
A Mobile Serious Game to Foster Music Sight Reading with Different
Clefs
Adriano Barat
`
e
a
, Andrea Brugaletta and Luca A. Ludovico
b
Laboratory of Music Informatics (LIM), Department of Computer Science “Giovanni Degli Antoni”,
University of Milan, via G. Celoria 18, 20133 Milan, Italy
Keywords:
Music, Education, Mobile Applications, Serious Games, Clefs.
Abstract:
This work introduces a mobile app that aims to promote the sight-reading of music with different positions of
the clef on the stave. Relying on the principles of game-based learning, the app offers applications primarily
in the didactic field: by facilitating and encouraging the learning of this challenging aspect of music, the app
on one side contributes to the preservation of intangible musical heritage and, on the other, serves practical
educational purposes such as the preparation for Conservatory exams. The results of early experimentation
show a general appreciation by test users as it concerns engagement, but also highlight a number of interaction
aspects to be improved.
1 INTRODUCTION
A game refers to a structured play with rules, goals,
and challenges for the purpose of entertainment
(Cheng et al., 2015). The term “gamification” first
emerged in the first decade of the 2000s and gained
increasing relevance since the 2010s. In contrast
to games, gamification is characterized by its seri-
ous purpose. Gamification is closely related to the
concepts of serious games and game-based learning
(Krath et al., 2021). The latter locution refers to the
achievement of defined learning outcomes through
game content and play and enhancing learning by in-
volving problem-solving spaces and challenges that
provide learners, who are also players, with a sense of
achievement. Serious games, being designed to have
a primary purpose other than pure entertainment, are
the means to achieve game-based learning.
Serious games have gained increasing attention in
recent years as a promising tool for education and
training. By leveraging the motivational power of
games, serious games offer a unique opportunity to
engage learners in a fun and interactive way while still
delivering meaningful content. The serious and the
game parts have to be carefully balanced in order to
meet quality criteria, as explained in (Caserman et al.,
2020).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8435-8373
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8251-2231
Serious games demonstrated to be effective in
various domains, such as health (Sharifzadeh et al.,
2020), military (Gace et al., 2019), and corporate
training (Larson, 2020). Moreover, it is worth men-
tioning the research on the effects of serious games
on people with intellectual disabilities, autism spec-
trum disorder, developmental disabilities, and cogni-
tive and physical impairments (Tsikinas and Xinoga-
los, 2019; de Vasconcelos et al., 2020; Kokol et al.,
2020; Vieira et al., 2021).
However, despite the growing interest in serious
games, there is still a need for more rigorous research
to investigate their effectiveness in different learning
contexts, as well as to identify best practices for their
design and implementation (Backlund and Hendrix,
2013; Bellotti et al., 2013; Giessen, 2015; Zhonggen,
2019).
This paper is the evolution of a previous work
that provided only the guidelines for the implemen-
tation of a serious game in the form of an app (Barat
`
e
and Ludovico, 2013). With respect to the mentioned
work, the main aspects of novelty concern the avail-
ability of a working prototype and, consequently, the
possibility to report on an early test phase. After com-
pleting the beta testing and passing the required pri-
vacy, security, and content verification by Apple, the
prototype will be made freely available in the App
Store.
In this work, we first present a systematic review
of the existing literature on serious games in music-
Baratè, A., Brugaletta, A. and Ludovico, L.
A Mobile Serious Game to Foster Music Sight Reading with Different Clefs.
DOI: 10.5220/0012059500003470
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2023) - Volume 1, pages 397-403
ISBN: 978-989-758-641-5; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
397

oriented learning environments, examining the evi-
dence base for serious games as a tool for learning
and considering the factors that contribute to their ef-
fectiveness. We also explore the design principles
that have been proposed for music-oriented serious
games. Then, we propose a mobile app that imple-
ments a serious game to encourage the practice of mu-
sic sight reading in a number of clefs, an activity often
considered boring and uninteresting by young music
learners. After an early test phase, we discuss the lim-
itations of current research and identify directions for
future research.
