
Comparative Analysis of Process Models for Data Science Projects
Damian Kutzias
1 a
, Claudia Dukino
1 b
, Falko Kötter
2
and Holger Kett
1 c
1
Fraunhofer IAO, Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Engineering IAO, Germany
2
Baden-Württemberg Cooperative State University, Germany
Keywords:
Data Science, Process Models, Methodology, Project Management, Artificial Intelligence.
Abstract:
When adopting data science technology into practice, enterprises need proper tools and process models. Data
science process models guide the project management by providing workflows, dependencies, requirements,
relevant challenges and questions as well as suggestions of proper tools for all tasks. Whereas process models
for classic software development have evolved for a comparably long time and therefore have a high maturity,
data science process models are still in rapid evolution. This paper compares existing data science process
models using literature analysis, and identifies the gap between existing models and relevant challenges by
performing interviews with experts.
1 INTRODUCTION
Introducing new technology to an enterprise poses
technical, organisational and social challenges. For
conventional software and machinery numerous stan-
dardised process models exist to assist in meeting these
challenges. For software development, process mod-
els aid the specification, implementation, roll-out and
maintenance with defined steps and methodologies,
either sequentially (e. g. waterfall) or iteratively up to
agile (e. g. scrum) (Andrei et al., 2019). When setting
up new machinery for production, there are also meth-
ods such as holistic operational analysis taking into
account humans, technology and organisation (Strohm
and Ulich, 1997). These methods assume that new
machinery presents a socio-technical system of interre-
lated social and technical subsystems, which should be
analysed as one when introduced into an organisation.
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems have similar-
ities and differences to machinery and conventional
software, in as much that they aid the automation of
tasks and business processes, but aren’t designed man-
ually but rather automatically (via machine learning).
Machine learning promises efficient creation of soft-
ware solutions without the labor-intensive process of
specification and programming for the core tasks.
Machine learning also promises solutions for prob-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9114-3132
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2556-3881
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2361-9733
lems which humans are unable to formalise and thus,
unable to solve by rule-based systems.
This problem is compounded by exaggerated ex-
pectations towards machine learning as “magic black
boxes” among non-experts. During applied science
projects we introduced AI-based prototypes in co-
operation with several companies, including startup
companies, small and medium enterprises to large na-
tional companies. During these projects, we learned
that aside from the research questions related to the
machine-learning-process itself, practical challenges
arise that are often underestimated by both researchers
and industry practitioners. These include legal and
compliance issues related to data, data quality, format-
ting and labeling, and prototype deployment. Also,
human-related aspects such as trainings and change
management bring up challenges, which can differ in
data-based projects compared to classical projects.
Even though project teams contained experienced
software engineers, we found classical software devel-
opment models didn’t address the specifics of machine-
learning-projects sufficiently. In general, the chal-
lenges of deploying a “laboratory” solution into pro-
duction are considerable (Paleyes et al., 2020).
Thus, data science projects are software develop-
ment projects but differ in most steps, posing new
challenges to industry practitioners: Machine learning
has an inherent uncertainty about the solution quality.
It stems from limited understanding of business case,
data quality and machine learning technology (Reggio
and Astesiano, 2020). Due to this uncertainty, clas-
1052
Kutzias, D., Dukino, C., Kötter, F. and Kett, H.
Comparative Analysis of Process Models for Data Science Projects.
DOI: 10.5220/0011895200003393
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2023) - Volume 3, pages 1052-1062
ISBN: 978-989-758-623-1; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

sic methods for planning project costs, duration and
complexity are of limited use. To aid the professionali-
sation of data science projects in an enterprise context,
new process models are needed, similarly to the in-
vention of software engineering during the software
crisis (Randell, 1979).
Data science process models are used to assist
the realisation of data science projects in enterprises
(Kutzias et al., 2021). Due to the rapid evolution of
data science and digitisation in general (the “second
digital revolution” (Rindfleisch, 2020)), up-to-date and
integrated methodologies are rare, but of crucial value
for project success, especially for small and medium
enterprises (SMEs) not originating from the informa-
tion technology sector.
In this work we perform a comparative analysis
of existing process models for data science projects.
Emerging data science project models are analysed
in a structured-literature review, taking into account
humans, processes, technology and organisation. This
analysis compares the contents of these project models,
i. e. the aspects and process steps addressed by the
models.
Based on this analysis we compare the state-of-the-
art with the needs of enterprises (in particular SMEs)
using expert interviews with researchers who partici-
pated in applied data science projects, identifying gaps
between literature and enterprise application.
In future work, we plan to use the findings as a
basis for a consolidated, integrated process model pro-
viding continuous assistance throughout the whole
lifecycle of data-based (AI) projects, thus lessening a
major barrier-of-entry for companies wishing to utilise
data science.
2 METHODOLOGY
Our analysis was guided by the foundations of the qual-
itative content analysis of Mayring (Mayring, 2019).
Our research questions were:
1.
Which contents of process models are of particular
importance for successful data-based projects in
practice?
2.
Where are the gaps in existing process models
according to the identified contents (from 1)?
(a) Regarding the coverage of the contents.
(b)
Regarding tool recommendations for handling
the contents.
The research questions are motivated by a pre-
viously published work that identified general prac-
ticioner requirements for data science process mod-
els (Kutzias et al., 2021).
According to Mayring’s method, the qualitative
content analysis is category-based. For the derivation
of the categories, the following steps were conducted:
1) In a previous work we investigated existing
data science process models and identified seven mod-
els as relevant based on practicioner requirements
identified in our applied research projects (Kutzias
et al., 2021). Our selection criteria were: the first
data science process model (Knowledge Discovery
in Databases [KDD] (Fayyad et al., 1996)), the in-
dustry standard (Cross Industry Standard Process for
Data Mining [CRISP-DM] (Chapman et al., 2000)),
modern industry-provided models (Analytics Solu-
tions Unified Method [ASUM] (IBM Corporation,
2016)), (The lightweight IBM Cloud Garage Method
for data science [ILG] (Kienzler, 2019b; Kienzler,
2019a)), (Team Data Science-Prozess [TDSP] (Mi-
crosoft, 2020)), and modern models from science (En-
gineering Data-Driven Applications [EDDA] (Hes-
enius et al., 2019)), (Data Science Process Model
[DASC-PM] (Schulz et al., 2020)).
