
Trustworthy Decentralized Last-Mile Delivery Framework Using
Blockchain
Ala’ Alqaisi
1
, Sherif Saad
1
and Mohammad Mamun
2
1
University of Windsor, Windsor, Canada
2
National Research Council Canada, New Brunswick, Canada
Keywords:
Last-Mile Delivery, Crowd-Shipping, Blockchain, Reputation Models.
Abstract:
The fierce competition in eCommerce is a painful headache for logistics companies. In 2021, Canada Post’s
parcel volume peaked at 361 million units with a minimum charge of $10 per each. Last-Mile Delivery (LMD)
is the final leg of the supply chain that ends with the package at the customer’s doorstep. LMD is the most
costly process, accounting for more than 50% of the overall supply chain cost. Platforms such as Uber Eats
and Amazon Flex help overcome this inefficiency and provide an outstanding delivery experience by enabling
crowd-shipping using freelancer drivers willing to deliver packages in exchange for compensation. However,
the current generation of LMD platforms that leverage crowd-shipping are centralized platforms and behave
as intermediaries that charge commission fees. They lack transparency, and most of them, if not all, are plat-
form monopolies in the making. This paper introduces the design of the next-generation LMD crowd-shipping
platforms by leveraging Blockchain and smart contracts. A decentralized crowd-shipping platform for LMD
that is scalable, reliable, secure and promotes fairness. The proposed platform connects the primary stake-
holders of LMD without intermediaries. The stakeholders could use the platform to manage shipping and
delivery, handle disputes, maintain fairness, and mitigate monopoly power. Our approach replaces the need
for a centralized intermediator such as Uber by introducing a decentralized reputation model that executes over
a cryptocurrency-less blockchain network. Our proof-of-concept implementation of the proposed framework
demonstrates the potential of blockchain technology to decentralize the crowd economy. We used informal
security analysis to illustrate how the proposed decentralized reputation model discourages misuse and en-
courages fairness between parties.
1 INTRODUCTION
Last-mile delivery (LMD) refers to the last segment of
the supply chain process that transfers goods from fi-
nal distribution centers to customers’ doorstep. Due
to consumers’ dispersed destination locations, last-
mile delivery is the most expensive and challenging
stage of the delivery process (Dolan, 2023). In the
last decade, the tremendous evolution of online shop-
ping and the recent pandemic have been causing spec-
tacular growth in the parcel shipping market across
the globe. For instance, Canadian e-Commerce sales,
which made up over $43 billion in 2018, are projected
to increase by another 25% by 2023 to reach $55.4
billion (Le, 2022). As a result, Canada spent over
$19.9 billion on last-mile delivery services in 2021
(Placek, 2022). Customers’ preferences and expec-
tations have increased along with the growth of e-
Commerce; they now require same-day shipping, free
home delivery, real-time package tracking, and free
returns. These new conditions pressure shipping pro-
fessionals to consider alternative LMD solutions.
Meanwhile, the world has witnessed a rapid evo-
lution of the sharing economy, which refers to a peer-
to-peer activity of obtaining, giving, or sharing access
to goods and services through e-applications. Logis-
tics providers exploited the same concept to develop
a new business model called Crowd-shipping. It del-
egates parcel delivery tasks to a crowd of local couri-
ers for monetary compensation using their vehicles or
other transportation modes. The most common ex-
ample of crowd-shipping LMD platforms is within
the food and restaurant industry, such as Uber Eats,
SkipTheDishes, DoorDash, and Instacart. Crowd-
shipping maximizes logistics efficiency by downsiz-
ing the operational costs of package delivery, enhanc-
ing customers’ flexibility to schedule deliveries with
online shipment tracking, and reducing traffic and
54
Alqaisi, A., Saad, S. and Mamun, M.
Trustwor thy Decentralized Last-Mile Delivery Framework Using Blockchain.
DOI: 10.5220/0012090300003552
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies (ICSBT 2023), pages 54-65
ISBN: 978-989-758-667-5; ISSN: 2184-772X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

emissions (Gatta et al., 2018).
However, while these applications make life eas-
ier for the customer, they make it harder for others.
To begin with, the organizations that run these appli-
cations act as intermediaries and deduct unjustifiable
high commission rates for managing the delivery pro-
cess between the retailer and the buyer. For instance,
SkipTheDishes and UberEats commission rates range
between 20% and 30% of each order’s value (Evans,
2020). Secondly, giant companies’ rivals and invest-
ments created a trend toward a monopoly and induced
an uneven distribution of the welfare produced in
the crowd-sourced delivery field, which forced small
businesses to consider whether they could afford to
continue playing in the delivery sector. Furthermore,
most of these platforms are deployed on a central-
ized architecture, which could expose the system to
data corruption, privacy breach, and single-point-of-
failure risks, resulting in monetary and credit dam-
age. For instance, DoorDash was a victim of hack-
ers who stole the information of 4.9 million users
(Breen, 2019), while similar incidents happened with
UberEats in 2020 (N, 2020).
From this perspective, there is a call to transform
the present platforms or construct an alternative busi-
ness model that overcomes these drawbacks. The pos-
sibility to respond to this call is the Blockchain, which
may potentially make a vital contribution to the sup-
ply chain and logistics field due to its critical features,
such as immutability, integrity, and confidentiality.
Blockchain can create trusted decentralized applica-
tions and reduce their reliance on third parties by uti-
lizing smart contracts that define an automatic agree-
ment between seller, courier, and consignee when
transacting. Plus, distributed ledger guarantees trans-
parency and avoids the risk of data tampering and in-
frastructure failure. Hence, this paper aims to design a
blockchain-based crowd-shipping platform managed
by retailers, customers, and couriers transparently and
without intermediaries.
The main contributions of this paper can be de-
scribed as follows:
• Propose a blockchain-based system to realize de-
centralized crowd-shipping services that elimi-
nate the need for a central authority or third-party
involvement.
