
Blended Approach for Deep Learning: A Framework for Teaching
Undergraduate Computer Programming Courses
Mohammad Tafiqur Rahman
Department of Business, Marketing, and Law, University of South-Eastern Norway, Norway
Keywords: Blended Approach, Computer Programming Courses, Deep Learning, Flipped Classroom, Knowledge
Construction, University Pedagogy, TEE Approach, Traditional Teaching.
Abstract: Teaching computer programming (CP) courses demands cutting-edge course practicalities that include (i)
updated course design with adequate content, (ii) modern pedagogy-enabled course conduction, and (iii)
course completion with adequate practically implementable knowledge. However, meeting such requirements
is not possible only through the traditional teaching (TT) approach, nor by any specific or individual ap-
proaches practiced in modern teaching. We need combined approaches to meet learners’ desires and industry
needs. I propose a teaching framework that blends traditional and flipped classroom (FC) approaches to fa-
cilitate deep learning toward essential knowledge construction on CP and provide practical experiences for
software system development. In the proposed framework, the TT approach emphasizes theoretical under-
standing, whereas the FC approach focuses on active engagement, active participation, and active learning.
The TEE (theory-example-exercise) approach binds the chosen approaches together, where the theory part is
handled in the TT approach, and the example and exercise parts are processed in the FC approach. Since I
successfully applied this blended approach framework to teaching undergraduate CP courses at a Norwegian
university, I believe it will be suitable not only for courses in this discipline but also in other disciplines with
necessary modifications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Technological advancement has introduced many op-
portunities to our daily life—from waking up in the
morning to going to bed at night, our daily activities
are, somehow, affected by digital tools. The educa-
tion sector is not outside that trend. Rather, it is the
most emergent area for digital development (Lundin
et al., 2018; O’Flaherty & Phillips, 2015). Exploring
and analyzing the technology-rich teaching and learn-
ing environment is essential to identifying different
challenges and opportunities for designing new
courses or upgrading old ones (Divjak et al., 2022).
Thus, learning computer programming (CP) is now
treated as a requirement to shine in this digital age
(O’Flaherty & Phillips, 2015). To facilitate students
with smooth teaching and learning experiences in CP
courses, we need to incorporate essential technologies
into our teaching philosophies along with suitable
pedagogy.
Because of its relevance and applicability in real
life, learning CP is always on a student’s priority list
of study (Sambe et al., 2021). We have already expe-
rienced how online teaching platforms preserved the
education sector during COVID-19 lockdowns (Barr
et al., 2020) and are now observing how digitalization
is ruling the world during post-pandemic situations.
Such technological advancement is not possible with-
out innovative digitalization (Müller et al., 2021), and
to do so, essential knowledge of CP is crucial. Hence,
programmers are in higher demand in the job market,
making current and future students extremely ambi-
tious about their careers (Ouhbi & Pombo, 2020). For
proper knowledge construction, they expect to ac-
quire practice-oriented knowledge from the course
and gain real-time experience to fulfill their desires
(Feijóo-García et al., 2021).
Teachers should inform their students that
knowledge is not limited to the two cover pages of the
course book or the provided course content; a clear
understanding of the topics learned is necessary.
Technology-oriented learning can help students gain
such an in-depth understanding of the subject (Dug-
girala et al., 2021). Along with the content from
394
Rahman, M.
Blended Approach for Deep Learning: A Framework for Teaching Undergraduate Computer Programming Courses.
DOI: 10.5220/0011959900003470
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2023) - Volume 2, pages 394-402
ISBN: 978-989-758-641-5; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

course books, essential online resources can be incor-
porated into lectures, assignments, projects, and ex-
aminations to stimulate students’ critical thinking and
train them with the analytical know-how to solve
practical problems (Einhorn, 2012). Thus, students
may become habituated with self-learning ap-
proaches not only for answering examinations crea-
tively but also for solving real-time problems in their
careers (Sambe et al., 2021).
Therefore, they require deeper insight and under-
standing of the course content defined by their teach-
ers with a clear indication of the goal and outcomes
of their study and training (Howie & Bangnall, 2015;
Paez, 2017). For deep learning, students are expected
to be active in learning processes that include under-
standing the problem and utilizing proper logic and
evidence to identify and implement solutions
(Entwistle, 2000). They are encouraged to collaborate
with their peers and teachers not only to solve the
problem but also to evaluate their proposed ideas.
Thus, deeper knowledge is constructed (Biggs &
Tang, 2011). In this way, deep learning ensures that
students have a more comprehensive grasp of the sub-
ject being studied and can successfully apply their
gained knowledge to the field (Howie & Bangnall,
2013).
To prepare students for their careers, a student-
centered, career-focused teaching philosophy needs
to be emphasized and applied. Since the traditional
way of teaching is mostly lecture-based (Erdogmus &
Péraire, 2017), students get little or limited opportu-
nities for discussion, practice, and exploration (Lin,
2021). On the other hand, the student-centric flipped
classroom (FC) approach is also limited to provide
the abovementioned facilities to students as it requires
extra time and effort from both teachers and students
(Amresh et al. 2013). For example, in traditional FC
approach, teachers are required to prepare and upload
video lectures and students need to go through them
before attending the session (Elliot, 2014). Thus, to
facilitate deep learning for CP students, the student-
centric FC concept can be blended with the traditional
teaching (TT) approach, as suggested by Divjak et al.