2) We analysed the selected models for their
addressed contents and derived a set of content-
categories.
3) We added content-categories based on practical
experience from project implementation and literature
review going beyond data science process models.
4) We conducted a series of interviews with 13
practitioners either from industry or applied research
and asked them about important contents and chal-
lenges in data-based projects (without bias from our
categories), then about the relevance of our categories
and finally again about additional contents and chal-
lenges. The resulting contents are the answer to re-
search question 1) and are described in detail in Sec-
tion 3.
The qualitative content analysis for answering re-
search question 2) was conducted as follows. The basis
for the analysis was a table structure mapping each
content-category to references and reasoning. Ref-
erences and assessments were given in two dimen-
sions for each category: 1) the addressing (not ad-
dressed, implicitly addressed, explicitly addressed)
and 2) realisation assistance (the “how” was not ad-
dressed, addressed, a concrete tool was provided or
recommended). Each process model was analysed in-
dependently by two scientists based on the underlying
table structure. This resulted in the answer for research
question 2), which is presented in Section 4.
Comparative Analysis of Process Models for Data Science Projects
1053

3 CONTENTS OF DATA SCIENCE
PROJECTS
When KDD was described as a process model in 1996,
the authors stated that most previous work was primar-
ily focused on the data mining step, but other steps
are equally or even more important for successful ap-
plication in practice (Fayyad et al., 1996). Activities
necessary to develop applications based on data must
be integrated into common software engineering pro-
cesses to ensure a project’s success. Therefore devel-
oping well-engineered products requires knowledge
and specialists from software development and data
processing working together (Hesenius et al., 2019).
This section gives an overview of core contents im-
portant for data-based projects. The contents were
identified as relevant for data-based projects during
our analysis (cf. Section 2). Contents are presented
with a concise description and reasoning for its rele-
vance. The contents are structured using four broad
project phases as shown in Figure 1. These phases are
the results of a manual clustering of all contents. The
structure is not necessary for the comparative analy-
sis, but guides through the results of this work. Each
of the four phases is briefly described in the follow-
ing subsections before elaborating the corresponding
contents.
3.1 Goals and Requirements
The first phase is about the project orientation, wherein
the main goal is the reason for the project and require-
ments as secondary objectives supplement the goal.
It is advisable to perform a structured requirements
analysis, explicitly considering different stakeholder
perspectives in order to get a reliable list of require-
ments.
Objective and Economy means the specification
of clear goals respecting economic context, i. e. prob-
lems or potentials from business perspective. The in-
vestigation of data without a goal or business objective
usually is the subject of basic research, whereas most
data science projects have some kind of goal. Many of
the existing data science process models have a promi-
nent phase covering the definition or derivation of such
a goal. CRISP-DM has “Business Understanding” as
the first of its six main phases, TDSP also starts with
“Business Understanding” in its data science lifecycle,
KDD starts with “Learning the application domain”
and ASUM has a first phase called “Analyze”. EDDA
contains a phase “Specification and Design” and in
addition a special phase “Is ML suitable?”.
Needs from User Perspective are relevant for de-
tailing the goal and deriving requirements. Users not
only have to work with solutions, but also accept them
in order for efficient cooperation between human and
machine. By analysing the social system in the user’s
environment, needs and potentials can be identified.
These are important sources of information when it
comes to deriving requirements for the new application
(Strohm and Ulich, 1997). Various models and pro-
cedures are available for this purpose (Rudolph et al.,
1987; Bauer et al., 2018).
The Analysis of Affected Processes takes the per-
spective of existing business processes affected by
the project. A process is carried out by employees
according to certain rules. The work process is an
independent, clearly delimitable component of a busi-
ness process and forms the smallest operative level
in the process that describes detailed tasks or work
steps. The classic description of processes by means
of Business Process Management (BPM) is subject to
increasing changes due to the use of new technologies
and especially data-based methods. This increases the
complexity and interconnection of work processes and
creates new additional quality dimensions for evalua-
tion such as flexibility, customer orientation (internal
and external), goals of social innovation and those of
competence development (Tombeil et al., 2020). The
modelling of existing processes is an indispensable
step that serves as the basis for the strategy and con-
crete project planning of the digital transformation
(Tombeil and Schletz, 2020).
The Analysis of Key Activities takes into account
the affected key activities as well as their related com-
petencies. It must be clarified which tasks and activ-
ities in the division of labour between humans and
technology can be automated to what extent (Tombeil
et al., 2020). To this end, it is necessary to analyse the
key activities of the users, as suggested by Strohm and
Ulich covering human-related, technical and organisa-
tional aspects (Strohm and Ulich, 1997). In research,
the notion of automation of activities is closely related
to the notion of routine (Autor et al., 2003; Frey and
Osborne, 2013; Bonin et al., 2015), and the appear-
ance of the activity and its usability in the analysis can
provide important indications of the extent to which
an activity can be automated or supported by data-
based solutions. Competencies are required in order to
perform an activity, which are reflected in interaction
requirements (Böhle et al., 2011) as well as cognitive
requirements (Hacker, 2016).
Legal issues might occur in relation to the project,
solution or processed data. Being able to access data
does not necessarily mean being allowed to use the
data: without a clear legal statement such as a license
or contract there is much room for confusion when it
comes to the usage even of public accessible data. The
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1054

Utilisation of the
Results
Goal and
Requirements
Concepts and
Implementation
Structured
Project Setup
Figure 1: Project structure for organisation of the data-based project contents in the gap-analysis.
European Union has laws about databases independent
from copyrights and even in countries without rights
for governing data, still the preparation of data might
be subject to restrictions (Oxenham, 2016). Legal
issues are not limited to the right to use certain data.
