
SoK: Towards CCA Secure Fully Homomorphic Encryption
Hiroki Okada
a
and Kazuhide Fukushima
KDDI Research, Inc., Fujimino-shi, 356-8502, Japan
Keywords:
Fully Homomorphic Encryption, Chosen-Ciphertext Attacks, Key-Dependent Message Security.
Abstract:
Fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) was realized by Gentry in 2009. Since then, the current FHE construc-
tion has an inherent theoretical problem: FHE schemes are not secure against adaptive chosen-ciphertext
attacks (CCA2), since FHE is malleable by definition. We conduct a survey on the existing works to
circumvent this problem toward achieving better security of FHE.
1 INTRODUCTION
Fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) was realized in
Gentry’s seminal work (STOC 2009) in 2009. Since
then, all exiting FHE schemes have required the as-
sumption that they are secure even when allowing the
adversary to access ciphertexts of messages that are
dependent on a secret key, which is called the key-
dependent message (KDM) security assumption. In
particular, when we allow the adversary ciphertexts
of the secret key, the assumption is called the circu-
lar assumption. Existing FHE schemes require the
bootstrapping key to evaluate an (unbounded) circuit,
which is the ciphertext of (parts of) the secret key, i.e.,
a key-dependent message. Thus, removing the circu-
lar/KDM assumption is a long-standing open prob-
lem, i.e., proving the circular/KDM security from the
standard assumption (or constructing FHE without ci-
phertexts of key-dependent messages).
As another important open problem, any FHE
schemes (more generally, any (partial) homomorphic
encryption schemes) cannot achieve IND-CCA2 (in-
distinguishability against adaptive chosen-ciphertext
attacks) security, because (F)HE schemes are mal-
leable by definition. In addition, IND-CCA1 (indis-
tinguishability against nonadaptive chosen-ciphertext
attacks) security is also challenging for FHE, since the
adversary can query the decryption of the bootstrap-
ping key and obtain (bits of) the secret key.
In this paper, we conduct a survey of the works on
the CCA security in Sect. 3, and provide a summary
in Sect. 4.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5687-620X
Related Work. Fauzi, Hovd and Raddum (Fauzi
et al., 2022) broadly investigated the feasibility of
IND-CCA1 attacks on the existing IND-CPA secure
FHE schemes, and they also gave a overview of the
existing generic construction of IND-CCA1 secure
FHE, namely, the works of (Loftus et al., 2012) and
(Canetti et al., 2017). Although the latter part some-
what overlaps with our paper, we give a survey in
broader perspectives towards achieving better secu-
rity of FHE, which includes the details of new al-
ternative security models (such as funcCPA (Akavia
et al., 2022), KH-CCA (Lai et al., 2016), which will
be defined later). We also give graphical explanations
(e.g., Figs. 1 to 3, and Tab. 1) for easier understanding.
2 PRELIMINARIES
First, we provide the definitions and preliminaries re-
quired for our work in this section.
The log and ln denote the base 2 logarithm and
the natural logarithm, respectively. We use bold lower
case for vectors and bold upper case for matrices. For
any natural number s ∈ N, the set of the first s positive
integers is denoted by [s] = {1, ·· · , s}. We sometimes
denote a vector (x
1
, . . . , x
l
) by (x
i
)
i∈[l]
.
2.1 Public Key Encryption
Due to the page limit, we omit the definition of the
PKE. The most important PKE security model is in-
distinguishability against the chosen plaintext attack
(CPA), chosen-ciphertext attack (CCA1), and adap-
tive chosen-ciphertext attack (CCA2).We illustrate the
IND-CPA/CCA1/CCA2 game in Fig. 1. We call
Okada, H. and Fukushima, K.
SoK: Towards CCA Secure Fully Homomorphic Encryption.
