
Semi-Active Damping Control of Vehicles Based on Negative Stiffness
Suspensions
Zhijie Li and Shaoping Shen
*
Department of Automation, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian, China
Keywords: Suspension System, Damping Control Algorithm, Matlab/Simulink.
Abstract: In order to design a suspension system with better ride comfort, the concept of negative stiffness is
introduced into the suspension system by analyzing the functional characteristics of elastic elements, and the
damping control algorithm is designed according to the functional characteristics of the spring suspension,
simulated and analyzed using Matlab/Simulink tools, and the results are compared with the passive
suspension, negative stiffness passive suspension and skyhook damping semi-active control suspension. The
results show that the new proposed algorithm combined with the negative stiffness suspension can
effectively improve the vehicle ride comfort.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a product of the civilization of our time, the
number of automobiles has been increasing day by
day since its creation in the late 19th century.
According to the website of the Chinese Ministry of
Public Security, the number of cars and motor
vehicles in China has also been gradually increasing
in recent years. In modern society, the car is not only
a means of travel, but also a way of daily life in
pursuit of a higher quality of life and better sensory
enjoyment. Therefore, improving the comfort and
safety of cars has become one of the important goals
of car design in modern society (Zhang, 2021).
As one of the most important parts of a car, the
suspension connects the body to the axle, and it is
not only the medium for transmitting all the forces
and moments between the wheels and the body, but
also plays an important role in cushioning and
suppressing the shock and vibration caused by the
unevenness of the road. Therefore, a well-designed
suspension can effectively improve the ride comfort
of the car (Olugbade,2021). Scholars at home and
abroad have focused more on the fault tolerance
capability of the strategy in the study of semi-active
suspension control strategy, while less attention has
been paid to the improvement of the overall
combined performance of the suspension control
strategy and the suspension. In this paper, based on
the previous research, we propose a negative
stiffness semi-active suspension damping algorithm
in combination with the vehicle suspension
performance.
2 DESIGN OF NEGATIVE
STIFFNESS SUSPENSION
The analysis of the spring characteristics of the
vehicle suspension (Zhang, 2017) shows that the
deflection of the vehicle suspension spring has two
parts: one is the static deflection, which is mainly
caused by the vehicle itself and the vehicle load, and
the other is the dynamic deflection, which is mainly
caused by the vibration. The main function of the
static deflection is to support the vehicle itself and its
load, and the main function of the dynamic
deflection is to transmit the vibration of the unsprung
part to the whole vehicle body. The expectation is
that the vibration of the unsprung part will be
reduced in the process of transferring it to the
vehicle body, which requires that the spring stiffness
of the unsprung part be as small as possible, because
the smaller the spring stiffness, the more the
vibration energy will be reduced. Such a spring
structure can be designed with the stiffness
characteristics shown in Figure 1. This ensures that
the spring has a small (or even negative) stiffness
(Shahadat, 2010) in the vibration region, while still
having a large stiffness coefficient to carry the
overall vehicle load. The spring stiffness
characteristics can be obtained by connecting a
spring with negative stiffness characteristics in
parallel with the normal spring operating at the
balance point, and the positive and negative stiffness
characteristics of the spring are shown in Figure 2.
126
Li, Z. and Shen, S.
Semi-Active Damping Control of Vehicles Based on Negative Stiffness Suspensions.
