
Toward a Goal-Oriented Methodology
for Artifact-Centric Process Modeling
Razan Abualsaud, Hanh Nhi Tran, Ileana Ober and Minh Khoi Nguyen
Institut de Recherche en Informatique de Toulouse, Toulouse, France
Keywords:
Process Management System, Process Modeling Methodology, Artifact-Centric Process Modeling, Process
Monitoring, Traceability.
Abstract:
Process management systems aim to enable a flexible yet systematic control of the execution of a process on
the basis of its model. Therefore, a process model should encompass all necessary information for achieving
the monitoring goals on the operational process. Up to this time, the research in process modeling has tended
to focus on developing process modeling languages to represent process models. However, it lacks concrete
guidelines for modelers to systematically define such models with the adequate details to enable an effective
control of process execution. In this study, we address this lack by proposing a goal-oriented methodology
for systematically modeling processes. Our methodology is dedicated to Artifact-Centric Process Modeling
(ACPM). ACPM is an emerging approach that combines both data and process in a holistic manner, thus it’s
more suitable to model complex unstructured processes. We illustrate the proposed methodology by applying
it practically to model a portion of the Rational Unified Process (RUP) with the intention of enhancing trace-
ability at execution time.
1 INTRODUCTION
A process is defined as a set of connected tasks, that
performed by process participants in order to carry
out a predetermined specific goal. Process Manage-
ment Systems (PMS) offer a great support for coor-
dinating process tasks by automating the workflow
based on the process model. Typical usage of a PMS
is process monitoring, which enables observing the
executing process with respect to specific monitoring
goals; such as measuring performance indicators for
tracking process’s artifacts to ensure that the process
meets expectations (Meroni, 2019).
As a process model serves as an input to enact a
process by a PMS, the PMS’s effectiveness on man-
aging the operational process relies on the quality of
the process model (Reijers, 2021). Process models
can have different granularity depending on the needs
that must be satisfied at operational level. Therefore,
for a successful process management implementation
project, it is crucial to create process models contain-
ing necessary details designed to meet certain process
monitoring goals.
Traditional activity-centric process modeling
mainly focuses on the workflow of process tasks and
gives a little importance to data resulted by process
execution. As a consequence, there is often a gap be-
tween process tasks and business operations on data
that leads to a separation between PMS and appli-
cations used for business operations. We adopt the
emerging paradigm Artifact-Centric Processes Mod-
eling (ACPM) that describes process based on opera-
tions on data, thus offers a more integrated manner to
take into account both data and process perspectives
(Cohn and Hull, 2009). Furthermore, in recent times,
synergies between IoT, Big Data and data-driven pro-
cess monitoring have taken place(Kun et al., 2015),
giving artifact-centric more preeminent.
The research literature shows considerable atten-
tion to developing artifact-centric process modeling
languages. However, few studies have investigated
the methodology to systematically model processes
based on the artifact-centric approach. Consequently,
modeling a process based on artifact-centric approach
stays quite challenging (Kun et al., 2015; Wan and
Liu, 2014), especially to elaborate a useful process
model for a specific monitoring goal.
To adresse this lack, we propose ArtProc-
sMod(Artifact Process Modeling), a goal-oriented
modeling methodology to assist modelers in creat-
ing an artifact-centric process model that satisfies a
specified process monitoring goal. The rest of the
656
Abualsaud, R., Tran, H., Ober, I. and Nguyen, M.
Toward a Goal-Oriented Methodology for Artifact-Centric Process Modeling.
DOI: 10.5220/0011989900003464
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE 2023), pages 656-663
ISBN: 978-989-758-647-7; ISSN: 2184-4895
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
paper is structured as follows: Section 2 introduces
the artifact-centric process modeling approach; Sec-
tion 3 describes the ArtProcsMod methodology and
illustrates it in a running example. Section 4 discusses
the related work. Section 5 concludes the paper and
outlines future works.
