
A Hybrid Approach to Overcome Requirements Challenges in the
Software Industry
Md. Tarek Hasan
1 a
, Nabil Mohammad Abu Bakar
1
, Nujhat Nahar
1
, Mahady Hasan
1 b
and M. Rokonuzzaman
2
1
Independent University, Bangladesh, Dhaka, Bangladesh
2
North South University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Keywords:
Hybrid Methodology, Requirements Gathering, Agile Methodology, Waterfall Approach, Requirement
Management, and Requirement Collection.
Abstract:
This research paper presents a hybrid approach to overcome the challenges related to inadequate or insufficient
client involvement and understanding during the software requirements phase. The aim of this study is to in-
vestigate the factors that contribute to this challenge and propose a solution that combines traditional and agile
methodologies. To accomplish this, a survey was conducted to collect responses from industry professionals in
the software development sector. The survey results showed that inadequate or insufficient client involvement
and understanding is a common issue that leads to delays and misunderstandings in software development
projects. To address this challenge, the proposed hybrid approach combines the traditional requirements en-
gineering process with agile techniques such as user stories, prototypes, and continuous feedback loops. The
hybrid approach aims to improve communication and collaboration between the client and the development
team, ensuring that the software’s requirements are well-understood and documented. The results of this study
indicate that the proposed hybrid approach is effective in overcoming the challenges related to inadequate or
insufficient client involvement and understanding. The findings of this research have practical implications
for software development organizations, highlighting the importance of adopting a hybrid approach to ensure
successful software development projects.
1 INTRODUCTION
A ”requirement” for a system is a representation that
describes an ability, trait, or attribute aspect of a sys-
tem, making it valuable and useful to a client (Young,
2002). Steve McConnell, in his book Software Project
Survival Guide, agrees that the most challenging part
of requirement gathering is not documenting what
clients ”want,” but finding what they ”need” that can
be effectively provided within the behavior and design
parameters available to the project team. Customers
often say one thing during requirement elicitation and
then do something very different (
˚
Afors and Zucker-
man, 2001).
Part of the difficulty lies in the reliance on tradi-
tional requirements collecting methods such as con-
centration groups, questionnaires, and interviews,
which do not adequately deal with discrepancies
in people’s responses. The goal of gathering re-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3777-2229
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9037-0181
quirements is to obtain information utilizing diverse
perspectives that portray what needs to be con-
structed. Gathering requirements may also be thought
of as bringing together diverse people’s opinions and
knowledge to come up with a solution to an issue.
Gathering requirements is both the most complex and
most important component of any project (Lane et al.,
2016). User involvement is crucial for successful
project completion and It also enables the understand-
ing of user requirements and ensures the delivery of
satisfactory software products (Islam. et al., 2023). It
is perplexing because it is such a complex procedure,
and so little effort is given to the approach utilized
to evoke the necessities needed to complete a project
successfully.
Most projects involve distinctive mission stages.
Project managers execute such hybrid philosophy by
merging both agile and traditional requirement col-
lection techniques into one philosophy in accordance
with the project type. Several tactics are used to join
numerous tiers to oversee the work. The stages are ei-
526
Hasan, M., Bakar, N., Nahar, N., Hasan, M. and Rokonuzzaman, M.
A Hybrid Approach to Overcome Requirements Challenges in the Software Industry.
DOI: 10.5220/0012125800003538
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Software Technologies (ICSOFT 2023), pages 526-533
ISBN: 978-989-758-665-1; ISSN: 2184-2833
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

ther agile or traditional but not a mix of both (Hidel-
laarachchi et al., 2021). Our investigation found that
software firms may lack a standard approach regard-
ing requirement collection methodology. Such com-
panies work with adaptive measures and go along
with simple adjusting contraptions that fulfill their ne-
cessities. These adaptive approaches to fulfilling ne-
cessities ultimately give birth to a Hybrid model.
