
Comparative Analysis of Segmentation Techniques for Reticular
Structures
Francisco J. Soler
1 a
, Luis M. Jim
´
enez
1 b
, David Valiente
1 c
, Luis Pay
´
a
1 d
and
´
Oscar Reinoso
1,2 e
1
Engineering Research Institute of Elche (I3E), Miguel Hernandez University, Elche, Spain
2
ValgrAI: Valencian Graduate School and Research Network of Artificial Intelligence, Valencia, Spain
Keywords:
Plane Segmentation, Point Clouds, Region Growing, RANSAC, Neural Networks, Climbing Robots.
Abstract:
Nowadays neural networks are widely used for segmentation tasks and there is a belief that these approaches
are synonymous of advances and improvements. This article aims to compare the performance of a neural
network, trained in our previous work, and an algorithm which is specifically designed for the segmentation
of reticular structures. As shown in this paper, in certain cases it is feasible to use conventional techniques
outside the paradigm of artificial intelligence achieving the same performance. To prove this, in this article a
quantitative and qualitative comparative analysis is carried out between an ad hoc algorithm for segmenting
reticular structures and the model of neural network that provided the best results in our previous work in this
task. Established techniques such as Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) and region growing have been
used to implement the proposed algorithm. For the quantitative analysis, standard metrics such as precision,
recall and f1-score are used. These metrics will be calculated with a self-generated dataset, consisting of
a thousand point clouds that were generated automatically in the previous work. The studied algorithm is
tailor-made for this database. For reproducibility, code and datasets are provided at https://github.com/Urwik/
rrss grnd filter.git.
1 INTRODUCTION
Most existing large-scale buildings use lattice systems
as structural elements due to their outstanding me-
chanical properties. These properties enable them to
withstand high loads, achieve a balanced distribution
of forces, exhibit high rigidity, and demonstrate effi-
ciency in terms of material usage.
Due to these excellent properties, lattice structures
(Figure 1) are widely used in high-voltage transmis-
sion lines, tower cranes, bridges, and other large-scale
infrastructures. Typically, these structures are assem-
bled using metallic bodies, in most cases these bodies
are composed of flat surfaces, as seen in the case of
transmission lines. In other cases these structures can
be built with cylindrical parts.
As a general rule, these infrastructures respond ad-
equately to adverse weather conditions and hostile en-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-7396-6596
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3385-5622
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2245-0542
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3045-4316
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1065-8944
vironments, nevertheless require regular maintenance
and inspection. A constantly evolving field of re-
search involves the use of climbing robots to perform
these types of tasks (Fang and Cheng, 2023). Climb-
ing robots are devices known for their ability to move
and operate on various surfaces, both horizontal and
vertical, such as walls, ceilings, or metallic structures.
Additionally, they can perform multiple inspection or
maintenance tasks in complex environments that are
difficult to access and pose significant risks to human
operators, who may be exposed to various hazards
such as falls or electric shocks.
These types of inspections and maintenance tasks
have been carried out by aerial robots in recent years
((Akahori et al., 2016), (Jung et al., 2019)). However,
quite often this type of robotic platform is unable to
complete such tasks due to its limitation in accessing
internal areas of the structures.
In order to carry out such tasks effectively, it is
necessary to have a proper environmental perception.
One of the sensors most widely used today for sensing
surroundings are the so-called LiDAR. These sensors,
widely used in numerous applications today, such as
Soler, F., Jiménez, L., Valiente, D., Payá, L. and Reinoso, Ó.
Comparative Analysis of Segmentation Techniques for Reticular Structures.
DOI: 10.5220/0012177100003543
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2023) - Volume 1, pages 413-423
ISBN: 978-989-758-670-5; ISSN: 2184-2809
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
413

Figure 1: Example of reticular structure used in an indus-
trial building.
localization (Liu et al., 2022), map building (Zhou
et al., 2021), object detection and segmentation (Zhu
et al., 2021), provide excellent range information.
Their high accuracy in providing detailed information
about the spatial distribution of the environment has
made this type of sensor widely used for localisation
and navigation in robotics in recent years.
A key aspect for accurate navigation is the clear
identification of flat surfaces in the surrounding en-
vironment (Xu et al., 2020). The presence of planes
in the structure allows us to build a parametric rep-
resentation of it, enabling a lightweight environment
model. Consequently, detecting these types of ele-
ments in the environment is a task of interest for nav-
igation in lattice structures.
Providing a climbing robot with a LiDAR sen-
sor allows it to know the spatial distribution of the
surrounding environment. Combined with the ability
to identify planar surfaces, it may constitute an ideal
solution to address navigation tasks in lattice struc-
tures, where virtually all components are made up of
planes. By combining the information from the Li-
DAR sensor and the detection of flat surfaces, the
robot can effectively navigate and interact with the
Figure 2: Example of captured cloud by the simulated sen-
sor.
structure, leveraging its knowledge of the planar el-
ements within the environment.
