
Turn-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Model Checking
Dennis Gross
Institute for Computing and Information Sciences, Radboud University,
Toernooiveld 212, 6525 EC Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Keywords:
Turn-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning, Model Checking.
Abstract:
In this paper, we propose a novel approach for verifying the compliance of turn-based multi-agent reinforce-
ment learning (TMARL) agents with complex requirements in stochastic multiplayer games. Our method
overcomes the limitations of existing verification approaches, which are inadequate for dealing with TMARL
agents and not scalable to large games with multiple agents. Our approach relies on tight integration of
TMARL and a verification technique referred to as model checking. We demonstrate the effectiveness and
scalability of our technique through experiments in different types of environments. Our experiments show
that our method is suited to verify TMARL agents and scales better than naive monolithic model checking.
1 INTRODUCTION
AI technology has revolutionized the game indus-
try (Berner et al., 2019), enabling the creation
of agents that can outperform human players us-
ing turn-based multi-agent reinforcement learning
(TMARL) (Silver et al., 2016). TMARL consists of
multiple agents, where each one learns a near-optimal
policy based on its own objective by making observa-
tions and gaining rewards through turn-based interac-
tions with the environment (Wong et al., 2022).
The strength of these agents can also be a problem,
limiting the gameplay experience and hindering the
design of high-quality games with non-player charac-
ters (NPCs) (Svelch, 2020; Nam et al., 2022). Game
developers want to ensure that their TMARL agents
behave as intended, and tracking their rewards can al-
low them to fine-tune their performance. However, re-
wards are not expressive enough to encode more com-
plex requirements for TMARL agents, such as ensur-
ing that a specific sequence of events occurs in a par-
ticular order (Littman et al., 2017; Hahn et al., 2019;
Hasanbeig et al., 2020; Vamplew et al., 2022).
This paper addresses the challenge of verifying
the compliance of TMARL agents with complex
requirements by combining TMARL with rigorous
model checking (Baier and Katoen, 2008). Rigor-
ous model checking is a formal verification technique
that uses mathematical models to verify the correct-
ness of a system with respect to a given property. It
is called ”rigorous” because it provides guarantees of
correctness based on rigorous mathematical reasoning
and logical deductions. In the context of this paper,
rigorous model checking is used to verify TMARL
agents. The system being verified is the TMARL
system, which is modeled as a Markov decision pro-
cess (MDP) treating the collection of agents as a joint
agent, and the property is the set of requirements that
the agents must satisfy. Our proposed method
1
sup-
ports a broad range of properties that can be expressed
by probabilistic computation tree logic (PCTL; Hans-
son and Jonsson, 1994). We evaluate our method on
different TMARL benchmarks and show that it out-
performs naive monolithic model checking
2
.
To summarize, the main contributions of this pa-
per are:
1. rigorous model checking of TMARL agents,
2. a method that outperforms naive monolithic
model checking on different benchmarks.
The paper is structured in the following way. First,
we summarize the related work and position our pa-
per in it. Second, we explain the fundamentals of
our technique. Then, we present the TMARL model
checking method and describe its functionalities and
1
GitHub-Repository: https://github.com/DennisGross/
COOL-MC/tree/markov games
2
Naive monolithic model checking is called ”naive” be-
cause it does not take into account the complexity of the
system or the number of possible states it can be in, and it
is called ”monolithic” because it treats the entire system as
a single entity, without considering the individual compo-
nents of the system or the interactions between them.
980
Gross, D.
Turn-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Model Checking.
DOI: 10.5220/0011872800003393
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2023) - Volume 3, pages 980-987
ISBN: 978-989-758-623-1; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

limitations. After that, we evaluate our method in
multiple environments from the AI and model check-
ing community (Lee and Togelius, 2017; Even-Dar
et al., 2006; Abu Dalffa et al., 2019; Hartmanns et al.,
2019). The empirical analysis shows that the TMARL
model checking method can effectively check PCTL
properties of TMARL agents.
2 RELATED WORK
PRISM (Kwiatkowska et al., 2011) and Storm (Hensel
et al., 2022) are tools for formal modeling and analy-
sis of systems that exhibit uncertain behavior. PRISM
is also a language for modeling discrete-time Markov
chains (DTMCs) and MDPs. We use PRISM to
model the TMARL environments as MDPs. Un-
til now, PRISM and Storm do not allow verifying
TMARL agents. PRISM-games (Kwiatkowska et al.,
2018) is an extension of PRISM to verify stochas-
tic multi-player games (including turn-based stochas-
tic multi-player games). Various works about turn-
based stochastic game model checking have been
published (Kwiatkowska et al., 2022, 2019; Li et al.,
2020; Hansen et al., 2013; Kucera, 2011). None of
them focus on TMARL systems. TMARL has been
applied to multiple turn-based games (Wender and
Watson, 2008; Pagalyte et al., 2020; Silver et al.,
2016; Videga
´
ın and Garc
´
ıa-S
´
anchez, 2021; Pagalyte
et al., 2020). The major work about model check-
ing for RL agents focuses on single RL agents (Wang
et al., 2020; Hasanbeig et al., 2020; Hahn et al., 2019;
Hasanbeig et al., 2019; Fulton and Platzer, 2019;
Sadigh et al., 2014; Bouton et al., 2019; Chatterjee
et al., 2017). However, model checking work ex-
ists for cooperative MARL (Riley et al., 2021a; Khan
et al., 2019; Riley et al., 2021b), but no work for
TMARL. Therefore, with our research, we try to close
the gap between TMARL and model checking.