The rest of this work is structured as follows: Sec-
tion 2 addresses the adoption of computer-supported
systems in music education, focusing in particular
on mobile apps for sight reading; Section 3 intro-
duces the music theory behind the problem we want
to solve, namely the development of abilities in sight
reading with different clefs; Section 4 describes the
technical details, the graphical interface, and the
gameplay of the proposed serious game; Section 5 re-
ports on early experimentation conducted on a small
number of test users; finally, Section 6 discusses the
applicability of such an approach to music education
and draws the conclusions.
2 RELATED WORKS
Serious games that use computer technology to teach
and learn music have been widely researched and
implemented. The scientific literature on computer-
based serious games related to music is extensive and
covers a wide range of topics, including simulated
instrumental practice, advanced ear training, music
composition, graphical representation and analysis of
scores, and motion-tracking techniques for control-
ling music and audio parameters. Barat
`
e et al. pro-
vide a number of significant examples (Barat
`
e et al.,
2013).
To our goals, the field can be narrowed to mobile-
oriented applications related to music edutainment
and ear training.
There are software tools aiming to simulate tradi-
tional musical instruments or implement brand-new
ones. Examples documented in the scientific liter-
ature include the Smule Ocarina (Wang, 2009) and
PhonHarp (Presti et al., 2021). A more recent in-
vestigation about the state of the art and the future
perspectives of mobile devices employed as musical
instruments is provided in (Essl and Lee, 2018).
Social interaction in music-making through mo-
bile devices is the basis of projects such as Momu, a
music toolkit for mobile devices (Bryan et al., 2010),
MoPhO, the Stanford Mobile Phone Orchestra (Oh
et al., 2010), and the Mobile Device Marching Band,
a revised version of the Princeton Laptop Orchestra
(Snyder and Sarwate, 2014). Mobile devices can also
be used to implement audience-participation tech-
niques based on social mobile computing (Oh and
Wang, 2011).
Zhou et al. describe the experience of MOG-
CLASS, a collaborative system of music to perform in
a classroom context (Zhou et al., 2011). Another rel-
evant early example is provided by Rhythmatical, an
educational application designed for iPhone and iPod
Touch that conveyed mathematical topics via musi-
cal, rhythmic, or movement interactive techniques
(Moorefield-Lang and Evans, 2011).
Particularly relevant to our goals are mobile apps
for sight reading (Loman and Wiradinata, 2014;
Larasati and Sukmayadi, 2021). Even if not docu-
mented in the scientific literature, it is worth mention-
ing applications such as Music Tutor (Sight-Reading)
by Jsplash Apps, Music Crab: Easy Music Theory
by Eric Zorgniotti, Notes Teacher by Yannis Richard,
Note Flash Music Sight Reading by Pranoy Chowd-
hury, and Note Brainer by James Buchanan. These
products are similar to our proposal as it concerns
the general goals and the graphical interface, but they
mainly address standard music notation and, as such,
are not aimed at sight reading with multiple alternat-
ing clefs.
3 THE 9-CLEF SYSTEM
In Western Music Notation, a clef is a musical symbol
that fixes which notes are represented by the lines and
spaces on a musical stave. Music theory, based on
the evolution of European music across the centuries,
currently recognizes three clef symbols: the C-clef,
F-clef, and G-clef. The placement of a given clef on
a specific stave position assigns a particular pitch to
one of the five lines, consequently defining the pitches
on the remaining lines and spaces. For example, the
G-clef on the second line of the stave states that the
pitches on that line are G notes of the central octave,
thus the pitches on the lower line are E notes and those
on the upper line are B notes.
The use of different clefs, concerning both the mu-
sic symbol and its placement on the stave, makes it
possible to write music for all instruments and voices,
taking into account differences in their range. Using
different clefs for different instruments and voices al-
lows each part to be written comfortably on a stave
with a minimum of ledger lines.
