
Proposed Model for Halal Blockchain Barrier: Literature Review and
Interview
Dwi Iryaning Handayani
1,2 a
, Iwan Vanany
1b
and Udi Subakti Ciptomulyono
1
1
Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember Kampus ITS Sukolilo,
Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Department of Industrial Engineering, Universitas Panca Marga, Probolinggo, Indonesia
Keywords: Halal Blockchain, Adoption, Barriers.
Abstract: Muslim consumers’ concern towards the quality and safety of food and halal is increasing for products
consumed according to Islamic law. Blockchain technology is a solution to increase trust and provide full
transparency to ensure product integrity throughout the halal supply chain. However, not all companies adopt
blockchain in their supply chains, and this is because the application of blockchain technology in the industry
faces various obstacles in adopting it. This study proposed model for halal blockchain adoption barriers and
factors that can hinder the potential of blockchain in the halal industry. Literature review and interviews with
practitioners have been carried out in this study. The SCOR (Plan, Source, Make, Delivery) is adopted to
determine the factors of halal blockchain in each of its business processes. The results show eight (8)
blockchain barriers, consisting of two barriers on the Plan, Source seven barriers, Make eight barriers, and
Delivery four barriers. The practical implication of this research is the barrier factors halal adoption of halal
blockchain that can affect companies.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blockchain is a digital technology that can provide
solutions to the reputation of halal products caused by
cases of halal violations (Tieman & Darun, 2017). As
for cases of halal violations such as halal fraud, halal
counterfeiting, cross-contamination, logistical
problems, and non-standard halal standards (Ali et al.,
2021). This halal violation has the potential to affect
the loss of consumer confidence in halal products
(Khan et al., 2021). Therefore, the use of halal
blockchain technology can increase trust and
transparency and ensure product integrity throughout
the halal supply chain(Vanany et al., 2020). In
addition, blockchain is a prospective technological
breakthrough and a significant solution in solving
supply chain problems and halal (Handayani et al.
2021)
However, blockchain technology is relatively new
and developing, so the immaturity of new
technologies often creates several barriers to its
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8849-9982
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0774-514X
implementation (Vafadarnikjoo et al., 2021). Besides,
technology blockchain still has unresolved problems
and challenges beyond technical, so it requires more
exploration and investigation (Xu et al., 2021). Even
the implementation of blockchain projects was
stopped, and the current blockchain adoption rate is
around 20% (Sanka et al., 2021). This indicates that
there are barriers to blockchain implementation, thus
motivating researchers to study blockchain barriers
such as (Saberi et al., 2019a), resulting in external
barriers, inter-organizational, intra- organizational,
and technical in sustainable supply chains.
Blockchain barriers in sustainable supply chains
were classified by technology, environment, and
organization (Kouhizadeh et al., 2021a).
Performance expectations, effort expectations,
social influence, and enabling factors, such as trust
are blockchain barriers in operations and supply chain
management (Queiroz et al., 2019). On the other
hand, in the context of a developing country such as
Indonesia, this obstacle becomes more critical, as
conveyed by the Directorate General of Information
Handayani, D., Vanany, I. and Ciptomulyono, U.
Proposed Model for Halal Blockchain Barrier: Literature Review and Interview.
DOI: 10.5220/0012105200003680
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technology (ICATECH 2023), pages 47-54
ISBN: 978-989-758-663-7; ISSN: 2975-948X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
47

Applications at the Ministry of Communication and
Information, stating that Indonesia has not been able
to utilize the potential of blockchain technology fully,
this is due to uneven penetration. Internet, quality,
and quantity of human resources, technical
challenges, and audit processes. It is moreover
facilitating conditions and trust.
Thus, there are several barriers to applying
blockchain technology, but the resulting barriers tend
to focus on general industries, not specific to the halal
industry. Therefore, the resulting barriers cannot be
referenced to the halal industry. This shows that there
is still little attention and research on the barriers to
blockchain technology in the halal industry, even
though blockchain has great potential to overcome the
halal problem. Therefore, this study will propose a
model for identifying halal blockchain barriers in
Indonesia. The proposed model is a conceptual model
based on the Supply Chain Operations Reference
(SCOR), which includes a plan, source, make, and
delivery. The SCOR model is a model that is believed
to be able to design, describe, and configure various
types of supply chain activities (Sundarakani et al.,
2018). With the SCOR model, identification of
barriers can be carried out starting from a plan,
source, make, and delivery activities. For this reason,
obtaining halal blockchain barriers is carried out
using literature reviews and expert interviews.
This research aims to obtain a model for
identifying and analysing halal blockchain barriers by
conducting literature reviews and interviews. This
paper consists of section I introducing the
background, section II literature review, and the
research methodology entered section III. Sections
IV-V present the proposed model, and discussion of
section VI conclusions.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Halal Blockchain is a technology that supports halal
supply chain management (Tieman et al., 2019) and
can improve the performance of the halal supply
chain (Surjandari et al., 2021). Blockchain Halal
provides several advantages for producers,
distributors, retailers, logistics service providers, and
halal certification bodies. With blockchain
technology, it can overcome various halal issues, and
product recalls.
