
Impact of COVID-19 on the Factors Influencing on-Time Software
Project Delivery: An Empirical Study
Mahmudul Islam
a
, Farhan Khan, Mehedi Hasan, Farzana Sadia and Mahady Hasan
b
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Independent University, Bangladesh
Keywords:
Empirical Study, COVID-19, Factors, on-Time Software Delivery, SDLC Models.
Abstract:
The objective of this research paper is to investigate the impact of COVID-19 on the factors influencing on-
time software project delivery in different Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) models such as Agile,
Incremental, Waterfall, and Prototype models. Also to identify the change of crucial factors with respect
to different demographic information that influences on-time software project delivery. This study has been
conducted using a quantitative approach. We surveyed Software Developers, Project Managers, Software Ar-
chitect, QA Engineer and other roles using a Google form. Python has been used for data analysis purposes.
We received 72 responses from 11 different software companies of Bangladesh, based on that we find that At-
tentional Focus, Team Stability, Communication, Team Maturity, and User Involvement are the most important
factors for on-time software project delivery in different SDLC models during COVID-19. On the contrary,
before COVID-19 Team Capabilities, Infrastructure, Team Commitment, Team Stability and Team Maturity
are found as the most crucial factors. Team Maturity and Team Stability are found as common important
factors for both before and during the COVID-19 scenario. We also identified the change in the impact level
of factors with respect to demographic information such as experience, company size, and different SDLC
models used by participants. Attentional focus is the most important factor for experienced developers while
for freshers all factors are almost equally important. This study finds that there is a significant change among
factors for on-time software project delivery before and during the COVID-19 scenario.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the main reasons for software project fail-
ure is not choosing the proper methodologies. There
are many Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
models such as Waterfall, Agile, Incremental, Proto-
type, Spiral, etc. Software companies follow different
SDLC models according to their needs and project re-
quirements. Cost overrun and on-time delivery is a
major issue in the software industry and the success
of a project depends on them (Chow and Cao, 2008).
Effort estimation is crucial for any software project
since it helps to deliver on time with the defined con-
straints (Jørgensen, 2004). This study investigates the
impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the crucial fac-
tors that impact on-time software project delivery in
different SDLC models and how the level of impact
of these factors shifted with respect to different de-
mographic information such as company size, devel-
opers’ years of experience and different SDLC mod-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3270-8877
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9037-0181
els used software professionals.
Covid 19 pandemic has impacted everything in-
cluding the software development paradigm. It was a
challenge for the team to interact properly although
online platforms such as Google meet, Zoom, and
other platforms made the interaction possible but it
was not quite smooth. Several factors impact on-time
delivery (Kula et al., 2021) and during the pandemic,
these factors might be changed to different degrees.
We investigated the research gap and found that no
study has yet been conducted that describes how the
important factors of on-time delivery have changed
over time, especially during COVID-19 in different
SDLC models. This has motivated us to conduct this
research study and measure the impact of COVID-19
on-time software project delivery in different SDLC
models. Previous studies were mostly Agile model
related therefore we cover different SDLC models in
this study. In another previous study, the success fac-
tors are stated (Tam et al., 2020) for Agile software
development but it is not determined how these fac-
tors influence on-time software delivery.
554
Islam, M., Khan, F., Hasan, M., Sadia, F. and Hasan, M.
Impact of COVID-19 on the Factors Influencing on-Time Software Project Delivery: An Empirical Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0011969000003464
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE 2023), pages 554-561
ISBN: 978-989-758-647-7; ISSN: 2184-4895
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

The main contributions of this paper are:
• An overview of the impact of COVID-19 on-time
software project delivery in different SDLC mod-
els.
• Identification of the top factors which are respon-
sible for on-time software project delivery in dif-
ferent SDLC models before and during COVID-
19.
• Identification the change of impact level of im-
portant factors for on-time software project deliv-
ery with respect to different demographic infor-
mation.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows. Re-
lated works have been described in Section 2. In Sec-
tion 3 research survey design has been explained. De-
tailed survey results have been presented in section 4.
Finally, conclusions have been discussed in section 5.
2 RELATED WORKS
(Chiyangwa and Mnkandla, 2017) investigated the
critical success factors (CSFs) of the Agile software
development model and found six different CSFs.
(Dhir et al., 2019) investigated both success and fail-
ure factors that impact project Implementation using
Agile methods. (Ram et al., 2019) surveyed two soft-
ware companies through semi-structured interviews
for evaluating process metrics in Agile software de-
velopment. (Ghayyur et al., 2018) reviewed previ-
ous studies and extracted 25 common motivators and
14 common demotivators factors. (Srivastava et al.,
2020) evaluated the Agile success factors.
(Marques et al., 2017) found that most of the fail-
ure factors had a direct impact on the project deliv-
ery. (Butt and Jamal, 2017) found that frequent re-
quest changes made by clients have a negative effect
on on-time delivery and cost. (Bergmann and Kar-
wowski, 2018) reviewed the previous studies and di-
vided project success factors into 6 main categories
such as management, process, project, organizational,
people, and technical factors. (Hujainah et al., 2018)
performed a systematic literature review to under-
stand and list newly developed Requirement Prior-
itization techniques. (Edison et al., 2021) investi-
gated how the implementation of a hybrid methodol-
ogy will enhance software project success and found
hybrid models are flexible and adaptable. This study
(Hussain et al., 2018) identified five motivator factors
for Agile adoption. (Kamal et al., 2020) explained
the benefits of Agile methods. (Arcos-Medina and
Mauricio, 2019) did a systematic literature review on
different SDLC models and discussed pros and cons
of each methods.