DOI: 10.5220/0012129800003555
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2023), pages 793-798
ISBN: 978-989-758-666-8; ISSN: 2184-7711
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
793

Adversary Challenger
A
1
pk
←−−−− (pk, sk) ← Gen(1
λ
)
ct
i
−−−−→
⟲
←−−−−
r
i
r
i
:= O
atk
1
(ct
i
)
m
0
,m
1
−−−−→ b ← U({0, 1})
A
2
ct
∗
←−−−− ct
∗
← Enc(pk, m
b
)
ct
j
−−−−→
⟲
←−−−−
r
j
r
j
:= O
atk
2
(ct
j
)
(for ct
j
̸= ct
∗
)
b∈{0,1}
−−−−→
Figure 1: IND-atk ∈ {CPA, CCA1, CCA2} GAME for the
PKE Σ := (Gen, Enc, Dec) with security parameter λ, where
the adversary is A := (A
1
, A
2
). Here, O
atk
1
(ct
i
) = ∅ if
atk = CPA, Dec(sk, ct
i
) otherwise, and O
atk
2
(·) = ∅ if
atk ∈ {CPA, CCA1}, Dec(sk, ct
i
) otherwise. The symbol
“⟲” indicates the interaction is repeatable (for any poly(λ)
times).
IND-CPA/CCA1/CCA2 security as CPA/CCA1/CCA2
(without IND-).
2.2 Key Dependent Message Security
The F -IND-KDM-atk ∈ {CPA, CCA1, CCA2} game
can be defined similarly to the IND-atk, where F :=
{ f | f : K → M } is the function family that defines
the dependence on the secret key sk. The difference
from the CPA game is that the message of the chal-
lenge ciphertext c is chosen from a key-dependent
message m
0
:= f (sk) for f ∈ F or message of 0,
m
1
:= 0
|m
0
|
. For example, the (1-)circular security
considers the ciphertext of a secret key, a special case
of KDM where f = identical map (copy of the secret
key). We describe the part of the game distinct from
the IND-atk game in Fig. 2.
2.3 Fully Homomorphic Encryption
We define the FHE scheme syntax and requirements.
Def. 2.1. A fully homomorphic encryption scheme is a
quadruple Σ
FHE
:= (Gen, Enc, Dec, Eval) of PPT al-
gorithms defined as follows: Σ
PKE
:= (Gen, Enc, Dec)
composes a PKE scheme. ct ← Eval(C, (ct
i
)
i∈[l]
):
The algorithm Eval takes a circuit C : M
l
→ M and
ciphertexts (ct
i
)
i∈[l]
as inputs, then outputs a new ci-
phertext ct.
An FHE scheme is correct if Σ
PKE
is a cor-
rect PKE scheme, and for every key pair (pk, sk) ←
Adversary Challenger
.
.
.
.
.
.
f ← F
f
−−−−−→
m
0
:= f (sk),
m
1
:= 0
|m
0
|
,
b ← U({0, 1})
ct
∗
←−−−−− ct
∗
← Enc(pk, m
b
)
.
.
.
.
.
.
Figure 2: The challenge ciphertext of F -IND-KDM-atk
∈ {CPA, CCA1, CCA2} game for F := { f | f : K → M },
where K and M are the key space and message space of the
scheme. The rest part of the game is identical to IND-atk
game described in Fig. 1.
Gen(1
λ
), every circuit C ∈ C , and every message
(m
i
)
i∈[l]
∈ M
l
, ct ← Eval(C, (ct
i
)
i∈[l]
), where ct
i
←
Enc(pk, m
i
), Dec(sk, ct) = C((m
i
)
i∈[l]
) holds with
overwhelming probability. An FHE scheme is com-
pact if the output size of Eval(·, ·) is poly(λ). The
leveled-FHE is a weaker version of the FHE defined
above; The leveled-FHE has an a priori defined bound
L = poly(λ) on the multiplicative depth of the circuit.
We sometimes call the FHE without the bound on the
circuit an unbounded FHE.
Gentry (Gentry, 2009) constructs a (somewhat)
leveled FHE and strengthens it to unbounded FHE
with a bootstrapping procedure. The procedure is es-
sentially a homomorphic evaluation of the decryption
circuit; it requires the ciphertexts of (projections of)
the secret key, which is called the bootstrapping key.
Since Gentry’s seminal work, all existing instantia-
tions have required the bootstrapping key to construct
unbounded FHE. Thus, we assume that unbounded
FHE schemes publish the bootstrapping key unless
otherwise stated.
If FHE uses the additional entity such as the boot-
strapping key, we can explicitly define it in the syntax
of FHE. We call the additional entity required for FHE
evaluation as the evaluation key (evk). We can define
the syntax of FHE scheme with the evaluation key by
redefining Gen and Eval as (pk, sk, evk) ← Gen(1
λ
)
and ct ← Eval(evk, C, (ct
i
)
i∈[l]
), respectively. The re-
quirements of the FHE with the evaluation key are
defined similarly to the FHE.