Another advantage is that halal supply chain
companies cannot commit fraudulent actions. This is
because the halal Blockchain has complete
information shared with all participants in the halal
supply chain network. So that if there are parties
committing fraud, it will be easy to identify the
perpetrators because this information can be seen
(Katuk, 2019). This is because the authenticity and
security of Halal Blockchain are a priority in securing
confidential data and minimizing the chances of
cyber-attacks (Surjandari et al., 2021). Besides, halal
Blockchain provides clear benefits and better
credibility for halal producers and certification
bodies. Therefore, it is essential to adapt to this
technology to ensure its haleness from upstream to
downstream of the supply chain process. Thus
standardization of the halal supply chain can be
realized to support the halal industry and its global
supply chain.
Halal Suppl
y
Chain
Halal Blockchain
Figure 1: Halal supply chain and halal blockchain.
According to Katuk (Universiti Utara Malaysia &
Katuk, 2019), there is a difference between a halal
supply chain using blockchain and without
blockchain, more details can be seen in Figure 1. All
transactions in the supply chain that implement halal
blockchain from suppliers, manufacturers,
distributors, retailers, logistics providers, and
customers store their transactions in a shared ledger,
and smart contracts control them. Thus, halal product
ICATECH 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technology
48

certification can be carried out efficiently and
uncomplicatedly. This is
because halal certification
bodies can access shared ledgers and smart contracts
for product certification. While the supply chain
system is without a halal blockchain, all entities in the
system record transactions in the internal ledger
separately. Halal certification bodies must ensure
halal conditions for all entities individually, making
the process complicated.
Empirically Chandra, Liaqat, and Sharma
(Chandra et al., 2019) have proven that ownership of
halal products can be traced on the blockchain. The
blockchain ledger provides a complete audit trail of
all operations performed from scratch, making it easy
to track product ownership. So Blockchain
technology can be a transformational force that
improves the status of halal regulations. Blockchain
technology in the halal industry will increase trust
among halal supply chain actors, ultimately enabling
consumers to make more informed and confident
choices. The halal supply chain is distinguished with
and without blockchain, as illustrated in Figure 1.
3 METHODOLOGY
The objective of this paper is to propose a model of
halal blockchain adoption barriers with two stages
such as (1) identifying barriers factors of halal
blockchain based on a literature review using the
scopus database and (2) interviewing experts. in
reviewing the literature, the scopus database is the
first step. the keywords that are used to search for
