
Success Factors for Mathematical e-Learning Exercises Focusing
First-Year Students
Malte Neugebauer
a
, Basile Tousside
b
and J
¨
org Frochte
c
Bochum University of Applied Sciences, 42579 Heiligenhaus, Germany
Keywords:
E-Learning, Higher Education, Mathematics, Gamification, Learning Management System.
Abstract:
How university students succeed in math courses at the beginning of their studies is of great relevance for
the overall study success in many study programs. Since the competence levels of candidates are different,
lecturers struggle to mediate knowledge to such heterogeneous audiences simultaneously. In tacit consent, a
catch-up of lower-skilled students is expected. Self-organized learning materials – which are often accessible
via e-learning – are mostly unattractive, especially to lower-skilled students. Since gamification is success-
fully used in other areas of education to support motivation and performance, we propose gamification as a
first success factor for mathematical exercises. Considering infrastructural aspects of higher education, we fur-
thermore suggest the gamification systems’ ability to be extended by lecturers, its integrability into universities
learning management systems and its affordability as success factors for mathematical e-learning exercises.
Therefore, we implemented an open-source and easy-to-extend software approach, which is integrable into
universities’ learning management systems. In an initial test run among first-year students (n = 115), we show
how this approach improves learning and motivation at the same time. We discuss these results and propose
this approach for testing in multiple group plans, to further investigate the influence of single game elements
on motivation and learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
During the last decade, e-learning in mathematics
grew in relevance for higher education institutions.
Not only was the COVID-19 pandemic, which forced
universities into switching entirely to distance learn-
ing during 2020, of great relevance for mathematical
e-learning (Lisnani et al., 2020; Irfan et al., 2020),
but also the broader diversity of students – regard-
ing life scripts and competence levels – boosted the
importance of self-paced e-learning materials (Liang
et al., 2018; Schulmeister, 2004). Especially intro-
ductory courses are challenged to offer learning ma-
terials to their students that fit learners’ different com-
petence levels (Gordon et al., 2013). Here, self-paced
learning with e-learning materials enables students to
revisit knowledge from school, helping lower-skilled
students catching up.
However, B
¨
uchele and Marten (2022) found that
students with low math competencies fall back even
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1565-8222
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9332-5060
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5908-5649
more during their studies due to a low motivation to-
wards self-regulated mathematical learning. Despite
the fact that math is of great relevance for the suc-
cess of many study programs, students have a smaller
motivation towards it. This can possibly be traced
back to a given distance of the chosen study program
(e. g. psychology, architecture or computer science) to
mathematics.
One promising method to raise motivation in dif-
ferent subjects is gamification, which is known as “the
use of game design elements in non-game contexts”
(Deterding et al., 2011). Especially in higher educa-
tion it is widely used to raise students’ motivation, re-
duce drop-out rates or support learners’ performance
(Zainuddin et al., 2020a; Dichev and Dicheva, 2017).
Despite the fact, that most studies about gamifi-
cation take place in higher education (Dicheva et al.,
2015), studies focusing on the specific case of math-
ematics in this context are rare. Surprisingly, math-
related gamification research is more common in the
context of elementary and secondary school. One
possible reason is the size of the target group. The
number of students of the university entrance phase,
especially if one splits them up by subjects, is consid-
306
Neugebauer, M., Tousside, B. and Frochte, J.
Success Factors for Mathematical e-Learning Exercises Focusing First-Year Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0011858400003470
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2023) - Volume 2, pages 306-317
ISBN: 978-989-758-641-5; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

erably smaller than within a school year. Commercial
solutions are economically less attractive in this con-
text or would have to be managed with smaller bud-
gets. Affordability appears to be a facilitating factor.
Since many universities are using learning man-
agement systems (LMS) to facilitate self-paced
and distance learning for their students, an LMS-
based gamification of mathematical e-learning con-
tent could be a useful alternative to commercial solu-
tions. Integrability into universities’ LMS will allow
a gamification solution to make use of an already es-
tablished platform and, in this, support existing tools
like question banks or learning analytics systems. By
using external gamification tools – even on equipping
them with an interface for data exchange to LMS –
more data protection law issues may arise compared
to an in-house, LMS-integrated solution.
An additional, more socio-scientific phenomenon
is the raising heterogeneity of students. This leads
to a diversification of students’ needs depending on
their age, social background and family responsibil-
ities. Here, a highly extendable software solution is
needed, to address a constantly changing target group.
Considering (i) gamification, (ii) affordability,
(iii) extendibility and (iv) integrability of the soft-
ware into university LMS platforms as success fac-
tors for mathematical exercises in e-learning, here we
develop a software architecture for LMS, that allows
lightweight implementation of gamification into ex-
ercises to support mathematical learning in the early
phase of higher education. In a first test run we show,
that this easy-to-implement approach is capable not
only of raising motivation, but also helps new students
revisiting their math knowledge, concluding to a score
progression during exercise accomplishment.
Our contributions are summarized as follows:
• We present a frontend-oriented software archi-
tecture, that allows lightweight gamification im-
plementations into universities LMS without any
server-sided changes.
• Focusing on mathematical e-learning, we de-
velop a gamification exercise design based on
the frontend-oriented approach and demonstrate a
possible implementation inside the LMS Moodle.
• We analyze the results of a first test run with the
given approach and show, how learners are moti-
vated to solve the most challenging exercises and
progress in their score performance.
• We discuss how specific game elements influence
learners’ motivation and learning outcomes.
• We propose to test this approach in multiple group
plans to shed more light on the effect of specific
gamification elements for specific learner groups.
2 RELATED WORK REGARDING
GAMIFICATION
Since its first mention in the early 2000s (see Khaitova
(2021) for genesis), gamification became a widely
spread phenomenon in various areas, such as market-
ing (Hofacker et al., 2016) or onboarding (Fischer and
Heinz, 2020). There are many studies showing the ef-
fectiveness of gamification in higher education in var-
ious ways, using a variety of different game design el-
ements, ranging from points, badges and leaderboards
over competitions to virtual goods, all accompanied
with evident effects (Dicheva et al., 2015).
Although gamification research mostly takes
place in higher education (Dicheva et al., 2015), stud-
ies regarding mathematics mostly focus on primary or
secondary school. Mathematics-related gamification
studies, that take place in higher education usually
investigate students’ feedback to quiz software solu-
tions like Kahoot!, Socrative or Quizizz or (Zabala-
Vargas et al., 2021; Zainuddin et al., 2020b; Bul-
lon et al., 2018). Those software solutions do not
fit all the success factors mentioned above since they
are commercial (affordability) and they are only inte-
grable into LMS by embedding or sharing them via
an external link (integrability). In contrast to this,
we take the special needs of higher education into ac-
count to offer an affordable, easily integrable and ex-
tendable gamification solution.
