
Virtual Private Networks in the Quantum Era: A Security in Depth
Approach
David Schatz
1
, Friedrich Altheide
1
, Hedwig Koerfgen
2
, Michael Rossberg
1
and Guenter Schaefer
1
1
Technische Universit
¨
at Ilmenau, Germany
2
Universit
¨
at der Bundeswehr M
¨
unchen, Germany
Keywords:
Virtual Private Networks, Internet Key Exchange, Quantum Key Distribution, Multipath Key Reinforcement.
Abstract:
Conventional asymmetric cryptography is threatened by the ongoing development of quantum computers. A
mandatory countermeasure in the context of virtual private networks (VPNs) is to use post-quantum cryptog-
raphy (PQC) as a drop-in replacement for the authenticated key exchange in the Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
protocol. However, the results of the ongoing cryptanalysis of PQC cannot be predicted. Consequently, this ar-
ticle discusses orthogonal methods for quantum-resistant key exchanges, like quantum key distribution (QKD)
and multipath key reinforcement (MKR). As each method has limitations when used on its own, we conclude
that it is best to maximize security by combining all available sources of symmetric key material to protect
traffic inside a VPN. As one possible realization, we propose a lightweight proxy concept that uses available
symmetric keys, like QKD and MKR keys, to implement a transparent cryptographic tunnel for all IKE pack-
ets, and consequently for PQC key exchanges. In contrast to combining PQC and symmetric key material
within the IKE protocol, our approach provides security in depth: If secure symmetric keys are available,
attacks on IKE and hence on PQC algorithms are infeasible. But even otherwise, the security properties of
IKE and thus PQC are not weakened, so the overall security of the VPN is guaranteed to increase.
1 INTRODUCTION
Asymmetric cryptography is a key enabler of mod-
ern virtual private networks (VPNs). However,
current algorithms are threatened by attackers with
access to sufficiently powerful quantum comput-
ers (called quantum attackers throughout this arti-
cle) (Shor, 1997; Proos and Zalka, 2003). Following
the recommendation of security agencies around the
world (Ehlen et al., 2022), one straightforward and
mandatory approach to resist quantum attackers is the
usage of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) as a drop-
in replacement for classical algorithms like RSA or
ECDSA within the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) pro-
tocol, or hybrid variants (Smyslov, 2022b).
Unfortunately, the confidence in PQC and its im-
plementations currently is not at the same level as it
was for classical algorithms in the pre-quantum era.
This is caused by the rather young field of crypt-
analysis of efficient PQC algorithms and flaws re-
cently discovered in former finalists of the NIST stan-
dardization process (Beullens, 2022; Castryck and
Decru, 2022). Consequently, one contribution of
this article discusses how orthogonal methods for a
quantum-resistant key exchange may be used to ad-
ditionally secure VPNs, e.g., quantum key distribu-
tion (QKD) (Bennett and Brassard, 2014) and mul-
tipath key reinforcement (MKR) (Rass and K
¨
onig,
2011; Lan et al., 2009; Deng and Han, 2008).
One approach to incorporate other key sources in
the context of VPNs is to extend the IKEv2 proto-
col (Fluhrer et al., 2020). However, we argue that
extending the already complex protocol and its im-
plementation is not the best possible approach (at
least for site-to-site VPNs). Instead, we propose a
lightweight proxy that can transparently tunnel all
IKE packets and consequently PQC key exchanges,
cryptographically secured by additionally available
symmetric key material. The main advantage of this
approach is the implementation of security in depth.
Furthermore, the proxy is easy to integrate into a va-
riety of VPN infrastructures, e.g., it can also protect a
hypothetical successor of IKE. The remaining article
is structured as follows: In Sec. 2, we recapitulate the
basic principles of VPNs. Our objectives and threat
model are defined in Sec. 3 and related work is dis-
cussed in Sec. 4. We present the design of the IKE
proxy in Sec. 5 and qualitatively evaluate it in Sec. 6.
486
Schatz, D., Altheide, F., Koerfgen, H., Rossberg, M. and Schaefer, G.
Virtual Private Networks in the Quantum Era: A Security in Depth Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0012121800003555
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2023), pages 486-494
ISBN: 978-989-758-666-8; ISSN: 2184-7711
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
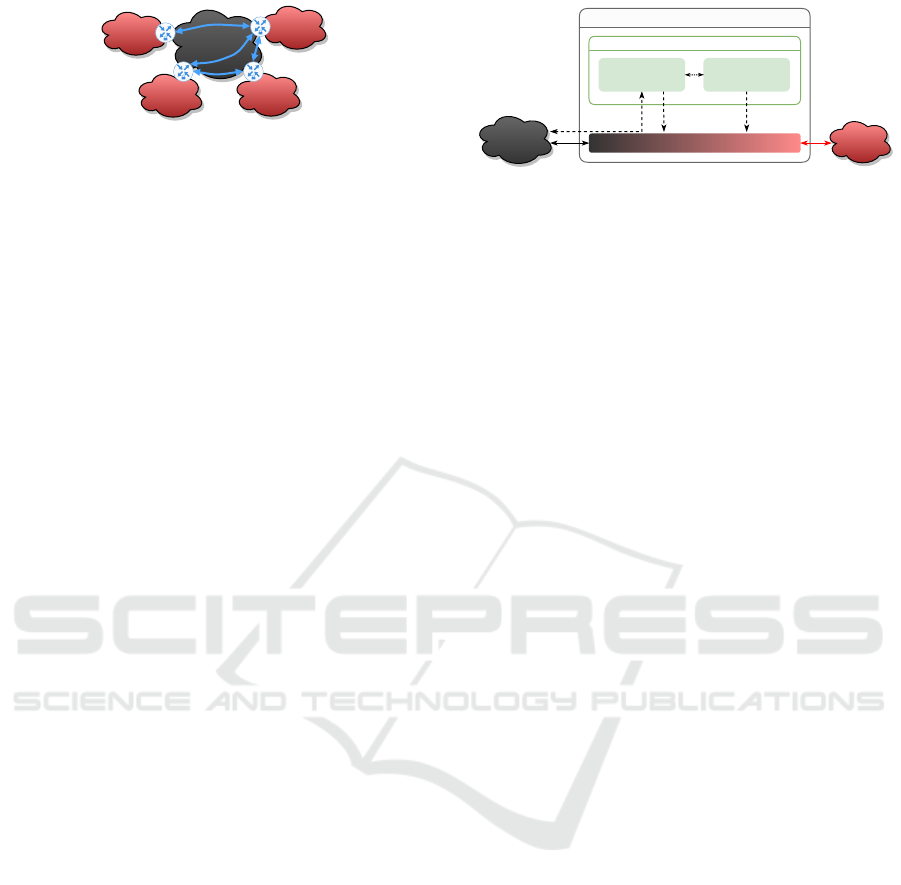
Private
network
Private
network
Public
network
Private
network
Private
network
Figure 1: Example for a site-to-site VPN deployment: VPN
gateways connect multiple (trusted) private networks via an
untrusted public network by establishing secure tunnels.
