
STEM in Elementary Teacher Training in Austria
Maritta Schalk
1 a
, Sara Hinterplattner
2 b
and Barbara Sabitzer
1 c
1
Department of STEM Education, Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria
2
Linz Institute of Technology, Dynatrace Austria, Linz, Austria
Keywords:
STEM, Elementary Education, Teacher Training.
Abstract:
Knowledge and skills from STEM subjects are becoming increasingly important. It is therefore important that
these elements be implied in the curriculum of all educational institutions, starting already in elementary edu-
cation. For this purpose, the training of elementary teachers in this field is very important and indispensable.
In Austria, STEM topics are included in the curriculum of the vocational secondary school at the Educational
Institute for Elementary Teachers. To find out about the actual implementation and impact of their STEM
training, elementary teachers were asked to what extent they had become acquainted with the contents of
STEM subjects in their teachers training, also with regard to their transfer into practice. The results show that
the elementary teachers have received hardly any practical and theoretical information about the teaching of
STEM content in their training. Moreover, without additional training, most of the elementary teachers do not
feel prepared to teach the required STEM contents defined in curricula for elementary education in their daily
work.
1 INTRODUCTION
In infants and toddlers 700 new neural connections
are created every second. This rapid brain develop-
ment, coupled with strong natural curiosity and drive
towards understanding the surroundings, presents
ideal conditions to present scientific inquiry to chil-
dren (Buchter et al., 2017). Moreover, research shows
that the early exposure to STEM (Science, Technol-
ogy, Engineering, and Mathematics) related activi-
ties supports children’s long term development and
achievements withing the field: Meaningful experi-
ences with scientific phenomena by young children
have been found to increase self-belief in own abili-
ties to understand scientific subject matters and fos-
ter greater interest in science (Patrick et al., 2009).
Such experiences can also create an appreciation for
the role and influence science have on our lives (Fleer
et al., 2006). Consequently, children’s earliest ex-
periences with science, technology, engineering, and
mathematics might subsidize future engagement and
success in these fields (Hassan et al., 2019).
Teachers play a key role in fostering children’s
STEM inquiry, as they can not only provide a physi-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5919-0441
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9601-433X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1304-6863
cal learning environment, but help to provide context,
ask questions, connect previous knowledge to preset
experiences and provide language to articulate new
concepts (Buchter et al., 2017). Despite this, interna-
tional research shows that STEM related activities in
early childhood classrooms are rare. Science instruc-
tions are none frequent and teachers do not spend sig-
nificant amounts of time on science-related subjects
in the classroom (L
¨
uck, 2018; Nayfeld et al., 2011;
Tu, 2006). Currently, their emphasis is on language
and literacy development, with relatively little math
in preschool. It has been found that in an ordinary
preschool, as little as 59 seconds of a 360-minute day
(less than 0.3 percent of the students’ time) would be
spent on math, and that introductions to science and
engineering were rarely part of the curriculum (Far-
ran et al., 2007). Moreover, preschool teachers are
poorly trained to support STEM learning (Clements
et al., 2013). It is critical that early childhood pro-
fessionals are highly qualified and competent to sup-
port young children’s scientific inquiry, as the devel-
opmental sensitivity and natural curiosity at this age
must be utilized to provide a sound foundation for fu-
ture engagements in the field of STEM (Clements and
Sarama, 2020; Worth, 2010).
Schalk, M., Hinterplattner, S. and Sabitzer, B.
STEM in Elementary Teacher Training in Austria.
DOI: 10.5220/0011858600003470
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2023) - Volume 2, pages 221-228
ISBN: 978-989-758-641-5; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
221

2 TRAINING FOR ELEMENTARY
TEACHERS IN AUSTRIA
In an international comparison, Austria is one of the
top performers in the field of vocational education.
Nearly 76% of graduates from an upper secondary
school earn a vocational degree (Federal Ministry of
Education, Science and Research, 2021). The OECD
average is 38.4%.
One such school with a vocational degree is
the “Educational Institute for Elementary Pedagogy”,
which aims to train elementary teachers. This school
can be completed in 2 different ways: in the form
of a 2-year technical school with diploma, but with
the prerequisite of a maturity examination, univer-
sity entrance qualification, or vocational maturity ex-
amination or a 5-year vocational secondary school
with diploma and Matura. In Austria, the Matura
is equivalent to a school-leaving qualification from
a secondary school with an associated higher educa-
tion entrance qualification and entitlement to attend a
college or university. There are some providers who
offer bachelor studies in the field of elementary edu-
cation. However, compared to other countries, Aus-
tria is one of the few countries where the necessary
training for staff in elementary education is below the
bachelor’s level (European Education and Culture Ex-
ecutive Agency and Eurydice, 2019).
