
Experimental Validation of an Actor-Critic Model Predictive Force
Controller for Robot-Environment Interaction Tasks
Alessandro Pozzi
1 a
, Luca Puricelli
1 b
, Vincenzo Petrone
2 c
, Enrico Ferrentino
2 d
,
Pasquale Chiacchio
2 e
, Francesco Braghin
1 f
and Loris Roveda
3 g
1
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Politecnico di Milano, 20133 Milano, Italy
2
Department of Computer Engineering, Electrical Engineering and Applied Mathematics (DIEM), University of Salerno,
84084 Fisciano, Italy
3
Istituto Dalle Molle di Studi sull’Intelligenza Artificiale (IDSIA), Scuola Universitaria Professionale della Svizzera
Italiana (SUPSI), Universit
`
a della Svizzera Italiana (USI), 6962 Lugano, Switzerland
Keywords:
Physical Robot-Environment Interaction, Artificial Neural Networks, Optimized Interaction Control,
Impedance Control.
Abstract:
In industrial settings, robots are typically employed to accurately track a reference force to exert on the sur-
rounding environment to complete interaction tasks. Interaction controllers are typically used to achieve this
goal. Still, they either require manual tuning, which demands a significant amount of time, or exact modeling
of the environment the robot will interact with, thus possibly failing during the actual application. A significant
advancement in this area would be a high-performance force controller that does not need operator calibration
and is quick to be deployed in any scenario. With this aim, this paper proposes an Actor-Critic Model Pre-
dictive Force Controller (ACMPFC), which outputs the optimal setpoint to follow in order to guarantee force
tracking, computed by continuously trained neural networks. This strategy is an extension of a reinforcement
learning-based one, born in the context of human-robot collaboration, suitably adapted to robot-environment
interaction. We validate the ACMPFC in a real-case scenario featuring a Franka Emika Panda robot. Com-
pared with a base force controller and a learning-based approach, the proposed controller yields a reduction
of the force tracking MSE, attaining fast convergence: with respect to the base force controller, ACMPFC
reduces the MSE by a factor of 4.35.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Context
Most of nowadays manufacturing processes require
the massive employment of robots. Industries are in-
creasingly deploying manipulators in their production
processes to accomplish interaction tasks like polish-
ing, deburring, or assembly, with the aim of increas-
ing the levels of quality and customization of the de-
livered products.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6460-4669
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1736-0822
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4777-1761
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0768-8541
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3385-8866
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0476-4118
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4427-536X
Given the wide range of practical scenarios ma-
nipulators are employed in, robot control is one of
the major interests of the current scientific research,
especially in the industrial sector. In order to accom-
modate the propensity of manufacturers to improve
the cost, accuracy and throughput of their production
plants, in the last decades researchers have proposed
a vast spectrum of advantageous alternatives to classi-
cal control techniques like the well-known and largely
used linear PID controllers.
Optimal control is among the most consolidated
disciplines in advanced control, given its capability
of explicitly optimizing a certain objective function,
appropriately parameterized to maximize desired per-
formance indices, according to the task requirements.
Generally speaking, the fields of application of opti-
mal control frameworks cover a broad variety of sce-
narios: in principle, they are suitable to optimize any
394
Pozzi, A., Puricelli, L., Petrone, V., Ferrentino, E., Chiacchio, P., Braghin, F. and Roveda, L.
Experimental Validation of an Actor-Critic Model Predictive Force Controller for Robot-Environment Interaction Tasks.
DOI: 10.5220/0012160700003543
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2023) - Volume 1, pages 394-404
ISBN: 978-989-758-670-5; ISSN: 2184-2809
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

system formulated as a dynamic model, from simple
linear integrators (Preitl et al., 2006) to complex bio-
logical systems (Rigatos et al., 2016).
In robotics, one can benefit from optimizing nu-
merous quantities, e.g. trajectory tracking or joint vi-
bration (Mohd Hanif et al., 2021), to ensure accu-
racy in the performed task. This fundamental prob-
lem can be addressed with various approaches, such
as fractional-order control (Atas¸lar-Ayyıldız, 2023) or
double PID controllers to manage both motor position
and velocity (Ucgun et al., 2022). Another popular
technique in this context is fuzzy logic control, used
to improve the system stability, rise time, and steady-
state error (Obadina et al., 2022). Furthermore, ex-
ploiting optimization algorithms like spiral dynam-
ics algorithms (Kasruddin Nasir et al., 2021) and
particle swarm optimization (Sathish Kumar et al.,
2023), fuzzy logic controllers can be optimally tuned
to tackle trajectory and velocity tracking (Liu et al.,
2022).
1.2 Related Works
Trajectory-tracking accuracy is not the only perfor-
mance roboticists aim at optimizing: indeed, one fun-
damental feature to control, particularly in industrial
applications, is robot-environment interaction. To this
aim, interaction controllers are adopted to guaran-
tee stability and safety of the working environment
while accurately tracking precise force profiles, so as
to maximize the production quality.
Delivering the aforementioned characteristics is
the core objective of interaction controllers: the pi-
oneering work in (Mason, 1981) set off the divi-
sions of interaction control strategies into two macro-
categories: direct force control (Khatib, 1987) and
impedance control (Hogan, 1984), with the latter be-
ing typically preferred to the former for its capability
of inherently providing the manipulator with a com-
pliant behavior. Unfortunately, impedance controllers
lack accurate force tracking, a feature requiring, as
demonstrated in (Jung et al., 2004), a complete and
exact characterization of the environment, which is,
in general, a utopian intent to accomplish.
Therefore, impedance controllers with force-
tracking capabilities have been widely addressed
in literature with various strategies, from variable
impedance (Jung et al., 2004; Duan et al., 2018;
Roveda et al., 2020; Shu et al., 2021) or variable
stiffness (Lee and Buss, 2008) techniques to refer-
ence generation methods (Seraji and Colbaugh, 1997;
Liang et al., 2018; Roveda et al., 2020; Li et al.,
2023): recently, (Roveda and Piga, 2021) proposed
using a PI direct force control law as reference gener-
ator for an inner-loop impedance controller.
Learning methods are specifically suitable
for robot-environment interaction tasks: these
optimization-based approaches are indeed a powerful
tool to learn unmodeled effects that can influence
the dynamics of the controlled plant, overcoming
the main limitation of the abovementioned standard
techniques, i.e. the human effort in tuning the
additional parameters needed by the introduced
force control law. For this reason, researchers are
currently focusing on applying AI-based strategies
on impedance controllers for parameter tuning
(Zhang et al., 2021) or residual action computation
(Johannink et al., 2019; Puricelli et al., 2023). Other
common approaches are exploiting neural networks
to estimate the human-robot (Roveda et al., 2022)
or robot-environment (Peng et al., 2021) interaction
dynamics, or adopting reinforcement learning (Jo-
hannink et al., 2019; Roveda et al., 2022) to optimize
a certain task. Most of them are task-specific, e.g.
(Zhang et al., 2021), and require a considerable
amount of trials (or simulation-to-real transfer) to
reach optimal performance (Johannink et al., 2019).
1.3 Contribution
This paper proposes an Actor-Critic Model Predictive
Force Controller (ACMPFC) capable of providing
force-tracking capabilities to a low-level impedance
controller. The ACMPFC is composed of two con-
trol loops: the outer loop (which we also term high-
level controller) computes a setpoint for the inner-
loop impedance controller to accurately follow a de-
sired force reference.