• Propose a reputation model for couriers based on
their prior behaviours to inject trust and discour-
age malicious behaviour in the system.
• Implement a proof of concept using Hyperledger
Fabric, a real-world permissioned blockchain
platform and conduct intensive experiments and
performance evaluations in a test network.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Sec-
tion 2 discusses related work in the literature. Section
3 briefly overviews the Hyperleger Fabric blockchain
and the transaction flow, as it is the development en-
vironment of the subject in this study. Section 4
presents the proposed blockchain-based last-mile de-
livery framework. Then, section 5 describes a proof of
concept implementation of the proposed framework
and the development environment. Next, section 6
presents experimental results and discusses the secu-
rity analysis of the implemented solution. Finally,
section 7 concludes the paper with some future work.
2 RELATED WORK
In the literature, several works have proposed that
leveraging blockchain technology in one way or an-
other improves the delivery of physical assets such as
parcels and packages. Here we concentrate on work
that focuses on last-mile delivery.
A blockchain-based shipping platform called
Lelantos was proposed in (AlTawy et al., 2017) to
hide the customers’ identity from shippers and pre-
vent linkability between the customer and the mer-
chant. Customers upload their real addresses to the
Blockchain encrypted, select at least two couriers, and
redirect shipments between different couriers with-
out a trusted third party. Once the courier arrives at
the customer’s address, their schema utilizes a secure
hashing to prove the delivery. However, their system
increases complexity for buyers, who must select at
least two delivery companies to ship their packages.
Additionally, the proof of delivery is not linked to the
package. Consequently, the courier can easily tamper
with the asset to be delivered.
Hasan and Salah designed a blockchain-based so-
lution for physical asset delivery (Hasan and Salah,
2018). Using automated ether payments, they ana-
lyzed a Proof of Delivery system to trade and track
sold items between two parties. Each party deposits
collateral equal to double the package price that each
party risks losing if any behaves maliciously. Their
protocol ensures asset handover verification through
a key exchange the seller provides to the courier and
the buyer. The solution also offers tamper-proof logs
for auditability and traceability. However, the scheme
does not fit a crowd-shipping environment since it re-
quires a double package price deposit per order. Be-
sides, the relationship between the key and the pack-
age is not stated.
Wang et al. presented an auditable protocol for
transparent, tamperproof, and verifiable transactions
between merchants, logistics companies, and con-
Trustworthy Decentralized Last-Mile Delivery Framework Using Blockchain
55

sumers (Wang et al., 2019). The schema requires a
regulator to authenticate users interested in partici-
pating in the network and register a smart contract
with their data in the Blockchain. It has offered a
pre-verification technique to prevent the parcel’s re-
placement during delivery by the courier. Also, it dis-
cussed the return of the product in two cases; when
consumers receive their products and when the deliv-
ery time of the products exceeds a predefined period.
Like previous work, it requires a security deposit per
order equal to the parcel’s worth.
A novel cash-of-delivery solution was presented
in (Ha et al., 2020) to address the courier’s traceabil-
ity during the delivery process and to integrate access
control protocols to protect sellers’ and customers’
privacy. A hash code is created for each package
based on its details and verified to ensure no change
could occur to the order details. Smart contracts in-
clude a penalty mechanism when trouble arises, such
as a damaged, missing, or incorrect package. The cus-
tomer selects the shipper, and once agreed, the system
sends the hash and the seller’s contact to the ship-
per. Only the shipper mortgage a deposit equal to
the package value, which is transferred to the seller
in case of late delivery. When the customer receives
the package, the shipper takes the cash payment and
divides the profit with the seller.
These previous blockchain-based solutions adopt
a collateral depositing approach to build trust be-
tween shipping parties. However, something else is
needed to fit the crowd-shipping environment because
it would be unfeasible for the courier to deposit col-
lateral that equals each package value he will ship
or double. The courier will have to deliver several
parcels on the same route. A delivery driver typically
ships 40–70 packages each day for close allocation of
addresses and 125–200 packages if the addresses are
super clustered (Wang, 2021). Hence, another mech-
anism is required to inject trust into the system while
providing a practical and cost-effective solution.
3 HYPERLEDGER FABRIC
This section describes one of the most well-known
distributed ledger frameworks, Hyperledger Fabric,
and its transaction flow. HyperLedger Fabric was
created by the HyperLedger blockchain open-source
project and supported by the Linux Foundation. It
aims to develop apps or solutions with a modu-
lar architecture and plug-and-play components for
membership and consensus. It is a permissioned
blockchain, and Table 1 lists its main components.
There were several reasons for selecting Hyperledger
fabric. Substantially, it is a non-cryptocurrency-based
blockchain, meaning there is no PoW algorithm and
crypto mining in Fabric. Thus, it delivers high scal-
ability and fast transactions. Hyperledger Fabric is
an open source with detailed documentation and sev-
eral implementation examples. Furthermore, it sup-
ports the minimum technical requirements to build the
proof of concept.
The ledger is divided into two sections, as illus-
trated in Figure 1, and a copy of ledger is maintained
on each peer that joins the channel in Hyperledger
Fabric. A blockchain data structure containing the
blocks makes up the first part (of transactions). The
second component, a world-state database, stores the
most recent state following a block’s commit. Upon
successful validation, the peer commits the new block
received from the ordering service into the ledger.
The block is added to the blockchain, and each trans-
action is updated in the world-state. Most of the
ledger is identical among peers inside a channel due
to the consensus. However, Private Data is an ex-
ception, as only specific organizations store it in the
world-state. In some cases, just a subset of the organi-
zations requires to keep data private from other orga-
nizations on a shared channel. To meet this demand,
Hyperledger Fabric introduces Private Data through
the definition of data collection. All peers inside the
subgroup can see the private data, while peers outside
the subgroup will preserve a record of the private data
hash as proof of data existence or for audit purposes.
Each organization has an implicit data collection for
private data by default.
Figure 1: HyperLedger Fabric Data Structure.