Questions about the responsibility might arise when
AI systems make decisions and fail in some way. The
legal domain for AI can be more challenging than
other disciplines and negative examples from practice
already exist (Sun et al., 2020). Some data science
process models name legal issues, but most of them
do not go into much detail. CRISP-DM, for example,
lists legal issues under business understanding in the
context of requirements and EDDA states that legal
experts might be needed as special domain experts.
Requirements define restrictions and side goals
which have to or should be respected during project re-
alisation in addition to the business goals. These may
range from resource restrictions over project deadlines
up to non-functional solution criteria such as predic-
tion quality or certain levels of explainability of the
results of an AI-model. The requirements may be of
different priority, difficulty, type and risk (ISO et al.,
2018). CRISP-DM covers the requirements by its busi-
ness understanding phases, which includes an activity
list for identifying requirements. ASUM also covers
the requirements within its phase “Analyze”. EDDA
on the other hand has a separate software engineering
phase called “Requirements Engineering” as the first
phase even before the specification.
3.2 Structured Project Setup
The second phase handles the preparations of the im-
plementation of projects, planning and structuring the
required steps to minimise risks for delays and miscal-
culated resource requirements.
The Data Access is an important aspect and covers
everything related to accessing the data starting with
the acquisition from customers over internal access
rights up to the generation of new data. As data is
a prerequisite for data-based projects, the access to
relevant data is prominent in most data science process
models. DASC-PM has a major phase called “Data
provisioning”. TDSP has a phase “Data Acquisition
& Understanding” in its data science lifecycle and
ILG has a second phase called “Extract, Transform,
Load”. CRISP-DM addresses “Sources of data and
knowledge” in its phase “Business Understanding”.
Project Management is about the structure and
organisation of the data-based project. Many data sci-
ence process models agree on the uncertainty as well
as the iterative character of data science projects and
emphasise this by proposing agile project management
or loops returning to previous phases of the project.
CRISP-DM proposes making a project plan in section
“Produce project plan” under business understanding
and underlines the importance of large-scale iterations,
ASUM has “Project Management” as one of its six
phases included, proposes agile project management
and recommends using the V model and TDSP also
describes an agile approach for managing data science
projects emphasising sprints and work items. Besides
general project management, the usage of data sci-
ence process models can be counted as a part of this
step. Depending on the project and the process models,
they can simply assist and prevent forgetting relevant
steps or even define the whole project management
structure.
The Selection of Technology means choosing pro-
gramming languages, tools, libraries and application
software. The choice of the proper software is an
important precondition for successful implementation
of advanced information technologies (Min, 1991),
especially for complex environments such as manufac-
turing companies. Various studies show the need for
guided support for technology selection (Hamzeh et al.,
2018). Technology selection is usually not contained
in vendor-independent data science process models,
but heavily discussed in data science process models
created by enterprises such as TDSP and ILG, which
provide many suggestions for the usage of software,
especially from the Microsoft or IBM portfolio.
The Project Team and Competences may vary
based on the objective, scope, requirements and en-
vironment due to the interdisciplinary character of
data-based projects. A recent investigation has identi-
fied six categories of knowledge, skills, abilities, and
other characteristics required by data scientists to per-
form their work effectively: organisational, social, an-
alytical, technical, ethical/regulatory, and cognitive
(Hattingh et al., 2019). Most data science process
Comparative Analysis of Process Models for Data Science Projects
1055

models agree in the interdisciplinary character of data
science projects. Whereas CRISP-DM lists “Personnel
sources”, some newer models give detailed descrip-
tions of roles and competencies: before describing the
process of EDDA, the roles are given in section “A.
Roles”. TDSP describes six “project roles” and maps
them to tasks and artefacts and DASC-PM provides
detailed descriptions of competence profiles as well as
roles, mapping requirements for each project phase in
competence and role diagrams.
3.3 Concepts and Implementation
The third phase is about the implementation, but may
also include several conceptual elements. The reason
for this is the uncertainty about the achievability of
the goals in many data-based projects. Early imple-
mentations can therefore be seen as risky investments
before a positive evaluation of the data-based core of
the project is reached.
Data Preparation is about quality assurance as
well as transformation of data for further processing.
In between the data understanding and model building
steps the data usually has to be transformed. Obvious
quality issues may be addressed during data acquisi-
tion, but this often does not solve all issues and dur-
ing data exploration more complex quality issues may
arise. This includes basic operations, such as removing
outliers, manage noise as well as deciding database
management system issues such as data types, schema,
and mapping of missing and unknown values, as it was
described in KDD’s third phase. The second aspect
of the data preparation is the preparation of the model
building in terms of feature engineering and necessary
transformations for the selected models to build. KDD
also covers this as a separate fourth phase, CRISP-DM
has a major phase “Data Preparation”, ILG contains
“Feature Creation” as its third phase and TDSP has
feature engineering as a part of its “Modeling”.
Data Understanding and Exploration means div-
ing into the data, understanding it both on the technical
level as well as the domain level. CRISP-DM has a
main phase “Data Understanding”, ILG has “Initial
Data Exploration” as its first phase, EDDA lists “Data
Exploration” as its second machine learning phase and
TDSP has “Data Acquisition & Understanding” in the
data science lifecycle. This step often influences the
objective and may even cause a (partial) redefinition
or even cancellation of the project.
The Selection of Models (also called algorithms
or techniques) is about finding appropriate models,
usually in an iterative process of model building. The
choices for the models to use next are normally based
on experience as well as best practice (Konstan and
Adomavicius, 2013). This may be as easy as simply us-
ing standard choices or own experiences from the past,
but can also be an elaborate activity with literature
research or technical investigation of model character-
istics and functionality. KDD contains it as its fifth
phase “Choosing the function of data mining” and lists
classes of models such as classification based on the
purpose of the model and the choice of data mining
algorithm(s) as its sixth phase. CRISP-DM does not
have it integrated prominently within the process itself,
but gives an extensive appendix named “Data mining
problem types” describing typical problems and ap-
propriate techniques to address these problem types.