3 CCA/MALICIOUS SECURITY
OF FHE
It is known that (F)HE schemes cannot achieve CCA2
since (F)HE is malleable by definition. However,
CPA-security is often insufficient for applications. In
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
794

settings where an adversary is allowed to inject its
own maliciously crafted ciphertexts, i.e., when an
adversary is malicious, we often need the following:
1) Support with further cryptographic tools: For ex-
ample, noninteractive zero-knowledge proof (NIZK)
helps FHE construct a system that is secure against
malicious adversaries. This type of construction can
often be seen in the context of secure multiparty com-
putation (MPC) based on multikey FHE schemes, e.g.,
(Asharov et al., 2012; L
´
opez-Alt et al., 2012).
2) Assume that adversaries are all semihonest.
This setting is widely assumed in the homomorphic
evaluation works of complicated tasks such as ma-
chine learning, e.g., (Bost et al., 2015).
Nonetheless, it would be desirable to construct
CCA1/CCA2 secure FHE. Although CCA1 security
FHE is not impossible, it remains difficult to address
KDM security issues raised by the existence of the
bootstrapping key. We describe the exiting CCA1 se-
cure FHE approach in Sect. 3.1. Then, in Sect. 3.2, we
discuss the existing works to circumvent the inherent
CCA2 insecurity of FHE.
3.1 CCA1 Secure FHE
The CCA1 secure leveled-FHE was first proposed by
Loftus et al. (Loftus et al., 2012). However, this
method is constructed by embedding the FHE cipher-
text into that of a CCA2-secure PKE. Therefore, no
homomorphic operation can be performed on the em-
bedded ciphertexts. In addition, the scheme in (Lof-
tus et al., 2012) requires a “lattice-based knowledge
assumption”, which is a nonstandard assumption.
Canetti et al. (Canetti et al., 2017) solved this
problem by showing 2 types of CCA1 secure FHE
construction:
1. Strengthen CPA secure FHE and zero-knowledge
succinct noninteractive argument of knowledge
(zk-SNARK) (Bitansky et al., 2013; Bitansky
et al., 2017) via the Naor-Yung transformation
(Naor and Yung, 1990).
2. Adapt the generic transformation of (Boneh
et al., 2007) to the multikey ID-based FHE
(MK-IBFHE) scheme. Furthermore, Canetti et
al. (Canetti et al., 2017) showed the 2 types of
MK-IBFHE construction:
(a) Extend from leveled multikey FHE (Brakerski
et al., 2016).
(b) Subexponentially secure indistinguishability
obfuscation (iO) (Barak et al., 2001) and subex-
ponentially secure lossy encryption by adapting
the framework in (Canetti et al., 2015), which
construct an FHE from iO.
Note that CCA1 secure “unbounded” FHE can only be
constructed from 2-(b) in Canetti et al.’s work above,
which requires iO as a building block. iO is virtually
“crypto-complete”; Studies on iO applications, e.g.,
(Sahai and Waters, 2014; Garg et al., 2014; Boneh and
Zhandry, 2014), have shown that most cryptographic
applications can be constructed from iO (and one-way
functions). Conversely, the instantiation of iO is still
arguable, and Gay and Pass (Gay and Pass, 2021)
have recently shown
1
an iO candidate construction
from the circular assumption on GSW (Gentry et al.,
2013) FHE and the subexponential hardness assump-
tion of LWE (with subexponential modulus-to-noise
ratio)
Thus, the construction from simpler primitives
than iO is desirable. However, construction from mul-
tikey FHE cannot be “unbounded”. Since the lattice-
based unbounded FHE (e.g., (Gentry, 2009)) requires
the bootstrapping key, it is basically insecure against
CCA1 (the adversary can query the bootstrapping key
plaintext, which is (a part of) the secret key).
3.2 Towards “CCA2 Secure” FHE
In this section, we surveyed the works that aim to
circumvent the inherent CCA2 insecurity of FHE. We
focus on 2 aspects in this research area; Relaxation of
the CCA2 security model (in Sect. 3.2.1), and an FHE
variant called keyed-FHE (in Sect. 3.2.2).