Endorsement, Ordering, and Validation are the
three stages of consensus in Hyperledger Fabric. En-
dorser nodes must endorse a transaction based on
policy, such as (m out of n) signatures. The order-
ing phase accepts the approved transactions and con-
sent to the order to be added to the ledger. Finally,
the validation phase examines a block of arranged
ICSBT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies
56

Table 1: Major components of HyperLedger Fabric.
Component Description
MSP
Membership Services Provider (MSP) is implemented as a Certificate Authority to manage certifi-
cates used to manage and authenticate member identity and roles of all participants on the network.
No unknown identities can transact in the Hyperledger Fabric network.
Peer
Peers are a vital element in the network that host ledgers and chaincode (smart contracts). An
application interface, ledger data access, endorsement of transactions, and chaincode execution are
all performed by a peer. Some peers can be endorsing peers which validate transaction requests from
the client, commit the block received from the Orderer and update its ledger.
Orderer
Orderer are nodes which produces a block containing the endorsed transactions after sorting them
according to the time they were received from peers, then distributes the blocks to all other peers.
Client
Clients act on behalf of the system end-user by submitting transaction-invocation requests to the
endorsers and broadcasting transaction proposals to the orderers.
Chaincode
Chaincode refers to the smart contracts used by Hyperledger Fabric. Chaincode is a program that
holds the system’s business logic and executed when predefined conditions are met. When an ap-
plication has to communicate with the ledger, the application invokes the Chaincode. Chaincode is
deployed to all peers at the initialization stage of the fabric network.
Channel
Channels are a logical structure formed by multiple organizations to create a separate ledger of
transactions. When configuring any channel, a set of policies must be agreed upon to govern the
interactions between organizations and define the permission to invoke the chaincode deployed on
this channel.
Organization
Organization is an entity that consists of a group of peers who have an identity (digital certificate)
assigned by a Membership Service Provider.
transactions to ensure accurate outcomes, including
reviewing endorsement policy and double-spending.
The current consensus algorithms in Hyperledger fab-
ric are CFT (crash fault-tolerant) or BFT (byzantine
fault-tolerant) to support different trust assumptions
of a particular deployment or solution (Androulaki
et al., 2018).
The Hyperledger Fabric transaction flow process con-
sists of eight phases, as outlined below:
1. The user enrolls in the MSP through an applica-
tion, and the MSP issues them a User ID and a
certificate.
2. The user proposes a transaction to network peers.
3. Endorsing peers who received the transaction
from the user perform a validation check on the
client’s identity to ensure they are authorized for
their request. The transaction is then simulated
using the pre-deployed Chaincode.
4. After successfully simulating the Chaincode, each
peer gives the user their endorsement.
5. The user gathers peer endorsements and sends
them to the orderer.
6. The orderer organizes the endorsed transactions
received in the previous step in chronological or-
der and constructs a block containing them.
7. Orderer distributes the block to all the network’s
peers after sorting the endorsed transactions re-
ceived from peers.
8. Each peer updates its ledger by appending the new
block to the prior block after receiving and verify-
ing it. At this stage, the ledger is identical for all
peers.
4 PROPOSED BLOCKCHAIN
SOLUTION
This chapter demonstrates the design and implemen-
tation of a Blockchain Crowd-shipping platform that
offers decentralization, rights to data accessibility,
visibility, and transparency using blockchain features.
The key objective is to provide a free-mediator plat-
form that ships goods and valuables among parties
without trust depending on a reputation model.
4.1 Operational Scenario
Parcel shipping processes include different actors
with each assigned task and role. The seller, Cus-
tomer, and Courier are the key players in the pro-
posed system, with an organization for each actor in
the blockchain network.
As illustrated in Figure 2, the shipping process
scenario starts with creating the parcel the seller wants
to ship to a customer. The parcel’s private details,
such as parcel size, quantity, appearance, price, etc.,
are stored in a private data collection and hashed to
generate the parcel ID. The seller who owns the par-
Trustworthy Decentralized Last-Mile Delivery Framework Using Blockchain
57

cel ID can only access these details. Using the same
function, the seller creates shared parcel data with
the customer. Shared Data is stored in a private data
collection called Parcel Collection, accessible by the
seller and customer to track updates on the shipping
process. The seller passes out of the band the parcel-
ID and the parcel properties to the customer. Next,
the customer adds the convenient shipping destination
and time and verifies the mutual package properties
before agreeing to transact. The provided parcel’s pri-
vate properties must generate a hash that identically
matches the hashed parcel ID; otherwise, this step is
failed. This step ensures that the agreed parcel infor-
mation meets the customer’s expectations.
Figure 2: Sequence diagram of successful shipping process
scenario.
Upon customer agreement, the seller creates an or-
der to assign a courier to fulfill the shipping request.
Any order consists of public data visible to any chan-
nel member. The order’s public data includes the
shipping date, time, locations, minimum reputation
value of the courier, and maximum amount paid by
the seller. On the other hand, the private data includes
the assigned courier, shipping cost, parcel ID, and ad-
ditional metadata. Order’s private data is stored in a
private collection shared between the selected courier
and the seller.
Each order is created with an Open status to en-
able couriers to submit their bids (requested compen-
sation). If the courier is interested in a particular or-
der, first, he creates his Full bid in his organization’s
implicit private data collection. The Full bid includes
the courier identity and requested pay. However, be-
fore adding the bid to his organization’s implicit pri-
vate data collection, the smart contract verifies that
the courier’s global reputation matches the minimum
threshold specified in the order and the provided price
is less than the maximum paid amount in the order. If
the bid is created successfully, the courier submits the
bid’s hash to the order without revealing the cost.
Meanwhile, the courier’s organization is added to
the list of organizations necessary to approve order
updates. After several bids join the order, the seller
closes it to prevent additional bids from being sub-
mitted and allows couriers to reveal their bids. The
smart contract automatically assigns the courier with
the lowest pay if the seller and courier organizations
endorse the same courier and pay. That prevents the
seller from prematurely assigning a courier to the
order or colluding with couriers with unfair prices.