2.1 Secondary School Education
The curriculum of the 5-year vocational secondary
school with Matura and diploma is divided into 10
semester with a total of of at least 168 teaching hours
per week. In addition to general education, these also
include the subjects for vocational training for the
profession of kindergarten teacher in elementary ed-
ucational institutions. STEM subjects account for 28
hours per week (16.6% of the total number of hours
per week) and are divided as follows: Applied Mathe-
matics, Applied Natural Sciences, Biology and Ecol-
ogy, Chemistry, Fundamentals of Computer Science
and Media, and Physics (Federal Ministry of Educa-
tion, Science and Research, 2016). The subject Ap-
plied Natural Sciences was added to the curriculum
in 2016. Before this change in the curriculum, there
was no comparable school subject.
As can be seen in Table 1, with the exception of
Fundamentals of Computer Science and Media, di-
dactic content is anchored in the curriculum of all
subjects. Applied Mathematics accounts for the most
teaching hours (10 out of 28 hours per week).
The learning fields of number, space and form,
patterns and sequences, sorting and classifying, time
and frequency and coincidence are developed in the
school subject of Applied Mathematics, divided over
five years, with a view to transfer to the pedagogi-
cal occupational field. In the school subject Physics
in 2 years on the one hand the naming of physical
phenomena and on the other hand accident preven-
tion, electric circuit, magnetism. In Chemistry, the
curriculum in the second and third year includes ex-
periments and related safety aspects as well as food
labeling, food ingredients. In the subject of Biol-
ogy and Ecology, nature observations, hygiene mea-
sures and dealing with children with special needs are
part of the curriculum in apprenticeship years one to
three. In terms of content, the subject of Applied Nat-
ural Sciences in the fourth year of teaching, in that
Biology, Chemistry and Physics have already been
completed in terms of content, takes up the follow-
ing natural science topics in the curriculum: Sustain-
ability, ecological footprint, energy, electric current,
forces, animate and inanimate nature, technology and
inventors, water, elements, soil, forest, time, measure-
ment, weather, sounds and noises, light, sky, bionics,
swimming-sinking, floating-flying. The focus is on
using technical language appropriate to the age group,
formulating research questions, planning and imple-
menting experiments and series of experiments, and
explaining scientific relationships in a way that is ap-
propriate to the target group. As a further point, the
importance of scientific education for the child is re-
flected (Federal Ministry of Education, Science and
Research, 2016).
It must be mentioned in this context that the teach-
ers employed in “Educational Institute for Elemen-
tary Pedagogy” are trained in teacher education in the
field of secondary education as well as school subject-
specific content, but there is no requirement for expe-
rience or studies in elementary education.
2.2 Technical School Education
In the 2-year training in the form of the college
prospective elementary teachers are taught 143 hours
per week, divided into 4 semesters. The subjects
are related to pedagogical practice and the associ-
ated subject areas. Looking at the STEM content,
there are no specifications in the curriculum. Only
the topic of media education is addressed. In a school
autonomous extension area - nature and technology,
which can be freely selected by the training institu-
tion, the following contents are anchored in the cur-
riculum: scientific topics and information, scientific
methods, dealing with children’s questions, experi-
ments, job-related technical literature, recordings, se-
curing results, mobility and sustainability, colors -
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
222

Table 1: Overview about the STEM subjects in the curriculum of the 5-year vocational secondary school.
Subject Semester Didactic Topics
Applied Mathematics
(10 teaching hours)
1+2 Learning field “Numbers”
4 Learning field “Space and shape”
6 Learning field “Patterns and sequences” and “Sorting and clas-
sifying”
8 Learning field “Time”
9+10 Learning field “Frequency and coincidence”
Applied Natural Sciences
(3 teaching hours)
7+8 Sustainability, Ecological footprint, Energy, Electric current,
Forces, Inanimate and animate nature, Technology and inven-
tors, Water, Elements, Soil, Forest, Time, Measuring, Weather,
Sounds and noises, Light, Sky, Bionics, Swimming-Sinking,
Floating-Flying
Biology and Ecology
(6 teaching hours)
1+2 Hygiene measures in everyday situations
4 Nature observations
6 Dealing with people with special needs
Chemistry
(3 teaching hours)
4 Experiments and safety aspects of experiments
4 Food labeling and food ingredients
Fundamentals of Computer
Science and Media
(2 teaching hours)
1-4 no didactic contents in the curriculum
Physics
(3 teaching hours)
4 Name physical phenomena
6 Accident prevention, electric circuit, magnetism
color mixing - optics, basic experiences with duration,
temporal sequence, rhythms, seriality, patterns, struc-
tures (Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Re-
search, 2016).
