Callison-Burch, C., Osborne, M., and Koehn, P. (2006). Re-
evaluating the role of Bleu in machine translation re-
search. In 11th Conference of the European Chap-
ter of the Association for Computational Linguistics,
pages 249–256, Trento, Italy. Association for Compu-
tational Linguistics.
Chan, Y.-H. and Fan, Y.-C. (2019). A recurrent BERT-
based model for question generation. In Proceedings
of the 2nd Workshop on Machine Reading for Ques-
tion Answering, pages 154–162, Hong Kong, China.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Chinkina, M., Ruiz, S., and Meurers, D. (2020). Crowd-
sourcing evaluation of the quality of automatically
generated questions for supporting computer-assisted
language teaching. ReCALL, 32(2):145–161.
Dong, L., Yang, N., Wang, W., Wei, F., Liu, X., Wang,
Y., Gao, J., Zhou, M., and Hon, H.-W. (2019). Uni-
fied Language Model Pre-training for Natural Lan-
guage Understanding and Generation. In Wallach,
H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., Alch
´
e-Buc, F. d.,
Fox, E., and Garnett, R., editors, Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems, volume 32. Curran
Associates, Inc.
Du, X., Shao, J., and Cardie, C. (2017). Learning to ask:
Neural question generation for reading comprehen-
sion. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the
Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1:
Long Papers), pages 1342–1352, Vancouver, Canada.
ACL.
Ferreira, J., Rodrigues, R., and Gonc¸alo Oliveira, H.
(2020). Assessing factoid question-answer genera-
tion for portuguese (short paper). In 9th Symposium
on Languages, Applications and Technologies (SLATE
2020). Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum f
¨
ur Infor-
matik.
Guo, H., Pasunuru, R., and Bansal, M. (2018). Soft layer-
specific multi-task summarization with entailment and
question generation. In Proceedings of the 56th An-
nual Meeting of the Association for Computational
Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 687–697,
Melbourne, Australia. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Harrison, V. and Walker, M. (2018). Neural generation of
diverse questions using answer focus, contextual and
linguistic features. In Proceedings of the 11th Interna-
tional Conference on Natural Language Generation,
pages 296–306, Tilburg University, The Netherlands.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
He, W., Liu, K., Liu, J., Lyu, Y., Zhao, S., Xiao, X., Liu, Y.,
Wang, Y., Wu, H., She, Q., Liu, X., Wu, T., and Wang,
H. (2018). DuReader: a Chinese machine reading
comprehension dataset from real-world applications.
In Proceedings of the Workshop on Machine Read-
ing for Question Answering, pages 37–46, Melbourne,
Australia. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Heilman, M. and Smith, N. A. (2010a). Good question!
statistical ranking for question generation. In Human
Language Technologies: The 2010 Annual Confer-
ence of the North American Chapter of the Associa-
tion for Computational Linguistics, pages 609–617,
Los Angeles, California. Association for Computa-
tional Linguistics.
Heilman, M. and Smith, N. A. (2010b). Rating computer-
generated questions with Mechanical Turk. In Pro-
ceedings of the NAACL HLT 2010 Workshop on Cre-
ating Speech and Language Data with Amazon’s Me-
chanical Turk, pages 35–40, Los Angeles. Association
for Computational Linguistics.
Ji, T., Lyu, C., Jones, G., Zhou, L., and Graham, Y. (2022).
Qascore — an unsupervised unreferenced metric for
the question generation evaluation. Entropy, 24(11).
Khullar, P., Rachna, K., Hase, M., and Shrivastava, M.
(2018). Automatic question generation using rela-
tive pronouns and adverbs. In Proceedings of ACL
2018, Student Research Workshop, pages 153–158,
Melbourne, Australia. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Kurdi, G., Leo, J., Parsia, B., Sattler, U., and Al-Emari,
S. (2020). A systematic review of automatic ques-
tion generation for educational purposes. Interna-
tional Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education,
30(1):121–204.
Leite, B. and Lopes Cardoso, H. (2022). Neural question
generation for the portuguese language: A prelimi-
nary study. In Marreiros, G., Martins, B., Paiva, A.,
Ribeiro, B., and Sardinha, A., editors, Progress in Ar-
tificial Intelligence, pages 780–793, Cham. Springer
International Publishing.
Leite, B., Lopes Cardoso, H., Reis, L. P., and Soares, C.
(2020). Factual question generation for the portuguese
language. In 2020 International Conference on INno-
vations in Intelligent SysTems and Applications (IN-
ISTA), pages 1–7. IEEE.
Lin, C.-Y. (2004). ROUGE: A Package for Automatic
Evaluation of Summaries. In Text Summarization
Branches Out, pages 74–81, Barcelona, Spain. ACL.
Lindberg, D., Popowich, F., Nesbit, J., and Winne, P.
(2013). Generating natural language questions to sup-
port learning on-line. In Proceedings of the 14th Eu-
ropean Workshop on Natural Language Generation,
pages 105–114, Sofia, Bulgaria. Association for Com-
putational Linguistics.
Liu, C.-W., Lowe, R., Serban, I., Noseworthy, M., Charlin,
L., and Pineau, J. (2016). How NOT to evaluate your
dialogue system: An empirical study of unsupervised
evaluation metrics for dialogue response generation.
Do Rules Still Rule? Comprehensive Evaluation of a Rule-Based Question Generation System
37

In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empiri-
cal Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages
2122–2132, Austin, Texas. Association for Computa-
tional Linguistics.