To address such problems, a hybrid approach
is proposed to overcome inadequate or insufficient
client involvement and understanding. This arti-
cle reviews the typical requirements-gathering land-
scape and conceptual underpinning, justifies recast-
ing the requirements-gathering process, discusses a
method for creating a requirement-collecting hybrid
technique combining traditional waterfall and agile
approach, and describes the requirements-gathering
design concepts. The paper concludes with a brief
conclusion.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Requirement Engineering (RE) is a circumstance in
which a system or portion of a system must be used to
meet contracts, requirements, specifications, or other
documents (Doe, 2011). RE alludes to the method
or levels utilized to compile requirements. RE is
the foremost vital stage within Software Development
Life Cycle (SDLC) since the proper determination
of requirements plays a vital role in achieving the
success of Software Development to meet client de-
sires (Weyns, 2019). Because the RE segment is a
segment of the SDLC and its order is inside the first
section of the SDLC level, it must be able to effec-
tively reduce the risk of software program develop-
ment failure and establish consumer demands (Ku-
mar et al., 2013). Traditional RE includes 5 major
techniques: elicitation, analysis, documentation, vali-
dation, and management (Bernard, 2012). Traditional
RE approaches are carried out in a sequential and it-
erative manner. The number of iterations performed
can be highly reliant on the delicacy with which cus-
tomers’ desires are captured.
Elicitation could be a RE handle that relies on ob-
taining data and records from clients based on con-
finements and criteria that are appropriate. In order to
meet the objectives established as raw requirements,
facts, and information might be gathered from formal
or non-formal files. Observation, interviews, surveys,
and questionnaires are some of the strategies or meth-
ods used to undertake elicitation (M and BB, 2018).
The Analysis is a RE system that navigates on
assessing sources and information elicited from dif-
ferent sources. The Analysis technique arranges data
and facts as basic essentials according to the type and
manner of customer want. This technique must be
carried out with caution in order for the analysis re-
sults to fulfill the requirements for clear, complete,
consistent, verified, detectable, appropriate, and prac-
tical parameters (Eduard and Shashkin, 2019). Doc-
umentation, often known as the specification, is a
RE method that concentrates on compiling a tradi-
tional file containing requirement specifications gath-
ered throughout the data collection and analysis tech-
niques. The functional and non-functional require-
ments collected from the analysis phase must be in-
cluded in the formal specification report. Validation
could be a procedure that concentrates on confirm-
ing the conformance between the specifications of the
requirements established during the analytical phase
and the user’s preferred demands (Chemuturi, 2012).
Before converting into the final model as spelled out
in a legal document, the validation method desires
to include users in providing comments and critiques
that are utilized to check the consequences of the raw
requirement requirements. The validation technique
must be repeated repeatedly until the developer and
the individual reach an agreement.
Process management is a process that focuses on
phase management and documentation from the elic-
itation process to the validation process, including
any alterations that occur. Starting with the devel-
opment phase and ending with the maintenance pro-
cess, the management process is a procedure that must
be repeated repeatedly and continuously (Geisser and
Hildenbrand, 2006).
Agile, on the other hand, presupposes that re-
quirements engineering continues throughout a sys-
tem’s lifecycle. RE is done in Agile by continuous
collaboration, with requirement gathering, develop-
ment, and testing occurring simultaneously. The evo-
lutionary requirements theory, which asserts that re-
quirements should evolve through time, is used to ac-
complish this. User testimonies, which are written
from the perspective of the user, are used to elicit
and capture business requirements in Agile (Mani-
festo, 2013). These user testimonies are utilized as a
fundamental work unit and expand over the project’s
lifespan. Continuous planning is a key component of
agile methodologies, release planning, iteration plan-
ning, and activity-level planning are all examples of
planning. For each iteration, iteration planning is con-
ducted that lasts between one and three weeks which
demands estimating user stories, acknowledging prior
iteration’s successes, and defining development and
objectives in general for the upcoming iteration. For
individual iterations, a release motive is created in
A Hybrid Approach to Overcome Requirements Challenges in the Software Industry
527

which the length of each iteration is set. Develop-
ers and customers agree on each iteration that will
be included, and velocity points are determined ev-
ery time. Task-level planning includes breaking down
user stories into future tasks, allocating tasks among
team members, and focusing on implementation is-
sues (Inayat et al., 2015; Jun et al., 2010).