The few studies focusing on gamification of math-
ematical learning in the specific context of the transi-
tion phase between school and university barely ad-
dress their technical implementations. Gordon et al.
(2013) for example present results of an approach us-
ing different game elements, paying special attention
to the possibility of repeating attempts (which is fur-
ther referred to as the freedom to fail gamification de-
sign principle). But the technical aspect of how the
game elements were implemented into the exercises
is not thematized, making this approach hardly re-
producible. In contrast to this, we propose an open-
source solution for web-based LMS, which explicitly
aims at being able to be adapted to the specific needs
of local students through its extendibility.
3 DERIVING GAMIFICATION
DESIGN PRINCIPLES FOR
MATHEMATICAL
E-LEARNING
For deriving appropriate game elements, we make
use of findings from behavioral economics and from
Success Factors for Mathematical e-Learning Exercises Focusing First-Year Students
307

psychology of learning. In the context of gamifica-
tion, the self-determination-theory (SDT) (Ryan and
Deci, 2000) is often referenced to explain raising
intrinsic and extrinsic motivation through gamifica-
tion (Zainuddin et al., 2020a). As per this theory, a
raise of intrinsic motivation appears, when three basic
needs are satisfied: competence, autonomy and relat-
edness. Game elements bear the potential to tackle
these needs (van Roy and Zaman, 2017).
Besides motivation, our approach aims at facili-
tating students’ learning process. The Fogg Behav-
ior Model (FBM) (Fogg, 2009) considers both mo-
tivation and ability at the same time to explain be-
havioral change. As per the FBM, behavior is seen
as a convergence of motivation, ability and a prompt.
When both, motivation and ability merge to a suffi-
cient degree, a prompt succeeds. Even if a hard task
is prompted, people will follow the prompt when the
motivation is high enough. For our use case, a rise
in motivation through gamification is expected. But
for our aim to facilitate learning in higher education
mathematics, solely raising motivation is not suffi-
cient. Additionally, we aim to raise the needed math-
competence, so that previously too difficult tasks be-
come solvable. Both, raising motivation towards ex-
ercise accomplishment and enabling learners to solve
challenging exercises complement each other when
behavioral change is desired.
As per Vygotsky’s model of proximal develop-
ment (Vygotsky, 1978; Podolskiy, 2012), learning
takes place when people go beyond their comfort
zone. In the so-called growth zone, challenging
tasks are accomplished and finally assimilated into
the comfort zone. Tutoring and repetition are facil-
itators for this process. Since math is highly modular
(Avigad, 2018), math exercises can be built upon each
other, so that learners can learn new things by deploy-
ing established knowledge on new challenges. In this,
their comfort zone increases exercise by exercise. Or
speaking with the FBM: They are more and more en-
abled to accomplish challenging tasks, reducing the
barrier of following the next prompt – which is the
next exercise.
To realize learning this way with the help of e-
learning exercises, learners have to be supplied with
additional material to understand those exercises, that
go beyond their comfort zone. Furthermore, feed-
back on their current performance in general and
on specific mistakes will support the assimilation of
challenging tasks into their comfort zone. Here we
use the design principles of gamification to increase
motivation on the one hand and to enable learning
progress on the other. State-of-the-art gamification re-
search demands elucidating the effects of single game
elements instead of giving a proof-of-concept for
an overall gamification approach (Behl et al., 2022;
Zainuddin et al., 2020a). Following this demand, we
base our reflections about game elements on a tax-
onomy which is derived from a systematic mapping
study for the context of education (Dicheva et al.,
2015). This taxonomy is already well-referenced
(Ayastuy et al., 2021; Jueru et al., 2019; Piteira et al.,
2018).
Out of the 15 so-called gamification design prin-
ciples from this taxonomy, it is reasonable to assume
that, based on the theoretical reflections above, the
following four principles will raise motivation and
support learning in a mathematical exercise e-learning
design.
1. Immediate Feedback: This principle will supply
learners with the needed information to solve ex-
ercises correctly, after failing them before. Re-
garding the SDT, in this the need of competence
is tackled.
2. Freedom to Fail: Since repetition is an important
facilitator of learning, learners have to be enabled
to repeat exercises without penalty. This allows
them to immediately apply the given feedback and
prove acquired knowledge – if any – to themselves
and to lecturers. The need for autonomy is tackled
here.
3. Freedom of Choice: Enabling learners to freely
move between easier and harder tasks will allow
them to identify gaps on their own and acquire
the needed knowledge. Regarding the SDT, here
again autonomy is enabled and a raise of motiva-
tion is expected.
4. Goals: Regarding the FBM, exercises fill the role
of the prompt. This prompt can be emphasized by
declaring motivating goals towards exercise ac-
complishment, boosting learners’ motivation.
From this, we derive an exercise design in which
learners have the opportunity to repeat exercises with-
out penalty and move freely back and forth through
the exercises. Furthermore, after accomplishing an
exercise, a sample solution and – where applicable –
additional specific feedback regarding the mistake is
given. On repeating exercises, another variant of the
exercise is presented (randomization) to enable learn-
ing (instead of typewriting the sample solution). Fi-
nally, the exercises are structured by topics and pre-
sented in raising difficulty. Solving the last (thus hard-
est) exercises is declared as the goal of this design.
To emphasize this goal, we use game-like wording by
calling the hardest exercises boss questions – marked
by a skull – and the topics math worlds.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
308

The button link
changes according
to performance, chal-
lenging learners with
fitting difficulty.
Goals,
freedom of
choice:
The exercise
sheet is struc-
tured by clear
goals: Solving
boss exercises.
Immediate feedback:
Additional material
to solve exercise,
adapted to learners
performance (e. g.
feedback on
specific mistakes).
Questions can be
added through
LMS to ensure
extendibility
Freedom to fail: After attending the question, a
button to repeat the question is presented here.
Gamification
Gamification system only
affects LMS frontend to ensure
affordability and integrability.
Figure 1: Adaptations of a mathematical exercise inside the LMS Moodle, serving the four success factors (bold). In italics:
The chosen gamification design principles.
Figure 1 gives an insight into the appearance in-
side the LMS Moodle.
4 PROPOSED SOFTWARE
SOLUTION AND
IMPLEMENTATION
After comparing different gamification software ar-
chitectures, we introduce a frontend-oriented archi-
tecture, to satisfy integrability and extendibility. This
will be presented in section 4.1. In comparison to a
plugin, this solution doesn’t require any server-sided
changes. An example implementation inside the LMS
Moodle will be presented in section 4.2. Finally,
the technical limitations of this approach will be ad-
dressed in section 4.3.