DOI: 10.5220/0012150800003562
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Data Processing, Control and Simulation (ICDPCS 2023), pages 126-132
ISBN: 978-989-758-675-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
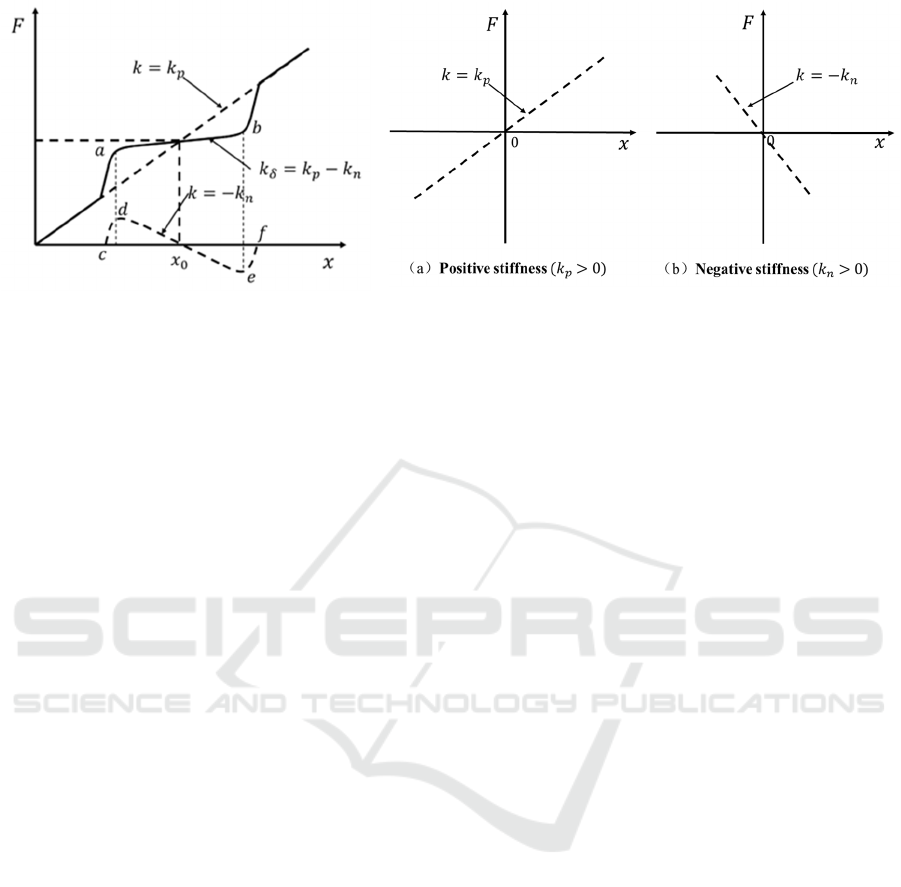
Figure 1: Negative stiffness characteristics of the
suspension concept.
Figure 2: Spring positive and negative stiffness characteristics.
When the incremental deformation of the elastic
element after the force is in the same direction as the
incremental load, the stiffness is positive and the
elastic element is said to have positive stiffness
characteristics, as shown in Figure 2(a); on the
contrary, when the incremental deformation of the
elastic element after the force is in the opposite
direction of the incremental load, the elastic element
is said to have negative stiffness characteristics, as
shown in Figure 2(b). A spring element with a small
range of negative stiffness characteristics can be
connected in parallel with a spring element with
positive stiffness characteristics at the vibration
balance point, allowing the suspension system to
have a small range of negative stiffness
characteristics at the vibration balance point. A steel
plate spring in parallel with a membrane air spring
gives us the desired negative spring stiffness
characteristics, with a local negative stiffness
characteristic at the design point and a load-
deflection curve roughly as shown in Figure 3. In
order to facilitate the analysis of the suspension
vertical dynamics, we established the two-degree-of-
freedom quarter-vehicle suspension model in Figure
4.
According to Newton's second law we can
obtain the following set of kinetic equations:
0
0
()() 0
()()() 0
ss s u s u switchs
uu su su tur switchs
mx g x x c x x c x
mx gx x c x x k x x c x
+−+ −+ =
−−− −+ −− =
(1)
Where 𝒎
𝒔
and 𝑚
are the spring loaded mass
and unsprung mass, respectively; 𝑥
and 𝑥
are the
spring loaded displacement and unsprung
displacement, respectively;
t
k
is the tire vertical
stiffness;
0
c
is the damper damping coefficient;
switch
c
is the variable switching control damping;
r
x
is the displacement excitation of the road surface
to the wheels;
()gx
is the restoring force of the
suspension system with negative stiffness
characteristics, and the expression can be fitted
according to the experimental simulation results
(preconceived).
3 DESIGN OF DAMPING
CONTROL ALGORITHM
3.1 Skyhook Control
The skyhook damper control algorithm was first
proposed by Karnopp in the United States (Karnopp,
1974), using an imaginary dampener connected with
the skyhook damper to suppress the vibration of the
body. The principle is to design and install an ideal
skyhook damper between the body and the sky, with
the sky remaining absolutely stationary. The ideal
skyhook damper can suppress the vertical motion of
the body, thus making the vehicle more stable and
improving the comfort of the ride and smoothness of
the vehicle during the driving process.