Indeed, LiDAR sensors often capture a large
amount of information, sometimes more than neces-
sary (Figure 2). Therefore, it becomes crucial to re-
move undesired data. At first, the main objective to
enable the navigation of the robotic platform through-
out this type of structures, is to identify from all the
information provided by the available sensory sys-
tems, the information relating only to the structure,
being necessary to identify which part of the informa-
tion belongs to it and which does not. This task could
be defined as a per point classification or a segmenta-
tion of the original information into certain classes.
In recent years, we can find related works that
employ artificial intelligence systems and algorithms
to address this problem. Thus, we find some works
on plane segmentation with neural networks such as
(Yang and Kong, 2020) or (Lee and Jung, 2021).
In these works, neural networks are used to iden-
tify planes in indoor and outdoor environments (ur-
ban environments) respectively. However, these envi-
ronments differ significantly from the target environ-
ments of our work, which is why in previous works
in the research group we approached this task with a
segmentation proposal using specific neural networks
(Soler et al., 2023).
Additionally, there are many methods for plane
identification with algorithms outside the artificial in-
telligence paradigm as in (Su et al., 2022). It proposes
a two-step segmentation, a first stage where planes
are selected by region growing and a second stage
where the border points between two planes are clas-
sified, where the region growing algorithm is not able
to work correctly. In (Gaspers et al., 2011) they sim-
ilarly use a two-stage segmentation but over multiple
resolutions. They extract for each resolution key fea-
tures based on the normals named surfels. These sur-
fels are intended to be associated with planes at lower
resolutions. Those surfels that are not associated with
any known plane are attempted to be grouped accord-
ing to their coplanarity using the Hough transform.
On the other hand, RANSAC is applied to the sets of
surfels that have been associated with the same plane
at lower resolutions to improve accuracy. Once the
maximum resolution is reached, nearby coplanar seg-
ments are identified and merged into a single plane.
The algorithm proposed in this study is similar
to the ones mentioned above, as it employs a two-
stage strategy, but unlike the previous ones (segment-
ing the point cloud provided by the LiDAR sensor
into multiple flat sets) its objective is to split the point
cloud only into two sets, structure and non-structure.
For this purpose, a coarse classification by RANSAC
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
414

is used and then a region growing procedure is per-
formed to improve the result.
The aim of this article is to evaluate the per-
formance of neural networks against the application
of such specific algorithm for segmenting reticular
structures in a specific environment. To do so, we
will compare our previous work, (Soler et al., 2023),
with a proposed application-specific algorithm using
a dataset that contains point clouds obtained from
reticular structures.
To provide a clear overview, this articles is divided
into the following parts. Second section (2) briefly re-
counts the previous work in order to put the reader in
context for further comparison. Section 3 explores the
proposed method for segmenting the lattice structures
of our database and discusses all its steps. Section
4 presents the conducted experiments. Then, Sec-
tion 5 develops a comparative analysis between the
segmentation of reticular structures using neural net-
works and conventional approaches. Finally, Section
6 discusses some brief reflections about the obtained
results.
2 PREVIOUS WORK
In this section, we provide a brief overview of the fun-
damental idea of our previous work. In previous stud-
ies (Soler et al., 2023), an specific training of neu-
ral networks was made to identify reticular structures
based on environment information provided by a Li-
DAR sensor.
Reticular structures are interconnected systems by
rigid joints forming a three-dimensional lattice con-
figuration. This type of system can be found in a mul-
titude of infrastructures, such as bridges, buildings,
electricity pylons or cranes, and is normally made by
metallic elements composed by multiple flat surfaces.
The aforementioned work was carried out with the
purpose of being implemented in the HyReCRo (Pei-
dro et al., 2015) robot. This series-parallel climb-
ing robot has ten degrees of freedom (DOF) and has
the ability to navigate through metallic structures by
using a magnetic adhesion mechanism based on me-
chanically switched permanent magnets.
2.1 Dataset Generation
One of the first challenges to be solved in order to
meet the objective of previous work was the lack of
training dataset.
There are recent studies on the use of simulators
for the automatic generation of labelled datasets. In
(Sanchez et al., 2019) Gazebo Simulator is used to
generate labelled 3D scans of natural environments,
but it has a limitation when it comes to generating
large datasets, as the position of the sensor has to be
indicated by the user. In a more autonomous way,
in (Wang et al., 2019) a modification of the CARLA
simulator (Dosovitskiy et al., 2017) is used to gener-
ate driving LiDAR point clouds with per point auto-
matic labels during the movement of a vehicle. More-
over, there are studies that merge real and synthetic in-
formation such as (Fang et al., 2018), where similar to
the work mentioned above its objective is to generate
driving data. To achieve that, they use a static labelled
point cloud as a background and introduce synthetic
elements, like cars or people, with pre-defined labels
in order to obtain a more realistic representation of
the environment.
Figure 3: Example of environment used for training. Red
circle indicates the position of the sensor.
The works mentioned above mainly focus on au-
tonomous driving navigation and segmentation of
such environments. To address the segmentation of
lattice structures where the environment differs sig-
nificantly from the previous ones, we have developed
a plugin in Gazebo Simulator. Similar to (Sanchez
et al., 2019), it uses this simulation software to gener-
ate labelled datasets automatically, with the advantage
that the position of the sensor and the elements of the
environment change automatically, enabling the gen-
eration of large databases.