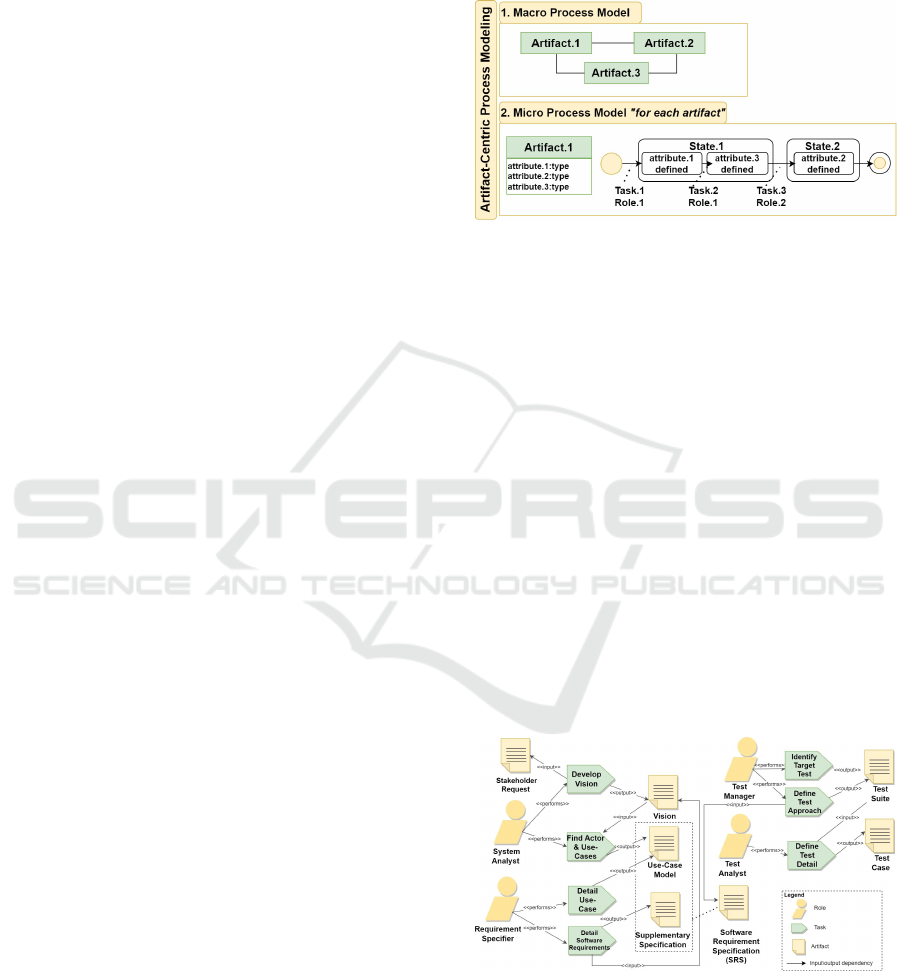
2 ARTIFACT-CENTRIC PROCESS
MODELING
The common ground for artifact-centric process mod-
eling can be described by the BALSA framework
(Hull, 2008). We outline here the four dimensions
of the framework:
• Business Artifact represents a key business-
relevant object used in the process. Each artifact
is characterized by data attributes.
• Life-cycle expresses the evolution of an artifact,
from its creation until its termination.
• Service or Task is an action manipulating an arti-
fact and making it evolve.
• Association associates a Task with an artifact to
represent the impact of the task on the evolution
of the artifact.
There are different works proposing concrete lan-
guages to represent the BALSA’s elements. Inspiring
by the works of (K
¨
unzle and Reichert, 2011), we rep-
resent an artifact-centric process model of ArtProc-
sMod methodology at two levels:
1. Macro Process Model: represents the process’s
artifacts and the relationships between them.
2. Set of Micro Process Model(s): For each artifact,
a corresponding micro process modelis created to
describe the artifact. Such that, a micro process
model consists of an information model and a life-
cycle model:
(A) The information model specifies the attributes
relevant to describe the artifact and its relation-
ships to other artifacts.
(B) Thelife-cycle model specifies the behavior of
an artifact, i.e. the possible ways that an arti-
fact might progress through the business. In this
paper, the life-cycle represents by a finite state-
machine. Tasks are associated to transitions to
express manipulations on the artifact that make
it change states. Each state represents the evo-
lution of the artifact after the task associated with
the state’s incoming transition is done. To reflect
a finer evolution of an artifact, a state can be de-
composed into a set of sub-states representing the
effects on manipulating a part of the artifact, e.g.
an attribute. Each task is associated with one role
responsible for performing the task.
Figure 1 illustrates the intended macro process model
and micro process models with the key components.
Figure 1: Artifact-Centric Process Model.
In this paper, we refer to the artifacts described
in a process model as ”observable artifacts”. I.e. an
artifact represents an item that a participant needs to
observe during the enactment of the process.
3 ArtProcsMod MODELING
METHODOLOGY
3.1 Motivating Example
This section briefly presents a motivating example
and points out the difficulties of modeling the pro-
cess using artifact-centric approach. In this example,
we model a software process based on the Rational
Unified Process®(Kruchten, 2004) (RUP). Due to the
limit of space, we only examine the partial RUP-based
process to define system requirements and test plan
for development iterations as depicted in Figure 2.
Figure 2: RUP Requirement and Test Defining Process.
The monitoring goal of the process’s participants is
supporting the traceability of working artifacts during
process execution. This goal is refined in a set of pro-
cess monitoring needs (c.f. Table 1) on the traceabil-
ity to gain further insights on the process execution.
Toward a Goal-Oriented Methodology for Artifact-Centric Process Modeling
657

Traceability means the ability to trace work items
across the development life-cycle. To do so, the
traceability model describes trace links between trace
items (Cleland-Huang et al., 2012). Artifact-Centric
Process Model could play the role of a traceability
model, where the observable artifacts are trace items
and the relations between artifacts are trace links.
The challenge here is how to provide accurate trace
links to fulfill the traceability needs. In other words,
the modeling difficulty is identifying the artifacts and
inter-artifacts relations that should be included in the
process model to enable an effective traceability.
3.2 Methodology Overview
ArtProcsMod can be characterized as being, in the
main, concerned with the modeling of a process based
on its monitoring goal. Making process monitoring
needs explicit, the designed methodology aims to pro-
vide a useful process model substantiating the process
monitoring ultimate goal.