Next, the selected courier can accept or reject the or-
der. If he rejects the order, a certain amount of his
reputation will be deducted.
In the following stage, the seller updates the parcel
and order state to Courier Assigned and transmits the
exact pickup and drop-off locations out of the chain
by email or any communication method to the courier.
The courier arrives at the pickup location and noti-
fies the seller on the chain by changing the order state
to Courier Arrived. The courier picks up the parcel,
and the seller updates the parcel and order state to
Out For Delivery. When the courier reaches the cus-
tomer’s destination, the courier asks the customer for
the parcel ID. If the parcel ID is correct, the courier
will successfully update the parcel to Handedover to
the customer. At the same time, the customer will
update the parcel state to Received by Customer and
provide an evaluation score for the courier. Finally,
the seller can verify the correctness of the parcel and
order states, provide an evaluation score of the courier
service, and set the parcel as Delivered and the or-
der as Completed. The smart contract automatically
collects all required data to estimate and update the
courier’s reputation score.
The seller can cancel the order before the parcel is
shipped. If the shipping order state change to courier
arrived, the shipping process has started, and cancel-
lation is not applicable after this point.
4.2 Proposed Reputation Model
Reputation plays a crucial role in establishing sys-
temic trust since it represents the service’s reliabil-
ity and the behaviour of participating entities. Pre-
vious works in literature established trust by reserv-
ICSBT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies
58

ing collateral deposits from each entity as cryptocur-
rency. The use of collateral deposits is not practical in
a decentralized crowd-shipping environment. Instead,
this work constructs trust through a reputation-based
network that uses blockchain immutability and offers
a confidence reputation score in an environment that
lacks a third party who maintains transparency and
solves disputes between participants.
Each courier is assigned a reputation score that
sellers will consider during selection. A high rep-
utation score reflects good courier behaviour. Fur-
thermore, unlike traditional crowd-shipping schemes
where the reputation is centralized, managed, and
controlled by a third party, our reputation system
is entirely decentralized and implemented on the
blockchain.
4.2.1 Local Reputation
It is not fair to directly use user evaluations to de-
termine the reputation scores of the courier. Mul-
tiple transactional elements such as shipping order
time, shipping cost, the credibility of the evaluation’s
source, and the courier’s completed orders are disre-
garded in the reputation’s computation, making the
reputation system vulnerable to attacks. To calculate
the courier’s reputation score, we weigh the received
evaluation, denoted by r and take the value of [-1,1],
according to the following factors:
1. Order Time: If the courier accepts several ship-
ping orders in a short time, the courier and the
seller may collude to receive good ratings. Thus,
for a current order, if the courier’s previous order
occurred a short time ago, the rating of the cur-
rent order should be set as a relatively low value
to deter the collusion attacks. Thus, the weighting
factor of order time is defined using the Hyper-
bolic Tangent function in equation 1 as suggested
by (Zhou et al., 2021):
ϕ(△T ) = tanh(△T ) (1)
where △T refers to the time interval between the
timestamp of current order T and that of previ-
ous transaction T
′
divided by T
a
which refers to
the average frequency of user interaction in the
system, △T > 0 and ϕ(△T ) ranges from 0 to 1.
A distant time interval △T will lead to a higher
value of the weighting factor.
2. Shipping Cost: It is not costly for the seller
to create orders with low asked prices to boost
courier ratings or unfairly submit low ratings to
the courier. Therefore, to overcome this concern,
the rating of an order should be related to the ship-
ping cost amount. The weighting factor of the
shipping cost amount is defined by equation 2,
where V refers to the shipping cost and ψ(V ) < 1.
The shipping cost is divided by 10 to avoid con-
vergence to 1 very quickly:
ψ(V ) = 1 −
1
(1 +
V
10
)
(2)
3. Number of Shipping Orders: A courier may in-
crease his trust value by being active in the net-
work and increasing the fulfilled shipping orders.
To distinguish a courier with a high reputation for
a few good orders from a courier with a high rep-
utation but with a large volume of orders, we need
to consider the number of transactions (Xiong
and Liu, 2004). This factor is denoted by T X
N
and defined by considering the maximum number
of completed orders by couriers in the network
and assigning different weight values for differ-
ent ranges. The network determines what factor’s
score to assign for each range of shipping requests
and updates it periodically.
4. Credibility of the Local Rating: The proposed
reputation model must be robust against unfair
ratings. A participant may make false statements
about the courier’s service due to malicious mo-
tives. Consequently, a trustworthy courier may
get many unsatisfactory ratings despite providing
satisfactory service in every order. Therefore, we
consider the fairness of the provided rating score
for each order to protect the courier from such in-
cidents. We adopt the approach presented in (Al-
lahbakhsh et al., 2012). First, we calculate the
average of all ratings given to a particular courier,
say c
j
, as per equation 3. r
k j
refers to the rating
received by user u
k
toward the courier c
j
. The N
j
refers to the total number of fulfilled shipping re-
quests by courier c
j
.
R
j
=
∑
k∈N
j
r
k j
N
j
(3)
In the second step, we calculate the average of all
ratings given to courier c
j
by the rater, say u
i
, us-
ing equation 4. The N
i j
refers to the number of
ratings that u
i
has provided toward the courier c
j
.
R
i j
=
∑
r
i j
N
i j
(4)
In the third step, we calculate the standard devia-
tion of all ratings given to a courier c
j
as shown in
equation 5.
SD
j
=
q
∑
k∈N
j
(r
k j
− R
j
)
2
N
j
(5)
Trustworthy Decentralized Last-Mile Delivery Framework Using Blockchain
59

In the last step, we measure the rating credibility
factor as follows:
Cr
i j
=
R
j
−SD
j
−R
i j
Max
Rep
if R
i j
< (R
j
− SD
j
)
1 if (R
j
− SD
j
) ≤ R
i j
1 if (R
j
+ SD
j
) ≥ R
i j
R
i j
−(R
j
+SD
j
)
Max
Rep
if (R
j
+ SD
j
) < R
i j
(6)
where Max
Rep
refers to the maximum value of the
reputation score and is equal 1.
