
Evaluation System Usability Scale (SUS) Method on Batik Website
Nur Rochman Wibisono
Department of Industrial Engineering, Islam University of Indonesia, Kaliurang Street 14,5 Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: System Usability Scale, Usability, Evaluation of Batik Website.
Abstract: Indonesia’s advanced technology has developed rapidly to become sophisticated and modern. According to
the data from the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology (2019), the number of internet
users in Indonesia has reached 153 million, with a penetration rate of 56 percent throughout the country. The
number of smartphone users has increased to 140.4 million, or 26.17 percent. Based on the available data,
many users have smartphones equipped with internet access that can access all kinds of information, including
websites. Most websites do not pay enough attention to the features, especially on batik websites, which
creates discomfort for users. Therefore, the aim of this research is to evaluate the factors in batik websites
using the system usability scale (SUS) method with 6 scenarios from 3 batik websites as samples. In scenario
1 to evaluate product catalogues, scenario 5 to evaluate the search form, and scenario 6 to evaluate product
promo information, batik Semar is the most superior with an average of 70 points. Meanwhile, in scenario 2
to evaluate product descriptions, scenario 3 to evaluate product specifications, and scenario 4 to evaluate
product name and location, batik Danarhadi is the most superior with an average of 70 points.
1 INTRODUCTION
The advancement of technology has developed
rapidly, becoming increasingly sophisticated and
moving towards a sophisticated and modern
information age, keeping up with all technological
advancements (Andry, 2018). Information
technology on smartphones is equipped with the
internet, which can access all information, one of
which is a website.
Batik is one of the distinctive cultural features of
Indonesia that must be preserved. The
implementation of industry 4.0 is one of the reasons
for the design of the Batik Raja Rizki website
prototype, to make it easier for consumers to find
information about Batik Raja Rizki products online.
Previous research has only focused on fashion, so
there has been no discussion of batik products.
Most websites do not pay attention to features,
especially functionality. This creates an
uncomfortable feeling for users. According to the
research of (Putra & Samsinar, 2016) on Raubel
Men's Wear, the processing of unstructured data is not
well structured. In WE Clothing, product ordering is
only done by phone or offline, which is not flexible
in terms of time and place, leading to the possibility
of large errors in inputting data (Harries et al., 2015).
The Mimoze product does not have an attractive
visual, so the Mimoze product is not well known
(Rizki & Hadiati, 2019). (Kurniawan's, 2019)
research on e-commerce batik clothing production
does not have a satisfaction variable, so the value of
the customer satisfaction variable for e-commerce is
unknown. (Santoso et al., 2018) in designing the batik
marketplace user interface, product selection cannot
be done via smartphone, making buyers less flexible
in choosing products online through the smartphone
browser website. The problems from the various
websites above can be evaluated by improving the
website interface. Benefits for user to make it easier
operation batik website with user friendly interface
feature and be accessed via smartphone browser.
A website has an interface that connects users
with the technology used. According to (Yasin &
Yumarlin, 2016), information technology has various
interface designs that suit the user's functions and
needs. (Nurlifa & Kusumadewi, 2014) argued that
what connects users with websites or technology can
be called a user interface. This user interface has
various designs that suit its needs. Based on the above
research, this study aims to analyse the factors that
increase the usability of the batik website interface
using the SUS approach.
82
Wibisono, N.
Evaluation System Usability Scale (SUS) Method on Batik Website.
DOI: 10.5220/0012110900003680
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technology (ICATECH 2023), pages 82-88
ISBN: 978-989-758-663-7; ISSN: 2975-948X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

2 METHOD
2.1 Questionnaire System Usability
Scale (SUS)
A usability testing concept introduced by John
Brooke in 1986, is a reliable usability scale that can
be used to evaluate the usability of a system broadly.
The results of calculations using the questionnaire
method will be collected into a value, which can be
used as a consideration to determine whether a
website is feasible or not feasible (Pudjoatmojo et. al,
2016). The following is the SUS questionnaire:
Table 1: SUS Questionnaire Statement.