3 BACKGROUND
In this section, we introduce the fundamentals of our
work. We begin by summarizing the modeling and
analysis of probabilistic systems, which forms the ba-
sis of our approach to check TMARL agents. We then
describe TMARL in more detail.
3.1 Probabilistic Systems
A probability distribution over a set X is a function
µ : X → [0, 1] with
∑
x∈X
µ(x) = 1. The set of all dis-
tributions on X is denoted Distr(X).
Definition 3.1 (Markov Decision Process). A
Markov decision process (MDP) is a tuple M =
(S, s
0
, A, T, rew) where S is a finite, nonempty set of
states; s
0
∈ S is an initial state; A is a finite set of ac-
tions; T : S × A → Distr(S) is a probability transition
function; rew: S × A → R is a reward function.
We employ a factored state representation where
each state s is a vector of features ( f
1
, f
2
, ..., f
n
) where
each feature f
j
∈ Z for 1 ≤ i ≤ n (n is the dimen-
sion of the state). The available actions in s ∈ S
are A(s) = {a ∈ A | T (s, a) 6= ⊥}. An MDP with
only one action per state (∀s ∈ S : |A(s)| = 1) is a
DTMC. A path of an MDP M is an (in)finite sequence
τ = s
0
a
0
, r
0
−−−→ s
1
a
1
, r
1
−−−→ ..., where s
i
∈ S, a
i
∈ A(s
i
),
r
i
:
= rew(s
i
, a
i
), and T (s
i
, a
i
)(s
i+1
) 6= 0. A state s
0
is reachable from state s if there exists a path τ from
state s to state s
0
. We say a state s is reachable if s is
reachable from s
0
.
Definition 3.2 (Policy). A memoryless deterministic
policy for an MDP M is a function π : S → A that maps
a state s ∈ S to an action a ∈ A(s).
Applying a policy π to an MDP M yields an
induced DTMC, denoted as D, where all non-
determinism is resolved. A state s is reachable by a
policy π if s is reachable in the DTMC induced by π.
We specify the properties of a DTMC via the specifi-
cation language PCTL (Wang et al., 2020).
Definition 3.3 (PCTL Syntax). Let AP be a set
of atomic propositions. The following gram-
mar defines a state formula: Φ ::= true | a | Φ
1
∧
Φ
2
| ¬Φ |P
p
|P
max
p
(φ) | P
min
p
(φ) where a ∈ AP, ∈
{<, >, ≤, ≥}, p ∈ [0, 1] is a threshold, and φ is a
path formula which is formed according to the fol-
lowing grammar φ ::= XΦ | φ
1
U φ
2
| φ
1
F
θt
φ
2
|G Φ
with θ = {<, ≤}.
For MDPs, PCTL formulae are interpreted over
the states of the induced DTMC of an MDP and
a policy. In a slight abuse of notation, we use
PCTL state formulas to denote probability values.
That is, we sometimes write P
p
(φ) where we
omit the threshold p. For instance, in this paper,
P(F collision) denotes the reachability probability
of eventually running into a collision. There exist
a variety of model checking algorithms for verify-
ing PCTL properties (Courcoubetis and Yannakakis,
1988, 1995). PRISM (Kwiatkowska et al., 2011)
and Storm (Hensel et al., 2022) offer efficient and
mature tool support for verifying probabilistic sys-
tems (Kwiatkowska et al., 2011; Hensel et al., 2022).
Definition 3.4 (Turn-based stochastic multi-player
game). A turn-based stochastic multi-player game
(TSG) is a tuple (S, s
0
, I, A, (S
i
)
i∈I
, T, {rew
i
}
i∈I
) where
Turn-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Model Checking
981
Agent 1 π(s)
Environment
a
s, r
Figure 1: This diagram represents a single RL system in
which an agent (Agent 1) interacts with an environment.
The agent observes a state (denoted as s) and a reward (de-
noted as r) from the environment based on its previous ac-
tion (denoted as a). The agent then uses this information to
select the next action, which it sends back to the environ-
ment.
S is a finite, nonempty set of states; s
0
∈ S is an initial
state; I is a finite, nonempty set of agents; A is a finite,
nonempty set of actions available to all agents; (S
i
)
i∈I
is a partition of the state space S; T : S ×A → [0, 1] is a
transition function; and rew
i
: S
i
× A → R is a reward
function for each agent i.