2 BACKGROUND: VIRTUAL
PRIVATE NETWORKS
In this article, we focus on site-to-site VPN deploy-
ments as depicted in Fig. 1: At each site, e.g., a pub-
lic authority or company office, there is one VPN
gateway that realizes secure tunneling of traffic from
clients inside the local private network to remote sites.
Real deployments are usually more complex from a
topological perspective, e.g., there may be nested or
load-balancing VPN gateways. We assume that the
VPN operates at network layer and uses the Inter-
net Protocol Security (IPsec) protocol family to im-
plement secure tunnels. That is, IKEv2 (Kaufman
et al., 2014) is used for entity authentication and key
exchange. Subsequently, a derived traffic encryption
key (TEK) is used by ESP (Encapsulating Security
Payload) (Kent, Stephen, 2005) to protect confiden-
tiality and data integrity inside tunnels, also denoted
as security associations (SAs).
Established SAs may be interpreted as an over-
lay topology. To implement highly scalable and ro-
bust VPNs, the topology is usually dynamically de-
termined by a topology control algorithm (Rossberg
and Schaefer, 2011). Furthermore, routing within the
overlay is required when some gateways cannot reach
each other directly via the public network, e.g., due
to external firewalls or nested scenarios. Packets must
still be protected end-to-end in this case, which may
be realized by implementing nested SAs (hop-by-hop
and end-to-end protection). In summary, this results
in a VPN gateway architecture as depicted in Fig. 2.
3 OBJECTIVES AND THREAT
MODEL
This section defines the objectives for a quantum-
resistant VPN and presents our threat model.
3.1 Objectives
A quantum-resistant VPN has a superset of objectives
of a conventional VPN, like detailed in (Rossberg and
VPN gateway
Control plane
Topology control
Data plane
RoutingIKEv2
Public
network
Private
network
IKE daemon
TEK
Figure 2: Basic architecture of a VPN gateway: A topol-
ogy control algorithm decides which SAs should be estab-
lished and manages overlay routing. The IKE daemon is
responsible for establishing SAs using an authenticated key
exchange. The data plane uses the derived TEK to protect
client packets using ESP and forwards them based on the
routing decision. Dashed lines represent control flow, solid
lines represent physical interfaces.
Schaefer, 2011). On top, quantum-resistance is re-
quired for the following security services, i.e., they
have to be implemented to defeat quantum attackers:
1. Entity authentication: Gateways must be able to
securely identify each other and private IP address
ranges must be securely linked to gateways.
2. Confidentiality: The confidentiality of client traf-
fic must be guaranteed. If it is routed via interme-
diate gateways, cryptographic protection must be
realized end-to-end, i.e., between the first and the
last gateway. Furthermore, forward secrecy is re-
quired. That is, the compromise of long-term keys
must not affect the confidentiality of past SAs.
Confidentiality of metadata may also be required,
e.g., private IP addresses.
3. Data integrity and replay protection: Non-
authorized modification and replay of data pack-
ets between sites must be detected.
Furthermore, quantum-resistance should be intro-
duced with cryptographic agility in mind. That
is, cryptographic mechanisms should be easily ex-
changeable, e.g., to react to new developments in
cryptanalysis (Ehlen et al., 2022). Last, implement-
ing quantum-resistance should not degrade important
non-functional properties of modern VPNs: Scala-
bility to thousands of VPN gateways, robustness to
denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, graceful degradation
in case of individual compromised devices, and im-
plementation security (Rossberg and Schaefer, 2011).
3.2 Threat Model
For external attacks, we assume an exceptionally
strong Dolev-Yao attacker (Dolev and Yao, 1983)
with access to a sufficiently large quantum computer.
That is, he can break classical asymmetric cryptogra-
phy on links that he controls. Moreover, he can store
traffic now and try to decrypt it later, e.g., after flaws
Virtual Private Networks in the Quantum Era: A Security in Depth Approach
487

in a PQC algorithm are found. We further assume that
it is possible to compromise a limited number of VPN
gateways or other security critical entities like QKD
devices. However, we assume the attacker’s compu-
tational power (both classical and quantum) and his
resources for eavesdropping links to be limited. Con-
sequently, he cannot break symmetric cryptographic
primitives if the algorithm is not flawed and key sizes
are large enough (≥ 256 bit) (Bennett et al., 1997),
and he cannot eavesdrop all links at all times.
4 RELATED WORK
Implementing the security services entity authentica-
tion, confidentiality, and data integrity in VPNs with
IPsec is a two step process:
1. Authenticated key exchange: To establish a new
SA between two VPN gateways, they first have to
authenticate each other. During this process, they
also derive a new symmetric TEK.
2. Authenticated encryption: Using the TEK, gate-
ways encrypt all client packets and add some form
of authentication tag to protect their integrity.
Because symmetric cryptography with keys ≥ 256 bit
remains secure in the quantum era, only the authenti-
cated key exchange has to be adapted to be quantum-
resistant. This may be realized by using PQC or
through symmetric cryptography as discussed next.
4.1 Post-Quantum Cryptography
Authenticated key exchanges in VPNs widely rely
on asymmetric cryptography (e.g., digital signatures
based on RSA or ECDSA, and the Diffie-Hellman
key exchange). While “classical” methods are not
quantum-resistant, several PQC algorithms have been
proposed as drop-in replacements. At the date of writ-
ing, three signature schemes and one key encapsula-
tion mechanism (KEM) are in the process of being
standardized by the NIST (NIST, 2022).