The high-level control strategy makes use of a
Reinforcement Learning (RL) approach, previously
used for physical human-robot collaboration (Roveda
et al., 2022): the contribution of this work is hence
to demonstrate how such a technique can be adapted
for robot-environment interaction tasks, guaranteeing
precise force tracking. This feature is fundamental
in several practical use-cases, e.g. welding, cutting or
polishing, for which our method delivers better per-
formance compared to standard controllers.
We have discussed in Sections 1.1 and 1.2 that op-
timal control and learning control are paramount for
improving the performance of robot-environment in-
teraction controllers. Therefore, motivated by the dis-
cussed necessities, our method exploits both frame-
works. Indeed, the ACMPFC makes uses of Neural
Networks (NNs) for a two-fold objective: (i) form-
ing a Model Approximator (MA), used for estimating
the interaction dynamics, and (ii) developing an Ac-
tor-Critic strategy for the computation of the optimal
Experimental Validation of an Actor-Critic Model Predictive Force Controller for Robot-Environment Interaction Tasks
395

setpoint to track.
We show that ACMPFC can reduce the force-
tracking error when compared to both a general-
purpose PI Force Controller (PIFC) (Roveda and
Piga, 2021) and a different AI-based optimal con-
troller, known as ORACLE (Puricelli et al., 2023).
In particular, ACMPFC outperforms PIFC in terms of
tracking accuracy, and, at the same time, it overcomes
the main disadvantage of ORACLE, which is a con-
sistent time delay in exerting the desired force profile.
All the experiments are run on a real manipulator, i.e.
the Franka Emika’s Panda robot shown in Figure 1,
whose kinematic structure consists of 7 serial revo-
lute joints.
The remainder of this article is structured as fol-
lows. Section 2 elaborates on the design of the pro-
posed methodology, whereas Section 3 presents the
results obtained by its employment; Section 4 con-
cludes the paper, discussing on the attained achieve-
ments and briefly presenting possible future develop-
ments.
2 METHODOLOGY
The ACMPFC is a RL-based strategy that provides
enhanced force-tracking capabilities to an impedance
controller. Given a desired wrench to exert on the
environment, it provides the underlying impedance
controller, not able to follow the reference wrench
by itself, with the correct setpoint to track. The
whole architecture, illustrated in the diagram of Fig-
ure 2, consists of the following components: (i) an
inner-loop impedance controller, that ensures a sta-
ble compliant behavior with respect to the envi-
ronment; (ii) three Feed-Forward Neural Networks
(FFNNs) that, by cooperation, constitute the out-
er-loop controller, computing the optimal setpoint for
the low-level impedance controller; (iii) data stor-
age, including the trajectories to execute to train the
ACMPFC over the episodes. All these components
are described in detail in the next sections.
2.1 Impedance Controller
In order to be able to compare the ACMPFC with the
control architectures in (Roveda and Piga, 2021; Puri-
celli et al., 2023), it is necessary to adopt the same
low-level impedance controller. This inner-loop con-
troller imposes the desired compliance on the robot’s
end-effector (EE) while controlling a setpoint pose,
that will be provided in advance by the outer-loop ref-
erence generator.
A manipulator robot with n Degrees of Freedom
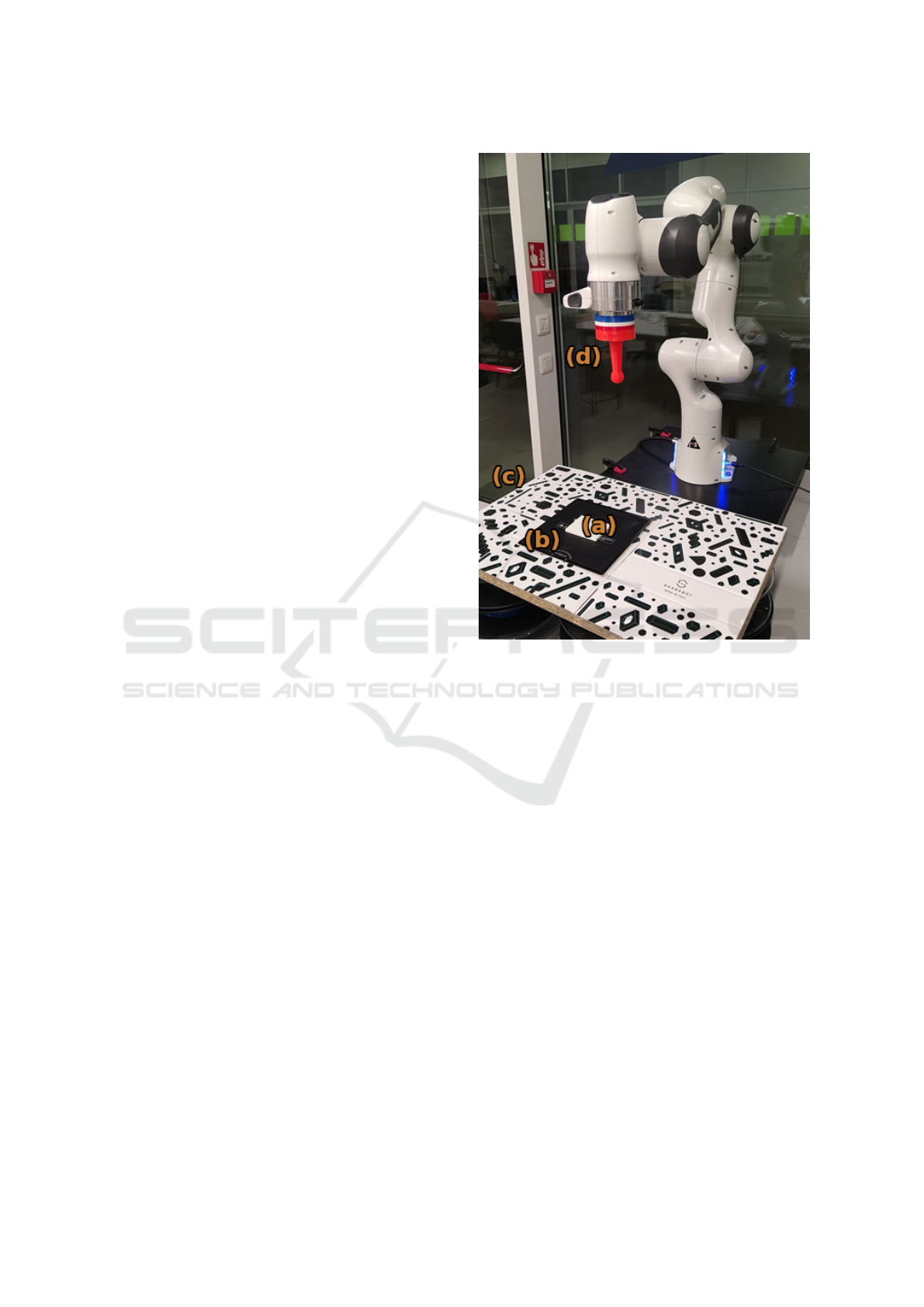
Figure 1: Real scenario testing bench. It features a Franka
Emika’s Panda robot coming into contact with the environ-
ment, represented by the white thin block (a) rigidly at-
tached to a larger surface (b) that slides over the plane (c).