In fact, the mentioned clef symbols not only iden-
CSME 2023 - 4th International Special Session on Computer Supported Music Education
398

Figure 1: Clefs commonly in use in musical practice. From left to right: French violin, Trable, Soprano, Mezzo-soprano,
Alto, Tenor, Baritone (two versions), Bass, and Subbass.
tify different reference notes but can also be theoreti-
cally placed on each stave line, thus moving the spe-
cific reference note across the stave. The combination
of 5 lines and 3 clefs originates 15 possibilities for
clef placement, but 6 would be redundant since they
would result in an identical assignment of the notes to
lines and spaces. For the sake of clarity, a G-clef on
the fourth line achieves the same note placement as a
C-clef on the second line. As a consequence, histori-
cally only 9 distinct clefs have been in use (see Fig. 1):
the G-clef on the two bottom lines, the C-clef on any
line, and the F-clef on the three top lines. Even if the
C-clef on the top line is equivalent to the F-clef on the
third one, both options have been employed in music
notation.
Concerning music notation, such a system has
been in disuse for more than a century. Nowadays,
leaving out the editions that use the ancient nota-
tion for philological reasons, the soprano, mezzo-
soprano, and contralto parts are written in the treble
clef, whereas the baritone and bass parts are written
in the bass clef; for the tenor part, the suboctave tre-
ble clef is used, i.e. a standard treble clef accompanied
by a sign to indicate the execution in the lower octave.
Concerning musical instruments, the alto clef is still
adopted by the viola and the alto trombone and the
tenor clef is an auxiliary notation for the cello, trom-
bone, bassoon, double bass, and contrabassoon. Mod-
ern instrumentation and orchestration texts still sug-
gest their use for specific instrumental scoring (Blat-
ter, 1997).
In the Italian formal music-education system, the
study of this subject is known as setticlavio, an Ital-
ian word literally standing for “seven clefs”. In fact,
seven is the number of male and female tessituras
used in vocal music (soprano, mezzo-soprano, alto,
tenor, baritone, and bass) plus the Treble clef. Any-
way, for extension, the study of setticlavio involves
all the possibilities shown in Fig. 1.
Setticlavio, intended as a solfeggio alternating all
the clefs, represents one of the sight-reading tests of
the Musical Theory and Solfeggio license in Italian
conservatories, both in a spoken and in a sung form.
Fig. 2 shows an example of setticlavio taken from
the final exam at the Conservatory of Brescia. More-
over, its use is required in Composition courses deal-
ing with ancient music. Due to its infrequent use in
Figure 2: An example of handwritten setticlavio for the final
test of Music theory and solfeggio at the Conservatory of
Brescia.
contemporary music notation, the study of the setti-
clavio is often considered difficult and perceived as
useless. This is particularly true for young music stu-
dents who are the typical participants of Musical The-
ory and Solfeggio courses.
4 THE APPLICATION
In this section, we describe in detail iClef, the serious
game we developed in the form of an app for mo-
bile devices. The application is currently available
to developers as a beta release and runs on iOS de-
vices only. A cross-platform implementation using
Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile, React Native, Xamarin,
or similar technologies is currently under study.
4.1 Design
During the design phase of iClef, we first analyzed the
factors that make a serious game effective. It is impor-
tant to consider the specificity and distinctive charac-
teristics of each game, but it is possible to find in the
literature some common components that involve an
increase in the effectiveness of serious games, i.e. in
their ability to achieve the intended purpose. From a
study conducted on 63 serious games (Ravyse et al.,
2017), five common factors emerged: storytelling, re-
alism, adaptability, interactivity, and feedback. In the
case of iClef, the first two items, typical of interactive
and immersive games, can be overlooked. Rather, we
focused on the last three, namely adaptability, inter-
A Mobile Serious Game to Foster Music Sight Reading with Different Clefs
399
activity, and feedback.