The hybrid technique is well-known for combin-
ing the development of a traditional waterfall ap-
proach with the adaptability of an agile methodol-
ogy (Kuhrmann et al., 2017). Joining both method-
ologies can settle various complications in projects
and can gain ground. which depends upon the kind
of project and its necessities (Muddangula and Chan-
drababu, 2020). Accepting such a hybrid system,
which combines procedures from both the waterfall
and agile models, can lead to success.
In spite of the way that we achieve different bene-
fits from traditional and agile strategies, project man-
agers are at this point standing up to various troubles
while executing gigantic extension projects (Jabar
et al., 2019). The execution of different project devel-
opment approaches, for instance, traditional and agile
doesn’t give the overall benefits that the Stockholders
are expecting (Copola Azenha et al., 2021).
Hayata and Han presented a methodology that
is hybrid in nature for developing IT projects, com-
bining agile-scrum processes with traditional water-
fall methodology. The waterfall method is used to
show project requirements, and the agile strategy is
employed during the design, execution, and closing
phases. In the testing step, the Waterfall framework
might be employed (Hayata and Han, 2011). Lozo
and Jovanovic created another adaptable hybrid tech-
nique for managing IT projects, with four different
phases of the SDLC. The waterfall technique is used
in the main and fourth turns of the project life cycle,
while the agile methodology is used in the second and
third phases. Waterfall and agile methodologies can
be utilized to implement a hybrid technique (Lozo and
Jovanovic, 2012). which however, is dependent on the
project type (Salah et al., 2017).
In today’s world, most software development is
focused on improving existing software rather than
creating entirely new software. Instead of consider-
ing waterfall and agile methodologies as two differ-
ent processes, hybrid development is more realistic.
The difficulties that appeared through utilizing new
procedures that might use new techniques require ex-
tra commitment and backing from the stakeholders.
Learning new strategies might be a tedious cycle for
the stakeholders. Any mission in which stakeholders
running in diverse time areas might have correspon-
dence troubles or inaccessibility of help on every oc-
casion for the project. Higher administration needs to
comprehend the project requirements and choose the
appropriate procedure to cope with the task.
Agile and Waterfall structures are wonderful
methodologies that can be associated to consolidate
the excellence of techniques to frame a crossover
method. This research pushes us to design a hy-
brid approach that incorporates agile methodologies
into traditional software and IT project development
and management. Our initial idea is to implement a
spiral model that incorporates agile management and
waterfall-style plan-driven development process and
project management. Our aim is to reduce failure, re-
search gap, and further modification requests once the
product is delivered by using this model. Our model
and scope will be very specific and explicit, and all
aspects of the desired product will be included in the
documentation.
3 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The problem addressed in this research is the chal-
lenges related to inadequate or insufficient client in-
volvement and understanding during the software re-
quirements phase (Bhat et al., 2006). The software
development industry often faces issues due to un-
clear, incomplete, or ambiguous software require-
ments, which can lead to delays, misunderstandings,
and unsatisfactory outcomes. The lack of client in-
volvement and understanding of the software’s do-
main and requirements is a significant factor that con-
tributes to these challenges (Cao et al., 2008).
In the software development industry, challenges
related to inadequate or insufficient client involve-
ment and understanding during the requirements
phase have been a persistent problem. Unclear or in-
complete software requirements can lead to delays,
misunderstandings, and unsatisfactory outcomes. The
lack of client involvement and domain knowledge
is a significant factor that contributes to these chal-
lenges (Gupta et al., 2020). Therefore, the research
problem addressed in this study is how to overcome
the challenges of inadequate or insufficient client in-
volvement and understanding of software require-
ments and propose an effective solution that combines
traditional and agile methodologies.