This particular configuration reduces stick-slip effects dur-
ing the interaction. The 3D-printed spherical end-effector
(d) provides a small interaction surface with the material,
making it possible to model the contact with the environ-
ment as a spring in the exploration phase (i.e. the phase dur-
ing which the Actor’s bounds are computed, as mentioned
in Section 2.3.4).
(DOFs), performing an m-dimensional task, with m ≤
6 ≤ n, can be described by the following dynamic
model:
M
M
M(q
q
q)
¨
q
q
q +C
C
C(q
q
q,
˙
q
q
q)
˙
q
q
q + τ
τ
τ
f
(
˙
q
q
q) + g
g
g(q
q
q) = τ
τ
τ
c
− J
J
J
T
(q
q
q) f
f
f
e
,
where M
M
M(q
q
q) ∈ R
n×n
is the manipulator’s inertia ma-
trix, C
C
C(q
q
q,
˙
q
q
q) ∈ R
n×n
is the matrix accounting for the
Coriolis and centrifugal effects, τ
τ
τ
f
(
˙
q
q
q) ∈ R
n×1
ac-
counts for static and viscous friction, g
g
g(q
q
q) ∈ R
n×1
represents the torque exerted on the links by grav-
ity, τ
τ
τ
c
∈ R
n×1
indicates the impedance control ac-
tion, J
J
J(q
q
q) ∈ R
m×n
is the geometric Jacobian, f
f
f
e
∈
R
m×1
is the vector of wrenches exerted by the robot
end-effector (EE) on the environment. The vectors
q
q
q,
˙
q
q
q,
¨
q
q
q ∈ R
n×1
represent positions, velocities, and ac-
celerations of the manipulator’s joints, respectively.
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
396

RL data
storage
Model
Approximator
Critic
Bellman (2)
CEM
Actor
Environment
Robotic arm
Impedance
controller (1)
Force
controller
(Actor)
Reference
wrench and pose
s
s
s
r
k
,a
a
a
k
s
s
s
r
k+1
–
+
ˆ
s
s
s
r
k+1
MA error
ˆ
Q
Q
Q
k
–
ˆ
Q
Q
Q
k+1
Q
Q
Q
∗
k
+
Critic error
s
s
s
k
,a
a
a
k
s
s
s
k+1
,a
a
a
k+1
s
s
s
k+1
ˆ
Q
Q
Q
k+1
ˆ
s
s
s
r
k+1
...
ˆ
s
s
s
r
k+T
a
a
a
∗
k+1
−
+
ˆ
a
a
a
k+1
Actor error
f
f
f
r
s
s
s
s
s
s
r
s
s
s
a
a
a
Weigths
update
x
x
x
f
+
+
x
x
x
r
x
x
x
d
τ
τ
τ
c
Online block
Physical plant
Input block
Offline block
Figure 2: ACMPFC functioning scheme. The RL data storage includes the system’s states and actions over the execution of a
trajectory, and forwards them to the NNs for off-line training between consecutive episodes.
The impedance control law with robot dynam-
ics compensation can be written as (Formenti et al.,
2022):
τ
τ
τ
c
= J
J
J
T
(q
q
q) f
f
f
c
+C
C
C(q
q
q,
˙
q
q
q)
˙
q
q
q + g
g
g(q
q
q), (1)
with
f
f
f
c
=M
M
M
x
(q
q
q)
¨
x
x
x
d
− f
f
f
e
+
M
M
M
x
(q
q
q)M
M
M
−1
imp
( f
f
f
e
− K
K
K
imp
∆x
x
x − D
D
D
imp
∆
∆
∆
˙
x
x
x),
where M
M
M
x
(q
q
q) ≜
J
J
J
T
(q
q
q)
†
M
M
M(q
q
q)
J
J
J(q
q
q)
†
∈ R
m×m
is
the task-space inertia matrix, with (·)
†
indicating the
pseudo-inverse matrix. ∆x
x
x ≜ x
x
x
d
− x
x
x is the error be-
tween the desired EE pose x
x
x
d
and the actual pose
x
x
x. With m = 6, x
x
x = (x,y,z, φ,ϑ, ψ)
T
represents the
full robot EE pose, composed of position (x,y,z)
and orientation (φ,ϑ, ψ). ∆
˙
x
x
x ≜
˙
x
x
x
d
−
˙
x
x
x represents the
pose error derivative. M
M
M
imp
,D
D
D
imp
,K
K
K
imp
∈ R
m×m
are
the impedance control parameters (i.e., mass, damp-
ing, and stiffness diagonal matrices, respectively),
which can be tuned, in accordance to the rules in
(Roveda and Piga, 2021), to ensure a medium-soft
robot-environment interaction and a bandwidth of
2.5Hz. Typically, the coefficients of D
D
D
imp
are chosen
as d
imp,i
= 2ξ
i
p
m
imp,i
k
imp,i
, with ξ
i
being the damp-
ing ratio and i = 1,2,.. ., m is the axis index.
2.2 Control Architecture
The high-level controller relies on an Actor-Critic
structure, a RL technique consisting of an agent inter-
acting with an environment with the goal of optimiz-
ing the reward received by performing actions on it.
The system to be controlled is modeled as a Markov
Decision Process (MDP) (Bellman, 1958), i.e. it is
represented as a tuple ⟨S ,A,P,R,λ⟩, where S repre-
sents the finite set of the system’s states, A is the finite
set of actions the actor can execute, P(s
k+1
| s
k
,a
k
) is
the state transition probability matrix from state s
k
to
state s
k+1
by taking the action a
k
, R(s,a) = E [r | s,a]
is the reward function outputting the expectation of
the reward r obtained from the environment at state s
if the agent’s action is a, and λ ∈ [0; 1] is the discount
factor.
Depending on the environment configuration, the
task objective, and the semantics of the reward func-
tion, the optimization problem can be stated as either
maximization or minimization of the reward function.
In the latter case, the reward function can be inter-
preted, without loss of generality, as a cost function.
Henceforth, we will use the term “reward function”
for convenience.
As a RL algorithm, the ACMPFC’s goal is to find
the optimal control policy π
∗
(a | s), which optimizes
the cumulative reward, by continuously interacting
with the environment. The components of the Actor-
Critic strategy are (i) the Actor, i.e. the agent that ap-
plies actions on the environment, modifying its state
and receiving rewards; (ii) the Critic, i.e. the entity
that establishes the value of actions taken by the ac-
tor, given the predicted evolution of the system.
In our case, the system to be controlled is the
robot-environment physical plant: its state is defined
as s
s
s = (x
x
x,
˙
x
x
x, f
f
f
e
,∆
∆
∆ f
f
f ), while the action is the control
variable a
a
a = x
x
x
f
, whose tracking minimizes the force
error ∆ f
f
f ≜ f
f
f
r
− f
f
f
e
, where f
f
f
r
is the force reference
to exert on the environment, specified by the task re-
quirements.
Experimental Validation of an Actor-Critic Model Predictive Force Controller for Robot-Environment Interaction Tasks
397

In brief, the controller design is led by the follow-
ing optimization problem:
x
x
x
f
= argmin {R
R
R(∆
∆
∆
˜
f
f
f )},
where R
R
R(∆
∆
∆
˜
f
f
f ) is the reward function, which will be
formalized later. Note that its argument is the ex-
pected force error ∆
∆
∆
˜
f
f
f ≜ f
f
f
r
−
˜
f
f
f
e
, which depends on
the expected interaction force
˜
f
f
f
e
. The actual inter-
action force f
f
f
e
is unknown because it strictly de-
pends on the environment, and is known by the agent
through measurements only after the control action x
x
x
f
is applied and the next state is observed.