According to Equation 6, the averages falling in
R
j
± SD
j
are trustworthy and dependable. Still,
those that fall out of that range have very low cred-
ibility, and their impact on reputation is decreased.
The Cr
i j
shows how close is the judgment of u
i
to the majority consensus about courier c
j
’s trust-
worthiness. Thus, we use credibility to reduce the
effect of ratings from raters who disagree with the
majority consensus about the courier. It is worth
noting that the credibility factor could be difficult
to measure if both rater and the courier are trans-
acting for the first time. Therefore, the credibil-
ity factor value will be 0.5 as the probability of a
fair/unfair rating score is 50%.
Finally, for each shipping request, we weigh the
received rating r (positive or negative) by all factors
using equation 7. Local reputation score ranges from
0 to 1.
e =
(r ×Cr) + ψ(V ) + ϕ(△T ) + T X
N
4
(7)
4.2.2 Global Reputation
As mentioned before, each courier has a local and
global reputation score. When the courier joins
the network, an initial global reputation score is
assigned, equaling 0.5. The global reputation in-
creases or decreases once a new local score is added.
Also, it decays if the courier has not been active
after some time. We have adopted the suggested
model by (Truong et al., 2021). Local reputation e
could be satisfactory or unsatisfactory depending on
a predefined threshold θ. The amount of increase,
decrease, and decay depends on the local reputation
score e and the current value of the global reputation
GRep , which can be modelled by linear difference
equations and a decay function as follow:
Increase Model. The current global reputation score
denoted by GRep increases once updated with a sat-
isfactory transaction (at the time t, indicated by the
local reputation score e
t
≥ θ) that follows the linear
difference equation:
GRep
t
= GRep
t−1
+ e
t
× ∆GRep
t
(8)
where ∆GRep
t
= α × (1 −
GRep
t−1
Max
Rep
) and α is the
maximum increase value of global reputation score
in two consecutive shipping requests and Max
Rep
is
the maximum global reputation and equals 1.
Decrease Model. Similarly, GRep decreases if the
local rating is unsatisfactory (indicated by the local
reputation score e
t
≤ θ), following the equation:
GRep
t
= Max(Min
Rep
,
GRep
t−1
− β × (1 − e
t
) × ∆GRep
t
)
(9)
The Min
Rep
is the minimum global reputation and
equal 0. The decrease rate β > 1 implies that it is
easier to lose the global reputation value due to an
unsatisfactory rating than to gain it (a satisfactory
rating).
Decay Model. Global reputation decays if there is no
transaction after a period of time. The decay rate is
assumed to be inversely proportional to the strength
of the trust relationship of the courier (value of the
Reputation). Based on these observations, the Decay
model is proposed as follows:
GRep
t
= Max(Min
Rep
, GRep
t−1
− ∆Decay
t
) (10)
where ∆Decay
t
= δ × (1 + γ −
GRep
t−2
Max
Rep
) , and δ is
the minimum decay value ensuring any global reputa-
tion degenerates if it is not maintained. And γ is a de-
cay rate controlling the amount of the decay. The net-
work administrator can identify the inactivity thresh-
old (e.g., three months) and periodically compare it
to the couriers’ last shipping request. If the courier
has been inactive more than the threshold, his global
reputation declines using equation 10.
5 PROOF OF CONCEPT
IMPLEMENTATION
As proof of concept, we implement our decentralized
crowd-shipping last-mile delivery framework using
Hyperledger Fabric. The source code of the proposed
framework is publicly available on GitHub (WAS-
PLab, 2022). In this section, we briefly describe the
blockchain network and how the network’s different
nodes interact. Besides, the deployment and imple-
mentation details.
ICSBT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies
60

5.1 Proposed Blockchain Network
Model
The blockchain network consists of four organiza-
tions, with one peer for each, as depicted in Figure 3.
A dedicated certificate authority is assigned to each
organization. The Peer node is intended to be an en-
dorsing peer where the system’s Chaincode resides.
Each peer maintains a current state database as the
couch DB. The sequence of our proposed work is cre-
ating a channel; each peer must join the channel, in-
stall the Chaincode, and approve it. If the peer re-
ceives sufficient approvals from the organizations, it
commits the Chaincode, invokes it, queries it, and en-
ables client communication with Postman API.
Figure 3: Proposed LMD Platform Network Architecture.
Each actor in the system has a specific organi-
zation that will provide the entity with the relevant
authorization and Chaincode access. The certifi-
cate authority is used to manage and authenticate
member identity and roles of all participants on the
network. No unknown identities can transact in the
Hyperledger Fabric network. Each organization has
a peer node that carries out the application interface,
ledger data access, endorsement of transactions,
and Chaincode execution. The Oderer organization
consists of three Orderer nodes that produce a block
containing the endorsed transactions after sorting
them according to the time they were received from
peers. Then, they distribute the blocks to the leader
peer in the network, which then forwards the blocks
to other peers. The peers receiving the data will use
gossip protocol to disseminate the data to all peers of
the same channel.
Hyperledger Fabric offers several implementa-
tions for achieving consensus between ordering ser-
vice nodes, Raft, Kafka, and Solo. In our network,
we use Raft, a crash fault-tolerant (CFT) that uses
the ”leader and follower” architecture, each channel
elects a leader node, and the followers replicate that
node’s decisions. Due to its endorsement policy of
majority vote, Raft provides a means for high avail-
ability for ordering services.
The platform’s business logic comprises Chain-
code, application SDK, and Application Program-
ming Interface (API) testing tool, which works to-
gether to deliver the application’s features. Chain-
code consists of the Data model designed to define
the data structures necessary for the application net-
work (Chaincode and Application SDK). The main
smart contract is written in Golang and verifies in-
voker roles, and executes the associated transaction
functions for each service capability’s logic.
