
A Recent Publications Survey on Reinforcement Learning for Selecting
Parameters of Meta-Heuristic and Machine Learning Algorithms
Maria Chernigovskaya, Andrey Kharitonov and Klaus Turowski
Faculty of Computer Science, Otto von Guericke University, Magdeburg, Germany
Keywords:
Reinforcement Learning, Deep Reinforcement Learning, Hyper-Parameter Optimization.
Abstract:
Nowadays, meta-heuristic and machine learning algorithms are often used for a variety of tasks in cloud
computing operations. The choice of hyper-parameter values has a direct impact on the performance of
these algorithms, making Hyper-Parameter Optimization (HPO) an important research field for facilitating
the widespread application of machine learning and meta-heuristics for problem-solving. Manual parameter-
ization of these algorithms is an inefficient method, which motivates researchers to look for a new and more
efficient approach to tackle this challenge. One such innovative approach is Deep Reinforcement Learning
(DRL), which has recently demonstrated a lot of potential in solving complex problems. In this work, we
aim to explore this topic more thoroughly and shed light on the application of DRL-based techniques in HPO,
specifically for Machine Learning and Heuristics/Meta-heuristics-based algorithms. We approach the problem
by conducting a systematic literature review of the recently published literature and summarizing the results
of the analysis. Based on the conducted literature review, within the selected sources, we identified 14 relevant
publications and a clear research gap in the cloud-specific use case for HPO via DRL.
1 INTRODUCTION
Modern cloud computing offers a multitude of op-
timization challenges for both providers and clients,
such as various size enterprises. These challenges in-
clude the pursuit of cost, performance, service, and
energy efficiency. These can be tackled with the use
of state-of-the-art meta-heuristics (e.g., virtual ma-
chine consolidation (Pourghebleh et al., 2021)) and
machine learning (ML) (e.g., cloud instance selection
(Samreen et al., 2016)).
Proper selection of the parameter values for such
algorithms is important for both meta-heuristics (Liao
et al., 2015) and ML (Mantovani et al., 2016), because
it can directly influence the quality of the solution and
algorithm’s performance. Manual selection of these
parameters is often difficult and time-consuming (Qi
and Xu, 2022) as it requires an understanding of
both, the algorithm’s internal workings and the prob-
lem. This, in turn, can potentially be a limiting factor
(Paleyes et al., 2022) for the application of these tech-
niques outside of the research community. Numer-
ous ways to tackle this challenge are proposed in the
form of various automatic hyper-parameter optimiza-
tion (HPO) for meta-heuristics (Huang et al., 2020;
Eryoldas¸ and Durmus¸oglu, 2022) and ML (Yang and
Shami, 2020). However, the application of these HPO
techniques does not fully alleviate the challenge of us-
ing state-of-the-art algorithms in real-world business
environments (Paleyes et al., 2022), which warrants
further investigation and research.
This aspect has stimulated increased investiga-
tion into novel methods for the automated optimiza-
tion of hyper-parameter values. Many researchers
have turned their attention to various techniques in
an attempt to identify more efficient ways to tackle
this challenge. Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)
is among such techniques as it have been demon-
strated to be successful in handling various optimiza-
tion problems (Zhang et al., 2022b).
Investigation of DRL-based techniques for tun-
ing hyper-parameters is a promising research topic
for enhancing application efficiency of ML and meta-
heuristics. Especially interesting is the possibility of
exploiting the ability of DRL to instantly infer solu-
tions (Tian et al., 2022), which can significantly in-
crease the efficiency and applicability of HPO in cer-
tain real-world scenarios.
To the best of our knowledge, there are no pub-
lished surveys that offer a thorough overview of the
DRL application for HPO of ML and meta-heuristic
algorithms. The available recent surveys that study
236
Chernigovskaya, M., Kharitonov, A. and Turowski, K.
A Recent Publications Survey on Reinforcement Learning for Selecting Parameters of Meta-Heuristic and Machine Learning Algorithms.
DOI: 10.5220/0011954300003488
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER 2023), pages 236-243
ISBN: 978-989-758-650-7; ISSN: 2184-5042
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

HPO, do not cover the perspectives of the appli-
cation of DRL (Huang et al., 2020; Eryoldas¸ and
Durmus¸oglu, 2022; Yang and Shami, 2020). To ad-
dress this research gap, we present a systematic liter-
ature analysis to summarize the current stand of the
research in this domain and highlight the existing ap-
plications.
Additionally, we outline the selected approaches
and compare their main insights based on the type of
algorithms used and how the key concepts, such as
action space and reward functions, are defined.
2 BACKGROUND
In this chapter, we provide the theoretical background
on the concepts and definitions that are relevant to
our work. In subsection 2.1 we shed light on Hyper-
parameter Optimization (HPO) and its current stand
and challenges. In subsection 2.2 we provide key
definitions of Machine Learning (ML). In subsec-
tion 2.3, we outline the fundamentals behind the con-
cept of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) and give
a brief description of its key components. We con-
clude this section with definitions of Heuristics and
Meta-heuristics in subsection 2.4.