No Questionnaire Statement
1 I think I will want to use this website more often
2 I find that this website does not need to be this complicated
3 I think the website is easy to use
4 I think I will need assistance from a technical person to be able to use this website
5 I found the various functions on this website well integrated
6 I think there are too many discrepancies on this website
7 I imagine that most people will learn this website very quickly
8 I find this website very complicated to use
9 I feel very confident using this website
10 I need to learn many things before I can start using this website
Then for the assessment of the SUS questionnaire
(Brooke, 2013), namely:
1) The scale used strongly disagrees (strongly
disagrees) to strongly agrees (strongly agrees) is 1 to
5; 2) For odd numbered statements it is calculated
based on the value of the user's response minus the
value of 1; 3) Even numbered statements are
calculated based on the value of 5 minus the value of
the user's response; 4) Add up the response values that
have been calculated in point 2 and point 3 above,
then multiply the result by the value of 2.5. The
results of this calculation will convert the value range
to 0 -100.
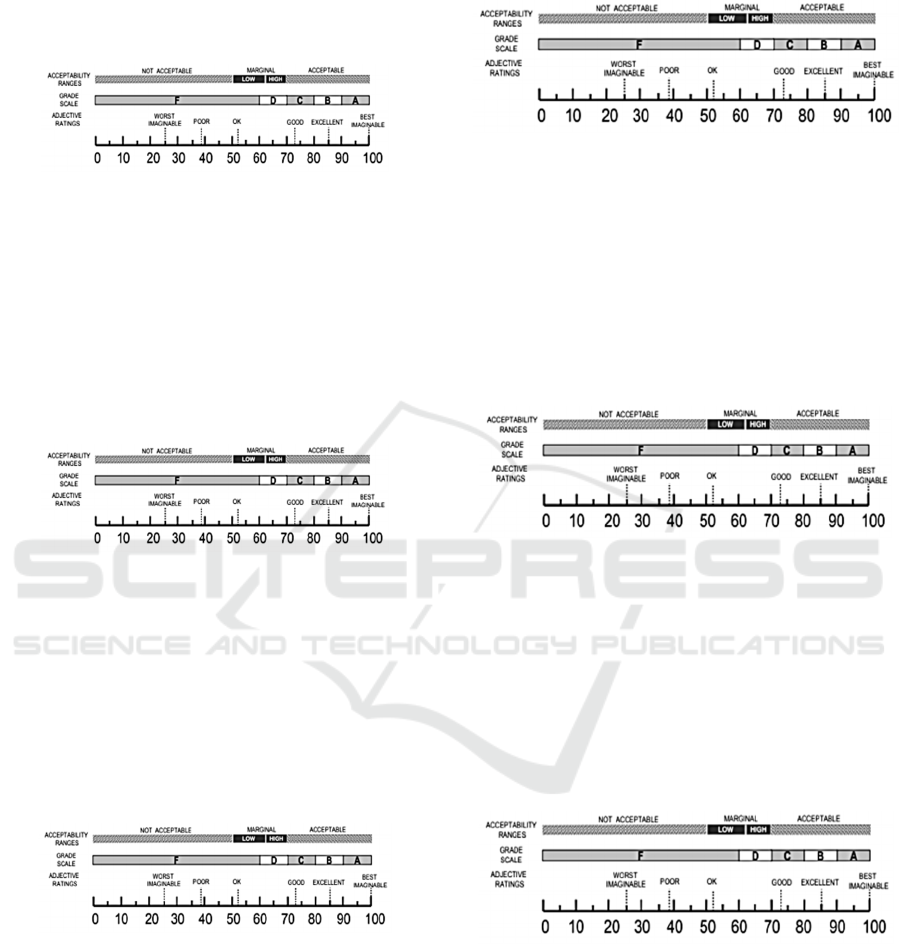
(Jeff Sauro, 2011) interprets the SUS score by
ranking the proportions and classes from A to F,
where A is the best class and F is the worst class.