The purpose of this study is to investigate this
problem and propose a hybrid approach that com-
bines traditional and agile methodologies to overcome
these challenges. According to our survey results, in-
adequate or insufficient client involvement and un-
derstanding is a common issue that software devel-
opment professionals face. Therefore, it is crucial
ICSOFT 2023 - 18th International Conference on Software Technologies
528

to find a solution that enhances communication and
collaboration between the client and the development
team to ensure that the software’s requirements are
well-understood and documented. The proposed hy-
brid approach aims to address this issue by com-
bining traditional requirements engineering with ag-
ile techniques, such as user stories, prototypes, and
continuous feedback loops. This study has practi-
cal implications for software development organiza-
tions, highlighting the importance of adopting a hy-
brid approach to overcome the challenges related to
inadequate or insufficient client involvement and un-
derstanding of software requirements. The proposed
solution can help organizations improve the quality
of their software and deliver satisfactory outcomes to
their clients.
4 RESEARCH DESIGN
The first author Identifies the research questions that
the study aims to answer. These questions focused
on the factors that contribute to the challenge of in-
adequate or insufficient client involvement and un-
derstanding during the software requirements phase,
and how a hybrid approach can overcome these chal-
lenges. The Authors also conduct a comprehensive
review of relevant literature to gain an understand-
ing of the current state of knowledge in the area of
software requirements gathering, traditional and ag-
ile methodologies, and hybrid approaches. This re-
view provides a foundation for the study’s theoretical
framework. Furthermore, the author designed a sur-
vey questionnaire that has been used to collect data
from industry professionals in the software develop-
ment sector. The survey included questions that will
help to identify the challenges related to inadequate
or insufficient client involvement and understanding,
as well as questions that will gather information about
the effectiveness of the proposed hybrid approach.
Identify the target population for the survey,
which in this case was industry professionals in the
software development sector. Use a sampling tech-
nique, such as random sampling or stratified sam-
pling, to select a representative sample from the popu-
lation. Data was collected through online surveys and
in-person interviews. Ensure that the data is collected
in a systematic and standardized manner to maintain
the validity and reliability of the results.
Analyze the survey data using appropriate statis-
tical techniques to identify patterns and trends. This
analysis included descriptive statistics to summarize
the data, as well as inferential statistics to test hy-
potheses and determine the significance of the find-
ings. The author then tried to present the results of
the study in a clear and concise manner, using tables,
charts, and graphs to illustrate the key findings.
These results include an analysis of the challenges
related to inadequate or insufficient client involve-
ment and understanding, as well as an evaluation of
the effectiveness of the proposed hybrid approach. To
draw conclusions from the study’s findings and pro-
vide recommendations for software development or-
ganizations on how to overcome the challenges re-
lated to inadequate or insufficient client involvement
and understanding. These recommendations should
highlight the importance of adopting a hybrid ap-
proach to ensure successful software development
projects.
In summary, the research design and methodology
for this study involved conducting a survey of indus-
try professionals in the software development sector
to identify the challenges related to inadequate or in-
sufficient client involvement and understanding and
evaluate the effectiveness of a proposed hybrid ap-
proach. The study’s findings will provide practical
implications for software development organizations
on how to overcome these challenges and ensure suc-
cessful software development projects.
4.1 Characteristics of Software
Firms/Companies Towards the
Topic
The survey evaluated 16 tech companies based on
various criteria, including work experience, company
size, location, and job roles. Among the respondents,
50% had 5-10 years of work experience, 45% had 2-5
years, and 5% had less than 1 year. The majority of re-
spondents identified as developers (35%), followed by
business analysts (25%), testers (20%), project man-
agers (10%), and product owners (10%).
Table 1: Survey profile characteristics.