Semi-Active Damping Control of Vehicles Based on Negative Stiffness Suspensions
127
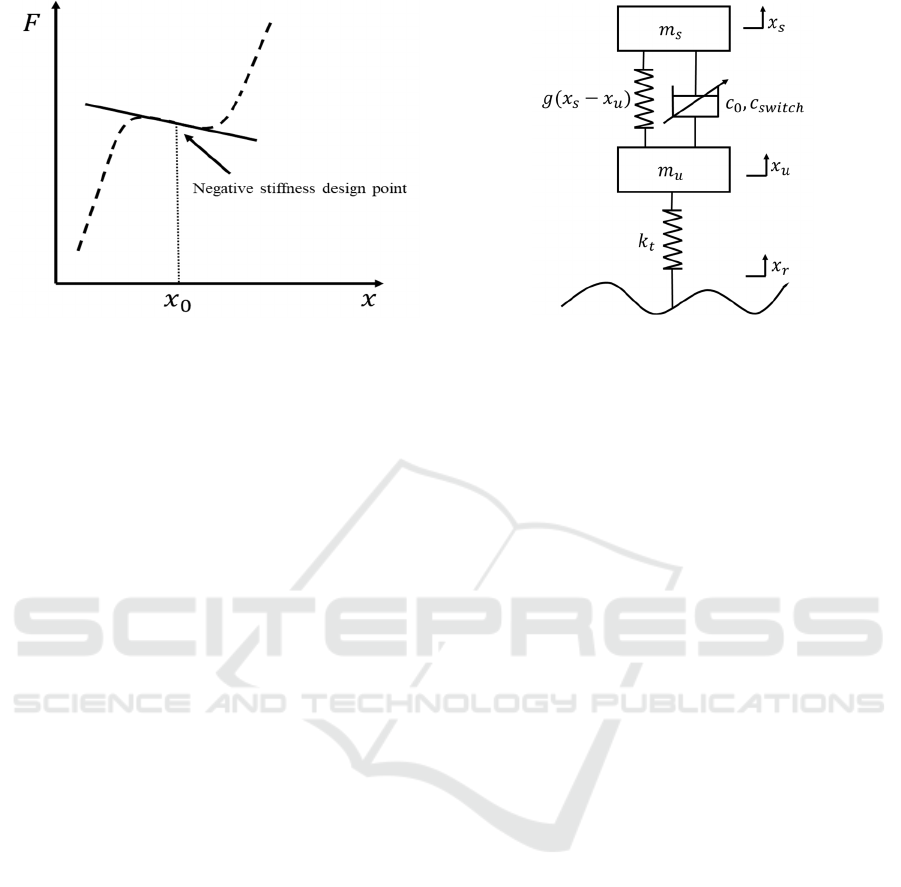
Figure 3: Spring design load-deflection curve. Figure 4: Vehicle suspension model.
Figure 5 shows the quarter vehicle suspension
dynamics model with ideal skyhook damper
damping control. where
s
m
and
u
m
are the spring
loaded mass and unsprung mass, respectively; 𝑥
and
u
x
are the spring loaded displacement and unsprung
displacement, respectively; 𝑘
and 𝑘
are suspension
stiffness and tire vertical stiffness, respectively;
s
c
is the damper damping coefficient; 𝑐
is the
skyhook damper damping coefficient; and 𝑥
is the
displacement excitation of the road surface to the
wheel. The kinetic equation can be expressed as
()() 0
()()()0
ss s s u s s u skys
uu s s u s s u t u r
mx k x x c x x c x
mx k x x c x x k x x
+−+−+=
−−−−+−=
(2)
In practical applications where the vehicle
cannot exert this ideal force, a controllable actuator
is generally used in the system to simulate the
skyhook damper control force. The actuation rules
for the skyhook damper damping coefficient
s
ky
c
are developed by measuring the relative velocity of
motion of the spring loaded and unsprung masses,
and the rules are as follows:
max
min
, ( ) 0
, ( ) 0
ss u
sky
ss u
cxxx
c
cxxx
−≥
=
−<
(3)
Where, 𝑐
and
min
c
represent the maximum and
minimum damping coefficients that skyhook
dampers can produce, respectively.