The application SDK provides access to Chain-
code running within that network and to which trans-
actions can be submitted or queries can be evaluated.
It is written in javascript and uses the Gateway class as
the network entry point. For testing Application Pro-
gramming Interface (API), we use the Postman tool
that enables the client to interact efficiently with the
system and determine how system resources are de-
fined and addressed.
5.2 Development Environment
One Virtual machine running Ubuntu Linux 20.04 has
been deployed on a 64-bit machine with 16 GB of
RAM and 2.3 GHz Intel Core i7 CPU. The require-
ments and specification of our proposed network has
been shown in Table 2. The following steps are taken
in order to run the blockchain network:
1. Generate Crypto Materials for Seller, Customer,
and Courier Organizations and RAFT Orderer. It
creates the node organization unit materials re-
lated to CA, MSP, peers, TLSca, admins and users
for all organizations.
2. Create Channel Artifacts auch as genesis block
and channel transaction files, and anchor peers.
3. Creating and Joining Channel.
4. Delivery Chaincode Deployment.
5. Install, Approve, Commit, and Invoke Delivery
Chaincode.
6. Launch the postman API server in order to allow
the interaction with the application and the Hyper-
ledger Fabric’s local environment.
Trustworthy Decentralized Last-Mile Delivery Framework Using Blockchain
61

Table 2: Requirements and specification of proposed LMD
Blockchain network.
Requirements Specification
cURL Tool 7.68.0
Docker engine 20.10.18
Docker Composer 1.25
Go 1.14.1
Node JS 13.14.0
NPM 6.14.4
Hyperledger Fabric 2.1.1
VS Code 1.74.1
Postman API 9.31.25
Hyperledger Caliper 0.5.0
Couch DB 0.4.20
Certificate Authority 1.4.7
6 DISCUSSION AND RESULTS
This section presents a feature-based comparison be-
tween our proposed system and related work reviewed
in section 2. Security, privacy, and scalability aspects
are also discussed. Then, we conduct reputation test
scenarios to evaluate the effectiveness of our reputa-
tion model, finally assess the application performance
using Hyperledger Caliper, and discuss the obtained
results.
6.1 Security Analysis
The suggested LMD solution leverages key security
features from blockchain by design, such as decen-
tralized trust, integrity, non-repudiation, and avail-
ability. Although existing blockchain and smart con-
tract technologies still have performance and security
threats, we assume that the decentralized feature of
the BC makes it impossible for an adversary to com-
promise the blockchain network and alter the ledgers’
contents.
Each actor in the system has a digital identity en-
capsulated in an X.509 digital certificate issued by
a Certificate Authority (CA). These identities deter-
mine the permissions over resources and access to in-
formation. Also, by design, our framework is secured
against Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks and re-
play attacks. Every message exchange is crypto-
graphically signed and timestamped, ensuring nobody
can repudiate their activities later. Integrity is essen-
tial in preventing critical information tampering. The
proposed framework provides the ability to use trans-
action logs to track back historical occurrences.
In our system, a seller and customer must per-
form a complete shipping request with the courier to
be able to provide a rating. The suggested reputation
strategy itself can thwart several reputational attacks.
For instance, Whitewashing is mitigated because a
central authority registers participants to the permis-
sioned network. A participant can only rejoin with the
network administrator’s permission if their identity is
revoked. Further, since registration requires a form of
identification, Sybil’s attacks are prevented.
Table 3 compares the examination of several fea-
tures offered in previously explored works in section
2 to the proposed system. We examine each system
using standard security criteria and offered features.
6.2 Reputation Model Testing Results
This section evaluates the reputation model’s effec-
tiveness in four different scenarios. Each scenario
examines the significance of each factor utilized in
the model. Before demonstrating the scenarios and
their results, it is worth noting that the parameters
controlling the Reputation model (α, β, γ, δ) must be
optimized per the business requirements due to its in-
fluence on the global reputation score growth or dwin-
dling speed.
Our data is from a unique dataset of ride-
hailing journeys produced by RideAustin, a nonprofit
ridesharing service based in Austin, Texas (Austin,
2017). The dataset has several features; we only se-
lect Ride ID, Rider ID, Driver ID, Rating, Order Cre-
ation Time, and Ride Cost. Table 4 shows the param-
eters configuration used in the following experiments
to assess our proposed reputation model.
The first test case examines the reputation model
resilience to the malicious behavior of the courier if
he conspires with a seller and performs consecutive
requests to boost his reputation score. Figure 4 de-
picts two couriers with identical data. The differ-
ence is that the malicious courier fulfilled requests
at intervals of less than an hour. In contrast, the
non-malicious courier has more than one hour dif-
ference between requests. The model can detect this
behaviour and control the courier’s reputation. The
non-malicious courier’s global reputation gradually
increased and reached 0.98, while the malicious re-
mained between 0.50 - 0.55.