(2022) and Gren (2020). But how can such blending
be done? Finding a way leads to this study’s research
question:
How does the blended approach contribute to
deep learning and knowledge construction?
In the following section, related works on recently
used pedagogical approaches are reviewed, especially
for teaching CP courses. The induced framework is
presented and described in section 3, and its applica-
tion and evaluation are discussed in sections 4 and 5,
respectively. Finally, section 6 concludes the paper,
along with research limitations and future research di-
rections.
2 RELATED WORKS
Academia is no longer just a privileged knowledge
provider but fosters a dialogical space to create soci-
etal values and human worth (Class et al., 2021).
The current academic course design at universities
has been highly influenced by social networking,
technology, and practice-oriented teaching and learn-
ing (Nørgård et al., 2019). Thus, teachers try different
approaches before selecting ones that are appropriate
to their classes and updating them accordingly.
In recent years, teachers of CP courses have advo-
cated an FC approach (Fetaji et al., 2019), bringing
in-class activities out of the classroom (Fulton, 2012).
Although widely tried, applying the FC technique in
CP is challenging because it covers not only the the-
ory, methods, and tools for developing new informat-
ics solutions (Feijóo-García et al., 2021) but also ac-
cepts students from non-scientific backgrounds for
admission (Sambe et al., 2021). We are experiencing
increased student enrollment in computing education,
especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, when we
were forced to switch to digital and online platforms
(Kawash et al., 2021; Arima et al., 2021).
Although mentioned as an active learning meth-
odology, Olivindo et al. (2021) incorporated the gam-
ification technique within the FC approach to im-
prove students’ acceptance and in-class engagement
during the COVID-19 pandemic. They reported
higher student satisfaction with their adopted ap-
proach. Similarly, Lin (2021) combined the learning
diagnostic methodology with the FC approach to sup-
port students with learning diagnosis activities. Ac-
cording to Lin (2021), simply following the FC ap-
proach is not sufficient to provide CP students with
adequate learning support or necessary feedback be-
fore class. Lin (2021) also reported outstanding per-
formance for students who followed the adopted ap-
proach.
El-Glaly (2020) applied the FC concept to her
teaching by assigning several related research papers
to the class and engaging students through a discus-
sion on selected research papers (three papers per
week) and presentations (one student per week). Alt-
hough the students’ and research papers’ selection
criteria were never discussed, she was supportive of
including necessary lectures and providing students
with hands-on experience where applicable. Paez
(2017) shared his experience with adopting the FC
Blended Approach for Deep Learning: A Framework for Teaching Undergraduate Computer Programming Courses
395
approach in software engineering courses and demon-
strated that students are required to maintain a mini-
mum workload during the semester (four to six hours
of homework per week for a four-hour long weekly
class). This allows for an easy estimation of the dedi-
cated workload for students who take several courses
per semester, and each course is instructed using the
FC method.
Although Paez (2017) asserts that a FC method–
supported teaching approach is suitable for smaller
classes with adequate teaching support (two teachers
for 15 students), Marasco et al. (2017) found the FC
approach helpful in teaching around 800 students
with different programming backgrounds enrolled in
the first year of their undergraduate study. They ex-
tensively utilized the online learning management
platform to conduct the introductory CP course by
posting weekly video lectures, hosting embedded
quizzes, and facilitating student collaboration on
course exercises. However, the authors for both arti-
cles emphasized, like earlier authors, the extensive re-
designing of course practicalities for running courses
in the FC format.
According to Barr et al. (2020), laboratory ses-
sions and group work suffer tremendously on online
platforms, although CP students engage and learn bet-
ter while being tied to programming activities (El-
Glaly, 2020). Hence, Gren (2020) claims that the FC
approach may facilitate students in getting better
grades, but a clear understanding of students’ percep-
tions of the course is always missing. Gren suggests a
blended learning platform for proper knowledge con-
struction and for its successful establishment. Fur-
thermore, Strayer (2012) recommends enabling or
carefully integrating information technology (FC ap-
proach, for example) in regular in-class activities (TT
approach, for example). Such an approach can pro-
vide students with an effective, efficient learning ex-
perience; thus, a meaningful subjective linking of the
materials they learned in the course can be demon-
strated (Garrison & Kanuka, 2004; Strayer, 2012).
These meaningful learning experiences point to the
deep learning of the concepts/topics covered in the
course (Beattie et al., 1997; Howie & Bangnall,
2013).
3 THE FRAMEWORK
Research and discussion on teaching and learning is
an ongoing process; the latest ideas and techniques
replace old or existing ones for better outcomes. Dif-
ferent approaches focus differently on the two main
entities of the process (teacher and student), and their
activities, collaboration, and communication.