Figure 1: Percentage Rating and Letter Grades.
Provisions for percentage ranking and letter
grades (Jeff Sauro, 2011), namely: 1) Grade A: score
≥ 80.3, percentage ≥ 90% ; 2) Grade B: 74 ≤ score <
80.3, 70% ≤ percentage < 90% ; 3) Grade C: 68 ≤
score < 74, 40% ≤ percentage < 90% ; 4) Value D: 51
≤ score < 68, 20% ≤ percentage < 40% ; 5) F value:
value < 51, percentage < 20%.
The SUS questionnaire can also be interpreted on
the nature of the rating to further clarify the level of
usability of a system, then translated into the level of
user acceptance of a system to determine whether the
system is acceptable or not by users (Bangor et. al,
2009).
Figure 2: Ranking of adjectives and ranges of acceptability.
The value of the SUS questionnaire obtained
represents the level of product usability. The final
score in this questionnaire is divided into 3, namely
Not Acceptable, with a value between 0-50.9, the
Marginal category, with a value between 51-70.9, and
Acceptable, with a value between 71-100
(Ardiansyah, 2016).
Evaluation System Usability Scale (SUS) Method on Batik Website
83
2.2 Test Scenario
Tests given to users make it easier for respondents to
assess a website (Sastramihardja et. al, 2008).
According to (Nielsen, 2014), several things must be
considered when designing scenario assignments,
namely: 1) The tester asks the user to do X without
explaining but gives a brief scenario of what the user
must do and gives a little explanation of why the user
does X; 2) Make real tasks, if you are going to test a
website, you must ensure that the user is a real
website user; 3) help the user to act, not for which the
user acts on personal will.
2.3 How to Choose SUS Factors and
Scenarios
According to ISO 9241-11, system usability scale
measurements can include effectiveness (user's
ability to complete a task), efficiency (level of
resources to complete a task), and satisfaction (user's
subjective reaction when running the system). To
determine the level of user satisfaction, use the
Usability Scale System which consists of 10 question
items regarding broad views regarding subjective
usability assessments (Brooke, 1996), as follows:
Table 2: SUS Questionnaire.
Questionnaire Statement
Strongly
Disagree
Disagree Doubtful Agree
Strongly
agree
-1 -2 -3 -4 -5
I think that I will want to use this website more
often
I found that this website does not need to be this
complicated
I think this website is easy to use
I thought that I would need assistance from a
technical person to be able to use this website
I found the various functions on this website well
integrated
I think there are too many discrepancies on this
website
I imagine that most people will find it easy to
learn this website very quickly
I found this website very complicated to use
I feel very confident to use this website
I need to learn many things before I can start
using this website
2.4 List of Questions per Scenario
In this study, a scenario was carried out that aimed to
find out the weaknesses of 3 similar websites (batik
danar hadi, batik keris, and batik semar so that it could
be used as a research analysis by determining an
object that needed to be tested using the SUS
questionnaire (Wilda Kusnawati, 2018 ), that is :
1) The user selects the desired batik product
catalog;
2) The user sees the description of the desired
batik product;
3) Users know the specifications of the desired
batik product;
4) Users search for information on the name
and location of the associated batik location;
5) Users search for certain products through the
search form;
6) Users search for the latest information on
products and promos from related batik.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Results of SUS Values per Scenario
Tested
3.1.1 Scenario 1
After conducting an assessment of 3 similar batiks,
namely Danar Hadi Batik, Keris Batik, and Semar
ICATECH 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technology
84
Batik with the SUS questionnaire, then scenario 1:
The user selects the desired batik product catalog to
get a score of 70 on Semar Batik, with a grade scale
of C, adjective risk (OK), and included in the
assessment provisions, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: SUS Score Scenario 1.