barriers in halal blockchain research topics are
“adoption," barriers, “blockchain," and “supply
chain". in the second step, interviews are conducted
with academics, practitioners, and professionals or
halal blockchain experts. in contrast, the expert
qualifications are at least a bachelor's degree and an
average work experience of five years in the field.
interview with experts or professionals aims to
understand experts/professionals' opinions based on
qualitative data and conclusions (Bryman, 2016).
interview protocol developed to understand barriers
to adoption factors of halal blockchain with three
sections: blockchain technology, blockchain
applications in the supply chain, and halal blockchain.
4 RESULTS
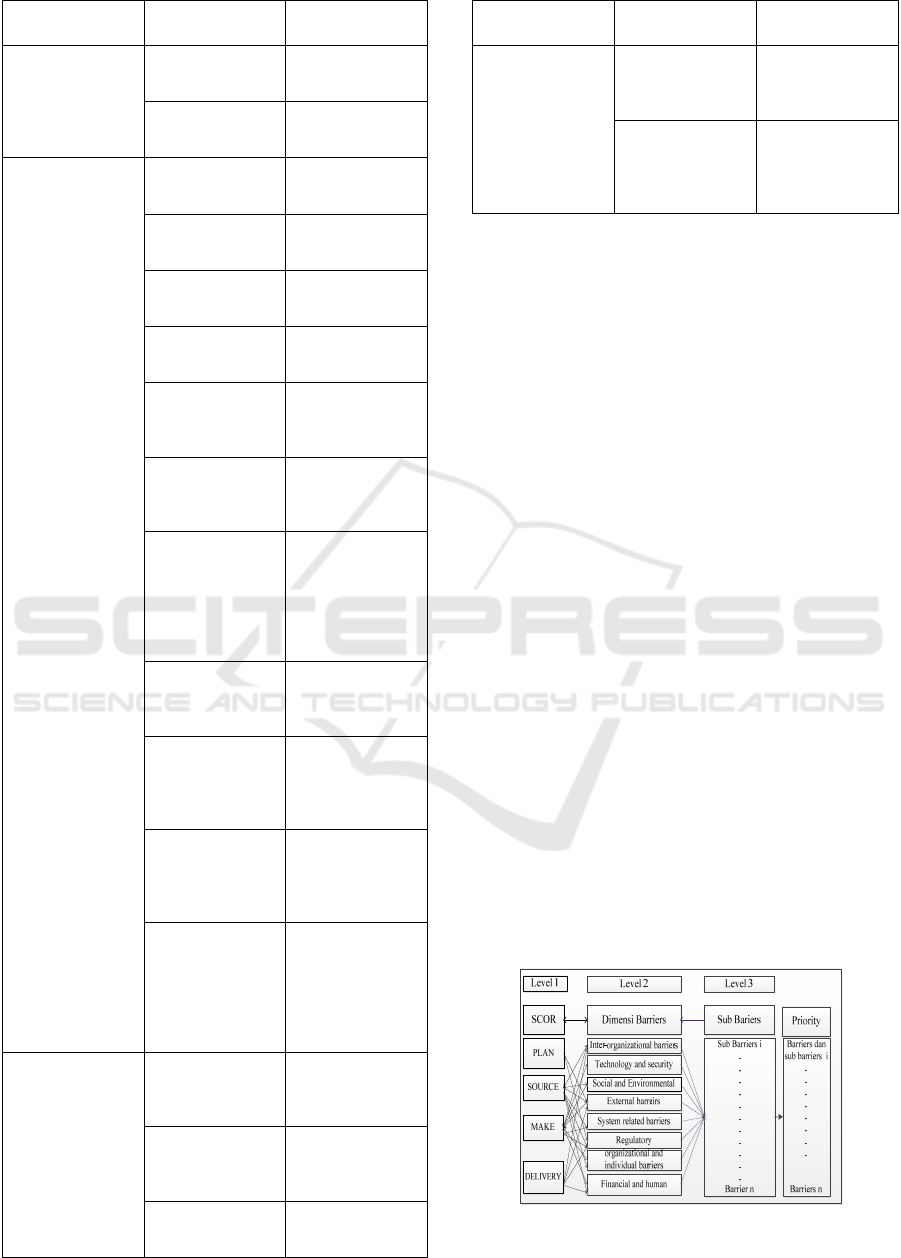
4.1 Proposed Adoption Barriers Model
for Halal Blockchain
The proposed model has three levels such as 1)
b u s i n e s s p r o c e s s e s r e l a t e d b a s e d o n t h e S C O R m o d e l ,
2) adoption barriers factors for halal blockchain, and
3) adoption sub barriers factors for halal blockchain;
The following is the description:
1)
Level 1: Business processes related based on the
SCOR model
Much previous research used four business processes
(Plan, Source, Make, and Delivery) from the SCOR
model (Nyoman Pujawan & Geraldin, 2009); (Lestari
et al., 2021)The following describes four business
processes as level 1 in the proposed model of halal
blockchain adoption barriers:
Plan: describes the entities or stakeholders
involved in the form of a Halal Assurance
Institution in a country. For example, in
Indonesia, BPJPH, MUI. Halal auditors
(LPPOM MUI, Sucofindo, etc.). BPJPH, as a
halal authority of the Indonesian government,
has control for supply chain planning in a halal
certification process.
Source: describes suppliers who fulfill raw
materials according to halal standards. For
example, chicken farming is a supplier of
chicken slaughtering companies.
Make: represents activities flow to the halal
production process. For example, chicken
slaughter companies' production processes are
stunning, pre-slaughtering and slaughtering.
Delivery: describes the halal distribution process
for finished goods to the end customers. For
example, in halal chicken food, chicken
slaughtering companies deliver the halal chicken
carcass to their customers, such as fried chicken
restaurants, supermarkets, and end customers.
2)
Level 2 and Level 3: Adoption barriers and sub-
factors for halal blockchain
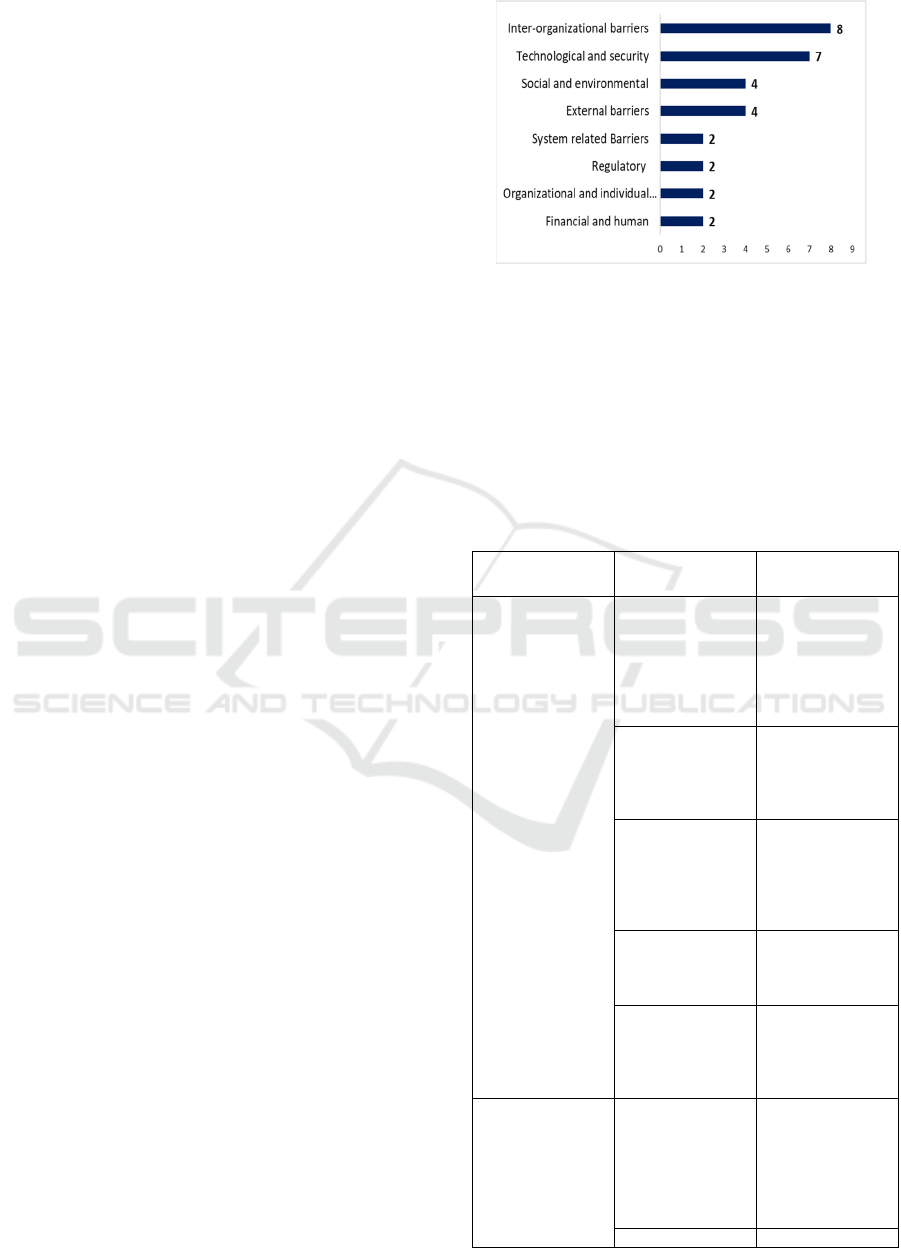
Based on searching in the Scopus database, eight (8)
factors of barrier adoption in blockchain
applications such as inter-organizational barriers,
technological and security, etc. Figure 2 shows the
eight barrier adoption factors of blockchain
applications based on review literature in the Scopus
database from 2017 - 2021
• Inter-organizational barrier. An organizational-
level barrier that hinders blockchain
implementation. Several inter-organizational
barrier factors such as the absence or weakness of