Here follows a brief explanation of the entities in-
volved in the ACMPFC; additional implementation
details, together with a proof of convergence of the
RL-based algorithm, can be found in (Roveda et al.,
2022).
2.2.1 Actor
The Actor computes the action
ˆ
a
a
a to be taken at state
s
s
s, with a FFNN approximating the optimal policy
π
∗
(a
a
a | s
s
s). By minimizing the MSE with respect to
the optimal action a
a
a
∗
, computed by the Critic via
the Cross-Entropy Method (which will be explained
next), the learning process will make the Actor’s ac-
tual policy
ˆ
π tend to the optimal policy π
∗
.
More specifically, the Actor’s NN is trained in
agreement with the following optimization problem:
min
θ
A
m
∑
i=0
a
a
a
∗
i
−
ˆ
a
a
a
i
θ
A
2
,
with the NN parameters θ
A
updated applying a
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) optimization.
2.2.2 Critic
The Critic assesses the value of the Actor’s policy by
approximating the action-value function (also called
Q-function) Q
π
(s,a), returning the value associated
with taking a particular action a in the state s, imple-
mented with a FFNN. Let
ˆ
Q
Q
Q
k
≜
ˆ
Q
Q
Q(s
s
s
k
,a
a
a
k
) be the out-
put of the Critic at time k, computing a different value
for each control direction. The Critic’s NN learning
goal is minimizing the MSE with respect to the op-
timal Q-value Q
Q
Q
∗
, computed according to Bellman’s
equation (Bellman, 1952):
Q
Q
Q
∗
k
= R
R
R
k
+ λ
ˆ
Q
Q
Q
k+1
, (2)
where Q
Q
Q
∗
k
≜ Q
Q
Q
∗
(s
s
s
k
,a
a
a
k
) and R
R
R
k
≜ R
R
R(s
s
s
k
,a
a
a
k
).
More formally, the minimization problem yield-
ing the Critic’s NN’s training is the following:
min
θ
C
m
∑
i=0
Q
Q
Q
∗
i
−
ˆ
Q
Q
Q
i
θ
C
2
,
with the NN parameters θ
C
updated applying a SGD
optimization.
It is now worth discussing how our architecture
compares to other common Actor-Critic structures,
i.e. DDPG (Lillicrap et al., 2015), SAC (Haarnoja
et al., 2018) and TD3 (Fujimoto et al., 2018). The
most immediate aspect to highlight is that our archi-
tecture foresees a single NN to implement the Critic,
whereas both SAC and TD3 require two Critic net-
works to explicitly leverage the problem of maxi-
mization bias, with the former employing an addi-
tional value network to compute the Q-value. On the
other hand, DDPG uses a single network, similarly
to our controller: the only difference is that DDPG
exploits two additional NNs, namely the target Ac-
tor and Critic networks, used to compute the target
Q-value Q
Q
Q
∗
needed to train the Critic, while in our ar-
chitecture it is computed with the Bellman equation
in (2).
2.2.3 Cross-Entropy Method
The Cross-Entropy Method (CEM) (de Boer et al.,
2005) computes the optimal action a
a
a
∗
so as to maxi-
mize the cumulative reward over a prediction horizon
T , computed by making inference on the Critic, in
fact implementing a Model Predictive Control (MPC)
strategy. The future states {s
s
s
i
}
k+T
i=k+1
are inferred from
the Model Approximator (MA).
The strategy of the algorithm is to sample the ac-
tion space, approximating the distributions of suitable
solutions, assumed to be, e.g., Gaussian. Sampling
from these distributions generates possible candidate
sequences of solutions. The distributions are itera-
tively updated on the basis of the best candidate se-
quences, i.e., in our case, the ones maximizing the cu-
mulative reward. As the algorithm progresses, the dis-
tributions become more and more refined, until con-
vergence to optimal solutions. The pseudo-code de-
scribing its implementation is given in Algorithm 1.
The reader should note that the CEM algorithm
overcomes the problem of overestimation bias, which
is one of the main issues with most Deep Actor-
Critic RL methods. Indeed, by randomly sampling
sequences of actions/states and updating the stochas-
tic distributions’ parameters according to the best se-
quences, the Actor is less influenced by the inherent
bias of explicitly selecting the action that optimizes
the Q-value computed by only one Critic.
2.2.4 Model Approximator
The Model Approximator estimates the robot-
environment system’s dynamics; thus, it considers the
reduced state s
s
s
r
≜ (x
x
x,
˙
x
x
x, f
f
f
e
) and its evolution over
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
398

Data: current state s
s
s
k
from the RL data
storage
Parameters: T , N
it
, N
samples
, N
elites
, α
Result: optimal control action a
a
a
∗
initialize the mean µ and the standard
deviation σ of the T stochastic distributions
{D
t
∼ N (µ
t
,σ
t
)}
T −1
t=0
;
for iter = 1,2,.. .,N
it
do
for j = 1, 2,.. ., N
samples
do
sample a random sequence of actions
{a
a
a
j
t
}
T −1
t=0
from D
t
;
predict the system evolution through
the MA: {s
s
s
j
t
}
T −1
t=1
, with s
s
s
j
0
:
= s
s
s
k
;
evaluate the cumulative reward as
r
j
=
∑
T −1
t=0
R
R
R
j
t
+
ˆ
Q
Q
Q
j
T −1
;
end
sort the sequences a
a
a
j
with respect to r
j
in
increasing order;
let a
a
a
elites
be the best N
elites
sequences;
for t = 0,1, ...,T − 1 do
compute mean µ
elites
t
and standard
deviation σ
elites
t
of a
a
a
elites
t
;
update µ
t
← (1 − α)µ
t
+ αµ
elites
t
;
update σ
t
← (1 − α)σ
t
+ ασ
elites
t
;
update D
t
with the new values of µ
t
and σ
t
;
end
end
Algorithm 1: Cross-Entropy Method (CEM).
time, as the state variable ∆
∆
∆ f
f
f is not related to its
actual dynamics. In particular, it embeds the transi-
tion of the system between two consecutive states, i.e.
ˆ
s
s
s
r
k+1
= s
s
s
r
k
+ δ
δ
δ
ˆ
s
s
s
s
s
s
r
k
,a
a
a
k
, under action a
a
a
k
, where δ
δ
δ
ˆ
s
s
s is
the MA’s output (Nagabandi et al., 2018), computed
by an ensemble of FFNNs (Chua et al., 2018) at each
time step k. It is exploited by the CEM to propagate
the system’s state over time, hence predicting its evo-
lution.
Thanks to the NN ensemble, the MA allows for
a data-efficient learning, as demonstrated in (Chua
et al., 2018). Opting for different architectures, e.g. a
single FFNN, would result in a less efficient training,
thus requiring either more data or a different learning
process, as in (Nagabandi et al., 2018).
The training procedure aims at minimizing the
MSE with respect to the actual state s
s
s
r
, recorded dur-
ing the execution of an episode, according to the fol-
lowing minimization problem:
min
θ
MA
m
∑
i=0
s
s
s
r
i
−
ˆ
s
s
s
r
i
θ
MA
2
,
with the NN parameters θ
MA
updated applying a SGD
optimization.