3 RESEARCH DESIGN
This research work is designed through the study of
various previous research papers. This helped us
to identify the research gap and design the research
questionnaires for this study. Previous studies fo-
cused particularly on Agile software development.
After identifying the research gap, in this study, we
explored how different factors affect on-time software
delivery in different SDLC models over the time, es-
pecially during COVID-19.
3.1 Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is to analyze and quantify
the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and other vari-
ables on the timely completion of software projects
in different SDLC models. In this study, we focused
on the following research questions (RQs) and these
questions have been adopted from this (Kula et al.,
2021) study, we have modified the questions with the
concept of COVID-19.
• RQ1: How much does each of the following fac-
tors influence on-time software project delivery
[Before and During COVID-19] ?
• RQ2: Do any other factors or certain types of cir-
cumstances, need to be added to ensure on-time
software project delivery?
There were 25 questions under RQ1 adopted from
(Kula et al., 2021; Tam et al., 2020; Chiyangwa and
Mnkandla, 2017).
• DQ1: Which of the following best describes your
role at your company?
• DQ2: How many years of work experience do
you have in the software development industry?
• DQ3: What is the size of your company?
• DQ4: Which software development life cycle
model has been practiced or followed by you ?
3.2 Research Method
This research study was conducted on different IT
professionals such as Project Manager, Software De-
veloper, Software Architect, QA Engineer, DevOps
from 11 different software companies in Bangladesh.
An extensive literature review was performed before
conducting this research study which helped us to
Impact of COVID-19 on the Factors Influencing on-Time Software Project Delivery: An Empirical Study
555

get a solid idea about the topic and identify research
gap. In this study, quantitative method in 4 point lik-
ert scale format has been used to collect data (Harpe,
2015). Python has been used in data analysis step.
We studied the previous literature (Laitinen, 2018)
and found that Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a metric
which is used to measure how likely people suggest a
thing to others. In this study, NPS along with mode
and mean have been calculated. The methodology in
Figure 1, represents the flow of research method that
was developed in four stages: Research Design, Data
Collection, Data Analysis and Final Result.
3.3 Data Collection Method
In this study, purposive sampling methods were used.
IT professionals who were involved in the software
project deliverable were included in the sample’s in-
clusion criteria. The individuals who possessed pri-
mary features for selection criteria were filtered and
addressed with proper instructions. The question-
naires were organized in two sections that addressed
the demographics and factors impacting on-time soft-
ware project delivery before and during Covid-19
pandemic.
Most of the questions were designed as close-
ended in a 4-point Likert scale format such as no im-
pact, small, moderate, and large impact. The factors
were presented in a random order to the survey partic-
ipants to reduce ordering bias and a short description
was included to explain the factors to participants. Af-
ter the design of questionnaires and selection of par-
ticipants, a pilot test was conducted before the initi-
ation of the data collection process. It ensured that
the interview questions were understandable to the IT
professionals. Therefore, after the successful identi-
fication of misinterpretations and corrections of ques-
tions in the pilot test, quantitative data collection was
initiated via Google form.
3.4 Data Analysis Method
After the completion of the data collection phase, an
in-depth data analysis was performed using Python.
Then, different statistical parameters such as NPS,
Mode, Mean were calculated. NPS calculation al-
lows to determine the most impactful factors while
the calculation of Mode help to identify the central
tendency. The factors were assessed from the ob-
tained data where respondents revealed their approach
to software deliverables before and during COVID-
19 and their correlation with on-time software project
delivery. As a result, taking these factors into account
improved the generalizability of the findings.
4 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
In this study, 72 responses have been received from
different roles such as Software Developer, Soft-
ware Architect, Project Manager, QA Engineer, De-
vOps, etc from 11 different software companies in
Bangladesh. In this section, we will describe the find-
ings of this study regarding the impact of COVID-19
on-time software project delivery and the change of
impact level of factors with respect to different pa-
rameters.
4.1 Demographics
Role: The survey participants were asked questions
regarding their role in the software company. ques-
tion DQ1 make sure that the participants are in the
target population. Figure 2 depicts the role of the re-
spondents in the software company. People working
in different roles at software companies participated
in this survey. The majority of the respondents were
Software Developers and Project Managers. Software
Architects, QA Engineers, and DevOps also partici-
pated in this survey as all of them play a role in on-
time software delivery.
Work Experience in Software Industry: Work ex-
perience in the software industry is important demo-
graphic information for our study. We asked ques-
tion DQ2 which reveals the work experience of par-
ticipants. Results are shown in figure 3, most of the
participants in this study have a software industry ex-
perience of one to five years while the least of partici-
pants have ten to twenty years of industry experience.
Company Size: Question DQ3 had been asked to the
participants to know the software company size. In
this study, we find that the level of impact of factors
for on-time software project delivery changes with re-
spect to company size which has been described in
detail later. Figure 4 shows the company size of the
survey respondents.
Use of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Models: We asked participants question DQ4 to
know about their followed SDLC models during soft-
ware developments. Participants in this study re-
sponded that they follow mainly four SDLC models
Agile, Incremental, Waterfall and Prototype Models.