4.1 Gamification Software Architecture
Requirements
To ensure the affordability, integrability and ex-
tendibility of a gamification implementation in higher
education, different gamification software architec-
tures (GSA) can be considered. Herzig et al. (2014)
cluster GSA into four different classes: achievement
systems (AS), generic gamification platforms (GGP),
integrated solutions (IG) and others. Assuming, that
extendibility can be understood as a combination of
flexibility, manageability and reusability, comparing
properties of GSA (see Table 1), the GGP achieves
the best results regarding flexibility, manageability,
reusability, and integrability. Nevertheless, this class
is still evaluated as low in performance, highly com-
plex and only a medium degree regarding integrabil-
ity.
Table 1: Comparison of classes (↑: high, →: medium, ↓:
low, ◦: not considered) (Herzig et al., 2014).
Degree of AS GGP IG
Flexibility → ↑ ↓
Invasivity → ↓ ↑
Reusability → ↑ ↓
Integrability ↓ → ◦
Performance → ↓ ↑
Analyzability → ↑ ↑
Manageability → ↑ ↓
Complexity ↓ ↑ ↓
Success Factors for Mathematical e-Learning Exercises Focusing First-Year Students
309

Most higher education institutions are using an
LMS as an information system for their students. It
can be used to overcome the just mentioned disad-
vantages of the GGP. In case of the web-based LMS
Moodle, with the help of the programming language
JavaScript, a gamification platform can be imple-
mented right into its frontend (Figure 2). This will
lead to a rise in integrability and performance, while
reducing the complexity, satisfying the demand for
extendibility and integrability.
To tackle affordability, we give an implementation
proposal for the LMS Moodle and publish it under an
open-source license.
Data Storage
Analytics
Rules & Logic
Gamification
API
Core Application
Frontend
Script
Script
Learning Managment
System
Figure 2: The suggested frontend-oriented software archi-
tecture.
This frontend-oriented architecture has the addi-
tional benefit that gamification can be implemented
without any security risks and without involving the
institution’s IT department, which could be an addi-
tional obstacle in higher education institutions’ infras-
tructure. In contrast to a plugin for example, this solu-
tion can directly be implemented by question authors.
4.2 Moodle Example Implementation
To demonstrate a practical implementation, we show
below how the chosen gamification design princi-
ples can be implemented with the help of a frontend-
oriented approach in the LMS Moodle. One reason
for choosing Moodle is that it is used by many lo-
cal partners, which facilitates testing the adaptability
in different universities. Furthermore, adaptations to
Moodle – e. g. with the web-programming language
JavaScript – can be easily transferred into other web-
based LMS (Blackboard, D2L, Canvas, ILIAS, ...).
To apply the gamification system inside the fron-
tend of a mathematical exercise in Moodle, as shown
in Figure 2, at first, a question element has to be cre-
ated and then the script has to be included inside the
question text as illustrated below:
<script src="alquiz.js></script>
<script>
ALQuiz.setCurrentQuestionId("questionId");
</script>
where alquiz.js and questionId are respectively
the path to the script offered in the repository pre-
sented and the identifier of the question declared in
the last quiz element as described below. Further-
more, the code line
<script>ALQuiz.incrementSolved();</script>
has to be added to the feedback text, which is shown
on success. This will inform the gamification system
that the user solved a question correctly.
Unless the question does not stand for itself but
is part of a series of exercises – in Moodle realized
by the quiz element – authors can structure questions
with the help of the proposed gamification system by
levels and worlds. In this, the goals principle is em-
phasized. To do this, in the last element of the quiz,
the questions have to be declared by a given syntax,
e. g.:
...
},
{
id:"fra_a",
needs:1,
onsuccess:"fra_b",
onfailure:"fra_instructions"
},
{
id:"fra_b",
needs:1,
onsuccess:"fra_c",
onfailure:"fra_a"
},
{ ...
In this example, two questions are declared identi-
fied by fra_a and fra_b (giving question authors
the hint that it is about the first and second ques-
tion of the fractions world). Solving the first ques-
tion will lead the user to the question identified by
fra_b (onsuccess attribute), while failing will lead
them to the instructions page of this math world
(onfailure attribute). To discern failure from suc-
cess, the script needs to know, how many times
the function ALQuiz.incrementSolved() has to be
called to validate an exercise as completely solved.
This is represented by the needs attribute.
Furthermore, we made use of the STACK question
type. This question type enables authors to test users’
input against specific error patterns to give specific
feedback. The authored feedback then is presented
automatically to those learners that run into specific
error patterns. The additional JavaScript moves the
feedback into the speech bubble of the supportive fig-
ure.
Figure 1 demonstrates how the frontend of a Moo-
dle exercise is adapted to implement the chosen gam-
ification design principles and serve the given success
factors. Enabling moving freely through exercises
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
310

and being able to repeat exercises without penalty af-
ter failing has to be configured by the quiz settings in
the backend of the Moodle course. See the repository
for further instructions and explanations.
4.3 Technical Limitations
Besides the advantages of a frontend-oriented soft-
ware architecture – gamification through an afford-
able, integrable and extendable approach – coping
without server communication is also accompanied
by limitations.
Social interaction is a well-used element in gami-
fication approaches. For example, automatically pre-
senting points or badges from other players or ranking
all participating local learners are known as additional
motivators (Majuri et al., 2018). Communicating in-
formation about other players is realized by a server.
A frontend-oriented approach is in itself not capable
of communicating this information to other players.
Coping without a server also comes along with the
impossibility to synchronize data between devices.
The frontend-oriented approach stores the data locally
by default. When users start an exercise on one device
and continue it later on another device, the data of the
gamification system is not transferred by default.
Adding an additional server to the architecture
would overcome this problem. However, this would
also lead to greater effort, which was originally in-
tended to be avoided considering higher education in-
stitutions’ infrastructure.
Such an additional server may be acting indepen-
dently of the LMS or can be combined with it. If a so-
cial interaction and/or data synchronization between
devices is desired, a conventional GSA – AS, GGP
or IG – would be more appreciated here, since server
communication is an integrated part of each of these
solutions (Herzig et al., 2014). But facing, that this
would mean to trade-off affordability, extendibility or
integrability, the frontend-oriented approach extended
with an additional server may be a good choice de-
spite the bigger effort.
Among the derived gamification design principles
for mathematical e-learning exercises (section 3), no
principle containing social elements was identified as
relevant. This would have been applied to the com-
petition and cooperation and visible status principles.
Since neither data synchronization nor social interac-
tion is required in this project, the frontend-oriented
approach without any server communication is the
tool of choice.
5 EXPERIMENT & RESULTS
The approach presented above – hereafter called
training area – was tested in two math preparatory
courses. The test aimed to get insight into the follow-
ing questions.
1. How motivated are students to accomplish the
training area? We used a standardized question-
naire and found that students perceive themselves
as motivated during accomplishment and expect
to be motivated to solve training areas like this in
the future. We will elaborate more on this in Sec-
tion 5.2.