The methodology, depicted in Figure 3, consists of
five steps which are split into two phases. We assume
that the process monitoring needs are determined and
provided as input along with the process description.
The methodology’s steps measure the fulfillment of
performance obligation i.e. delivering an ACPM cen-
tered on the process monitoring needs. The intended
delivery outputs from this methodology are a macro
process model and a set of micro process models. For
each step, we describe the purpose, the inputs, the out-
puts and the guidelines (i.e. modeling best practices).
In addition, we demonstrate each step by applying it
in a running example.
3.2.1 Pre-Modeling Phase
The aim of pre-modeling phase is to have a clear un-
derstanding of the process and the process monitoring
needs, in order to propose a set of process modeling
requirements that will be used as a base to direct mod-
elers during the modeling phase.
Step 1: Analyze Artifact Relations
Objective: to provide a holistic view of the managed
artifacts, their relations and characteristics.
Input: process description, which can be gathered ei-
ther through interviews or documentation.
Output:initial macro process model showing the pro-
cess’s participating artifacts and their relationships.
Guidelines: in this step, the modeler needs to ana-
lyze the process description in order to identify the
artifacts participating in the process and the relations
between them. The complexity of this step depends
on the level of formality of the process description.
Application in the Running Example: from the RUP
process description in Figure 2, we identify the partic-
ipating artifacts corresponding to the “trace artifacts”
of RUP. By analyzing the inputs and outputs of RUP
activities, we can deduce the dependencies between
the artifacts as shown in Figure 4.
Step 2: Specify Modeling Requirements
Objective: to develop a set of process modeling re-
quirements from a given process monitoring needs.
Input: Process Monitoring Needs (PMN), which are
statements specifying in-details the process monitor-
ing goal. Each need expresses the information that
the process participants want to know when executing
the process. In general, such information concerns the
process items that must be traced at run-time. Those
items are in fact the instances of some observable arti-
facts in the process model. An extraction of the PMN
for the running example is given in Table 1. They
specify the concrete needs of traceability as the mon-
itoring goal.
Table 1: Process Monitoring Need (PMN).
PMN1
Identify the impacted Use-Cases (UC) when changing the
concern of a particular Stakeholder Need (SKN).
PMN2
Identify the impacted UCs when changing the content of the
Iteration Test Package.
PMN3
Identify the Users who are responsible for manipulating a
particular UC.
Output: Process Modeling Requirements (PMR),
which are statements that are requisite to confirm the
process monitoring needs. The idea of stating the
process model requirements is to ensure the specifi-
cation of the observable artifacts and/or relations that
we need to have in the process model.Guidelines: for
each monitoring need:
a. Identify the required observable artifacts.
b. Identify the required observable relations.
c. Identify the set of required observable tasks that
entails the set of actions required to manipulate a
specific artifact.
The challenge of this step is to make an abstraction
from the needs expressed on instance level into the
requirements on the process elements on the model
level. To facilitate this model requirement elicita-
tion step, we collected and analyzed various PMN
and their corresponding PMR to identify the common
transformation rules. As a result of this work, we pro-
pose some transformation patterns to transform a need
PMN to a requirement PMR.
ENASE 2023 - 18th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
658
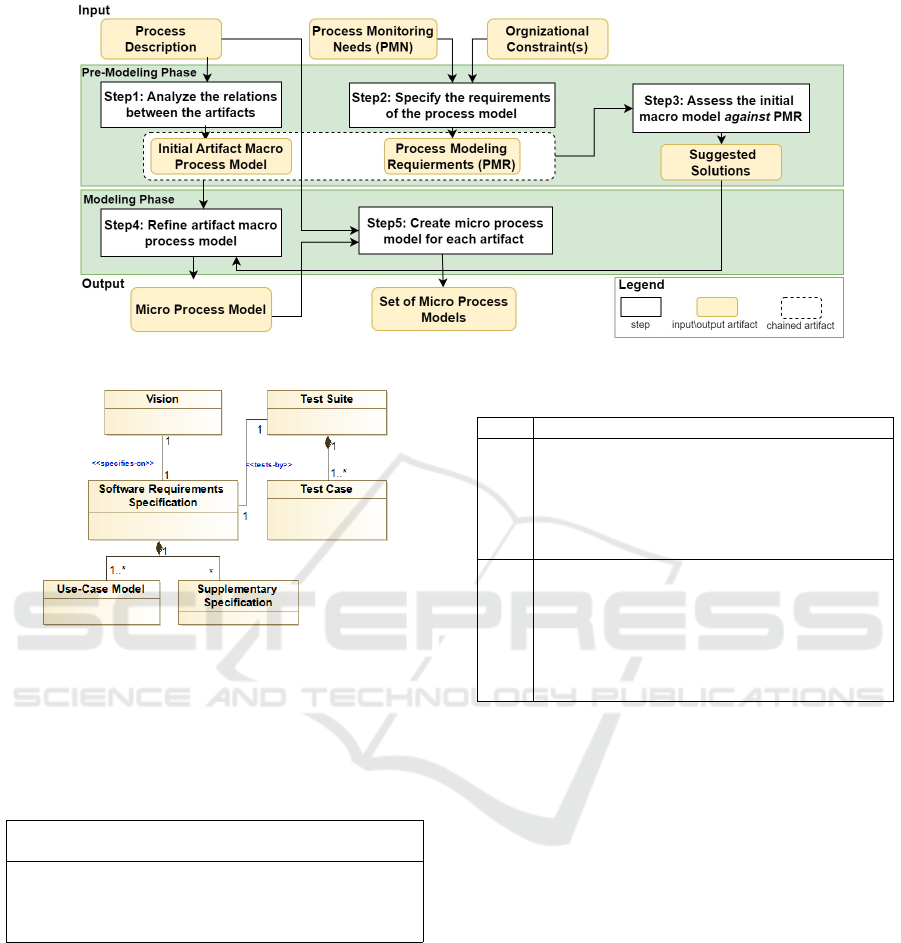
Figure 3: Schematic overview of ArtProcsMod Methodology.