Results shown in figure 5 describe the use of SDLC
models by survey participants. The Agile model is
followed by most of the participants while the Proto-
type model is practiced or followed by the least of the
participants during software development.
ENASE 2023 - 18th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
556
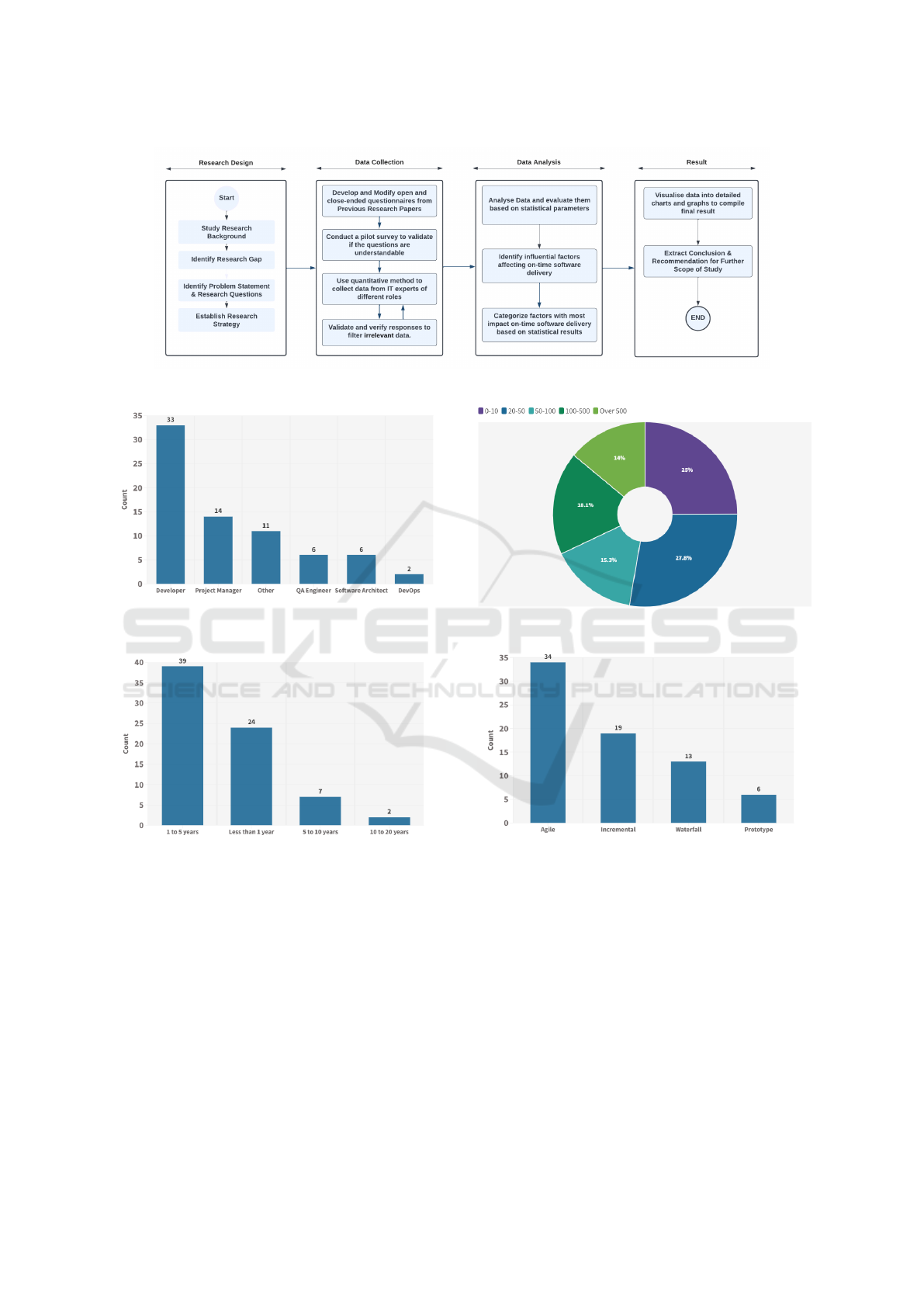
Figure 1: Research Methodology.
Figure 2: Survey Respondents’ Role in the Software Com-
pany.
Figure 3: Survey Respondents’ Work Experience in the
Software Industry.
4.2 Impact of COVID-19 on-Time
Software Project Delivery
In this research survey, we identified the top factors
which influenced on-time software delivery before
and during COVID-19. Data have been collected on
a 4-point Likert scale. In this study, the collected data
have been mapped using table 1. Quantitative analy-
sis has been applied to the survey data based on the
mapping. We identified the top factors that impact
on-time software project delivery during and before
COVID-19. We also identified changes in the level
Figure 4: Survey Respondents’ Company Size.
Figure 5: Use of SDLC Models by Survey Respondents.
of impact of factors with respect to different parame-
ters such as respondents’ company size and software
industry experience. Net Promoter Score (NPS) has
been used to identify the top factors (Laitinen, 2018).
Mode and Mean are also calculated.
NPS = ( Count of Promoters - Count of Detractors
) / Total Participants
Influential Factors for On-Time Software Project
Delivery During COVID-19: Figure 6 represents
identified top 5 factors during COVID-19 that have
the highest NPS which means they have the highest
impact or influence on-time software project delivery
during COVID-19 according to survey participants.