2. How do students perceive the use of game ele-
ments in this exercise design? In the given ques-
tionnaire, we also asked students for their evalua-
tion of the used game elements. It shows up that
students overall perceive the usage of game ele-
ments as suitable, but mostly appreciate, that ex-
ercises appear in ascending difficulty as shown in
section 5.3.
3. How do students move through the training area?
Here we analyzed students’ usage data and found
that students retry boss questions more often than
other questions. This can be interpreted as a raised
motivation to solve boss questions as described in
section 5.4.
4. How does the tutor feedback affect students be-
havior? Section 5.5 deals with this question. We
conducted a deeper analysis of students’ tries of
the boss questions and found that a considerable
number of students progressed toward the correct
answer.
Furthermore, students were asked about their overall
satisfaction with the current course design. This, and
asking for their improvement suggestions, aimed to
generate ideas for further development of the training
area.
5.1 Experiment Design
The test took place at university in two different loca-
tions in a given time slot of 90 minutes. Overall 115
participants took part in it. For our use case, the ap-
proach consisted of 28 math questions from the top-
ics fractions, binomial formulas, pq formula, power
laws and trigonometry. Furthermore, the approach in-
cluded 9 questions to learn how to enter answers to
be correctly interpreted by the underlying computer
algebra system (CAS).
After finishing the training area, a standardized
questionnaire awaited each user as the last part of the
training area. This questionnaire aimed to evaluate
Success Factors for Mathematical e-Learning Exercises Focusing First-Year Students
311
the usability of the training area and how motivated
students were by the exercise design. It contains 7
scaled evaluation questions, 2 multiple choice ques-
tions and 2 free text questions.
In the scaled questions, the participants are asked,
to what extent they agree with the given statements
shown in Table 2 from 1 (completely disagree) to 5
(completely agree).
Table 2: Questionnaire evaluation questions (EQ).
EQ1 Compared to solving exercises in
school, I was more motivated to solve
exercises in the just accomplished
training area.
EQ2 The provided support helped me with
solving the exercises.
EQ3 The ascending difficulty combined
with the question design helped me to
stay on track.
EQ4 I appreciated that the questions ap-
peared in ascending difficulty.
EQ5 I can well imagine to use training ar-
eas like this as accompanying learning
tools for my studies.
EQ6 I perceived the use of gamification el-
ements (levels, worlds, bosses) as suit-
able.
EQ7 I think that illustrating the support by
an icon was basically a good idea.
The evaluation questions (EQ) can be divided into
three groups.
• EQ1, EQ3 and EQ5 aim to evaluate the perceived
motivation to accomplish the training area now or
in the future.
• EQ2, EQ4, EQ6, EQ7 aim to get insights into how
satisfied students are with the course design and
what adaptations would be welcome in the future.
The multiple-choice questions (MCQ) ask for
the used device during accomplishment (MCQ1) and
where the participants expect to use it in the future
(MCQ2). The free text questions (FTQ) are shown in
Table 3. The answers to these two questions were an-
alyzed using the qualitative content analysis (Fenzl,
2014).
Table 3: Questionnaire free text questions (FTQ).
FTQ1 What general feedback about the
gamification elements (level, worlds,
bosses) do you want to provide?
FTQ2 What general feedback regarding the
usability of the training area do you
want to provide?
To get further insights into how the learners used
the training area, the usage data that was automati-
cally logged by the LMS was acquired. In addition
to the common data the Moodle web surface offers to
course administrators, this enables us to see how of-
ten users repeat questions and in what amount users
succeeded in a question after failing it before.
Thanks to the STACK question type (see section
4.2) additionally to the default logged data we were
able to recapitulate what error patterns users pass
through and how the specific feedback helped learners
to progress in their score performance.
5.2 Students Perceived Motivation
Figure 3 shows different aspects of students’ per-
ceived motivation.
Most users state to be motivated to solve the exer-
cises of the training area during accomplishment com-
pared with solving exercises in school (EQ1).
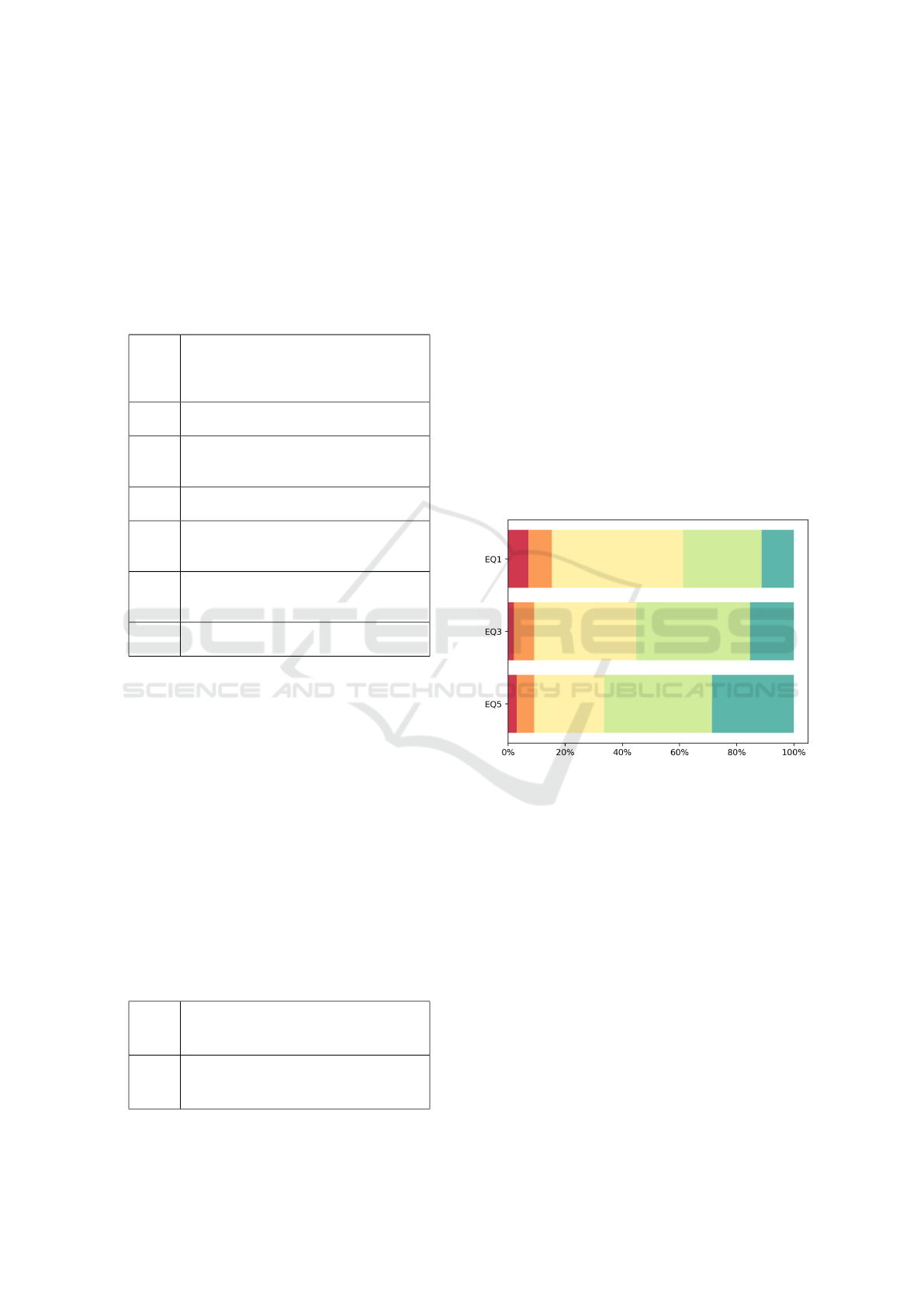
Figure 3: Users evaluation of their motivation towards the
training area from total disagreement (red) to total agree-
ment (dark green) in percent.