3.2 Improved Skyhook Control
According to the mechanical properties of the
damper, we can know that the damping force is
always in the opposite direction of its relative motion
speed and proportional to its size. The main role of
the dampers in the suspension is to absorb energy to
reduce the relative speed displacement changes
between the body and the wheels, thus playing a role
in energy consumption and attenuation of vibration.
(Chen, 2010) In the process of evaluating the ride
comfort and smoothness of the vehicle, we pay more
attention to the magnitude of the vertical
displacement, vertical velocity and vertical
acceleration of the spring-loaded part of the vehicle.
Skyhook damping control is designed to install an
ideal skyhook damper between the body and the sky,
which is essentially achieved by suppressing the
vertical velocity of the vehicle body. It is based on
the relationship between the car body vertical speed
and the suspension speed relative to the car body
speed to act. Since it takes some time for the
suspension speed to change with respect to the
vehicle speed, this can make the damping action
behavior lag in time, which will lead to the method
not better improve the ride comfort.
In this paper, the main purpose is to improve
the ride comfort, and the improved canopy damping
control algorithm is proposed for the negative
stiffness suspension model mentioned in the
previous paper. The damping adjustment is based on
different speed relationship, so as to achieve the
effect of suppressing the vehicle vibration and
improving the vehicle ride comfort. Figure 6 shows
the relationship between the body vertical velocity
and the suspension vertical velocity.
ICDPCS 2023 - The International Conference on Data Processing, Control and Simulation
128
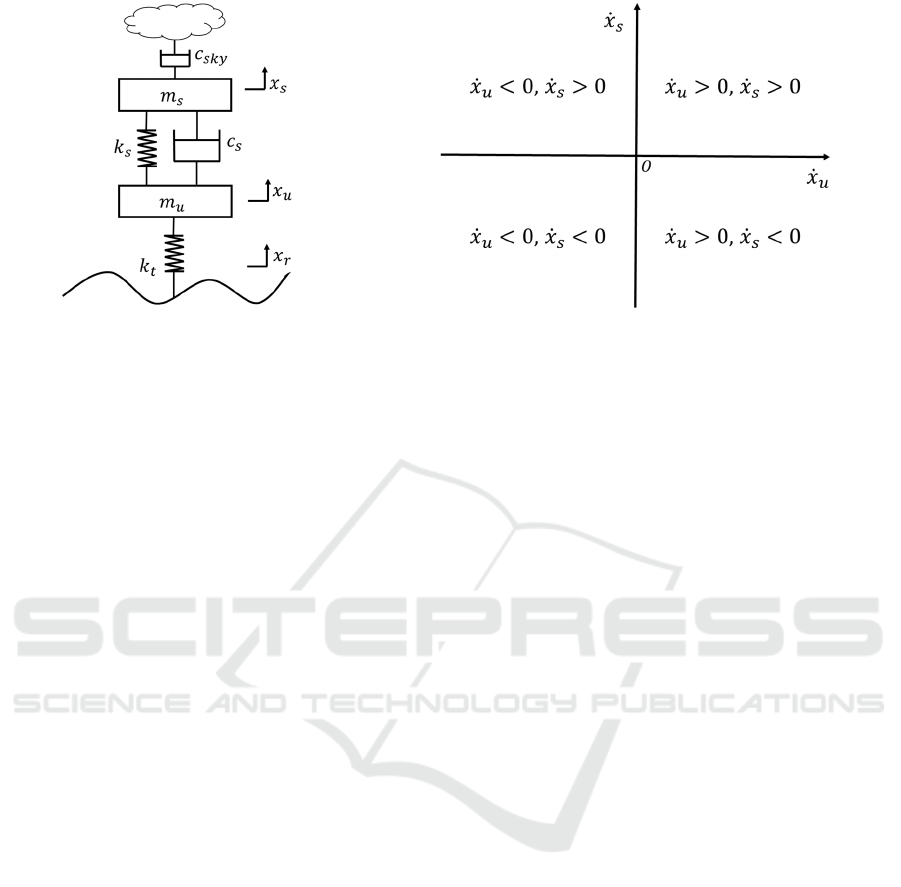
Figure 5: Vehicle suspension model.