The mode and mean of those factors have also been
Impact of COVID-19 on the Factors Influencing on-Time Software Project Delivery: An Empirical Study
557
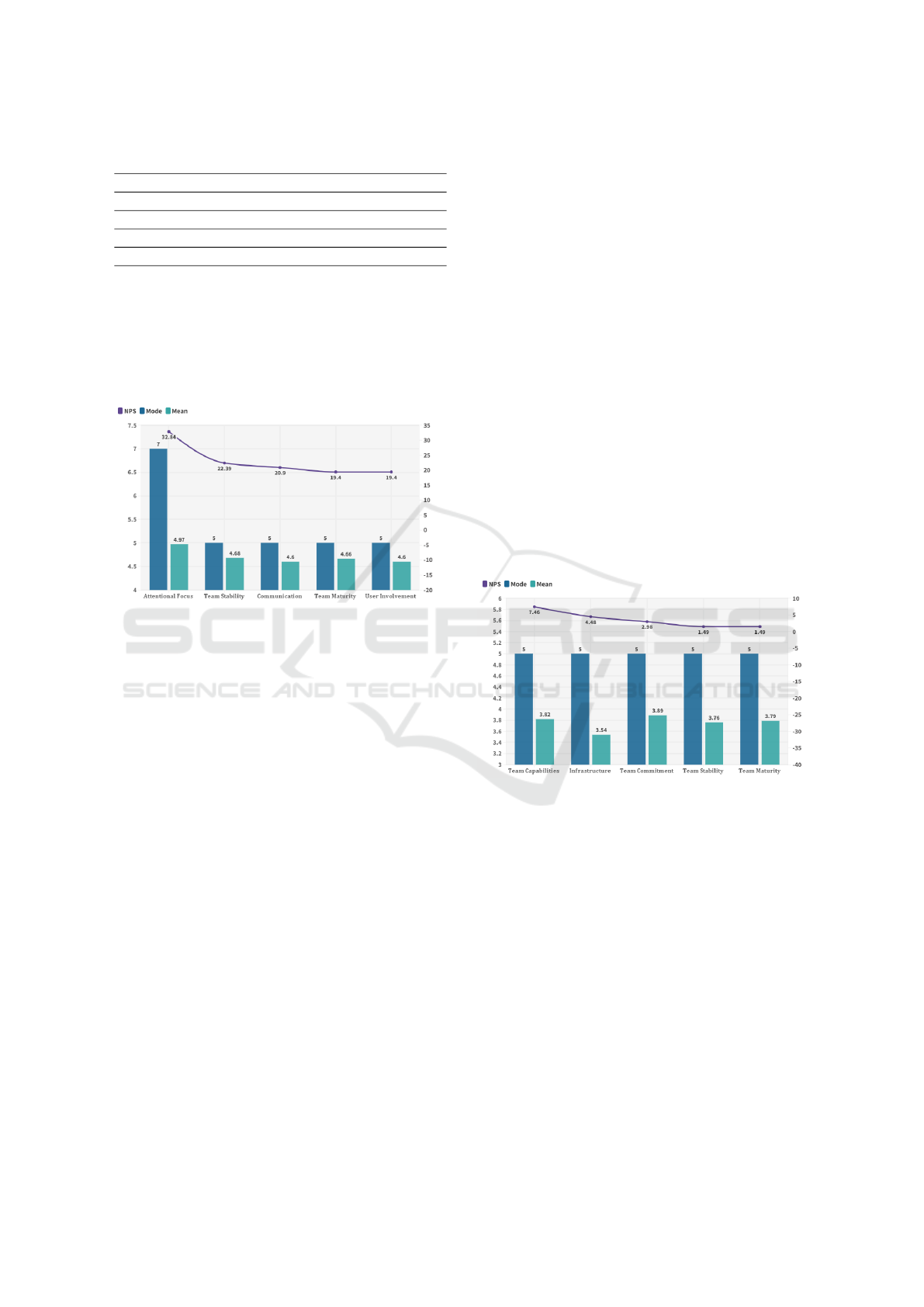
Table 1: Likert Scale Data Mapping.
Text Rating Quantitative Rating Type
No Impact 1 Detractors
Small Impact 3 Neutral
Medium Impact 5 Neutral
Large Impact 7 Promoters
calculated. Attentional focus was the most influen-
tial factor for on-time software project delivery during
COVID-19. Team Stability, Communication, Team
Maturity, and User Involvement were also significant
factors for on-time software project delivery respec-
tively. The identified factors are described below.
Figure 6: Top Five Factors for On-Time Software Project
Delivery During COVID-19.
Attentional Focus: In software development, Atten-
tional Focus is an essential key element to accomplish
the assigned task. Attentional Focus is to concen-
trate dedicatedly on a specific task or increased fo-
cus on a specific task which helps to achieve the task.
Our findings in figure 6 from this study indicate that
the most important factor impacting on-time software
project delivery is Attentional Focus.
Team Stability: In software development, Team Sta-
bility is a major factor for a company’s success as well
as to deliver software projects timely to the clients
(D
¨
onmez et al., 2016). Results of this study are
presented in figure 6 where team stability has been
deemed as the second most important factor.