3.2.1 CCA2 Relaxation
Recently, Akavia et al. (Akavia et al., 2022) defined a
new CCA2-like security model called funcCPA (in-
distinguishability against function-chosen-plaintext
attacks). The funcCPA attacker has adaptive ac-
cess to the “decrypt-function-encrypt” oracle. The
oracle query of the funcCPA-game, where C =
{C : M
l
→ M }
k∈N
is a function (circuit) fam-
ily. In the game, O
1
, O
2
= O((ct
i,k
)
k∈[l]
, C
i
) :=
Enc(pk, C
i
({Dec(sk, ct
i,k
)})), and the rest part of the
game is identical to IND-atk described in Fig. 1. They
showed that funcCPA is separated from (i.e., strictly
stronger than) CPA: There exists a nontrivial appli-
cation (e.g., client-aided outsourcing protocols) such
that CPA security is not sufficient but funcCPA se-
curity suffices. As a general result, (Akavia et al.,
2022, Thm. 7) showed that any CPA secure (F)HE
can be funcCPA secure if it is equipped with saniti-
zation algorithms for circuit privacy. The sanitization
1
Although Brakerski et al. (Brakerski et al., 2020) also
proposed a candidate construction of iO from a variant of
FHE, it requires a nonstandard random oracle model vari-
ant; the security proof was given only in a sketch
SoK: Towards CCA Secure Fully Homomorphic Encryption
795
Adversary Challenger
A
1
pk
←−−−−−
(pk, sk, evk) ← Gen(1
λ
)
D
∗
:= ∅, st
RevHK
:= ∅
C
i
← C
(ct
i,k
)
k∈[l]
,C
i
−−−−−→
⟲
←−−−−−
r
i
r
i
:= O((ct
i,k
)
k∈[l]
, C
i
)
m
0
,m
1
−−−−−→ b ← U({0, 1})
A
2
ct
∗
←−−−−−
ct
∗
← Enc(pk, m
b
)
D
∗
:= {ct
∗
}
C
j
← C
(ct
j,k
)
k∈[l]
,C
j
−−−−−→
⟲
←−−−−−
r
j
r
j
:= O((ct
j,k
)
k∈[l]
, C
j
)
b∈{0,1}
−−−−−→
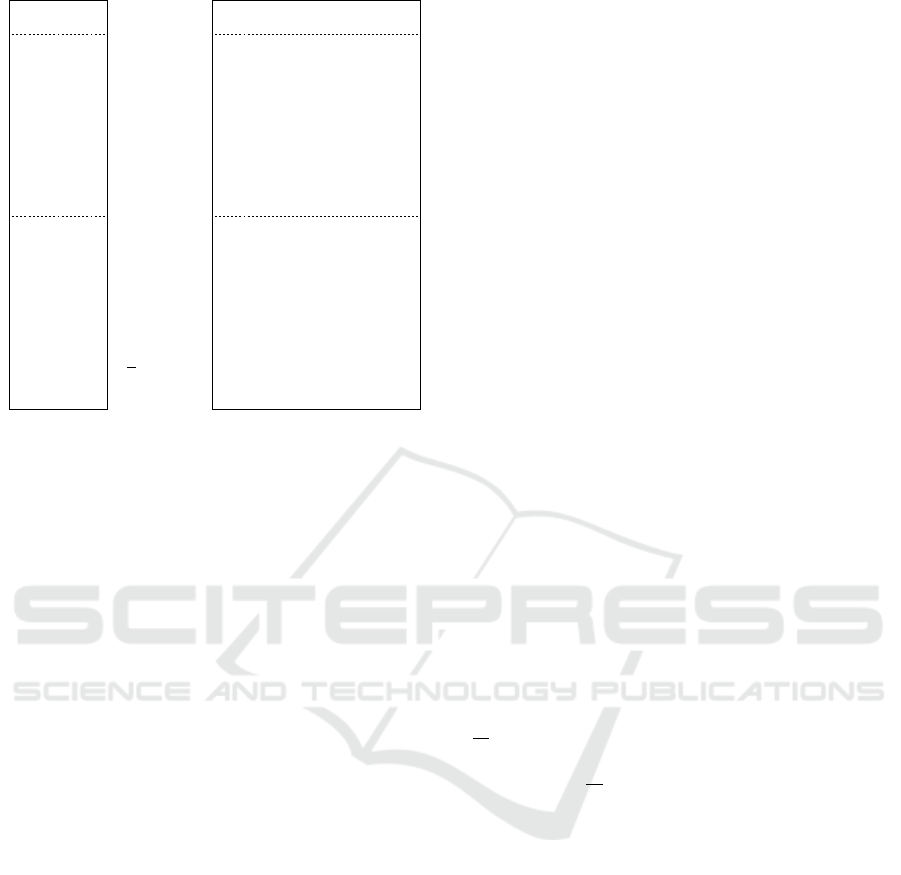
Figure 3: The KH-CCA-game (Emura et al., 2013). The
oracle O is defined in Def. 3.1.