2.1 Hyper-Parameter Optimization
HPO could be defined as the task of finding optimal
hyper-parameter values within a search space com-
prised of valid parameter values in order to improve
the performance of a certain algorithm (Motz et al.,
2022). The process of optimizing, also often referred
to as tuning, hyper-parameters varies amongst differ-
ent algorithms due to the numerous types of hyper-
parameter values, which can be categorical, discrete,
or continuous. Manual parameter value selection is
typical in research but it is a challenging and time-
consuming process, thus automated hyper-parameter
selection became an active research field(Yang and
Shami, 2020).
The primary goal of automated HPO is to sim-
plify the hyper-parameter tuning process and enable
users to efficiently apply parameterized algorithms to
practical problems. Since many HPO problems are
non-convex or non-differentiable optimization prob-
lems, conventional optimization techniques may not
be suited for them and may provide a local rather than
a global optimum. DRL and RL-based techniques are
shown to be effective in solving optimization prob-
lems (N. Xu et al., 2022) and therefore there are at-
tempts to use these for HPO.
2.2 Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) incorporates algorithms that
make decisions or predictions, often based on specific
data, without a need for every detail of such decision-
making to be predefined explicitly. These are par-
ticularly sensitive to the selection of hyper-parameter
values (Yang and Shami, 2020). Depending on the
kind of problem that has to be solved, machine learn-
ing algorithms can be divided into three subcategories
(Agrawal, 2021): Supervised, Unsupervised, and Re-
inforcement Learning.
Supervised learning in ML uses labeled datasets to
train algorithms to precisely categorize inputs or pre-
dict outcomes. It is called supervised because these
algorithms rely on labeled training data to build a
model. In contrast to supervised learning, unsuper-
vised machine learning employs algorithms to an-
alyze and classify unlabeled data. Without human
oversight, these algorithms may find hidden patterns
in data and infer relationships between different fea-
tures in the data. The third type of ML is Reinforce-
ment Learning. Reinforcement Learning (RL) algo-
rithm learns from its environment and generally does
not require training data. Hyperparameters in ML are
diverse and vary from algorithm to algorithm.
Important subclass of ML approaches, called
Deep Learning (DL) (LeCun et al., 2015), is worth
mentioning specifically since it presents particular
HPO problems. DL is an area of ML, based on the
use of artificial neural networks, and is specifically
concerned with deep neural networks (DNN), which
can be used in all three aforementioned ML types.
Number of hidden neuron layers and the number of
neurons in each layers, are primary hyper-parameters
examples of DL models (Yang and Shami, 2020).
Each type of ML algorithm has different key
hyper-parameters that must be tuned. For super-
vised Learning algorithms such as k-nearest neigh-
bors (KNN), the number of considered nearest neigh-
bors, k is the most important hyper-parameter. In
Unsupervised Learning, many clustering algorithms
like k-means, the expectation-maximization (EM) al-
gorithm, and hierarchical clustering — the number of
clusters is the most crucial hyper-parameter to tune
(Yang and Shami, 2020). For RL algorithms, the crit-
ical hyper-parameters to tune are Learning rate (α)
and Gamma (γ). The first one, α, allows the agent
to learn faster about its environment, but it may pre-
vent it from exploring the space of possibilities, γ, on
the other hand, helps agent to develop optimal ac-
tion strategies by teaching it to prioritize immediate
rewards versus future rewards (Sun, 2017).
A Recent Publications Survey on Reinforcement Learning for Selecting Parameters of Meta-Heuristic and Machine Learning Algorithms
237

2.3 Deep Reinforcement Learning
The goal of RL is to determine the best behavior for
an agent while it is exploring a given environment by
interacting with it (Asadulaev et al., 2020). The en-
vironment can be an interface or a representation of
a system or an optimization problem. Recently RL
gained interest in research due to a number of ad-
vancements in the area, specifically in the subset of
RL algorithms commonly named as Deep Reinforce-
ment Learning (Alves and Mateus, 2020).
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) is an ML
technique that combines RL and DL. The fundamen-
tal DRL mechanism is, in principle, identical to RL
and consists of an iterative process in which the agent
observes the state of the environment within its ob-
servation space and acts in accordance with the state,
the environment transitions to a new state as a result
of the agent’s action, and the agent receives feedback
(reward). The agent’s goal is to maximize the reward
(Alves and Mateus, 2020).
DRL implementations may be classified into three
categories based on the type of supported action
space: discrete action space, continuous action space,
and discrete-continuous (hybrid) action space (Zhu
et al., 2021). In the discrete action space, we can pre-
cisely quantify the number of possible options. The
number of options in the continuous action space is
not pre-defined as a closed set, but defined as a value
range. For discrete-continuous (hybrid) action spaces,
the algorithm should generate discrete actions as well
as the continuous parameters performed by the dis-
crete actions (Zhu et al., 2021). This distinction is
important for HPO problems because the nature of
the tuned parameters can fall into any of these three
categories.