The training database was conformed by ten thou-
sand point clouds simulating the properties of a real
LiDAR sensor (Ouster OS1-128 channels). Each
measure is taken from the sensor origin and the sensor
pose is set randomly around the environment. With
the objective of generalising the database for a vari-
ety of lattice structures, the training dataset is formed
using environments composed of parallelepipeds and
elements such as trees and soil modelling a real envi-
ronment (Figure 3).
In the same way as for the training data, the eval-
uation dataset (which is the one used to evaluate the
metrics in this paper) has been generated automati-
Comparative Analysis of Segmentation Techniques for Reticular Structures
415

(a) Example of the evaluation environment. (b) Example of the point cloud generated with automatic la-
bels.
Figure 4: Example of the evaluation dataset.
cally. It is composed of 904 point clouds and with a
lattice structure model instead of parallelepipeds. A
representation of the evaluation environment and the
simulated data are shown in the Figure 4.
Different neural network architectures were
trained and analysed for reticular structure segmenta-
tion, PointNet (Qi et al., 2016), PointNet++ (Qi et al.,
2017) and MinkUNet34C (Choy et al., 2019). The
best results were obtained with the MinkUNet34C ar-
chitecture, which uses the MinkowskiEngine to per-
form 3D convolutions in a sparse way, only on those
points that contain information. The latter architec-
ture shows better results in terms of recall and f1 score
than the others as shown in Figure 5, therefore it has
been selected as the best model for comparison.
Their results are discussed and compared in fur-
ther detail with the algorithm presented in the present
article in Section 5.
Figure 5: Metrics obtained in previous work.
3 PROPOSED ALGORITHM
The algorithm proposed in this study is structured in
two steps. The first step performs a coarse classi-
fication, identifying the ground plane and elements
close to it. Secondly, a process is run in which the
classification is refined. This method adopts well-
known algorithms in the literature for plane segmen-
tation and identification such as region growing or
Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) with the aim
of classifying points into two classes, structure and
non-structure.
It is important to notice that this algorithm has
been specifically designed to work in the environ-
ments that have been generated for the test dataset in
our previous work. While defining its behaviour, it is
taken into consideration that within the sensor read-
ing there will be a large number of points belonging
to the ground, in addition to the fact that these occupy
a large area of the environment. Figure 6 shows a
flowchart that describes the process followed to com-
plete the segmentation. The implementation of this
work relies on the Point Cloud Library (PCL) (Rusu
and Cousins, 2011) library to perform the point cloud
processing. The following subsections describe each
of its stages in more detail.
To reduce the computational cost of the algorithm,
a two-stage approach is adopted. Based on the pre-
liminar experiments, the highest computational cost
of the algorithm is due to the normal estimation, a
process that consumes about 80% of the total execu-
tion time of the algorithm. If the fine classification
step is used directly, it would be necessary to estimate
the normals of the entire cloud, in addition to having
to calculate and evaluate the eigenvalues of a larger
number of ensembles. Such an approach would re-
quire on average 20% more runtime per cloud to ob-
tain the same results.
3.1 Coarse Segmentation
In the initial stage of the algorithm a coarse clas-
sification is performed to extract the ground points.
This stage involves Voxel filtering followed by the ex-
traction of the largest plane in the environment using
RANSAC.
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
416

Coarse Ground
Density Filter
Original
Point Cloud
Voxel
Filter
RANSAC
Largest Plane
Region Growing
Eval
EigenValues
Coarse Truss
Final GroundFinal Truss
Yes
Yes
No
No
Fine Segmentation
Coarse Segmentation
Figure 6: Flowchart of the proposed algorithm.
Since RANSAC selects the best plane candidate
based on the number of inliers, if there are areas with
high point density, RANSAC tends to select planes in
these areas. To avoid this problem, Voxel filtering is
first applied, a process by which the point density is
homogenised across the entire cloud, thus favouring
the extraction of the largest plane (ground plane).
In order to cover as many ground points as pos-
sible, a high threshold is established to obtain the
largest plane, around 0.5 metres, thus avoiding slopes
in the terrain.
3.2 Fine Segmentation
Coarse classification produces a smaller cloud con-
taining ground points as well as points close to it
within a certain threshold. On this reduced cloud, a
more accurate classification is applied. The idea of
this stage is to split the cloud into planar clusters and
to classify them according to their size.
In order to segment the different planar clusters,
region growing based on the normals is applied. The
clustering process is based on the similarity of the
normals of nearby points, so the estimation of these
features is a very important aspect in the resultant
clusters.
In the following subsections, the normal estima-
tion for each point and the decision criteria for cluster
filtering are further discussed.
3.2.1 Normal Estimation
As mentioned in the previous section, normal esti-
mation is a key component in establishing correct
planar clusters. The normal estimation function im-
plemented in PCL consists of computing the eigen-
values and eigenvectors over the neighbourhood of
each point, where the eigenvector associated with the
smallest eigenvalue is considered the normal vector of
the point. Eigenvalues and eigenvectors are obtained
by principal component analysis (PCA) on the covari-
ance matrix for each point and its neighbourhood en-
vironment.