The second test case analyzes the reputation
model action toward unfair ratings. Figure 5 presents
two identical couriers who accomplished 50 requests
with a positive rating rate of 70% and 30% negative
ratings. The first reputation is computed using our
proposed computation, while the other is without the
credibility factor. After fifty shipping requests, the at-
tained reputation for the first and the second courier
reached 0.83 and 0.78, respectively. We notice that
ICSBT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies
62
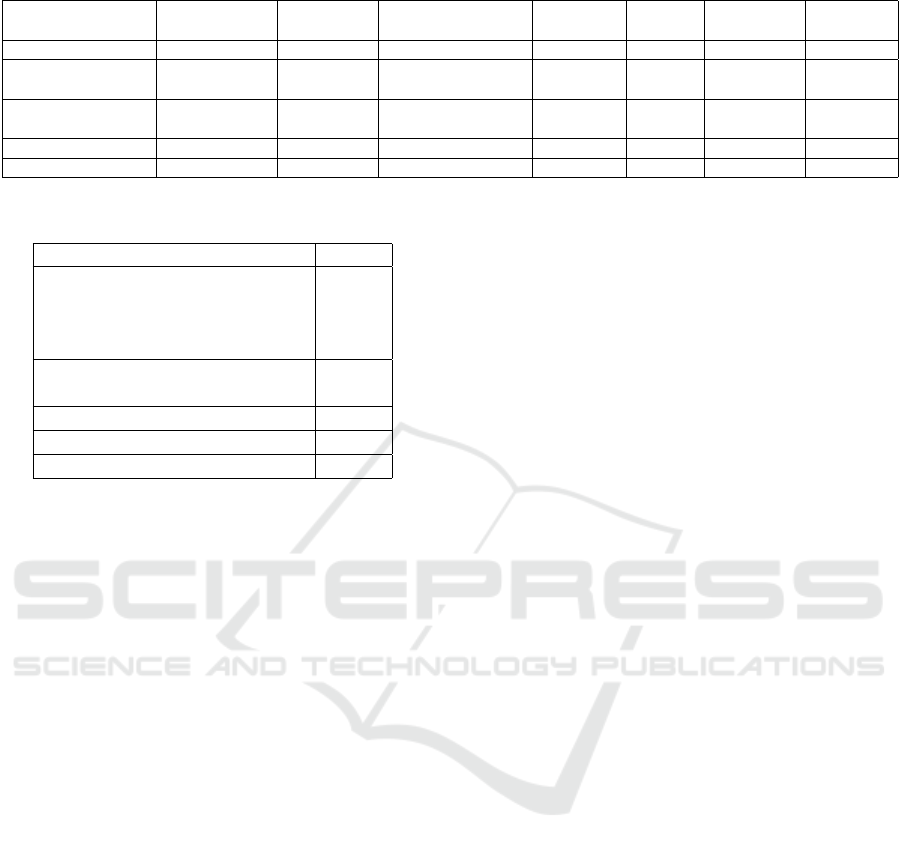
Table 3: Features Comparison Between Related Work and The Proposed Solution.
System Name Accountability Auditability Anonymity
Courier
Reputation
Proof of
Delivery
Traceability Scalability
Lelantos X X ✓ X ✓ X X
Single and Multiple
Transporters
✓ ✓ X X ✓ ✓ X
Auditable Protocols
for Fair Payment
✓ ✓ Only for Customers X ✓ ✓ X
DeM-CoD ✓ ✓ X X ✓ ✓ X
Proposed System ✓ ✓ X ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
Table 4: Reputation Test configuration.
Parameter Value
1-25 requests
26-50 requests
51-75 requests
> 76 requests
0.25
0.50
0.75
1
Normal time difference between
two consecutive requests T
a
1 hour
Local reputation threshold θ
0.5
Maximum increase value α
0.1
Decrease rate β
1.6
using the credibility factor alleviates the negative rat-
ing impacts provided unfairly by the same user.
The third test case investigates the influence of
shipping cost over reputation. Figure 6 depicts two
couriers with identical data except for the shipping
cost. All the shipping costs of the malicious courier’s
requests are set to 3$, while the non-malicious courier
to 10$. The cause of the steady reputation of the
malicious courier for the first 25 requests is that
the local reputation score is less than the threshold
that distinguishes between satisfactory and unsatis-
factory requests. When the malicious courier com-
pleted more than 25 requests, the number of transac-
tions factor became 0.50, which made the local repu-
tation score higher than the specified threshold. Later,
the courier’s reputation gradually increases, similar
to any honest courier, which indicates that detecting
low-priced requests and malicious behaviour using
the model is temporal. Once the courier has a higher
weight of the other factors, it would be undetectable.
The fourth test shows how the reputation grows
with increasing the total number of shipping requests.
Figure 7 presents two couriers; the first completed
50 shipping requests while the other 25 shipping re-
quests. The first courier’s reputation value is 0.98,
while the other is 0.89. The weight of the number
of shipping requests factor will increase as long as
the courier fulfills more requests; consequently, his
global reputation will thrive.
6.3 Performance Evaluation
Blockchain systems utilize a performance measuring
tool called Hyperledger Caliper (HL Caliper) (Hyper-
ledger, 2018) to evaluate the system based on several
performance indicators. This study conducts exper-
iments locally using the Hyperledger Caliper tool to
assess the transaction latency and throughput. We
perform two experiments using the Fixed Rate Con-
troller. This controller submits the transactions at a
predetermined interval, denoted as TPS (transactions
per second). We evaluate the system performance for
each experimental scenario under two different send
TPS rates; at 20 TPS and 40 TPS. Five different net-
work loads (total Transactions) are selected to inves-
tigate the TPS rate impact on the platform’s network
performance in terms of throughput and latency.
Figures 8 and 9 illustrate the transaction through-
put with TPS equals 20 and 40, respectively. It is ob-
served that the throughput at a transaction send rate
of 40 is slightly higher than when it is 20. Also, when
the TPS is 20, it shows consistency in the throughput,
which reflects the reliability and availability of Hyper-
ledger. The throughput ranges between 17-19, except
for the Create Order function. Create Order function
has less throughput since it performs one read opera-
tion and two write operations (one on the ledger and
the other on private data collection). When the TPS is
40, the throughput is approximately similar for each
function in figure 9, disregarding the transaction load.
Figures 10 and 11 describe the latency after exe-
cuting the Chaincode’s functions, using 100 to 500 si-
multaneous transactions. it is noticed that when TPS
is 20, the average latency follows a particular pattern
and remains consistent. The Create Order achieved
the highest average latency, 9.33 seconds when TPS
is 20 and 16.43 seconds when TPS is 40. Create Or-
der transactions require more time to be executed and
written successfully on world state and private data
collection. Furthermore, there is a continuous growth
in the average latency as the number of transactions
increases when TPS is 40. The reason is that the trans-
actions waiting at the orderer node are considerably
growing each second.
Trustworthy Decentralized Last-Mile Delivery Framework Using Blockchain
63

Figure 4: Test Case 1 - Timestamp Factor Impact.