ILG has a fourth phase “Model Definition” separately
before its fifth phase “Model Training”.
Model Building is the process of configuring and
training models to fit the data regarding the chosen
objectives and requirements, including optimisation.
This is the technical core of data science projects: cre-
ation and application of models from statistics and AI.
Most data science process models contain a prominent
phase for this. KDD covers it with its phase “Data
mining”, CRISP-DM has the main phase “Modeling”,
EDDA’s fourth machine learning phase is “Model De-
velopment” and DASC-PM contains the phase “Anal-
yse” to name a few.
Robustness and Model-Security is about the vul-
nerability of models against noise, outliers, (tempo-
rary) missing data or attacks on the data level. Models
can be intentionally broken or even tricked to pro-
duce different outcomes (by slightly modified data)
or simply fail due to noise in the data. If this is to
be expected and model functionality is required under
such circumstances, measures have to be developed
to increase model robustness and security. Whereas
some causes such as sensor failure can be identified by
simple monitoring measures, missing recognisability
can be a threat in case of attacks: for example, neural
nets can be caused to misclassify images by apply-
ing certain hardly perceptible perturbations which can
be found by maximising the network’s prediction er-
ror (Szegedy et al., 2013). Moreover the challenge
to achieve this is small: it is easy to produce image
changes which are completely unrecognisable to hu-
mans, but that state-of-the-art deep neural networks
believe to recognise as something completely different
with 99.99 percent confidence (Nguyen et al., 2014).
System Architecture is about the overall system
of the solution application including all its compo-
nents as well as relations, i. e. interfaces as integration
points. Whereas some data-based solutions can exist
without an extensive context and integration, complex
systems can evolve. In that case the solutions have to
be integrated, especially when the Internet of Things
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1056

(IoT) is an integral part and data has to be gathered
by sensors: system components and their interfaces
may be many and they can be located in the environ-
ment such as a shop floor, networks may be part of the
system for accessing and managing devices, data man-
agement can be a complex subsystem instead of simple
databases and applications may require to be properly
integrated. Also the consumers of the application have
to access results, and they may be technology instead
of humans (Kutzias et al., 2019). Generally, for system
architectures it is increasingly necessary to apply con-
cepts, principles, procedures and tools to make better
architecture-related decisions to create more effective
architectures and increase architecture maturity. (IEEE
Computer Society/Software & Systems Engineering
Standards Committee, 2019). System architecture is
rarely a prominent aspect of existing data science pro-
cess models. Some list it, but most only address it
implicitly, e. g. as a part of the deployment. ILG has a
separated part “Architectural decisions guidelines: An
architectural decisions guide for data science” which
was written to complement the process model.
The Data Architecture has two dimensions: first,
the database schema and types (relational, document
based, graph based etc.) and secondly the high level
(enterprise) data architecture (dedicated silos, ware-
houses or data lakes). As data is often used from
several sources, it can be characterised as heteroge-
neous, incomplete and usually involves a large amount
of records (Pérez et al., 2007). This heterogeneity
of data sources makes it difficult to discover knowl-
edge in data and currently hinders the (unsupervised)
application of data mining methods. Therefore, an ar-
chitecture, which automatically integrates data sources
and enables the usage of different analysis tools, with-
out limitations towards the specific data formats of
the sources, could greatly enhance the impact of data
analysis (Trunzer et al., 2017). One approach heav-
ily discussed over the last decades is the creation of
a data warehouse. The data in a warehouse is sub-
ject oriented, integrated, time variant, and nonvolatile.
But data warehousing is expensive (Gray and Watson,
1998). Therefore, (intensive and profitable) analytics
should be the goal behind investments in storing large
volumes of data (Ramesh, 2015).
The data architecture may already exist and there-
fore not be subject to change within the project and
also may be a (different) strategic project as itself. If
that is not the case, some decisions about data stor-
age and integration may be required within the project.
The context-free project-internal version is to make
all decisions on the project level. The downside of
this approach comes when developing persistent sys-
tems: developing ad-hoc solutions is expensive and
error-prone when it comes to integration and analysis
(Pedersen, 2007).
In addition to the architecture on the enterprise or
system level, the data model or format may be of rele-
vance: should it be relational, graph-based, document-
based or something else? Data models for different
systems may differ considerably. Thus, complex in-
terfaces are required between systems that share data.
These interfaces can account for 25 - 70 percent of the
cost of systems (West, 2003). Conventional data mod-
els are appropriate for representing large amounts of
structured data usually stored in business applications.
They do not provide constructs for representing hierar-
chically structured data, nor do they provide constructs
for derived data definition and manipulation (Savnik
et al., 1993). Currently, it is only easy to use structured
data, hard to work with semi-structured and predomi-
nantly unexplored how to work with unstructured data.
Architecture should be designed to support all three, if
necessary (Hou and Pan, 2018).
The Evaluation concludes the implementation
phase and judges the suitability of bringing the results
into practice. Data science projects contain several
kinds of evaluation: in the early phases, existing so-
lutions and the environment are evaluated as a basis
for the project. During the iterative model selection
and building, intermediate results are evaluated for op-
timisation. In contrast to these evaluations, this phase
evaluates solutions regarding their usefulness and their
fulfilment of the (business) objectives and require-
ments. It may be unclear before realisation whether
the objectives can be fulfilled or not. Thus, possible
outcomes explicitly can be the return to any previous
phase, project cancellation or complete restart instead
of deployment. This is already considered by CRISP-
DM, which has a path from its fifth phase “Evaluation”
back to the first phase. Even before CRISP, KDD de-
scribes its phase “Interpretation” as interpreting the
discovered patterns and possibly returning to any of the
previous steps. Also most of the newer process models
contain evaluation as a prominent phase, EDDA con-
tains “System Test” as its fourth software engineering
phase and TDSP includes “Model Evaluation” in its
Phase “Modeling”.