Communication: In software development, proper
communication is a major criteria to understand the
user requirements and deliver quality software prod-
ucts(Rasheed et al., 2021). Figure 6 shows that Com-
munication is perceived as the third most important
factor for on-time software project delivery during
COVID-19.
Team Maturity: Team Maturity or Group Maturity
is significant for the efficiency of the software devel-
opment team (Ram
´
ırez-Mora et al., 2020). Figure 6
demonstrates that during COVID-19, Team Maturity
was considered as the fourth most crucial factor for
timely software project delivery.
User Involvement: In software development, User
Involvement is a key factor for successful project
completion (Bano et al., 2018). User Involvement
helps to understand the user requirements and deliver
proper software products which eventually leads to
user satisfaction.
Influential Factors for On-Time Software Project
Delivery Before COVID-19: In this survey, we also
investigated the influential factors which were re-
sponsible for on-time software project delivery be-
fore COVID-19. The higher NPS value of a fac-
tor means the higher impact of that factor on-time
software project delivery according to survey partic-
ipants who were Software Developers, Software Ar-
chitects, Project Managers, QA Engineers, and De-
vOps. Figure 7 represents the top five factors that
have the highest impact on-time software project de-
livery before COVID-19, they are Team Capabili-
ties, Infrastructure, Team Commitment, Team Stabil-
ity, and Team Maturity. Team Stability and Team Ma-
turity are found as common important factors both be-
fore and during COVID-19.
Figure 7: Top Five Factors for On-Time Software Project
Delivery Before Covid-19.
Team Capabilities: In software development, Team
Capabilities is the expertise or skills of the software
development team’s members which is a crucial fac-
tor for successful project delivery (Vishnubhotla et al.,
2018). In this survey we find Team Capabilities was
the most important factor for on-time software project
delivery before COVID-19. Results are shown in fig-
ure 7.
Infrastructure: Infrastructure is essential for soft-
ware development, testing, and maintenance. Un-
availability of Infrastructure leads to late delivery of
software projects to the clients(Harter and Slaughter,
2003). Figure 7 shows that Infrastructure was a ma-
jor factor for on-time software project delivery before
COVID-19.
Team Commitment: Team Commitment is the ded-
ENASE 2023 - 18th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
558
ication of the team member to the timely delivery of
the product and their concentration on attaining the
team’s goal. Team Commitment is an important fac-
tor for on-time delivery (Moe et al., 2009). In this
survey, Team commitment is also found as a major
factor for on-time delivery of the software project be-
fore COVID-19 as shown in figure 7.
Comparison of Factors Before & During COVID-
19: The comparison in table 2 shows that during
COVID-19 the most important factor for on-time
project delivery was Attentional Focus while before
COVID-19 Team Capabilities was the most important
factor. Team Stability and Team Maturity were impor-
tant for on-time software project delivery both before
and during COVID-19. The results are shown in Ta-
ble 2 and it is clear that there is a change of factors
that are responsible for on-time software project de-
livery during and before COVID-19. Before COVID-