The main role of adaptability is to adjust the
training pace, with the goal of avoiding frustration on
one side and keeping the engagement level high on
the other. Specifically, in this scenario, adaptability
can be seen as the ability to adjust the difficulty of the
game according to the skill displayed by the player
during the gameplay. To this end, a user-performance
analysis mechanism has been implemented, with par-
ticular reference to response times. Within the app,
there are four elements that make the game more or
less complex:
• the time available to guess a note, which naturally
decreases during the gameplay, unless a mistake
occurs;
• the number of keys which, is chosen before the
game starts (see Section 4.3);
• the width of the interval between two consecutive
notes, which normally increases during the game-
play, unless a mistake occurs;
• the number of accidentals applied to the notes. At
the beginning of the gameplay, only natural notes
are proposed, but soon single and even double ac-
cidentals can appear.
Adaptability is implemented by making all the
mentioned parameters change to either increase or de-
crease the difficulty in relation to the user’s behavior.
Interactivity is strictly connected to the game
mode proposed to the player, which implies the timed
presentation of a sequence of notes written in dif-
ferent clefs and the consequent choice of the pitch
considered correct by the user through a point-and-
click action to perform on the device. Interactivity is
multimodally reinforced through the use of sound, as
shown below.
The feedback component is mainly conveyed
through two factors: the score, whose progression is
closely related to the user’s performance, and some
simple visual and audio cues. In particular, in the case
of success, the graphical representation of the note is
colored in green, and the pitch is aurally performed; in
the other case, the note is colored in red, and an audio
icon remarks on the mistake. The feedback compo-
nent allows players to immediately perceive a cause-
and-effect link between their actions and the game re-
sult.
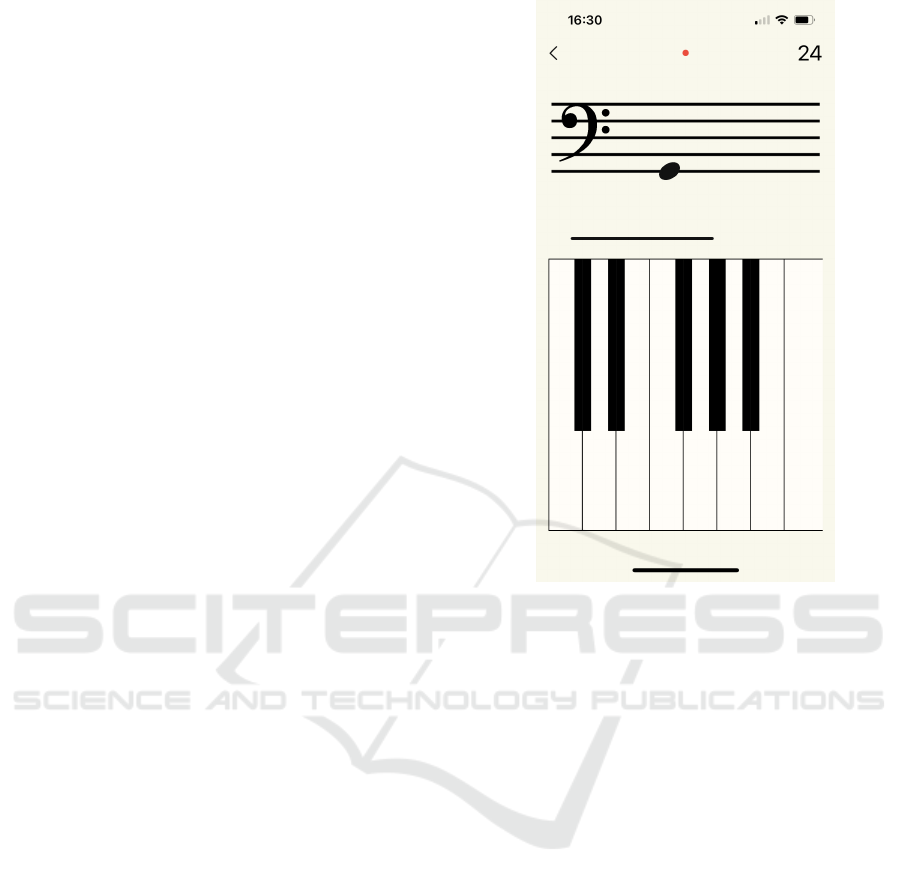
4.2 Graphical Interface
The graphical interface of the app during the game-
play is shown in Fig. 3. The screen is roughly divided
into two areas: the upper one is aimed to contain the
Figure 3: The graphical interface of iClef.
music notation to recognize, while the lower one is a
one-octave keyboard to input results.