Published surveys (Arulkumaran et al., 2017;
Wang et al., 2022b) discuss various specific examples
of algorithms that fall into the aforementioned cate-
gories. Q-Learning and Q-learning-based algorithms
such as Deep Q-Network (DQN) are well suited for
discrete action spaces. Proximal Policy Optimization
(PPO) and Policy Gradient methods (e.g., Deep De-
terministic Policy Gradient (DDPG)) handle continu-
ous action spaces. Algorithms such as Asynchronous
Advantage Actor Critic (A3C) and Advantage Actor
Critic (A2C) belong to the hybrid type.
2.4 Heuristics and Meta-Heuristics
Heuristics are optimization methods that are designed
for a specific problem and try to exploit problem-
specific knowledge. They do not attempt to find an
optimal solution but focus on producing optimum so-
lution procedures. Two types of heuristics are de-
fined in the literature(Rothlauf, 2011): Construction
and Improvement heuristics.
Construction heuristics develop a solution from
the ground up step-wise, where components of the so-
lution are fixed at every step. Improvement heuristics
start with a complete solution and iteratively aim to
enhance it (Rothlauf, 2011).
Meta-heuristic algorithms are a set of techniques
used to address complicated optimization problems.
Usually, researchers distinguish three types of meta-
heuristic techniques: based on the local search algo-
rithm (Tabu search, simulated annealing), evolution-
ary computing (genetic algorithms), or swarm intelli-
gence (Ant colony optimization, particle swarm opti-
mization (PSO)) (Pereira et al., 2021). Each of these
meta-heuristic algorithms has critical parameters that
need to be tuned in order for these algorithms to work
optimally. In the case of the GA, three numeric pa-
rameters are usually considered of the most impor-
tance: population size, mutation rate, and crossover
rate (Eryoldas¸ and Durmus¸oglu, 2022). For PSO, crit-
ical hyper-parameters are particle number m, acceler-
ate constant c
1
and c
2
, inertia weight w, and maxi-
mum limited velocity v
max
(He et al., 2016).
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
The core of this study is a systematic literature review
that gives an overview of recent publications that ap-
ply DRL-based (or RL-based) approaches to address
HPO concerns. We begin this section with a descrip-
tion of the applied literature survey methodology in
subsection 3.1. As a result, a number of relevant stud-
ies is identified and evaluated to provide a summary
of the current state of the research in subsection 3.2.
Additionally, in subsection 3.3, we discuss a couple
of publications that fall outside of the survey’s criteria
but still present concepts potentially relevant to HPO
with DRL.
3.1 Methodology
To identify the current state of the research on hyper-
parameter tuning using DRL and RL, we conduct a
systematic literature review. The search for the rel-
evant papers is performed using the following aca-
demic research databases: ScienceDirect
1
, Springer
2
,
ACM
3
and IEEE
4
. We focus on the publications that
1
https://www.sciencedirect.com
2
https://link.springer.com
3
https://dl.acm.org
4
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
238

apply DRL or RL for hyper-parameter tuning for ML
and Meta-heuristics (or Heuristics). The focus of this
work is recent research on DRL in HPO; therefore,
only works published since 2017 were considered for
all DRL-related queries. The range for RL-based
approaches is extended to include works published
since 2015. In our research, we also applied forward
and backward searches. Additionally, only accessi-
ble, peer-reviewed publications written in the English
language were considered.
To conduct a systematic literature analysis for the
selected topic, four categories of the research were
defined:
• DRL for HPO of Heuristics and Meta-heuristics
• RL for HPO of Heuristics and Meta-heuristics
• DRL for HPO of ML
• RL for HPO of ML
To narrow down the most relevant papers, three filter-
ing phases were carried out for each category. First,
all papers with relevant titles were selected for each
category. Secondly, the abstract relevance of the
remaining papers was examined. Lastly, we thor-
oughly researched the entire contents of the remain-
ing papers to select the relevant candidates. Addition-
ally, the differences in spelling of terms like hyper-
parameters (e.g., hyperparameters or hyper parame-
ters) and meta-heuristics (e.g., metaheuristics or meta
heuristics) are considered. Worth mentioning that all
variations of spelling are present in the published lit-
erature.
For each defined category, we came to the follow-
ing results:
• DRL for HPO of Heuristics and Meta-heuristics -
Out of the 28 papers that were initially taken into
consideration, 3 were deemed relevant
• RL for HPO of Heuristics and Meta-heuristics -
Out of the 21 papers that were initially taken into
consideration, 1 was deemed relevant
• DRL for HPO of ML - Out of the 50 papers
that were initially taken into consideration, 8 were
deemed relevant
• RL for HPO of ML - Out of the 19 papers that
were initially taken into consideration, 2 were
deemed relevant
Furthermore, in the process of assessing the relevance
of publications, the inclusion and exclusion criteria
are defined.