Vaughan et al. (2013) defined blended learning as a
pedagogical and technological innovation that is sig-
nificantly redesigned to enhance students’ engage-
ment in the entire learning process. They emphasize
bringing both physical and online learning activities
into the process rather than simply adding online
components. Koehler and Mishra (2009) suggest a
proper balance between technology, pedagogy, and
content knowledge in course design and conduction.
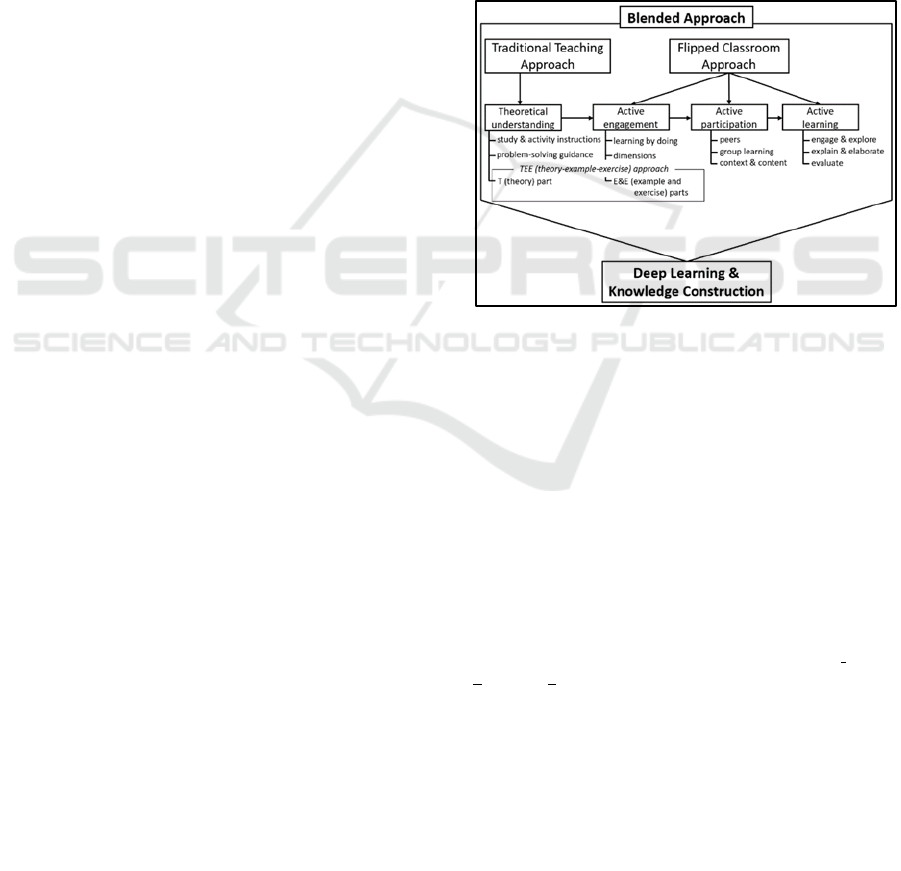
Figure 1 illustrates how the blended approach contrib-
utes to students’ deep learning and knowledge con-
struction in CP. If sufficiently modified and up-
graded, this framework can also be applied to courses
in other disciplines.
Figure 1: Framework for the blended teaching approach.
The proposed teaching and learning framework in
Figure 1 combines the FC approach with the TT ap-
proach (hence, conceptualized as a blended approach)
(Strayer, 2012). Here, the TT approach works to de-
velop an adequate theoretical understanding of the
course content (as suggested by McNally et al.
(2017)), whereas the FC approach focuses on con-
firming students’ active engagement, participation,
and learning. This combination of entities constructs
deeper knowledge of the course content. The overall
knowledge construction process is elaborated on in
the rest of this section.
To actuate the blending, I introduced the theory-
example-exercise (TEE) approach to deliver lectures
for CP courses by following a static order of three
steps: (i) theory or concept, (ii) coding examples, and
(iii) testing exercises. In this approach, the teacher
starts each class with a regular lecture in the tradi-
tional way. This includes concept development,
providing study materials, and offering problem-solv-
ing guidance with sufficient activity instructions
(Kim et al., 2014). As soon as theory building is con-
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
396

firmed, the teacher provides related examples (prac-
tice coding) for deeper understanding of the
topic/concept and for preparing students for problem-
solving (exercises) sessions. This unobstructed vision
of course conduction is essential in the FC approach
because it protects students from being disengaged
with the course and its designed activities (Strayer,
2012). To facilitate quick access to the course con-
tent, the teacher must share all the covered materials
(lecture, examples, exercises, homework, etc.) on the
online platform (e.g., Canvas, Learning Management
System, GitHub) before or immediately after each
session.
Practice coding can be conducted in three ways:
(i) coding together: coding is done by the teacher and
the students follow him/her; (ii) supervised coding:
the code is provided by the teacher in a non-copyable
format (e.g., jpeg, png, gif), and the students type the
code to see the result; and (iii) combined coding: mix-
ing (i) and (ii). While coding, it is important that the
teacher explains the code in every viable way. Hence,
the teacher should bring smaller and simpler prob-
lems for the “example” session, whereas extensive
problems can be saved for the “exercise” session to
test students’ understanding.