Right below the stave, there is an indicator that
provides feedback about the time left to guess the
pitch.
In addition, in the upper area, there is a control to
go back to the main menu (left position) and two in-
dicators for the number of mistakes made by the user
(middle position) and the score achieved (right posi-
tion).
The graphical interface is intentionally very plain
and clean, so as not to distract the player from the
main goal, which is guessing the pitch. The nota-
tion is represented as widely as possible. Unfortu-
nately, the horizontal dimension of the screen limits
the width of keys; nevertheless, during the early test
phase, the pointing mechanism proved to be adequate
to allow precise identification of pitches.
4.3 Gameplay
The aim of iClef is to guess the pitch of the notes pro-
posed on a stave and shown for a limited time. Such
a choice is done using the on-screen representation of
a piano keyboard, the range of which is limited to one
octave. The pitches must therefore be recognized on
the basis of their name and independently of the oc-
CSME 2023 - 4th International Special Session on Computer Supported Music Education
400

tave information. The notes can be altered and the
accidentals must be correctly recognized by the user.
iClef was conceived as a potentially infinite game.
The game ends either by the player’s decision or by
reaching the maximum number of errors allowed in a
match, namely three mistakes.
The start menu of the app lets the user select one
of four levels. The main difference between them lies
in the number of clefs that will randomly appear:
• the first level – Beginner allows the user to prac-
tice in the Treble clef only;
• the second level – Intermediate presents notation
in the Treble and Bass clefs;
• the third level – Advanced contains the four most
used clefs, i.e. Treble, Bass, Alto, and Tenor;
• finally, the last level – Expert lets the user practice
on all clefs.
After the initial choice, there is no level advance-
ment. In other words, a good performance, say, in the
Beginner level does not take the player to the Interme-
diate level after a while. Anyway, during the game-
play, the level of difficulty increases according to the
factors illustrated in Section 4.1. Beating the top score
should provide enough motivation to perform better
and better. The score awarded for each guessed note
changes from level to level, ranging from 2 at Begin-
ner level to 32 at Expert level.
iClef can be used both for sight-reading practice
and for teacher assessment in game-based learning.
Please note that multiple gameplay modes can be con-
ceived. Basically, iClef is a single-player endless run-
ner game, but it can be easily adapted to become a
time-challenge game, as we did in our early experi-
mentation (see Section 5). Moreover, even if a mul-
tiplayer mode is not available, user scores and per-
formances can be easily compared in a class environ-
ment, thus fostering competition, motivation, and en-
gagement (Cagiltay et al., 2015).
5 EARLY EXPERIMENTATION
A session of tests has been conducted with a small
number of users. The employed devices included an
iPhone 12 Pro and an iPhone 13 Pro. Ten test users
have been involved in the test campaign, aged 30 to
50, with formal/informal music education and some
experience in musical scores. For reasons of space,
we have selected three particularly significant cases
in order to represent different categories of potentially
interested users:
• User A is a 46-year-old professional in the field
of sound and music computing, with past formal
studies in piano and composition. He/she can rep-
resent users interested in this application to pre-
pare for a Conservatory exam;
• User B is a 48-year-old musician who is used to
reading sheet music (in particular, he/she plays the
trumpet in a jazz band) but has never had the need
to learn clefs other than the G-clef. He/she can
represent users willing to improve orchestral score
sight-reading;
• User C is a 40-year-old amateur musician who
plays the saxophone in small ensembles for fun
in his/her spare time. He/she can represent a pop-
ulation of users who is completely unaware of the
9-clef system.