This matrix (C ) follows the formulation indicated
in Equation 1, where k is the number of neighbors,
p is the centroid of the neighbor set, λ
j
is the eigen-
value, and
⃗
v
j
is the eigenvector for j.
C =
1
k
k
∑
i=1
·(p
i
− p) · (p
i
− p)
T
C ·
⃗
v
j
= λ
j
·
⃗
v
j
, j ∈ {0,1, 2}
(1)
The normal estimation method described in the
previous paragraph requires the selection of a set of
neighbouring points to fulfil its task. The imple-
mentation of the library allows two exclusive options
for this purpose: to select all points located within
a sphere of defined radius, or to select those closest
points with a limit in number.
Depending on the neighbour selection method, the
eigenvectors and eigenvalues can differ significantly.
An example of this can be seen in Figure 7 where the
point cloud is represented as a function of its curva-
ture (2), defined as the coefficient between the small-
est eigenvalue and the sum of all eigenvalues. In Fig-
ure 7(a) neighbours are selected by radius and in Fig-
ure 7(b) by nearest neighbours.
Curvature =
λ
0
λ
0
+ λ
1
+ λ
2
(2)
Comparative Analysis of Segmentation Techniques for Reticular Structures
417

(a) By radius
(b) By neighbours
Figure 7: Point clouds displayed by its curvature.
Based on the conducted experiments, it has been
concluded that the estimation of the normal vector of
each point is more accurate when a certain number of
close neighbours are used. The normal estimation by
radius is highly erroneous in areas with a low density
of points, i.e. there are not enough points in the indi-
cated radius to estimate the normal vector. In contrast,
the calculation of curvature, which is somewhat in-
dicative of point spread, is more accurate when neigh-
bour selection by radius is used, as seen in Figure 7,
where in the radius selection method, points with high
curvature correspond to the cutting edges of the dif-
ferent planes of the structure. The curvature value
is important since, as described below, it is used as
a termination criteria for growing regions. As indi-
cated in (Pauly et al., 2002), if we look at equation
(2), the maximum curvature value will be λ
max
= 1/3
which occurs when λ
0
= 1, since λ
0
≤ λ
1
≤ λ
2
and
λ
0−2
∈ {0, 1}.
This means that small values of curvature indicate
that the points are poorly sparse along the smallest
eigenvector (most of the points fall on a plane) and
values close to 1/3 in curvature mean that the points
are uniformly sparse throughout the selected neigh-
bourhood space.
3.2.2 Region Growing
The region growing method is a frequently employed
approach for detecting and grouping data sets into
cohesive regions. It operates on the fundamental
premise that neighboring points exhibiting similar at-
tributes should be grouped together.
In this study, the existing implementation in the
PCL library is used, which facilitates region growth
based on the normal vector associated with each
point. Primarily, it is imperative to estimate the nor-
mals and their corresponding curvature. Once this
estimation is accomplished, the initial seed point is
selected based on the lowest curvature value across
the entire point cloud. Subsequently, the cluster’s size
expands by incorporating neighboring points that sat-
isfy specific criteria. In order to include a new point
in the set, two conditions must be satisfied. The first
condition involves assessing the angular disparity be-
tween the point’s normal and the initial seed’s nor-
mal. If the difference falls below a specific threshold,
the new point is incorporated into the set. The sec-
ond condition entails examining the curvature of the
newly added points. If the curvature is below a certain
threshold, these points become new seeds for further
expansion of the set. This growth process continues
until no more seeds are available, indicating the com-
pletion of set expansion.
3.2.3 Eigenvalues Evaluation
To determine whether a region belongs to the struc-
ture or not, the eigenvalues and eigenvectors are em-
ployed as indicators. These properties are derived
through a principal component analysis conducted on
the covariance matrix of the local neighborhood sur-
rounding a specific point, similar to the method de-
scribed in the preceding section for normal estima-
tion.
The algorithm has been assessed with three dif-
ferent variations, differing in the approach utilized to
determine whether a cluster of points belongs to the
structure or not. These variations focus on distinct
methods of utilizing eigenvalues or eigenvectors for
this discrimination process.
By Ratio. This particular variant builds upon exist-
ing knowledge of the structure, assuming that struc-
tural planes exhibit an elongated and slender geome-
try. Taking this into account, this variant relies solely
on the ratio between the two largest eigenvalues (re-
ferred to as the ”ratio” in Equation 3) to calculate
a value representing the length-to-width ratio of the
candidate set. This value is then utilized to determine
the classification of the cluster in question.
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
418

ratio =
λ
1
λ
2
(3)
By Module. Applying a similar methodology to the
previous variant, having prior knowledge of the bar-
like geometry of the structure enables filtering based
on the projection module of the farthest point along
its principal axes. Thresholds are then defined for
the two dimensions of the plane formed by the set of
points.