In problem-solving (or “exercise”) sessions, the
teacher sets complex and extensive programming ex-
ercises that the students are required to solve in class.
They are encouraged to code the assigned exercises
by themselves so that they can gain a good foundation
in problem solving. All kinds of discussion, brain-
storming, analysis, and coding must be done in
groups, and the teacher provides adequate support
and guidance in person for solving the programming
problems. Thus, the TEE approach ensures that stu-
dents successfully practice the “learning by doing”
method, which is the absolute learning technique for
CP courses (Kawash et al., 2021). Furthermore, it can
also be a regular practice to recap the main point of
the previous lecture at the beginning of the class so
that the students receive the opportunity to clear their
conceptual misunderstandings, if any.
Thus, the TEE approach influences active engage-
ment and its components as proposed by Fredricks et
al. (2004)—behavioral, cognitive, and emotional/af-
fective. It ensures students’ involvement in active
learning by responding to the teacher’s directions in
activities (behavioral engagement), preference in
problem-solving activities and fault tolerance (cogni-
tive engagement), and commitment to belonging and
values in group activities (emotional engagement).
Since the FC method emphasizes students’ active en-
gagement in the learning process, it contributes well
to deep learning (Jensen et al., 2015; Steen-Utheim &
Foldnes, 2018).
To ensure active learning, the FC approach re-
quires proper activity design. Bybee et al. (2015) pro-
posed a 5E instructional model for improved active
learning (applied in Jensen et al. (2015)): engage, ex-
plore, explain, elaborate/extend, and evaluate. Hence,
in conjunction with in-class activities, assignments
and projects should be designed in the context of in-
quiry-based learning that incorporates role plays, sim-
ulations, brainstorming, and so on. To enrich their
software engineering understanding of system devel-
opment, students are encouraged to work with real-
time clients to build their projects on practical scenar-
ios. Student groups should be able to explain and
elaborate on their projects and divide them into real-
istic, meaningful, and achievable milestones. Thus,
they can make hands-on observations, solve interest-
ing and practical problems, and achieve explorable
models of practical projects in real life. Such an ac-
complishment makes them ready to plan and carry out
successful computer system development projects to-
gether with others in practical setups. Finally, various
initiatives can be taken to evaluate students’ learning,
both individually and in groups. For example, passing
group assignments/project can be set as a prerequisite
for the individual final examination. Thus, both their
deep learning (conceptual and analytical capabilities)
and their surface learning (memorizing capabilities)
can be effectively measured and correctly valued
(Photopoulos et al., 2021).
Altogether, the proposed blended teaching and
learning approach is expected to help students
sharpen their skills not only for developing dynamic
full-fledged software applications but also for plan-
ning and carrying out tasks from scratch (as projects)
with others. They can utilize their competencies in
project management, system development, and pro-
gramming to pave a smoother software engineering
journey. In this way, their professional qualifications
(i.e., knowledge construction) can be highlighted for
their future careers in practice (i.e., deep learning)
(Bachnak & Maldonado, 2014).
4 DISCUSSION
The FC concept expects students to cover literature
and short video lectures before coming to class and
applying their understanding to classroom activities
(El-Glaly, 2020; Lin, 2021). However, this technique
is not fully effective for CP courses because students
may struggle to understand complex programming
Blended Approach for Deep Learning: A Framework for Teaching Undergraduate Computer Programming Courses
397

concepts, business logic, and mathematical algo-
rithms. In my teaching, I experienced my students
struggling to understand a concept by watching the
short video lectures posted either by me (as their
teacher) or on other online platforms. The situation
was worse for weaker students, who often expect
teachers to go through complex logic and algorithms
in person in class, even when study materials are
made available before lectures. Since adequate and
in-time learning is the focal point in academia, edu-
cators cannot overlook the demands or desires of stu-
dents. This indicates doubling the time used for the
same tasks (Phillips & Trainor, 2014). The time both
parties already invested becomes useless—the
teacher must conduct the lecture once again, and so
the students attend it twice. We can avoid this incon-
venience by starting the class with traditional lectures
and then gradually incorporating the FC approach;
thus, the blended approach can easily address this
problem.
Conducting lectures (for theory) and laboratory
sessions (for practice coding) in separate slots is a
regular practice for teaching CP courses. Such a pair-
ing sometimes happens in back-to-back slots or
weekly slots (Marasco et al., 2017). Again, this is in-
effective (to some degree) since students get involved
in many other activities during the gap between the-
ory and laboratory sessions, and thus may forget some
parts of the learned concept they are expected to apply
in laboratory sessions. To address this issue, Bachnak
and Maldonado (2014) emphasized students’ inten-
sive involvement in their education and the applica-
tion of their learning. The TEE approach helps facili-
tate such extensive learning by conducting laboratory
sessions in parallel with lectures. However, practicing
this approach is not possible for a shorter class time;
instead, a four-hour-long weekly class can be con-
ducted with sufficient breaks in between. The success
ratio of this practice is demonstrated in the next sec-
tion, along with student feedback.