3.4 Utilisation of the Results
Within the last phase, project results are to be brought
to practice. Depending on the project’s character, this
phase can be as easy as just using the knowledge from
a report up to a complex technical integration with new
and adapted processes (e. g. for automating a decision)
and establishing new roles in the company.
The Deployment is about bringing the solution
Comparative Analysis of Process Models for Data Science Projects
1057

into technical productivity. The utilisation of created
solutions fitting requirements and goals is one of the
most important parts according to most of the data sci-
ence process models. The last phase of KDD is “Using
discovered knowledge”, which is described as incor-
porating this knowledge into the performance system,
taking actions based on the knowledge, or simply docu-
menting it and reporting it to interested parties, as well
as checking for and resolving potential conflicts with
previously believed (or extracted) knowledge. The
last phase of CRISP-DM is “Deployment” following
a positive decision within the evaluation, ASUM has
a phase called “Deploy”, TDSP also has a phase “De-
ployment” in the data science lifecycle and DASC-PM
comes with a phase “Utilisation”. EDDA has “Model
Integration” as a machine learning phase and “Imple-
mentation” as a software engineering phase.
Qualification and Adjustment of the Job Profiles
might be necessary depending on the changes induced
by the project. Competency requirements in the digi-
tal world of work are changing, so that in future they
might be more demanding, diverse and complex, and
will lead to changed occupational profiles (Apt et al.,
2018). Cooperation between people and technology,
especially with AI, should be specifically promoted.
New hybrid job profiles and forms of work in particu-
lar are still lacking and are largely ignored by today’s
business and research community (Weisbecker et al.,
2018). Daugherty and Wilson call them the “missing
middle” between human and machine activities. That
is, supporting activities that humans perform for the AI
and on the other hand activities where the machine sup-
ports the human being, for example through assistance
systems (Daugherty and Wilson, 2018).
These new profiles require adjustments in work or-
ganisation and activities, and the associated demands
on the employees themselves. Possible design ap-
proaches for this are many and require the develop-
ment and use of digital tools and assistance systems
(Link et al., 2020).
Process Integration is often necessary to change
or bring up new business processes. ILG goes more
into the integration of the application with the existing
system, as this approach involves a very extensive cat-
alogue of questions that the company should answer,
although it is limited to questions about rights manage-
ment and operation. In DASC-PM the topic is explic-
itly mentioned in some places and it is pointed out that
the integration into the existing processes should be
considered. The success of AI applications does not
only depend on the development, selection and imple-
mentation, but also on whether a process improvement
has been addressed in this context (Partnership on AI,
2018). It should be noted that even IT-supported bad
solutions remain bad solutions (Hacker, 2018).
4
CONTENTS OF CURRENT DATA
SCIENCE PROCESS MODELS
Even though the evolution of data science process mod-
els is still in an early phase, several models already
exist. The evolution of process models including influ-
ences among them are described by Martínez-Plumed
et al. (Martinez-Plumed et al., 2020). The basis for
this analysis was given by Marsical et al. (Mariscal
et al., 2010), which also conducted a content analysis
of different data science process models. The authors
identified 17 contents (called “subprocesses”), mapped
them mutually between the analysed process models
and showed that none of the analysed process models
cover all 17 contents. To reduce bias in our research,
we conducted an independent analysis and ended up
with the 21 contents presented in Section 3.
A brief overview of the analysed process models
was given in (Kutzias et al., 2021). A vision for future
data science process models was outlined by certain
characteristics of such models: continuity (the embed-
ding of the early and late non-technical project phases),
suitability for small enterprises, independence from
special business sections, based on the experience of
practitioners, unrestricted usability (in terms of licens-
ing), vendor-neutrality and tool recommendation. Our
analysis focuses the two content-related vision charac-
teristics, i. e. continuity and tool recommendation.
The seven process models introduced in Section 2
were analysed regarding the contents from Section 3,
assessing continuity and tool provisioning following
the methodology described in Section 2. During the
analysis, ASUM was only available as a short white pa-
per. We reached out to the authors for further informa-