EQ3 asks for the student’s perception, of how the
combination of question design and the raising diffi-
culty of questions helped the students to stay on track.
Figure 3 shows, that most students affirm, that this is
the case.
Even more users say, that they can well imagine,
to use training areas like this as accompanying learn-
ing tools for their studies (EQ5).
One can overall say, that the use of this training
area is accompanied by a basic motivation, to solve
exercises like this now and in the future. Unfortu-
nately, there is no comparable data to further prove
that. A control- and test-group research design is ad-
dressed in section 7 to overcome this weakness of this
study.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
312
Apart from that, it is important to consider, that
students state to be motivated, although they were un-
satisfied with the correct input of math syntax in a
large amount.
On analyzing the answers to the free text ques-
tions, we found 111 entities encoded as described be-
low (amount of entities in brackets).
1. General positive feedback (49),
2. negative feedback regarding the syntax(-input)
(26),
3. general negative feedback (17),
4. negative feedback regarding the input for multi-
plication (15)
5. feedback regarding solution(-paths) (4).
Hence, negative feedback is predominantly re-
lated to the input of math calculations. Especially the
necessity of using the * as a multiplication sign, even
though a multiplication could be implied by the CAS
(like e. g. in 2 x), was noted as “annoying”, “taking
away the pleasure in solving the exercises”. For ex-
ample: users had to write 2 ∗x instead of 2x for a valid
answer. Originally, the question designers intended to
make the users familiar with math input in program-
ming languages or CAS, because these are often used
during the soon to be starting studies of the partici-
pants. Due to the given feedback, it has to be consid-
ered anew, whether this approximation to CAS syntax
is worth the loss of pleasure during exercise solving.
Although this interferes with the unsatisfactory
kind of how math is entered, an overall perceived ba-
sic motivation can be derived from the given answers
of the students. All the more, that students still stated
to be motivated, despite the fact that the input of math
was recognized as annoying, can be interpreted as a
special benefit of this approach. It has to be assumed,
that the perceived motivation is even higher, when the
affliction to enter math forumlas in the same way as
for a programming language or a CAS is removed.
The motivating aspect of the exercise design is
also mirrored in the answers to the free-text questions.
For example, users say about the training area:
• “This makes it a little more motivating to solve the
exercises.”
• “I think the concept is a great idea and incredibly
motivating for learners. It’s notably less boring
and jog-trot than conventional learning.”
Apart from asking for the perceived motivation, ex-
amining the usage data gives further insight into how
learners were motivated to solve the most challenging
exercises. This will be described below.
5.3 Students’ Evaluation of Game
Elements
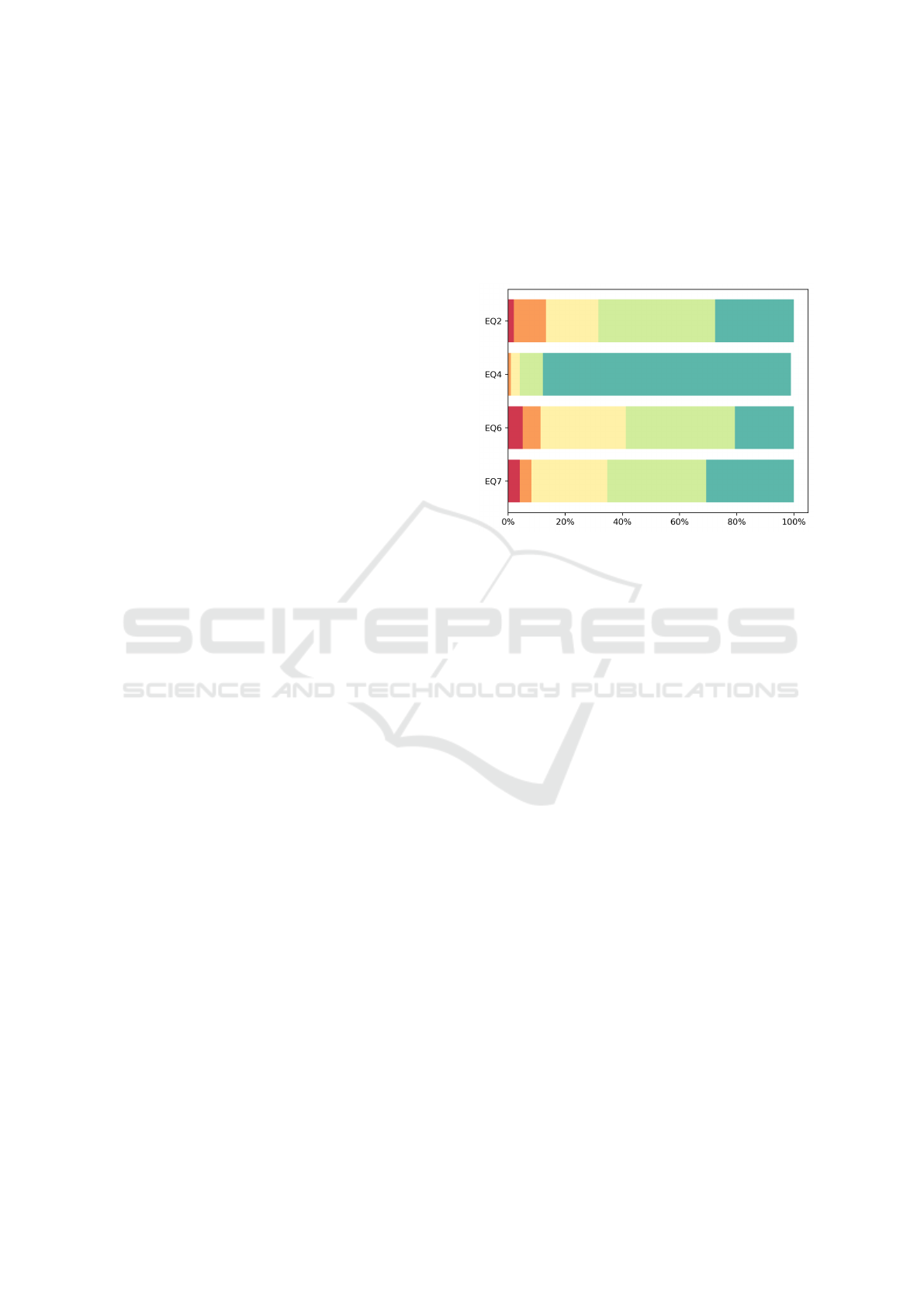
As shown in Figure 4, students evaluate the feedback,
the ascending difficulty, the game-like structure (lev-
els, worlds, bosses) and the tutor-icon mainly posi-
tively.