Each agent i ∈ I has a policy π
i
: S
i
→ A that maps
a state s
i
∈ S
i
to an action a
i
∈ A. The joint policy π
induced by the set of agent policies {π
i
}
i∈I
is the map-
ping from states into actions and transforms the TSG
into an induced DTMC.
3.2 Turn-Based Multi-Agent
Reinforcement Learning (TMARL)
We now introduce TMARL. The standard learning
goal for RL is to find a policy π in an MDP such that
π maximizes the expected discounted reward, that is,
E[
∑
L
t=0
γ
t
R
t
], where γ with 0 ≤ γ ≤ 1 is the discount
factor, R
t
is the reward at time t, and L is the total
number of steps (Kaelbling et al., 1996). TMARL
extends the RL idea to find near-optimal agent poli-
cies π
i
in a TSG setting (compare Figure 1 with Fig-
ure 2). Each policy π
i
is represented by a neural
network. A neural network is a function parameter-
ized by weights θ
i
. The neural network policy π
i
can
be trained by minimizing a sequence of loss func-
tions J(θ
i
, s, a
i
) (Mnih et al., 2013).
4 MODEL CHECKING OF
TMARL AGENTS
We now describe how to verify trained TMARL
agents. Recall, the joint policy π induced by the set of
all agent policies {π
i
}
i∈I
is a single policy π. The tool
COOL-MC (Gross et al., 2022) allows model check-
ing of a single RL policy π against a user-provided
PCTL property P(φ) and MDP M. Thereby, it builds
the induced DTMC D incrementally (Cassez et al.,
2005).
Environment
Agent 1 π
1
(s)
Agent 2 π
2
(s)
a
1
s
1
, r
1
a
2
s
2
, r
2
Figure 2: This diagram represents a TMARL system in
which two agents (Agent 1 and Agent 2) interact in a turn-
based manner with a shared environment. The agents re-
ceive states (denoted as s
1
and s
2
) and rewards (denoted as
r
1
and r
2
) from the environment based on their previous
actions (denoted as a
1
and a
2
). The agents then use this in-
formation to select their next actions, which they send back
to the environment.
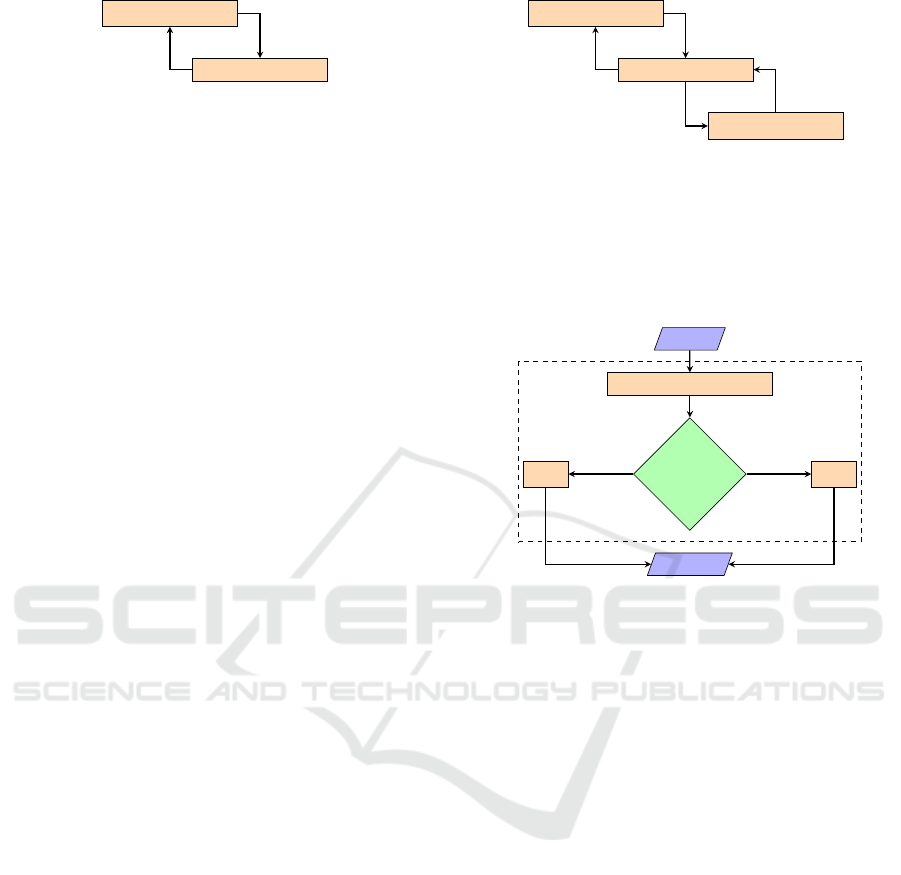
State s
Extract turn from state s
Which turn?