3.1.2 Scenario 2
After conducting an assessment of 3 similar batiks,
namely Danar Hadi Batik, Keris Batik, and Semar
Batik with the SUS questionnaire, then scenario 2:
The user sees the description of the desired batik
product, gets a score of 71 on Danar Hadi Batik, with
a grade scale C, adjective rating (OK ) and enter into
the terms of assessment, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: SUS Score Scenario 2.
3.1.3 Scenario 3
After assessing 3 similar batiks, namely Danar Hadi
Batik, Keris Batik, and Semar Batik with the SUS
questionnaire, then scenario 3: The user knows the
specifications of the desired batik product, gets a
score of 71.2 on Danar Hadi Batik, with a grade scale
C, adjective rating (OK) and enter the terms of the
assessment, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: SUS Score Scenario 3.
3.1.4 Scenario 4
After assessing 3 similar batiks, namely Danar Hadi
Batik, Keris Batik, and Semar Batik with the SUS
questionnaire, then scenario 4: The user searches for
information on the name and location of the related
batik location, getting a score of 70.2 on Danar Hadi
Batik, with a grade C scale, adjective rating (OK) and
enter the terms of the assessment, as shown in Figure
6.
Figure 6: SUS Score Scenario 4.
3.1.5 Scenario 5
After evaluating 3 similar batiks, namely Danar Hadi
Batik, Keris Batik, and Semar Batik with the SUS
questionnaire, then scenario 5: The user searches for
a particular product through the search form and gets
a value of 70.8 on Batik Semar, with a grade scale of
C, an adjective rating (OK) and enter the terms of
assessment, as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7: SUS Score Scenario 5.
3.1.6 Scenario 6
After assessing 3 similar batiks, namely Danar Hadi
Batik, Keris Batik, and Semar Batik with the SUS
questionnaire, then scenario 6: The user searches for
the latest information on products and promos from
related batik gets a score of 71.7 on Danar Hadi Batik,
with grade scale C, adjective rating (OK) and enter
the terms of the assessment, as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8: SUS Score Scenario 6.
Evaluation System Usability Scale (SUS) Method on Batik Website
85
3.2 Problems / Insights
Table 3: Defining the problem.
Proble
m
Insi
g
hts
Candidate user difficulty when doing search
type batik products.
Add feature type in category batik search, so could make
it easy for the respondent moment look for type desired batik
p
roduct
Candidate users lack information about the
size of batik products.
Add an explanation size chart on every batik product for
sale on the website, so respondents do wrong choose the size
desired batik product.
The candidate user has difficulty for contact
customer service.
Add feature live chat online real-time, so respondents get
clear information
_
from
p
art
y
customer service on the website.
Candidate user confusion moment choose
b
atik products.
Repair feature election batik products on the website, so
existing features _ could be integrated with good and clear.
Candidate users look for desired batik
products but are not found on related websites.
Do maintenance routine to the website, so available batik
products will always be up to date every week following the
develo
p
ment offered batik
p
roducts.
Prospective users find it difficult to find batik
products based on price ranges.
Added category-based feature price, thus anticipating
misunderstandings between prospective buyers and sellers
re
g
ardin
g
the
p
rice of batik
p
roducts.
Prospective users feel that the selection of
expedition options for sending batik products is
incomplete.
Adding expedition options for sending batik products
according to the destination of prospective buyers, so that
prospective users can be flexible in selecting expeditions to all
destination cities for batik
p
roduct bu
y
ers.
Prospective users do not know the appearance
of batik products that are in great demand by
buyers.
Adding features to the home section in the form of best-
seller batik products, promos, batik product categories, and tag
lines, so that potential users can find out the batik products
offered by the batik website.
Prospective users lack information on the
category of these batik products.
Added features for the types of batik product categories in
the form of men, women, and children, so that potential users
can easily understand when making selections in the category
of types of batik products.
Prospective users are confused about finding
offline stores.
Added a description of the google map to the offline batik
shop address description feature, making it easier for potential
users when they want to come offline.
Prospective users need an attractive user
interface display.
Beautify the appearance of the website prototype in the
form of website colors, dominantly white and blue according to
the image of the batik shop, so that prospective prototype users
are interested in buying the desired batik products.