While retaining the same flexibility as existing
solutions, deploying PQC also has two drawbacks:
PQC algorithms are not as efficient as classical elliptic
curve cryptography, when considering computational
overhead, size of public keys, or size of signatures.
Furthermore, cryptanalysis, especially of the efficient
candidates, is not as mature as for classical cryptog-
raphy. This was recently highlighted by the discovery
of flaws in two former finalists of the NIST standard-
ization process (Beullens, 2022; Castryck and Decru,
2022). Consequently, hybrid modes combining clas-
sical and PQC algorithms are recommended for an au-
thenticated key exchange (Ehlen et al., 2022).
4.2 Symmetric Key Management
Another way to achieve quantum-resistance is to in-
clude authenticated symmetric key material in the SA
establishment.
Pre-Shared Keys. One option is to deploy pairwise
pre-shared keys (PSKs) between all gateways out of
band, e.g., by sending a courier in person. However,
this is cumbersome, especially when deploying new
gateways and when updating PSKs for the sake of
forward secrecy. A far less cumbersome approach is
to equip all gateways with a static group key during
deployment. But if a gateway is ever compromised,
the static group key provides no security. Another
option for convenient management of pairwise PSKs
are protocols relying on a trusted third party (TTP),
e.g., Kerberos (Neuman and Ts’o, 1994). However,
the TTP is a single point of failure for the security
and availability of keys. Probabilistic key distribu-
tion (Eschenauer and Gligor, 2002) is another simple
approach for distributing pairwise PSKs. However, it
provides no end-to-end security, as each key may be
known to a random subset of other gateways.
Quantum Key Distribution. QKD uses qubits to
exchange a key between two parties, often in the form
of single photons. The confidentiality of the key re-
lies on the detectability of eavesdropping due to the
laws of quantum mechanics, e.g., the no-cloning the-
orem (Wootters and Zurek, 1982). By design, QKD
protocols like BB84 (Bennett and Brassard, 2014) re-
quire a quantum channel for qubit transmission and a
classical channel, e.g., for error correction. The clas-
sical channel must be authenticated a priori in a way
that prevents man-in-the-middle attacks by quantum
attackers.
When building networks, QKD has two draw-
backs: Quantum channels are restricted to links with
a direct optical connection and have a limited reach
because quantum signal repeating is not possible
with current technologies, i.e., without quantum re-
peaters (Cao et al., 2022). On top, operating a QKD
link is expensive. Consequently, QKD may only be
expected in very specific scenarios. Current standard-
ization efforts (ETSI, 2022; ITU-T, 2019) and com-
mercial products tackle the limited reach by assum-
ing QKD nodes to also act as key relays between ad-
jacent links (“trusted nodes”). This approach does
also not provide end-to-end security because individ-
ual “trusted nodes” could be compromised. Another
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
488

drawback is that deploying a QKD network would
increase the overall complexity by duplicating many
features already implemented within the VPN over-
lay, e.g., authentication and internal routing. Never-
theless, if a direct QKD link between gateways is fea-
sible, it could provide an additional level of security
for the corresponding SA. In particular, if the initial
authentication is secure, QKD may be used to regu-
larly exchange fresh PSKs to provide forward secrecy.
Multipath Key Reinforcement. The idea of MKR
is to split a key into multiple shares and send each
share over a different path through a network to a
common receiver. If attackers cannot eavesdrop on
all paths, the sender and receiver will agree on a se-
cret key. Furthermore, multiple MKR keys may be
combined over time to significantly increase the ef-
fort for attackers to compromise all paths at all times.
Previously, MKR has been proposed in the context
of wireless ad-hoc networks (Lan et al., 2009), wire-
less sensor networks (Deng and Han, 2008), and QKD
networks (Rass and K
¨
onig, 2011). Similarly, MKR
may also be implemented within a VPN overlay.
A limitation of MKR is that it only acts as a “dis-
seminator” of security. That is, if a secure (overlay)
path exists between two VPN gateways, and the path
is found and used by MKR, the hop-by-hop secu-
rity is “disseminated” to the end-to-end SA between
the two gateways. If no such path exists or is never
used, MKR has no benefit. Furthermore, the proba-
bility that the final key is secure, is only maximized
when paths are as disjoint as possible. In scenarios
where VPN gateways only have a single physical ac-
cess link to the public network and it is not secured
by other means like QKD, attackers might be able to
attack MKR with relatively little effort.
Using PSKs in IPsec. For usage in IKE, all “exter-
nally” exchanged keys may be considered as PSKs,
including the ones derived by QKD and MKR. While
the original IKEv2 only supported PSKs for entity au-
thentication, there is an extension to also incorporate
a PSK into the TEK of a SA (Fluhrer et al., 2020).
An alternative proposal also protects the IKE packets
using the PSK as far as possible, avoiding unneces-
sary metadata leakage (Smyslov, 2022a). However,
neither approach protects from potential flaws in the
complex implementation of IKE daemons, which po-
tentially lead to a full compromise of the gateway.
In the context of QKD, another proposal is to com-
pletely replace IKE, only using QKD keys (Mark-
steiner and Maurhart, 2015). However, this is cur-
rently explicitly ruled out by various national security
agencies (Ehlen et al., 2022).
Last, while a static group key does not provide
end-to-end security, it may simply be used to apply
an additional layer of authenticated encryption to all
packets without relying on extensions to IKE.
4.3 Lessons Learned
PQC is a straightforward and mandatory approach
to secure VPNs for the quantum era. As a drop-in
replacement or in addition to classical asymmetric
cryptography, PQC is best implemented in the well-
established IKE protocol. Still, it is desirable to ad-
ditionally protect IKE with pairwise PSKs whenever
available. Unfortunately, our discussion has shown
that each method to exchange pairwise PSKs has its
limitations. Consequently, a flexible mechanism to
combine all previously and currently available sym-
metric keys from different sources is desirable. This
requires a synchronization mechanism between gate-
ways to agree on one active master key.