Figure 6: The relationship between the action of parameters
u
x
and
s
x
.
We can discuss in two cases: the first case is
when the spring-loaded velocity 𝑥
and the unsprung
velocity 𝑥
are in the same direction (quadrant I and
III in Fig. 6), at this time the car body and the
suspension show the tendency to move in the same
direction, which we can understand as encountering
the convex block road or concave block road, since
there is already a negative stiffness characteristic
restoring force to prompt the suspension to act after
the disturbance, considering that the restoring force
will increase the dynamic travel of the suspension,
the speed change difference between the suspension
and the body is reduced by increasing the coefficient
of the damper, so that the vibration transmitted by
the suspension to the body can be reduced, which
can directly reduce the speed change of the body and
the travel of the body. The second case is when the
spring-loaded velocity 𝑥
is opposite to the unsprung
velocity 𝑥
(quadrant II and IV in Figure 6), when
the car body and the suspension show a tendency to
move in the opposite direction, which can be
interpreted as the back-range condition when
encountering a bumpy road or a concave road, and
the difference in velocity between the suspension
and the car body is reduced by reducing the damper
coefficient. The speed change difference between the
suspension and the car body is reduced, so that the
vibration of the car body can be reduced when the
suspension returns to its original state, which can
also directly reduce the speed change of the car
body. Considering the simplicity of the algorithm,
we attribute the case of the presence of 0 to the first
case. According to the above discussion, the
expression of the damping coefficient in the
improved skyhook control algorithm is:
max
min
, 0
, 0
su
sky
su
cxx
c
cxx
≥
=
<
(4)
Bringing equation (4) into equation (1), we can
obtain a dynamics expression for the application of
the improved damping control strategy on a negative
stiffness suspension, and we call it new negative
stiffness improved damping control strategy.
4 NEGATIVE STIFFNESS
SEMI-ACTIVE SUSPENSION
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
In order to analyze the effectiveness of the algorithm
improved in this paper on the role of the designed
negative stiffness suspension, this paper uses the
more widely used passive suspension, skyhook semi-
active control suspension as a comparison, while for
better quantitative analysis, we add the negative
stiffness passive suspension as a comparison. The
body vibration displacement, body vibration velocity
and body vibration acceleration are used as
indicators for time domain analysis.
4.1 Random Pavement Excitation
Response
Random pavement is the closest model to the real
pavement, and the response analysis under random
pavement excitation is an important method to
comprehensively examine the overall performance
of the suspension. (Hongbin, 2011) We use the
random pavement excitation curve fitted by the finite
bandwidth white noise as the input of the simulated
pavement, as shown in Figure 7, and the time
