
How to Create a Biological Sample Collection: Requirements and
Tips from an Academic Research Example in France
M. Medina Calderon
1,2 a
, C. Viennet
3b
, Y. Pellequer
4c
, F. Aubin
3,5 d
, P. Guillem
6,7 e
,
K. Mouyabi-Nkombo
8
, T. Lihoreau
1,9 f
and G. Rolin
1,3 g
1
Inserm CIC 1431, CHU Besançon, F-25000 Besançon, France
2
UFR Sciences de la Santé, Université de Franche-Comté, Besançon, France
3
Université de Franche-Comté, UMR 1098 RIGHT INSERM EFS, Besançon, France
4
Université de Franche-Comté, EA 4267 PEPITE, Besançon, France
5
Department of Dermatology, University Hospital of Besançon, Besançon, France
6
Department of Surgery, Clinique du Val d'Ouest, Ecully, France
7
RésoVerneuil, Paris, France
8
Department of Clinical Research and Innovation, University Hospital of Besançon, Besançon, France
9
Tech4Health Network - FCRIN, France
Keywords: Clinical Research, Tissue Collection, Biological Sample, Regulatory Approach.
Abstract: This short paper examines the regulatory needs behind the creation of a biological sample collection in France.
Many research projects, including for medical devices development and evaluation, need biological sample
collections, this article’s ambition is to provide a clear view of the requirements to create such collections.
Numerous laws from the Public Health Code frame research in the health sector in France, starting with the
definition of the research type, and going through the various documents needed, especially securing patient
safety (in link with Good Clinical Practices –GCPs) and data protection. To have a better insight into the
requirements to create a biological sample collection, the use of an on-going academic research will help
illustrate our purpose. This research did not involve human subjects, and therefore had a “simplified” path
regarding national competent authority approval, and what is called “reference methodologies”. Even though
the procedure was labelled “simplified”, numerous interactions are required such as with clinicians,
researchers, the clinical investigation center, the hospital research department, and different public
administrations including the Hospital, the Minister of Higher Education, Research and Innovation, the
National Commission for Data Processing and Liberty (CNIL), and the University of Franche-Comté.
1 INTRODUCTION
Collecting biological samples from patients is a key
for investigating and researching diseases and
treatments. A biological sample can refer to biopsies,
fragments of surgical specimens (tumorous or not),
blood, serum, umbilical cord blood, bone marrow,
bone, stem cells, or microorganisms isolated from
patients (https://www.chu-besancon.fr/la-recherche/
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8841-2514
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3538-7837
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4318-974X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1421-4996
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5449-3897
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8417-6609
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6234-869X
faire-de-la-recherche-au-chu/declaration-des-collecti
ons-dechantillons-biologiques.html). It is important
to note that the extraction of samples of tissues and
cells from the human body may only be carried out in
authorised health establishments.
A collection of human biological samples is taken
from a specific group of people identified and
selected according to their clinical or biological
characteristics. This collection must have a scientific
222
Medina Calderon, M., Viennet, C., Pellequer, Y., Aubin, F., Guillem, P., Mouyabi-Nkombo, K., Lihoreau, T. and Rolin, G.
How to Create a Biological Sample Collection: Requirements and Tips from an Academic Research Example in France.
DOI: 10.5220/0011924500003414
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2023) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 222-228
ISBN: 978-989-758-631-6; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

purpose (Légifrance, 2021).
Eventually, a sample collection will help to
understand the changes in tissues and cells related to
a disease, and thus help to develop better treatments,
diagnosis or medical devices specifically designed for
that illness. For exemple PrediMAP an in-vitro
diagnostic medical device in development that uses
collections of vaginal secretions, placenta and
membranes (Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris,
2022).
The law provides a framework for the collection
and conservation of these samples. However, the
creation of the procedure will involve many
interactions with different partners.
In France, the creation of a biological sample
collection requires a clear understanding of the
scientific and regulatory procedures. Therefore, the
French laws regarding the definition of a study and
the different categories of research are the starting
point. Then, to help illustrate the different interactions
the example of a French academic study that intends
to create a tissue and cell collection to further study a
skin disease will be used.