2.3 Learning Procedure
The control architecture described in Section 2.2
was originally developed and employed in the Q-
Learning-based Model Predictive Variable Impedance
Controller (QLMPVIC) (Roveda et al., 2022), instan-
tiated for a Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC) sce-
nario. Therein, an online learning strategy for the
NNs is implemented: the high-level control loop fre-
quency is set to 6 Hz and every 5 control steps, whose
data are collected in the buffer, the training is per-
formed and the networks’ weights are updated. With
respect to the work in (Roveda et al., 2022), several
modifications are needed to adapt the learning proce-
dure to a robot-environment scenario.
2.3.1 Offline Reinforcement Learning
The training of the NNs is performed offline, i.e.
between two consecutive episodes. This allows the
ACMPFC to work at 1 kHz since, as shown in Fig-
ure 2, during the online phase, the Actor’s weights
are fixed, and its NN is only used to infer the con-
trol action x
x
x
f
. During the episode execution, the sys-
tem’s states and the controller actions are stored in
the buffer, and used in the next episode. This modifi-
cation is crucial for the robot-environment interaction
problem, as the controller must work at the robot’s
control frequency in order to properly manage the in-
teraction forces.
2.3.2 Reward Function
In (Roveda et al., 2022), the objective is minimizing
the exerted wrench f
f
f
e
, so as to make the human in-
teraction as comfortable as possible. So, we intro-
duce a modification in the reward function in order to
properly pursue the objective of force tracking. In our
case, the reward function is hence the following:
R
R
R
k
= c
c
c
0
· | f
f
f
r
(k) − f
f
f
e
(k)| + c
c
c
1
· |x
x
x
f
(k) − x
x
x
f
(k − 1)|,
(3)
where the term | f
f
f
r
(k) − f
f
f
e
(k)| is needed for force
tracking purposes, whereas the term |x
x
x
f
(k) − x
x
x
f
(k −
1)| is needed to reduce overshoot or excessive varia-
tions of the desired set point x
x
x
f
, with operator ‘·’ indi-
cating the element-wise product between vectors. The
coefficients in c
c
c
0
and c
c
c
1
balance the trade-off between
these relative contributions and must be selected by
the user.
2.3.3 Impedance Control Setpoint
The hybrid force/position control law that generates
the setpoint for the impedance controller can be writ-
Experimental Validation of an Actor-Critic Model Predictive Force Controller for Robot-Environment Interaction Tasks
399

ten as follows:
x
x
x
d
= (I
I
I − Γ
Γ
Γ)x
x
x
r
+ Γ
Γ
Γx
x
x
f
,
where x
x
x
r
is the reference pose, I
I
I ∈ R
m×m
is the iden-
tity matrix, and, assuming the common case in which
m = 6, Γ
Γ
Γ ≜ diag
γ
x
,γ
y
,γ
z
,γ
φ
,γ
ϑ
,γ
ψ
is the task speci-
fication matrix (Khatib, 1987), with γ
i
= 1 if the i−th
direction is subject to force control, 0 otherwise.
2.3.4 Actor’s Action Space Bounds
Since the controller must always guarantee the safety
of both the robot structure and the working environ-
ment, the Actor’s control action must be limited to
a fixed range. The bounds of this range, as well as
the environment’s rest position x
x
x
e
, can be retrieved in
a preliminary phase, in which the ACMPFC is deac-
tivated, with only the impedance controller running.
During this phase, the robot slowly approaches the
environment, until a force threshold is registered. The
lower bound on x
x
x
f
is set to the position at which x
x
x
e
is
reached, while the upper bound is set to the position
at which the force threshold is measured.
2.3.5 Contact Position Information Embedment
The last modification applied to the Q-LMPVIC
comes consequently to the change of use case. In-
deed, a problem occurs when feeding the NNs with
the data as collected during training: x
x
x represents an
absolute pose, so if the position of the environment
changes, even slightly, from episode to episode, the
NNs are not able to account for it. Therefore, we pro-
cess the data before the training process, to make all
poses relative. Consider, for instance, the case where
the force reference has to be tracked along the z di-
rection. The resultant ∆z position that will be fed to
the NNs will be ∆z ≜ z − z
e
. Instead of feeding the
robot’s EE z coordinate directly, subtracting the envi-
ronment position z
e
allows making the NNs training
and execution independent of the contact position and
dealing only with penetrations.
3 RESULTS
We employ the proposed control approach on a real
scenario, after first testing it in simulation. The
real robot test is shown in the attached video
1
. The
GitHub source code
2
makes it possible, for interested
users, to reproduce our simulation and test it on new
trajectories.
1
https://youtu.be/7ysG4lz5lVY
2
https://github.com/unisa-acg/actor-critic-model-
predictive-force-controller
Table 1: Hyperparameters for ACMPFC NNs: depth indi-
cates the number of fully-connected layers, width indicates
the number of neurons per layer.
Parameter Actor Critic MA
Depth 2 2 3
Width 200 128 300
Learning rate 1e−4 1e−4 1e−3
Optimizer Adam Adam Adam
Loss function MSE MSE MSE
Dropout probability 0.1 0.1 0.2
Activation function ReLU ReLU ReLU
3.1 Task Setup and Materials
Both in simulation and real environments, the
ACMPFC strategy is tested on a Franka Emika’s
Panda robot, a 7-DOF robotic arm. This platform ex-
poses an interface to retrieve, via software, estima-
tions of f
f
f
e
from joint torque measurements. Alterna-
tively, one can use flange-mounted force/torque sen-
sors. The simulation tests are performed in MuJoCo
(Todorov et al., 2012) for a realistic representation of
the real-case scenario. The task consists of moving
the EE, with a fixed orientation, along a planar tra-
jectory, so as to exert a force normal (i.e. along the z
axis) to the xy plane, also termed contact surface, i.e.
Γ
Γ
Γ = diag (0,0,1, 0,0, 0).
Novel force control techniques are typically val-
idated by assessing their performance, in terms of
force-tracking error, against specific 1-dimensional
force profiles, e.g. constants (Seraji and Colbaugh,
1997; Jung et al., 2004; Liang et al., 2018; Roveda
et al., 2020; Li et al., 2023), step functions (Iskandar
et al., 2023), or sine waves with periods in the order
of seconds (Duan et al., 2018; Shu et al., 2021).
In our scenarios, the manipulator is asked to learn
to track a mixed force reference, consisting of three
subsequent sections: a ramp from 25 N to 35 N, a con-
stant at 35 N, and finally a sine wave, whose mean
value linearly decreases down to 15 N, of amplitude
8 N and frequency 1.5 Hz, chosen as in (Puricelli
et al., 2023) for a fair comparison.
The ACMPFC performances are placed in opposi-
tion to two other force control strategies, already com-
pared to each other in (Puricelli et al., 2023): one is
based on classical control theory, i.e. a Proportional-
Integral Force Controller (PIFC) (Roveda and Piga,
2021), the other is based on a pre-trained NNs ensem-
ble (ORACLE) (Puricelli et al., 2023). Both control
approaches are configured with the same parameters
as proposed in (Puricelli et al., 2023).