domain curves of each index for different control
methods of different suspensions under the random
pavement excitation are shown in Figures 8-10.
Semi-Active Damping Control of Vehicles Based on Negative Stiffness Suspensions
129
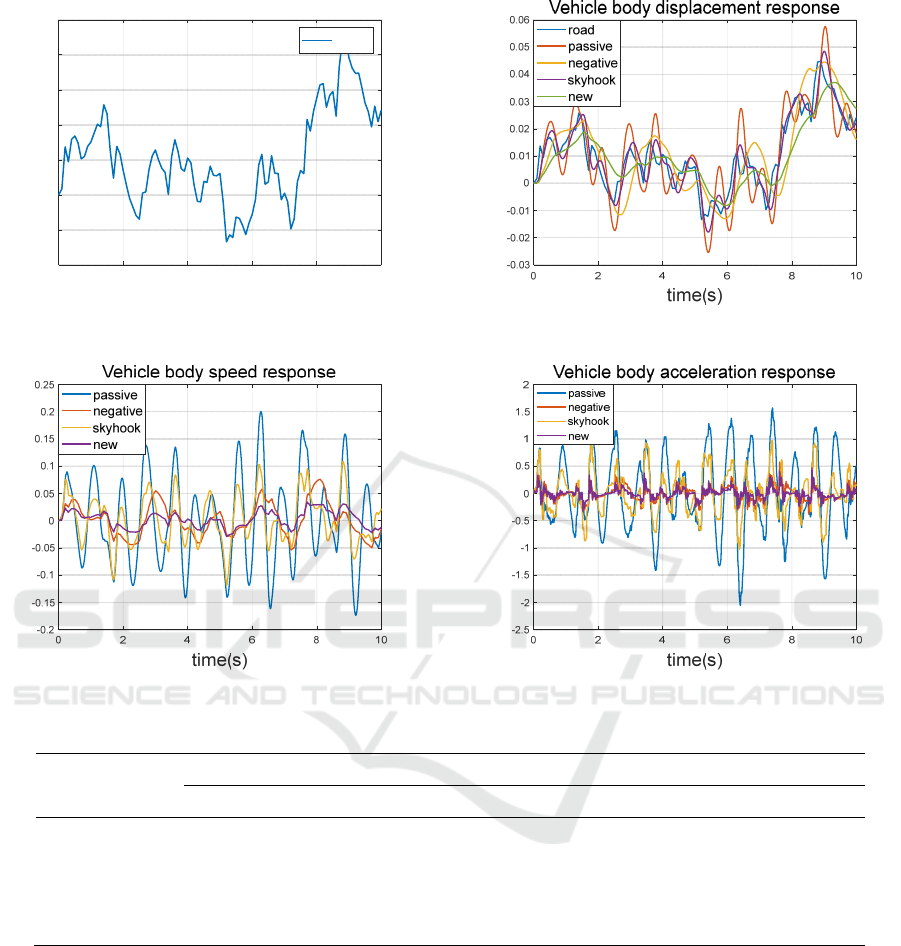
Figure 7: C-class pavement model. Figure 8: Vehicle body displacement response.
Figure 9: Vehicle body speed response. Figure 10: Vehicle body acceleration response
Table 1: Calculation results of suspension indexes.
Algorithm
Amplitude(m) Velocity(m s
-1
) Acceleration(m s
-2
)
RMS Improve RMS Improve RMS Improve
Passive 0.0154
——
0.0851
——
0.7157
——
Negative 0.0158 -2.60% 0.0303 64.39% 0.1534 78.57%
Skyhook 0.0137 11.04% 0.0538 36.78% 0.4194 41.40%
New 0.011 28.57% 0.0157 81.55% 0.0942 86.84%
As can be seen from the figure, the improved
damping control strategy combined with the negative
stiffness suspension can effectively attenuate the
body vibration amplitude, while the speed and
acceleration of the body vibration are also
effectively suppressed. In order to be able to
quantitatively analyze, we calculate the root mean
square (RMS) values of body vibration amplitude
response, body speed response and body acceleration
response indexes and the calculation results of
optimization degree are shown in Table 1.
According to the data analysis in the table, we
can know that different suspension control methods
have different effects on body vibration amplitude,
body speed and body acceleration suppression. In
terms of body vibration amplitude suppression,
compared with the passive suspension, the negative
stiffness suspension has a slight deterioration of
2.60%, the skyhook semi-active control suspension
has an 11.04% improvement, and the new improved
damping control negative stiffness suspension has a
28.57% improvement. In terms of body speed
suppression, compared to the passive suspension,
0246810
time/s
-0.02
-0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
Amplitude/m
C-class pavement model
road
Xs(m)
dXs(m/s)
ddXs(m/s2)
ICDPCS 2023 - The International Conference on Data Processing, Control and Simulation
130
there is a 64.39% improvement for the negative
stiffness suspension, a 36.78% improvement for the
skyhook semi-active control suspension, and an
81.55% improvement for the new improved damping
control negative stiffness suspension. In terms of
body acceleration suppression, compared to the
passive suspension, the negative stiffness suspension
has a 78.57% improvement, the skyhook semi-active
control suspension has a 41.40% improvement, and
the new improved damping control negative stiffness
suspension has an 86.84% improvement. It can be
seen that our proposed new improved damping
controlled negative stiffness suspension system has
some or greater improvement compared to other
suspension systems under random road excitation.
4.2 Impact Response of Bumpy
Pavement
Bump pavement is usually used for suspension
impact tests, which mainly simulate road conditions
such as speed bumps or potholes on the road. (Khot,
2017) We use the following equation to simulate the
clod pavement excitation.