Figure 4: Students’ evaluation of different elements of the
game-like interface from total disagreement (red) to total
agreement (dark green) in percent: Feedback (EQ2), as-
cending difficulty (EQ4), game-like structure (EQ6), tutor-
icon (EQ7).
The averages of each statement lie above a neutral
center. Special attention can be paid to the ascending
difficulty (EQ4). Here, 87% of learners totally agree
with the statement “I appreciated, that the questions
appeared in ascending difficulty.” Obviously, learners
enjoyed especially the challenging aspect of the exer-
cise design.
5.4 Students’ Pathway Decisions
In the given approach students were able to move
freely through the course as described above with
the freedom of choice gamification design principle
(section 2). By analyzing students’ pathways, we
found, that people decide more often to visit and retry
boss questions compared to other questions. Figure 5
shows in what amount users reattend questions after
their first try. The five boss questions (red) all have a
mean number of retry of at least or equal 0.5, which
is significantly higher than for most other questions
(r = 3.43, p = 0.0015, t-test).
To clarify the reason for that, the relation between
the mean number of retries to other values was tested
with a person’s correlation test. Beforehand, the last
but one question was removed from the dataset as an
outlier. But neither for question difficulty (r = 0.059,
p = 0.752) nor for number of attempters (r = −0.137,
Success Factors for Mathematical e-Learning Exercises Focusing First-Year Students
313
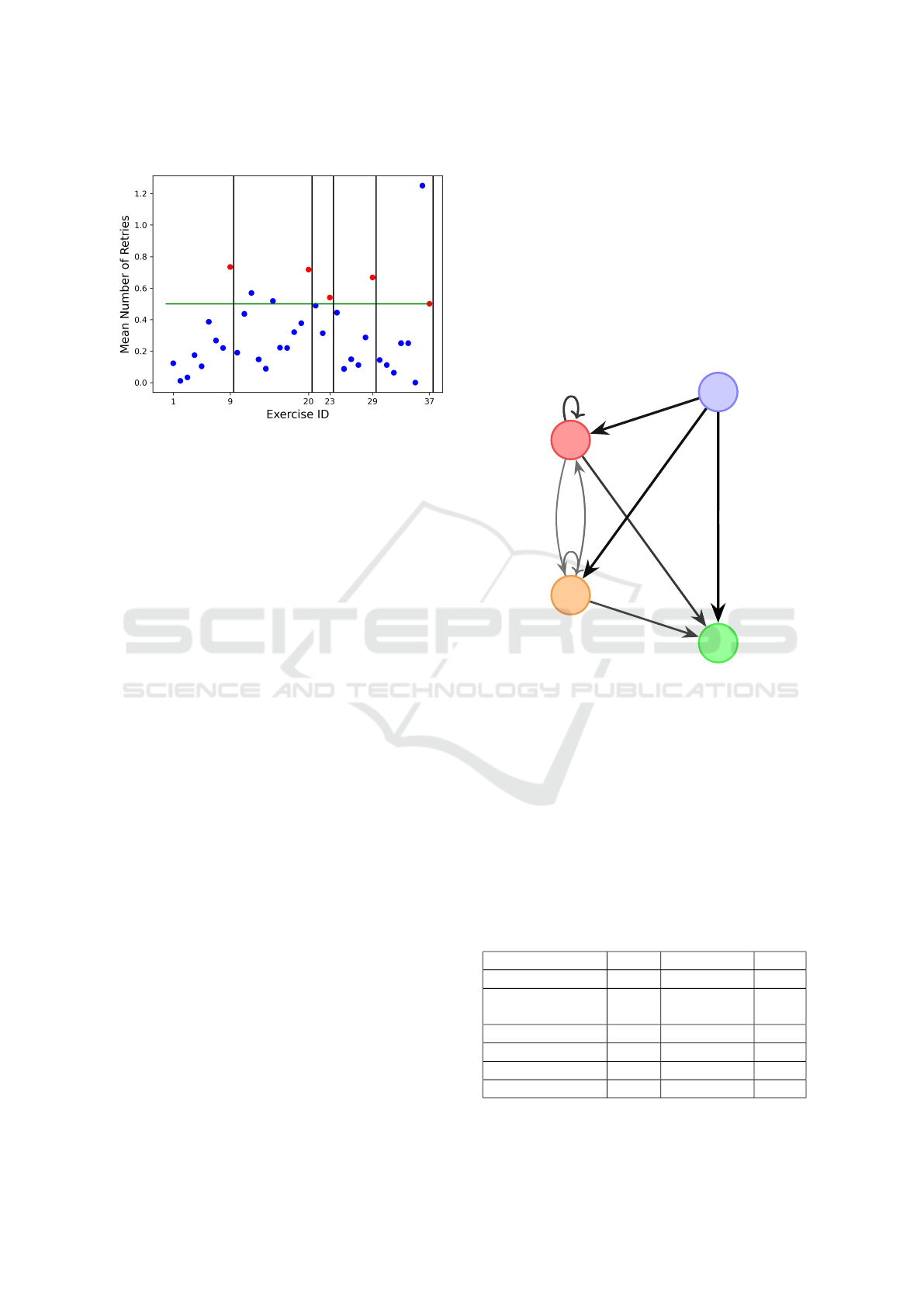
Syntax
Binom. formulas
& fractions
Pq
Power
laws
Trigonometry
Figure 5: Mean number of retries by questions after first
accomplishment, structured in the five worlds.
p = 0.418) a significant correlation to the mean num-
ber of retries of normal questions was found.
This makes it presumable, that the raised mean
number of retries of boss questions traces back to an
enhanced motivation of students to solve them in ac-
count of the question design. This is supported by
some of the free-text answers of the students from the
accompanying questionnaire. E. g. students say about
the training area:
• “Makes learning more varying and structures it by
clear goals (boss).”