tion but have not received an answer upon submission
time. The detailed results can be seen in Figure 2.
Our interviews included seven managers (including
five CEOs of SMEs, two of them being part of a group
of companies) and six data scientists. The only data sci-
ence process model which was named more than once
was the CRISP-DM. Five interviewees did know it and
four stated to use it. Six interviewees responded that
they or their enterprise works without clear processes
or methods at least in some areas. In addition, the
interviewees named a broad variety of challenges for
data-based projects: communicating the advantages of
data-based solutions, data acquisition, missing com-
petences, user-acceptance, maintaining privacy, data
availability, proper team set-ups for projects, unclear
methodology, change management (especially in per-
sonnel resources), technology selection, aligning the
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1058
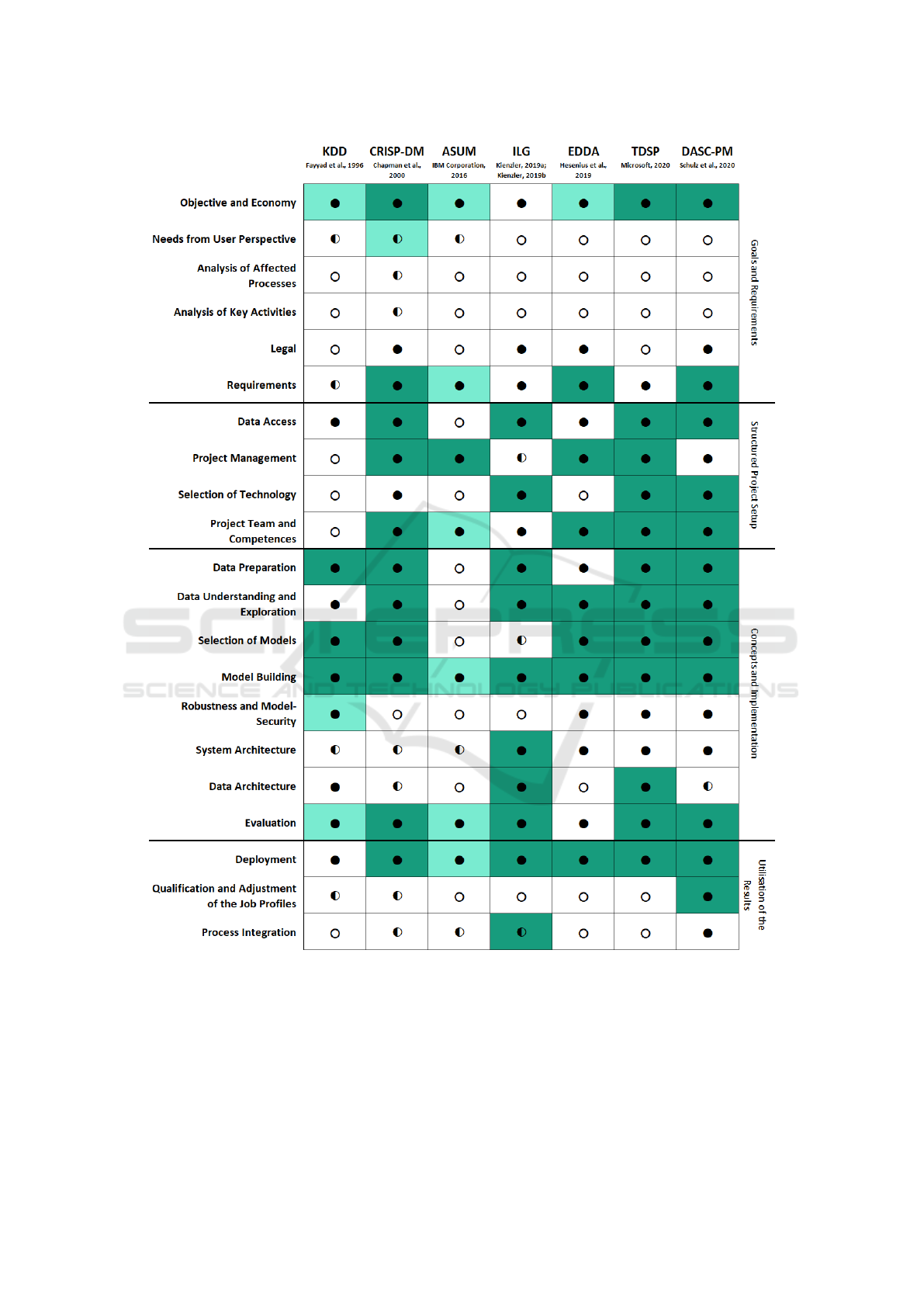
Figure 2: Overview of data science process models and their contents. An empty circle indicates that the content is not
addressed, a half circle indicates that the topic is addressed implicitly, and a full circle that a content is explicitly addressed.
White shows that the “how” is not addressed, light green shows that it is addressed and dark green that a concrete tool is given
or referenced.
new technology with users in practice, missing ex-
plainability, and data analysis in general. The broad
spectrum of named challenges is another indicator for
the need of structured methodology including the con-
tinuity aspect.
Summarising the results of the review, full or near
continuity according to the previously identified con-
tents is not achieved by any of the process models.
Comparative Analysis of Process Models for Data Science Projects
1059

Most of them do cover the technical core of data sci-
ence projects in a detailed manner, but the structured
preparations of the project as well as the late phases,
i. e. the utilisation of the results beyond technical de-
ployment are sparsely covered. The human aspects
and affected processes of the project context can be
important for project success (Ganz et al., 2021), but
are rarely addressed in detail. Whereas many chal-
lenges and approaches may be the same as for tradi-
tional projects, some important differences exist for
data science projects and not addressing them in an in-
tegrated way bears risks, especially for process model
users which are new to the domain of data science.
Such users are common nowadays, since our econ-
omy has reached a stage at which it cannot develop
independently from AI anymore (Bovenschulte and
Stubbe, 2019). The occurrence of said challenges for
data-based projects in practice and the need for clear
methodology was emphasised by our interviews.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
RESEARCH
We analysed existing data science process models
as well as knowledge and structure about classic
(software) projects to derive contents of data science
projects. For these contents, we’ve shown their rele-
vance for such projects and validated them in expert
interviews. We analysed several existing data science
process models including KDD as the first, CRISP-
DM as the industry standard, and several modern mod-
els from industry and science and conclude that none
of these models are complete in terms of continuity
or tool recommendations: several gaps exist for each
model, especially in the early and late phases of data
science projects when it comes to the interaction with
the business context such as humans and processes.
From these insights about necessary contents of
data science process models as well as gaps in exist-
ing ones, the next relevant step is closing them. Most
of these gaps require a deep understanding of data
science and artificial intelligence in the context of busi-
ness projects and are not independent of all the other
contents, therefore not only the gaps, but also their
integration within data science projects have to be
addressed. In order to provide useful results for prac-
titioners, industry demands are of importance, which
can be respected by means of business research.
We aim for a data science process model fulfilling
the vision characteristics published in (Kutzias et al.,
2021), especially filling the gaps discussed in this anal-
ysis. To ensure practical relevance of the model we
are currently developing a model which we iteratively
evaluate together with enterprises in current real-world
data science projects.
REFERENCES
Andrei, B.-A., Casu-Pop, A.-C., Gheorghe, S.-C., and
Boiangiu, C.-A. (2019). A Study on Using Waterfall
and Agile Methods in Software Project Management.
Apt, W., Bovenschulte, M., Priesack, K., Weiß, C., and
Hartmann, E. A. (2018). Einsatz von digitalen Assis-
tenzsystemen im Betrieb.
Autor, D. H., Levy, F., and Murnane, R. J. (2003). The
Skill Content of Recent Technological Change: An
Empirical Exploration.