Making students code in class is another challenge
for teaching CP courses. Students’ expectations in
such courses vary to a large extent: One group of stu-
dents may have high expectations of coding in class,
while another group may prefer coding later or at
home. Better students may grab the concept easily
and quickly, whereas weaker students may struggle.
Thus, it becomes difficult for teachers to balance class
activities with a moderated workload, because better
students may easily get bored if the pace is too slow
and the weaker students may struggle to up if the pace
is too fast. Alternatively, students may feel insecure
about coding flexibility if the “coding together”
method is followed. Slow typing is time-consuming,
and erroneous code could demand the entire class
time to fix a bug that could go unsolvable. For exam-
ple, missing a simple semicolon (;) is enough to ruin
the productivity of the class. Thus, a class would gen-
erate a small outcome in which the expectation was
high. Therefore, to keep students interested and en-
gaged in classroom activities, the TEE approach en-
courages teachers to prepare exercises with extended
complexities. The brighter students can attempt to
solve these problems by utilizing their capabilities of
applying advanced logic.
However, Ouhbi and Pombo (2020) highlight that
enhancing students’ class participation is the greatest
challenge for teaching CP—they might not partici-
pate in class discussions, answer questions, take the
lead in group activities, and so on. Students rarely ask
questions to their teachers during class time or mostly
feel insecure about answering the questions asked
(Strayer, 2012). They foster a mindset of being teased
by fellow classmates if they answer incorrectly. How-
ever, there are always a couple of familiar faces who
answer questions or discuss raised issues. To ascer-
tain students’ understandings and guide their
knowledge construction, the proposed blended ap-
proach suggests that teachers speak to individual stu-
dents in person and monitor their activities on their
computer screens. Thus, they could step out of their
cocoons, although some students may find it incon-
venient due to their screen privacy.
Additionally, active engagement does not bring
about active participation all the time (Strayer, 2012).
Free riders are always there; they try to escape hurdles
but enjoy group grading. For example, some members
engaged in group activities (e.g., discussion, task
analysis, requirement elicitation, etc.) but did not par-
ticipate enough in coding for software system devel-
opment. Such piggybacking brings overhead to other
group members and thus, in most cases, produces
poor group performance. Hence, to make the pro-
posed blended approach functional toward in-depth
knowledge construction, forming effective groups is
one of the key requirements (Gren, 2020), and it
should not be done randomly (Barr et al., 2020). It is
important that teachers guide group members to en-
compass a good understanding not only of the work-
ing attitude and responsibilities but also of communi-
cation, information sharing, and leadership (Oliveira
& da Silva Borges, 2021). Therefore, students should
be independent to form their own groups and select
their group leaders by themselves. This will help them
become accustomed to co-learning in various con-
texts and complete the course project successfully. To
stop free-riders, groups must be restricted to a man-
ageable size (four to six students per group) (Barr et
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
398
al., 2020; Gren, 2020). It is true that self-formulating
group establishment is rarely practiced in real-time
setups; however, we can use it in academia for better
student engagement in assigned tasks/projects and ac-
tive participation in group learning.
Effective teaching and learning require both
teachers and students to actively participate in the
learning process. Teachers are authority figures in
this pedagogy model who provide students with es-
sential study materials and supervise their learning
(Steen-Utheim & Foldnes, 2018). Thus, to meet the
curriculum objectives, the proposed blended ap-
proach clarifies the expectations, stipulates the objec-
tives, and assigns the required activities to students at
the beginning of each class. According to Brookfield
(2017), these are the requirements for generating ef-
fective teaching methods. In addition to the planned
classroom lectures, CP teaching pedagogy should in-
clude in-class problem solving, self-learning, relevant
classroom entertainment, question-and-answer ses-
sions, presentation and demonstration sessions, and
support for technical report writing. Besides orga-
nized instructions on physical and/or digital lectures,
the necessary guidance and supervision are required
to be provided to groups and individuals on case study
discussions, group work, assignments, and projects
(Kim et al., 2014). To strengthen understanding of the
topics covered, the blended teaching approach en-
courages students to use online video lectures upon
necessity. Since teaching and learning are connected,
this approach suggests a continuous assessment of
student learning during the semester.
5 FRAMEWORK EVALUATION
Following Bachnak and Maldonado’s (2014) recom-
mendations, student feedback on course structure and
conduction was used to evaluate the proposed frame-
work. A survey was designed using Google Forms
and sent to 70 students who completed an introduc-
tory web programming course in the 2021 fall semes-
ter at a Norwegian university. In the survey, the par-
ticipants were asked to answer two questions (“How
did you find the content for this course?” and “How
did you find the lecturing in this course?”), and to pro-
vide their reflections as free-text comments. Analyz-
ing these free-text comments can guide quality im-
provement initiatives, supported by deeper insights
from students’ experiences (Arditi et al., 2020). By
anonymously evaluating the course, 42 students eval-
uated the proposed framework for the blended teach-
ing and learning method. The analytical results are
presented below. To restrict students from responding
neutrally, a Likert scale of 6 was used in this survey.