All publications, where the authors implement
concepts of DRL (RL) in HPO for meta-heuristics and
ML algorithms and demonstrate their results, were in-
cluded. Likewise, the authors that present more con-
ceptual and theoretical background on the HPO con-
cept and provide in-depth definitions of relevant DRL
components like state space (observation space), ac-
tion space, and reward function, those papers are also
considered in the literature analysis, since they may
offer interesting insights for our research.
If the key concepts such as DRL, RL, and HPO
were not presented and important definitions such as
state space, action space, and reward function were
missing – those papers were excluded. Moreover,
publications with HPO approaches, which are not
based on DRL (RL) algorithms or where no HPO ap-
proach is implemented, were not considered by us.
The same exclusion strategy we follow with the pa-
pers whose main topic was irrelevant to our litera-
ture survey, therefore they don’t offer any valuable
insights.
3.2 Literature Analysis
In this section, we summarise the results of the con-
ducted literature analysis. The reviewed publications
are divided into four categories in order to discuss the
findings methodically. The presented categorization
is based on two factors, particularly, which solution
approach was used in chosen publications, whether it
is a DRL-based or RL-based approach and to what
type of algorithms were these solutions applied: to
ML algorithms or heuristics and meta-heuristics al-
gorithms.
In the analyzed literature, various approaches have
been used to tune the parameters of meta-heuristic,
heuristics, and ML algorithms using DRL or RL. Re-
sults of the literature are summarized in the Table 1,
including mentioning type of the action space and
used base algorithm.
For instance, (Zhang et al., 2022b) in their work
propose a DRL-based framework in order to solve
combinatorial problems. The presented framework
is based on a heuristic method that uses a Dou-
ble Deep Q-network (DDQN) algorithm (Marchesini
et al., 2019). The authors define the action space
as a set of parameterized heuristics that could be ad-
justed in order to get the desired performance. A sim-
ilar approach takes (Dong et al., 2021), which uses
Deep Q-Learning (DQN) (Mnih et al., 2015) to op-
timize hyper-parameters of the proposed heuristics-
based framework for visual object tracking. The au-
thors define the action space as the adjustment of the
hyper-parameter numeric values in a continuous man-
ner. The author’s proposed approach demonstrates
high accuracy of the performance in comparison with
chosen methods. A further example of applying DRL
to optimizing parameters of meta-heuristics is pre-
A Recent Publications Survey on Reinforcement Learning for Selecting Parameters of Meta-Heuristic and Machine Learning Algorithms
239
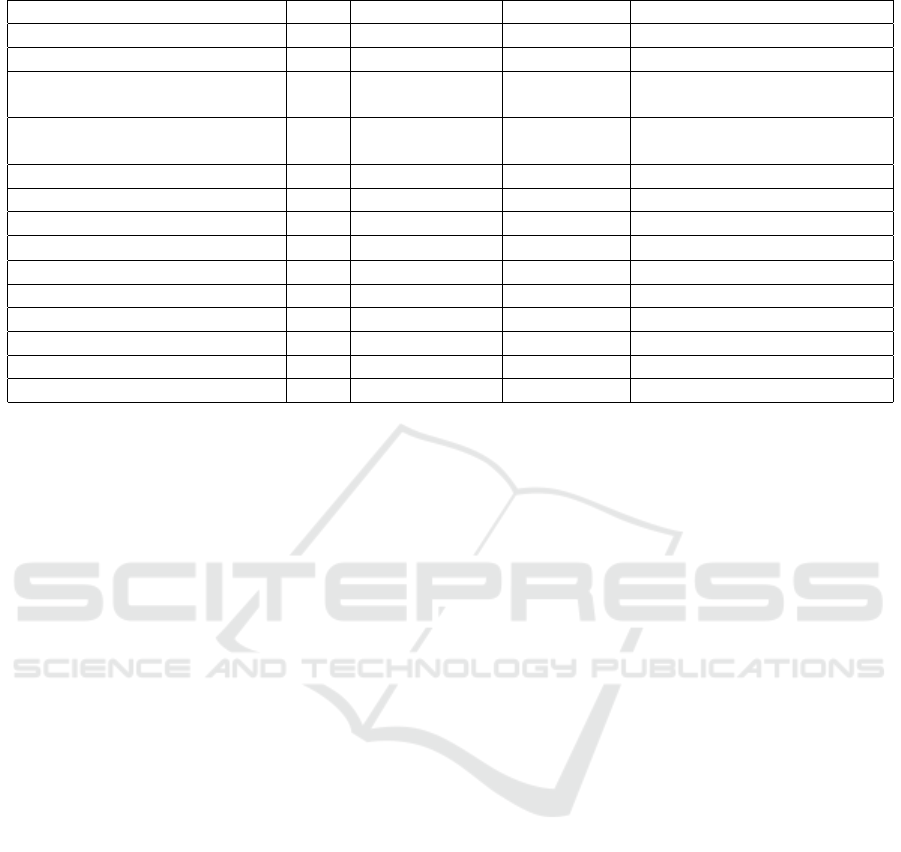
Table 1: Literature analysis summary.