algorithms are based on the garbled circuit (Gentry
et al., 2010; Ostrovsky et al., 2014), or bootstrap-
ping (Ducas and Stehl
´
e, 2016). Note that the garbled
circuit based sanitization is not efficient since super-
polynomial noise flooding is needed, and (Ducas and
Stehl
´
e, 2016) is not applicable to leveled FHE (with-
out bootstrapping). Interestingly, (Bourse et al., 2016)
showed that (slightly modified) GSW FHE is circuit-
private by nature, without bootstrapping. In addition,
(Akavia et al., 2022, Thm. 11) shows that the leveled
FHE schemes of BV (Brakerski and Vaikuntanathan,
2011), BGV (Brakerski et al., 2012) and BFV (Brak-
erski, 2012; Fan and Vercauteren, 2012) achieve
(leveled-) funcCPA security with a slight modifica-
tion of evaluation key generation. More generally,
the above holds for every leveled FHE scheme whose
evaluation key (or keyswitching key) is generated in-
dependently from the level secret key (i.e., generated
dependently from the sk of different levels). As noted
in (Chillotti et al., 2017), some leveled FHE schemes
(Benarroch et al., 2017) generate the evaluation key
(a.k.a., key switching key) dependent on the secret
key of the same level. Thus, these schemes do not di-
rectly achieve funcCPA security without sanitization
algorithms.
3.2.2 Keyed-(F)HE
Emura et al. (Emura et al., 2013) proposed the keyed
(partially) homomorphic PKE scheme, and showed
that CCA2-like security, which is KH-CCA secu-
rity, and the homomorphic property coexist in sit-
uations in which the user(s) who can perform ho-
momorphic operations should be controlled. Lai et
al. (Lai et al., 2016) proposed a CCA2 secure lev-
eled keyed-FHE from (a variant of) IBFHE and signa-
ture schemes. However, they constructed the IBFHE
from iO, which is a “costly” cryptographic applica-
tion (as mentioned in Sect. 3.1). Recently, Sato,
Emura and Takayasu (Sato et al., 2022) have shown
the construction of CCA2 secure leveled keyed-FHE
without relying on iO. Their paradigm is different
from that of Lai et al.. They constructed a CCA2
secure leveled keyed-FHE scheme from a CCA1 se-
cure (leveled) FHE scheme and a strong dual-system
simulation-sound NIZK (strong DSS-NIZK). Canetti
et al. showed 3 methods to construct CCA1 secure
FHE scheme, Items 1, 2a and 2b listed in Sect. 3.1.
The (Sato et al., 2022) requires Item 1, the construc-
tion from CPA secure FHE and zk-SNARK via the
Naor-Yung transformation because the public verifia-
bility of ciphertexts is needed.
The syntax of keyed-FHE is the same as the FHE
with a evaluation key defined in Sect. 2.3, but the
evaluation key of keyed-FHE is a private entity, while
the evaluation key of FHE is usually in public. We
show in Fig. 3 the KH-CCA game, and the oracle O is
defined as follows:
Def. 3.1. The oracle O of the KH-CCA game consists
of the three oracles defined as follows: The homo-
morphic evaluation key reveal oracle RevHK(): Upon
request, this oracle outputs evk and set st
RevHK
:= ⊥.
The evaluation oracle Eval(evk, ·, ·): If RevHK has
already been queried before, i.e., if st
RevHK
= ⊥, then
this oracle is not available. Otherwise, this ora-
cle responds to a query (ct
i
)
i∈[l]
with the result of
ct ← Eval(evk, (ct
i
)
i∈[l]
). In addition, if ct
i
∈ D
∗
for some i ∈ [l], then the oracle updates the list by
D
∗
:= D
∗
∪ {ct}. (Thus, D
∗
is a list of ciphertexts
that are dependent on the challenge ciphertext ct
∗
).