Prospective users need a visual form of the
batik product in detail.
Adding photos of batik products in the form of slide shows,
batik products according to availability with the image of the
batik shop, so that it becomes an attraction for potential users to
b
u
y
the desired batik
p
roduct.
Prospective users do not yet know which batik
products are in demand by buyers.
Adding the best seller feature in the form of self-produced
batik products, namely: robe, hem/shirt, and blouse (lawasan,
slogan), making it easier for prospective users to make a
detailed selection of the batik products to be purchased.
Characteristics of the seller need to
differentiate from other batik shops.
Adding a confusing tagline, looking for a batik outfit? we
p
rovide various options for you,
Prospective users are confused when looking
for the desired batik product.
Add search features to the navbar, so that you can
recommend batik products that you are looking for according to
the product you want.
How do users avoid getting confused when
looking for the desired batik product?
Added search features to the nav bar.
How do users avoid getting confused when
lookin
g
for the desired batik
p
roduct? Added search features to the nav bar.
ICATECH 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technology
86

3.3 How / Might
At this stage to broaden the point of view of solving
the problems in table 3. The researcher used the How
Might We (HMW) method. The way this method
works is to change all existing statements into a
question. Statements on this problem are answered
regarding every possible way to solve it (Might).
Information and steps to complete the solution using
the How Might We method. The following is the
process from HMW, namely:
Table 4: How Might We.
How? Might?
How method resolve the difficulty in doing search
type batik products by a user?
Make a feature new in the category batik search ie
feature type of batik on the website.
How did users know full-size details to offer batik
p
roducts on the website?
Explain the size chart of batik products in the column
description product on the website.
How do users contact customer service regularly
responsive?
Make a feature new that is feature live chat online in
real-time.
how the user could with easy choose desired batik
p
roduct?
Repair system on feature election batik products with
eas
y
inte
g
ration
_
user.
How user could look for desired batik products in a
manner complete on the website?
schedule time maintenance and product updates in a
manner routine to the website.
How can users search for batik products based on
price ranges?
Added category-based feature price
How can users choose the desired batik shipping
expedition option?
Adding expeditionary options for shipping batik
products according to the destination of prospective buyers.
How do users find out the appearance of batik
products that are in great demand by buyers?
Adding features to the home section in the form of
best-seller batik products, promos, batik product categories,
and ta
g
lines
How can users not lack information about the
category of batik products?
Adding features for the types of batik product
categories in the form of men, women, and children.
How to make it easier for users to easily find offline
store locations?
Added a description of the google map to the offline
batik shop address description feature, making it easier for
potential users when they want to come offline.
How do you make a user interface display that is
attractive to website users?
Website prototype in the form of website colors,
dominantly white and blue according to the image of the
b
atik shop.
How can users see the visual appearance of batik
products in detail?
Add photos of batik products in the form of slide
shows, batik products according to availability with the
image of the batik shop.
How do users find out which batik products are of
interest to buyers?
Adding the best seller feature in the form of self-
produced batik products, namely: robe, hem/shirt, blouse
(
lawasan, so
g
an
)
.
What are the characteristics of the seller's shop to
differentiate it from other batik shops?
Adding a confusing tagline, looking for a batik outfit?
we provide various options for you.
How to make it easier for users to find the desired
batik product?
Adding search features to the navbar,
How to see batik products based on the price range? Added category-based feature price.
How do users avoid getting confused when looking
for the desired batik product? Added search features to the nav bar.