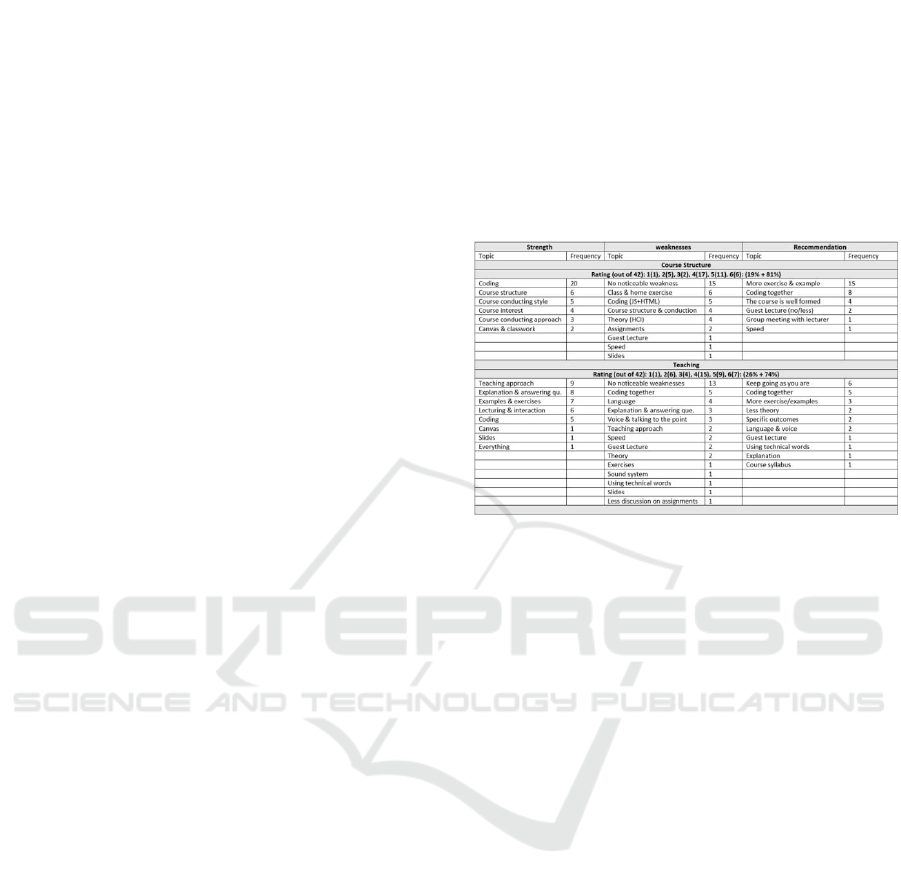
A summary of the students’ written feedback
(free-text comments) is presented in Table 1. It
demonstrates not only the strengths and weaknesses
of the course and the teaching they emphasized, but
also their recommendations for future improvement
in the course.
Table 1: Students’ reactions to course content and teaching.
Most of the students who completed the survey
were happy with the course content and lecturing.
Although “no noticeable weakness” was mostly re-
ported, it can be identified that they expected more
examples and exercises in both formats (in-class and
homework), which is good. They preferred the “cod-
ing together” method rather than the implemented
“supervised coding” method. However, they were not
happy with the amount of content covered in the
class—they wanted less. Students looked for direct
answers to their questions without getting a heavy
background and not using technical words. Although
they reported good reviews for course conducting
style, lecturing, and interaction, they suggested fur-
ther development for teaching language and lecturing
slide content (some of them preferred Norwegian
speakers and more content in the slides). Lastly, stu-
dents expected more discussion on the course struc-
ture, assignments, evaluation, and conduction.
The feedback on the course content and organiza-
tion was positive. More than 80% of the students
found that the course topics improved their software
system development skills. They liked the lectures,
assignments, and literature because they could con-
nect the theory they learned in the course to real-
world web application development. Figure 2 demon-
strates the statistics.
Blended Approach for Deep Learning: A Framework for Teaching Undergraduate Computer Programming Courses
399

Figure 2: How much the students liked the course.
To understand and improve teaching quality, stu-
dents were also requested to provide their feedback
on lecturing. 74% of students found the implemented
TEE approach was helpful to them in following the
course content. Besides this online survey, they were
invited to have discussions on course structure, con-
tent, and conduction in person and to provide feed-
back accordingly. Instead of dividing the class be-
tween theory and laboratory sessions, the TEE prac-
tice was well accepted in the class. They appreciated
the immediate help they received from the teacher
when stuck somewhere in the code. Figure 3 demon-
strates the statistics.
Figure 3: How much the students liked the teaching.