3 METHODOLOGY
With regard to the actual implementation of the cur-
ricula in the training of elementary school teachers,
questionnaires were created and trained elementary
school teachers were asked what content they actually
learned in the course of their training. The question-
naires in form of a internet-mediated questionnaire
were sent to two different groups. On the one hand
to individuals, in order to ensure a deliberate cross-
section of different federal states in Austria, years
of service and public/private institutions, and on the
other hand shared via an internet platform for ex-
change between kindergarten teachers. The decision
to choose a questionnaire came from the fact that a
large number of questionnaires should ensure the di-
versity of elementary teachers with different training
institutions, different years of graduation, and thus
different teachers at the training institutions. This is
to ensure that individual teachers in the training cen-
ters do not distort the final result. The questionnaire
consisted of two parts. The first part of the questions
was with the help of a 4-part answer scale to deter-
mine how intensively the didactic topics of the teach-
ing contents in Applied Mathematics, Biology and
Ecology, Chemistry, and Physics listed in the curricu-
lum were really dealt with in the training (1- not dealt
with at all; 4- discussed in detail and explained with
practical examples). The question did not contain the
subject Applied Natural Sciences, because of the in-
troduction of Applied Natural Sciences in the curricu-
lum in 2016 resulting in the fact that the elementary
teachers participating in this study did not have this
subject in their training. All questions in this part refer
to the curriculum content of all subjects with STEM
content in secondary education for prospective ele-
mentary school teachers The second part of the ques-
tionnaire relates to the implementation in practice and
the question of how far the elementary teachers feel
prepared to implement the STEM content in kinder-
garten practice. There were four possible answers (1-
I feel prepared in this area; 2- thanks to further train-
ing I feel prepared; 3- I would have to read up on it
first; 4- I can’t do anything with it). In the question-
ing all didactic topics in the STEM subjects (Applied
Mathematics, Applied Natural Sciences, Biology and
Ecology, Chemistry, Fundamentals of Computer Sci-
STEM in Elementary Teacher Training in Austria
223
ence and Media, Physics) from the curriculum were
included. The data collection method was chosen to
survey a large number of educators and to obtain open
and honest responses through anonymity. The stan-
dardized questions made it possible to systematically
record and compare the answers. It was mandatory
to answer all questions to complete the survey. Due
to the lack of proper STEM training in the technical
school education, only the 111 respondents with the
secondary school education were analyzed.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Experienced Intensity of Taught
Topics
The first part of the questionnaire determines how in-
tensively the teaching contents listed in the curricu-
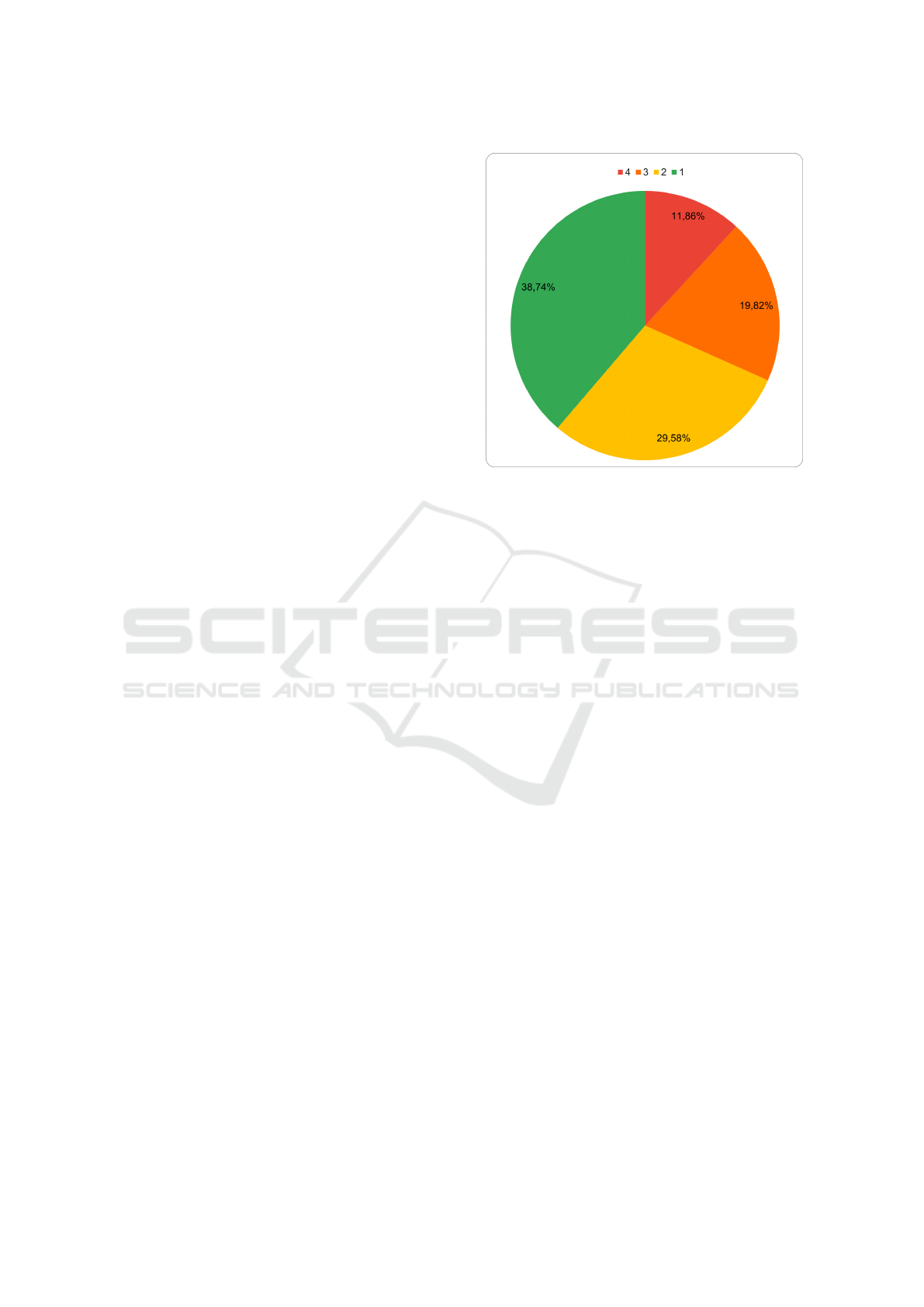
lum were really dealt with in the training. The results
show that all of the topics were discussed in detail
and explained with practical examples, but only for
3.60%-25.23% of the participants.