The test campaign focused on single-player
matches organized as time challenges. The tests were
sized considering two conflicting needs: they had to
be short enough to keep the attention high, but long
enough to provide players with non-trivial challenges.
The maximum duration for each game session was 90
seconds, but the game could stop even earlier in the
case of 3 errors achieved. Each player was subjected
to 4 game sessions of increasing difficulty, spaced by
1-minute-long rests: one match at the Beginner, Inter-
mediate, Advanced, and Expert levels. There was no
previous training about the use of the app since this
campaign was not intended to assess learning effects.
Rather, the goal was to test the functions of the soft-
ware, the effectiveness of the gameplay, and the level
of engagement. Moreover, we retrieved some useful
comments and remarks from the test users.
The results achieved by selected users during the
gameplay are shown in Table 1. Not surprisingly,
User A achieved a better success rate and a higher
number of correctly recognized notes in each round.
Anyway, User A, more skilled in sight-reading due to
his/her formal studies, was overconfident and used a
frantic approach, trying to guess the highest number
of notes in the smallest time, but this brought him/her
to commit a high number of mistakes (for example, at
the Beginner level he/she concluded the match in ad-
vance due to mistakes). Conversely, User B and User
C spent more time reading the notation, thus slow-
ing down the pace but also paying more attention to
some game pitfalls. A typical example, in this sense,
is the presentation of two successive notes with the
same position on the stave but corresponding to dif-
ferent pitches due to the occurrence of a clef change:
at a glance, this situation can be misinterpreted by a
frantic player.
Now, we summarize the main remarks and sug-
gestions emerging from post-activity interviews.
A Mobile Serious Game to Foster Music Sight Reading with Different Clefs
401

Table 1: Results achieved by Users A, B, and C in 90-second time challenges for each of the 4 levels.
User Level Nr. of right notes Nr. of mistakes Elapsed time (s) Success rate (notes/s)
A 1 87 3 78 1.12
B 1 70 0 90 0.78
C 1 56 3 65 0.86
A 2 61 3 66 0.92
B 2 45 3 84 0.54
C 2 26 3 50 0.52
A 3 63 2 90 0.7
B 3 36 2 90 0.4
C 3 8 3 44 0.18
A 4 13 3 21 0.62
B 4 3 3 24 0.13
C 4 12 3 55 0.22
User A was not completely satisfied with the
graphical interface, in his/her opinion poor in infor-
mation about game progression during the gameplay.
According to User A, a lacking option is the num-
ber of subsequent notes to be read in the same clef,
in accordance with solfeggio exercises in use in Con-
servatories; nevertheless, User A recognized that be-
ing able to sight-reading notes in everchanging clefs
would provide a good test bed for easier tasks.
User B noticed a lack of continuity when (not)
passing from one level to another: in his/her opin-
ion, a good performance at Level n should automati-
cally bring to Level n + 1. Concerning the interface,
some elements typical of gamification, such as stars or
awards, are missing. Regarding the automatic selec-
tion of pitches, the distribution of notes is not consid-
ered optimal compared to the limited keyboard range.
Furthermore, User B pointed out that game perfor-
mances are influenced by the type of controller the in-
strumentalist is used to: a keyboard interface is more
intuitive for a pianist than for a trumpet player. Fi-
nally, he/she would have appreciated the presence of
a dashboard with historical scores, trends, and some
diagrams.
Finally, User C considered the game engaging and
its interface fit for the goals of the app. Nevertheless,
if intended for non-expert users, the game needs a tu-
torial and some theoretical explanation. A shortcom-
ing detected in the gameplay, especially in the initial
phase of each level, is the repetitiveness of pitches,
which causes a decrease in the player’s interest. In
conclusion, User C pointed out that he/she would use
the game again if he/she had to learn sight-reading in
different clefs (which, anyway, was not his/her inten-
tion at the moment of the interview).