000
1
[1 cos( ( ) )] ,
()
2
0 ,
r
A
tt t tt T
Zt
other
ωπ
+−−≤≤+
=
(5)
Where 𝐴 is the peak height of the bump
pavement, 𝑡
is the start time of the bump pavement
(s), and
T
is the sine wave period (s), which is the
duration of the bump pavement. The excitation
curves are shown in Fig. 11, and the time domain
curves of each index for different control methods of
different suspensions under bump pavement
excitation are shown in Figs. 12-14.
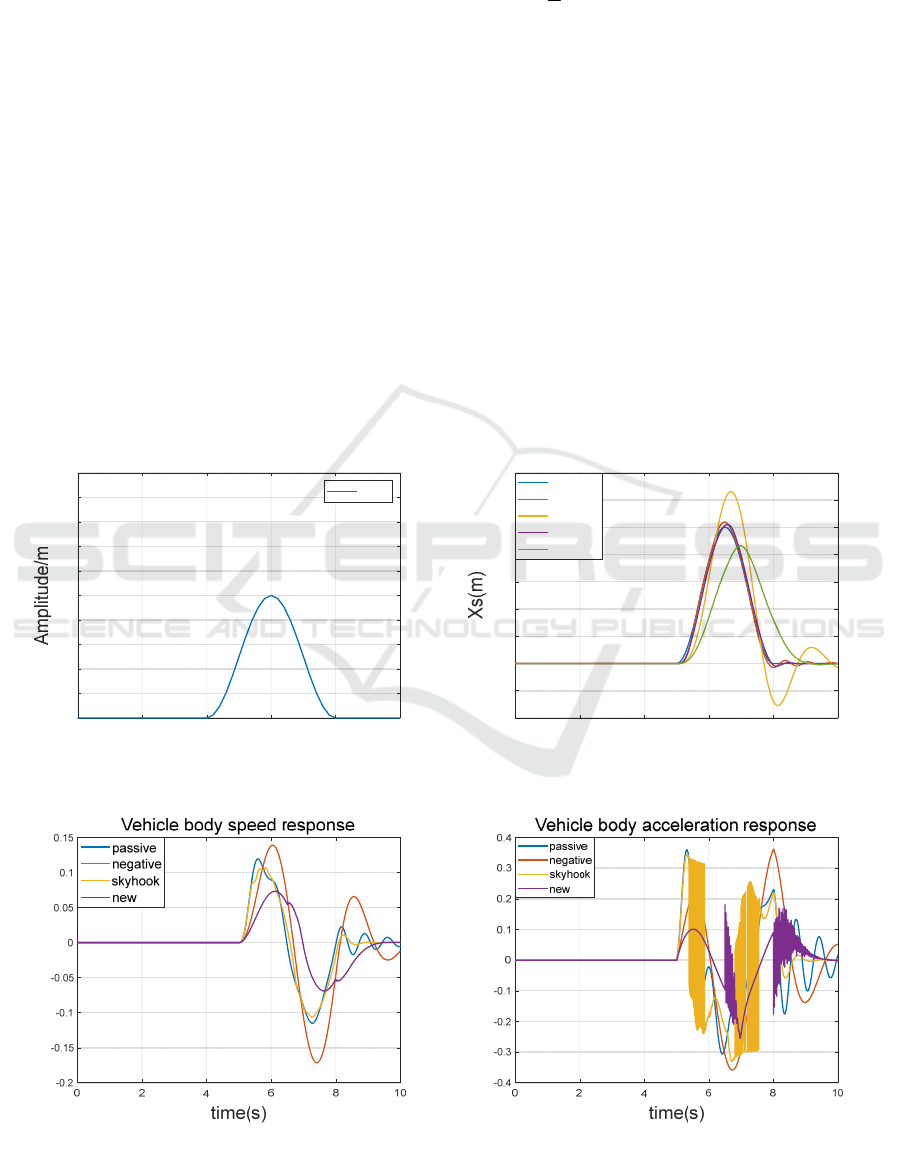
As can be seen from the figure, under the action
of bump road excitation, improved damping control
strategy combined with negative stiffness suspension
has good performance relative to passive suspension,
skyhook semi-active suspension and negative
stiffness passive suspension in terms of attenuating
the vibration amplitude of the body and the vibration
speed of the body. However, at this time in terms of.