While IKE could be extended accordingly, this
would further increase its complexity and conse-
quently the attack surface of the gateway via public
channels. Instead, we suggest to handle additional
symmetric key material in a separate, lightweight
component. This component can use the derived mas-
ter key to implement a transparent tunnel for all IKE
packets, providing security in depth: If the master key
is secure and the implementation of the component is
not flawed, attackers cannot access the IKE packets in
plaintext. Consequently, any attacks on IKE (includ-
ing PQC algorithms) or its implementation are infea-
sible. Breaking the additional key material allows for
a direct attack on IKE, which has however not been
touched and therefore not been weakened in any way.
5 IKE PROXY DESIGN
This section presents a lightweight proxy design that
transparently tunnels and cryptographically protects
IKE packets as discussed above. We refer to this com-
ponent as the IKE proxy for the remaining article and
present an overview of its required functions and the
resulting architecture in a VPN gateway in the follow-
ing. Subsequently, further details are presented.
5.1 Overview
Our envisioned architecture of a VPN gateway with
an IKE proxy is shown in Fig. 3. In summary, the
proxy requires the following functions:
1. Packet Interception: To mandatorily protect the
packets sent by the IKE daemon, the proxy must
Virtual Private Networks in the Quantum Era: A Security in Depth Approach
489
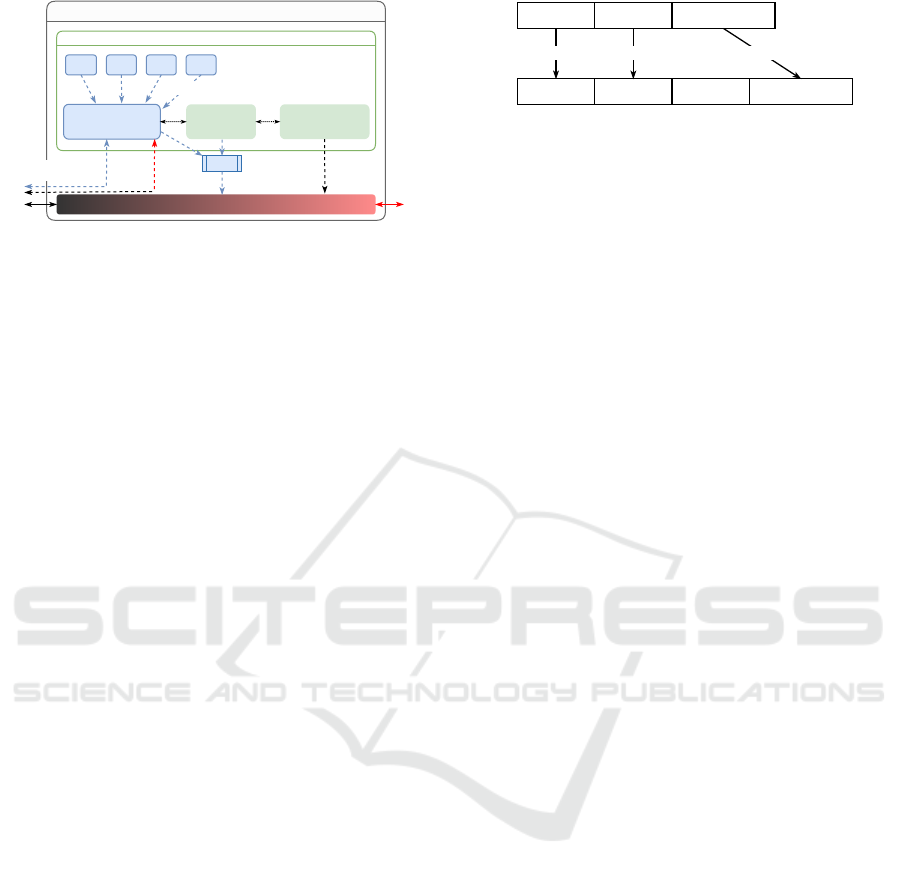
VPN gateway
Control plane
Topology controlIKE proxy IKE daemon
QKD PSK MKR ...
Symmetric key material
Data plane
Routing
Key sync
KDF
TEK
IKEv2 over quantum-
resistant tunnel
Figure 3: Envisioned architecture of a VPN gateway with
an IKE proxy, which interfaces to various sources of sym-
metric key material. Using a key synchronization proto-
col, pairs of proxies agree on sets of keys to be combined
to a master key. The master key is used to implement a
quantum-resistant tunnel for IKE. Moreover, the resulting
TEK is reinforced by the master key. Dashed lines represent
control flow, solid lines represent physical interfaces.
intercept all IKE packets. Depending on the spe-
cific implementation of the control plane, dif-
ferent options are conceivable. For example,
on Linux-based systems, firewall rules may steer
packets to the IKE proxy, implemented as a user-
space process (Welte, 2023).
2. Proxy Header: Implementing a cryptographic
tunnel requires the proxy to introduce a header as
further detailed in Sec. 5.2.
3. Dynamic address mapping: Protecting IKE using
pairwise keys requires a mapping of key mate-
rial to the corresponding remote proxy. In gen-
eral, the IKE proxy only has access to the IP and
UDP headers of IKE packets, i.e., it may only in-
fer the transport address (IP address and port) of
the remote gateway. Consequently, a mapping of
transport addresses to static peer IDs of remote
proxies is required. Because the IP address and
port may change over time, e.g, due to network
address translation (NAT), this mapping must be
dynamic. To implement this mapping within the
proxy, we suggest a minimal greeting protocol as
further detailed in Sec. 5.3.
4. Key Synchronization: A key synchronization pro-
tocol is required to agree on a set of symmetric
keys that shall be combined to derive the current
master key between two proxies. To make use of
new keys as soon as possible, the key synchro-
nization protocol (as further detailed in Sec. 5.4)
runs independently of the IKE traffic. For exam-
ple, the protocol may be tunneled via the VPN
similar to client traffic, i.e., over an established
SA. This has the advantage that the IKE proxy
does not have to re-implement complex functions
like NAT traversal or routing. A drawback is that
the IKE exchange to establish the very first SA
IP header UDP header IKEv2 payload
IP header UDP header IKEv2 payloadProxy header
Update length/checksum Authenticated encryption
Figure 4: Tunneling IKE packets is implemented similar
to the transport mode in IPsec. The original IP and UDP
headers are updated (lengths and checksums) and a proxy
header is introduced before the IKE payload. The latter is
protected by the proxy using authenticated encryption.
between two gateways can only be protected by
a key that was synchronized out of band, e.g., a
static group key.