Figure 4: Initial macro process model.
Table 2 illustrates one transformation pattern that
can be applied to the needs PMN1 and PNM2 in Ta-
ble 1. An in-depth discussion of the full list of pat-
terns are omitted to conserve space.
Table 2: PMN2PMR Transformation Pattern.
PMN
Identify the impacted Artifacts A2 when changing Artifacts
A1 by doing Action S
PMR1 A1 must be an observable artifact
PMR2 A2 must be an observable artifact
PMR3 The relation between A1 and A2 must be observable
PMR4 The action S must be observable
Application in the Running Example: Table 3
depicts the requirements developed from the need
PMN1 in Table 1, by applying the pattern in Table
2.
Step 3: Assess the Initial Macro Process Model
Against the PMR
Objective: to verify if the initial macro process model
satisfies the PMR identified in the previous step.
Input: PMR and initial macro process model.
Output: list of suggested solutions, which propose the
modeling solutions for unachievable requirements.
Table 3: PMRs developed from PMN1 and PMN2.
PMN Process Modeling Requirement (PMR)
PMN1 PMR1: SKN must be an observable artifact.
PMR2: UC must be an observable artifact.
PMR3: The relation between SKN and Use-Cases. must be
observable.
PMR4: The actions of changing the concerns of a SKN
must be observable.
PMN2 PMR5: Use-Case must be an observable artifact.
PMR6: The Iteration Test Package must be an observable
artifact.
PMR7: The relation between Use-Case and the Iteration
Test Package must be observable
PMR8: The actions of changing the content of an Iteration
Test Package must be observable.
Guidelines: for each PMR
a. Identify the required improvements and/or lack
relative to the initial macro process model. The
lack might be a missing artifact(s) or relation(s)
in the initial macro process model.
b. Analyze the cause of the lack. The lack includes a
missing artifact in the initial macro process model
and/or missing relation. Accordingly, the most
common causes include: the missing artifact is a
composite attribute specified in another artifact or
the missing artifact does not described in the pro-
cess description.
c. Suggest solution to the defined lack. The sug-
gested solution proposes a solution to enrich the
initial macro process model to ensure that the
process model encompasses the details necessary
to achieve the corresponding PMN. The solution
will be used as a base for the modeling phase.
Once more, to facilitate the generation of solutions for
recurrent problems, we analyzed common causes of
lacks and proposed some modeling patterns for such
problems. Table 4 shows two of these modeling pat-
Toward a Goal-Oriented Methodology for Artifact-Centric Process Modeling
659
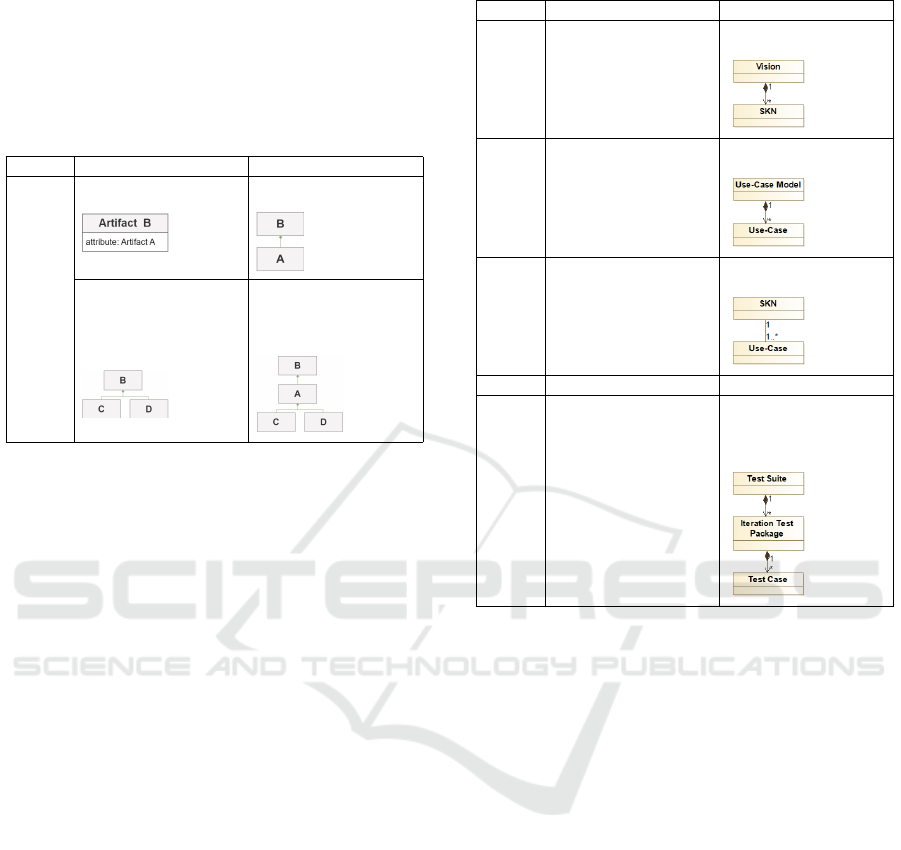
terns to handle the problem of a missing artifact A.