Groups of points exceeding the specified thresh-
olds (maximum length and width of the structural el-
ements) are excluded from the classification as part of
the structure.
Hybrid. In the final variant, a combination of the
two preceding approaches is employed, incorporating
both the module filtering and the ratio-based classifi-
cation. This integrated method yields the most favor-
able outcomes, as evident from the results presented
in Table 1.
3.2.4 Density Filter
Lastly, considering the proximity of the robot and sen-
sor to the structure, it is expected that areas belong-
ing to the structure will exhibit a higher point den-
sity, while the ground and surrounding environment
will show lower density. Taking advantage of this ob-
servation, the final step aims to eliminate remaining
spurious points in the environment, retaining only the
points corresponding to the structure. This step effec-
tively filters out outlier points, resulting in a represen-
tation that solely encompasses the desired structure.
3.3 Limitations
It is important to emphasize that the algorithm is
specifically tailored for the available dataset, which
encompasses a wealth of information regarding the
environment and the ground. This dataset is ob-
tained through a realistic simulation of the commer-
cial Ouster OS1 LiDAR sensor, ensuring that the gen-
erated data adheres to the sensor’s specifications. The
configuration of the simulated sensor includes a res-
olution of 512x128 points, a maximum range of 30
meters, vertical and horizontal fields of view of 45
degrees and 360 degrees respectively. Additionally,
the dataset incorporates Gaussian noise with a mean
of zero and a standard deviation of 0.008 meters.
The extensive fields of view and range of the sensor
enable comprehensive information capture from the
ground and surrounding environment, enabling the
algorithm’s initial stage to successfully identify the
ground plane.
4 EXPERIMENTS
The hardware used for the experiments is as follows.
An NVIDIA RTX3090 graphics card in the case of the
neural network. An Intel i7-10700 processor for all
variants of the proposed ad hoc algorithm. The results
obtained during the experiments are shown in Table
1, where the metrics evaluated (Section 5.1) are listed
together with the execution time in milliseconds.
4.1 Ratio
Experiments with this algorithm variant have been
performed with a threshold for the ratio given by the
prior knowledge of the structure, taken as the quotient
between the width of the beams and the height men-
tioned in Section 3.1 by which the points close to the
estimated ground plane are selected. Assessing clus-
ters with this variant yields poor results because it is
not able to classify correctly large clusters belonging
to the ground, whose elongated proportions are simi-
lar to those of the beams.
4.2 Module
For this approach, the threshold has been taken as the
height above which points close to the ground are se-
lected to obtain a coarse classification. This distance
is taken as the threshold since it is the maximum bar
length visible after coarse classification. The results
of this variant are considerably better than the previ-
ous one, since it is able to identify the clusters ob-
tained according to their size, thus overcoming the
problem of the previous method. Despite this, it is
possible that the clusters meet the size requirement,
but not the ratio requirement (Figure 8).
Figure 8: Example of a cluster that can not be correctly
classified by its module.
Comparative Analysis of Segmentation Techniques for Reticular Structures
419

Table 1: Evaluated results in the comparison. W/O = without.
Precision Recall F1-Score TP FP TN FN
Execution Time
(ms)
MinkUNet34C 0,9425 0,9840 0,9622 10213 623 14006 158 45
RATIO 0,6972 0,9658 0,7961 10024 5133 9492 349 62
MODULE 0,9920 0,9645 0,9775 10007 70 14555 366 72
HYBRID 0,9922 0,9643 0,9775 10004 67 14558 368 72
W/O Coarse Seg 0,9952 0,4422 0,6123 4587 22 14603 5786 89
W/O Fine Seg 0,9935 0,9575 0,9744 9940 52 14574 433 31
4.3 Hybrid
The same thresholds are used for this variant as for
the previous ones. The hybrid filter allows us to take
into account those clusters that meet the modulus re-
quirement but do not meet the ratio requirement, as
in the example in Figure 8. This result is not signif-
icant in the evaluated metrics as it hardly appears in
the available data (only when there are certain occlu-
sions). In Figure 8, an example of this type of situa-
tion is shown, where a cluster that meets the module
requirements, does not meet the ratio requirements
and therefore has to be discarded.
4.4 Without Coarse Segmentation
This experiment has been carried out with the hy-
brid method as it is the most complete for the given
task. Applying directly a fine classification, i.e. re-
gion growing to segment the input cloud does not pro-
vide the best results. This fact is supported by the
results in Table 1.
In the later one, it can be seen that in this case a
good precision is achieved, which implies that those
points identified as structure are indeed structure. On
the other hand, its recall is only close to 50%, which
means that only this percentage of the structure can
be identified.
This method is mainly based on the accurate esti-
mation of the clusters by region growing, which de-
pends on a multitude of parameters and requires an
exhaustive adjustment of these for an ideal perfor-
mance. By evaluating each of the clusters formed us-
ing the decision criteria (hybrid criteria in this case),
the sets are classified as structure and non-structure.
In order to obtain better results with this method, it
would be necessary to carry out an improvement pro-
cess to adjust the parameters of normal estimation and
region growing.