π
1
(s) π
2
(s)
Action a
turn = 1 turn = 2
a
1
a
2
Joint Policy Wrapper
Figure 3: An example of a joint policy wrapper with two
policies. The wrapper takes in a state (denoted as s) and
extracts the current turn from that state. It then uses this
information to determine which of two policies (π
1
and π
2
)
should choose the next action. The selected policy then pro-
duces an action, which is output by the joint policy wrapper.
To verify a TMARL system, we model it as a nor-
mal MDP. We have to extend the MDP with an addi-
tional feature called turn that controls which agent’s
turn it is. To support joint policies π(s), and there-
fore multiple TMARL agents, we created a joint pol-
icy wrapper that queries the corresponding TMARL
agent policy at every turn (see Figure 3). With the
joint policy wrapper, we build the induced DTMC the
following way. For every state s that is reachable via
the joint policy π, we query for an action a = π(s).
In the underlying MDP M, only states s
0
that may be
reached via that action a ∈ A(s) are expanded. The
resulting DTMC induced by M and π is fully deter-
ministic, as no action choices are left open and ready
for efficient model checking.
Limitations. Our method allows the model check-
ing of probabilistic policies by always choosing the
action with the highest probability at each state. We
support any environment that can be modeled us-
ing the PRISM language (Kwiatkowska et al., 2011).
However, our method does not consider PCTL prop-
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
982

erties with the reward operator (Hansson and Jonsson,
1994). When creating the joint policy, there is no sep-
aration of which agent receives which reward.
TSGs with more than two agents must handle
inactive agents who no longer participate in the
game. Our method handles this by allowing non-
participating agents to only apply actions that only
change the turn feature, allowing the next agent to
make a move. This must be considered when using
the expected time step PCTL operator Hansson and
Jonsson (1994).
Our method is independent of the learning algo-
rithm and allows for the model checking of TMARL
policies that select their actions based on the cur-
rent and fully-observed state. For simplicity, we fo-
cus on TMARL agents with the same action space
in this paper. However, extending our method to
support TMARL agents with different action spaces
and different partial observations for different agents
is straightforward.
5 EXPERIMENTS
We now evaluate our proposed model checking
method in multiple environments.
5.1 Setup
In this section, we provide an overview of the ex-
perimental setup. We first introduce the environ-
ments, followed by the trained TMARL agents. Next,
we describe the model checking properties that we
used, and finally, we provide details about the tech-
nical setup.
Environments. Pokemon is an environment from
the game franchise Pokemon that was developed
by Game Freak and published by Nintendo in
1996 (Freak, 1996). It is used in the Showdown AI
competition (Lee and Togelius, 2017). In a Pokemon
battle, two agents fight one another until the Poke-
mon of one agent is knocked out (see Figure 4). The
impact of randomness in Pokemon is significant, and
much of the game’s competitive strategy comes from
accurately estimating stochastic events. The dam-
age calculation formula for attacks includes a random
multiplier between the values of 0.85 and 1.0. Each
Pokemon has four different attack actions (tackle,
punch, poison, sleep) and can use items (for example,
heal pots to recover its hit points (HP)). The attacks
tackle and punch decrease the opponent’s Pokemon
HP, poison decreases the HP over multiple turns, and
Figure 4: This screenshot shows a scene from the Show-
down AI competition, in which two Pokemon characters
are engaged in a battle. We model this scene in PRISM.
The AI-controlled Pokemons use different policies π
i
to try
and defeat their opponent. The outcome of the battle will
depend on the abilities and actions of the two Pokemons, as
well as on random elements.
sleep does not allow the opponent’s Pokemon to at-
tack for multiple turns. All actions in Pokemon have
a success rate, and there is a chance that they fail.
S = {(turn, done, HP
0
, sleeping
0
, poisoned
0
,
heal pots
0
, sleeps
0
, poisons
0
, punches
0
,
HP
1
, sleeping
1
, poisoned
1
, heal pots
1
, sleeps
1
,
poisons
1
, punches
1
), ...}
Act = {sleep, tackle, heal, punch, poison}
rew
i
=
if agent i wins:
5000
+max(100 − HP
1
− 0.2 ∗ (100 − HP
0
), 0)
otherwise:
max(100 − HP
1
− 0.2 ∗ (100 − HP
0
), 0)
The main purpose of this environment is to show that
it is possible to verify TMARL agents in complex en-
vironments. The main difference to the Showdown AI
competition is that each agent observes the full game
state, each agent has only the previously mentioned
action choices, and our environment allows one Poke-
mon per agent.
The multi-armed bandit problem (MABP) is a
problem in which a fixed limited set of resources must
be allocated between competing choices in a way that
maximizes their expected gain when each choice’s
properties are only partially known at the time of al-
location and may become better understood as time
passes or by allocating resources to the choice (Even-
Dar et al., 2006; Shahrampour et al., 2017). It is a
classic RL problem. We transformed this problem
Turn-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Model Checking
983

Table 1: The table presents the results of running probabilistic model checking via our method on various environments. For
each environment, the table lists the label for the probabilistic computation tree logic (PCTL) property query that was used,
the result of the query, the number of states in the environment, the number of transitions, and the time it took to run the query.