Proposed Model for Halal Blockchain Barrier: Literature Review and Interview
49
communication, collaboration, and coordination
among
members of supply chain. Saberi (Saberi
et al., 2019b) stated that collaboration is essential
in sharing information between supply chain
partners, lack of effective the communication,
collaboration, coordination, and among supply
chain partners can disrupt blockchain
implementation. 2) Challenge information
exposes policy between partners in the supply
chain. Saberi (Saberi et al., 2019b) and Farooque
(Farooque et al., 2020) stated that challenging
information was the most significant obstacle. 3)
Challenges in integration issues with blockchain
technology and sustainability in SC. 4) The
cultural diversity of supply chain participants,
according to Farooque (Farooque et al., 2020)
and Saberi (Saberi et al., 2019b) less relevant, so
this barrier was excluded from several identified
barriers. 5) Lack of consumer awareness of
sustainability issues and a willingness to use
blockchain technology is an obstacle to the
implementation of sustainability(Saberi et al.,
2019b). 6) Transparency versus privacy dilemma
and uncertainty about blockchain suitability.
• Technological and security barriers. The most
crucial obstacle is because blockchain
technology has many essential features such as
distributed database security and transparency.
• Social and environmental barriers. Covers
environmental health and safety issues that are
essential application focus for blockchain.
• External barriers. These barriers come from
external stakeholders, industry, institutions, and
government.
• System-related barrier. A limitation of access to
technology in obtaining real-time information
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi, 2020).
• Regulatory barrier. Balancing the opportunities
offered with potential unforeseen effects is a
difficult task because of regulatory ambiguity
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi, 2020).
• Organizational and individual barriers.
Organizational internal impediments include
financial limitations, a lack of management
commitment and support, a lack of available
company policy for using technology, a lack of
knowledge and experience, and a lack of new
company procedures (Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020).
• Financial and human barrier. A barrier that often
occurs in technology adoption because the
adoption of new technology causes high
investment costs and a lack of information
technology personnel.
Figure 2. Barrier’s adoption factors of blockchain
application
Figure 2 is a dimension in identifying various
barriers that hinder the adoption of blockchain
technology. The results of identifying barriers from
the literature review and expert interviews are shown
in Table 1. The identified barriers are from the expert
as many as eleven (11), while the other barriers result
from the literature review.
Table 1: Review and interview for barriers factors.