In sum, the answer “discussed in detail and ex-
plained with practical examples”, representing the an-
swer for the highest intensity of curriculum coverage,
was given 198 times (11.89%) by 63 different par-
ticipants (56.76%), the answer representing the sec-
ond most intensive coverage was given 328 times
(19.70%) by 95 different participants (85.59%), the
answer representing the second least intensive cover-
age was given 492 times (29.55%) by 106 different
participants (95.50%) and the answer “not dealt with
at all” representing the answer for the least intensive
coverage 647 times (38.86%) by 98 different partic-
ipants (88.29%). The distribution of given answers
can be seen in Figure 1.
When looking more into the depth, the topic that
was most discussed in detail and explained with prac-
tical examples was “Experiments and safety aspects
of experiments” (n=28) followed by “Nature observa-
tions” (n=24) , “name physical phenomena” (n=19)
, “Accident prevention, electric circuit, magnetism”
(n=18) , “Learning field Frequency and coincidence”
(n=16) , “Learning field Patterns and sequences and
Sorting and classifying” (n=14) , “Hygiene measures
in everyday situations” (n=13) , “Explain scientific
relationships in a way that is appropriate for the tar-
get group, transfer the acquired practical skills and
knowledge to the professional field, reflect on the im-
portance of science education for the child” (n=11)
and “explain scientific relationships in a way that
is appropriate for the target group, transfer the ac-
quired practical skills and knowledge to the profes-
Figure 1: The distribution of given answers to all questions
in part 1 how intensively the topics were taught reaching
from 1 (“not dealt with it at all”) to 4 (“discussed in detail
and explained with practical examples”) by all participants.
sional field, reflect on the importance of science ed-
ucation for the child” (n=11) , “Dealing with people
with special needs” (n=9) and “Learning field Patterns
and sequences and Sorting and classifying” (n=9) ,
“Learning field ”Numbers”” (n=8) and “Use technical
language appropriate to age, formulate research ques-
tions, plan experiments or series of experiments and
implement experimental designs.” (n=8) , “Learning
field ”time”” (n=6) , and “Food labeling and food
ingredients” (n=4). The topic that was most men-
tioned as “not dealt with at all” was “Food labeling
and food ingredients” (n=67) followed by “Dealing
with people with special needs” (n=55) , “Use tech-
nical language appropriate to age, formulate research
questions, plan experiments or series of experiments
and implement experimental designs.” (n=54) , “Ex-
plain scientific relationships in a way that is appropri-
ate for the target group, transfer the acquired practical
skills and knowledge to the professional field, reflect
on the importance of science education for the child”