According to the PMR, A must be observable but it
cannot be found in the current macro process model.
There are two possible causes of such a problem as
shown in Table 4. For each cause, the pattern sug-
gests a solution.
Table 4: Solution Patterns for Missing Artifact Problem.
Lack Cause Suggested Solution
Artifact
A is
missing
A is a “hidden“ component of
a composite artifact B
Represent A as an artifact
connected to B
A is not explicitly described
in the standard process
description, but in some
specific constraints of the
project
Define a new artifact A and
create the relation from A to
related artifacts based on the
given constraints
Application in the Running Example. Table 5 illus-
trates the results of the assessment of the initial macro
process (c.f. Figure 4) against the requirements re-
lated to the PMN1 and PMN2. We only show some
requirements concerning the macro process model,
concretely the PMR1, PMR2, PMR3 and PRM5 and
PMR6.
Consider the PMR1 “SKN must be an observable
artifact”. From the initial macro process model, a
SKN is a missing artifact because it is “hidden” in
the artifact Vision as a component. Thus, we suggest
a refinement of the artifact Vision to model its com-
ponents as observable artifacts as well. Thus, SKN
becomes an observable artifact as required in PMR1.
Another example considers the PMR3 “The rela-
tion between SKN and Use-Cases. must be observ-
able”. From the initial macro process model, the re-
lation between SKN and UC is missing because these
two artifacts are not observable. However, there exists
an indirect dependency between these two artifacts
through their parents, i.e. the relation between Vi-
sion and Software Requirement Specification(SRS).
In order to facilitate traceability of changes impacts
on UC when changing SKN, a direct relation should
be established between these two artifacts.
3.2.2 Modeling Phase
Step 4: Refine Macro Process Model
Objective: to refine the initial macro process
model by taking into consideration thesuggested so-
lutions proposed in Step 3.Input: suggested solu-
tions and the initial macro process model. The
Table 5: Suggested Solution.
PMR Lack & Cause Suggested Solution
PMR1
SKN is missing
SKN is a hidden component of
the artifact Vision
Represent SKN as an artifact
connected to Vision.
PMR2
UC is missing
UC is a hidden component of
the artifact Use-Case Model
Represent UC as an artifact
connected to Use-Case
PMR3
Relation between UC and
SKN is missing
The artifacts in this relation
are missing in the initial
model
Make an observable relation
between UC and SKN
PMR5 c.f. PMR2 c.f. PMR2
PMR6
Iteration Test Package is
missing
The Iteration Test package is
not a standard RUP artifact
but an local organizational
artifact
Define Iteration Test Package
artifact which contains the
Test-Case planned for an
iteration
suggested solutions indicate which observable arti-
facts and relations should be added to the initial
macro process model.Output: Final Macro Process
Model.Guidelines: In this step, we need to consider
the suggested solutions from Step 3 and refine the ini-
tial macro process model accordingly.Application in
the Running Example: Figure 5 shows the macro
process model as the result of this modeling step on
the running example.
Step 5: Create Micro Process Models
Objective: to create a micro process model for each
artifact defined in the macro process model in Step 4.