Barriers Dimension Barriers Factors Authors
1. Inter-
organizational
Barriers
1.1. Coordination,
communication,
and collaboration
in SC
(Saberi et al.,
2019b); (Farooque
et al.,
2020);(Öztürk &
Yildizbaşi,
2020);(Choi et al.,
2020)
1.2. Challenge
information
disclosure policy
between partners
in SC
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
1.3 Challenges in
integration issues
with blockchain
technology and
sustainability in
SC
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
1.4 the cultural
diversity of
supply chain
partners
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020);(Choi et al.,
2020)
1.5 Lack of consumer
awareness of
sustainability
issues and
technology
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
2. Technological And
security barriers
2.1 A lack of
technological
sophistication
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020); (Choi et al.,
2020); (Sabbagh,
2021);
(Mathivathanan et al.,
2021)
2.2 Data security (Sabbagh,
ICATECH 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technology
50
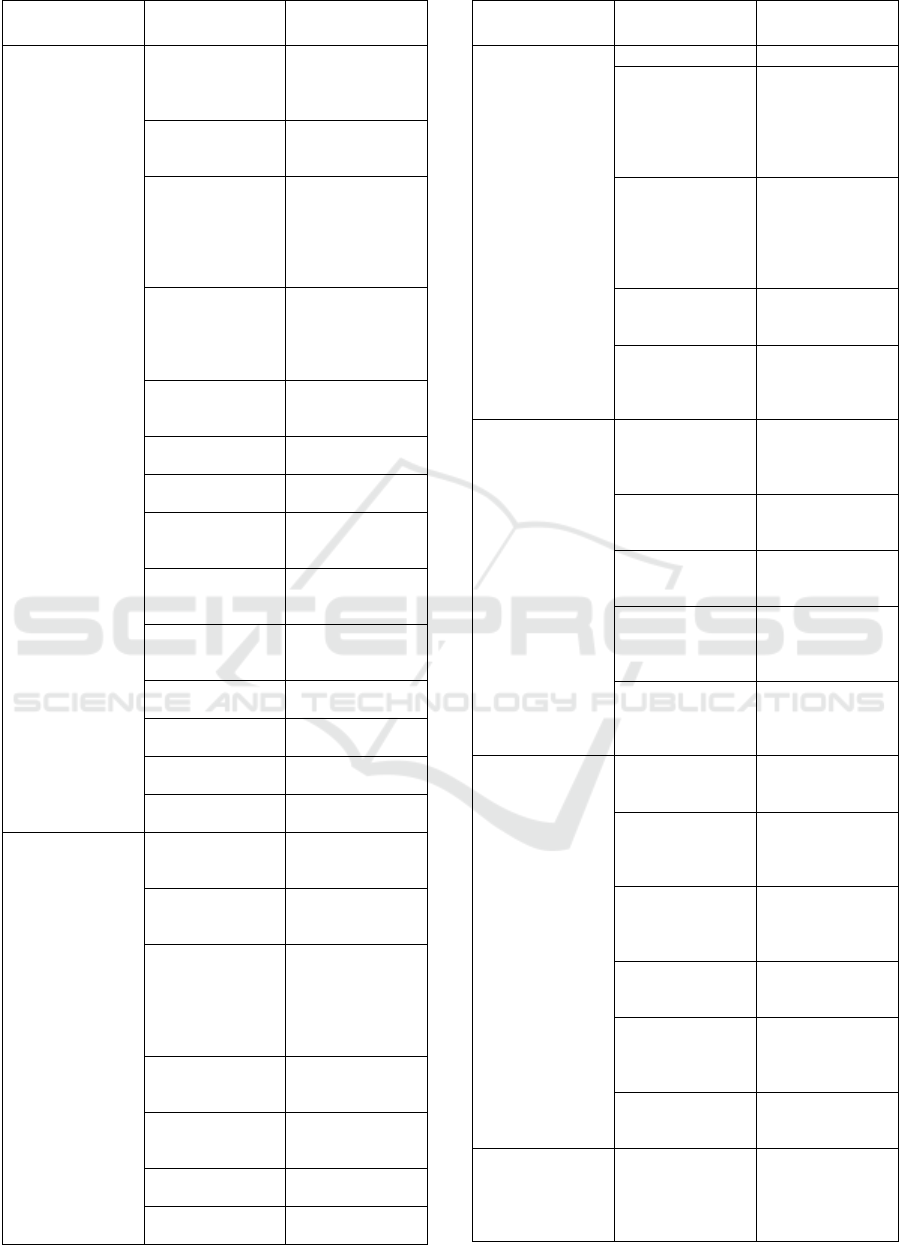
Barriers Dimension Barriers Factors Authors
2021);(Öztürk &
Yildizbaşi, 2020);
(Kouhizadeh et al.,
2021a)
2.3 Usability
(Sabbagh,
2021);(Öztürk &
Yildizbaşi, 2020)
2.4 Complexity
(Sabbagh,
2021);(Öztürk &
Yildizbaşi, 2020);
(Choi et al.,
2020);(Biswas &
Gupta, 2019)
2.5 Interoperability
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020); (Choi et al.,
2020); (Sabbagh,
2021) [Expert
Opinion]
2.6 Forking
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020); (Sabbagh,
2021)
2.7 Performance and
scalability
(Choi et al., 2020);
(Sabbagh, 2021)
2.8 Cost
[Expert Opinion];
(Choi et al., 2020)
2.9 Negative
perception toward
technology
(Kouhizadeh et al.,
2021a);(Choi et al.,
2020)
2.10 Access to
technology
(Kouhizadeh et al.,
2021a);(Choi et al.,
2020)
2.11 Unclear
Governance
Structure
(Lohmer & Lasch,
2020)
2.12 Missing
standards,
(Lohmer & Lasch,
2020)
2.13 Complex
p
rotocol selection
(Lohmer & Lasch,
2020)
2.14 Trial and
reversibility
(Choi et al., 2020)
2.15 Lack of large
computing powe
r
(Mathivathanan et al.,
2021)
2 Social and
environmental
barriers
3.1 Information
sharing
(Sabbagh,
2021);(Öztürk &
Yildizbaşi, 2020);
3.2 Wasted resources
(Choi et al.,
2020);(Öztürk &
Yildizbaşi, 2020)
3.3 Lack of industry
participation in
blockchain
adoption and
moral and secure
procedures
(Kouhizadeh et al.,
2021a); (Choi et al.,
2020)
3.4 Governmental
p
olicies
(Kouhizadeh et al.,
2021a); (Choi et al.,
2020)
3.5 Lack of external
stakeholders
‘involvemen
t
(Kouhizadeh et al.,
2021a) ;[Expert
Opinion]
3.6 Lack of rewards
and incentives
(Kouhizadeh et al.,
2021a)
3.7 Market
competition and
(Kouhizadeh et al.,
2021a)
Barriers Dimension Barriers Factors Authors
uncertainty
3.8 Perceived
impediment to
blockchain's
correct legal
structure and
legislation
(Choi et al., 2020)
3.9 Perceived
restriction on an
infrastructure
that is
technologically
effective
(Choi et al., 2020)
3.10 The perception
of a governance
constrain
t
(Choi et al., 2020);
[Expert Opinion]
3.11 Perceived
constraint on
encouragement
program
(Choi et al., 2020)
4. External
barriers
4
.1 Lack of
government policies
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020); (Lohmer &
Lasch, 2020)
4.2 Market
competition and
uncertainty
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
4.3 Lack of external
stakeholders’
involvemen
t
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
4.4 Lack of industry
p
articipation in moral
and secure
p
rocedures
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
4.5 Lack of reward
and
encouragement
programs