(n=51) and “Learning field Time” (n=51) , “Hygiene
measures in everyday situations” (n=48) and “Learn-
ing field Frequency and coincidence” (n=48) and “ex-
plain scientific relationships in a way that is appropri-
ate for the target group, transfer the acquired prac-
tical skills and knowledge to the professional field,
reflect on the importance of science education for
the child” (n=48) , “ learning field Sorting and clas-
sifying” (n=45) , “Learning field Numbers” (n=44)
, “Learning field Patterns and sequences” (n=37) ,
“name physical phenomena” (n=27) , “Nature ob-
servations” (n=25) and “Accident prevention, electric
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
224
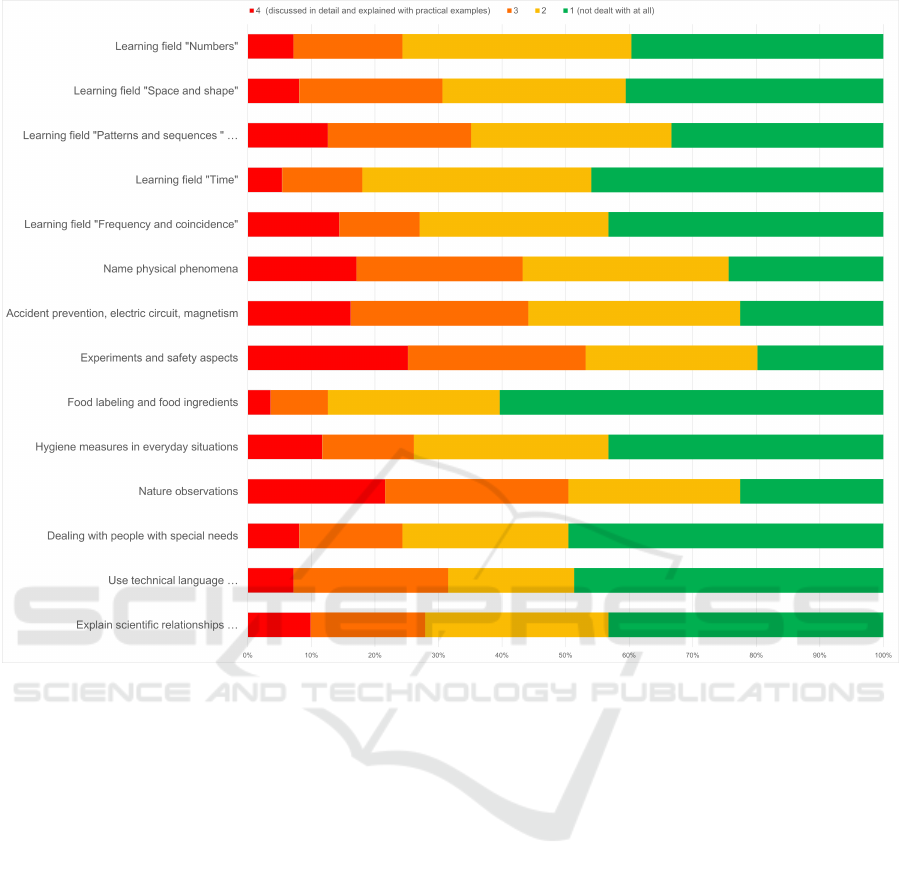
Figure 2: Overview about the intensity of taught topics at the secondary school education for prospective elementary teachers.
circuit, magnetism” (n=25) , and “Experiments and
safety aspects of experiments” (n=22). An overview
of these results can be seen in Figure 2.
Sixty-three participants answered at least once
that the intensity of learning a topic was “discussed
in detail and explained with practical examples”
(56.76%) resulting in 48 participants who did not an-
swer this for any of the topics (43.24%). One partic-
ipant answered for all the topics that she/he/* did not
deal with them at all.
4.2 Teachers’ Self Confidence in STEM
Implementation
The third part of the questionnaire relates to the im-
plementation in practice and the question of how far
the elementary teachers feel prepared to implement
the STEM content in kindergarten practice. The re-
sults show that most of the teachers are prepared
(56,15%), however, without additional training only
38.54% of the kindergarten teachers feel prepared for
the STEM content in practice. And also with ad-
ditional training, there are still 43.85% kindergarten
teachers who do not feel prepared for STEM topics in
kindergarten. The distribution of given answers can
be seen in Figure 3.
When looking more into the details about the
contents in teacher training, the teachers feel the
most prepared for the topic “Weather” (n=77),
followed by “Forest” (n=71) and “Sounds and
noises” (n=71), “Nature Observations” (n=66), “Wa-
ter” (n=64), “Learning field Sorting and classify-
ing” (n=61), “Swimming-Sinking” (n=60), “Learn-
ing field Patterns and sequences” (n=58), “Dealing
with people with special needs” (n=55), “Measure”
(n=54), “Hygiene measures in everyday situations”
(n=53), “Learning field Numbers” (n=51) and “Sus-
tainability, ecological footprint” (n=51), “Elements”
(n=48), “Light” (n=44) and “Floating-Flying” (n=44),
“Learning field Space and shape” (n=44), “Time”
(n=42), “Soil” (n=41), “Learning field Time” (n=36),
“Inanimate and animate nature” (n=35) and “Sky”
(n=35), “Experiments and safety aspects of experi-
ments” (n=28), “Technology and inventors” (n=22)