The decryption oracle Dec(sk, ·): This oracle is not
available if A has queried to RevHK and A has ob-
tained the challenge ciphertext ct
∗
; i.e., st
RevHK
:= ⊥
and D
∗
̸= ∅. Otherwise, this oracle responds to a
query ct with the result of Dec(sk, ct) only if ct ̸∈ D
∗
(returns ⊥ otherwise).
The basic concept of keyed FHE is to control who
is allowed to perform the homomorphic operation.
The adversary who has evk is not allowed to query
on Dec oracle (and Eval oracle, albeit may not be
needed). In the setting homomorphic evaluation is
allowed in public (st
RevHK
:= ⊥ by default), which
would be the most common setting in the context of
(F)HE, KH-CCA is almost equivalent to CPA. When
the homomorphic evaluation is controlled, which is
the setting of greater concern, the adversary is al-
lowed to query arbitrary evaluation, but all the evalua-
tion outputs dependent on the challenge ciphertext ct
∗
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
796

Table 1: Summery of our survey. The symbol “∅” means
impossibility.
leveled-FHE
evk is KDM evk is not KDM
CPA
e.g., (Chillotti
et al., 2017)
e.g., (Brakerski
and
Vaikuntanathan,
2011)
funcCPA
(Bourse et al.,
2016)
e.g., (Brakerski
and
Vaikuntanathan,
2011)
CCA1
∅ (query on evk)
(Canetti et al.,
2017)
KH-CCA
NA (evk is private) (Lai et al., 2016)
CCA2
∅ (malleable) ∅ (malleable)
FHE
from LWE from iO
CPA
e.g., (Gentry,
2009)
(Canetti et al.,
2015)
funcCPA
(Ducas and Stehl
´
e,
2016)
(Ostrovsky et al.,
2014)
CCA1
∅ (query on bk)
(Canetti et al.,
2017)
KH-CCA
(Sato et al., 2022) (Lai et al., 2016)
CCA2
∅ (malleable) ∅ (malleable)
are recorded in the list D
∗
, and queries on Dec(sk, ct)
are aborted if ct ∈ D
∗
. In other words, the mal-
leability on the challenge ciphertext is controlled and
monitored by the challenger.
4 SUMMARY
We summarize this survey in Tab. 1, and explain it in
this section.
We can categorize the leveled FHE as 2 types in
terms that the evk is level-independent, (Brakerski
and Vaikuntanathan, 2011; Brakerski et al., 2012;
Brakerski, 2012; Fan and Vercauteren, 2012) or not
(Benarroch et al., 2017; Chillotti et al., 2017), as
described in Sect. 3.2.1. The unbounded-FHE can be
categorized as the standard FHE realized by (Gentry,
2009) and the construction from iO (Canetti et al.,
2015).
Any CPA FHE can achieve funcCPA (Akavia
et al., 2022) by adapting the sanitization algorithms.
The standard FHE with a bootstrapping algorithm can
be sanitized by (Ducas and Stehl
´
e, 2016), and garbled
circuit can sanitize any FHE, e.g., (Ostrovsky et al.,
2014). (Bourse et al., 2016) showed that (slightly
modified) GSW FHE is circuit-private, and (Akavia
et al., 2022) shows that the level-independent leveled
FHE schemes (Brakerski and Vaikuntanathan, 2011;
Brakerski et al., 2012; Brakerski, 2012; Fan and Ver-
cauteren, 2012) are (leveled-)funcCPA secure by na-
ture.
CCA1 cannot be achieved if the scheme publishes
the KDM ciphertext, namely, evk or bk since the
CCA1 attacker simply queries the plaintext of the
KDM ciphertext. Canetti et al. (Canetti et al., 2017)
showed a CCA1 secure (level-independent) leveled
FHE and an unbounded FHE (relying on iO), as we
described in Sect. 3.1.
While CCA2 is impossible by definition of FHE,
the construction of KH-CCA secure (leveled / un-
bounded) keyed-FHE system was first shown (Lai
et al., 2016). The keyed-FHE defines evk (bk) as
a private entity that is not accessed by adversaries,
and thus, evk is not queried to the decryption oracle.