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we presented an app for mobile de-
vices whose purpose is to encourage the study and
learning of reading at the first sight of music written
with multiple alternating clefs. The main applicabil-
ity fields have a didactic nature and range from the
enhancement of intangible musical heritage (for ex-
ample, the development of the ability to read ancient
music) to practical educational purposes (for exam-
ple, the preparation of specific Conservatory exams).
The effectiveness of game-based learning in this
scenario must be verified in an experimental context,
while, at the moment of writing, we have investigated
mainly implementation and gameplay aspects. Con-
cerning the experimental phase, one of the critical as-
pects to consider is the difficulty of conducting mas-
sive test campaigns due to the niche of users the app
is aimed at. In fact, the expected audience for this
kind of serious game is made of musicians or music
students interested in sight reading with alternating
clefs, which is not a common scenario in music prac-
tice or even in basic music education. For this reason,
we hope that the described solution will be brought
into conservatories and music schools, so as to ana-
lyze learning results and retrieve comments and sug-
gestions from a more numerous and differently char-
acterized pool of users.
REFERENCES
Backlund, P. and Hendrix, M. (2013). Educational games-
are they worth the effort? a literature survey of the
effectiveness of serious games. In 2013 5th interna-
tional conference on games and virtual worlds for se-
rious applications (VS-GAMES), pages 1–8. IEEE.
Barat
`
e, A., Bergomi, M. G., and Ludovico, L. A. (2013).
Development of serious games for music educa-
CSME 2023 - 4th International Special Session on Computer Supported Music Education
402

tion. Journal of e-Learning and Knowledge Society,
9(2):93–108.
Barat
`
e, A. and Ludovico, L. A. (2013). Serious games
for music education. a mobile application to learn
clef placement on the stave. In Foley, O., Helfert,
M., Restivo, M. T., and Uhomoibhi, J., editors, Pro-
ceedings of the 5th International Conference on Com-
puter Supported Education (CSEDU 2013), pages
234–237, Set
´
ubal. SCITEPRESS - Science and Tech-
nology Publications, Lda.
Bellotti, F., Kapralos, B., Lee, K., Moreno-Ger, P., and
Berta, R. (2013). Assessment in and of serious games:
an overview. Advances in human-computer interac-
tion, 2013:1–1.
Blatter, A. (1997). Instrumentation and orchestration.
Schirmer Books.
Bryan, N. J., Herrera, J., Oh, J., and Wang, G. (2010).
MoMu: A mobile music toolkit. In NIME, pages 174–
177. Citeseer.
Cagiltay, N. E., Ozcelik, E., and Ozcelik, N. S. (2015). The
effect of competition on learning in games. Computers
& Education, 87:35–41.
Caserman, P., Hoffmann, K., M
¨
uller, P., Schaub, M.,
Straßburg, K., Wiemeyer, J., Bruder, R., G
¨
obel, S.,
et al. (2020). Quality criteria for serious games: seri-
ous part, game part, and balance. JMIR serious games,
8(3):e19037.
Cheng, M.-T., Chen, J.-H., Chu, S.-J., and Chen, S.-Y.
(2015). The use of serious games in science education:
a review of selected empirical research from 2002 to
2013. Journal of computers in education, 2:353–375.
de Vasconcelos, D. F. P., J
´
unior, E. A. L.,
de Oliveira Malaquias, F. F., Oliveira, L. A.,
and Cardoso, A. (2020). A virtual reality based
serious game to aid in the literacy of students with in-
tellectual disability: Design principles and evaluation.
Technology and Disability, 32(3):149–157.
Essl, G. and Lee, S. W. (2018). Mobile devices as musi-
cal instruments-state of the art and future prospects.
In Music Technology with Swing: 13th Interna-
tional Symposium, CMMR 2017, Matosinhos, Portu-
gal, September 25-28, 2017, Revised Selected Papers
13, pages 525–539. Springer.