5. Secure and Persistent Key Storage: VPN gate-
ways may be rebooted at any time, e.g., due to
power loss. Consequently, a persistent key stor-
age for keys that are in progress of being syn-
chronized and the derived master key is required.
Otherwise, the first IKE exchange after a reboot
can only be protected by currently available key
sources, which may not be as secure as the pre-
vious master key. We present a secure design in
Sec. 5.5.
6. TEK Reinforcement: While the cryptographic tun-
nel implicitly protects the TEK generated by IKE,
the TEK should be further reinforced by combin-
ing it with the master key of the proxy (or a deriva-
tion thereof). This protects from potential funda-
mental flaws in PQC algorithms or an underlying
random number generator, e.g., when predictable
keys are generated. This combination may either
be implemented within the IKE daemon like in
RFC 8784 (Fluhrer et al., 2020), or externally us-
ing a suitable key derivation function (KDF).
5.2 Proxy Header
For tunneling IKE packets, we suggest a design simi-
lar to the transport mode in IPsec because the crypto-
graphic endpoints (IKE proxies) and the communica-
tion endpoints (IKE daemons) are on the same host:
The proxy introduces an additional header between
the UDP header and the payload (see Fig. 4). This has
the advantage that the proxy does not break features
of the IKE daemon, like NAT traversal. The IKE pay-
load is protected by the proxy using a symmetric au-
thenticated encryption scheme. The protocol header
itself requires at least the following fields:
1. An algorithm ID of the applied authenticated en-
cryption scheme.
2. A nonce for the authenticated encryption scheme.
3. The authentication tag generated by the authenti-
cated encryption scheme.
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
490
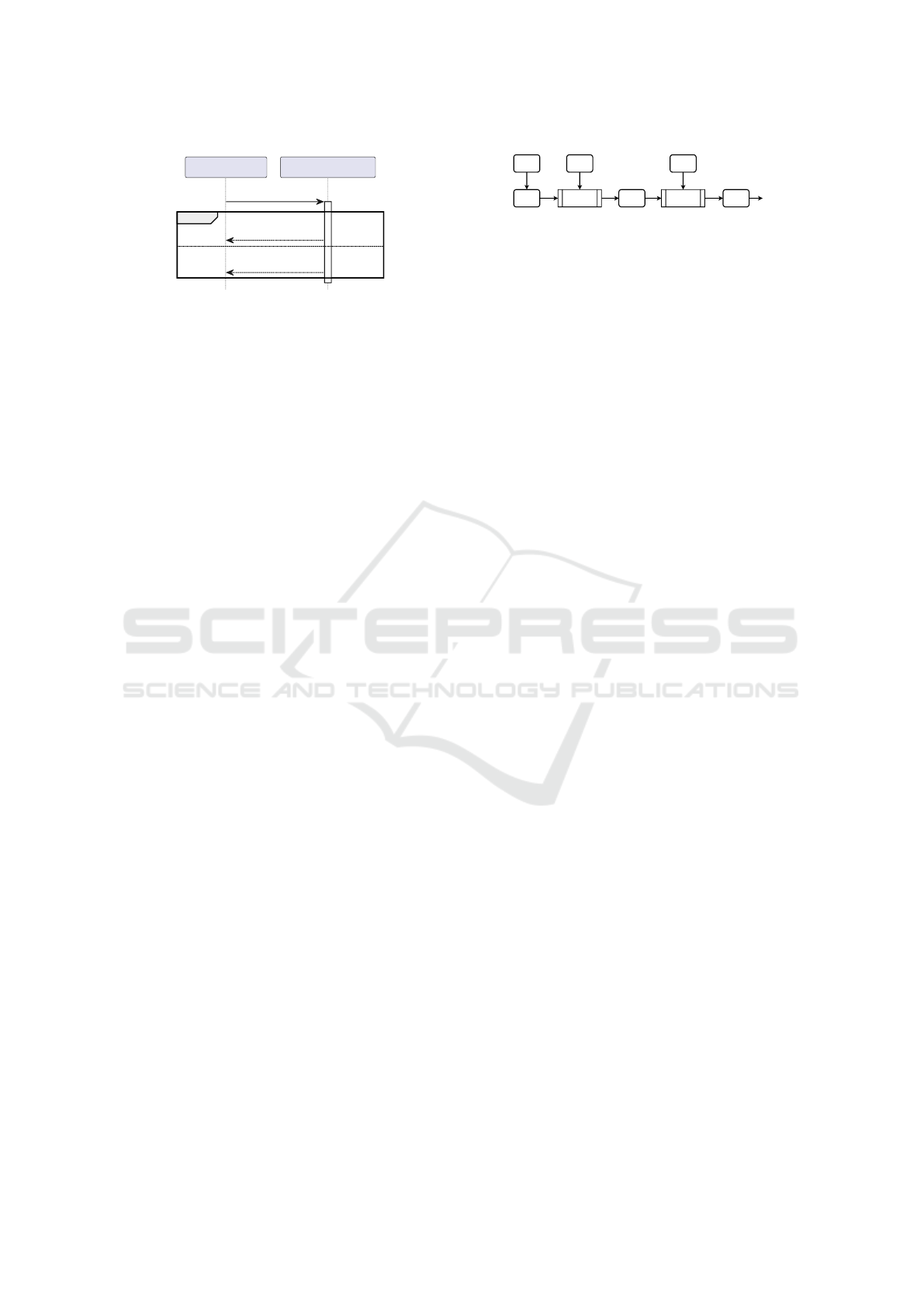
Proxy u (Initiator) Proxy v (Responder)
{Initiator peer ID}
g
alt
[No master key available]
{Responder peer ID}
g
[Master key k available]
{Ack}
k
Figure 5: Greeting protocol to query the peer ID corre-
sponding to an unknown IP address and port: Authenticated
encryption with key x is denoted by curly braces {. . .}
x
.