TO indicates that the query did not complete within 24 hours, and therefore the time taken is unknown.
Env. Label PCTL Property Query (P(φ)) = |S| |T | Time (s)
Pokemon won1 P(F won
1
) TO TO TO TO
Pokemon (5HP) HP5NoHealP1 P(F won
1
) 0.34 213 640 14
Pokemon (5HP) HP5NoHealP2 P(F won
2
) 0.66 222 667 14
Pokemon (5HP) usePoisons0HealP1 P(poisons
1
= 2 U poisons
1
< 2) 0.0 238 715 17
Pokemon (20HP) useHeal20P1 P(heal pot
1
= 1 U healpot
1
= 0) 0.65 6720 40315 401
MABP 25 lost1 P(F lost
1
) 0.0 50 51 5
MABP 100 lost1 P(F lost
1
) 0.0 100 100 296
Tic-Tac-Toe marking order P(((cell
10
= 0 U cell
10
= 2) U cell
12
= 2) U cell
11
= 2) 1.0 18 30 0.5
CC CC1KO P(F player1 ko) 0.0 205 281 54
CC CC2KO P(F player2 ko) 0.001 197 273 53
CC CC3KO P(F player3 ko) 0.0 205 281 54
CC collision P(F collision) 0.36 199 275 47
into a turn-based MABP. At each turn, an agent has
to learn which action maximizes its expected reward.
S = {(HP
1
, HP
2
, ..., HP
N
,turn, done), ...}
Act = {bandit
1
, bandit
2
}
rew
i
=
(
1, if agent i is alive
0, otherwise
The Tic-Tac-Toe environment is a paper-and-
pencil game for two agents who take turns mark-
ing the empty cells in a 3x3 grid with X or O. The
agent who succeeds in placing three of their marks
in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row is the win-
ner (Abu Dalffa et al., 2019). With a probability
of 10%, an agent does not draw in the grid during
its turn.
S = {(cell
00
, cell
01
, cell
02
, cell
10
, cell
11
, cell
12
,
cell
20
, cell
21
, cell
22
,turn, done), ...}
Act = A mark action per cell.
rew
i
=
(
500, if agent i wins
0, otherwise
The Coin Collection (CC) environment is a game in
which three agents must collect coins in a 4x4 grid
world without colliding with each other. If an agent
collides with another, the environment terminates. An
agent can attack another agent by standing next to
them with a success rate of 0.4. Each agent receives a
reward for every round it is not knocked out (its HP is
not 0) and a larger reward for collecting coins. The
CC environment is inspired by the QComp bench-
mark resource gathering (Hartmanns et al., 2019).
S = {(x
1
, y
1
, hp
1
, x
2
, y
2
, hp
2
, x
3
, y
3
, hp
3
,
coin
x
, coin
y
, done,turn), ...}
Act = {up, right, down, le f t,
hit
up, hit right, hit down, hit le ft}
rew
i
=
(
100, if agent i collects coin
1, otherwise
Trained TMARL Agents. In the training results,
agent 1 in Pokemon has an average reward of 818.23
over 100 episodes, while agent 2 has an average re-
ward of 690.32 over the same number of episodes
(50, 000 episodes in total). In Tic-Tac-Toe (10, 000
episodes in total), agent 1 has an average reward of
370.0, while agent 2 has an average reward of 100.
In CC (10, 000 episodes in total), agent 1 has an aver-
age reward of 29.72, agent 2 has an average reward of
111.58, and agent 3 has an average reward of 117.69.
The reward of the TMARL agents can be neglected
because we only use them for performance measure-
ments. All of our training runs used a seed of 128, an
ε = 0.5. ε
min
= 0.1, ε
dec
= 0.9999, γ = 0.99, a learn-
ing rate of 0.0001, batch size of 32, replay buffer size
of 300, 000, and a target network replacement interval
of 304. The Pokemon agents have four layers, each
with 256 rectifier neurons. The Tic-Tac-Toe, MABP,
and CC agents have two layers, each with 256 recti-
fier neurons.
Properties. Table 1 presents the property queries of
the trained policies. For example, HP5NoHealP1 de-
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
984

scribes the probability of agent 2 winning the Poke-
mon battle when both Pokemon have HP = 5 and no
more heal pots. Note, at this point, that our main goal
is to verify the trained TMARL policies and that we
do not focus on training near-optimal policies.
Technical Setup. We executed our benchmarks
on an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1060 Mobile GPU,
16 GB RAM, and an Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-8750H
CPU @ 2.20GHz x 12. For model checking, we use
Storm 1.7.1 (dev).
5.2 Analysis
In this section, we address the following research
questions:
1. Does our proposed method scale better than naive
monolithic model checking?