Input: the final macro process model m, the sug-
gest solutions s and the process description p. The
macro process model defines the set of artifacts that
micro process models must be created for. The Sug-
gested solutions indicate the required actions that
must be observable in the micro process life-cycle
model. The business rules, (provided in the process
description), give details on the tasks corresponding
to the actions manipulating a specific artifact. Gen-
erally, business rules specify the role performing an
action, the precondition to enable the action and the
post-condition to describe the effect of the action on
ENASE 2023 - 18th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
660
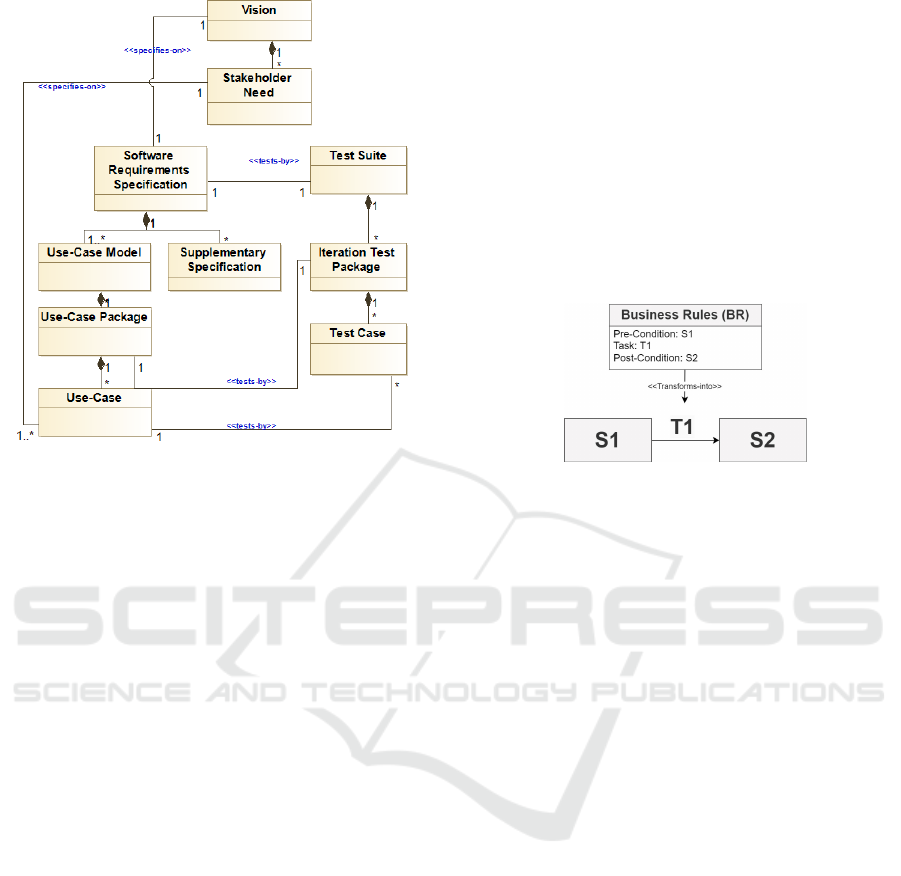
Figure 5: Final Macro Process Model.
an artifact. Output: a set of micro process models.
Such that, for each artifact defined in the macro pro-
cess model, a corresponding micro process model is
created. A micro process model consists of two mod-
els. Namely, information model and life-cycle pro-
cess model.Guidelines: for each artifact a ∈ m :
1. Create the Information Model of a: describing a’s
attributes extracted from the given process descrip-
tion.
2. Create the Life cycle Model of a: defining a be-
havioral model for an artifact is not a trivial task. We
propose some guidelines to progressively create the
life cycle model of an artifact.
2.1. Create an initial life-cycle model
In this step, we create an initial life-cycle from the
process description. We suggest the following Mod-
eling Rules (MR) to realize the step:
a. MR.1. For each artifact’s attribute att of the ar-
tifact a, define a corresponding state attDe f ined
corresponding to the data acquisition of the at-
tribute att.
b. MR.2. For the attributes that are manipulated by
one named task specified in one of the business
rules, group their corresponding states into a com-
posite state. To do so, from the process descrip-
tion, identify the business rules that must be sat-
isfied by the artifact a. From those business rules
we can infer if some attributes can be manipulated
simultaneously, accordingly they can be enclosed
by one state.
c. MR.3. Establish the transition between the states.
From the process description, identify the busi-
ness rules that must be satisfied by the artifact a.
From the pre and post conditions of those rules,
infer the transitions between the states of a.
Some rules are not easy to translate in a straightfor-
ward way. Thus, in order to streamline the work for
modelers, we provide some patterns to generate the
life-cycle’s states from the business rules. One trans-
formation pattern is shown in Figure 6 illustrates how
the preconditions and post-conditions of a task spec-
ified by the business rule are transferred into states
in the life-cycle model with the task is the transition
between these states.
Figure 6: Business rule to life-cycle transformation.
2.2. Assess the initial life-cycle model against the
process modeling requirements
In this step, we refine the initial life-cycle based on
the suggestion solutions obtained from Step 3 in or-
der to ensure that PMRs are satisfied. The assessment
includes defining the lacks (e.g. required observable
actions) from the PMR Step 2 and refine the life-cycle
accordingly.
Application of the step in the running example: We
develop a micro process model for the artifact Stake-
holder Need (SKN).
First, we create the SKN information model by
identifying its attributes. Second, we create the SKN
life-cycle model following the guidelines. Figure 8
illustrates the SKN micro process model. As illus-
trated in the Figure 8 (A) implies defining the states
of SKN by applying the MR.1, which states that for
each attribute a corresponding state is created. Figure
8 (B) represents the SKN initial life-cycle after group-
ing attributes that can be manipulated simultaneously
into one state by applying the MR.2. Figure 8 (C) rep-
resents the refined life-cycle (i.e. satisfies the PMR4
for the PMN1, which states “The actions of changing
the concern of a SKN must be observable”. From this
requirement we can infer the need of tracing the SKN
state when its related concerns are changed, and ac-
cordingly, we translate this by creating a correspond-
ing observable state.
The running example shows that the steps in Art-
ProcsMod confer benefits to create viable Artifact-
centric Models that are aligned with the process mon-
itoring needs.