Title Measure
Total No Of Company 16
Work Experience
50% 5-10 years
45% 2-5 years
5% 0-1 year
Project Types Software
Project Location Bangladesh
Respondent Location Bangladesh
Respondent Role
Developer 35%
Business Analyst 25%
Tester 20%
Project Manager 10%
Product owner 10%
A Hybrid Approach to Overcome Requirements Challenges in the Software Industry
529
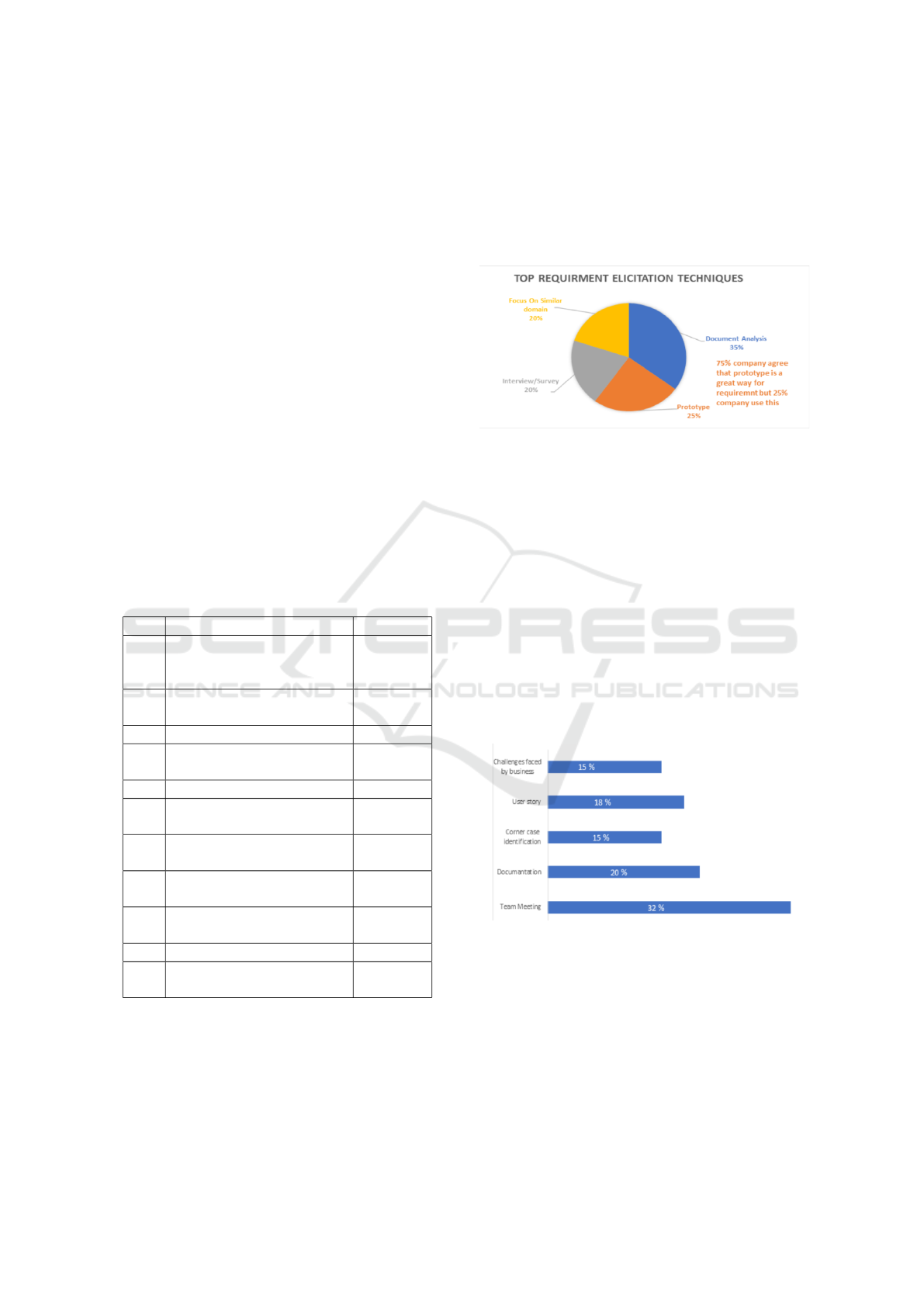
5 FINDINGS
Each project in Bangladesh has unique features that
can impact its success and completion. Develop-
ment teams may be unable to provide accurate esti-
mates due to uncertainty about specific tasks within
the project. The responsibility of getting all stake-
holders on the same page lies with the requirement
team. However, conflicts are expected during the
requirement-gathering process due to. Discussions
are the most common way to resolve such issues. To
address this inadequate or insufficient client involve-
ment and understanding of flaws in the requirement
engineering cycle and resolve conflicts, we propose a
hybrid requirement management model that can ben-
efit both stakeholders and developers. Our survey fo-
cuses on various requirements, including gathering,
management, verification, change management, elic-
itation, and improvement. We have reviewed several
works and studies to address the challenges and of-
fer solutions to improve the quality of requirements.