2. How many TMARL agents can our method han-
dle?
3. Do the TMARL agents perform specific game
moves?
We will provide detailed answers to these questions
and discuss the implications of our findings.
Does Our Proposed Method Scale Better than
Naive Monolithic Model Checking? In this exper-
iment, we compare our method with a naive mono-
lithic model checking in the Pokemon environment.
For a whole Pokemon battle (starting with HP=100,
unlimited tackle attacks, 5 punch attacks, 2 sleep at-
tacks, 2 poison attacks, and 3 heal pots), naive mono-
lithic model checking runs out of memory. On the
other hand, our method runs out of time (time out af-
ter 24 hours). However, we can train TMARL agents
in the Pokemon environment and can, for example,
analyze the end game. For instance, our method al-
lows the model checking of environments with HP of
20 and 1 heal pot left, and we can quantify the prob-
ability that Pokemon 1 uses the heal pot with 0.65
(see useHeal20P1 in Table 1). On the other hand, for
naive monolithic model checking, it is impossible to
extract this probability because it runs out of mem-
ory with a model that contains 31, 502, 736 states and
51, 6547, 296 transitions. However, at some point, our
model checking method is also limited by the size of
the induced DTMC and runs out of memory (Gross
et al., 2022).
How Many TMARL Agents Can Our Method
Handle? We perform this experiment in the MABP
environment with multiple agents because, in this
Figure 5: The diagram shows the time it takes to build a
state for a TMARL system as the number of agents in the
system increases. The curve in the diagram indicates that
the time it takes to build a state increases exponentially as
the number of agents increases.
environment, it is straightforward to show how our
method performs with different numbers of TMARL
agents. To evaluate our method, we train multiple
agents using TMARL to play the MABP game with
different numbers of agents. We then compare the
performance of our method to naive monolithic model
checking, and evaluate the scalability of both methods
as we increase the number of agents in the game.
Naive monolithic model checking is unable to ver-
ify (P
max
(F lost
1
)) 24 agents in the MABP environ-
ment due to memory constraints. The largest possi-
ble MDP that can be checked using monolithic model
checking contains 23 agents and has 100, 663, 296
states and 247, 463, 936 transitions. In contrast, our
method allows the model checking up to over 100
TMARL agents, and we can verify in each of the
TMARL systems that agent 1 never uses the riskier
bandit (see, for 25 agents, the property query lost1 in
Table 1). This experiment shows, that the limitation
of our approach is the action querying time, which in-
creases with the number of agents (see Figure 5).
Do the TMARL Agents Perform Specific Game
Moves? In the Pokemon environment, agent 1
uses a heal pot with only 20 HP remaining (see
useHeal20P1 in Table 1). This is a reasonable
strategy in a late game when the agent is low on
HP and needs to restore its HP to avoid being de-
feated. Furthermore, agent 1 wins in the end game
with HP=5 and no heal pot left with a probability
of HP5NoHealP1 = 0.33, and agent 2 wins with a
probability of HP5NoHealP2 = 0.66. In Tic-Tac-
Toe, agent 2 first marks cell
10
, then cell
12
, and fi-
nally cell
11
in a specific order. In the CC environ-
Turn-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Model Checking
985

ment, we observe that only the second agent may get
knocked out (CC2KO=0.001) and that a collision oc-
curs in 36% of the cases (collision). Overall, these
details show that our method gives insight into policy
behaviors in different environments.
6 CONCLUSION
In this work, we presented an analytical method for
model checking TMARL agents. Our method is
based on constructing an induced DTMC from the
TMARL system and using probabilistic model check-
ing techniques to verify the behavior of the agents.
We applied our method to multiple environments and
found that it is able to accurately verify the behavior
of the TMARL agents. Our method can handle sce-
narios that can not be verified using naive monolithic
model checking methods. However, at some point,
our technique is limited by the size of the induced
DTMC and the number of TMARL agents in the sys-
tem.
In future work, we plan to extend our method to
incorporate safe TMARL approaches. This has been
previously done in the single agent RL domain (Jin
et al., 2022; Jothimurugan et al., 2022), and we be-
lieve it can also be applied to TMARL systems. We
also plan to combine our proposed method with inter-
pretable RL techniques (Davoodi and Komeili, 2021)
to better understand the trained TMARL agents. This
could provide valuable insights into the behavior of
the agents.
REFERENCES
Abu Dalffa, M., Abu-Nasser, B. S., and Abu-Naser, S. S.
(2019). Tic-tac-toe learning using artificial neural net-
works.
Baier, C. and Katoen, J. (2008). Principles of model check-
ing. MIT Press.