In addition, KH-CCA is achievable (F)HE in spite
of the malleability, since homomorphically evaluated
ciphertexts that depend on the challenge ciphertext
are recorded and not allowed to be queried to the
decryption oracle. While the construction of (Lai
et al., 2016) relies on iO, (Sato et al., 2022) showed a
construction without iO.
REFERENCES
Akavia, A., Gentry, C., Halevi, S., and Vald, M. (2022).
Achievable CCA2 relaxation for homomorphic en-
cryption. In Kiltz, E. and Vaikuntanathan, V., editors,
TCC 2022, pages 70–99. Springer Nature Switzer-
land.
Asharov, G., Jain, A., L
´
opez-Alt, A., Tromer, E., Vaikun-
tanathan, V., and Wichs, D. (2012). Multiparty com-
putation with low communication, computation and
interaction via threshold FHE. In Pointcheval, D.
and Johansson, T., editors, EUROCRYPT 2012, pages
483–501. Springer.
Barak, B., Goldreich, O., Impagliazzo, R., Rudich, S., Sa-
hai, A., Vadhan, S., and Yang, K. (2001). On the
(im)possibility of obfuscating programs. In Kilian, J.,
editor, CRYPTO 2001, pages 1–18. Springer.
Benarroch, D., Brakerski, Z., and Lepoint, T. (2017). Fhe
over the integers: Decomposed and batched in the
post-quantum regime. In Fehr, S., editor, PKC 2017,
pages 271–301. Springer.
Bitansky, N., Canetti, R., Chiesa, A., Goldwasser, S., Lin,
H., Rubinstein, A., and Tromer, E. (2017). The hunt-
ing of the snark. Journal of Cryptology, 30(4):989–
1066.
Bitansky, N., Canetti, R., Chiesa, A., and Tromer, E. (2013).
Recursive composition and bootstrapping for snarks
SoK: Towards CCA Secure Fully Homomorphic Encryption
797

and proof-carrying data. STOC ’13, page 111–120.
Association for Computing Machinery.
Boneh, D., Canetti, R., Halevi, S., and Katz, J. (2007).
Chosen-ciphertext security from identity-based en-
cryption. SIAM Journal on Computing, 36(5):1301–
1328.
Boneh, D. and Zhandry, M. (2014). Multiparty key ex-
change, efficient traitor tracing, and more from in-
distinguishability obfuscation. In Garay, J. A. and
Gennaro, R., editors, CRYPTO 2014, pages 480–499.
Springer.
Bost, R., Popa, R. A., Tu, S., and Goldwasser, S. (2015).
Machine learning classification over encrypted data.
In NDSS Symposium 2015.
Bourse, F., Del Pino, R., Minelli, M., and Wee, H. (2016).
FHE circuit privacy almost for free. In Robshaw, M.
and Katz, J., editors, CRYPTO 2016, pages 62–89.
Springer.
Brakerski, Z. (2012). Fully homomorphic encryption with-
out modulus switching from classical gapsvp. In
Safavi-Naini, R. and Canetti, R., editors, CRYPTO
2012, pages 868–886. Springer.
Brakerski, Z., Cash, D., Tsabary, R., and Wee, H. (2016).
Targeted homomorphic attribute-based encryption. In
Hirt, M. and Smith, A., editors, TCC 2016, pages 330–
360. Springer.
Brakerski, Z., D
¨
ottling, N., Garg, S., and Malavolta, G.
(2020). Candidate iO from homomorphic encryption
schemes. In Canteaut, A. and Ishai, Y., editors, EU-
ROCRYPT 2020, pages 79–109. Springer.
Brakerski, Z., Gentry, C., and Vaikuntanathan, V. (2012).
(Leveled) fully homomorphic encryption without
bootstrapping. In ITCS 2012, pages 309–325. Associ-
ation for Computing Machinery.
Brakerski, Z. and Vaikuntanathan, V. (2011). Fully ho-
momorphic encryption from Ring-LWE and security
for key dependent messages. In Rogaway, P., editor,
CRYPTO 2011, pages 505–524. Springer.
Canetti, R., Lin, H., Tessaro, S., and Vaikuntanathan, V.