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
5. System related
Barriers
5.1 Security
challenge
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
5.2 Access to
technology
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020) [Expert
Opinion]
5.3 The reluctance to
use blockchain
technology
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020) [Expert
Opinion]
5.4 Because of
unfavorable public
opinion
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
5.5 Immutability
challenge of
blockchain
technology
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
5.6 Immaturity of
technology
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020)
6. Regulatory barrier
6.1 Regulations differ
between nations,
but nevertheless
practical
b
lockchain
(Sabbagh, 2021)
(Mathivathanan et al.,
2021)
Proposed Model for Halal Blockchain Barrier: Literature Review and Interview
51
Barriers Dimension Barriers Factors Authors
regulations are still
in the development
stage.
6.2 No universal
regulatory binding
in each country
(Biswas & Gupta,
2019).
7. Organizational and
individual barrier
7.1 Strong
bureaucracy and a
hierarchical structure
(Sabbagh, 2021):
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020)
7.2 Rigorous
administrative
oversigh
t
(Sabbagh, 2021):
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020)
7.3 Information
sharing obstacles
(Sabbagh, 2021):
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020)
7.4 Mindset of people
needs to be changed
(Sabbagh, 2021):
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020)
7.5 Financial
Constraints
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020);(Kouhizadeh et
al., 2021a)
7.6 A lack of
dedication and
assistance from
management
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020);(Kouhizadeh et
al., 2021a)
7.7 The absence of
updated
organizational
guidelines for
utilizing
blockchain
technology
(Kouhizadeh et al.,
2021a)
7.8 Lack of
experience and
knowledge
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020); [Expert
Opinion]
7.9 Challenges with
modifying
corporate culture
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020);(Kouhizadeh et
al., 2021a); [Expert
Opinion]
7.10 Reluctance to
switch to new
systems
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020);(Kouhizadeh et
al., 2021a); [Expert
Opinion]
7.11 Insufficient
tools for
integrating
blockchain
technology into
sustainable
supply chains
(Saberi et al., 2019b)
;(Farooque et al.,
2020);(Kouhizadeh et
al., 2021b)
8. Financial and
human
8.1 Lack of IT
p
ersonnel
(Sabbagh, 2021):
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020) ; [Expert
Opinion]
8.2 High investment
cost
(Sabbagh, 2021):
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020) ;[Expert
Opinion]
8.3 A lack of units
for research and
developmen
t
(Sabbagh, 2021):
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020)
Barriers Dimension Barriers Factors Authors
8.4 Poor financial
support for
technological
infrastructure
(Sabbagh, 2021):
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020) ; [Expert
Opinion]
8.5 Block chain
technology does
not receive
enough financial
suppor
t
(Sabbagh, 2021):
(Öztürk & Yildizbaşi,
2020) ; [Expert
Opinion]
5 DISCUSSION
Barriers in plan are in touch with the government as
a policy provider supporting blockchain
implementation for the halal assurance system in
Indonesia. This is in line with (Sanka et al., 2021),
who stated that uncertainty in government
regulations is a significant barrier to blockchain
implementation. The barriers in plan are External and
regulatory barriers. Proposed adoption barriers
model for halal Blockchain is shown in Figure 3.