Berner, C., Brockman, G., Chan, B., Cheung, V., Debiak,
P., Dennison, C., Farhi, D., Fischer, Q., Hashme,
S., Hesse, C., J
´
ozefowicz, R., Gray, S., Olsson, C.,
Pachocki, J., Petrov, M., de Oliveira Pinto, H. P.,
Raiman, J., Salimans, T., Schlatter, J., Schneider, J.,
Sidor, S., Sutskever, I., Tang, J., Wolski, F., and
Zhang, S. (2019). Dota 2 with large scale deep re-
inforcement learning. CoRR, abs/1912.06680.
Bouton, M., Karlsson, J., Nakhaei, A., Fujimura, K.,
Kochenderfer, M. J., and Tumova, J. (2019). Rein-
forcement learning with probabilistic guarantees for
autonomous driving. CoRR, abs/1904.07189.
Cassez, F., David, A., Fleury, E., Larsen, K. G., and Lime,
D. (2005). Efficient on-the-fly algorithms for the anal-
ysis of timed games. In CONCUR, volume 3653
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 66–80.
Springer.
Chatterjee, K., Novotn
´
y, P., P
´
erez, G. A., Raskin, J., and
Zikelic, D. (2017). Optimizing expectation with guar-
antees in pomdps. In AAAI, pages 3725–3732. AAAI
Press.
Courcoubetis, C. and Yannakakis, M. (1988). Verifying
temporal properties of finite-state probabilistic pro-
grams. In FOCS, pages 338–345. IEEE Computer So-
ciety.
Courcoubetis, C. and Yannakakis, M. (1995). The complex-
ity of probabilistic verification. J. ACM, 42(4):857–
907.
Davoodi, O. and Komeili, M. (2021). Feature-based in-
terpretable reinforcement learning based on state-
transition models. In SMC, pages 301–308. IEEE.
Even-Dar, E., Mannor, S., Mansour, Y., and Mahadevan, S.
(2006). Action elimination and stopping conditions
for the multi-armed bandit and reinforcement learning
problems. Journal of machine learning research, 7(6).
Freak, G. (1996). Pokemon series.
Fulton, N. and Platzer, A. (2019). Verifiably safe off-model
reinforcement learning. In TACAS (1), volume 11427
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 413–
430. Springer.
Gross, D., Jansen, N., Junges, S., and P
´
erez, G. A. (2022).
Cool-mc: A comprehensive tool for reinforcement
learning and model checking. In SETTA. Springer.
Hahn, E. M., Perez, M., Schewe, S., Somenzi, F., Trivedi,
A., and Wojtczak, D. (2019). Omega-regular objec-
tives in model-free reinforcement learning. In TACAS
(1), volume 11427 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 395–412. Springer.
Hansen, T. D., Miltersen, P. B., and Zwick, U. (2013). Strat-
egy iteration is strongly polynomial for 2-player turn-
based stochastic games with a constant discount fac-
tor. J. ACM, 60(1):1:1–1:16.
Hansson, H. and Jonsson, B. (1994). A logic for reasoning
about time and reliability. Formal Aspects Comput.,
6(5):512–535.
Hartmanns, A., Klauck, M., Parker, D., Quatmann, T.,
and Ruijters, E. (2019). The quantitative verifica-
tion benchmark set. In TACAS (1), volume 11427 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 344–350.
Springer.
Hasanbeig, M., Kroening, D., and Abate, A. (2019).
Towards verifiable and safe model-free reinforce-
ment learning. In OVERLAY@AI*IA, volume 2509
of CEUR Workshop Proceedings, page 1. CEUR-
WS.org.
Hasanbeig, M., Kroening, D., and Abate, A. (2020). Deep
reinforcement learning with temporal logics. In FOR-
MATS, volume 12288 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 1–22. Springer.
Hensel, C., Junges, S., Katoen, J., Quatmann, T., and Volk,
M. (2022). The probabilistic model checker Storm.
Int. J. Softw. Tools Technol. Transf., 24(4):589–610.
Jin, P., Tian, J., Zhi, D., Wen, X., and Zhang, M. (2022).
Trainify: A cegar-driven training and verification
framework for safe deep reinforcement learning. In
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
986

CAV (1), volume 13371 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 193–218. Springer.
Jothimurugan, K., Bansal, S., Bastani, O., and Alur, R.
(2022). Specification-guided learning of nash equi-
libria with high social welfare. In CAV (2), volume
13372 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages
343–363. Springer.
Kaelbling, L. P., Littman, M. L., and Moore, A. W. (1996).
Reinforcement learning: A survey. Journal of artifi-
cial intelligence research, 4:237–285.
Khan, A., Zhang, C., Li, S., Wu, J., Schlotfeldt, B., Tang,
S. Y., Ribeiro, A., Bastani, O., and Kumar, V. (2019).
Learning safe unlabeled multi-robot planning with
motion constraints. In IROS, pages 7558–7565. IEEE.
Kucera, A. (2011). Turn-based stochastic games. In Lec-
tures in Game Theory for Computer Scientists, pages
146–184. Cambridge University Press.
Kwiatkowska, M., Norman, G., and Parker, D. (2019). Ver-
ification and control of turn-based probabilistic real-
time games. In The Art of Modelling Computational
Systems, volume 11760 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 379–396. Springer.