Publication Type Tuning Action space Base algorithm
(Zhang et al., 2022b) DRL Heuristics Discrete Double Deep Q-network
(Qi and Xu, 2022) RL ML Discrete Q-learning
(N. Xu et al., 2022) DRL ML Discrete
Attention and Memory
Enhancement
(Zhang et al., 2022a) DRL ML Discrete
Twin Delayed Deep
Deterministic Policy Gradient
(Wang et al., 2022a) RL ML Discrete Q-learning
(Dong et al., 2021) DRL Heuristics Continuous Continuous Deep Q-learning
(Wan et al., 2021) DRL ML Continuous Double Deep Q-network
(Mills et al., 2021) DRL ML Continuous L
2
NAS
(de Santiago J
´
unior et al., 2020) RL Meta-Heuristics Not defined Not defined
(Liu et al., 2020) RL ML Continuous Proximal Policy Optimization
(S. Chen et al., 2019) DRL ML Discrete Policy Gradient
(Sharma et al., 2019) DRL Meta-Heuristics Discrete Double Deep Q-Learning
(WU et al., 2019) DRL ML Discrete Policy Gradient
(P. Neary, 2018) RL ML Discrete Not defined
sented by the authors of (Sharma et al., 2019) for con-
trolling mutation strategies of an evolutionary algo-
rithm.
RL-based approaches can also be successfully ap-
plied to heuristics and meta-heuristics algorithms for
solving HPO problems. For example, (de Santiago
J
´
unior et al., 2020) presents an innovative approach
for solving parameter optimization problems by com-
bining meta-heuristics and RL-based algorithms. The
action space is defined by authors as a set of low-
level heuristics and reward is designed as as reward
or penalties based on its performance.
A good example of the RL application for ML al-
gorithms would be the work of (Qi and Xu, 2022). In
their research, authors apply a Q-learning-based al-
gorithm (Sun, 2017) to optimize the hyper-parameter
tuning strategy in a Deep Learning approach. They
define action space as discrete, where only one hyper-
parameter is tuned at a time, and the reward func-
tion as the difference between the evaluation metric of
neural network models before hyper-parameter tun-
ing and the current one. A further example (Wang
et al., 2022a) of HPO in ML optimization is also rely-
ing on Q-Learning but for selecting optimal Spatial-
Temporal Graph Convolutional Network models for a
given problem. For this purpose, the authors present
a way to construct a network model from predefined
blocks and attempt to automate the construction pro-
cess by employing an RL algorithm.
An illustration of applying DRL to ML models
would be the work of (S. Chen et al., 2019). The au-
thors propose an architecture based on DRL, which
should be able to optimize hyper-parameters for any
ML model using Policy Gradient Algorithm (Parisi
et al., 2014). They approach the problem by creat-
ing a DRL agent which can automatically select the
optimal hyper-parameters for ML models on a given
dataset. Another approach takes (Wan et al., 2021),
where the authors propose an HPO method based on
DRL, which is used to balance image service quality
and privacy protection. The authors present a method
where a Neural Network is trained as an agent to find
the best hyper-parameter adjustment. To tackle the
problem, they use the Double Deep Q-network al-
gorithm (DDQN). Another example of searching for
optimal neural network hyper-parameters is presented
in (Mills et al., 2021). In that work, authors present
a DRL-based L
2
NAS algorithm, which employs an
actor neural network to automatically optimize and
update architecture hyper-parameters within an actor-
critic algorithm. For the presented approach, authors
define an action as a continuous architecture hyper-
parameter, which is then deterministically mapped
into a discrete one. An interesting approach in au-
tomatically determining the best clustering parame-
ters take (Zhang et al., 2022a). The authors propose
a parameter search framework based on the Twin De-
layed Deep Deterministic strategy gradient algorithm
(TD3), where a DRL agent attempts to find the best
parameter values of a classic ML-based clustering al-
gorithm by taking discrete actions for increasing or
decreasing individual continuous values of the algo-
rithm’s parameters. Another instance of DRL being
applied to ML models is the work of (WU et al.,
2019). In their research, the authors present a DRL-
based architecture where they create an agent that se-
lects a set of hyper-parameters and uses the accuracy
of an ML model as a reward signal to update its pa-
rameters. The authors define the action space as a
set of decisions where each decision corresponds to a
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
240

selection of a hyper-parameter. A similar approach is
taken by authors of (N. Xu et al., 2022). In their work,
the authors introduce a configuration searcher to se-
lect appropriate hyper-parameters for ML models. To
enhance the performance of the proposed searcher, a
new Attention and Memory Enhancement (AME) al-
gorithm is developed to tackle the problem of opti-
mizing all types of hyper-parameters. Similarly to
previous work, this is also a DRL-based algorithm.
The authors define the action space for the problem
as a set of new configurations, one of which the agent
picks from search space and the reward function as
the evaluation of the taken action.