To hide peer IDs from external attackers, packets should at
least be encrypted using a static group key g. If the respon-
der already shares a pairwise master key k with the initiator,
he alternatively uses k to encrypt a simple acknowledgment.
Then, the initiator can map the temporary key ID included
in the proxy header to the responder peer ID.
4. A temporary key ID of the master key in use.
5. A message type, e.g., whether the packet belongs
to the greeting or key synchronization protocol.
As the message type is only relevant after success-
ful decryption, it is the only header field that is
transmitted encrypted.
Including the key ID in the header simplifies the
greeting and key synchronization protocol. However,
using a static master key ID more than once would
allow attackers to track a gateway after (deliberately)
changing its IP address. Consequently, we suggest
transmitting a temporary key ID and changing it for
every packet instead. One option to deterministically
generate n such temporary key IDs for a synchronized
master key at both proxies is to encrypt the num-
bers 1 ≤ i ≤ n using a derivation of the key.
5.3 Greeting Protocol
Tunneling a packet with an unknown destination re-
quires the IKE proxy to first learn the corresponding
remote peer ID to use the correct master key for en-
cryption. A protocol to do so should not leak any
metadata. Especially, peer IDs should not be leaked to
external attackers. Otherwise, they could also repro-
duce the mapping and identify gateways of the VPN
after they (deliberately) change their IP address. The
greeting protocol is a simple request and reply proto-
col as shown in Fig. 5. The peer ID of the initiator can
only be protected by a static group key. The respon-
der may protect its peer ID using their pairwise master
key if available. The greeting protocol uses UDP, re-
using the IP addresses and ports of the IKE packet that
triggered the greeting, which itself is queued till the
greeting reply is received or a timeout occurs. Packet
loss is handled by retransmission mechanisms in the
IKE daemon, again triggering the greeting protocol.
k
0
k
1
g
s
1
k
2
KDF
s
2
KDF ...
Figure 6: Derivation of master keys k
i
by combining the
previous master key k
i−1
and a new symmetric key s
i
using
a key derivation function (KDF). Similar, a key ID for k
i
may be derived in a deterministic way at both proxies, not
shown for brevity. In the depicted example, the first master
key k
0
is a static group key g.
5.4 Key Synchronization Protocol
The basic idea to combine all available symmetric
keys from different sources over time to a master
key is depicted in Fig. 6. To keep the master key in
sync between two proxies, we assume that all sym-
metric keys s
i
provided to the proxy have a unique
key ID id(s
i
). Still, the key synchronization protocol
between two proxies u and v has to deal with two pos-
sible race conditions:
1. Two keys s
i
and s
i+1
might become available in a
different order at u and v, potentially leading to si-
multaneous, conflicting synchronization requests.
2. A new key s
i
might become available at u and v at
different points in time.
The first race condition may be avoided by having two
master keys between u and v, one for each direction.
Then, u and v can independently initiate the synchro-
nization of new keys for their egress master key, one at
a time. Still, every key is synchronized in both direc-
tions eventually. Regarding the second race condition,
the proxy that may safely initiate the key synchroniza-
tion first can easily be determined out of band for our
envisioned key sources: For PSKs and MKR keys, it
is the proxy which receives the key s
i
last. Further-
more, QKD protocols ensure that a key is available
at both sides before passing it to consumers. Conse-
quently, two proxies may independently request new
QKD keys, together with their key IDs, and subse-
quently initiate their synchronization.
In result, the key synchronization protocol may be
implemented as a simple request/reply protocol as de-
picted in Fig. 7. To handle packet loss, a simple re-
transmission mechanism after a timeout may be im-
plemented. Depending on the policy, synchroniza-
tion of individual keys may be skipped after too many
failed attempts. However, this should trigger a warn-
ing because it may indicate an attacker trying to pre-
vent the synchronization of keys unknown to him.
5.5 Secure and Persistent Key Storage
State-of-the-art VPN gateways are usually equipped
with a trust anchor, e.g., a smartcard with PIN pro-
Virtual Private Networks in the Quantum Era: A Security in Depth Approach
491

Proxy u Proxy v
s
i
available
s
i
available
{Sync id(s
i
)}
Derive new ingress master key
and queue sync of s
i
for
egress master key
{Ack id(s
i
)}
Derive and use new
egress master key
Potential synchronization of other keys
{Sync id(s
i
)}
Derive new
ingress master key
{Ack id(s
i
)}
Derive and use new
egress master key
Figure 7: Synchronization of key s
i
between proxies u and v
in both directions. All messages are encrypted using the ac-
tive master key, denoted by curly braces. Alongside id(s
i
),
request and acknowledgment contain a proof of knowledge
of s
i
, e.g., a cryptographic hash value, not shown for brevity.
Otherwise, failures within key sources could result in mas-
ter keys being out of sync.
tection, to protect (asymmetric) private keys from
temporary physical access by attackers. One option
would be to also persistently store symmetric key ma-
terial on this trust anchor. However, storage capacity
on trust anchors is usually very limited, so this ap-
proach may not be suitable for storing keys for thou-
sands of gateways. Another option is to encrypt keys
using a static key encryption key (KEK) inside the
trust anchor and persist their ciphertext on the gate-
way’s hard drive. However, the trust anchor might be-
come a performance bottleneck if many keys need to
be stored or loaded simultaneously. To avoid the bot-
tleneck, the KEK could also be loaded into the main
memory of the gateway. Unfortunately, this offers
less security as the KEK is more likely to be leaked
to attackers with temporary physical access.
An orthogonal approach is to only store corre-
sponding recovery keys, avoiding to store the keys
themselves. As one option, we suggest that for ev-
ery shared key k
i
, proxies u and v generate the same
recovery key r = h(k
i
), using a cryptographic hash
function h, and store r on their hard drive. In case
either u or v have to restore keys, e.g., after a reboot,
they both independently perform the following steps
to recover their previous egress master key:
1. Proxy u initiates the recovery of his egress master
key k
i
by creating a nonce n
u
and sends it to v,
together with a temporary key ID of k
i
.