2 DEFINITION OF RESEARCH IN
FRANCE
As mentioned before, the creation of a collection
must have a scientific purpose, and must be part of a
research program, defined as a set of research
activities organized with a goal to facilitate and
accelerate discoveries in a specific scientific field,
defined by an organization carrying out or promoting
research activities (Légifrance, 2021).
In France, research in the health field can be
schematically divided into:
Research “under Jardé law” or Research
projects Involving Human Subjects (RIPH
Recherche Impliquant la Personne Humaine);
Research “outside Jardé law” or Research
projects not Involving Human Subjects.
It is to note that for medical devices, research falls
under the European Union Medical Device
Regulation (MDR) (European Parliament, Council of
the European Union, 2017). These categories will
lead to different procedures regarding the
authorisations required to start a biological sample
collection.
2.1 Research Projects Involving
Human Subjects
The research under Jardé law can be divided into
three different categories, each with their own
specifications according to the article L1121-1 from
the public health code (Légifrance, 2022a) :
“ 1° Interventional research which includes an
intervention on the subject not justified by their
usual treatment;
2° Interventional research involving only
minimal risks and constraints, the list of which
is specified by […] the Minister of health […];
3° Non-interventional research that does not
involve any risks or constraints in which all the
medical acts are performed and the products
are used in the usual way.”
These different studies will later need different
authorisations.
For example, a study falling under 1° (or RIPH 1)
can only be conducted after a favourable opinion
from the Ethical Committee “Committee for the
Protection of Persons” (in France Comités de
Protection des Personnes or CPP) and after
authorisation from the national competent authority
(in France the Agence Nationale de Sécurité du
Médicament et des Produits de Santé or ANSM ). On
the other hand, the studies falling under 2° (or RIPH
2) and 3° (or RIPH 3) only need a favourable opinion
from the CPP. Here, the national competent authority
only needs to be informed of the opinion of the CPP
and sent a summary of the research (Légifrance,
2016).
On the same note, to follow the General Data
Protection Regulation (GDPR or RGPD from French
Règlement Général sur la Protection des Données)
different approaches will be required. To help the
implementation of these regulations the National
Commission for Data Processing and Liberty (CNIL
from French Commission Nationale de l'Informatique
et des Libertés) created reference methodologies (MR
from French Méthodologies de Reference) which
offer a framework for the implementation of research
treatments in the field of health. If the research
complies with these reference methodologies, a
referral to the ethic and scientific committee for
research, studies and evaluations in the field of health
(CESREES from French Comité éthique et
scientifique pour les recherches, les études et les
évaluations dans le domaine de la santé) is not
required. For RIPH the reference methodologies are
MR001 or MR003 (Section 3.3) (https://
www.cnil.fr/).
How to Create a Biological Sample Collection: Requirements and Tips from an Academic Research Example in France
223
2.2 Research Projects not Involving
Human Subjects
Research projects not involving human subjects are
studies that do not meet the definition of research
involving human subjects (section 2.1), in particular
studies relating to the reuse of data. The research must
also be in the public interest or a legitimate interest
(GDPR Info, 2016a).
This collection must also be submitted to the
CNIL and comply with the reference methodology
MR004 (Section 3.3) (Commission Nationale de
l’Informatique et des Libertés, 2018a).
3 TISSUES AND CELL
COLLECTION IN FRANCE
To illustrate the establishment of a biological sample
collection the example of a tissue and cell collection
in an academic research project will be used.
This study aimed to better understand the
biological processes that interfere with the
effectiveness of the local treatment of a skin disease.
The project uses tissue samples from a surgery
performed in the normal treatment of the patients in
the hospital in Besançon and a private clinic in Lyon.
In addition, these tissues, after pathological
examination, are considered as biological operative
waste, meaning that if they were not collected for this
research they would be discarded. It must be noted
that these samples can only be used after approval
from the patient.