Gace, I., Jaksic, L., Murati, I., Topolovac, I., Zilak, M., and
Car, Z. (2019). Virtual reality serious game prototype
for presenting military units. In 2019 15th Interna-
tional Conference on Telecommunications (ConTEL),
pages 1–6.
Giessen, H. W. (2015). Serious games effects: an overview.
Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174:2240–
2244.
Kokol, P., Vo
ˇ
sner, H. B., Zavr
ˇ
snik, J., Vermeulen, J.,
Shohieb, S., and Peinemann, F. (2020). Serious game-
based intervention for children with developmental
disabilities. Current pediatric reviews, 16(1):26–32.
Krath, J., Sch
¨
urmann, L., and von Korflesch, H. F. (2021).
Revealing the theoretical basis of gamification: A sys-
tematic review and analysis of theory in research on
gamification, serious games and game-based learning.
Computers in Human Behavior, 125:106963.
Larasati, M. T. L. and Sukmayadi, Y. (2021). Mobile learn-
ing design for sight reading. In 3rd International Con-
ference on Arts and Design Education (ICADE 2020),
pages 70–73. Atlantis Press.
Larson, K. (2020). Serious games and gamification in the
corporate training environment: A literature review.
TechTrends, 64(2):319–328.
Loman, C. T. and Wiradinata, T. (2014). Design and de-
velopment of sight-reading application for kids. IC-
ITECHS, 1:51–55.
Moorefield-Lang, H. and Evans, M. A. (2011). Rhythmat-
ical: A game to combine music and mathematics for
mobile devices. Music Reference Services Quarterly,
14(1-2):46–51.
Oh, J., Herrera, J., Bryan, N. J., Dahl, L., and Wang, G.
(2010). Evolving the Mobile Phone Orchestra. In
NIME, pages 82–87. Sydney.
Oh, J. and Wang, G. (2011). Audience-participation tech-
niques based on social mobile computing. In ICMC.
Presti, G., Adriano, D., Avanzini, F., Barat
`
e, A., and Lu-
dovico, L. A. (2021). Phonharp: A hybrid digital-
physical musical instrument for mobile phones ex-
ploiting the vocal tract. In AM’21: Proceedings of the
16th International Audio Mostly Conference: Sonic
experiences in the era of the Internet of Sounds, ACM
International Conference Proceeding Series, pages
276–279. ACM.
Ravyse, W. S., Seugnet Blignaut, A., Leendertz, V., and
Woolner, A. (2017). Success factors for serious games
to enhance learning: a systematic review. Virtual Re-
ality, 21(1):31–58.
Sharifzadeh, N., Kharrazi, H., Nazari, E., Tabesh, H.,
Edalati Khodabandeh, M., Heidari, S., and Tara,
M. (2020). Health education serious games tar-
geting health care providers, patients, and public
health users: scoping review. JMIR serious games,
8(1):e13459.
Snyder, J. and Sarwate, A. (2014). The mobile device
marching band. In Proceedings of the International
Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expres-
sion.
Tsikinas, S. and Xinogalos, S. (2019). Studying the effects
of computer serious games on people with intellectual
disabilities or autism spectrum disorder: A system-
atic literature review. Journal of Computer Assisted
Learning, 35(1):61–73.
Vieira, C., da Silva Pais-Vieira, C. F., Novais, J., Perrotta,
A., et al. (2021). Serious game design and clinical
improvement in physical rehabilitation: systematic re-
view. JMIR Serious Games, 9(3):e20066.
Wang, G. (2009). Designing smule’s ocarina: The iphone’s
magic flute. In NIME, pages 303–307.
Zhonggen, Y. (2019). A meta-analysis of use of serious
games in education over a decade. International Jour-
nal of Computer Games Technology, 2019.
Zhou, Y., Percival, G., Wang, X., Wang, Y., and Zhao, S.
(2011). MOGCLASS: evaluation of a collaborative
system of mobile devices for classroom music educa-
tion of young children. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI
Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems,
pages 523–532.
A Mobile Serious Game to Foster Music Sight Reading with Different Clefs
403