• “I only solved the boss questions, because I was
looking for the greatest challenge. I liked, that I
could directly jump there.”
Furthermore, the boss questions are a recurring part in
the suggestions for improvements. Students suggest:
• “An indicator, that a world is solved after finishing
the boss.”
• “In the end, you could add a health points bar to
the boss.”
This makes it assumable, that the given gamifica-
tion approach – especially the feature related to the
game attribute goals –, motivates students to confront
themselves with the hardest exercises.
5.5 Feedback Effects
Immediate feedback was identified as one important
principle in gamification approaches in higher educa-
tion mathematics preparatory courses (section 2). To
analyze the effects of this on students and their moti-
vation, we examined the usage data regarding retries
of single questions.
Figure 6 shows for the boss task of the syntax
math world as an example, that at the beginning (0)
34 persons succeeded at the first attempt (C), 28 per-
sons failed (W) and 30 persons were partially correct
(P1). If the answer is not correct, a sample solution is
shown to the students. If the answer is partially cor-
rect, the specific error is described additionally. In the
specific example of the syntax boss task, the students
will be asked to give two possible solutions, if they
only gave one. The students are then free to skip the
question or to repeat it with different numbers (ran-
domization).
0
W
P1
C
19
17
2
15
5
4
34
28
30
Figure 6: Users progress in the syntax boss question. 0:
Starting point, C: Correct, W: Wrong, P1: Partially correct
(offered only one solution where two were expected). An-
notated arrows represent the amount of movements.
Proceeding from these initial movements, we see
here, that students do not only retry questions in a
notable amount (as already shown in section 5.4),
but that they also progress towards a correct answer.
There are for example 19 movements from wrong (W)
to correct (C) and 15 movements from partially cor-
rect (P) to correct (C).
Table 4: Amount of learners that were initially wrong (W)
or partially correct (P) in boss exercises, mapped onto the
amount of movements toward a correct answer.
World W / P Score-Raise Ratio
Syntax 58 36 62%
Binom. formulas
& fractions
41 23 56%
Pq formula 34 11 32%
Power laws 16 9 56%
Trigonometry 9 1 11%
Sum 158 80 51%
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
314

Summing up the movements towards a better
score (e. g. 36 movements for the syntax world –
movements from wrong to partially correct included)
divided by the number of learners, that initially failed
or accomplished only partially correct (58 learners),
the amount of progression movements can be ex-
pressed in relation to the learners (62%). Regarding
the boss questions, there is an overall progression of
51% (see Table 4).
6 DISCUSSION
Each of the questions regarding learners’ perceived
motivation is answered positively, on average lying
above neutral. One can say, that learners are overall
motivated to accomplish exercises designed this way.
Surprisingly, this positive result is achieved despite
overall displeasure with the way multiplications have
to be entered to be validated by the CAS.
The answers to the questions regarding spe-
cific elements of the exercise design are also lying
above neutral. The majority of students evaluate the
feedback-element as helpful. Furthermore, the tutor-
icon and the usage of a game-like structure (levels,
worlds, bosses) are perceived as suitable. The ascend-
ing difficulty of exercises is especially appreciated.
The significantly higher repetition rate of boss
questions shows, that the high motivation is espe-
cially channeled towards these most challenging ex-
ercises. Obviously, learners focus on accomplishing
these hardest questions, following the prompt derived
by the goals gamification design principle.
Taking a closer look at the progress learners make
in repeating boss exercises it shows, that there is an
overall progression towards the correct answer, which
can be expressed by the relation between the number
of learners who don’t solve the exercise at first to the
number of learners who raise their score in this ex-
ercise. Here we measured an overall progression of
51%, meaning, that on average half of the learners
that were initially wrong or partially correct in a boss
exercise raised their score in this exercise by retrying
it once, twice or more.
We showed that gamification can be implemented
into universities LMS by a frontend-oriented software
architecture. Thus, enabling the implementation of
an affordable, integrable and extendable gamification
solution is possible. Independent from the techni-
cal limitations accompanying a such lightweight ap-
proach, a raise of motivation and a learning progress
can be seen.
Combining the gamification design principles
goals, immediate feedback, freedom to fail and free-
dom of choice, the given exercise design leads to a
raised motivation, where the highest motivation ap-
plies to the boss exercises. To solve these is the de-
clared goal of the design (goals principle). Unless
there is not enough knowledge yet to solve the boss
exercises, learners are encouraged to fill these gaps,
either by getting immediate feedback (enabled by im-
mediate feedback principle) after failure (enabled by
freedom to fail principle) and/or by skipping back to
easier questions of the same world (enabled by free-
dom of choice principle). In this, the most challenging
tasks are not only attended thanks to a raised motiva-
tion but also solved finally thanks to a raised under-
standing.
7 CONCLUSION & FUTURE
PROSPECTS
In this work, four success factors to handle differ-
ent competence levels in higher education mathemat-
ical e-learning are identified. Based on this factors,
a frontend-oriented software approach for mathemat-
ical e-learning exercises is presented, that enables
lightweight gamification implementation inside uni-
versities LMS. Four gamification design principles
were derived, which led to an exercise design struc-
tured by math worlds and boss exercises, where learn-
ers get immediate feedback and are enabled to move
along and repeat exercises without penalty. This ex-
ercise design was implemented with the help of the
given frontend-oriented software architecture in the
LMS Moodle.
In a first test run, we showed: (i) Students fo-
cus on solving the most challenging exercises (boss
exercises). To achieve this, they repeat those ex-
ercises more often or jump back to previous ques-
tions, to acquire the needed knowledge. (ii) Students
progress in their score performance by repeating ex-
ercises when being supplied with additional material
(feedback). (iii) The perceived motivation of students
towards present and future accomplishment of exer-
cises lies above neutral, which indicates a raise in mo-
tivation. (iv) Students perceive the usage of game el-
ements overall as suitable, but especially appreciate,
that exercises appear in ascending difficulty.
In the future, this approach has to be tested in a
test- and control-group research design, to give these
findings more evidence. By additionally applying a
math-skill pre-test, differences in effects regarding
lower- and higher-skilled students can be measured.
By this, more light is shed on how to facilitate a catch-
up of lower-skilled students.
Success Factors for Mathematical e-Learning Exercises Focusing First-Year Students
315

Thanks to its lightweight structure, this approach
is not only extendable by the set of exercises, but also
regarding the overall functionality. Using JavaScript,
other gamification principles can be added easily to
this basic implementation. Here, the presented ap-
proach offers possibilities to tackle a demand of re-
cent gamification research (Behl et al., 2022; Zain-
uddin et al., 2020a): Elucidating the effects of single
game elements (instead of overall gamification prod-
ucts). By adding or removing game elements with
the help of JavaScript, specific outcomes (motivation,
learning progress) can be mapped onto specific game
elements (e. g. storytelling), regarding specific groups
(e. g. lower- vs. higher-skilled students). In this, re-
search regarding the question of how a catch-up of
lower-skilled students regarding math with gamified
e-learning exercises can be boosted.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is part of the Digital Mentoring project,
which is funded by the Stiftung Innovation in der
Hochschullehre under FBM2020-VA-219-2-05750.