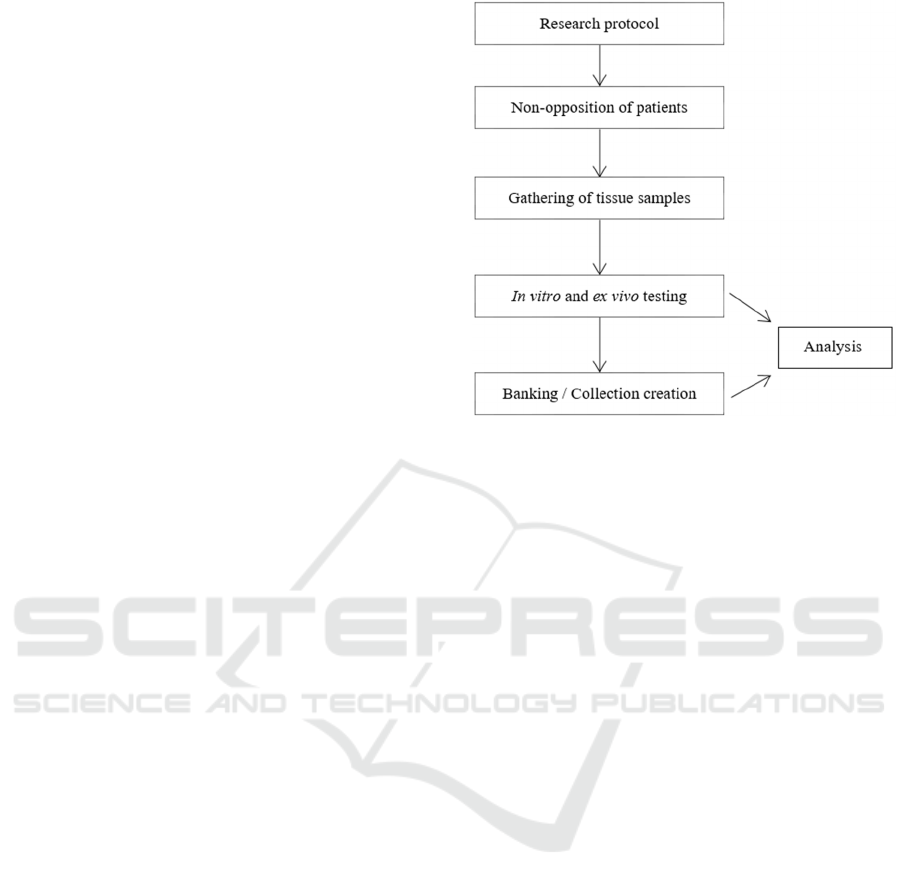
Once the tissue samples have been gathered,
multiple in vitro and ex vivo tests will be performed.
Afterwards, a tissue (microscope slides) and cell
(primary cell culture) collection will be stored in the
university research laboratory. This research will
allow making numerous analyses for this disease
(Figure 1) from data gathered from the initial testing
but also after the collection has been created. It is
important to note that the objective of this collection
it is not to be distributed to other organizations but
only to be used in the research programs of the
institution (if the aim is to distribute the samples to
other organizations other documents are needed).
3.1 French Laws
Tissues, cells and human products removed during a
medical intervention when stored for later use, are
subject to the public health code (CSP from French
Code de la Santé Publique), and more precisely to
Figure 1: Schematic structure of the proposed academic
research and use of tissue samples.
Articles L1241-1 to L1245-8 about “Tissues, cells,
products of the human body and their derivatives”.
(Légifrance, 2022b).
During the establishment of a biological sample
collection within the context of an RIPH, the
collection no longer must be declared to the Ministry
of Higher Education, Research and Innovation
(Figure 2). However, the declaration of these samples
is necessary if they are stored following the study and
if this is the case, a requalification of the collection
before a CPP will be needed (Lemaire, 2019).
If the collection is formed during research
“outside Jardé law”, the collection must be declared
to the Ministry of Higher Education, Research and
Innovation but does not require the opinion of a CPP
(although it is recommended to have an opinion from
a local ethics committee for research).