Altogether, the students’ feedback helped me, as
the course teacher, identify the strengths and weak-
nesses of the course design and its conduction. By an-
alyzing their reflection data, we can easily identify the
concentration points for further development of the
course. Students sometimes suggest or recommend
their preferences and thus contribute to improving the
course and lecturing to achieve balanced teaching and
learning. Hence, such an evaluation of the overall
teaching framework—course content, assessment
forms, course organization, and teaching activities—
is always considered a resource for teachers of differ-
ent courses. It will assist us in improving our teaching
in the next semester and to be more prepared to mas-
ter the course in the case of a sudden shift between
offline and online modes of teaching.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This study presented and evaluated a framework for a
blended approach to teaching CP, such as in technical
courses. It discussed how this teaching method ena-
bles students to gain an adequate understanding of the
subject matter and apply it in practice. To provide
deep learning for proper knowledge construction, this
pedagogical technique merges traditional teaching
with the flipped classroom approach. It used the TEE
approach to perform this merging, where the theory
was addressed in traditional lectures to understand the
study foundation, and example and exercise parts
were used to ensure students’ active engagement in
their education as well as their active participation
and learning in the flipped classroom. This overall ap-
proach was found to be effective by the students who
participated in the course. Like any other research,
this study has some limitations. The proposed teach-
ing technique was applied to a specific first-semester
course, where basic programming was taught. Its ap-
plicability to other advanced programming courses
and its acceptance to other faculty members remains
unevaluated. For future work, I intend to investigate
students’ recommendations for their applicability in
further adjustment of the proposed framework and en-
hance it accordingly by incorporating a structured
process for course design and course evaluation, es-
pecially the examination system for computer pro-
gramming courses.
REFERENCES
Amresh, A., Carberry, A. R., & Femiani, J. (2013). Evalu-
ating the effectiveness of flipped classrooms for teach-
ing CS1. In FIE (pp. 733–735). IEEE.
Arditi, C., Walther, D., Gilles, I., Lesage, S., Griesser, A.
C., Bienvenu, C., Eicher, M., & Peytremann-Bride-
vaux, I. (2020). Computer-assisted textual analysis of
free-text comments in the Swiss Cancer Patient Experi-
ences (SCAPE) survey. BMC Health Service Re-
search, 20(1), 1–12.
Arima, S., Assilmia, F., Maekawa, M. S., & Okawa, K.
(2021). Design and practice of ESD in high school in
Japan through online video co-creation workshop.
In CSEDU (1) (pp. 640–647). SciTePress.
Bachnak, R., & Maldonado, S. C. (2014). A flipped class-
room experience: Approach and lessons learned.
In ASEE (pp. 24–50). ASEE PEER.
Barr, M., Nabir, S. W., & Somerville, D. (2020). Online de-
livery of intensive software engineering education dur-
ing the COVID-19 pandemic. In CSEE&T (pp. 1–6).
IEEE.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
400

Beattie, V., Collins, B., & McInnes, B. (1997). Deep and
surface learning: A simple or simplistic dichotomy? Ac-
counting Education, 6(1), 1–12.
Biggs, J., & Tang, C. (2011). Teaching for quality learning
at university. McGraw-Hill Education (UK).
Brookfield, S. D. (2017). Becoming a critically reflective
teacher. John Wiley & Sons.
Bybee, R. W., Taylor, J. A., Gardner, A., Van Scotter, P.,
Powell, J. C., Westbrook, A., & Landes, N. (2006). The
BSCS 5E instructional model: Origins and effective-
ness. Colorado Springs, Co: BSCS, 5, 88–98.
Class, B., Soulikhan, F., Favre, S., & Cheikhrouhou, N.
(2021). A framework for an open education supply
chain network. In CSEDU (pp. 617–625). SciTePress.
Divjak, B., Rienties, B., Iniesto, F., Vondra, P., & Žižak, M.
(2022). Flipped classrooms in higher education during
the COVID-19 pandemic: Findings and future research
recommendations. IJETHE, 19(1), 1–24.
Duggirala, V. D., Butler, R. S., & Kashani, F. B. (2021).
iTA: A digital teaching assistant. In CSEDU (2) (pp.
274–281). SciTePress.
Einhorn, S. (2012). Microworlds, computational thinking,
and 21st century learning. LCSI White Paper, 1–10.
El-Glaly, Y. N. (2020). Teaching accessibility to software
engineering students. In TSCSE (pp. 121–127). IEEE.
Elliot, R. (2014). Do students like the flipped classroom?
An investigation of student reaction to a flipped under-
graduate IT course. In FIE (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
Entwistle, N. (2000). Promoting deep learning through
teaching and assessment: Conceptual frameworks and
educational contexts. In TLRP (1), (pp. 9-20). ESRC.
Erdogmus, H., & Péraire, C. (2017). Flipping a graduate-
level software engineering foundations course.
In ICSE: Software Engineering Education and Train-
ing Track (ICSE-SEET) (pp. 23–32). IEEE.
Feijóo-García, M. A., Ramírez-Arévalo, H. H., & García,
P. G. F. (2021). Collaborative strategy for software en-
gineering courses at a South American university.
In CSEDU (2) (pp. 266–273). SciTePress.
Fetaji, M., Fetaji, B., & Ebibi, M. (2019). Analyses of pos-
sibilities of flipped classroom in teaching computer sci-
ence courses. In MIPRO (pp. 747–752). IEEE.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004).
School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of
the evidence. Review of Education Research, 74(1),
59–109.
Fulton, K. (2012). Upside down and inside out: Flip your
classroom to improve student learning. Learning &
Leading with Technology, 39(8), 12–17.