Bauer, W., Schlund, S., and Strölin, T. (2018). Mod-
ellierungsansatz für ein arbeitsplatznahes Beschrei-
bungsmodell der "Arbeitswelt Industrie 4.0". In Wis-
chmann, S. and Hartmann, E. A., editors, Zukunft der
Arbeit – Eine praxisnahe Betrachtung. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Böhle, F., Bolte, A., Neumer, J., Pfeiffer, S., Porschen, S.,
Ritter, T., Sauer, S., and Wühr, D. (2011). Subjek-
tivierendes Arbeitshandeln – Nice to have oder ein
gesellschaftskritischer Blick auf das Andere der Verw-
ertung? Arbeits- und Industriesoziologische Studien.
Bonin, H., Gregory, T., and Zierahn, U. (2015). Übertragung
der Studie von Frey/Osborne (2013) auf Deutschland.
Bovenschulte, M. and Stubbe, J. (2019). Intelligenz ist nicht
das Privileg von Auserwählten. In Wittpahl, V., editor,
Künstliche Intelligenz, pages 215–220. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Chapman, P., Clinton, J., Kerber, R., Khabaza, T., Reinartz,
T., Shearer, C., and Wirth, R. (2000). CRISP-DM 1.0:
Step-by-step data mining guide.
Daugherty, P. R. and Wilson, H. J. (2018). Human + Ma-
chine: Reimagining Work in the Age of AI. Harvard
Business Review Press, Boston, Massachusetts.
Fayyad, U., Piatetsky-Shapiro, G., and Smyth, P. (1996).
The KDD Process for Extracting Useful Knowledge
from Volumes of Data. Communications of the ACM,
Vol. 39, No. 11.
Frey, C. B. and Osborne, M. A. (2013). The Future of
Employment: How Susceptible Are Jobs to Computer-
isation?
Ganz, W., Kremer, D., Hoppe, M., Tombeil, A.-S., Dukino,
C., Zaiser, H., and Zanker, C. (2021). Arbeits- und
Prozessgestaltung für KI-Anwendungen, volume 3 of
Automatisierung und Unterstützung in der Sachbear-
beitung mit Künstlicher Intelligenz. Fraunhofer Verlag,
Stuttgart.
Gray, P. and Watson, H. J. (1998). Present and Future Di-
rections in Data Warehousing. The DATA BASE for
Advances in Information Systems.
Hacker, W. (2016). Vernetzte künstliche Intelligenz / Internet
der Dinge am deregulierten Arbeitsmarkt: psychische
Arbeitsanforderungen. Journal Psychologie des Allt-
agshandelns.
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1060

Hacker, W. (2018). Menschengerechtes Arbeiten in der digi-
talisierten Welt: Eine Wissenschaftliche Handreichung,
volume Band 49 of Mensch - Technik - Organisation.
vdf Hochschulverlag AG an der ETH Zürich, Zürich,
1. auflage edition.
Hamzeh, R., Zhong, R., Xu, X. W., Kajati, E., and Zolotova,
I. (2018). A Technology Selection Framework for Man-
ufacturing Companies in the Context of Industry 4.0.
In 2018 World Symposium on Digital Intelligence for
Systems and Machines (DISA), pages 267–276. IEEE.
Hattingh, M., Marshall, L., Holmner, M., and Naidoo, R.
(2019). Data Science Competency in Organisations. In
de Villiers, C. and Smuts, H., editors, Proceedings of
the South African Institute of Computer Scientists and
Information Technologists 2019 on ZZZ - SAICSIT ’19,
pages 1–8, New York, New York, USA. ACM Press.
Hesenius, M., Schwenzfeier, N., Meyer, O., Koop, W., and
Gruhn, V. (2019). Towards a Software Engineering
Process for Developing Data-Driven Applications. In
2019 IEEE/ACM 7th International Workshop on Re-
alizing Artificial Intelligence Synergies in Software
Engineering (RAISE), pages 35–41. IEEE.
Hou, Z. and Pan, C. (2018). Data Mining Method and Em-
pirical Research for Extension Architecture Design. In
2018 International Conference on Intelligent Trans-
portation, Big Data & Smart City (ICITBS), pages
275–278. IEEE.
IBM Corporation (2016). Analytics Solutions Unified
Method: Implementations with Agile principles.
IEEE Computer Society/Software & Systems Engineering
Standards Committee (2019). Software, systems and
enterprise — Architecture processes: International
Standard: ISO/IEC/IEEE 42020:2019.
ISO, IEC, and IEEE (2018). ISO/IEC/IEEE 29148:2018(E):
ISO/IEC/IEEE International Standard - Systems and
software engineering – Life cycle processes – Require-
ments engineering.
Kienzler, R. (2019a). Architectural decisions guidelines: An
architectural decisions guide for data science.
Kienzler, R. (2019b). The lightweight IBM Cloud Garage
Method for data science: A process model to map
individual technology components to the reference ar-
chitecture.
Konstan, J. A. and Adomavicius, G. (2013). Toward identifi-
cation and adoption of best practices in algorithmic rec-
ommender systems research. In Bellogín, A., Catells,
P., Said, A., and Tikk, D., editors, Proceedings of the
International Workshop on Reproducibility and Repli-
cation in Recommender Systems Evaluation - RepSys
’13, pages 23–28, New York, New York, USA. ACM
Press.
Kutzias, D., Dukino, C., and Kett, H. (2021). Towards a
Continuous Process Model for Data Science Projects.
In Leitner, C., Ganz, W., Satterfield, D., and Bassano,
C., editors, Advances in the Human Side of Service
Engineering, volume 266 of Lecture Notes in Networks
and Systems, pages 204–210. Springer International
Publishing, Cham.
Kutzias, D., Falkner, J., and Kett, H. (2019). On the Com-
plexity of Cloud and IoT Integration: Architectures,
Challenges and Solution Approaches. In Proceed-
ings of the 4th International Conference on Internet
of Things, Big Data and Security, pages 376–384.
SCITEPRESS - Science and Technology Publications.