and “Physical phenomena” (n=22), “Energy, elec-
tric current” (n=19), “Forces” (n=18), “Learning field
STEM in Elementary Teacher Training in Austria
225
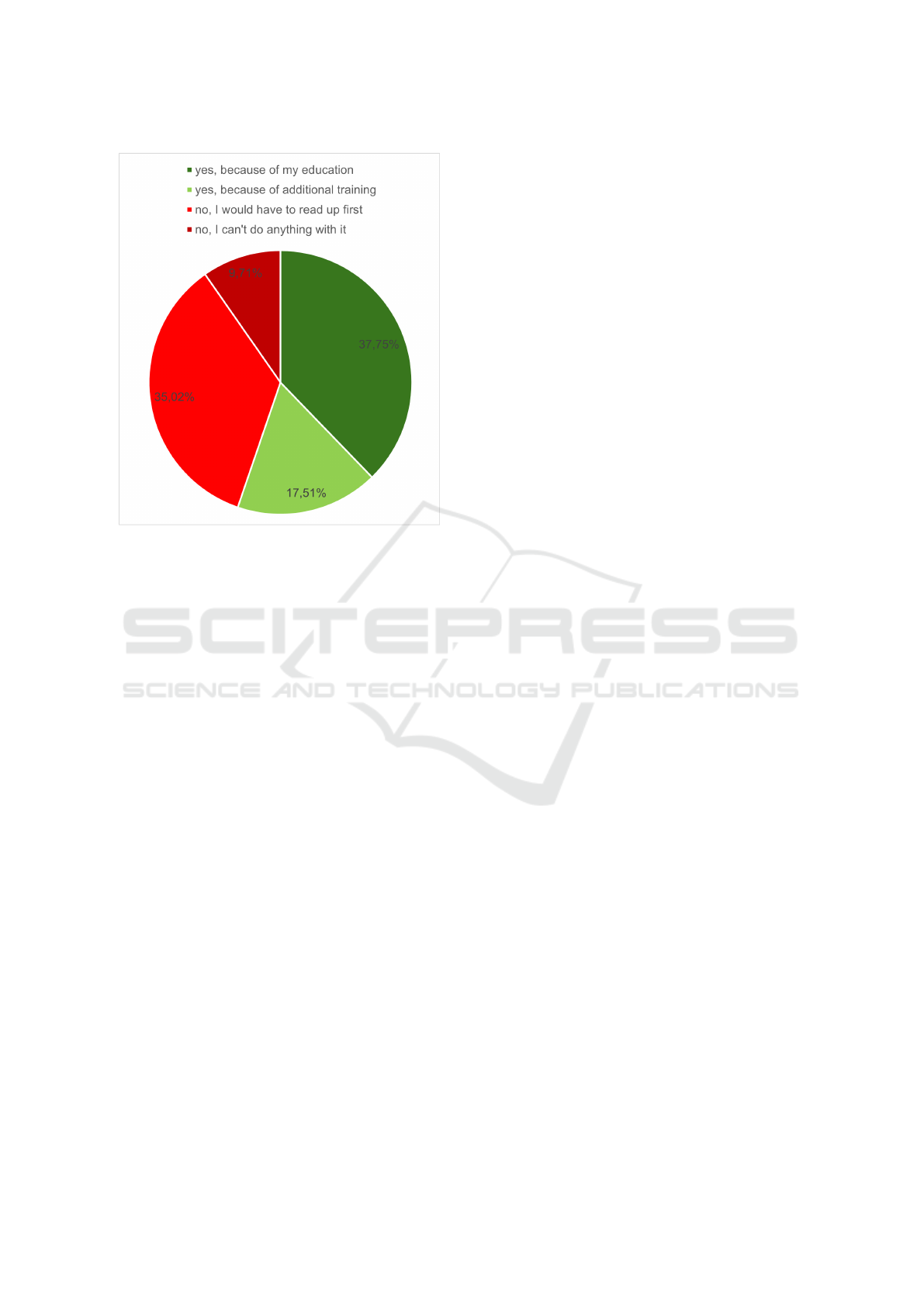
Figure 3: The distribution of given answers to all questions
in part 2 how far the elementary teachers feel prepared to
implement the STEM content in kindergarten practice.
Frequency and coincidence” (n=17), “Food label-
ing and food ingredients” (n=16), “Accident pre-
vention, electric circuit, magnetism” (n=15). The
topic were the teachers answered “I can’t do any-
thing with it” the most often was “Bionics” (n=40),
followed by “Forces” (n=25), “Technology and in-
ventors” (n=21), “Energy, electric current” (n=19),
“Learning field Frequency and coincidence” (n=17),
“Name physical phenomena” (n=16) and “Food la-
beling and food ingredients” (n=16), “Experiments
and safety aspects of experiments” (n=15), “Accident
prevention, electric circuit, magnetism” (n=14) and
“Sky” (n=14), “Soil” (n=13), “Light” (n=12), “Inani-
mate and animate nature” (n=11), “Elements” (n=10),
“Time” (n=10), “Measure” (n=10) and “Floating-
Flying” (n=10), “Swimming-Sinking” (n=7), “Sus-
tainability, ecological footprint” (n=6) and “Water”
(n=6), “Dealing with people with special needs”
(n=5), “Forest” (n=5) and “Weather” (n=5), “Hygiene
measures in everyday situations” (n=4) and “Learn-
ing field Time” (n=4), “Sounds and noises” (n=3),
“Learning field Numbers” (n=2), “Learning field Pat-
terns and sequencies” (n=2), “Learning field Space
and Shape” (n=2), “Learning field Sorting and clas-
sifying” (n=2), and “Nature observations” (n=2). An
overview of these results can be seen in Figure 4.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The Teaching about the didactic implementation of
STEM topics in the training of elementary teachers
is anchored in the curriculum in the subjects Applied
Mathematics, Applied Natural Sciences, Biology and
Ecology, Chemistry and Physics of the vocational sec-
ondary schools in Austria. In comparison, the expe-
riences of 111 interviewed elementary school teach-
ers show that the content has not been taken up and,
above all, has not always been worked on in terms
of how it can be integrated in the elementary schools.
Observations of nature, weather and sound and noises
stand out as topics that were more dealt with in the
class. However, there are also topics where not even
20% of elementary educators feel prepared, to include
it in there everyday work in elementary school. A
clear picture emerges from the study: the experiences
of the elementary educators do not for the most part
match the content from the curriculum that is actually
mandatory to teach. Accordingly, it can be concluded
that more than 2/3 of the elementary teachers were
not sufficiently prepared by the training alone for the
teaching of STEM content by the school.