The RL-based approaches can also be successfully
used for tuning ML models. An interesting exam-
ple of it would be the work of (Liu et al., 2020).
The authors in their research present a model-based
Reinforcement Learning for solving HPO problems.
The action space for the designed research objective
is defined as a set of hyper-parameter configurations
to tune. The authors describe the reward function as
the accuracy of a validation set. A similar approach
takes (P. Neary, 2018). The authors present an Asyn-
chronous Reinforcement Learning algorithm to set
optimal neural network configurations by adjusting its
hyper-parameters. The authors define the state space
for the presented problem as a network architecture,
the action space as a set of hyper-parameters to tune,
and the reward function as the accuracy achieved by
changing a single hyper-parameter while keeping all
others fixed.
3.3 Conceptually Related Research
In addition to the previously discussed works, we dis-
covered two publications that are dedicated to the
optimization of parameterization in real-world sys-
tems. While these papers are not directly connected
to the application of DRL for HPO for ML and Meta-
heuristics, the insights they provide are potentially in-
teresting within the scope of our research.
(Lindstah and Lan, 2020) in their work combine
Imitation and Reinforcement Learning in order to ef-
ficiently tune hyper-parameters of cavity filters. The
action space is defined as a set of screw adjustments
in a specific range. Therefore the adjustments are rep-
resented as continuous values. The reward is defined
by the authors as a heuristic function of the error after
the adjustment.
(Tom
´
e De Andrade e Silva, Manuel and Azevedo,
2022) in their research investigating the potential of
dynamical adjustment of work in process (WIP) cap
limits. The authors approach the problem by applying
the PPO algorithm to minimize the WIP levels with-
out reducing production’s throughput performance.
The action space is discrete and defined as the set of
natural numbers, which represent the WIP cap(limit)
to be applied to the production system.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the findings of our research, we can con-
clude that the number of publications attempting to
use DRL-based techniques is quite low, especially for
HPO for Heuristics and Meta-heuristics. In fact, only
14 papers are considered relevant as they address the
topic of selection of optimal parameter values within
meta-heuristic, conventional ML, and deep learning
algorithms, as well as a selection of the most appro-
priate parameterized heuristics. Discovered relevant
publications present various approaches for parame-
terization of the algorithms to fit an optimization or
data processing problem at hand, including the ways
to tackle the challenge of discretization of continu-
ous parameter values to fit specific RL and DRL tech-
niques.
Additionally, the reviewed publications demon-
strate that various DRL-based algorithms may be suit-
able for solving HPO problems. Within the discov-
ered relevant publications, the authors demonstrate
that it can be advantageous to use DRL techniques
in HPO to achieve higher performance in comparison
with the conventional techniques (e.g., Bayesian opti-
mization and Random Search), which they chose as
a baseline. This, coupled with the relatively small
amount of discovered relevant publications, merits
further systematic investigation of the DRL applica-
tion in HPO problems. The discovered publications
do not concentrat on optimization problems oriented
to cloud operations or any specific use-case, which
indicates a research gap.
Another interesting observation is that the action
space is often defined by the authors as a set of hyper-
parameters to adjust for ML algorithms and as a set of
heuristics (meta-heuristics) for Heuristics and Meta-
heuristics algorithms. Additionally, in the case of
ML, the Reward function is commonly characterized
as the accuracy gained by each adjustment of the
hyper-parameters.
5 FUTURE WORK
The next step of the research is the formulation of
observation spaces, action spaces, and reward func-
tions for DRL to solve HPO problems for algorithms
typically present in cloud operations research. These
A Recent Publications Survey on Reinforcement Learning for Selecting Parameters of Meta-Heuristic and Machine Learning Algorithms
241

include, but are not limited to, virtual machine con-
solidation (Varasteh and Goudarzi, 2017) and cloud
service composition (Vakili and Navimipour, 2017)
based on heuristic or meta-heuristic algorithms, cloud
security enhancement via machine learning (Nassif
et al., 2021). DRL implementations of HPO for such
problems are then to be compared against the tra-
ditional HPO approaches (Yang and Shami, 2020;
Huang et al., 2020) in order to determine the advan-
tages and disadvantages of applying one or another
in the cloud operations-related HPO problems. At
the same time, it would be prudent to investigate ap-
plying a tuning technique to the DRL approach used
for HPO itself to increase training efficiency in look-
ing for optimal deep neural network architecture, and
hyper-parameters (Wang et al., 2021).
REFERENCES
Agrawal, T. (2021). Hyperparameter Optimization in Ma-
chine Learning. Apress, Berkeley, CA.
Alves, J. C. and Mateus, G. R. (2020). Deep reinforcement
learning and optimization approach for multi-echelon
supply chain with uncertain demands. In Lalla-Ruiz,
E., Mes, M., and Voss, S., editors, Computational Lo-
gistics, volume 12433 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 584–599. Springer, Cham.
Arulkumaran, K., Deisenroth, M. P., Brundage, M., and
Bharath, A. A. (2017). Deep reinforcement learning:
A brief survey. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,
34(6):26–38.