Besides, in this case it is necessary to adjust the
thresholds used in the previous experiments, setting as
module the maximum length of the bars of the struc-
ture (since they are complete and not trimmed) and
consequently the ratio with mentioned length.
4.5 Without Fine Segmentation
A further studied scenario is the use of the algo-
rithm without the fine classification section. Its ac-
curacy is very high, because with ground voxelization
and RANSAC we are able to accurately identify the
ground plane, as these are structures that rise from
the ground, everything above a certain height is eas-
ily classified as structure. By using this method, the
execution time can be reduced by almost half.
Despite these facts, this method is not able to iden-
tify the points where the structure meets the ground
and discards all of them. Since the point density in
these areas of the structure is not very high and their
number is very small compared to the rest, the metrics
evaluated are not affected to any large extent.
However, in order to obtain the best results, the
fine classification stage is proposed to meet the needs
of identifying areas where the structure meets the
ground. Although its behaviour is far from ideal due
to the reduced density of points in these areas, its
use implies an improvement in certain cases. An ex-
ample of this type of situation is shown in Figure 9,
where the fine segmentation stage is able to identify
the points corresponding to the elements of the struc-
ture in contact with the ground, improving the final
classification. In this case, the use of this type of clas-
sification with respect to the hybrid method means an
increase in precision, as expected, but a reduction in
recall of around 4%.
4.6 Density Filter
Applying the density filter to the initial cloud or after
the proposed methods has also been evaluated. It has
been observed that the best results of the algorithm are
obtained when the density filter is used last. This may
be due to the larger amount of information available
to the fine and coarse stages to operate.
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
420
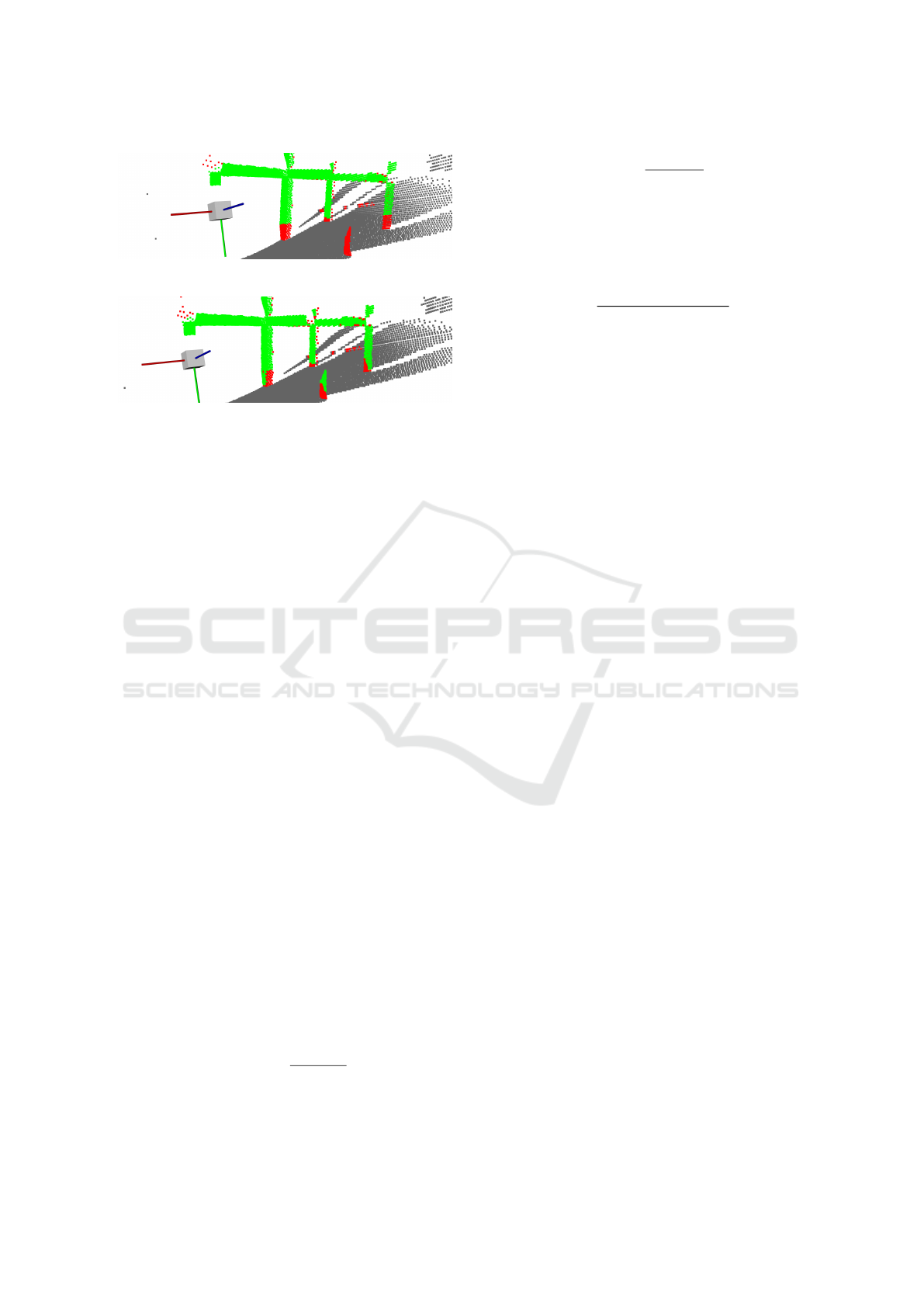
(a) Without Fine Segmentation
(b) With Hybrid Method
Figure 9: Example of improvement using fine segmentation
with the hybrid method versus just coarse segmentation.