Based on our survey, the following are the challenges
that companies are facing with requirements manage-
ment:
Table 2: Project Challenges.
No. Challenges Problems
P1
The client is not properly,
educated not have enough
product/domain knowledge
62.5%
P2
Inactivity of the
contact person
18.75%
P3 Lack of skill 32.5%
P4
Lack of proper
documentation
43.75%
P5 Communication Gap 37.5%
P6
Misinterpretation about
requirement document
62.5%
P7
Lack of access
to end-user
43.75%
P8
Focus on visual aspect
rather than functional
37.5%
P9
The client is not willing
to give proper requirement
56.25%
P10 Inadequate resources 37.5%
P11
Struggle with
Change Request
62.5%
Another common issue we found is that budget
limitations can prevent some companies from having
a dedicated designer to create the prototype, which
can hinder their ability to accurately visualize the fi-
nal output of the project. This can lead to a lack of un-
derstanding of the project’s requirements and objec-
tives, ultimately leading to delays, errors, and costly
rework. It is essential for companies to recognize the
value of prototyping and allocate the necessary re-
sources to ensure its effective implementation. This
includes investing in skilled designers and providing
adequate time and budget for the prototyping process.
Figure 1: Requirement’s elicitation techniques.
According to our survey, many companies tend
to prioritize team meetings over other important as-
pects of requirements management, such as address-
ing challenges faced by the business and capturing
edge cases and corner cases. This can result in in-
complete or inaccurate requirements, leading to de-
lays, errors, and rework. To address this issue, com-
panies should allocate sufficient time and resources to
thoroughly understand the business context and iden-
tify all possible edge cases and corner cases. Addi-
tionally, companies should involve all relevant stake-
holders, including clients and end-users, throughout
the requirements gathering and management process
to ensure that all necessary requirements are captured
and the final product meets their needs.
Figure 2: Requirement analysis techniques.
5.1 Problem Analysis
After surveying 16 companies to identify the prob-
lems they face when collecting requirements, we used
a pivot chart and linear regression line (including out-
liers) to prioritize the problems. By analyzing the
data, we were able to determine which issues were
most common and severe, and we developed a plan to
address them accordingly.
ICSOFT 2023 - 18th International Conference on Software Technologies
530

Based on the graph mentioned earlier, it is evident
that Problem 1 is the most commonly faced challenge
by companies, followed by P6 and P11. Problem 9
was faced by only one company during the survey.
Problems 4 and 7 are also significant challenges and
are considered high-priority issues.
Regarding the remaining problems, P3, P5, P8,
and P10, we consider them as medium focus areas
based on their values. The slope of the linear line rep-
resents P7, and since all medium values are close to
this line, P7 is also a high-priority issue. According to
the collected data, P2 is the lowest priority problem.
As mentioned in figure 4
Figure 3: Problem prioritization.
5.2 Regression Graph
Regression analysis indicates that the points above
the linear regression line (outliers), including P1, P6,
P9, and P11, require the highest priority. Companies
should focus more on these issues to optimize the gap
and improve their requirements collection processes.
See the following Figure 5
Figure 4: Linear regression.
6 PROPOSED SOLUTION
According to Kotonya and Sommerville (Kotonya and
Sommerville, 1996), the normal RE process used in
our analysis consists of four phases, each of which
contains a number of activities. The solution will
commence by addressing the process of requirement
collection, followed by a comprehensive review and
analysis section. Within this phase, activities such
as gap analysis, handling change requests, and for-
mulating test cases will be carried out, while concur-
rently finalizing the design. The subsequent segment
of the cycle will focus on specifying system require-
ment details, architectural design, test cases, and test-
ing instructions. Finally, the client will verify the re-
quirements, potential conflicts will be identified, and
a mechanism for tracking document changes will be
established to ensure accurate recordkeeping.