Link, M., Dukino, C., Ganz, W., Hamann, K., and Schnalzer,
K. (2020). The Use of AI-Based Assistance Systems
in the Service Sector: Opportunities, Challenges and
Applications. In Nunes, I. L., editor, Advances in
Human Factors and Systems Interaction, volume 1207
of Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing,
pages 10–16. Springer International Publishing, Cham.
Mariscal, G., Marbán, Ó., and Fernández, C. (2010). A sur-
vey of data mining and knowledge discovery process
models and methodologies. The Knowledge Engineer-
ing Review, 25(2):137–166.
Martinez-Plumed, F., Contreras-Ochando, L., Ferri, C., Her-
nandez Orallo, J., Kull, M., Lachiche, N., Ramirez
Quintana, M. J., and Flach, P. A. (2020). CRISP-
DM Twenty Years Later: From Data Mining Processes
to Data Science Trajectories. IEEE Transactions on
Knowledge and Data Engineering, page 1.
Mayring, P. (2019). Qualitative Content Analysis: Demar-
cation, Varieties, Developments. Forum: Qualitative
Social Research, 20(3).
Microsoft (2020). Team Data Science Process Documenta-
tion.
Min, H. (1991). Selection of Software: The Analytic Hi-
erarchy Process. International Journal of Physical
Distribution & Logistics Management,, 1991(22):42–
52.
Nguyen, A., Yosinski, J., and Clune, J. (2014). Deep Neural
Networks are Easily Fooled: High Confidence Predic-
tions for Unrecognizable Images.
Oxenham, S. (2016). Legal maze threatens to slow data
science. nature, 2016(536):16–17.
Paleyes, A., Urma, R., and Lawrence, N. D. (2020). Chal-
lenges in deploying machine learning: a survey of case
studies. CoRR, abs/2011.09926.
Partnership on AI (2018). AI, Labor, and Economy Case
Studies: Compendium Synthesis.
Pedersen, T. B. (2007). Warehousing The World – A Few
Remaining Challenges. ACM, New York, NY.
Pérez, M. S., Sánchez, A., Robles, V., Herrero, P., and Peña,
J. M. (2007). Design and implementation of a data
mining grid-aware architecture. Future Generation
Computer Systems, 23(1):42–47.
Ramesh, B. (2015). Big Data Architecture. In Mohanty, H.,
Bhuyan, P., and Chenthati, D., editors, Big Data, vol-
ume 11 of Studies in Big Data, pages 29–59. Springer
India, New Delhi.
Randell, B. (1979). Software engineering in 1968. Comput-
ing Laboratory Technical Report Series.
Reggio, G. and Astesiano, E. (2020). Big-data/analytics
projects failure: A literature review. In 2020 46th
Euromicro Conference on Software Engineering and
Advanced Applications (SEAA), pages 246–255.
Rindfleisch, A. (2020). The Second Digital Revolution.
Marketing Letters, 31(1):13–17.
Rudolph, E., Schönfelder, E., and Hacker, W. (1987).
Tätigkeitsbewertungssystem - Geistige Arbeit.
Comparative Analysis of Process Models for Data Science Projects
1061

Savnik, I., Mohori
ˇ
c, T., Dolenc, T., and Novak, F. (1993).
Database model for design data. ACM SIGPLAN OOPS
Messenger, 4(3):26–40.
Schulz, M., Neuhaus, U., Kaufmann, J., Badura, D., Kerzel,
U., Welter, F., Prothmann, M., Kühnel, S., Passlick,
J., Rissler, R., Badewitz, W., Dann, D., Gröschel, A.,
Kloker, S., Alekozai, E. M., Felderer, M., Lanquillon,
C., Brauner, D., Gölzer, P., Binder, H., Rhode, H., and
Gehrke, N. (2020). DASC-PM v1.0 - Ein Vorgehens-
modell für Data-Science-Projekte.
Strohm, O. and Ulich, E., editors (1997). Unternehmen
arbeitspsychologisch bewerten: Ein Mehr-Ebenen-
Ansatz unter besonderer Berücksichtigung von Mensch,
Technik und Organisation, volume 10 of Mensch, Tech-
nik, Organisation. vdf Hochschulverl. an der ETH
Zürich, Zürich.
Sun, C., Zhang, Y., Liu, X., and Wu, F. (2020). Legal In-
telligence: Algorithmic, Data, and Social Challenges.
In Huang, J., Chang, Y., Cheng, X., Kamps, J., Mur-
dock, V., Wen, J.-R., and Liu, Y., editors, Proceedings
of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on
Research and Development in Information Retrieval,
pages 2464–2467, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Szegedy, C., Zaremba, W., Sutskever, I., Bruna, J., Erhan,
D., Goodfellow, I., and Fergus, R. (2013). Intriguing
properties of neural networks.
Tombeil, A.-S., Kremer, D., Neuhüttler, J., Dukino, C., and
Ganz, W. (2020). Potenziale von Künstlicher Intelli-
genz in der Dienstleistungsarbeit. In Bruhn, M. and
Hadwich, K., editors, Automatisierung und Personal-
isierung von Dienstleistungen, Forum Dienstleistungs-
management, pages 135–154. Springer Gabler, Wies-
baden.
Tombeil, A.-S. and Schletz, A. (2020). Prozessmodellierung
als Basis für Innovation der Sachbearbeitung mit Digi-
talisierung und Künstlicher Intelligenz.
Trunzer, E., Kirchen, I., Folmer, J., Koltun, G., and Vogel-
Heuser, B. (2017). A Flexible Architecture for Data
Mining from Heterogeneous Data Sources in Auto-
mated Production Systems. In 2017 IEEE International
Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Piscat-
away, NJ. IEEE.
Weisbecker, A., Zaiser, H., and Wilke, J. (2018). Das
Phänomen "Technik" aus arbeitswissenschaftlicher Per-
spektive. In Zinn, B., Tenberg, R., and Pittich, D., edi-
tors, Technikdidaktik. Franz Steiner Verlag, Stuttgart.
West, M. (2003). Developing High Quality Data Models.
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1062