Figure 11: Bump pavement model. Figure 12: Vehicle body displacement response.
Fi
g
ure 13: Vehicle bod
y
s
p
eed res
p
onse. Fi
g
ure 14: Vehicle bod
y
acceleration res
p
onse.
0246810
time/s
0
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.1
0.12
0.14
0.16
0.18
0.2
Bump pavement model
road
0246810
time
(
s
)
-0.04
-0.02
0
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.1
0.12
0.14
Vehicle body displacement response
road
passive
negative
skyhook
new
dXs(m/s)
ddXs(m/s2)
Semi-Active Damping Control of Vehicles Based on Negative Stiffness Suspensions
131

body acceleration there will be high-frequency jitter
vibration phenomenon, due to the high frequency,
the vibration can consume most of the energy after it
is transmitted to the human body through the seat,
the follow-up will be dedicated to the study. This
shows that the combination of improved damping
control strategy and negative stiffness suspension
system can provide better ride comfort and driving
smoothness under the road conditions through the
bumpy road
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, with the main purpose of improving
vehicle ride comfort, the concept of negative
stiffness is introduced into the suspension system by
analyzing the functional characteristics of elastic
elements, and the damping control algorithm is
designed according to the functional characteristics
of the spring suspension, and the following
conclusions are obtained after simulation and
analysis:
The new improved damping control negative
stiffness suspension has superior vibration
suppression performance compared to other
suspension systems on normal random road surfaces,
effectively reducing the root mean square value of
vehicle amplitude and significantly improving the
comfort of the vehicle ride.
When the new improved damping control
negative stiffness suspension passes through the
bump road surface such as the acceleration belt or
the pit, the vehicle body vibration amplitude is also
obviously smaller than other suspensions, and its
callback time is longer, which can better reduce the
vibration energy of vehicle body vibration and
improve the ride comfort.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research is supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation (NNSF) of China under Grants
61333008, 61603320, 61733017, 61673327 and
Xiamen Key Lab. Of Big Data Intelligent Analysis
and Decision.
REFERENCES
Zhang Y, Wang P, editors. Study on the Ride Comfort of
the Rhombic Car. 2021 International Conference of
Social Computing and Digital Economy (ICSCDE);
2021 28-29 Aug. 2021.
Olugbade T, Cho Y, Morgan Z, Ghani MAE, Bianchi-
Berthouze N, editors. Toward Intelligent Car Comfort
Sensing: New Dataset and Analysis of Annotated
Physiological Metrics. 2021 9th International
Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent
Interaction (ACII); 2021 28 Sept.-1 Oct. 2021.
Zhang N, Zhang Y, Li X, Kan Z, editors. Simulation study
on vibration reduction characteristics of two-degree
of freedom suspension system in a quarter vehicle.
2017 IEEE 3rd Information Technology and
Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC);
2017 3-5 Oct. 2017.
Shahadat MMZ, Mizuno T, Ishino Y, Takasaki M, editors.
Active horizontal suspension system using negative
stiffness control. ICCAS 2010; 2010 27-30 Oct. 2010.
Karnopp DC, Crosby MJ, Harwood RA. Vibration Control
Using Semi-Active Force Generators. Journal of
Engineering for Industry. 1974;96:619-26.
Chen E, Si C, Liu J, editors. Experimental study of
Magneto-Rheological materials and its damper
dynamic characteristics. 2010 Sixth International
Conference on Natural Computation; 2010 10-12
Aug. 2010.
Hongbin R, Sizhong C, Zhicheng W, editors. Model of
excitation of random road profile in time domain for a
vehicle with four wheels. 2011 International
Conference on Mechatronic Science, Electric
Engineering and Computer (MEC); 2011 19-22 Aug.
2011.
Khot SM, Patil S, Bhaye NA, editors. Simulation study of
MR damper for bump road profile. 2017
International Conference on Nascent Technologies in
Engineering (ICNTE); 2017 27-28 Jan. 2017.
ICDPCS 2023 - The International Conference on Data Processing, Control and Simulation
132