We thank our project partners from the Westphalian
University and the University of Applied Sciences
and Arts Dortmund for their support. We also thank
Ralf Erlebach from the University of Wuppertal. Find
the mentioned repository here: http://bit.ly/3HRpyu0.
REFERENCES
Avigad, J. (2018). Modularity in mathematics. The Review
of Symbolic Logic, 13(1):47–79.
Ayastuy, M. D., Torres, D., and Fern
´
andez, A. (2021).
Adaptive gamification in collaborative systems, a sys-
tematic mapping study. Computer Science Review,
39:100333.
Behl, A., Jayawardena, N., Pereira, V., Islam, N., Giu-
dice, M. D., and Choudrie, J. (2022). Gamification
and e-learning for young learners: A systematic lit-
erature review, bibliometric analysis, and future re-
search agenda. Technological Forecasting and Social
Change, 176:121445.
Bullon, J. J., Encinas, A. H., Sanchez, M. J. S., and Mar-
tinez, V. G. (2018). Analysis of student feedback
when using gamification tools in math subjects. In
2018 IEEE Global Engineering Education Confer-
ence (EDUCON), pages 1818–1823. IEEE.
B
¨
uchele, S. and Marten, C. (2022). Math skill growth and
learning differences in higher education. Can lower-
skilled students catch up? MAGKS Joint Discussion
Paper Series in Economics, 15(202236):1–33.
Deterding, S., Dixon, D., Khaled, R., and Nacke, L. (2011).
From game design elements to gamefulness. In Pro-
ceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek
Conference on Envisioning Future Media Environ-
ments - MindTrek '11. ACM Press.
Dichev, C. and Dicheva, D. (2017). Gamifying education:
what is known, what is believed and what remains un-
certain: a critical review. International Journal of Ed-
ucational Technology in Higher Education, 14(1).
Dicheva, D., Dichev, C., Agre, G., and Angelova, G. (2015).
Gamification in education: A systematic mapping
study. Educational Technology & Society, 18:75–88.
Fenzl, Thomas; Mayring, P. (2014). Qualitative Inhaltsanal-
yse. In Handbuch Methoden der empirischen Sozial-
forschung, pages 543–556. Springer VS.
Fischer, H. and Heinz, M. (2020). Onboarding by gamifi-
cation. Design and evaluation of an online service to
support first year students. In EdMedia + Innovate
Learning Conference 2020.
Fogg, B. (2009). A behavior model for persuasive design.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on
Persuasive Technology - Persuasive '09. ACM Press.
Gordon, N., Brayshaw, M., and Grey, S. (2013). Maximis-
ing gain for minimal pain: Utilising natural game me-
chanics. Innovation in Teaching and Learning in In-
formation and Computer Sciences, 12(1):27–38.
Herzig, P., Ameling, M., Wolf, B., and Schill, A. (2014).
Implementing gamification: Requirements and gami-
fication platforms. In Gamification in Education and
Business, pages 431–450. Springer International Pub-
lishing.
Hofacker, C. F., de Ruyter, K., Lurie, N. H., Manchanda, P.,
and Donaldson, J. (2016). Gamification and mobile
marketing effectiveness. Journal of Interactive Mar-
keting, 34:25–36.
Irfan, M., Kusumaningrum, B., Yulia, Y., and Widodo, S. A.
(2020). Challenges during the pandemic: Use of e-
learning in mathematics learning in higher education.
Infinity Journal, 9(2):147.
Jueru, T., e Silva, R. F., and Ferrao, S. (2019). Success fac-
tors for using gamification in language teaching. In
2019 International Symposium on Computers in Edu-
cation (SIIE). IEEE.
Khaitova, N. F. (2021). History of gamification and its
role in the educational process. International Jour-
nal of Multicultural and Multireligious Understand-
ing, 8(5):212.
Liang, L., Yeung, K., Lui, R. K. W., Cheung, W. M. Y.,
and Lam, K. F. (2018). Lessons learned from a cal-
culus e-learning system for first-year university stu-
dents with diverse mathematics backgrounds. In Dis-
tance Learning, E-Learning and Blended Learning in
Mathematics Education, pages 69–92. Springer Inter-
national Publishing.
Lisnani, L., Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, and Somakim (2020).
Designing moodle features as e-learning for learn-
ing mathematics in COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of
Physics: Conference Series, 1657:012024.
Majuri, J., Koivisto, J., and Hamari, J. (2018). Gamifica-
tion of education and learning: A review of empiri-
cal literature. In Proceedings of the 2nd International
GamiFIN conference, pages 11–19. CEUR.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
316

Piteira, M., Costa, C. J., and Aparicio, M. (2018). Computer
programming learning: How to apply gamification on
online courses? Journal of Information Systems Engi-
neering & Management, 3(2).
Podolskiy, A. I. (2012). Zone of proximal development.
In Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning, pages
3485–3487. Springer US.
Ryan, R. M. and Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination the-
ory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social
development, and well-being. American Psychologist,
55(1):68–78.
Schulmeister, R. (2004). Diversity of students and the con-
sequences for e- learning. In Proceedings of the 6.
ICNEE.
van Roy, R. and Zaman, B. (2017). Why gamification
fails in education and how to make it successful: In-
troducing nine gamification heuristics based on self-
determination theory. In Serious Games and Edutain-
ment Applications, pages 485–509. Springer Interna-
tional Publishing.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in Society. Harvard Univer-
sity Press.
Zabala-Vargas, S. A., Garc
´
ıa-Mora, L. H., Arciniegas-
Hernandez, E., Reina-Medrano, J. I., Benito-Crosetti,
B. D., and Darder-M
´
esquida, A. (2021). Strengthen-
ing motivation in the mathematical engineering teach-
ing processes – a proposal from gamification and
game-based learning. International Journal of Emerg-
ing Technologies in Learning (iJET), 16(06):4.
Zainuddin, Z., Chu, S. K. W., Shujahat, M., and Perera,
C. J. (2020a). The impact of gamification on learn-
ing and instruction: A systematic review of empirical
evidence. Educational Research Review, 30:100326.
Zainuddin, Z., Shujahat, M., Haruna, H., and Chu, S. K. W.
(2020b). The role of gamified e-quizzes on student
learning and engagement: An interactive gamification
solution for a formative assessment system. Comput-
ers & Education, 145:103729.
Success Factors for Mathematical e-Learning Exercises Focusing First-Year Students
317