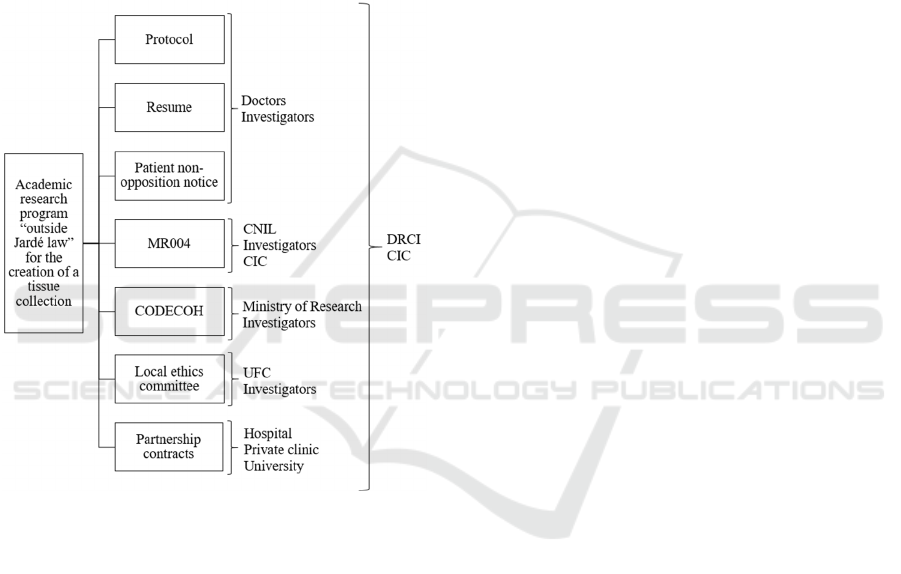
This academic research project is listed as a study
“outside Jardé law”. It will then need (Figure 2):
The approval of the Ministry of Higher
Education, Research and Innovation ;
Compliance with the CNIL Reference
Methodology MR004 (Section 3.3);
A favourable opinion from a local ethics
committee (not mandatory but recommended).
ClinMed 2023 - Special Session on European Regulations for Medical Devices: What Are the Lessons Learned after 1 Year of
Implementation?
224

Figure 2: Non-exhaustive diagram about the requirements
for the creation of a biological sample collection with
research “under Jardé law” and “outside Jardé law”.
3.2 Ministry of Higher Education,
Research and Innovation
To have the approval of the Ministry of Higher
Education, Research and Innovation for the
conservation of elements of the human body a
declaration must be made. This declaration consists
of a letter signed by the legal representative of the
applicant organization and a supporting document.
These two documents must be transmitted to the
Ministry of Higher Education, Research and
Innovation using the online webpage to submit the
files: “CODECOH” (from French COnservation
d'Eléments du COrps Humain) (https://
appliweb.dgri.education.fr/appli_web/codecoh/Ident
Codec.jsp).
The supportive document as explained by the
CODECOH has three essential parts: administrative,
methodologic, and scientific. The administrative part
will provide the basic information of the organization.
The methodologic part however needs the expertise
of field investigators familiar with the structure and
procedures of the laboratory where the samples will
be stored. Lastly, the scientific part guarantees the
compliance with the law; for example justifying the
importance of the envisioned research, data
protection procedures, or patient consent. Overall, the
procedure and information needed for the document
is documented by the Ministry of Higher Education,
Research and Innovation.
After the submission of a complete file, the
Ministry of Higher Education, Research and
Innovation has two months to notify its disagreement.
If there is no feedback during those months, the
project is allowed to start. (Ministère de
l’Enseignement supérieur, recherche et innovation,
2018).
3.3 CNIL
The CNIL is an administrative authority that helps
organizations comply with the RGPD (section 2.1).
This study “outside Jardé law” will need to act in
accordance with the CNIL reference method 004
(Commission Nationale de l’Informatique et des
Libertés, 2018a). To fulfil the MR004, multiple
procedures will have to be considered (Table 1).
This study will only collect the needed
information from the patient, more specifically
information about the progression of the disease and
the drugs the patient administered to treat it.
Additionally, this information will only be used by
the laboratory of the University to create a correlation
between the tissue structures and the progression of
the disease.
Concerning the reference method MR004, the
study must justify in the protocol why this
information about the patient must be collected.
Additionally, a procedure must be put together in
order to protect the privacy and data of the patients:
the information must be anonymised, the
correspondence table (patient-code) must be kept
secure and whoever has access to the information
must be identified from the beginning and be bound
to professional secrecy.