2. Upon reception of n
u
, v also creates a nonce n
v
and uses the trust anchor to derive the recovered
version k
′
i
= kdf(r, n
u
, n
v
, u, v, g) of the key. For
this, r, n
u
, n
v
and the remote proxy ID u are passed
to the trust anchor. Furthermore, the trust an-
chor internally (“baked-in”) incorporates the own
proxy ID v and a static group key g into the key
derivation. Consequently, even if attackers can
send queries to the trust anchor of v, they may
only use it to recover keys which belong to v.
3. The proxy v sends n
v
to u, together with a proof
of knowledge for k
′
i
to detect (byzantine) errors.
Then, u also derives the recovered version k
′
i
and
subsequently uses it to protect all packets to v.
Note that the use of nonces ensures that both proxies
still have access to their trust anchor. Recovery of key
material that has not yet been synchronized may be
handled analogously during the normal key synchro-
nization protocol. The advantage of this approach is
that the trust anchor is only required for recovery after
a reboot, but poses no performance bottleneck during
normal operation. To implement security in depth,
recovery keys may further be encrypted in memory
using a KEK before being stored on the hard drive.
6 DISCUSSION
This section discusses the IKE proxy approach re-
garding the objectives defined in Sec. 3.
Entity Authentication. If the combination of PQC
and classical digital signature schemes implemented
by the IKE daemon is secure, entity authentication is
quantum-resistant because our design does not mod-
ify the IKE protocol. Furthermore, as soon as the
proxy synchronizes at least one symmetric key that
is unknown to the attacker, all following master keys
provide authenticity: From this time on, an exter-
nal attacker cannot exploit potential flaws in the used
PQC signature scheme to impersonate u with respect
to v or vice versa because the proxy would reject all
packets that are not authenticated with the current
master key. Replays may be detected based on the
temporary key IDs because they may only be used
once (see Sec. 5.2). Nevertheless, as long as a flawed
signature algorithm is used, an attacker may be able to
impersonate u or v with respect to a third gateway w
to which u and v did not synchronize a key yet.
Confidentiality. The confidentiality of client traffic
is protected by the TEK derived by IKE, using a hy-
brid key exchange (PQC and classical). However, at-
tackers could store IKE exchanges and client traffic
now, in the hope that a flaw in the PQC algorithm is
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
492

found later, enabling them to break the TEK and de-
crypt the traffic. Fortunately, if IKE and the final TEK
are protected by the proxy using a master key k
i
that
is not known to the attacker, the described “store now,
decrypt later” attack is far more expensive. Because
then, the attacker would also need to compromise all
symmetric keys s
0
, . . . , s
i
that have been used by the
proxy to derive k
i
. The effort to compromise a key s
i
depends on its source:
1. Using a static group key as s
0
forces the attacker
to compromise at least one (arbitrary) gateway.
2. QKD keys s
i
may be expected to be secure if ad-
jacent QKD devices are not compromised and the
classical channel has been securely authenticated
once, e.g., using a PSK or PQC. Similar as dis-
cussed above (entity authentication), QKD is then
able to securely generate fresh keys, even after a
used PQC signature scheme becomes insecure.
3. Provisioning two proxies with a pairwise PSK s
i
by a trustworthy person will require the attacker
to compromise one of the adjacent gateways of an
SA to still be successful.
4. Using MKR to derive s
i
forces the attacker to not
only store and decrypt IKE packets for a targeted
SA between u and v, but also for many other SAs
in the VPN. If some MKR paths are protected by
additional means like QKD, and no gateway on a
path is compromised, the security guarantees of
that path also transfer to the SA between u and v.
If at least one key s
i
is not compromised, all mas-
ter keys k
j
with j ≥ i are also not known to the at-
tacker, see Fig. 6. Consequently, all client packets
sent after an IKE rekey that is protected by k
j
are also
protected. Master keys themselves are protected from
physical access by using a secure persistent storage as
discussed in Sec. 5.5. Last, metadata required by the
IKE proxy (especially peer IDs and their mapping to
IP addresses) is protected by using temporary key IDs
(Sec. 5.2) and during the greeting protocol (Sec. 5.3).
Data Integrity and Replay Protection. Unautho-
rized manipulation or replay of client and key syn-
chronization packets is detected if attackers do not
know the used TEK. The TEK itself is protected by
PQC exchanges within the IKE protocol and addition-
ally by the master key of the proxy. Similar, IKE
packets are protected by PQC and by the proxy.
Cryptographic Agility. The IKE proxy can syn-
chronize pairwise symmetric key material from arbi-
trary sources. Furthermore, the symmetric authenti-
cated encryption scheme used to protect all IKE pack-
ets may easily be exchanged due to the algorithm ID
in the proxy header. Last, any modifications to IKE
or its configuration are possible without changing the
proxy. Moreover, alternative protocols with clearly
separated control and data plane can be supported.
Scalability. As the IKE proxy only uses symmet-
ric cryptography, it poses no performance bottleneck
for establishing/rekeying thousands of SAs. Further-
more, the memory and disk consumption of the proxy
scales linearly with the total number of gateways in
the VPN. This is because old key material from
the various key sources and old master keys can and
must be deleted after a successful key synchroniza-
tion. Similar, stale entries in the mapping of IP ad-
dress and port to peer ID can be deleted. Finally, only
a constant number of temporary key IDs need to be
stored for active master keys.
Robustness to DoS. The IKE proxy does not pose
a viable target for DoS attacks, because it only uses
symmetric cryptography and only has to store a con-
stant amount of information per remote gateway.
Moreover, simple request/reply mechanisms (greeting
and key synchronization protocol) allow no amplifi-
cation attacks. The key synchronization protocol is
further protected by an established SA and it checks
to only synchronize key material which is identical
at both sides. Consequently, attackers cannot force
master keys to become out of sync, which would oth-
erwise permanently block IKE.
Graceful Degradation. Compromising the IKE
proxy does not enable any attacks which are not
also possible by compromising other components of
a gateway, e.g., the IKE daemon.
Implementation Security. The sleek design and
the sole usage of symmetric cryptography allows for a
small implementation of the IKE proxy, leading only
to a small increase of the size of the trusted comput-
ing base. Further, if the master keys of a proxy are not
known to the attacker, the attack surface via public
channels is significantly reduced compared to an IKE
daemon communicating without a proxy. A small im-
plementation also facilitates formal security analyses.