6.1 Requirement Collection
Initialization: The initiation phase of requirement
collection involves communicating with stakehold-
ers to establish the project’s goals, objectives, and
scope. This includes determining the project’s pur-
pose, desired outcomes, and benefits, and identifying
the tasks, resources, and timeline required to achieve
them.
Documentation: The documentation phase of re-
quirement collection involves recording the require-
ments in a clear, concise, and comprehensive format
that the project team can understand and use. The
documentation provides a detailed description of the
requirements that the project must meet.
6.2 Requirement Review and Analysis
The gap analysis should be used to identify gaps and
inconsistencies in actual project requirements com-
pared to desired requirements. Change requests from
stakeholders are managed by evaluating their feasibil-
ity and prioritizing them. The project team then final-
izes the design, including creating detailed specifica-
tions and visual aids. Finally, test cases are introduced
to ensure that the project meets all requirements and
functions as expected.
6.3 Requirement Specification
The requirement specification step involves identify-
ing system requirements, creating a software archi-
tecture design, developing a test plan, and prepar-
ing testing instructions for user verification. The sys-
tem requirements should be clear and complete, and
the software architecture design should describe how
the system will be structured. The test plan should
cover all functional and non-functional requirements
and the testing instructions should be easy to follow
and cover all aspects of the system.
A Hybrid Approach to Overcome Requirements Challenges in the Software Industry
531

6.4 Requirements Validation
In this step, the process of ensuring that the require-
ments gathered are accurate, complete, and feasible.
This involves validating the requirements with stake-
holders, identifying potential conflicts between the re-
quirements, and documenting and tracking changes.
The goal of requirements validation is to ensure that
the requirements align with the stakeholders’ expec-
tations and that they are achievable and aligned with
the project’s goals.
Figure 5: Proposed Model.
We can use the following model as a mix of all like
hybrid so that any review or change can be handled
during the requirement collection. Since most of the
companies failed to use the best approaches due lack
of knowledge, time, and budget constraints. Some-
times ignoring any steps in the process could lead to
a bigger problem. So, the author recommends using
figure 5 and consider illustrated each and every step
with significance. One has to follow mentioned steps
with a spiral.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, this research paper provides valuable
insights into the challenges related to client involve-
ment and understanding during the software require-
ments phase. The survey results indicate that inade-
quate client involvement and understanding is a com-
mon issue that leads to delays and misunderstandings
in software development projects. The proposed hy-
brid approach, which combines traditional require-
ments engineering processes with agile techniques,
has been found to be effective in improving commu-
nication and collaboration between the client and the
development team. This approach has practical impli-
cations for software development organizations, high-
lighting the importance of adopting a hybrid approach
to ensure successful software development projects.
Overall, this research contributes to the field of soft-
ware engineering by providing a practical solution to
a common challenge in the industry. In future work,
authors will check the proposed model’s validity in
terms of their industry.
REFERENCES
Bernard, Y. (2012). Requirements management within a
full model-based engineering approach. Syst. Eng.,
15:119–139.
Bhat, J. M., Gupta, M., and Murthy, S. N. (2006). Overcom-
ing requirements engineering challenges: Lessons
from offshore outsourcing. IEEE Software, 23(5):38–
44.
Cao, L., Ramesh, B., and Li, Q. (2008). The effects of in-
terface usability on client learning of software appli-
cations. Information & Management, 45(7):419–428.
Chemuturi, M. (2012). Requirements engineering and man-
agement for software development projects. Springer
Science & Business Media.
Copola Azenha, F., Aparecida Reis, D., and Leme Fleury,
A. (2021). The role and characteristics of hybrid ap-
proaches to project management in the development
of technology-based products and services. Project
Management Journal, 52(1):90–110.
Doe, J. (2011). Recommended practice for software re-
quirements specifications (ieee). IEEE.
Eduard, A. and Shashkin, A. (2019). Journal of physics:
Conference series.
Geisser, M. and Hildenbrand, T. (2006). A method for
collaborative requirements elicitation and decision-
supported requirements analysis. In IFIP World Com-
puter Congress, TC 2, pages 108–122, Boston, MA.