Source, make, and delivery, namely regulatory and
external barriers. Meanwhile, the other six barriers
are source, make, and delivery. Thus, the SCOR
model can investigate the connections between all
the players in the halal supply chain in the face of
all obstacles to implementing halal blockchain.
suppliers and supporting suppliers must have a halal
certificate. For this reason, integrating producers,
suppliers, and the government in realizing safe and
halal products is the key to the success of halal
certificates. However, there are
obstacles to
implementing halal blockchain-based food safety,
including the lack of knowledge, employee skills,
costs, and infrastructure (Biswas & Gupta, 2019).
These barriers are included in the category of
barriers,
including Inter-Organizational Barriers –
Social environmental – System related barriers,
External barriers – Regulatory – Organizational and
individual barriers, Financial and human.
Figure 3: Proposed adoption barrier model for halal
blockchain.
ICATECH 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technology
52

Barriers that occur in Make are not only limited
to the production process but are extended to
physical separation in packaging, and storage, which
is guided by HAS 2300 in maintaining the
sustainability of the halal production process. All
information related to the halal production process
from various stakeholders throughout the supply
chain is stored in the Halal Blockchain. The
involvement of all stakeholders in an integrated
system creates barriers to its implementation. The
barriers in make stage consist of Inter- Organizational
Barriers, Technology, and security barriers, Social
environmental- System-related barriers, External
barriers- Regulatory- Organizational and individual
barriers, Delivery barriers that are both financial and
human in nature are the basis of logistics and its most
obvious expressions. In halal delivery, non-halal and
halal goods cannot be mixed. To maintain the
haleness of the product during operation, it must be
handled with the proper process by the assigned
person (Tieman & Darun, 2017). But there is still a
lack of comprehension of the appropriate methods
for implementing blockchain technology for
distribution systems (Marsusvita et al., 2021), so there
are barriers to halal blockchain. Barriers to
delivery
include Inter-Organizational Barriers, External
barriers, Regulatory, Financial, and human.
6 CONCLUSION
This study applies the SCOR model's theory to
identify impediments to halal blockchain usage. The
identification results show that there are eight
blockchain barriers consisting of two barriers in plan,
seven barriers to source, and eight barriers to make
and deliver to four barriers. Of the eight barriers,
there are two main barriers in plan, barriers in plan,
source, make, and delivery, namely regulatory and
external barriers. Meanwhile, the other six barriers
are source, make, and delivery. Thus, the SCOR
model can explore the relationship between all actors
involved in the halal supply chain in the face of all
obstacles to implementing halal blockchain
.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are very grateful to The Ministry of
Research, Technology and Higher Education of the
Republic of Indonesia for providing a Doctoral
Dissertation Research Grant.
REFERENCES
Ali, M. H., Iranmanesh, M., Tan, K. H., Zailani, S., &
Omar, N. A. (2021). Impact of supply chain integration
on halal food supply chain integrity and food quality
performance. Journal of Islamic Marketing, ahead-of-
print(ahead-of-print). https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-
08-2020-0250
Biswas, B., & Gupta, R. (2019). Analysis of barriers to
implement blockchain in industry and service sectors.
Computers & Industrial Engineering, 136, 225–241.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.07.005
Bryman, A. (2016). Social research methods (Fifth
Edition). Oxford University Press.
Chandra, G. R., Liaqat, I. A., & Sharma, B. (2019).
Blockchain Redefining: The Halal Food Sector. 2019
Amity International Conference on Artificial
Intelligence (AICAI), 349–354.
https://doi.org/10.1109/AICAI.2019.8701321
Choi, D., Chung, C. Y., Seyha, T., & Young, J. (2020).
Factors Affecting Organizations’ Resistance to the
Adoption of Blockchain Technology in Supply
Networks. Sustainability, 12(21), 8882.
https://doi.org/10.3390/su12218882
D. I. Handayani and I. Vanany, “Blockchain Application in
Halal Supply Chain: Literature Review and Future
Research,” 2021 IEEE International Conference on
Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management
(IEEM), 2021, pp. 1387-1391, doi:
10.1109/IEEM50564.2021.9673084. (n.d.).
Farooque, M., Jain, V., Zhang, A., & Li, Z. (2020). Fuzzy
DEMATEL analysis of barriers to Blockchain-based
life cycle assessment in China. Computers & Industrial
Engineering, 147, 106684.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106684
Khan, S. N., Loukil, F., Ghedira-Guegan, C., Benkhelifa,
E., & Bani-Hani, A. (2021). Blockchain smart
contracts: Applications, challenges, and future trends.
Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 14(5),
2901–2925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-021-
01127-0
Kouhizadeh, M., Saberi, S., & Sarkis, J. (2021a).
Blockchain technology and the sustainable supply
chain: Theoretically exploring adoption barriers.
International Journal of Production Economics, 231,
107831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107831
Kouhizadeh, M., Saberi, S., & Sarkis, J. (2021b).