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
400
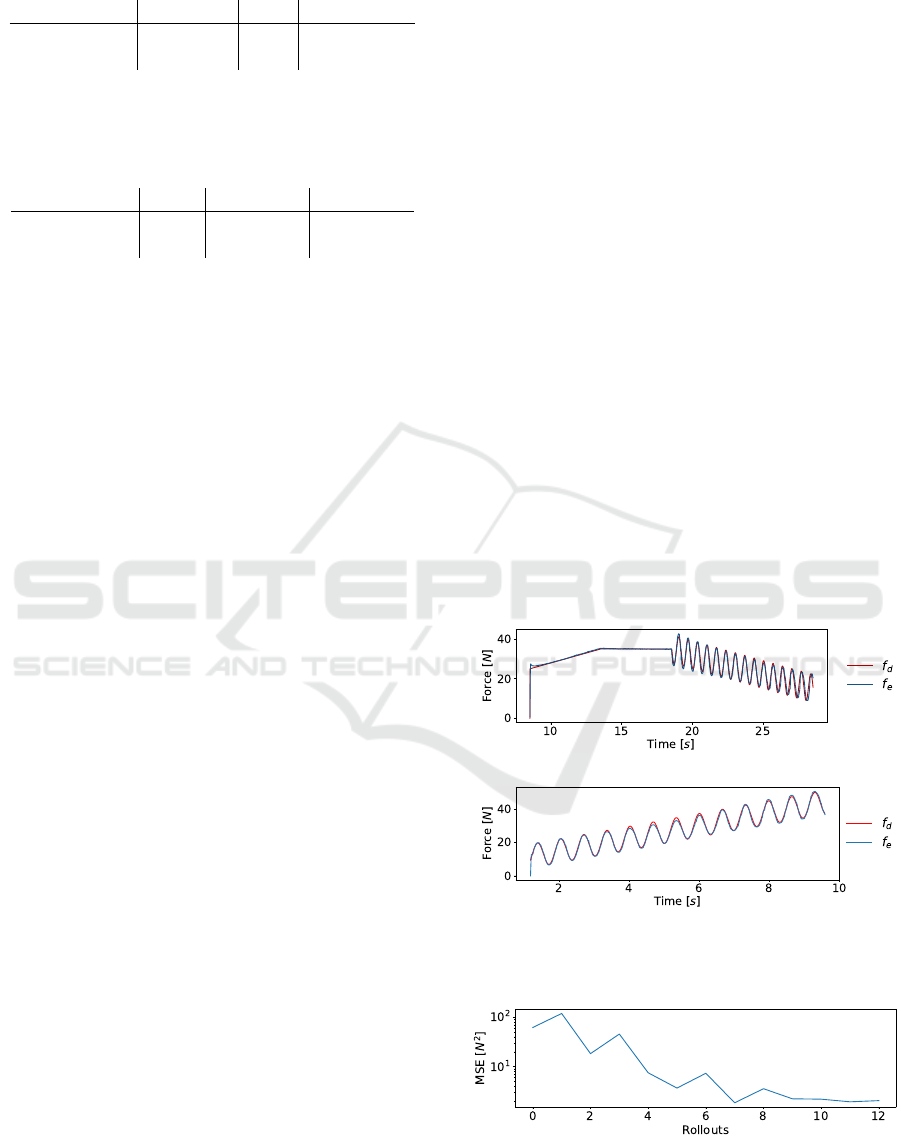
Table 2: Impedance control parameters along the z axis.
Environment M
imp
[kg] ξ K
imp
[N/m]
Simulated 8 1.42 12000
Real 10 1.42 10500
Table 3: MSE [N
2
] comparison between the PIFC (Roveda
and Piga, 2021), the ORACLE (Puricelli et al., 2023) and
the ACMPFC (ours), with force control active only along
the z axis.
Environment PIFC ORACLE ACMPFC
Simulated 8.16 1.55 3.07
Real 9.62 3.45 2.21
3.2 Implementation Setup
All the modules involved in the architecture shown
in Figure 2 interface with each other via ROS
(Robot Operating System) communication mecha-
nisms. They are developed in Python3, with the NNs
implemented through the PyTorch framework (Paszke
et al., 2019). The discount factor in (2) is set to
λ = 0.95, while the coefficients of the reward func-
tion (3) are chosen as c
0
= 1 and c
1
= 2. The param-
eters for the CEM are T = 5, N
it
= 3, N
samples
= 128,
N
elites
= 4, and α = 0.95 (see Algorithm 1).
As regards the NNs design, their hyperparameters
are listed in Table 1. In particular, the model approx-
imator column refers to the values of the 3 base esti-
mators of the ensemble. An exponential epoch-based
scheduler is applied to the learning rate to improve the
training speed.
The low-level impedance controller is tuned fol-
lowing the principles of (Roveda and Piga, 2021);
the resulting parameters are listed in Table 2, which
solely reports the gains for the z axis since it is the
only direction of interest for the polishing-like task
considered in this work.
3.3 Simulation Results
As mentioned in Section 3.1, the simulation setup is
set to mimic the real environment of Figure 1 ex-
ploiting the Robosuite framework (Zhu et al., 2020)
to control the virtual robot in the MuJoCo simula-
tor (Todorov et al., 2012). The manipulator is com-
manded via the control scheme of Figure 2, whose
control loop frequency is set at 1 kHz.
The robot, during the execution of a trajectory,
slowly approaches the table and, once the contact
is established, the high-level force control loop is
activated. The gains of the base PIFC are K
P
=
0.0008m/N and K
I
= 0.008 s m/N.
The simulation results are collected in Table 3:
after convergence, the ACMPFC strategy improves
the performances compared to the PIFC, while they
are slightly worse than ORACLE. The force-tracking
MSE = ( f
d
− f
e
)
2
is computed on the reference tra-
jectory described in Section 3.1.
As regards training and convergence, 10 episodes
are needed to reach a stable MSE in tracking. Each
reference trajectory takes 30 seconds and, between
episodes, the NNs training time takes, on average, ca.
60 seconds. These times are achieved on a configu-
ration composed of an i5-7300HQ CPU, GTX1050Ti
GPU (Mobile), and Ubuntu 20.04.
3.4 Experimental Results
In the real scenario, a thin block is placed onto a
larger and stiffer thin layer, sliding over the table, and
dragged by the robot during motion. Figure 1 dis-
plays the experimental configuration. The parame-
ters are the same as those in Section 3.2, while the
PIFC’s parameters are, as in (Puricelli et al., 2023),
K
P
= 0.001 m/N and K
I
= 0.008 s m/N.
As reported in Table 3, the real-world experiments
confirm a performance improvement for the force
profiles under test, plotted in Figure 3. In fact, once
convergence is reached (around the 10
th
episode, as
shown in Figure 4), the MSE obtained by the PIFC
(Roveda and Piga, 2021) is reduced by a factor of
4.35; also, compared to the ORACLE learning-based
(a) Training trajectory
(b) Test trajectory
Figure 3: ACMPFC force tracking along z direction in the
real scenario after convergence.
Figure 4: ACMPFC Mean Squared Error trend evolution
over the training episodes. Force tracking is active only
along the z direction. Convergence is reached after the 10
th
episode.
Experimental Validation of an Actor-Critic Model Predictive Force Controller for Robot-Environment Interaction Tasks
401
strategy (Puricelli et al., 2023), our ACMPFC further
reduces the MSE by a factor of 1.56.
It can be noticed that the MSE is high at the be-
ginning of the training process, since the Actor be-
haves almost randomly (in the limited action range,
as specified in Section 2.3.4), and decreases exponen-
tially as the rollouts progress, demonstrating the ef-
fectiveness of the Actor-Critic RL strategy. The evi-
dent non-monotonic trend might be avoided by low-
ering the NN’s learning rate; however, this would re-
quire more rollouts for convergence. Thus, the MSE
trend is justified by jumps in the action’s policy space
during the Actor’s training throughout the episodes.