How to Create a Biological Sample Collection: Requirements and Tips from an Academic Research Example in France
225
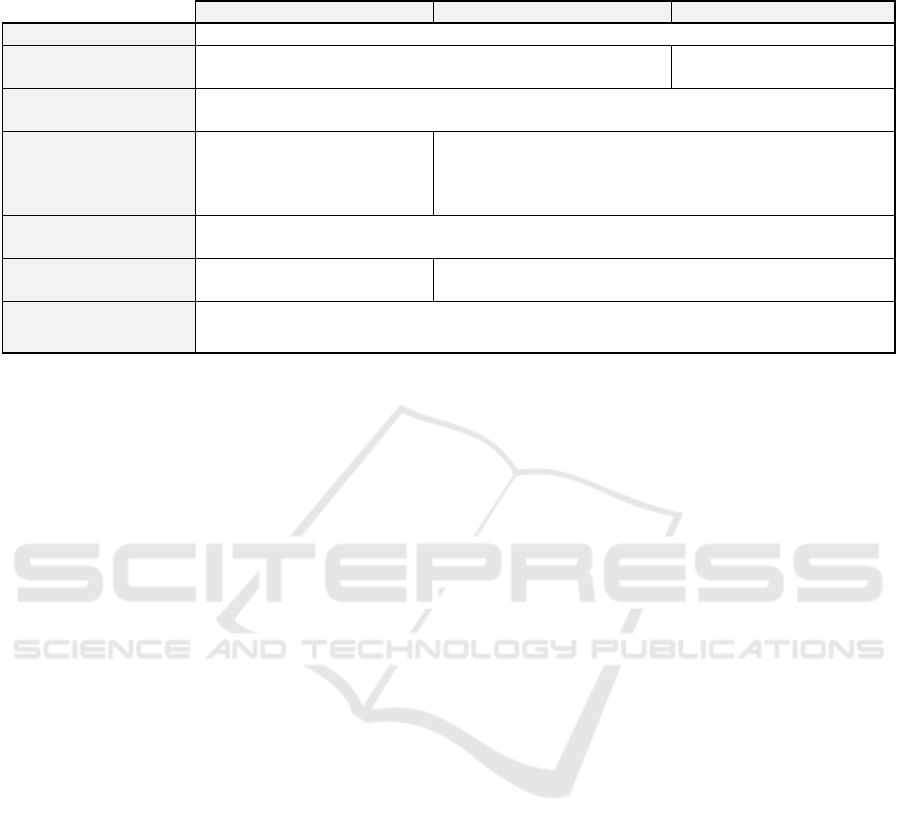
Table 1: Non-exhaustive comparison of the different reference methodologies by the CNIL. (Commission Nationale de
l’Informatique et des Libertés, 2018b).
MR001 MR003 MR004
Data controlle
r
Stud
y
s
p
onso
r
Health Data Hub
registration
No Yes
Patient information
Only necessary information may be collected and a scientific justification in the protocol is
needed.
Duration of data
storage
Until the market launch of the
studied product or the same
duration as MR003 and
MR004.
Two years after the last publication of the research results or
until the release of the final research report.
Access to the data
Clear distinction between accesses to directly and indirectly identifying data. Whoever has
access to the information must be identified and be bound to professional secrecy.
Informing people and
res
p
ectin
g
their ri
g
hts
Written, free and informed
consent from the
p
atient.
Patient does not object to participating after having been
individuall
y
informed.
Security and Privacy
Data protection impact assessment carried out by the data controller.
Implement and monitor the application of a security and confidentiality policy.
Also, for this study, in order to comply with the
provisions of Article 13 of the GDPR (GDPR Info,
2016b), the patient must be notified of the
information that will be collected and its purposes.
Furthermore, the patient must be “not opposed” to the
collection of the biological sample or of data
concerning the disease in order to be included in the
study. For this, a patient information notice and non-
opposition will be written and handed in to the doctor
for the patient.
If information regarding the patient or doctors is
shared in the European Union, the reasons must also
be justified (Commission Nationale de l’Informatique
et des Libertés, 2018a).
3.4 University
The University of Franche-Comté (UFC) not only has
various research laboratories but also an ethical
committee for research.
This research project will take place in the
university laboratories with the required material for
ex vivo and in vitro sample testing and storage of
samples.