5 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
To assess and compare the effectiveness of the afore-
mentioned custom algorithm with the most success-
ful neural network model derived from prior research,
this section conducts a comparative analysis. The ob-
jective is to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of
each method. First, the metrics used are presented and
then the most important aspects of each method are
discussed separately. Finally, the numerical results of
both methods are discussed.
5.1 Evaluated Metrics
For the assessment of performance, we employ iden-
tical evaluation metrics as in our previous research,
which are widely utilized to evaluate neural net-
works. These metrics include Precision, Recall, and
F1-Score, which effectively measure the accuracy and
effectiveness of the segmentation. Furthermore, we
also evaluate the inference time, representing the av-
erage computational time needed to obtain the seg-
mentation of an input point cloud. In the following
equations T P, FP, T N, FN are the well-known pa-
rameters representing true positives, false positives,
true negatives and false negatives respectively.
Precision (Precision) eq. (4) reflects the algo-
rithm’s or neural network’s certainty or confidence
level. In other words, it indicates the percentage of
correct predictions.
Precision =
T P
T P + FP
(4)
Recall (Recall) eq. (5) measures the volume of
data that we are able to predict correctly.
Recall =
T P
T P + FN
(5)
Finally, the F1-score (F1-score) eq. (6) is a metric
that combines the previous ones, providing a single
indicator of the overall performance of the process.
F1 =
2 ∗ Precision ∗ Recall
Precision + Recall
(6)
5.2 Neural Network
In this comparison, the neural network employed
is MinkUNet34C, which is a 3D convolutional net-
work that uses sparse convolutions. This architec-
tural choice significantly reduces computational time
compared to conventional convolutions. The net-
work demonstrates promising outcomes in segment-
ing reticular structures and presents remarkable gen-
eralization capabilities. It successfully identifies var-
ious types of reticular structures across diverse envi-
ronments, highlighting its versatility and adaptability.
Some of the drawbacks of the neural network in-
clude the need for a sufficiently large training and
evaluation dataset to achieve good performance. In
addition to this, the network requires a long train-
ing time, leading to extended waiting times when-
ever any configuration changes are applied. More-
over, the network requires specific hardware for fast
execution. The recorded training times are approxi-
mately 12 hours on an NVIDIA RTX 3090 with 24GB
of memory for a dataset consisting of 10.000 point
clouds with 25.000 points per cloud.
5.3 Ad Hoc Algorithm
The method presented in this article attains remark-
ably good results, compared to those achieved by
the neural network. Notably, it offers several ad-
vantages over the neural network, including inde-
pendence from specific databases, hardware require-
ments, and training time. In terms of training time,
the algorithm possesses a significant advantage as pa-
rameter adjustments can be made, and immediate re-
sults can be obtained without the need for a complete
learning process. Furthermore, the algorithm has the
capability to run on multiple CPU cores, thereby fur-
ther reducing the execution time shown in this study.
Nevertheless, the primary limitation of this algo-
rithm resides in its lack of generalizability. Cus-
tomization and adaptation of the algorithm to each
specific environment and structural geometry are im-
perative for its effective application.
Comparative Analysis of Segmentation Techniques for Reticular Structures
421

(a) Results of the proposed algorithm. (b) Results of MinkUNet34C
Figure 10: Examples of the segmentation performed by both methods. Red color shows classification errors.
5.4 Results
Examining the results presented in Table 1, it is evi-
dent that the modular and the hybrid versions of our
algorithm outperform the neural network in terms of
precision, resulting in an improvement of around 5%
in this metric. Conversely, the neural network exhibits
higher recall (98%), denoting its capability to identify
a greater percentage of structure points. The F1-score,
encompassing both precision and recall, shows a 1%
improvement in the proposed algorithm over the neu-
ral network. Figure 10 visually illustrates the striking
similarity in results obtained by both approaches, cor-
roborating the findings outlined in Table 1.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The findings from this study underscore that neural
networks are not always the optimal choice for every
task. Remarkably similar outcomes to those of neu-
ral networks can be achieved without the need of a
training process, which requires a labelled dataset for
training and subsequent evaluation. Upon careful ex-
amination of the comparative results, it becomes evi-
dent that an algorithm specifically tailored for the de-
sired task, with a shorter development time compared
to neural networks, can be more advantageous in cer-
tain scenarios. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm
can be executed in parallel, significantly reducing the
current execution time and enabling its utilization on
small mobile devices with limited computational ca-
pabilities.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is part of the project PID2020-116418RB-
I00 funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033.