Asadulaev, A., Kuznetsov, I., Stein, G., and Filchenkov, A.
(2020). Exploring and exploiting conditioning of re-
inforcement learning agents. IEEE Access, 8:211951–
211960.
de Santiago J
´
unior, V. A.,
¨
Ozcan, E., and de Carvalho,
V. R. (2020). Hyper-heuristics based on reinforcement
learning, balanced heuristic selection and group deci-
sion acceptance. Applied Soft Computing, 97:106760.
Dong, X., Shen, J., Wang, W., Shao, L., Ling, H., and
Porikli, F. (2021). Dynamical hyperparameter opti-
mization via deep reinforcement learning in tracking.
IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine
intelligence, 43(5):1515–1529.
Eryoldas¸, Y. and Durmus¸oglu, A. (2022). A literature sur-
vey on offline automatic algorithm configuration. Ap-
plied Sciences, 12(13):6316.
He, Y., Ma, W., and Zhang, J. (2016). The parame-
ters selection of pso algorithm influencing on perfor-
mance of fault diagnosis. MATEC Web of Confer-
ences, 63:02019.
Huang, C., Li, Y., and Yao, X. (2020). A survey of
automatic parameter tuning methods for metaheuris-
tics. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computa-
tion, 24(2):201–216.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learn-
ing. Nature, 521(7553):436–444.
Liao, T., Molina, D., and St
¨
utzle, T. (2015). Performance
evaluation of automatically tuned continuous optimiz-
ers on different benchmark sets. Applied Soft Comput-
ing, 27:490–503.
Lindstah, S. and Lan, X. (2020). Reinforcement learn-
ing with imitation for cavity filter tuning. In 2020
IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced
Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), pages 1335–1340,
[Piscataway, NJ]. IEEE.
Liu, X., Wu, J., and Chen, S. (12/14/2020 - 12/16/2020). Ef-
ficient hyperparameters optimization through model-
based reinforcement learning and meta-learning. In
2020 IEEE 22nd International Conference on High
Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE
18th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE
6th International Conference on Data Science and
Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), pages 1036–1041.
IEEE.
Mantovani, R. G., Horv
´
ath, T., Cerri, R., Vanschoren, J.,
and Carvalho, A. C. d. (2016). Hyper-parameter
tuning of a decision tree induction algorithm. In
2016 5th Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems
(BRACIS), pages 37–42.
Marchesini, E., Corsi, D., Benfatti, A., Farinelli, A., and
Fiorini, P. (2019). Double deep q-network for trajec-
tory generation of a commercial 7dof redundant ma-
nipulator. In 2019 Third IEEE International Confer-
ence on Robotic Computing (IRC), pages 421–422.
Mills, K. G., Han, F. X., Salameh, M., Changiz Rezaei,
S. S., Kong, L., Lu, W., Lian, S., Jui, S., and Niu,
D. (2021). L2nas: Learning to optimize neural archi-
tectures via continuous-action reinforcement learning.
In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Con-
ference on Information & Knowledge Management,
CIKM ’21, page 1284–1293, New York, NY, USA.
Association for Computing Machinery.
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Rusu, A. A., Veness,
J., Bellemare, M. G., Graves, A., Riedmiller, M., Fid-
jeland, A. K., Ostrovski, G., et al. (2015). Human-
level control through deep reinforcement learning.
Nature, 518(7540):529–533.
Motz, M., Krauß, J., and Schmitt, R. H. (2022). Bench-
marking of hyperparameter optimization techniques
for machine learning applications in production. Ad-
vances in Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering,
5:100099.
N. Xu, J. Chang, X. Nie, C. Huo, S. Xiang, and C. Pan
(2022). Ame: Attention and memory enhancement
in hyper-parameter optimization. In 2022 IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion (CVPR), pages 480–489.
Nassif, A. B., Talib, M. A., Nasir, Q., Albadani, H., and
Dakalbab, F. M. (2021). Machine learning for cloud
security: A systematic review. IEEE Access, 9:20717–
20735.
P. Neary (2018). Automatic hyperparameter tuning in deep
convolutional neural networks using asynchronous re-
inforcement learning. In 2018 IEEE International
Conference on Cognitive Computing (ICCC), pages
73–77.
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
242

Paleyes, A., Urma, R.-G., and Lawrence, N. D. (2022).
Challenges in deploying machine learning: A survey
of case studies. ACM Comput. Surv., 55(6).
Parisi, S., Pirotta, M., Smacchia, N., Bascetta, L., and
Restelli, M. (2014). Policy gradient approaches for
multi-objective sequential decision making: A com-
parison. In 2014 IEEE Symposium on Adaptive
Dynamic Programming and Reinforcement Learning
(ADPRL), pages 1–8.
Pereira, I., Madureira, A., Costa e Silva, E., and Abraham,
A. (2021). A hybrid metaheuristics parameter tun-
ing approach for scheduling through racing and case-
based reasoning. Applied Sciences, 11(8):3325.