Kwiatkowska, M., Norman, G., Parker, D., and San-
tos, G. (2022). Symbolic verification and strategy
synthesis for turn-based stochastic games. CoRR,
abs/2211.06141.
Kwiatkowska, M., Parker, D., and Wiltsche, C. (2018).
PRISM-games: verification and strategy synthesis for
stochastic multi-player games with multiple objec-
tives. Int. J. Softw. Tools Technol. Transf., 20(2):195–
210.
Kwiatkowska, M. Z., Norman, G., and Parker, D. (2011).
PRISM 4.0: Verification of probabilistic real-time sys-
tems. In CAV, volume 6806 of Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science, pages 585–591. Springer.
Lee, S. and Togelius, J. (2017). Showdown AI competition.
In CIG, pages 191–198. IEEE.
Li, J., Zhou, Y., Ren, T., and Zhu, J. (2020). Exploration
analysis in finite-horizon turn-based stochastic games.
In UAI, volume 124 of Proceedings of Machine Learn-
ing Research, pages 201–210. AUAI Press.
Littman, M. L., Topcu, U., Fu, J., Isbell, C., Wen, M., and
MacGlashan, J. (2017). Environment-independent
task specifications via GLTL. CoRR, abs/1704.04341.
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Graves, A.,
Antonoglou, I., Wierstra, D., and Riedmiller, M. A.
(2013). Playing atari with deep reinforcement learn-
ing. CoRR, abs/1312.5602.
Nam, S., Hsueh, C., and Ikeda, K. (2022). Generation
of game stages with quality and diversity by rein-
forcement learning in turn-based RPG. IEEE Trans.
Games, 14(3):488–501.
Pagalyte, E., Mancini, M., and Climent, L. (2020). Go with
the flow: Reinforcement learning in turn-based battle
video games. In IVA, pages 44:1–44:8. ACM.
Riley, J., Calinescu, R., Paterson, C., Kudenko, D., and
Banks, A. (2021a). Reinforcement learning with
quantitative verification for assured multi-agent poli-
cies. In 13th International Conference on Agents and
Artificial Intelligence. York.
Riley, J., Calinescu, R., Paterson, C., Kudenko, D., and
Banks, A. (2021b). Utilising assured multi-agent re-
inforcement learning within safety-critical scenarios.
In KES, volume 192 of Procedia Computer Science,
pages 1061–1070. Elsevier.
Sadigh, D., Kim, E. S., Coogan, S., Sastry, S. S., and Se-
shia, S. A. (2014). A learning based approach to con-
trol synthesis of Markov decision processes for linear
temporal logic specifications. In CDC, pages 1091–
1096. IEEE.
Shahrampour, S., Rakhlin, A., and Jadbabaie, A. (2017).
Multi-armed bandits in multi-agent networks. In
ICASSP, pages 2786–2790. IEEE.
Silver, D., Huang, A., Maddison, C. J., Guez, A., Sifre, L.,
van den Driessche, G., Schrittwieser, J., Antonoglou,
I., Panneershelvam, V., Lanctot, M., Dieleman, S.,
Grewe, D., Nham, J., Kalchbrenner, N., Sutskever, I.,
Lillicrap, T. P., Leach, M., Kavukcuoglu, K., Graepel,
T., and Hassabis, D. (2016). Mastering the game of
go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nat.,
529(7587):484–489.
Svelch, J. (2020). Should the monster play fair?: Recep-
tion of artificial intelligence in Alien: Isolation. Game
Stud., 20(2).
Vamplew, P., Smith, B. J., K
¨
allstr
¨
om, J., de Oliveira Ramos,
G., Radulescu, R., Roijers, D. M., Hayes, C. F.,
Heintz, F., Mannion, P., Libin, P. J. K., Dazeley, R.,
and Foale, C. (2022). Scalar reward is not enough:
a response to silver, singh, precup and sutton (2021).
Auton. Agents Multi Agent Syst., 36(2):41.
Videga
´
ın, S. and Garc
´
ıa-S
´
anchez, P. (2021). Performance
study of minimax and reinforcement learning agents
playing the turn-based game iwoki. Appl. Artif. Intell.,
35(10):717–744.
Wang, Y., Roohi, N., West, M., Viswanathan, M., and
Dullerud, G. E. (2020). Statistically model checking
PCTL specifications on Markov decision processes
via reinforcement learning. In CDC, pages 1392–
1397. IEEE.
Wender, S. and Watson, I. D. (2008). Using reinforcement
learning for city site selection in the turn-based strat-
egy game civilization IV. In CIG, pages 372–377.
IEEE.
Wong, A., B
¨
ack, T., Kononova, A. V., and Plaat, A. (2022).
Deep multiagent reinforcement learning: Challenges
and directions. Artificial Intelligence Review, pages
1–34.
Turn-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Model Checking
987