19 most important factors were Team Capabilities, In-
frastructure and Team Commitment. Whereas during
COVID-19, these factors did not play any significant
role.
Table 2: Comparison of factors before and during COVID-
19.
Top 5 factors during COVID-19 Top 5 factors before COVID-19
Factors Mode Mean NPS Factors Mode Mean NPS
Attentional
Focus
7 4.97 32.84
Team
Capabilities
5 3.82 7.46
Team
Stability
5 4.68 22.39 Infrastructure 5 3.54 4.48
Communication 5 4.6 20.9
Team
Commitment
5 3.89 2.98
Team Maturity 5 4.66 19.4
Team
Stability
5 3.76 1.49
User
Involvement
5 4.58 19.4
Team
Maturity
5 3.79 1.49
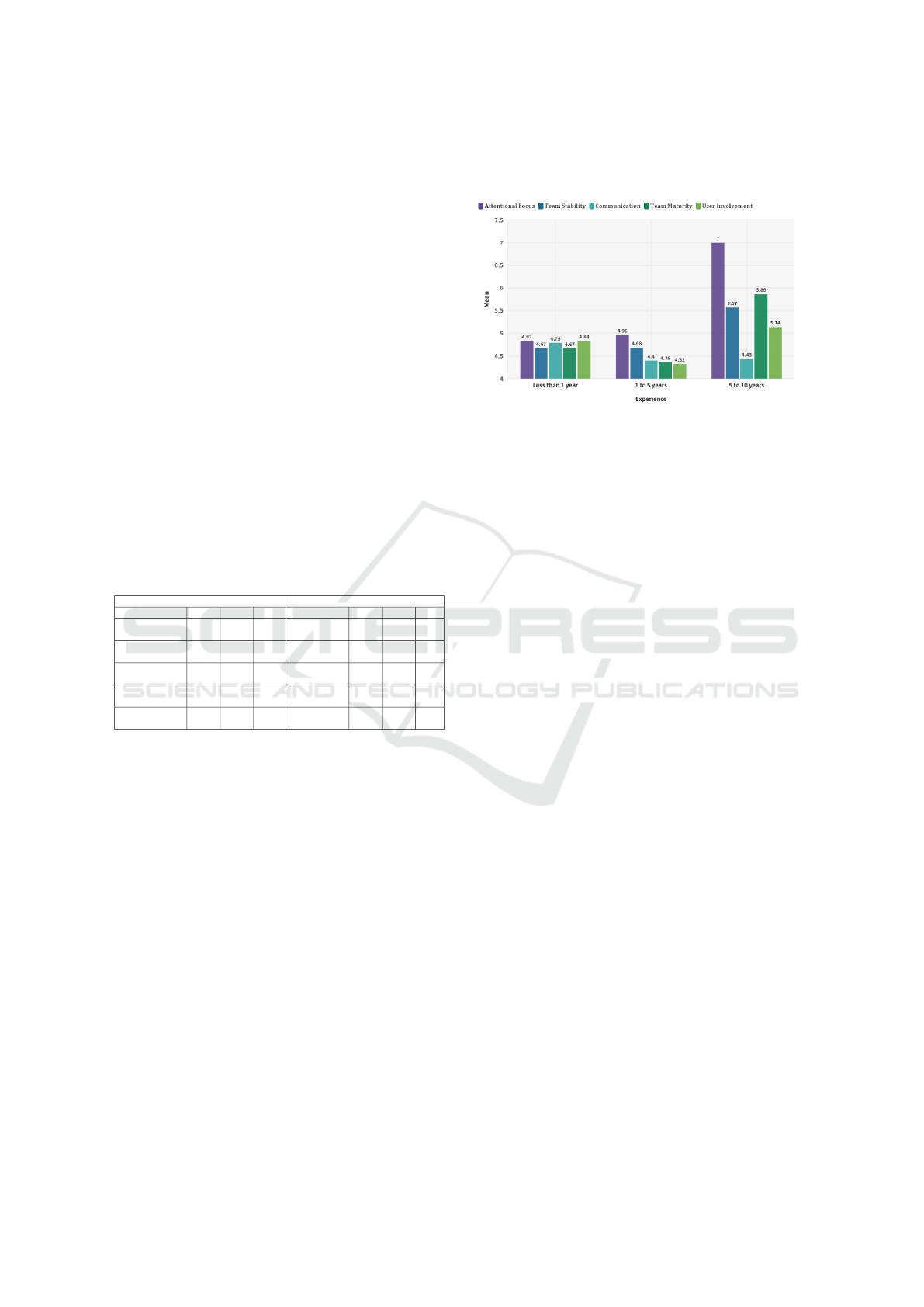
Change of Impact Level of Factors with Respect to
Employee Experience: We have already identified
the top five factors for on-time software project de-
livery both before and during COVID-19. In the sec-
ond level of analysis, we investigated how the impact
level of these identified factors changes with respect
to different demographic information. The Mode has
almost same value for factors and NPS has already
been calculated to determine the factors. In the sec-
ond level of analysis, The Mean value of these fac-
tors with respect to employee experience and com-
pany size has been calculated and presented in figure
8,9,10, and 11 respectively.
Figure 8 depicts change of impact level of identi-
fied top factors with respect to software professionals’
experience during COVID-19. These factors do not
have the same level of impact on the different levels
of experienced people. In figure 8, results show that
more experienced software professionals (5-10 years
of experience) voted for Attentional Focus more. For
fresh graduates or software professionals (0-1 years
of experience) all the factors have a similar type of
impact.
Figure 8: Change of Impact Level of Factors with Respect
to Professionals’ Experience.
In figure 9, two patterns or trends of factors with
respect to software professionals’ experience have
been presented. There are two figures side by side
in figure 9 where the left figure shows that Atten-
tional Focus and Team Stability are increasing as ex-
perience increases. This means that these two factors
were more significant during COVID-19 for experi-
enced software professionals compared to less expe-
rienced software professionals for delivering software
projects timely. On the other hand, the right figure
shows that Communication, Team Maturity, and User
Involvement have dropped for 1 to 5 years of experi-
enced software professionals but increased again for
5 to 10 years of experienced software professionals.
Change of Impact Level of Factors with Respect to
Company Size: In figure 10, results show that more
emphasis is placed on Attentional Focus in large soft-
ware companies. However, Team Stability becomes
more crucial in mid-sized (100-500) companies. Fig-
ure 11 shows that the trend of all the factors upward
for large software companies (Over 500).
Change of Impact Level of Factors with Respect to
Different SDLC Models: In this study, we find that
the impact level of factors is not the same in differ-
ent SDLC models. Figure 12 shows that Attentional
Focus and Team Maturity were most significant for
Agile practitioners during COVID-19. For Waterfall
practitioners, User Involvement was less significant
and this is perceptible as in the waterfall model re-
quirements are defined at the beginning, and in the
whole development process, users do not get involve-
ment.