Blockchain technology and the sustainable supply
chain: Theoretically exploring adoption barriers.
International Journal of Production Economics, 231,
107831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107831
Lestari, F., Nurainun, T., Kurniawati, Y., & Adzkia, M. D.
(2021). Barriers and Drivers for Halal Supply Chain on
Small-Medium Enterprises in Indonesia. Hong Kong, 6.
Lohmer, J., & Lasch, R. (2020). Blockchain in operations
management and manufacturing: Potential and barriers.
Computers & Industrial Engineering, 149, 106789.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106789
Proposed Model for Halal Blockchain Barrier: Literature Review and Interview
53

Marsusvita, A., Suprayogi, S., & Sucipto, S. (2021). Barrier
and motivations implementation of safety and halal
assurance for apple processed products: A review. IOP
Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science,
924(1), 012068. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-
1315/924/1/012068
Mathivathanan, D., Mathiyazhagan, K., Rana, N. P.,
Khorana, S., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2021). Barriers to the
adoption of blockchain technology in business supply
chains: A total interpretive structural modelling (TISM)
approach. International Journal of Production
Research, 59(11), 3338–3359.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2020.1868597
Nyoman Pujawan, I., & Geraldin, L. H. (2009). House of
risk: A model for proactive supply chain risk
management. Business Process Management Journal,
15(6), 953–967.
https://doi.org/10.1108/14637150911003801
Öztürk, C., & Yildizbaşi, A. (2020). Barriers to
implementation of blockchain into supply chain
management using an integrated multi-criteria decision-
making method: A numerical example. Soft Computing,
24(19), 14771–14789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-
020-04831-w
Queiroz, M. M., Telles, R., & Bonilla, S. H. (2019).
Blockchain and supply chain management integration:
A systematic review of the literature. Supply Chain
Management: An International Journal, 25(2), 241–
254. https://doi.org/10.1108/SCM-03-2018-0143
Sabbagh, P. (2021). An Uncertain Model for Analysis the
Barriers to Implement Blockchain in Supply Chain
Management and Logistics for Perishable Goods:
International Journal of Computational Intelligence
Systems, 14(1), 1292.
https://doi.org/10.2991/ijcis.d.210308.002
Saberi, S., Kouhizadeh, M., Sarkis, J., & Shen, L. (2019a).
Blockchain technology and its relationships to
sustainable supply chain management. International
Journal of Production Research, 57(7), 2117–2135.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1533261
Saberi, S., Kouhizadeh, M., Sarkis, J., & Shen, L. (2019b).
Blockchain technology and its relationships to
sustainable supply chain management. International
Journal of Production Research, 57(7), 2117–2135.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1533261
Sanka, A. I., Irfan, M., Huang, I., & Cheung, R. C. C.
(2021). A survey of breakthrough in blockchain
technology: Adoptions, applications, challenges and
future research. Computer Communications, 169, 179–
201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2020.12.028
Sundarakani, B., Abdul Razzak, H., & Manikandan, S.
(2018). Creating a competitive advantage in the global
flight catering supply chain: A case study using SCOR
model. International Journal of Logistics Research and
Applications, 21
(5), 481–501.
https://doi.org/10.1080/13675567.2018.1448767
Surjandari, I., Yusuf, H., Laoh, E., & Maulida, R. (2021).
Designing a Permissioned Blockchain Network for the
Halal Industry using Hyperledger Fabric with multiple
channels and the raft consensus mechanism. Journal of
Big Data, 8(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-020-
00405-7
Tieman, M., & Darun, M. R. (2017). Leveraging
Blockchain Technology for Halal Supply Chains. Islam
and Civilisational Renewal, 8(4), 547–550.
https://doi.org/10.12816/0045700
Tieman, M., Darun, M. R., Fernando, Y., & Ngah, A. B.
(2019). Utilizing Blockchain Technology to Enhance
Halal Integrity: The Perspectives of Halal Certification
Bodies. In Y. Xia & L.-J. Zhang (Eds.), Services –
SERVICES 2019 (Vol. 11517, pp. 119–128). Springer
International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-
030-23381-5_9
Katuk, N. (2019). The application of blockchain for halal
product assurance: A systematic review of the current
developments and future directions. International
Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and
Engineering, 8(5), 1893–1902.
https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2019/13852019
Vafadarnikjoo, A., Badri Ahmadi, H., Liou, J. J. H.,
Botelho, T., & Chalvatzis, K. (2021). Analyzing
blockchain adoption barriers in manufacturing supply
chains by the neutrosophic analytic hierarchy process.
Annals of Operations Research.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04048-6
Vanany, I., Rakhmawati, N. A., Sukoso, S., & Soon, Jan.
M. (2020). Indonesian Halal Food Integrity: Blockchain
Platform. 2020 International Conference on Computer
Engineering, Network, and Intelligent Multimedia
(CENIM), 297–302.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CENIM51130.2020.9297968
Xu, Y., Chong, H.-Y., & Chi, M. (2021). Modelling the
blockchain adoption barriers in the AEC industry.
Engineering, Construction and Architectural
Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/ECAM-04-2021-
0335
ICATECH 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technology
54