Liu, M., Calvo, R. A., and Rus, V. (2010). Automatic ques-
tion generation for literature review writing support.
In Aleven, V., Kay, J., and Mostow, J., editors, Intel-
ligent Tutoring Systems, pages 45–54, Berlin, Heidel-
berg. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Mazidi, K. and Nielsen, R. D. (2014). Linguistic consider-
ations in automatic question generation. In Proceed-
ings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for
Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers),
pages 321–326, Baltimore, Maryland. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Mazidi, K. and Tarau, P. (2016a). Automatic question gen-
eration: From nlu to nlg. In Micarelli, A., Stamper,
J., and Panourgia, K., editors, Intelligent Tutoring Sys-
tems, pages 23–33, Cham. Springer International Pub-
lishing.
Mazidi, K. and Tarau, P. (2016b). Infusing NLU into au-
tomatic question generation. In Proceedings of the
9th International Natural Language Generation con-
ference, pages 51–60, Edinburgh, UK. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Pan, L., Lei, W., Chua, T.-S., and Kan, M.-Y. (2019). Recent
advances in neural question generation. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1905.08949.
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., and Zhu, W.-J. (2002).
Bleu: a Method for Automatic Evaluation of Ma-
chine Translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual
Meeting of the Association for Computational Lin-
guistics, pages 311–318, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
USA. ACL.
Pirovani, J., Spalenza, M., and Oliveira, E. (2017). Gerac¸
˜
ao
Autom
´
atica de Quest
˜
oes a Partir do Reconhecimento
de Entidades Nomeadas em Textos Did
´
aticos. Brazil-
ian Symposium on Computers in Education (Simp
´
osio
Brasileiro de Inform
´
atica na Educac¸
˜
ao - SBIE),
28(1):1147.
Qi, P., Dozat, T., Zhang, Y., and Manning, C. D. (2018).
Universal dependency parsing from scratch. In Pro-
ceedings of the CoNLL 2018 Shared Task: Multilin-
gual Parsing from Raw Text to Universal Dependen-
cies, pages 160–170. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Rajpurkar, P., Zhang, J., Lopyrev, K., and Liang, P. (2016).
SQuAD: 100,000+ questions for machine comprehen-
sion of text. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on
Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing,
pages 2383–2392, Austin, Texas. ACL.
Rodrigues, H., Nyberg, E., and Coheur, L. (2022). Towards
the benchmarking of question generation: introduc-
ing the monserrate corpus. Language Resources and
Evaluation, 56(2):573–591.
Rus, V., Cai, Z., and Graesser, A. (2008). Question gener-
ation: Example of a multi-year evaluation campaign.
Proc WS on the Question Generation Shared Task and
Evaluation Challenge.
Trischler, A., Wang, T., Yuan, X., Harris, J., Sordoni, A.,
Bachman, P., and Suleman, K. (2017). NewsQA:
A machine comprehension dataset. In Proceedings
of the 2nd Workshop on Representation Learning for
NLP, pages 191–200, Vancouver, Canada. Associa-
tion for Computational Linguistics.
Wang, B., Wang, X., Tao, T., Zhang, Q., and Xu, J. (2020a).
Neural question generation with answer pivot. Pro-
ceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelli-
gence, 34(05):9138–9145.
Wang, W., Wei, F., Dong, L., Bao, H., Yang, N., and
Zhou, M. (2020b). Minilm: Deep self-attention dis-
tillation for task-agnostic compression of pre-trained
transformers. CoRR, abs/2002.10957.
Xiao, D., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Sun, Y., Tian, H., Wu, H.,
and Wang, H. (2020). ERNIE-GEN: An Enhanced
Multi-Flow Pre-training and Fine-tuning Framework
for Natural Language Generation. In Bessiere, C.,
editor, Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International
Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-20,
pages 3997–4003. International Joint Conferences on
Artificial Intelligence Organization.
Yang, Z., Qi, P., Zhang, S., Bengio, Y., Cohen, W.,
Salakhutdinov, R., and Manning, C. D. (2018). Hot-
potQA: A dataset for diverse, explainable multi-hop
question answering. In Proceedings of the 2018 Con-
ference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language
Processing, pages 2369–2380, Brussels, Belgium. As-
sociation for Computational Linguistics.
Yao, B., Wang, D., Wu, T., Zhang, Z., Li, T., Yu, M., and
Xu, Y. (2022). It is AI’s turn to ask humans a ques-
tion: Question-answer pair generation for children’s
story books. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meet-
ing of the Association for Computational Linguistics
(Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 731–744, Dublin, Ire-
land. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Zhang, L. and VanLehn, K. (2016). How do machine-
generated questions compare to human-generated
questions? Research and practice in technology en-
hanced learning, 11(1):1–28.
Zhang, R., Guo, J., Chen, L., Fan, Y., and Cheng, X. (2021).
A review on question generation from natural lan-
guage text. ACM Transactions on Information Systems
(TOIS), 40(1):1–43.
Zhang, T., Kishore, V., Wu, F., Weinberger, K. Q., and
Artzi, Y. (2019). Bertscore: Evaluating text genera-
tion with bert. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.09675.
Zhou, Q., Yang, N., Wei, F., Tan, C., Bao, H., and Zhou,
M. (2017). Neural question generation from text: A
preliminary study. In National CCF Conference on
Natural Language Processing and Chinese Comput-
ing, pages 662–671. Springer.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
38