Springer.
Gupta, V., Fernandez-Crehuet, J. M., Hanne, T., and
Telesko, R. (2020). Requirements engineering in soft-
ware startups: A systematic mapping study. Applied
Sciences, 10(17):6125.
Hayata, T. and Han, J. (2011). A hybrid model for it project
with scrum. In Proceedings of 2011 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Service Operations, Logistics
and Informatics, pages 285–290. IEEE.
Hidellaarachchi, D., Grundy, J., Hoda, R., and Madampe,
K. (2021). The effects of human aspects on the re-
quirements engineering process: A systematic litera-
ture review. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineer-
ing.
Inayat, I., Salim, S. S., Marczak, S., Daneva, M., and
Shamshirband, S. (2015). A systematic literature re-
view on agile requirements engineering practices and
ICSOFT 2023 - 18th International Conference on Software Technologies
532

challenges. Computers in Human Behavior, 51:915–
929.
Islam., M., Khan., F., Hasan., M., Sadia., F., and Hasan.,
M. (2023). Impact of covid-19 on the factors influ-
encing on-time software project delivery: An empir-
ical study. In Proceedings of the 18th International
Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to
Software Engineering - ENASE, pages 554–561. IN-
STICC, SciTePress.
Jabar, M. A., Abdullah, S., Jusoh, Y. Y., Mohanarajah, S.,
and Ali, N. M. (2019). Adaptive and dynamic char-
acteristics in hybrid agile management model for soft-
ware development project success. In 2019 6th Inter-
national Conference on Research and Innovation in
Information Systems (ICRIIS), pages 1–5. IEEE.
Jun, L., Qiuzhen, W., and Lin, G. (2010). Application of
agile requirement engineering in modest-sized infor-
mation systems development. In 2010 Second World
Congress on Software Engineering, volume 2, pages
207–210. IEEE.
Kotonya, G. and Sommerville, I. (1996). Requirements
engineering with viewpoints. Software Engineering
Journal, 11(1):5–18.
Kuhrmann, M., Diebold, P., M
¨
unch, J., Tell, P., Garousi, V.,
Felderer, M., and Prause, C. R. (2017). Hybrid soft-
ware and system development in practice: waterfall,
scrum, and beyond. In Proceedings of the 2017 Inter-
national Conference on Software and System Process,
pages 30–39.
Kumar, M., Shukla, M., and Agarwal, S. (2013). A hybrid
approach of requirement engineering in agile soft-
ware development. In 2013 International Conference
on Machine Intelligence and Research Advancement,
pages 515–519. IEEE.
Lane, S., O’Raghallaigh, P., and Sammon, D. (2016). Re-
quirements gathering: the journey. Journal of Deci-
sion Systems, 25(sup1):302–312.
Lozo, G. and Jovanovic, S. (2012). A flexible hybrid
method for it project management. Journal of Emerg-
ing Trends in Computing and Information Sciences,
3(7):1027–1036.
M, M. and BB, I. (2018). A review of requirement engi-
neering process models. J Archit Eng Tech, 7:215.
Manifesto, C. H. A. O. S. (2013). Think big, act small.
Technical report, The Standish Group International
Inc.
Muddangula, A. and Chandrababu, A. (2020). Adoption of
hybrid methodology in projects. International Jour-
nal of Management, Technology, and Social Sciences
(IJMTS), 5(1):1–7.
Salah, A., Darwish, N. R., and Hefny, H. A. (2017). To-
wards a hybrid approach for software project manage-
ment using ontology alignment. International Journal
of Computer Applications, 975:8887.
Weyns, D. (2019). Software engineering of self-adaptive
systems. In Handbook of Software Engineering, pages
399–443. Springer, Cham.
Young, R. R. (2002). Recommended requirements gather-
ing practices. CrossTalk, 15(4):9–12.
˚
Afors, C. and Zuckerman, M. (2001). A quick, accurate way
to determine customer needs. imprint analysis helps
companies win loyalty and determine future prefer-
ences. Quality Progress, 34(7):82–87.
A Hybrid Approach to Overcome Requirements Challenges in the Software Industry
533