Toward a Goal-Oriented Methodology for Artifact-Centric Process Modeling
661
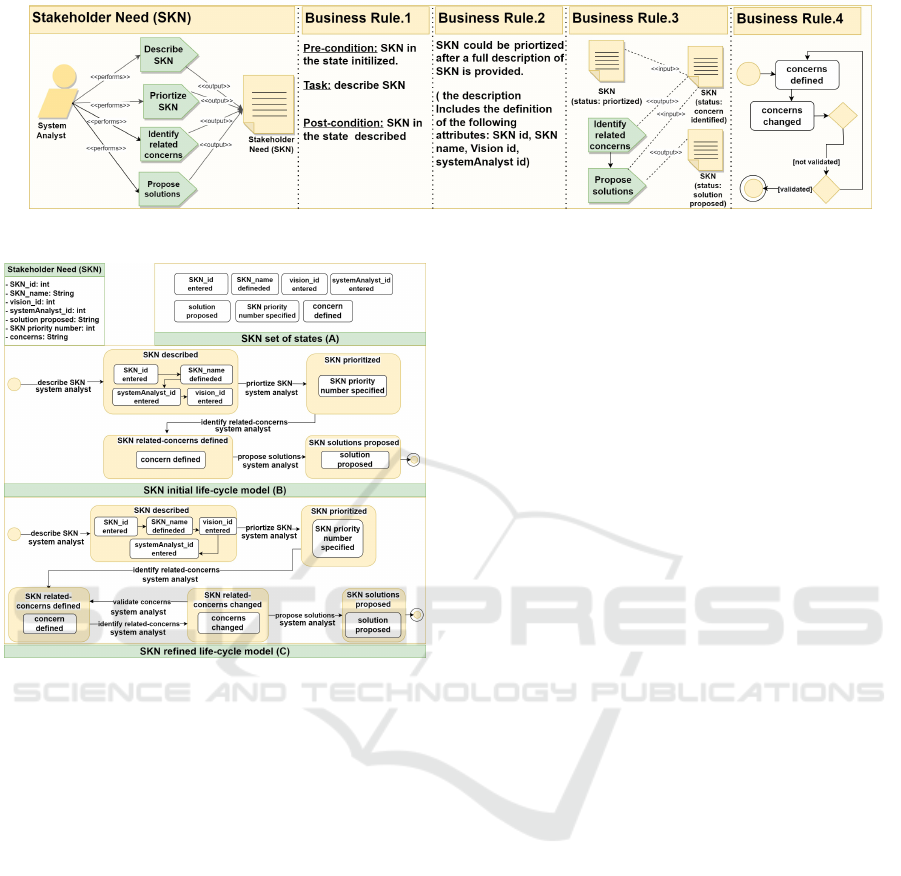
Figure 7: SKN - related tasks and business rules (extracted from the process description document).
Figure 8: Stakeholder Need micro process model creation
steps.
4 RELATED WORKS
In this section, we examine the related work in two
areas: first, the works on representing processes from
the artifact-centric perspective; second, the works
proposing methodology to create artifact-centric pro-
cess models. Artifact-Centric Process Modeling
(ACPM), first introduced in (Nigam and Caswell,
2003), with a view to focuses on the data that is
needed to carry out the different tasks in a process,
and the dependencies between these data.(Hull, 2008)
presents the BALSA framework in order to facili-
tate the definition and the structuring of ACPM. In
2010, a declarative style of ACPM, called Guard-
Stage-Milestone (GSM), was introduced(Hull et al.,
2011). Other approaches related to ACPM intro-
duced by (Van der Aalst et al., 2017), who provides
an object-centric behavioral constraint approach com-
bines ideas from declarative, constraint-based lan-
guages, and from data modeling techniques. A con-
tinuous research on developing a flexible framework
for an object-aware process management system is
realizing by PHILharmonic Flows group(K
¨
unzle and
Reichert, 2011).
Concerning the methodologies to model processes
based on ACPM, there are some works such as (Fritz
et al., 2009; Eshuis and Gorp, 2015; Popova and Du-
mas, 2013; Kumaran et al., 2008; Governatori and
Rotolo, 2010) study the formal aspect to enable de-
riving an artifact-centric specification from a process-
centric one or vice-versa. However, small number of
studies investigate a methodology to systematically
model processes based on ACPM. To our knowledge,
there is only (Bhattacharya et al., 2009) that proposes
a data-centric design methodology to define different
life-cycles for different artifacts from scratch. And
(Yongchareon and Liu, 2010) that develops a bottom-
up abstraction mechanism to derive views from un-
derlying process models according to view require-
ments. The works in (Bhattacharya et al., 2009) and
(Yongchareon and Liu, 2010), however, do not pro-
vide concrete guidelines for modelers to define pro-
cess based on ACPM.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents ArtProcsMod, a goal-oriented
modeling methodology to create an Artifact-Centric
Process Model (ACPM) that satisfies a specified pro-
cess monitoring goal. The study reveals several chal-
lenges when modeling the process to support a spe-
cific monitoring goal in the running time, such as
defining the right level of granularity of an artifact or
the need of defining intermediate artifacts. We pro-
pose solutions to address these challenges as part of
our iterative application of ArtProcsMod in model-
ing a portion of the Rational Unified Process (RUP)
with the intention of enhancing traceability at execu-
tion time.