6 DISCUSSION
Looking at the growing shortage of STEM special-
ists, it is obvious to support projects to spark the chil-
dren’s interest in STEM. Introducing children to the
fascinating aspects of STEM content at an early age
is an important step for children to develop a positive
association with this branch of science (Patrick et al.,
2009; Fleer et al., 2006; Hassan et al., 2019). How-
ever, in order for students to experience such content
in the most positive and affirmative way possible, ba-
sic training for pedagogues from a subject oriented as
well as a didactic point of view is necessary (Buchter
et al., 2017). Nevertheless, elementary school teach-
ers have little training to transfer their STEM knowl-
edge into their practice (Clements et al., 2013). As the
study shows, this is also the case in Austria: Didactic
STEM training does not sufficiently take place as part
of the education of elementary teachers. It is there-
fore even more important to provide further training
that conveys both the professional expertise and the
practical transfer that is lacking, as the questionnaires
indicate.
Moreover, the results show how unprepared ele-
mentary teachers feel for the STEM subjects. Cor-
responding to the results of previous scientific stud-
ies it was shown that the teachers were mostly pre-
pared for teaching observations of nature in elemen-
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
226
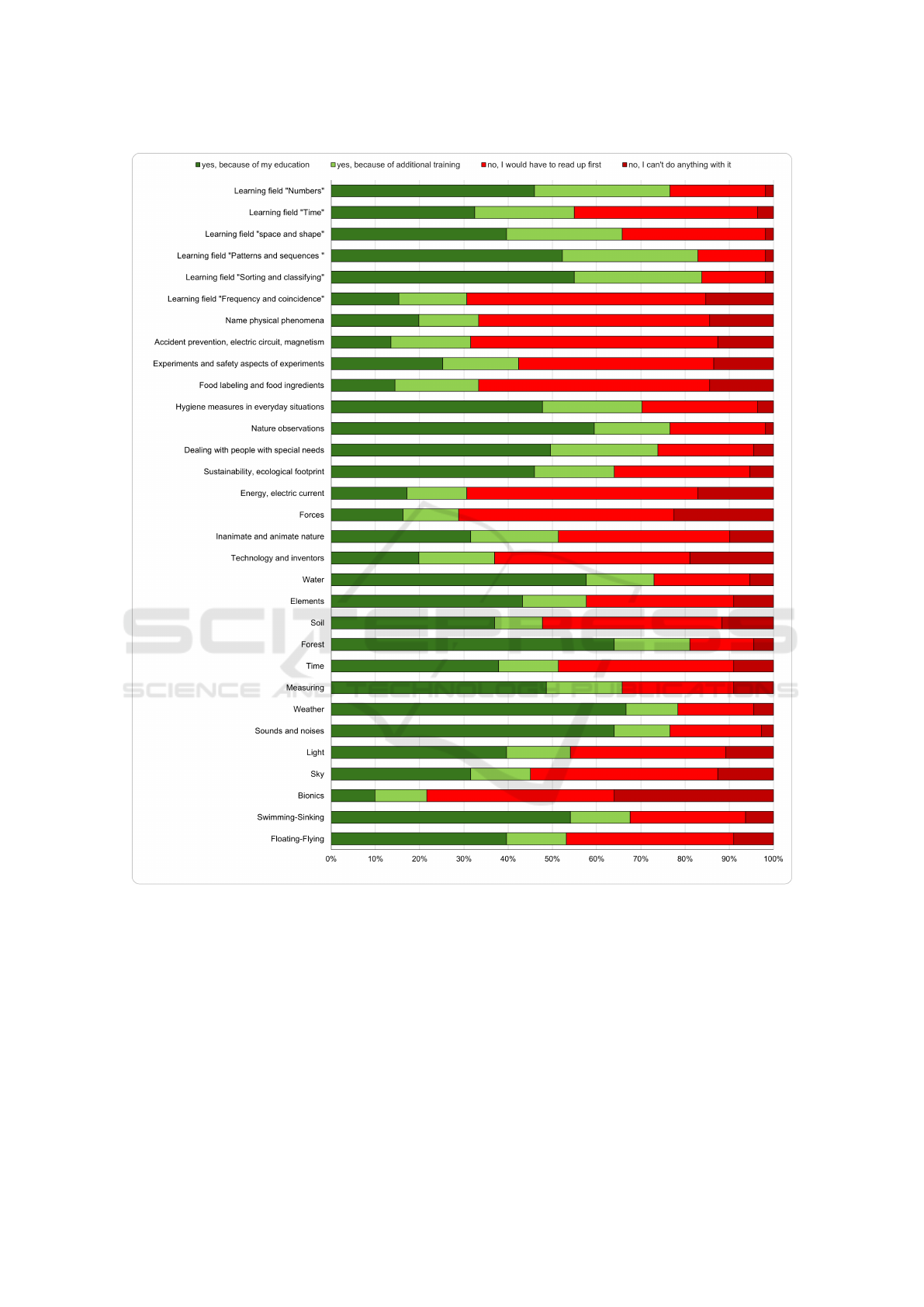
Figure 4: Overview about the teachers’ self confidence in STEM implementation in elementary schools regarding the curricu-
lum’s topics.
tary classes (L
¨
uck, 2018). In most subjects the trans-
fer to the practice was missing to non existent. A
reason for this lack could be the training of teachers
working at the secondary schools to educate future el-
ementary school teachers. They are educated in a spe-
cific subject, such as Physics,Chemistry or Maths and
do not have to show any previous training or practice
in the field of elementary education. In this context,
the question arises as to how teachers without experi-
ence in this area are supposed to convey the didactic
transfer to the professional field of elementary school
teachers.