Pourghebleh, B., Aghaei Anvigh, A., Ramtin, A. R., and
Mohammadi, B. (2021). The importance of nature-
inspired meta-heuristic algorithms for solving vir-
tual machine consolidation problem in cloud environ-
ments. Cluster Computing, 24(3):2673–2696.
Qi, X. and Xu, B. (2022). Hyperparameter optimization of
neural networks based on q-learning. Signal, Image
and Video Processing.
Rothlauf, F. (2011). Application and Adaptation of
Heuristic Optimization Methods. Natural Computing.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg.
S. Chen, J. Wu, and X. Chen (2019). Deep reinforcement
learning with model-based acceleration for hyperpa-
rameter optimization. In 2019 IEEE 31st International
Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (IC-
TAI), pages 170–177.
Samreen, F., Elkhatib, Y., Rowe, M., and Blair, G. S.
(2016). Daleel: Simplifying cloud instance selec-
tion using machine learning. In NOMS 2016 -
2016 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Manage-
ment Symposium, pages 557–563.
Sharma, M., Komninos, A., L
´
opez-Ib
´
a
˜
nez, M., and Kaza-
kov, D. (2019). Deep reinforcement learning based
parameter control in differential evolution. In Pro-
ceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computa-
tion Conference, GECCO ’19, page 709–717, New
York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Machin-
ery.
Sun, C. (2017). Fundamental q-learning algorithm in find-
ing optimal policy. In 2017 International Conference
on Smart Grid and Electrical Automation (ICSGEA),
pages 243–246.
Tian, Y., Chao, M. A., Kulkarni, C., Goebel, K., and Fink,
O. (2022). Real-time model calibration with deep re-
inforcement learning. Mechanical Systems and Signal
Processing, 165:108284.
Tom
´
e De Andrade e Silva, Manuel and Azevedo, A. (2022).
Self-adapting wip parameter setting using deep re-
inforcement learning. Computers & Operations Re-
search, 144:105854.
Vakili, A. and Navimipour, N. J. (2017). Comprehen-
sive and systematic review of the service composition
mechanisms in the cloud environments. Journal of
Network and Computer Applications, 81:24–36.
Varasteh, A. and Goudarzi, M. (2017). Server consolidation
techniques in virtualized data centers: A survey. IEEE
Systems Journal, 11(2):772–783.
Wan, J., Cao, Z., Ma, Y., Zhao, G., and Sun, Z. (2021).
A parameter selection method based on reinforce-
ment learning: The qos-privacy trade-off for adver-
sarial training framework. In Sun, X., editor, Ad-
vances in artificial intelligence and security, volume
1422 of Communications in computer and informa-
tion science, 1865-0929, pages 338–350. Springer,
Cham, Switzerland.
Wang, C., Zhang, K., Wang, H., and Chen, B. (2022a).
Auto-stgcn: Autonomous spatial-temporal graph con-
volutional network search. ACM Trans. Knowl. Dis-
cov. Data. Just Accepted.
Wang, X., Wang, S., Liang, X., Zhao, D., Huang, J., Xu, X.,
Dai, B., and Miao, Q. (2022b). Deep reinforcement
learning: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Neural Net-
works and Learning Systems, pages 1–15.
Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Li, Y., Gong, Q., Luo, W., and Zhao,
J. (2021). Automated reinforcement learning based
on parameter sharing network architecture search. In
2021 6th International Conference on Robotics and
Automation Engineering (ICRAE 2021), pages 358–
363, Piscataway, NJ. IEEE.
WU, J., CHEN, S., and CHEN, X. (2019). Rpr-bp: A deep
reinforcement learning method for automatic hyper-
parameter optimization. In 2019 International Joint
Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pages 1–8.
Yang, L. and Shami, A. (2020). On hyperparameter opti-
mization of machine learning algorithms: Theory and
practice. Neurocomputing, 415:295–316.
Zhang, R., Peng, H., Dou, Y., Wu, J., Sun, Q., Li, Y.,
Zhang, J., and Yu, P. S. (2022a). Automating db-
scan via deep reinforcement learning. In Proceed-
ings of the 31st ACM International Conference on
Information & Knowledge Management, CIKM ’22,
page 2620–2630, New York, NY, USA. Association
for Computing Machinery.
Zhang, Y., Bai, R., Qu, R., Tu, C., and Jin, J. (2022b). A
deep reinforcement learning based hyper-heuristic for
combinatorial optimisation with uncertainties. Euro-
pean Journal of Operational Research, 300(2):418–
427.
Zhu, J., Wu, F., and Zhao, J. (2021). An overview of the ac-
tion space for deep reinforcement learning. In 2021
4th International Conference on Algorithms, Com-
puting and Artificial Intelligence (ACAI 2021), ICPS,
pages 1–10, New York, New York. The Association
for Computing Machinery.
A Recent Publications Survey on Reinforcement Learning for Selecting Parameters of Meta-Heuristic and Machine Learning Algorithms
243