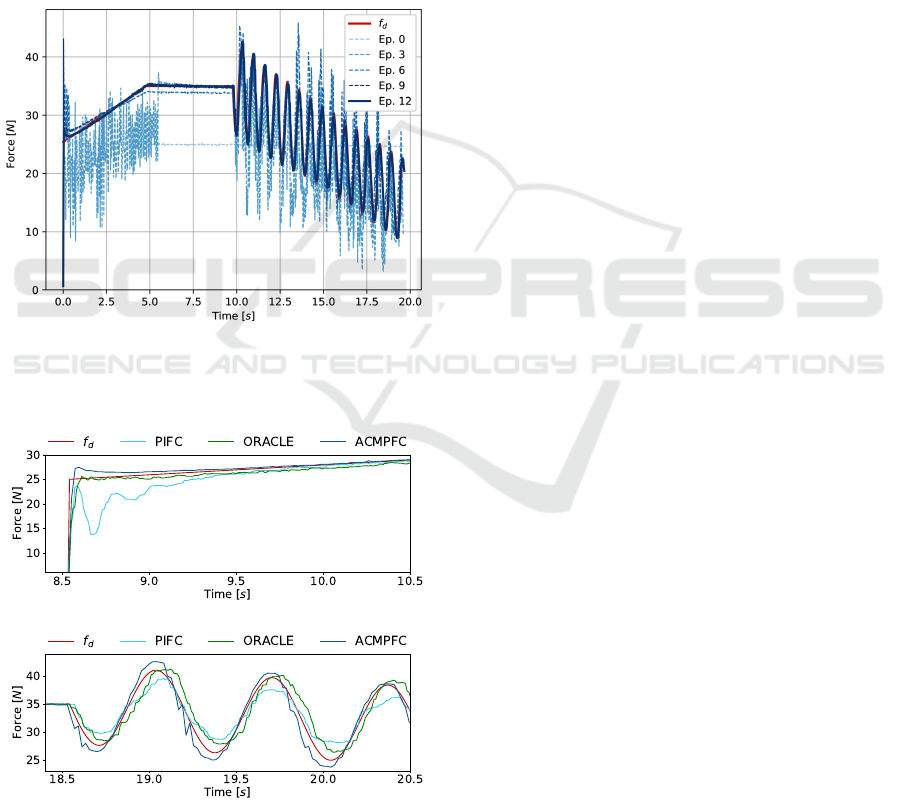
The effect of the convergent phenomenon can be bet-
Figure 5: Exerted force over the episodes: throughout the
rollouts, the actual force tends to the desired force, demon-
strating the convergence of the Actor’s policy to the optimal
one.
(a) Contact phase
(b) Sine wave
Figure 6: Force tracking at some critical points. Three
control strategies are compared: PIFC (Roveda and Piga,
2021), ORACLE (Puricelli et al., 2023), and ACMPFC
(ours).
ter visualized in Figure 5: it is immediate to deduce
that, as the rollouts advance, the exerted force profile
tends to the desired one, proving that the Actor’s pol-
icy converges to the optimal one.
Figure 6 shows the performance of the three dif-
ferent strategies at particular points of the trajectory.
The ACMPFC is able to track the reference, with
overshoots of ca. 2 N during the initial contact and
sine peaks. However, the ACMPFC strategy, com-
pared to ORACLE (Puricelli et al., 2023), does not
present any delay in tracking the desired force profile
(as evident from Figure 6b), thus its performances in
terms of MSE are in general better, as quantitatively
confirmed by the results in Table 3.
Finally, the fact that the system is capable of track-
ing force references accurately, by efficiently learn-
ing the interaction dynamics, is proven by asking the
robot to perform a validation trajectory, different than
the training one. The training trajectory is that of Fig-
ure 3a, while the system’s performance on the valida-
tion trajectory is reported in Figure 3b; in the latter,
MSE = 2.73 N
2
is achieved, which is comparable to
the result obtained on the former.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This work proposes an Actor-Critic Model-Predictive
Force Controller (ACMPFC), adapting and validat-
ing an already existing methodology (Roveda et al.,
2022) in a context of accurate force tracking, i.e. ex-
tending its scope from human-robot collaboration to
robot-environment interaction. The strategy is com-
posed of two control loops: a low-level Cartesian
impedance controller, and a high-level NN-based con-
troller, whose inference optimizes the impedance con-
troller’s setpoint, allowing for accurate force tracking
when performing a contact task in an unknown envi-
ronment.
The NNs constituting the high-level controller are
trained according to a RL-based approach. An Actor-
Critic learning strategy computes optimal actions by
making use of a model approximator, i.e. a NN en-
semble modeling the robot-environment interaction
dynamics.
The ACMPFC is tested both through MuJoCo
simulations and in a real scenario, proving capable
of overcoming the performance of a PI direct force
controller (Roveda and Piga, 2021) and the AI-based
ORACLE strategy (Puricelli et al., 2023), in terms
of force-tracking MSE, while achieving fast conver-
gence.
Future work could be devoted to the employment
of the proposed strategy in higher-dimensional tasks.
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
402

REFERENCES
Atas¸lar-Ayyıldız, B. (2023). Robust Trajectory Tracking
Control for Serial Robotic Manipulators Using Frac-
tional Order-Based PTID Controller. Fractal and
Fractional, 7(3):250.
Bellman, R. (1952). On the Theory of Dynamic Program-
ming. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sci-
ences, 38(8):716–719.
Bellman, R. (1958). Dynamic programming and stochastic
control processes. Information and Control, 1(3):228–
239.
Chua, K., Calandra, R., McAllister, R., and Levine, S.
(2018). Deep Reinforcement Learning in a Handful of
Trials using Probabilistic Dynamics Models. In Proc.
Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst., volume 31, pages
4754–4765.
de Boer, P.-T., Kroese, D. P., Mannor, S., and Rubin-
stein, R. Y. (2005). A Tutorial on the Cross-Entropy
Method. Annals of Operations Research, 134:19–67.
Duan, J., Gan, Y., Chen, M., and Dai, X. (2018). Adap-
tive variable impedance control for dynamic contact
force tracking in uncertain environment. Robot. Au-
ton. Syst., 102:54–65.
Formenti, A., Bucca, G., Shahid, A. A., Piga, D., and
Roveda, L. (2022). Improved impedance/admittance
switching controller for the interaction with a variable
stiffness environment. Complex Eng. Syst., 2(3):12.
Fujimoto, S., van Hoof, H., and Meger, D. (2018). Address-
ing Function Approximation Error in Actor-Critic
Methods. arXiv preprint.
Haarnoja, T., Zhou, A., Abbeel, P., and Levine, S.
(2018). Soft Actor-Critic: Off-Policy Maximum En-
tropy Deep Reinforcement Learning with a Stochastic
Actor. arXiv preprint.
Hogan, N. (1984). Impedance Control: An Approach to
Manipulation. In Proc. Amer. Contrl. Conf., pages
304–313, San Diego, CA, USA.
Iskandar, M., Ott, C., Albu-Sch
¨
affer, A., Siciliano, B., and
Dietrich, A. (2023). Hybrid Force-Impedance Control
for Fast End-Effector Motions. IEEE Robotics and
Automation Letters, 8(7):3931–3938.