Garrison, D. R., & Kanuka, H. (2004). Blended learning:
Uncovering its transformative potential in higher edu-
cation. JIHEDUC, 7(2), 95–105.
Gren, L. (2020). A flipped classroom approach to teaching
empirical software engineering. IEEE Transactions on
Education, 63(3), 155–163.
Howie, P., & Bagnall, R. (2013). A critique of the deep and
surface approaches to learning model. Teaching in
Higher Education, 18(4), 389–400.
Howie, P., & Bagnall, R. (2015). A critical comparison of
transformation and deep approach theories of learn-
ing. IJLE, 34(3), 348–365.
Jensen, J. L., Kummer, T. A., & Godoy, P. D. D. M. (2015).
Improvements from a flipped classroom may simply be
the fruits of active learning. CBE—LSE, 14(1), ar5.
Kawash, J., Horacsek, J., & Wong, N. (2021). What we
learned from the abrupt switch to online teaching due to
the COVID-19 pandemic in a post-secondary computer
science program. In CSEDU (pp.148–155). SciTePress.
Kim, M. K., Kim, S. M., Khera, O., & Getman, J. (2014).
The experience of three flipped classrooms in an urban
university: An exploration of design principles. JI-
HEDUC, 22, 37–50.
Koehler, M., & Mishra, P. (2009). What is technological
pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK)?
JCITTE, 9(1), 60–70.
Lin, Y. T. (2021). Effects of flipped learning approaches on
students’ learning performance in software engineering
education. Sustainability, 13(17), 9849.
Lundin, M., Bergviken Rensfeldt, A., Hillman, T., Lantz-
Andersson, A., & Peterson, L. (2018). Higher education
dominance and siloed knowledge: A systematic review
of flipped classroom research. IJETHE, 15(1), 1–30.
Marasco, E. A., Moshirpour, M., & Moussavi, M. (2017).
Flipping the foundation: A multi-year flipped class-
room study for a large-scale introductory programming
course. In ASEE (pp. 1-9). ASEE PEER.
McNally, B., Chipperfield, J., Dorsett, P., Del Fabbro, L.,
Frommolt, V., Goetz, S., Lewohl, J., Molineux, M.,
Pearson, A., Reddan, G., Roiko, A, & Rung, A. (2017).
Flipped classroom experiences: Student preferences
and flip strategy in a higher education context. Higher
Education, 73(2), 281–298.
Müller, W., Grassinger, R., Schnebel, S., Stratmann, J.,
Weitzel, H., Aumann, A., Bernhard, G., Gaidetzka, M.,
Heiberger, L., Kreyer, I., Schmidt, C., Uhl, P., Vi-
sotschnig, M.S., & Widmann, J. (2021). Integration of
digital competences into a teacher education program:
A sensitive approach. In CSEDU (1) (pp. 232–242).
SciTePress.
Nørgård, R. T., Mor, Y., & Bengtsen, S. S. (2019). Net-
worked learning in, for, and with the world. In NPL (pp.
71–88). Springer, Cham.
O’Flaherty, J., & Phillips, C. (2015). The use of flipped
classrooms in higher education: A scoping review. The
Internet and Higher Education, 25, 85–95.
Oliveira, E. W., & da Silva Borges, M. R. (2021). Support-
ing educators to design collaborative learning scenar-
ios. In CSEDU (2) (pp. 95–103). SciTePress.
Olivindo, M., Veras, N., Viana, W., Cortés, M., & Rocha,
L. (2021). Gamifying flipped classes: An experience re-
port in software engineering remote teaching.
In BSSE (pp. 143–152). ACM.
Ouhbi, S., & Pombo, N. (2020). Software engineering edu-
cation: Challenges and perspectives. In
EDUCON (pp. 202–209). IEEE.
Paez, N. M. (2017). A flipped classroom experience teach-
ing software engineering. In SECM (pp. 16–20). IEEE.
Blended Approach for Deep Learning: A Framework for Teaching Undergraduate Computer Programming Courses
401

Phillips, C. R., & Trainor, J. E. (2014). Millennial students
and the flipped classroom. ASBBS, 21(1), 519.
Photopoulos, P., Tsonos, C., Stavrakas, I., & Triantis, D.
(2021). Preference for multiple choice and constructed
response exams for engineering students with and with-
out learning difficulties. In CSEDU (1) (pp. 220–231).
SciTePress.
Sambe, G., Drame, K., & Basse, A. (2021). Towards a
framework to scaffold problem-solving skills in learn-
ing computer programming. In CSEDU (1) (pp. 323–
330). SciTePress.
Steen-Utheim, A. T., & Foldnes, N. (2018). A qualitative
investigation of student engagement in a flipped class-
room. Teaching in Higher Education, 23(3), 307–324.
Strayer, J. F. (2012). How learning in an inverted classroom
influences cooperation, innovation and task orienta-
tion. JLER, 15(2), 171–193.
Vaughan, N. D., Cleveland-Innes, M., & Garrison, D. R.
(2013). Teaching in blended learning environments:
Creating and sustaining communities of inquiry. Atha-
basca University Press.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
402