Even though is not legally needed to have an ethics
committee’s approval to perform the study, having one
will allow the publication of the study in American
journals too (Lemaire, 2006). The local ethical
committee for research will make sure the patients
included in the study are protected. For example, they
will assess the potential effect on patients, evaluate the
information given to participants, the treatment of
personal data and the potential threat of identification
(https://www.ubfc.fr/en/research/ethical-committee-
for-research/).
3.5 Hospital
The sponsor of this study is the University Hospital
of Besançon. Additionally, the tissue samples used in
this project will be acquired in the hospital and clinic.
The hospital department of Clinical Research and
Innovation (DRCI from French Délégation à la
recherche clinique et à l'innovation) and the Clinical
Investigation Centre (Inserm CIC 1431) have an
undeniable role in the regulatory aspect of the study.
The legally defined purposes of the DRCI are
(Légifrance, 2011) :
“Promotion (organization, administration,
management, control, technical regulatory
support for clinical trials);
Methodological assistance, data management;
and biostatistics (editorial help, clinical trial
design, database management)”.
According to the same legal document
(Légifrance, 2011), the CIC is a research structure of
the hospital that helps to develop studies by relying
on one side on an efficient research environment with
multiple parties and on the other side on the
recruitment of patients.
Thus, the multiple files needed will be handled by
the DRCI and the CIC: protocol, resume, budget,
patient notice, CODECOH, local ethics committee
document and partnership document between
hospital and university but also with the private clinic.
It must be noted that having more than one research
location (in this case hospital, university and private
clinic) will need more procedures regarding storage
and transport of the biological samples but also
legal documents confirming the agreements and
partnerships with the different sites.
ClinMed 2023 - Special Session on European Regulations for Medical Devices: What Are the Lessons Learned after 1 Year of
Implementation?
226
On the same note, it must not be forgotten to
classify the biological sample especially if it could be
an infectious substance and if it might go across
country borders. The rules on storage, packaging and
transportation (Genève : Organisation mondiale de la
Santé, 2019) are to be taken into account for the
protocol, partnership and CODECOH documents.
Overall, writing the protocol needed not only
information exchange with the DRCI and the CIC but
also with the hospital and the clinic doctors, as well
as with the university researchers, in order to provide
a strong clinical and scientific justification (the
“rational” of the study).
Figure 3: List summarizing the documents needed and the
exchanges of information: example from our proposed
academic research.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Biological sample collections are important to help
increase the understanding of a disease and eventually
improve patient care. The process needs to be part of
a clinical study, and as such various procedures and
documents are required to collect biological samples
from patients, posing an entry barrier.
In France, the procedure is regulated in a very
specific way that requires multiple contributors with
different skills in order to complete the project. There
is no “simple” way to obtain approvals, but this work
hopes to facilitate the approach.
It must be noted that this is only an example for a
French study, many of these procedures are not yet
harmonised in the European Union.
Even if there are tools to help identify the
applicable laws (http://campus.ecrin.org/) or to
identify the administrative authorities in the European
countries (such as the national competent authority
(https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/partners-networks/
eu-partners/eu-member-states), the ethics committee
(http://www.eurecnet.org/) or the data protection
authority (https://edpb.europa.eu/about-edpb/about-
edpb/members_en)), the research project’s specific
regulatory requirements need to be evaluated case by
case. Therefore, it is not surprising that the regulatory
needs of a study are dependent on the nature of the
research, the countries involved and the timing of
application of new regulations (the laws regarding
European clinical trials and clinical investigations are
constantly changing and databases might not be up-
to-date yet). Some examples of these complex
procedures can be seen in retrospective studies in
Europe (Houg, Lihoreau, Hennessy, Mouyabi, et al.,
2022), non-interventional studies in the European
Union (Ramirez, 2015) or multinational clinical
investigations for medical devices (Houg, Lihoreau,
Hennessy, Esperou, et al., 2022).
Consequently, for a multicentre and international
study aiming to create a biological sample collection
from different countries, the procedure will have a
tendency to become more complex. The study will
need to comply with multiple competent authorities
and possibly adapt to local requirements too (center
dependant).
REFERENCES
Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris. (2022).