Johannink, T., Bahl, S., Nair, A., Luo, J., Kumar, A.,
Loskyll, M., Ojea, J. A., Solowjow, E., and Levine, S.
(2019). Residual Reinforcement Learning for Robot
Control. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom.,
pages 6023–6029, Montreal, QC, Canada.
Jung, S., Hsia, T. C. S., and Bonitz, R. G. (2004). Force
Tracking Impedance Control of Robot Manipulators
Under Unknown Environment. IEEE Trans. Control
Syst. Technol., 12(3):474–483.
Kasruddin Nasir, A. N., Ahmad, M. A., and Tokhi, M. O.
(2021). Hybrid spiral-bacterial foraging algorithm for
a fuzzy control design of a flexible manipulator. Jour-
nal of Low Frequency Noise, Vibration and Active
Control, 41(1):340–358.
Khatib, O. (1987). A unified approach for motion and force
control of robot manipulators: The operational space
formulation. IEEE J. Robot. Autom., 3(1):43–53.
Lee, K.-k. and Buss, M. (2008). Force Tracking Impedance
Control with Variable Target Stiffness. IFAC Proc.
Vol., 41(2):6751–6756.
Li, K., He, Y., Li, K., and Liu, C. (2023). Adaptive
fractional-order admittance control for force tracking
in highly dynamic unknown environments. Industrial
Robot: the international journal of robotics research
and application.
Liang, X., Zhao, H., Li, X., and Ding, H. (2018). Force
tracking impedance control with unknown environ-
ment via an iterative learning algorithm. In Proc.
IEEE 3rd Int. Conf. Adv. Robot. Mechatron., pages
158–164, Singapore, Singapore.
Lillicrap, T. P., Hunt, J. J., Pritzel, A., Heess, N., Erez, T.,
Tassa, Y., Silver, D., and Wierstra, D. (2015). Contin-
uous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv
preprint.
Liu, Y., Jiang, D., Yun, J., Sun, Y., Li, C., Jiang, G., Kong,
J., Tao, B., and Fang, Z. (2022). Self-Tuning Con-
trol of Manipulator Positioning Based on Fuzzy PID
and PSO Algorithm. Frontiers in Bioengineering and
Biotechnology, 9.
Mason, M. T. (1981). Compliance and Force Control for
Computer Controlled Manipulators. IEEE Trans. Syst.
Man Cybern.: Syst., 11(6):418–432.
Mohd Hanif, M. I. F., Ahmad, M. A., and Jui, J. J. (2021).
PID Tuning Method Using Chaotic Safe Experimen-
tation Dynamics Algorithm for Elastic Joint Manip-
ulator. Journal Europ
´
een des Syst
`
emes Automatis
´
es,
54(5):693–698.
Nagabandi, A., Kahn, G., Fearing, R. S., and Levine, S.
(2018). Neural Network Dynamics for Model-Based
Deep Reinforcement Learning with Model-Free Fine-
Tuning. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., Bris-
bane, QLD, Australia.
Obadina, O. O., Thaha, M. A., Mohamed, Z., and Sha-
heed, M. H. (2022). Grey-box modelling and fuzzy
logic control of a Leader–Follower robot manipulator
system: A hybrid Grey Wolf–Whale Optimisation ap-
proach. ISA Transactions, 129:572–593.
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J.,
Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N.,
Antiga, L., Desmaison, A., K
¨
opf, A., Yang, E., De-
Vito, Z., Raison, M., Tejani, A., Chilamkurthy, S.,
Steiner, B., Fang, L., Bai, J., and Chintala, S. (2019).
PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance
Deep Learning Library. In Proc. Adv. Neural Inform.
Process. Syst., Red Hook, NY, USA. Curran Asso-
ciates Inc.
Peng, G., Philip Chen, C. L., He, W., and Yang, C. (2021).
Neural-Learning-Based Force Sensorless Admittance
Control for Robots With Input Deadzone. IEEE Trans.
Ind. Electron., 68(6):5184–5196.
Preitl, Z., Precup, R.-E., Tar, J. K., and Tak
´
acs, M. (2006).
Use of multi-parametric quadratic programming in
fuzzy control systems. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica,
3(3):29–43.
Puricelli, L., Pozzi, A., Petrone, V., Ferrentino, E., Chi-
acchio, P., Braghin, F., and Roveda, L. (2023). Op-
timized Residual Action for Interaction Control with
Learned Environments. TechRxiv Preprint.
Experimental Validation of an Actor-Critic Model Predictive Force Controller for Robot-Environment Interaction Tasks
403

Rigatos, G., Siano, P., Selisteanu, D., and Precup, R.-E.
(2016). Nonlinear Optimal Control of Oxygen and
Carbon Dioxide Levels in Blood. Intelligent Indus-
trial Systems, 3(2):61–75.
Roveda, L., Castaman, N., Franceschi, P., Ghidoni, S., and
Pedrocchi, N. (2020). A Control Framework Defini-
tion to Overcome Position/Interaction Dynamics Un-
certainties in Force-Controlled Tasks. In 2020 IEEE
International Conference on Robotics and Automation
(ICRA), pages 6819–6825.
Roveda, L. and Piga, D. (2021). Sensorless environ-
ment stiffness and interaction force estimation for
impedance control tuning in robotized interaction
tasks. Auton. Robots, 45(3):371–388.
Roveda, L., Testa, A., Shahid, A. A., Braghin, F., and Piga,
D. (2022). Q-Learning-based model predictive vari-
able impedance control for physical human-robot col-
laboration. Artificial Intelligence, 312:103771.
Sathish Kumar, A., Naveen, S., Vijayakumar, R., Suresh,
V., Asary, A. R., Madhu, S., and Palani, K.
(2023). An intelligent fuzzy-particle swarm optimiza-
tion supervisory-based control of robot manipulator
for industrial welding applications. Scientific Reports,
13(1):8253.
Seraji, H. and Colbaugh, R. D. (1997). Force Tracking in
Impedance Control. Int. J. Robot. Res., 16(1):97–117.
Shu, X., Ni, F., Min, K., Liu, Y., and Liu, H. (2021).
An Adaptive Force Control Architecture with Fast-
Response and Robustness in Uncertain Environment.
In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Biomim., pages 1040–
1045, Sanya, China.
Todorov, E., Erez, T., and Tassa, Y. (2012). MuJoCo:
A physics engine for model-based control. In Proc.
IEEE Int. Conf. Intell. Robots Syst., pages 5026–5033,
Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal. IEEE.
Ucgun, H., Okten, I., Yuzgec, U., and Kesler, M. (2022).
Test Platform and Graphical User Interface Design
for Vertical Take-Off and Landing Drones. Roma-
nian Journal of Information Science and Technology,
25(3–4):350–367.
Zhang, X., Sun, L., Kuang, Z., and Tomizuka, M. (2021).
Learning Variable Impedance Control via Inverse Re-
inforcement Learning for Force-Related Tasks. IEEE
Robot. Autom. Lett., 6(2):2225–2232.
Zhu, Y., Wong, J., Mandlekar, A., Mart
´
ın-Mart
´
ın, R., Joshi,
A., Nasiriany, S., and Zhu, Y. (2020). robosuite: A
Modular Simulation Framework and Benchmark for
Robot Learning. arXiv preprint.
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
404