3.4 Brainstorming
At the stage of gathering ideas through brainstorming,
the aim is to collect ideas so that they can solve all
existing problems. This process is carried out with the
owner and potential users of similar websites. Each –
Each write down all the ideas that focus on solving
the core problem. The results of the brainstorming
process will be processed based on aspects of user
interest and the prototype of the Batik Raja Rizki
Evaluation System Usability Scale (SUS) Method on Batik Website
87

website. The results obtained are: 1) Website
prototype maintenance; 2) Features of the location of
the batik shop are included in the google map; 3)
Available stock information for batik products; 4)
Added size chart to the product description; 5) Added
features for the category of batik products; 6) Live
chat feature in real-time.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the research conducted on three similar
websites (Batik Danar Hadi, Batik Keris, and Batik
Semar) using SUS and HMW (Brainstorming)
methods, it can be concluded that:
a) The catalog of batik displayed on the website still
does not meet the user's needs to view the required
batik visual; b) The description, specifications and
size of batik products on the website are still
incomplete; c) The number of batik stock on the
website is not clearly displayed, and often not in
accordance with the actual stock; d) The websites
studied do not have a unique characteristic that makes
it easier for users to remember the batik brand; e)
Sales/Customer services are difficult to reach via the
website; f) It is difficult to find the location of the
offline batik outlet if checked via the website.
Based on the issues and the objective of this research
to evaluate the factors of the batik website problems
and provide improvement suggestions for the future,
the steps are:
a)The batik catalog is displayed with an attractive,
clear and user-friendly visual model; b) The
description, specifications, and size of the batik
products are written in detail, concise and
informative; c) Batik stock is updated regularly with
a fixed schedule and the schedule for regular stock
update is posted on the website; d) A tagline is created
according to the batik brand, becoming the
characteristic of the brand and placed on the
homepage in a bold font for easy user recognition. e)
Sales/customer service can be chatted in real-time
through the website or a third-party application such
as WhatsApp. f) The location of the batik outlet must
be registered on Google Maps and posted on the
website.
REFERENCES
Andreas Schumacher, SelimErol, & Wilfried Sihn. (2016).
A Maturity Model for Assessing Industry 4.0 Readiness
and Maturity of Manufacturing Enterprises. Procedia
CIRP , 161-166.
Alimuddin Yasin, Yumarlin MZ. (2016). UJB Web
Evaluation Using Theo Mandel's Golden Rules Of User
Interface Design. Journal of Information Technology
and Multimedia. STMIK Amikom Yogyakarta. Vol 4
No 1
Aditia Julianto.(2020). Website-Based Application
Interface Design Redesign Using the User-Centered
Design Method (Case Study: Petshopgrosir). Doctoral
Dissertations. Indonesian Computer University.
Deif, A. (2011). A system model for green manufacturing.
Journal of Cleaner Production, 27–36.
Deny Andry, Johanes Fernandes. (2018). Measurement of
E-Learning Success by Adopting the Delone & Mclean
Model. Journal of Business Information Systems. Her
Majesty's University. Vol 8 Nos 68-75.
Foster. (2014). Software Engineering. A Methodical
Approach. Apress, New York, USA.
Fakhruddin, Dimas et al. (2018). "Development of
Information Design and Learning Javanese Script
Through Website Media." ANDHARUPA: Journal of
Visual & Multimedia Communication Design, vol. 5,
no. 01, pp. 1-23.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
Switzerland. SO FDIS 9241-210. 2009. Ergonomics of
human-system interaction – Part 210: Human-Centered
design for interactive systems (formerly known as
13407)
Supraptini. (2002). The Effect of Industrial Waste on the
Environment in Indonesia. Health Research and
Development Media Volume XII Number 2.
Sutalaksana, IZ (2006). Work Procedure Technique.
Laboratory of Working Procedures & Ergonomics of
Industrial Engineering ITB Bandung.
Kusnawati, W., Rokhmawati, RI, & Rachmadi, A. (2018).
User Experience Analysis on E-Commerce Websites
(Studies on klikindomaret.com and alfacart.com).
Journal of Development of Information Technology and
Computer Science e-ISSN , 2548 , 964X.
Lallemand, C., Gronier, G., & Koenig, V. (2015). User
experience: A concept without consensus? Exploring
practitioners' perspectives through an international
survey. Computers in Human Behavior. 43:35-48.
ICATECH 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technology
88