Furthermore, the issue surfaces whether the teach-
ing of STEM topics should not actually be part of spe-
cial didactic subjects and not the science subjects, as
is the case, for example, with language aspects. This
results in a call for a revision of the curriculum for
STEM subjects and in line with the last paragraph, di-
dactic or better and more specific training for teachers
of STEM subjects.
STEM in Elementary Teacher Training in Austria
227

Additional, there is the problem that the students
in the vocational secondary education have to go
through the topics for the early final examination (part
of the Matura) in one of the science subjects (incl. Ge-
ography, excl. Mathematics). As a result, the content
related aspect of the STEM curriculum predominates
in contrast to the options of the pedagogical imple-
mentation.
In sum, the study shows that the education in
the vocational secondary school does not sufficiently
train the elementary teachers in the area of imple-
mentation of STEM topics. As mentioned before,
the lack of training of their teachers in the Educa-
tional Institutes for Elementary Pedagogy, the focus-
ing on the Matura and therefore less time for transfer-
ring their knowledge and implement it the elementary
schools, and the curriculum of the STEM subjects as
well as Didactic in vocational secondary school might
be reasons for this issue. Furthermore, for the al-
ready trained elementary teachers, training in the area
of STEM subjects would not only be recommend-
able but also indispensable in order to enable a high-
quality educational offer in the area of STEM in el-
ementary schools. Looking at the long way of re-
vising the curriculum, the lack of training provides
a sensible opportunity for elementary teachers in the
STEM field. It is important to include the results of
the study and to design a teacher training course that
encourages and enables elementary teachers to imple-
ment STEM in elementary school. The results of this
study cannot be generalized to all worldwide forms
of training for early childhood educators because the
collected data was limited to institutions and early
childhood educators within Austria. Additionally, the
educators who filled out the questionnaires voluntar-
ily participated and therefore may not necessarily be
representative of educators from other types of train-
ing and other countries.
REFERENCES
Buchter, J., Kucskar, M., Oh-Young, C., Welgarz-Ward, J.,
and Gelfer, J. (2017). Supporting stem in early child-
hood education.
Clements, D. H., Agodini, R., and Harris, B. (2013). In-
structional practices and student math achievement:
Correlations from a study of math curricula.
Clements, D. H. and Sarama, J. (2020). Young children and
mathematics learning. Learning and Teaching Early
Math, pages 1–17.
European Education and Culture Executive Agency and Eu-
rydice (2019). Key data on early childhood education
and care in Europe : 2019 edition. Publications Of-
fice.
Farran, D. C., Lipsey, M. W., Watson, B., and Hurley, S.
(2007). Balance of content emphasis and child content
engagement in an early reading first program.
Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Re-
search (2016). Curriculum of the educa-
tional institute for elementary education.
https://api.abc.berufsbildendeschulen.at/uploads/
BA-\ fuer\ Elementarpaedagogik\ c0f7272de0.pdf.
[Online; accessed 17-November-2022].
Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Research
(2021). OECD Study. https://www.bmbwf.gv.at/
Ministerium/Presse/2021-0916.html. [Online; ac-
cessed 17-November-2022].
Fleer, M., March, S., and Gunstone, D. (2006). Investiga-
tions into the engagement of pre-school and primary
aged children in science, engineering and technology.
Hassan, M. N., Abdullah, A. H., Ismail, N., Suhud, S. N. A.,
and Hamzah, M. H. (2019). Mathematics curricu-
lum framework for early childhood education based
on science, technology, engineering and mathematics
(stem). International Electronic Journal of Mathemat-
ics Education,, 14:15–31.
L
¨
uck, G. (2018). Handbuch naturwissenschaftliche Bildung
in der Kita. Herder GmbH.
Nayfeld, I., Brenneman, K., and Gelman, R. (2011). Sci-
ence in the classroom: Finding a balance between au-
tonomous exploration and teacher-led instruction in
preschool settings. Early Education and Develop-
ment, 22:970–988.
Patrick, H., Mantzicopoulos, P., and Samarapungavan, A.
(2009). Motivation for learning science in kinder-
garten: Is there a gender gap and does integrated in-
quiry and literacy instruction make a difference. Jour-
nal of Research in Science Teaching, 46:166–191.
Tu, T. (2006). Preschool science environment: What is
available in a preschool classroom? Early Childhood
Education Journal, 33:245–251.
Worth, K. (2010). Science in early childhood classrooms:
Content and process.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
228