Impact of COVID-19 on the Factors Influencing on-Time Software Project Delivery: An Empirical Study
559
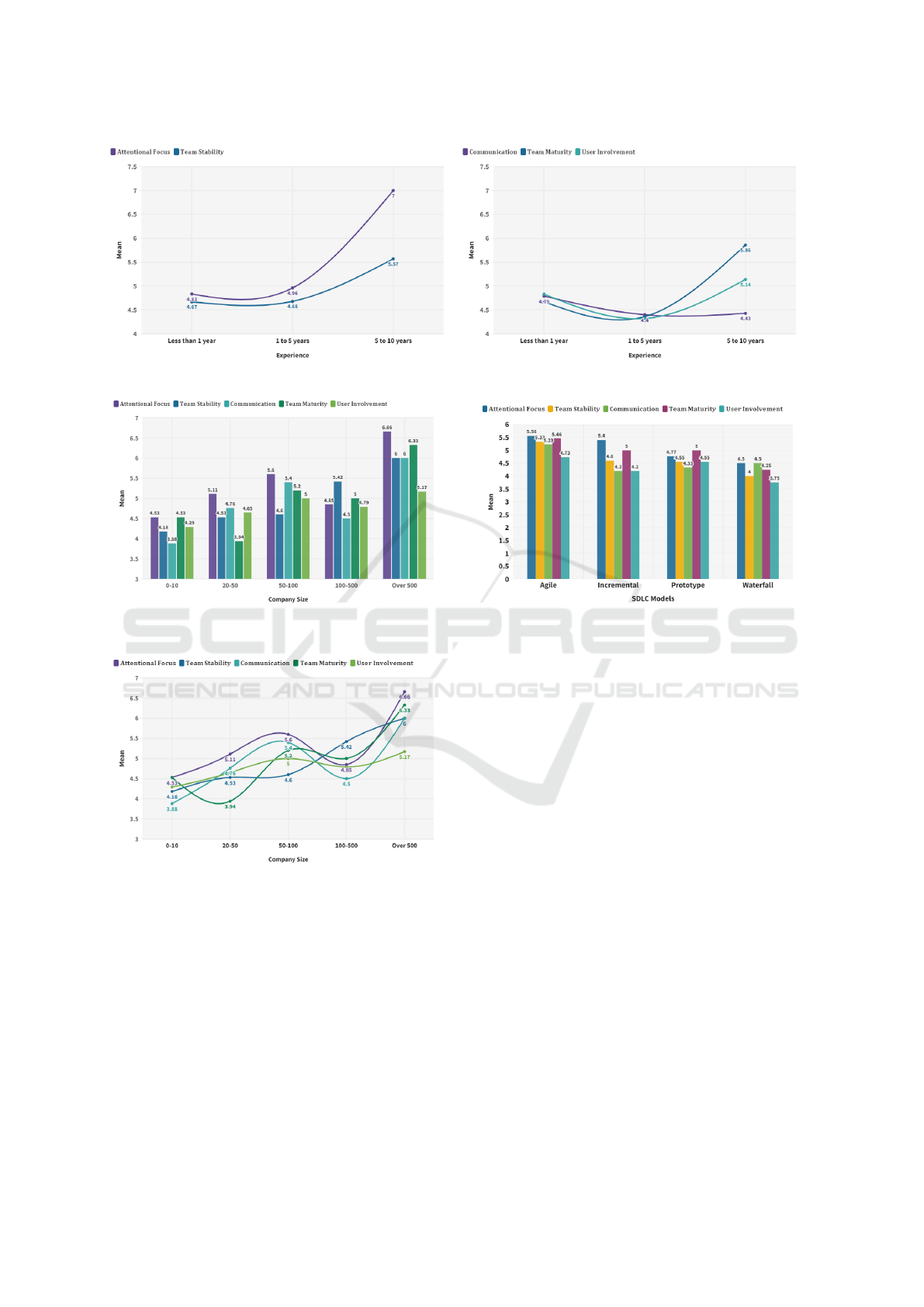
Figure 9: Change of Impact Level of Factors with Respect to Professionals’ Experience.
Figure 10: Change of Impact Level of Factors with Respect
to Company Size.
Figure 11: Change of Impact Level of Factors with Respect
to Company Size.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we investigated the impact of COVID-
19 on the factors which are influencing on-time soft-
ware project delivery. For our inquiry, we used
quantitative methods. Based on 72 responses from
11 different software companies of Bangladesh, we
conclude that User Involvement, Attentional Focus,
Team Stability, Communication, and Team Maturity
were the most important factors for on-time software
Figure 12: Change of Impact Level of Factors with Respect
to different SDLC.
project delivery in during COVID-19. On the con-
trary, Team Capabilities, Infrastructure, Team Com-
mitment, Team Stability, and Team Maturity were the
most important factors prior to COVID-19.
Team Stability and Team Maturity found as com-
mon factors both before and during COVID-19. We
also looked into the impact level change of these iden-
tified factors with respect to company size, software
professionals’ experience and use of SDLC models
by software professionals. For experienced develop-
ers, Attentional Focus was found as the most signif-
icant factor, however, for new developers, all factors
are almost equally important. For large software com-
panies, Attentional Focus was crucial whereas Team
Stability for mid-sized software companies. Atten-
tional Focus and Team Maturity were most crucial for
the developers who follow Agile. On the other hand,
as requirements are established at the beginning of
the waterfall model and users are not involved dur-
ing the entire development process, user engagement
was less important in the Waterfall development. This
study will help software companies to make strate-
gic decisions regarding on-time software project de-
livery based on the crucial identified factors. Collect-
ing data from software professionals was the great-
est challenge in this study. Therefore, conducting this
ENASE 2023 - 18th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
560

study on a large population in the future will help to
reveal more insights.
REFERENCES
Arcos-Medina, G. and Mauricio, D. (2019). Aspects of soft-
ware quality applied to the process of agile software
development: a systematic literature review. Interna-
tional Journal of System Assurance Engineering and
Management, 10(5):867–897.
Bano, M., Zowghi, D., and da Rimini, F. (2018). User
involvement in software development: the good, the
bad, and the ugly. IEEE Software, 35(6):8–11.