7 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, implementing a transparent tunnel for
IKE via our proposed IKE proxy design does not
degrade any functional, non-functional, or security
properties of existing VPNs. Instead, it implements
Virtual Private Networks in the Quantum Era: A Security in Depth Approach
493

an additional line of defense (on top of PQC within
the IKE protocol) against quantum attackers in a flex-
ible way by combining symmetric keys from arbitrary
key sources like pairwise PSKs, QKD, or MKR.
In future work, we plan more formal analyses of
the correctness and security of our proposed proto-
cols and their implementation. Furthermore, we study
comfortable ways to automatically distribute pairwise
PSKs, e.g., laptops of personnel acting as key carriers
on business trips between VPN sites, and the impli-
cations for MKR. Last, to further reduce the overall
complexity and attack surface of VPNs, we study the
possibility to tunnel the classical channel of QKD de-
vices via the co-located VPN gateway.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work is funded by dtec.bw – Digitalization
and Technology Research Center of the Bundeswehr
[project MuQuaNet]. dtec.bw is funded by the Euro-
pean Union - NextGenerationEU.
REFERENCES
Bennett, C. H., Bernstein, E., Brassard, G., and Vazirani, U.
(1997). Strengths and Weaknesses of Quantum Com-
puting. SIAM J. Comput., 26(5):1510–1523.
Bennett, C. H. and Brassard, G. (2014). Quantum cryptog-
raphy: Public key distribution and coin tossing. The-
oretical Computer Science, 560:7–11.
Beullens, W. (2022). Breaking Rainbow Takes a Weekend
on a Laptop. In Advances in Cryptology – CRYPTO
2022, volume 13508, pages 464–479.
Cao, Y., Zhao, Y., Wang, Q., Zhang, J., Ng, S., and Hanzo,
L. (2022). The evolution of quantum key distribution
networks: On the road to the qinternet. IEEE Commu-
nications Surveys & Tutorials, 24:839–894.
Castryck, W. and Decru, T. (2022). An efficient key recov-
ery attack on SIDH (preliminary version). Cryptology
ePrint Archive, Paper 2022/975.
Deng, J. and Han, Y. (2008). Multipath Key Establishment
for Wireless Sensor Networks Using Just-Enough Re-
dundancy Transmission. IEEE Trans. Dependable and
Secure Comput., 5(3):177–190.
Dolev, D. and Yao, A. (1983). On the security of public key
protocols. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 29(2):198–
208.
Ehlen, S., Hagemeier, H., Hemmert, T., Kousidis, S.,
Lochter, M., Reinhardt, S., and Wunderer, T. (2022).
Quantum-safe cryptography – fundamentals, current
developments and recommendations. Technical
report, Federal Office for Information Security
(BSI). https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/
Downloads/EN/BSI/Publications/Brochure/
quantum-safe-cryptography.html?nn=916626.
Eschenauer, L. and Gligor, V. D. (2002). A key-
management scheme for distributed sensor networks.
In Proceedings of the 9th ACM CCS, pages 41–47.
ETSI (2022). ETSI GS QKD 015 - Quantum key distri-
bution (QKD); control interface for software defined
networks. Group Specification Version 2.1.1.
Fluhrer, S., Kampanakis, P., McGrew, D., and Smyslov,
V. (2020). Mixing Preshared Keys in the Internet
Key Exchange Protocol Version 2 (IKEv2) for Post-
quantum Security. Technical report. https://www.
rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc8784.
ITU-T (2019). Overview on networks supporting quantum
key distribution. Recommendation ITU-T Y.3800.
Kaufman, C., Hoffman, P., Nir, Y., Eronen, P., and Kivinen,
T. (2014). Internet Key Exchange Protocol Version
2 (IKEv2). Technical report. https://www.rfc-editor.
org/rfc/rfc7296.
Kent, Stephen (2005). IP Encapsulating Security Payload
(ESP). Technical report. https://www.rfc-editor.org/
rfc/rfc4303.
Lan, T., Lee, R., and Chiang, M. (2009). Multi-Path Key Es-
tablishment against REM Attacks in Wireless Ad Hoc
Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE GLOBECOM
2009, pages 1–8.
Marksteiner, S. and Maurhart, O. (2015). A Protocol for
Synchronizing Quantum-Derived Keys in IPsec and
its Implementation. In Proceedings of the 9th ICQNM.
Neuman, B. and Ts’o, T. (1994). Kerberos: An authentica-
tion service for computer networks. IEEE Commun.
Mag., 32(9):33–38.
NIST (2022). PQC Standardization Process: Announc-
ing Four Candidates to be Standardized, Plus Fourth
Round Candidates. https://csrc.nist.gov/News/2022/
pqc-candidates-to-be-standardized-and-round-4.
Proos, J. and Zalka, C. (2003). Shor’s discrete logarithm
quantum algorithm for elliptic curves. Quantum In-
formation and Computation, 3(4):317–344.
Rass, S. and K
¨
onig, S. (2011). Indirect eavesdropping in
quantum networks. In Proceedings of the 5th ICQNM,
pages 83–88.
Rossberg, M. and Schaefer, G. (2011). A survey on auto-
matic configuration of virtual private networks. Com-
puter Networks, 55(8):1684–1699.
Shor, P. W. (1997). Polynomial-Time Algorithms for Prime
Factorization and Discrete Logarithms on a Quantum
Computer. SIAM J. Comput., 26(5):1484–1509.
Smyslov, V. (2022a). Alternative Approach
for Mixing Preshared Keys in IKEv2 for
Post-quantum Security. Technical report.
https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/internet-drafts/
draft-smyslov-ipsecme-ikev2-qr-alt-06.html.
Smyslov, V. (2022b). Intermediate Exchange in the Internet
Key Exchange Protocol Version 2 (IKEv2). Technical
report. https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc9242.html.
Welte, H. (2023). The netfilter.org ”libnetfilter queue”
project. https://www.netfilter.org/projects/libnetfilter
queue/.
Wootters, W. K. and Zurek, W. H. (1982). A single quantum
cannot be cloned. Nature, 299(5886):802–803.
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
494