From the present study, we observe that the
artifact-centric process model can play the role of
the Traceability Information Model(TIM)(Cleland-
Huang et al., 2012), detailing the artifacts and the
ENASE 2023 - 18th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
662

relation between them. A particular strength of an
ACPM created with ArtProcsMod with enhancing the
traceability is that it derived from designated pro-
cess monitoring needs. The application of the process
monitoring needs allow ACPM to specify intermedi-
ate artifacts that lead to enhance the accuracy of the
trace path. In addition, ACPM supports the integra-
tion of roles in the informational model. Hence, al-
lowing the creation of trace paths between the roles
and the produced or manipulated artifacts. And fi-
nally, ACPM keeps track of the tasks that are meant
to produce an artifact.
As part of our future work, we plan to further eval-
uate the methodology by applying it in real-life cases
where traceability is important, e.g. software devel-
opment and healthcare system. Another direction in-
cludes discovering more modeling patterns for some
determined methodology’s steps. More thoroughly,
we intend to propose a process modeling language,
that directly specifies process modeling requirements
and enables automatic transformations of some Art-
ProcsMod’s steps.
REFERENCES
Bhattacharya, K., Hull, R., and Su, J. (2009). A data-centric
design methodology for business processes. In Hand-
book of Research on Business Process Modeling.
Cleland-Huang, J., Heimdahl, M., Huffman Hayes, J., Lutz,
R., and Maeder, P. (2012). Trace queries for safety
requirements in high assurance systems. In Regnell,
B. and Damian, D., editors, Requirements Engineer-
ing: Foundation for Software Quality, pages 179–193,
Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Cohn, D. and Hull, R. (2009). Business artifacts: A data-
centric approach to modeling business operations and
processes. IEEE Data Eng. Bull., 32:3–9.
Eshuis, R. and Gorp, P. V. (2015). Synthesizing data-centric
models from business process models. Computing,
98:345 – 373.
Fritz, C., Hull, R., and Su, J. (2009). Automatic con-
struction of simple artifact-based business processes.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference
on Database Theory, ICDT ’09, page 225–238, New
York, NY, USA. ACM.
Governatori, G. and Rotolo, A. (2010). Norm compliance in
business process modeling. In Dean, M., Hall, J., Ro-
tolo, A., and Tabet, S., editors, Semantic Web Rules,
pages 194–209, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Hull, R. (2008). Artifact-centric business process mod-
els: Brief survey of research results and challenges.
In Meersman, R. and Tari, Z., editors, On the Move
to Meaningful Internet Systems: OTM 2008, pages
1152–1163, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Hei-
delberg.
Hull, R., Damaggio, E., Masellis, R. D., Fournier, F.,
Gupta, M. P., Heath, F. T., Hobson, S. F., Linehan,
M. H., Maradugu, S., Nigam, A., Sukaviriya, N., and
Vacul
´
ın, R. (2011). Business artifacts with guard-
stage-milestone lifecycles: managing artifact interac-
tions with conditions and events. In Distributed Event-
Based Systems.
Kruchten, P. B. (2004). The rational unified process - an
introduction, 3rd edition. In Addison Wesley object
technology series.
Kumaran, S., Liu, R., and Wu, F. Y. (2008). On the dual-
ity of information-centric and activity-centric models
of business processes. In Bellahs
`
ene, Z. and L
´
eonard,
M., editors, Advanced Information Systems Engineer-
ing, pages 32–47, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Kun, N., Yu, J., and Yongchareon, S. (2015). A survey on
approaches to modeling artifact-centric business pro-
cesses. pages 117–132.
K
¨
unzle, V. and Reichert, M. (2011). Philharmonicflows:
Towards a framework for object-aware process man-
agement. Journal of Software Maintenance and Evo-
lution Research and Practice, 23:205–244.
Meroni, G. (2019). Artifact-driven business process mon-
itoring: A novel approach to transparently moni-
tor business processes, supported by methods, tools,
and real-world applications. Artifact-Driven Business
Process Monitoring.
Nigam, A. and Caswell, N. S. (2003). Business artifacts: An
approach to operational specification. IBM Systems
Journal, 42(3):428–445.
Popova, V. and Dumas, M. (2013). From petri nets to guard-
stage-milestone models. In La Rosa, M. and Soffer,
P., editors, Business Process Management Workshops,
pages 340–351, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Reijers, H. A. (2021). Business process management: The
evolution of a discipline. Computers in Industry,
126:103404.
Van der Aalst, W., Artale, A., Montali, M., and Tritini, S.
(2017). Object-centric behavioral constraints: inte-
grating data and declarative process modelling. CEUR
Workshop Proceedings. CEUR-WS.org.
Wan, X. and Liu, G. (2014). Complexity of construct-
ing fsm model of artifact lifecycle. 2014 10th In-
ternational Conference on Semantics, Knowledge and
Grids, pages 29–32.
Yongchareon, S. and Liu, C. (2010). A process view frame-
work for artifact-centric business processes. volume
6426, pages 26–43.
Toward a Goal-Oriented Methodology for Artifact-Centric Process Modeling
663