Development and Clinical Evaluation of an Innovative
Medical Device to Predict Preterm Birth: From Basic
Research to Obstetric Emergencies (Clinical Trial
Registration No. NCT05586334). clinicaltrials.gov.
Retrieved from clinicaltrials.gov website: https://
clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05586334
Commission Nationale de l’Informatique et des Libertés.
(2018a, July). Recherches n’impliquant pas la personne
humaine, études et évaluations dans le domaine de la
santé Méthodologie de référence MR-004. Retrieved 18
December 2022, from CNIL website: https://www.
cnil.fr/fr/declaration/mr-004-recherches-nimpliquant-
pas-la-personne-humaine-etudes-et-evaluations-dans-le
Commission Nationale de l’Informatique et des Libertés.
(2018b, July 16). Recherches dans le domaine de la
santé: La CNIL adopte de nouvelles mesures de
simplification. Retrieved 20 December 2022, from
CNIL website: https://www.cnil.fr/fr/recherches-dans-
How to Create a Biological Sample Collection: Requirements and Tips from an Academic Research Example in France
227

le-domaine-de-la-sante-la-cnil-adopte-de-nouvelles-
mesures-de-simplification
GDPR Info. Article 6 RGPD. , Regulation (EU) 2016/679
Règlement général sur la protection des données §
(2016).
GDPR Info. Article 13 RGPD. , Regulation (EU) 2016/679
Règlement général sur la protection des données §
(2016).
Genève : Organisation mondiale de la Santé. (2019). Guide
pratique sur l’application du Règlement relatif au
Transport des matières infectieuses. WHO/WHE/CPI/
2019.20. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/fr/
publications-detail/WHO-WHE-CPI-2019-20
Houg, C., Lihoreau, T., Hennessy, M., Esperou, H.,
Benamore, R., Palussiere, J., & Pazart, L. (2022).
Analysis of Impact of European Medical Device
Regulation and Brexit on the Regulatory Approaches in
a Clinical Investigation Study on a New Class III
Medical Devices Conducted in Europe and United
Kingdom. 250–258. Retrieved from https://www.
scitepress.org/Link.aspx?doi=10.5220/0010968600003
123
Houg, C., Lihoreau, T., Hennessy, M., Mouyabi, K.,
Benamore, R., Palussiere, J., … Pazart, L. (2022).
Regulatory Approaches for a Retrospective Multicentre
Multinational Study on Data: An Example Conducted
in France, Ireland and England. 289–293. Retrieved
from https://www.scitepress.org/Link.aspx?doi=10.52
20/0010971800003123
Légifrance. Circulaire n° DGOS/PF4/2011/329. , Pub. L.
No. DGOS/PF4/2011/329, Circulaires et instructions
Droit national (2011).
Légifrance. Article L1121-4. , Pub. L. No. Article L1121-
4, Code de la santé publique (2016).
Légifrance. Article L1243-3. , Pub. L. No. Article L1243-
3, Code de la santé publique (2021).
Légifrance. Article L1121-1. , Pub. L. No. Article L1121-
1, Code de la santé publique (2022).
Légifrance. Titre IV : Tissus, cellules, produits du corps
humain et leurs dérivés. , Pub. L. No. Articles L1241-1
à L1245-8, Titre IV Code de la santé publique (2022).
Lemaire, F. (2006). Do All Types of Human Research Need
Ethics Committee Approval? American Journal of
Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 174(4), 363–
364. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2603003
Lemaire, F. (2019). La loi Jardé: Ce qui change. La Presse
Médicale, 48(3, Part 1), 238–242. doi: 10.1016/j.
lpm.2019.01.006
Ministère de l’Enseignement supérieur, recherche et
innovation. (2018, août). CODECOH. Retrieved 18
December 2022, from Identification CODECOH
website: https://appliweb.dgri.education.fr/appli_web/
codecoh/IdentCodec.jsp
Ramirez, I. (2015). Navigating the maze of requirements
for obtaining approval of non-interventional studies
(NIS) in the European Union. GMS German Medical
Science, 13, Doc21. doi: 10.3205/000225.
ClinMed 2023 - Special Session on European Regulations for Medical Devices: What Are the Lessons Learned after 1 Year of
Implementation?
228