Figure 5: Test Case 2 - Credibility Factor Impact.
Figure 6: Test Case 3 - Shipping Cost Factor Impact.
Figure 7: Test Case 4 - Number of Shipping Requests Factor
Impact.
Figure 8: Experiment I - Throughput with TPS = 20. Figure 9: Experiment II - Throughput with TPS = 40.
Figure 10: Experiment I - Latency with TPS = 20. Figure 11: Experiment II - Latency with TPS = 40.
ICSBT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies
64

7 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposes a blockchain-based crowd-
shipping system that eliminates the need for third-
party involvement, using a reputation management
algorithm to encourage honest conduct and aid sell-
ers in selecting trustworthy couriers. The study in-
cludes a prototype implementation of the proposed
platform and conducts performance measurements,
experiments, and feature comparisons to related re-
search. The proposed schema uses Hyperledger Fab-
ric, which is entirely free and open-source and avoids
costly consensus protocols to develop a feasible and
practical solution. However, the research has limita-
tions, such as the need for sellers to wait for couriers
to reveal their bids and the potential need for off-chain
computation of couriers’ reputations in large-scale en-
vironments. Future work could also consider allow-
ing couriers to submit multiple bids and deploying
the application on a Cloud with high computational
resource capabilities.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This project was partly supported by collaborative re-
search funding from the National Research Council
of Canada’s Artificial Intelligence for Logistics Pro-
gram.
REFERENCES
Allahbakhsh, M., Ignjatovic, A., Benatallah, B., Beheshti,
S.-M.-R., Foo, N., and Bertino, E. (2012). An ana-
lytic approach to people evaluation in crowdsourcing
systems. https://arxiv.org/abs/1211.3200.
AlTawy, R., ElSheikh, M., Youssef, A. M., and Gong, G.
(2017). Lelantos: A blockchain-based anonymous
physical delivery system. 2017 15th Annual Confer-
ence on Privacy, Security and Trust (PST).
Androulaki, E., Barger, A., Bortnikov, V., Cachin, C.,
Christidis, K., Caro, A. D., Enyeart, D., Ferris,
C., Laventman, G., Manevich, Y., Muralidharan, S.,
Murthy, C., Nguyen, B., Sethi, M., Singh, G., Smith,
K. A., Sorniotti, A., Stathakopoulou, C., Vukolic, M.,
Cocco, S. W., and Yellick, J. (2018). Hyperledger fab-
ric: a distributed operating system for permissioned
blockchains. Proceedings of the Thirteenth EuroSys
Conference.
Austin, R. (2017). Ride-austin-june6-april13 - dataset by
ride-austin. https://data.world/ride-austin/ride-austi
n-june-6-april-13.
Breen, K. (2019). Food delivery app doordash reports data
breach affecting 4.9m users - national. https://global
news.ca/news/5957123/doordash-data-breach/.
Dolan, S. (2023). The challenges of last mile delivery lo-
gistics and the tech solutions cutting costs in the final
mile. https://www.insiderintelligence.com/insights/l
ast-mile-delivery-shipping-explained.
Evans, P. (2020). Food delivery apps cut some restaurant
fees amid surging demand due to covid-19 — cbc
news. https://www.cbc.ca/news/business/food-del
ivery-apps-fees-1.5765790.
Gatta, V., Marcucci, E., Nigro, M., Patella, S., and Serafini,
S. (2018). Public transport-based crowdshipping for
sustainable city logistics: Assessing economic and en-
vironmental impacts. Sustainability, 11:145.
Ha, X. S., Le, H. T., Metoui, N., and Duong-Trung, N.
(2020). Dem-cod: Novel access-control-based cash
on delivery mechanism for decentralized marketplace.
In 2020 IEEE 19th International Conference on Trust,
Security and Privacy in Computing and Communica-
tions (TrustCom), pages 71–78.
Hasan, H. R. and Salah, K. (2018). Blockchain-based solu-
tion for proof of delivery of physical assets. Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, page 139–152.
Hyperledger (2018). Measuring blockchain performance
with hyperledger caliper. https://www.hyperledger.
org/blog/2018/03/19/measuring-blockchain-perform
ance-with-hyperledger-caliper.
Le, C. (2022). Canada - ecommerce. https://www.trade.go
v/country-commercial-guides/canada-ecommerce.
N, B. (2020). Hackers leaked ubereats data on darkweb.
https://cybersecuritynews.com/hackers-leaked-ubere
ats-data-on-darkweb/.
Placek, M. (2022). Couriers and local delivery services mar-
ket size in canada 2018-2021. https://www.statista.c
om/statistics/1156206/couriers-and-local-delivery-s
ervices-market-size-canada/.
Truong, N., Lee, G. M., Sun, K., Guitton, F., and Guo,
Y. (2021). A blockchain-based trust system for de-
centralised applications: When trustless needs trust.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.10920.
Wang, M. (2021). I tried delivering parcels for a day. https:
//www.linkedin.com/pulse/i-tried-delivering-parcels
-day-mark-wang.
Wang, S., Tang, X., Zhang, Y., and Chen, J. (2019). Au-
ditable protocols for fair payment and physical as-
set delivery based on smart contracts. IEEE Access,
7:109439–109453.
WASPLab (2022). Wasplab/bc crowdshipping: This is the
blockchain network of a crowdshipping platform us-
ing hyperledger fabric. https://github.com/WASPLab
/BC Crowdshipping.
Xiong, L. and Liu, L. (2004). Peertrust: Supporting
reputation-based trust for peer-to-peer electronic com-
munities. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data
Engineering, 16(07):843–857.
Zhou, Z., Wang, M., Yang, C.-N., Fu, Z., Sun, X., and
Wu, Q. J. (2021). Blockchain-based decentralized rep-
utation system in e-commerce environment. Future
Gener. Comput. Syst., 124(C):155–167.
Trustworthy Decentralized Last-Mile Delivery Framework Using Blockchain
65