The present research has also been possible thanks
to the project TED2021-130901B-I00, funded by
MCIN/AEI/10.13039501100011033 and the Euro-
pean Union ”NextGenerationEU”/PRTR.
REFERENCES
Akahori, S., Higashi, Y., and Masuda, A. (2016). Develop-
ment of an aerial inspection robot with epm and cam-
era arm for steel structures. In 2016 IEEE Region 10
Conference (TENCON), pages 3542–3545.
Choy, C., Gwak, J., and Savarese, S. (2019). 4d spatio-
temporal convnets: Minkowski convolutional neural
networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages
3075–3084.
Dosovitskiy, A., Ros, G., Codevilla, F., L
´
opez, A. M., and
Koltun, V. (2017). CARLA: an open urban driving
simulator. CoRR, abs/1711.03938.
Fang, G. and Cheng, J. (2023). Advances in climbing robots
for vertical structures in the past decade: A review.
Biomimetics, 8(1).
Fang, J., Yan, F., Zhao, T., Zhang, F., Zhou, D., Yang, R.,
Ma, Y., and Wang, L. (2018). Simulating lidar point
cloud for autonomous driving using real-world scenes
and traffic flows. ArXiv, abs/1811.07112.
Gaspers, B., St
¨
uckler, J., Welle, J., Schulz, D., and Behnke,
S. (2011). Efficient multi-resolution plane segmen-
tation of 3d point clouds. In 4th International
Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications
(ICIRA), pages 145–156.
Jung, S., Song, S., Kim, S., Park, J., Her, J., Roh, K.,
and Myung, H. (2019). Toward autonomous bridge
inspection: A framework and experimental results.
In 2019 16th International Conference on Ubiquitous
Robots (UR), pages 208–211.
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
422

Lee, H. and Jung, J. (2021). Clustering-based plane seg-
mentation neural network for urban scene modeling.
Sensors, 21:8382.
Liu, Y., Wang, C., Wu, H., Wei, Y., Ren, M., and Zhao, C.
(2022). Improved lidar localization method for mo-
bile robots based on multi-sensing. Remote Sensing,
14(23).
Pauly, M., Gross, M., and Kobbelt, L. (2002). Efficient
simplification of point-sampled surfaces. In IEEE Vi-
sualization, 2002. VIS 2002., pages 163–170.
Peidro, A., Gil, A., Marin, J., and Reinoso, O. (2015). In-
verse kinematic analysis of a redundant hybrid climb-
ing robot. International Journal of Advanced Robotic
Systems, 12:1.
Qi, C. R., Su, H., Mo, K., and Guibas, L. J. (2016). Pointnet:
Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and
segmentation. CoRR, abs/1612.00593.
Qi, C. R., Yi, L., Su, H., and Guibas, L. J. (2017). Point-
net++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets
in a metric space. CoRR, abs/1706.02413.
Rusu, R. B. and Cousins, S. (2011). 3d is here: Point cloud
library (pcl). In 2011 IEEE International Conference
on Robotics and Automation, pages 1–4.
Sanchez, M., Mart
´
ınez, J., Morales, J., Robles, A., and
Moran, M. (2019). Automatic generation of labeled
3d point clouds of natural environments with gazebo.
pages 161–166.
Soler, F. J., Peidr
´
o, A., Fabregat, M., Pay
´
a, L., and Reinoso,
O. (2023). Segmentaci
´
on de planos a partir de nubes
de puntos 3d en estructuras reticulares. In XIII Jor-
nadas Nacionales de Rob
´
otica y Bioingenier
´
ıa, pages
91–98, Madrid, Spain.
Su, Z., Gao, Z., Zhou, G., Li, S., Song, L., Lu, X., and
Kang, N. (2022). Building plane segmentation based
on point clouds. Remote Sensing, 14(1).
Wang, F., Zhuang, Y., Gu, H., and Hu, H. (2019). Automatic
generation of synthetic lidar point clouds for 3-d data
analysis. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and
Measurement, 68(7):2671–2673.
Xu, Y., Ye, Z., Huang, R., Hoegner, L., and Stilla, U.
(2020). Robust segmentation and localization of
structural planes from photogrammetric point clouds
in construction sites. Automation in Construction,
117:103206.
Yang, H. and Kong, H. (2020). 3dpmnet: Plane segmenta-
tion and matching for point cloud registration. In 2020
3rd International Conference on Unmanned Systems
(ICUS), pages 439–444.
Zhou, L., Wang, S., and Kaess, M. (2021). Pi-lsam: Lidar
smoothing and mapping with planes. In 2021 IEEE
International Conference on Robotics and Automation
(ICRA), pages 5751–5757.
Zhu, X., Zhou, H., Wang, T., Hong, F., Ma, Y., Li, W., Li,
H., and Lin, D. (2021). Cylindrical and asymmetri-
cal 3d convolution networks for lidar segmentation.
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages
9939–9948.
Comparative Analysis of Segmentation Techniques for Reticular Structures
423