Bergmann, T. and Karwowski, W. (2018). Agile project
management and project success: A literature review.
In International Conference on Applied Human Fac-
tors and Ergonomics, pages 405–414. Springer.
Butt, S. A. and Jamal, T. (2017). Frequent change request
from user to handle cost on project in agile model.
Proc. of Asia Pacific Journal of Multidisciplinary Re-
search, 5(2):26–42.
Chiyangwa, T. B. and Mnkandla, E. (2017). Modelling the
critical success factors of agile software development
projects in south africa. South African Journal of In-
formation Management, 19(1):1–8.
Chow, T. and Cao, D.-B. (2008). A survey study of critical
success factors in agile software projects. Journal of
systems and software, 81(6):961–971.
Dhir, S., Kumar, D., and Singh, V. (2019). Success and fail-
ure factors that impact on project implementation us-
ing agile software development methodology. In Soft-
ware engineering, pages 647–654. Springer.
D
¨
onmez, D., Grote, G., and Brusoni, S. (2016). Routine in-
terdependencies as a source of stability and flexibility.
a study of agile software development teams. Infor-
mation and Organization, 26(3):63–83.
Edison, H., Wang, X., and Conboy, K. (2021). Comparing
methods for large-scale agile software development:
A systematic literature review. IEEE Transactions on
Software Engineering.
Ghayyur, S. A. K., Ahmed, S., Ali, M., Razzaq, A., Ahmed,
N., and Naseem, A. (2018). A systematic literature
review of success factors and barriers of agile soft-
ware development. International Journal of Advanced
Computer Science and Applications, 9(3):278–291.
Harpe, S. E. (2015). How to analyze likert and other rating
scale data. Currents in pharmacy teaching and learn-
ing, 7(6):836–850.
Harter, D. E. and Slaughter, S. A. (2003). Quality improve-
ment and infrastructure activity costs in software de-
velopment: A longitudinal analysis. Management Sci-
ence, 49(6):784–800.
Hujainah, F., Bakar, R. B. A., Abdulgabber, M. A., and
Zamli, K. Z. (2018). Software requirements prioriti-
sation: a systematic literature review on significance,
stakeholders, techniques and challenges. IEEE Ac-
cess, 6:71497–71523.
Hussain, S., Fangwei, Z., Siddiqi, A. F., Ali, Z., and Shab-
bir, M. S. (2018). Structural equation model for eval-
uating factors affecting quality of social infrastructure
projects. Sustainability, 10(5):1415.
Jørgensen, M. (2004). A review of studies on expert es-
timation of software development effort. Journal of
Systems and Software, 70(1-2):37–60.
Kamal, T., Zhang, Q., Akbar, M. A., Shafiq, M., Gumaei,
A., and Alsanad, A. (2020). Identification and pri-
oritization of agile requirements change management
success factors in the domain of global software de-
velopment. IEEE Access, 8:44714–44726.
Kula, E., Greuter, E., Van Deursen, A., and Gousios, G.
(2021). Factors affecting on-time delivery in large-
scale agile software development. IEEE Transactions
on Software Engineering, 48(9):3573–3592.
Laitinen, M. A. (2018). Net promoter score as indicator
of library customers’ perception. Journal of Library
Administration, 58(4):394–406.
Marques, R., Costa, G., Silva, M., and Gonc¸alves, P. (2017).
A survey of failures in the software development pro-
cess.
Moe, N. B., Dingsøyr, T., and Dyb
˚
a, T. (2009). Overcoming
barriers to self-management in software teams. IEEE
software, 26(6):20–26.
Ram, P., Rodriguez, P., Oivo, M., and Mart
´
ınez-Fern
´
andez,
S. (2019). Success factors for effective process met-
rics operationalization in agile software development:
A multiple case study. In 2019 IEEE/ACM Interna-
tional Conference on Software and System Processes
(ICSSP), pages 14–23. IEEE.
Ram
´
ırez-Mora, S. L., Oktaba, H., and Patl
´
an P
´
erez, J.
(2020). Group maturity, team efficiency, and team ef-
fectiveness in software development: A case study in
a cmmi-dev level 5 organization. Journal of Software:
Evolution and Process, 32(4):e2232.
Rasheed, A., Zafar, B., Shehryar, T., Aslam, N. A., Sajid,
M., Ali, N., Dar, S. H., and Khalid, S. (2021). Re-
quirement engineering challenges in agile software
development. Mathematical Problems in Engineer-
ing, 2021.
Srivastava, A., Mehrotra, D., Kapur, P., and Aggarwal,
A. G. (2020). Analytical evaluation of agile success
factors influencing quality in software industry. In-
ternational Journal of System Assurance Engineering
and Management, 11(2):247–257.
Tam, C., da Costa Moura, E. J., Oliveira, T., and Varaj
˜
ao,
J. (2020). The factors influencing the success of on-
going agile software development projects. Inter-
national Journal of Project Management, 38(3):165–
176.
Vishnubhotla, S. D., Mendes, E., and Lundberg, L. (2018).
An insight into the capabilities of professionals and
teams in agile software development: A systematic lit-
erature review. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th Inter-
national Conference on Software and Computer Ap-
plications, pages 10–19.
Impact of COVID-19 on the Factors Influencing on-Time Software Project Delivery: An Empirical Study
561