(2015). Obfuscation of probabilistic circuits and ap-
plications. In Dodis, Y. and Nielsen, J. B., editors,
TCC 2015, pages 468–497. Springer.
Canetti, R., Raghuraman, S., Richelson, S., and Vaikun-
tanathan, V. (2017). Chosen-ciphertext secure fully
homomorphic encryption. In Fehr, S., editor, PKC
2017, pages 213–240. Springer.
Chillotti, I., Gama, N., Georgieva, M., and Izabach
`
ene, M.
(2017). Faster packed homomorphic operations and
efficient circuit bootstrapping for TFHE. In Takagi, T.
and Peyrin, T., editors, ASIACRYPT 2017, pages 377–
408. Springer International Publishing.
Ducas, L. and Stehl
´
e, D. (2016). Sanitization of FHE ci-
phertexts. In Fischlin, M. and Coron, J.-S., editors,
EUROCRYPT 2016, pages 294–310.
Emura, K., Hanaoka, G., Ohtake, G., Matsuda, T., and
Yamada, S. (2013). Chosen ciphertext secure keyed-
homomorphic public-key encryption. In Kurosawa,
K. and Hanaoka, G., editors, PKC 2013, pages 32–50.
Springer.
Fan, J. and Vercauteren, F. (2012). Somewhat practical fully
homomorphic encryption. Cryptology ePrint Archive,
Paper 2012/144.
Fauzi, P., Hovd, M. N., and Raddum, H. (2022). On the
IND-CCA1 security of FHE schemes. Cryptography,
6(1).
Garg, S., Gentry, C., Halevi, S., and Raykova, M. (2014).
Two-round secure mpc from indistinguishability ob-
fuscation. In Lindell, Y., editor, TCC 2014, pages 74–
94. Springer.
Gay, R. and Pass, R. (2021). Indistinguishability ob-
fuscation from circular security. STOC 2021, page
736–749. Association for Computing Machinery.
Gentry, C. (2009). Fully homomorphic encryption using
ideal lattices. In STOC 2009, pages 169–178. Associ-
ation for Computing Machinery.
Gentry, C., Halevi, S., and Vaikuntanathan, V. (2010). i-
hop homomorphic encryption and rerandomizable yao
circuits. In Rabin, T., editor, CRYPTO 2010, pages
155–172. Springer.
Gentry, C., Sahai, A., and Waters, B. (2013). Homomorphic
encryption from learning with errors: Conceptually-
simpler, asymptotically-faster, attribute-based. In
Canetti, R. and Garay, J. A., editors, CRYPTO 2013,
pages 75–92. Springer.
Lai, J., Deng, R. H., Ma, C., Sakurai, K., and Weng, J.
(2016). Cca-secure keyed-fully homomorphic encryp-
tion. In Cheng, C.-M., Chung, K.-M., Persiano, G.,
and Yang, B.-Y., editors, PKC 2016, pages 70–98.
Springer.
Loftus, J., May, A., Smart, N. P., and Vercauteren, F. (2012).
On CCA-secure somewhat homomorphic encryption.
In Miri, A. and Vaudenay, S., editors, SAC 2012, pages
55–72. Springer.
L
´
opez-Alt, A., Tromer, E., and Vaikuntanathan, V. (2012).
On-the-fly multiparty computation on the cloud via
multikey fully homomorphic encryption. STOC 2012,
page 1219–1234. Association for Computing Machin-
ery.
Naor, M. and Yung, M. (1990). Public-key cryptosys-
tems provably secure against chosen ciphertext at-
tacks. STOC ’90, page 427–437. Association for
Computing Machinery.
Ostrovsky, R., Paskin-Cherniavsky, A., and Paskin-
Cherniavsky, B. (2014). Maliciously circuit-private
fhe. In Garay, J. A. and Gennaro, R., editors, CRYPTO
2014, pages 536–553. Springer.
Sahai, A. and Waters, B. (2014). How to use indistinguisha-
bility obfuscation: Deniable encryption, and more.
STOC ’14, page 475–484. Association for Computing
Machinery.
Sato, S., Emura, K., and Takayasu, A. (2022). Keyed-fully
homomorphic encryption without indistinguishability
obfuscation. In Ateniese, G. and Venturi, D., editors,
ACNS 2022, pages 3–23. Springer.
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
798
